Figure 9. CNO-mediated bilateral activation of hM3Dq-containing LHA CART neurons leads to increased body skin temperature in Cartptcre/cre and Cartptcre/+ mice.
Temperatures of the interscapular brown adipose tissue (BAT) (A, B), the lumbar back (D,E), the tail (G,H) and differences between BAT and lumbar temperatures (J, K) measured by high-sensitivity infrared imaging 1, 3 and 6 hr after i.p. injection of saline or CNO. The difference of these parameters between Cartptcre/cre and Cartptcre/+ mice was assessed by subtracting the value of CNO from that of saline at the corresponding time point for each mouse (C,F, I, L). Data are means ± SEM. n = 6–7; *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001 for saline versus CNO treatments.
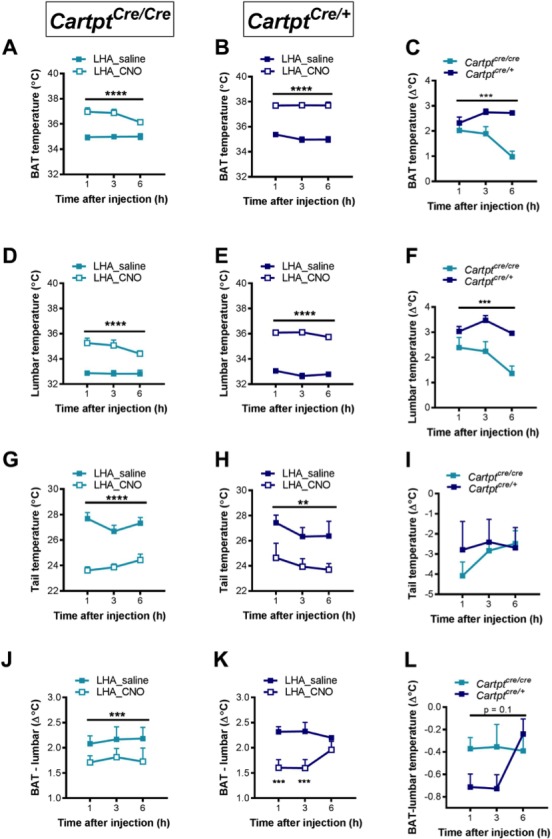
Figure 9—figure supplement 1. CNO does not exert any effects on body skin temperature in the absence of hM3Dq-expression in Cartptcre/cre, Cartptcre/+ and wild type mice.