Abstract
Introduction
Carbohydrate restriction markedly improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) but necessitates prompt medication changes. Therefore, we assessed the effectiveness and safety of a novel care model providing continuous remote care with medication management based on biometric feedback combined with the metabolic approach of nutritional ketosis for T2D management.
Methods
We conducted an open-label, non-randomized, controlled, before-and-after 1-year study of this continuous care intervention (CCI) and usual care (UC). Primary outcomes were glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), weight, and medication use. Secondary outcomes included fasting serum glucose and insulin, HOMA-IR, blood lipids and lipoproteins, liver and kidney function markers, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP).
Results
349 adults with T2D enrolled: CCI: n = 262 [mean (SD); 54 (8) years, 116.5 (25.9) kg, 40.4 (8.8) kg m2, 92% obese, 88% prescribed T2D medication]; UC: n = 87 (52 (10) years, 105.6 (22.15) kg, 36.72 (7.26) kg m2, 82% obese, 87% prescribed T2D medication]. 218 participants (83%) remained enrolled in the CCI at 1 year. Intention-to-treat analysis of the CCI (mean ± SE) revealed HbA1c declined from 59.6 ± 1.0 to 45.2 ± 0.8 mmol mol−1 (7.6 ± 0.09% to 6.3 ± 0.07%, P < 1.0 × 10−16), weight declined 13.8 ± 0.71 kg (P < 1.0 × 10−16), and T2D medication prescription other than metformin declined from 56.9 ± 3.1% to 29.7 ± 3.0% (P < 1.0 × 10−16). Insulin therapy was reduced or eliminated in 94% of users; sulfonylureas were entirely eliminated in the CCI. No adverse events were attributed to the CCI. Additional CCI 1-year effects were HOMA-IR − 55% (P = 3.2 × 10−5), hsCRP − 39% (P < 1.0 × 10−16), triglycerides − 24% (P < 1.0 × 10−16), HDL-cholesterol + 18% (P < 1.0 × 10−16), and LDL-cholesterol + 10% (P = 5.1 × 10−5); serum creatinine and liver enzymes (ALT, AST, and ALP) declined (P ≤ 0.0001), and apolipoprotein B was unchanged (P = 0.37). UC participants had no significant changes in biomarkers or T2D medication prescription at 1 year.
Conclusions
These results demonstrate that a novel metabolic and continuous remote care model can support adults with T2D to safely improve HbA1c, weight, and other biomarkers while reducing diabetes medication use.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier
Funding
Virta Health Corp.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s13300-018-0373-9) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Beta-hydroxybutyrate, Carbohydrate restriction, HbA1c, Ketosis, Type 2 diabetes, Weight loss
Plain Language Summary
Treatments for type 2 diabetes (T2D) have improved, yet T2D and being overweight are still significant public health concerns. Blood sugar in patients with T2D can improve quickly when patients eat significantly fewer dietary carbohydrates. However, this demands careful medicine management by doctors, and patients need support and frequent contact with health providers to sustain this way of living. The purpose of this study was to evaluate if a new care model with very low dietary carbohydrate intake and continuous supervision by a health coach and doctor could safely lower HbA1c, weight and need for medicines after 1 year in adults with T2D. 262 adults with T2D volunteered to participate in this continuous care intervention (CCI) along with 87 adults with T2D receiving usual care (UC) from their doctors and diabetes education program. After 1 year, patients in the CCI, on average, lowered HbA1c from 7.6 to 6.3%, lost 12% of their body weight, and reduced diabetes medicine use. 94% of patients who were prescribed insulin reduced or stopped their insulin use, and sulfonylureas were eliminated in all patients. Participants in the UC group had no changes to HbA1c, weight or diabetes medicine use over the year. These changes in CCI participants happened safely while dyslipidemia and markers of inflammation and liver function improved. This suggests the novel care model studied here using dietary carbohydrate restriction and continuous remote care can safely support adults with T2D to lower HbA1c, weight, and medicine use.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s13300-018-0373-9) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Introduction
The number of people living with diabetes worldwide nearly quadrupled since 1980, estimated at 422 million in 2014 [1]. In the USA, the Centers for Disease Control reports 30.3 million adults presently live with diabetes, and it is among the leading causes of death [2]. Treatment modalities for type 2 diabetes (T2D) have demonstrated varying success. Intensive lifestyle interventions are effective treatments for obese individuals with T2D when weight loss is achieved and sustained [3]. Evidence for improved cardiovascular outcomes in patients with T2D prescribed glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1) and sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT-2) is increasing [4, 5]. Forty percent of patients undergoing bariatric surgery demonstrate substantial improvements in glycemic control after 1 year and many achieve T2D remission [6]. Despite advancements in treatment options, cost, side effects, adherence, and disease progression remain barriers.
Guidelines for T2D management recommend lifestyle change and weight loss [7, 8]. However, a fraction of individuals are successful at long-term weight loss maintenance and true disease remission is uncommon [3, 9]. Mediterranean-style, DASH, and plant-based diets, sometimes with prescribed energy restriction, are recommended, but effectiveness data are limited [7] and low fat diets have not been shown to be superior for weight loss [10]. Commercially available weight loss programs have demonstrated short-term success in glycemic control, but continued success at 1 year is uncommon [11].
Glycemic control can be achieved quickly with carbohydrate restriction via very low energy diets (400–800 kcal day−1; VLCD) [12]. However, VLCD are necessarily temporary and outcomes often revert when patients resume former dietary patterns. Alternatively, nutritional ketosis, achieved by consuming moderate protein and greatly reduced carbohydrate, results in similarly increased serum beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) concentrations as observed during VLCD, which signifies a shift to using fat as the body’s primary fuel source [12]. This nutritional therapy may help patients achieve sustainable glycemic control without prescribed energy restriction. Benefit may accrue from decreased circulating glucose and insulin [13], ketone signaling [14, 15], or eventual weight loss. Studies utilizing carbohydrate restriction observed improved glycemic control and cardiometabolic markers, but were often short-term trials of small groups, excluded subjects prescribed insulin, or infrequently monitored or achieved ketosis [16–20].
The chronic nature of diabetes care presents an additional challenge requiring sustained behavioral change that is difficult to support with traditional medical care including infrequent provider contact [21]. Adherence to lifestyle changes may be poor in the absence of support from providers and peers. We therefore hypothesized that a comprehensive care model that supports patients to achieve sustained nutritional ketosis while eating to satiety may have robust benefits in T2D management. This intervention utilizes continuous care through intensive, digitally enabled support including telemedicine access to a medical provider (physician or nurse practitioner), health coaching, nutrition and behavior change education and individualized care plans, biometric feedback, and peer support via an online community. Thus, the purpose of this study was to assess the effectiveness and safety of a novel care model (Virta Clinic, Virta Health; San Francisco, CA, USA) for the management of T2D after 1 year. Secondary aims were (1) to determine if a difference in primary outcomes existed between participants who self-selected on-site versus web-based education delivery and (2) explore the time course of biomarker change at 70 days and 1 year into the CCI. Primary endpoints to assess effectiveness of the intervention were change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), body weight, and medication prescription after 1 year. Secondary outcomes, including clinical biomarkers of associated physiological systems and adverse events, were assessed to determine safety of the intervention.
Methods
We utilized an open-label, non-randomized, controlled, before-and-after study design with a cohort of patients who self-selected to participate in the metabolic and continuous care intervention (CCI) for T2D and a comparison group of patients who self-selected to participate while receiving their usual care (UC) from their own medical providers and diabetes education program (Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier NCT02519309). Adults diagnosed with T2D were recruited via clinical referrals, local advertisements, and word of mouth in Lafayette, Indiana, USA and surrounding region from August 2015 through March 2016. This study was approved by the Franciscan Health Lafayette Institutional Review Board. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Continuous Care Intervention
Participants in the CCI underwent history and physical exam followed by laboratory testing to ensure they met inclusion and exclusion criteria (Supplementary Materials A). Upon qualifying, CCI participants received biomarker tracking tools including a cellular-connected body weight scale (BT003, Body Trace; New York, NY, USA), a finger-stick blood glucose and ketone meter (Precision Xtra, Abbott; Alameda, CA, USA), and a blood pressure cuff if hypertension was diagnosed (BP742 N, Omron Healthcare, Inc.; Lake Forest, IL, USA). Access to a web-based software application (app) was provided for biomarker reporting and monitoring, education, and communication with remote care team (via telemedicine) consisting of a health coach and medical provider (physician or nurse practitioner) for advice and medication management. Social support was provided via an online peer community. Participants in the CCI retained their primary care provider (PCP) for conditions other than metabolic disease, and care coordination between the PCP and CCI provider occurred as needed. Frequency and type of biomarker tracking were individualized on the basis of care needs and recorded by participants in the app; initial participant instructions were to weigh and measure blood BHB concentration daily, and to measure blood glucose one to three times daily. The remote care team monitored this information; a medical provider made medication changes as indicated by the participant-reported biomarkers (Supplementary Materials B).
Participants were provided individualized nutrition recommendations that allowed them to achieve and sustain nutritional ketosis with a goal of 0.5–3.0 mmol L−1 blood BHB. Participants were encouraged to report daily hunger, cravings, energy, and mood on a four-point Likert scale. These ratings and BHB concentrations were utilized to adjust nutritional guidance. With the insulin resistance characteristic of T2D, patients typically require total dietary carbohydrates to be restricted to less than 30 g day−1 to achieve nutritional ketosis. Health coaches monitored blood BHB concentrations logged by participants and worked with participants individually to adjust dietary carbohydrate intake to a level that would allow them to achieve nutritional ketosis. Daily protein intake was initially targeted to a level of 1.5 g kg−1 of reference (i.e., medium-frame “ideal”) body weight and adjusted as necessary to aid participants in achieving nutritional ketosis based on participant-logged blood BHB concentrations. Participants were coached to incorporate dietary fats to satiety. Participants were advised to consume adequate intake of omega-3 (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) and omega-6 (linoleic acid) polyunsaturated fats [22], while it was recommended that the remainder of their intake from fat come from both monounsaturated and saturated sources. Other aspects of the diet were individually prescribed to ensure safety, effectiveness, and satisfaction, including consumption of 3–5 servings of non-starchy vegetables and adequate mineral and fluid intake for the ketogenic state. At onset of dietary changes, participants were advised to consume a multivitamin, 1000–2000 IU vitamin D3, and up to 1000 mg omega-3 daily. If participants exhibited signs of magnesium depletion (e.g., muscle twitches or cramps), daily supplementation (500 mg magnesium oxide or 200 mg magnesium chloride) was suggested. If participants exhibited headaches, constipation, or lightheadedness, adequate sodium and fluid intake was recommended. BHB concentrations were also utilized as a marker of adherence to nutritional ketosis. Behavior change strategies were utilized by the remote care team and tailored to the needs of each participant to help achieve glycemic control. Examples of techniques utilized include education of natural consequences, shaping knowledge, goal setting, self-monitoring, feedback, monitoring and reinforcement from health coach and medical provider, self-belief, social support, relapse prevention, associations, and repetition.
Participants in the CCI self-selected how they would receive most of their education: (1) via on-site group education classes that met weekly for 12 weeks, bi-weekly for 12 weeks, and monthly for 6 months (n = 136; CCI-onsite) or (2) via web-based, recorded educational content viewed independently through the app (n = 126; CCI-web). Educational content was the same regardless of delivery method (Supplementary Materials C), and all other aspects of care were the same. During on-site classes, health coaches presented educational content and medical providers met with participants individually. Participants receiving web-based education could schedule visits with the CCI medical provider if desired. Apart from education delivery, both groups received remote care from health coaches.
Usual Care
Participants in the UC group were patients with diagnosed T2D who were recently referred to the local diabetes education program by their primary care physician or endocrinologist where they were counseled by registered dietitians on diabetes self-management, nutrition, and lifestyle [7]. Medical care for their T2D was provided by their primary care physician or endocrinologist. No modification to the care that they received for their T2D was made by the study. This group was observed at baseline and 1 year as reference for typical disease treatment and progression over 1 year within the same geographical, health care, and laboratory locations. UC participants attended a separate information session and informed consent was obtained followed by laboratory testing to ensure they met all inclusion and exclusion criteria. Patients were informed that the trial also had an intervention arm and could participate in that group if they chose to do so.
Outcome Measures
In-clinic vital signs and anthropometrics were obtained at baseline, 70-days (CCI only [23]), and 1-year follow-up. Height was assessed via stadiometer for calculation of body mass index. In-clinic weight for all participants was measured to the nearest 0.1 lb (Model 750, Detecto; Webb City, MO, USA) and converted to kg. In-clinic blood pressure was obtained manually by trained staff after participants rested in a seated position for 5 min. Adverse events were reported to the Principal Investigator and reviewed by the Institutional Review Board.
Fasted blood draws occurred at baseline, 70-days (CCI only [23]), and 1-year follow up. Blood analytes were determined via standard procedures at a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendment (CLIA) accredited laboratory on the day of sample collection or from stored serum (Supplementary Materials D).
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using JMP software (version 5.1, SAS Institute; Cary, SC, USA) for all analyses except multiple imputation, for which we used Stata software (version 11, StataCorp; College Station, TX, USA). Multiple imputation was used to estimate means and standard errors that include the variability between imputations. Missing values were estimated from 700 imputations from multivariate normal regression. The number of missing data points for each measure can be determined from the difference between all participants and completers in Tables 1 and S1. Across all biomarkers, 4% of baseline values and 24% of 1-year values were missing (due to dropout, incalculable values, or inability to procure timely samples) and thus imputed to conduct the intention-to-treat analysis. Two-sample t tests were used to test whether baseline differences and differences between 1-year biomarker changes were significant. Within-group changes were tested using paired t test and analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) when adjusted for baseline covariates (sex, age, baseline BMI, insulin use versus non-use, and African-American race). Although tables present triglyceride and hsCRP summary statistics in clinical units, significance levels were obtained from log-transformed values to reduce skewness. For completer analysis, percent change was calculated as the mean difference (Table 2) divided by the mean baseline value (Table 1). Significant changes in medication use and the proportion of patients with HbA1cat least 48 mmol mol−1 (≥ 6.5%) were tested using McNemar test with continuity correction in completers, and linear regression of the changes in the dichotomous states when missing outcome data were imputed. Standard deviations are presented within parentheses and standard errors following “±”. Nominal significance levels (P) are presented in tables; however, a significance level of P < 0.0017 ensures simultaneous significance at P < 0.05 with Bonferroni adjustment for the 30 variables examined. Results presented are intention-to-treat analyses (all), where missing values were estimated by imputation, unless otherwise noted. Participants who withdrew or lacked biomarkers at 1 year were not included in the analyses of completers.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the recruited sample, completers, and participants with missing data by treatment arm
| All | Completers with data | Dropout or missing data | Completers-Dropouts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean (SD) or ±SE | N | Mean (SD) or ±SE | N | Mean (SD) or ±SE | Mean ± SE | |
| Age (years) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 53.75 (8.35) | 218 | 54.09 (8.35) | 44 | 52.09 (8.25) | 2.0 ± 1.37 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 52.33 (9.52) | 78 | 51.71 (9.62) | 9 | 57.78 (6.85) | − 6.07 ± 2.53* |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 1.42 ± 1.14 | 2.38 ± 1.23* | − 5.69 ± 2.6* | ||||
| Female (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 66.79 ± 2.91 | 218 | 65.14 ± 3.23 | 44 | 75.0 ± 6.53 | − 9.86 ± 7.28 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 58.62 ± 5.28 | 78 | 60.26 ± 5.54 | 9 | 44.44 ± 16.56 | 15.81 ± 17.47 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 8.17 ± 6.03 | 4.88 ± 6.41 | 30.56 ± 17.8 | ||||
| African American (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 6.87 ± 1.56 | 218 | 5.96 ± 1.6 | 44 | 11.36 ± 4.78 | − 5.4 ± 5.05 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 78 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 9 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 6.87 ± 1.56§ | 5.96 ± 1.6‡ | 11.36 ± 4.78* | ||||
| Years with type 2 diabetes | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 261 | 8.44 (7.22) | 217 | 8.4 (7.28) | 44 | 8.61 (6.97) | − 0.21 ± 1.16 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 7.85 (7.32) | 71 | 7.85 (7.32) | Not collected | ||
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.59 (0.9) | 0.56 ± 1.0 | |||||
| Beta-hydroxybutyrate (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 248 | 0.17 (0.15) | 186 | 0.17 (0.15) | 62 | 0.19 (0.16) | − 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 0.15 (0.13) | 59 | 0.14 (0.12) | 20 | 0.17 (0.15) | − 0.03 ± 0.03 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.04 | ||||
| Hemoglobin A1c (mmol mol−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 59.55 (16.4) | 204 | 58.35 (15.3) | 58 | 63.49 (19.57) | − 28.66 ± 2.73 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 59.99 (19.24) | 72 | 61.08 (19.89) | 15 | 54.52 (14.87) | − 16.97 ± 4.48 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.44 ± 2.3 | − 2.73 ± 2.62 | 8.96 ± 4.59* | ||||
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 7.60 (1.50) | 204 | 7.49 (1.4) | 58 | 7.96 (1.79) | − 0.47 ± 0.25 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 7.64 (1.76) | 72 | 7.74 (1.82) | 15 | 7.14 (1.36) | 0.60 ± 0.41 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.04 ± 0.21 | − 0.25 ± 0.24 | 0.82 ± 0.42* | ||||
| Fasting glucose (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 258 | 8.92 (3.41) | 202 | 8.8 (3.28) | 56 | 9.36 (3.83) | − 0.55 ± 0.56 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 8.67 (4.03) | 71 | 8.71 (3.96) | 15 | 8.5 (4.5) | 0.21 ± 1.25 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.25 ± 0.48 | 0.1 ± 0.52 | 0.86 ± 1.27 | ||||
| Insulin all (pmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 248 | 198.35 (165.85) | 186 | 197.65 (167.17) | 62 | 200.5 (163.21) | − 2.85 ± 24.1 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 202.17 (172.58) | 59 | 206.68 (187.93) | 20 | 188.77 (119.18) | 17.99 ± 36.18 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 3.82 ± 22.09 | − 9.1 ± 27.36 | 11.74 ± 33.75 | ||||
| C-peptide (nmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 247 | 1.45 (0.71) | 185 | 1.47 (0.72) | 62 | 1.39 (0.69) | 0.07 ± 0.1 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 1.38 (0.82) | 59 | 1.35 (0.82) | 20 | 1.49 (0.84) | − 0.14 ± 0.22 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.07 ± 0.1 | 0.12 ± 0.12 | − 0.09 ± 0.21 | ||||
| HOMA-IR (insulin derived), all | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 244 | 11.8 (13.14) | 179 | 11.19 (12.75) | 65 | 13.48 (14.12) | − 2.3 ± 1.99 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 10.64 (9.12) | 56 | 11.31 (10.05) | 22 | 8.94 (6.03) | 2.36 ± 1.86 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 1.16 ± 1.33 | − 0.12 ± 1.65 | 4.54 ± 2.17 | ||||
| HOMA-IR (insulin derived), excluding exogenous users | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 172 | 11.77 (13.87) | 129 | 11.00 (13.53) | 43 | 14.09 (14.76) | − 3.08 ± 2.55 |
| Usual carea | 43 | 9.40 (8.25) | 25 | 9.36 (9.39) | 18 | 9.45 (6.61) | − 0.09 ± 2.44 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 2.37 ± 1.64 | 1.64 ± 2.22 | 4.63 ± 2.74 | ||||
| HOMA-IR (C-peptide derived) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 239 | 11.52 (7.15) | 170 | 11.44 (6.26) | 69 | 11.72 (9.04) | − 0.28 ± 1.19 |
| Usual carea | 72 | 11.16 (7.26) | 47 | 10.56 (7.70) | 25 | 12.29 (6.33) | − 1.73 ± 1.69 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.36 ± 0.97 | 0.88 ± 1.22 | − 0.56 ± 1.67 | ||||
| Weight-clinic (kg) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 257 | 116.51 (25.94) | 184 | 115.42 (24.62) | 73 | 119.25 (29.01) | − 3.83 ± 3.85 |
| Usual carea | 83 | 105.63 (22.15) | 69 | 106.79 (22.18) | 14 | 99.94 (21.86) | 6.84 ± 6.42 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 10.87 ± 2.92§ | 8.63 ± 3.23† | 19.3 ± 6.76† | ||||
| BMI (kg m−2) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 257 | 40.43 (8.81) | 184 | 39.87 (7.88) | 73 | 41.82 (10.75) | − 1.94 ± 1.39 |
| Usual carea | 83 | 36.72 (7.26) | 69 | 37.14 (7.62) | 14 | 34.66 (4.8) | 2.48 ± 1.58 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 3.7 ± 0.97‡ | 2.73 ± 1.09† | 7.15 ± 1.8§ | ||||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 260 | 131.94 (14.09) | 187 | 132.51 (14.54) | 73 | 130.47 (12.84) | 2.05 ± 1.84 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 129.8 (13.61) | 67 | 128.72 (12.65) | 12 | 135.83 (17.49) | − 7.12 ± 5.28 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 2.14 ± 1.76 | 3.8 ± 1.88* | − 5.37 ± 5.27 | ||||
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 260 | 82.09 (8.25) | 187 | 81.59 (8.05) | 73 | 83.37 (8.67) | − 1.78 ± 1.17 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 82.0 (8.93) | 67 | 81.1 (8.07) | 12 | 87.0 (11.95) | − 5.9 ± 3.59 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.09 ± 1.13 | 0.49 ± 1.15 | − 3.63 ± 3.6 | ||||
| Total cholesterol (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 247 | 4.76 (1.07) | 186 | 4.68 (1.03) | 61 | 4.99 (1.15) | − 0.31 ± 0.17 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 4.76 (1.19) | 59 | 4.72 (1.26) | 20 | 4.88 (0.93) | − 0.16 ± 0.27 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.0 ± 0.15 | − 0.04 ± 0.18 | 0.11 ± 0.26 | ||||
| LDL-cholesterol (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 232 | 102.51 (32.89) | 172 | 100.08 (32.56) | 60 | 109.47 (33.13) | − 9.39 ± 4.94 |
| Usual carea | 70 | 101.50 (36.16) | 48 | 100.38 (37.93) | 22 | 103.95 (32.67) | − 3.58 ± 8.86 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 1.01 ± 4.83 | − 0.29 ± 6.01 | 5.51 ± 8.17 | ||||
| Apo B (g L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 248 | 1.05 (0.29) | 186 | 1.03 (0.28) | 62 | 1.1 (0.31) | − 0.06 ± 0.04 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 1.07 (0.28) | 59 | 1.06 (0.3) | 20 | 1.11 (0.24) | − 0.05 ± 0.07 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.02 ± 0.04 | − 0.02 ± 0.04 | − 0.01 ± 0.07 | ||||
| HDL-C (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 247 | 1.09 (0.35) | 186 | 1.1 (0.36) | 61 | 1.08 (0.32) | 0.02 ± 0.05 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 0.97 (0.29) | 59 | 0.96 (0.29) | 20 | 1.02 (0.29) | − 0.06 ± 0.08 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.12 ± 0.04† | 0.14 ± 0.05† | 0.06 ± 0.08 | ||||
| Triglycerides (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 247 | 2.23 (1.62) | 186 | 2.27 (1.73) | 61 | 2.11 (1.25) | 0.15 ± 0.2 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 3.2 (4.53) | 59 | 3.36 (5.17) | 20 | 2.72 (1.56) | 0.64 ± 0.76 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.97 ± 0.52* | − 1.09 ± 0.68 | − 0.61 ± 0.38* | ||||
| Total/HDL-cholesterol | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 247 | 4.72 (1.7) | 186 | 4.65 (1.72) | 61 | 4.93 (1.65) | − 0.28 ± 0.25 |
| Usual carea | 79 | 5.37 (2.42) | 59 | 5.44 (2.63) | 20 | 5.17 (1.72) | 0.27 ± 0.52 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.65 ± 0.29* | − 0.79 ± 0.36* | − 0.24 ± 0.44 | ||||
| hsC-reactive protein (nmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 249 | 81.33 (138.0) | 193 | 85.62 (153.05) | 56 | 66.76 (62.1) | 18.86 ± 13.81 |
| Usual carea | 85 | 84.67 (82.1) | 70 | 86.95 (86.95) | 15 | 73.81 (73.81) | 13.14 ± 19.14 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 3.24 ± 12.48 | − 1.33 ± 15.05 | − 7.05 ± 18.19 | ||||
| ALT (µkat L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 257 | 0.51 (0.38) | 201 | 0.52 (0.41) | 56 | 0.47 (0.27) | 0.05 ± 0.05 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 0.46 (0.33) | 71 | 0.45 (0.34) | 15 | 0.51 (0.29) | − 0.05 ± 0.09 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | − 0.04 ± 0.08 | ||||
| AST (µkat L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 257 | 0.4 (0.25) | 201 | 0.41 (0.28) | 56 | 0.36 (0.15) | 0.04 ± 0.03 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 0.4 (0.32) | 71 | 0.39 (0.35) | 15 | 0.42 (0.16) | − 0.03 ± 0.06 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.0 ± 0.04 | 0.01 ± 0.05 | − 0.06 ± 0.05 | ||||
| Alkaline phosphatase (µkat L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 256 | 1.24 (0.37) | 200 | 1.24 (0.37) | 56 | 1.23 (0.36) | 0.01 ± 0.05 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 1.29 (0.44) | 71 | 1.31 (0.45) | 15 | 1.22 (0.38) | 0.09 ± 0.11 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.05 ± 0.05 | − 0.07 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.11 | ||||
| Serum creatinine (µmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 258 | 77.79 (21.22) | 202 | 77.79 (20.33) | 56 | 81.33 (24.75) | − 3.54 ± 3.54 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 80.44 (22.1) | 71 | 78.68 (20.33) | 15 | 86.63 (25.64) | − 7.07 ± 7.07 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 1.77 ± 2.65 | − 1.77 ± 2.65 | − 5.3 ± 7.07 | ||||
| BUN (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 258 | 6.03 (2.34) | 202 | 6.06 (2.15) | 56 | 5.9 (2.96) | 0.16 ± 0.42 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 5.73 (2.23) | 71 | 5.59 (1.86) | 15 | 6.38 (3.52) | − 0.79 ± 0.94 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.3 ± 0.28 | 0.47 ± 0.27 | − 0.47 ± 0.99 | ||||
| eGFR (mL s−1 m−2) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 258 | 1.34 (0.23) | 202 | 1.35 (0.22) | 56 | 1.33 (0.25) | 0.02 ± 0.04 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 1.32 (0.23) | 71 | 1.34 (0.22) | 15 | 1.26 (0.28) | 0.08 ± 0.08 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.08 | ||||
| Anion gap (mmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 257 | 6.83 (1.67) | 201 | 6.79 (1.7) | 56 | 6.98 (1.53) | − 0.19 ± 0.24 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 6.93 (1.82) | 71 | 6.92 (1.82) | 15 | 7.0 (1.89) | − 0.08 ± 0.53 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.1 ± 0.22 | − 0.12 ± 0.25 | − 0.02 ± 0.53 | ||||
| Uric acid (µmo L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 261 | 347.99 (86.85) | 202 | 348.58 (86.25) | 59 | 346.2 (89.82) | 2.38 ± 13.09 |
| Usual carea | 85 | 333.12 (87.44) | 71 | 330.74 (85.66) | 14 | 345.01 (98.75) | − 14.28 ± 28.55 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 14.87 ± 10.71 | 17.25 ± 11.9 | 1.19 ± 29.15 | ||||
| TSH (mIU L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 259 | 2.32 (1.74) | 200 | 2.31 (1.79) | 59 | 2.38 (1.55) | − 0.07 ± 0.24 |
| Usual carea | 85 | 1.97 (1.16) | 70 | 2.09 (1.16) | 15 | 1.38 (1.03) | 0.71 ± 0.3* |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.36 ± 0.17* | 0.21 ± 0.19 | 1.0 ± 0.33† | ||||
| Free T4 (pmol L−1) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 260 | 11.84 (2.19) | 202 | 11.84 (2.32) | 58 | 11.58 (2.19) | 0.26 ± 0.39 |
| Usual carea | 86 | 11.33 (3.73) | 71 | 11.33 (3.86) | 15 | 10.94 (2.32) | 0.39 ± 0.77 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.51 ± 0.39 | 0.51 ± 0.51 | 0.64 ± 0.64 | ||||
| Any diabetes medication, excluding metformin (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 56.87 ± 3.06 | 218 | 55.50 ± 3.37 | 44 | 63.64 ± 7.25 | − 8.13 ± 8.00 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 66.67 ± 5.05 | 73 | 68.49 ± 5.44 | 14 | 57.14 ± 13.23 | 11.35 ± 14.32 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 9.80 ± 5.91 | − 12.99± 6.39* | 6.49 ± 15.08 | ||||
| Sulfonylurea (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 23.66 ± 2.63 | 218 | 24.31 ± 2.91 | 44 | 20.45 ± 6.08 | 3.86 ± 6.74 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 24.14 ± 4.59 | 73 | 23.29 ± 4.95 | 14 | 28.57 ± 12.07 | − 5.28 ± 13.05 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.48 ± 5.29 | 1.02 ± 5.74 | − 8.12± 13.52 | ||||
| Insulin (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 29.77 ± 2.82 | 218 | 28.44 ± 3.06 | 44 | 36.36 ± 7.25 | − 7.92 ± 7.87 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 45.98 ± 5.34 | 78 | 50.0 ± 5.66 | 9 | 11.11 ± 10.48 | 38.89 (1.91)‡ |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 16.21 ± 6.04† | − 21.56 ± 6.43‡ | 25.25 ± 12.74* | ||||
| Thiazolidinedione (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 1.53 ± 0.76 | 218 | 1.83 ± 0.91 | 44 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 1.83 ± 0.91* |
| Usual carea | 87 | 1.15 ± 1.14 | 73 | 1.37 ± 1.36 | 14 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 1.37 ± 1.36 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.38 ± 1.37 | 0.46 ± 1.64 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | ||||
| SGLT-2 (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 10.31 ± 1.88 | 218 | 10.55 ± 2.08 | 44 | 9.09 ± 4.33 | 1.46 ± 4.81 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 13.79 ± 3.7 | 73 | 15.07 ± 4.19 | 14 | 7.14 ± 6.88 | 7.93 ± 8.06 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 3.48 ± 4.15 | − 4.52 ± 4.68 | 1.95 ± 8.13* | ||||
| DPP-4 (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 9.92 ± 1.85 | 218 | 10.09 ± 2.04 | 44 | 9.09 ± 4.33 | 1.0 ± 4.79 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 8.05 ± 2.92 | 73 | 8.22 ± 3.21 | 14 | 7.14 ± 6.88 | 1.08 ± 7.60 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 1.87 ± 3.45 | 1.87 ± 3.81 | 1.95 ± 8.13 | ||||
| GLP-1 (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 13.36 ± 2.1 | 218 | 12.84 ± 2.27 | 44 | 15.91 ± 5.51 | − 3.07 ± 5.96 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 14.94 ± 3.82 | 73 | 16.44 ± 4.34 | 14 | 7.14 ± 6.88 | 9.30 ± 8.14 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 1.58 ± 4.36 | − 3.59 ± 4.89 | 8.77 ± 8.82 | ||||
| Metformin (%) | |||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 262 | 71.37 ± 2.79 | 218 | 71.56 ± 3.06 | 44 | 70.45 ± 6.88 | 1.11 ± 7.53 |
| Usual carea | 87 | 60.92 ± 5.23 | 73 | 61.64 ± 5.69 | 14 | 57.14 ± 13.23 | 4.50 ± 14.40 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 10.45 ± 5.93 | 9.92 ± 6.46 | 13.31 ± 14.91 | ||||
See Table S1 (electronic supplemental material) for CCI-web, CCI-onsite, and additional comparisons
aMean and standard deviations for continuous variables, percentages and standard errors for categorical variables
bDifference between means or percentages ± 1 standard error of the difference. Significant baseline difference between means or percentages at 0.05 > P ≥ 0.01 (*); 0.01 > P ≥ 0.001 (†); 0.001 > P ≥ 0.0001 (‡); and P < 0.0001 (§)
Table 2.
Mean changes in biomarkers between baseline and 1-year for participants receiving the CCI and UC
| Completers | All starters (dropouts imputed)d | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted for baselinec | Unadjusted | |||||||
| N | Difference (SD) or ± SE | 1 Year | Significancee | Difference ±SE | Signif-icancee | Difference ± SE | 1 Year | Significancee | |
| Beta-hydroxybutyrate (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | 0.14 (0.36) | 0.31 (0.35) | 2.2 × 10−5 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 2.8 × 10−7 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 0.3 ± 0.02 | 5.8 × 10−7 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 0.04 (0.23) | 0.18 (0.21) | 0.24 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.38 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.1 (0.0) | 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.04 | |||
| Hemoglobin A1c (mmol mol−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 204 | − 14.1 (14.43) | 44.25 (10.28) | <10−16 | − 14.43 ± 0.98 | <10−16 | − 14.21 ± 0.98 | 45.23 ± 0.77 | <10−16 |
| Usual carea | 72 | 2.19 (14.76) | 63.27 (19.89) | 0.21 | 2.4 ± 1.75 | 0.17 | 2.19 ± 1.64 | 62.18 ± 2.08 | 0.18 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 16.29 ± 1.97 | 4.4 × 10−16 | − 16.83 ± 2.08 | 4.4 × 10−16 | − 16.4 ± 1.86 | <10−16 | |||
| Hemoglobin A1c (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 204 | − 1.29 (1.32) | 6.20 (0.94) | <10−16 | − 1.32 ± 0.09 | <10−16 | − 1.30 ± 0.09 | 6.29 ± 0.07 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 72 | 0.20 (1.35) | 7.94 (1.82) | 0.21 | 0.22 ± 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.20 ± 0.15 | 7.84 ± 0.19 | 0.18 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 1.49 ± 0.18 | 4.4 × 10−16 | − 1.54 ± 0.19 | 4.4 × 10−16 | −1.50 ± 0.17 | < 10−16 | |||
| Fasting glucose (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | − 1.96 (3.2) | 6.84 (1.87) | <10−16 | − 2.02 ± 0.26 | 6.0 × 10−15 | − 1.95 ± 0.23 | 6.98 ± 0.17 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.59 (4.59) | 9.3 (4.74) | 0.28 | 0.81 ± 0.45 | 0.07 | 0.63 ± 0.49 | 9.29 ± 0.49 | 0.2 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 2.55 ± 0.59 | 1.5 × 10−5 | − 2.83 ± 0.53 | 7.9 × 10−8 | − 2.58 ± 0.54 | 2.1 × 10−6 | |||
| Insulin, all (pmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | − 75.01 (178.49) | 122.58 (169.6) | 9.9 × 10−9 | − 91.4 ± 12.15 | 5.5 × 10−14 | − 73.62 ± 12.5 | 126.26 ± 12.5 | 4.3 × 10−9 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 12.15 (210.23) | 218.91 (239.46) | 0.66 | 36.88 ± 29.66 | 0.21 | 5.97 ± 24.52 | 206.27 ± 26.11 | 0.81 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 87.23 (29.86) | 0.004 | − 127.58 ± 32.43 | 0.0009 | − 79.59 ± 27.5 | 0.004 | |||
| C-peptide (nmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 185 | − 0.36 (0.57) | 1.11 (0.59) | <10−16 | − 0.34 ± 0.05 | 1.1 × 10−13 | − 0.33 ± 0.04 | 1.11 ± 0.04 | 2.2 × 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 0.08 (0.77) | 1.43 (0.92) | 0.41 | 0.02 ± 0.09 | 0.79 | 0.06 ± 0.09 | 1.44 ± 0.1 | 0.5 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.44 ± 0.11 | 5.4 × 10−5 | − 0.37 ± 0.1 | 0.0004 | − 0.4 ± 0.1 | 5.3 × 10−5 | |||
| HOMA-IR (insulin derived), all | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 179 | − 5.54 (12.19) | 5.65 (8.71) | 1.2 × 10−9 | − 5.87 ± 0.92 | 2.2 × 10−10 | − 5.58 ± 0.86 | 6.16 ± 0.69 | 7.5 × 10−11 |
| Usual carea | 56 | 1.65 (12.46) | 12.96 (12.9) | 0.32 | 2.4 ± 1.76 | 0.17 | 1.82 ± 1.49 | 12.2 ± 1.42 | 0.22 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 7.19 (1.9) | 0.0002 | − 8.27±2.04 | 4.9 × 10−5 | − 7.4 ± 1.72 | 1.6 × 10−5 | |||
| HOMA-IR (insulin derived), e × cluding e × ogenous insulin users | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 129 | − 6.03 (10.67) | 4.98 (5.69) | 1.4 × 10−10 | − 6.13 ± 0.98 | 4.2 × 10−10 | − 6.82 ± 0.9 | 5.61 ± 0.51 | 3.2 × 10−5 |
| Usual carea | 25 | 3.99 (12.76) | 13.35 (14.71) | 0.12 | 4.1 ± 2.34 | 0.08 | 1.84 ± 1.96 | 13.3 ± 1.56 | 0.35 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 10.01 ± 2.72 | 0.0002 | − 10.23 ± 2.56 | 6.3 × 10−5 | − 8.65 ± 2.16 | 6.0 × 10−5 | |||
| HOMA-IR (C-peptide derived) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 170 | − 3.53 (5.59) | 7.9 (3.89) | 2.2 × 10−16 | − 3.53 ± 0.55 | 1.2 × 10−10 | − 3.45 ± 0.46 | 8.25 ± 0.4 | 1.0 × 10−13 |
| Usual carea | 47 | 1.94 (10.54) | 12.49 (10.46) | 0.21 | 1.77 ± 1.12 | 0.11 | 1.65 ± 1.13 | 12.6 ± 1.11 | 0.14 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 5.47 (1.6) | 0.0006 | − 5.29 ± 1.28 | 3.3 × 10−5 | − 5.11 ± 1.22 | 3.0 × 10−5 | |||
| Weight-clinic (kg) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 184 | − 14.24 (10.29) | 101.17 (22.06) | <10−16 | − 13.81 ± 0.63 | <10−16 | − 13.8 ± 0.71 | 102.72 ± 1.5 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 69 | 0.04 (5.94) | 106.82 (22.52) | 0.95 | − 1.11 ± 1.06 | 0.29 | − 0.16 ± 0.84 | 107.31 ± 2.55 | 0.85 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 14.29 ± 1.04 | <10−16 | − 12.7 ± 1.26 | <10−16 | − 13.65 ± 1.1 | < 10−16 | |||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 187 | − 6.77 (16.3) | 125.84 (13.22) | 1.3 × 10−8 | − 6.52 ± 1.24 | 1.6 × 10−7 | − 6.36 ± 1.12 | 125.57 ± 0.91 | 1.3 × 10−8 |
| Usual carea | 67 | 0.25 (17.8) | 128.57 (11.82) | 0.91 | − 0.45 ± 2.15 | 0.83 | − 0.9 ± 2.07 | 129.01 ± 1.72 | 0.67 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 7.02 (2.4) | 0.005 | − 6.07 ± 2.55 | 0.02 | − 5.46 ± 2.36 | 0.02 | |||
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 187 | − 3.59 (9.33) | 78.0 (7.55) | 1.4 × 10−7 | − 3.5 ± 0.7 | 6.2 × 10−7 | − 3.51 ± 0.65 | 78.58 ± 0.56 | 7.2 × 10−8 |
| Usual carea | 67 | − 0.12 (10.15) | 80.99 (9.59) | 0.92 | − 0.39 ± 1.21 | 0.75 | − 0.9 ± 1.2 | 81.12 ± 1.08 | 0.45 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 3.47 ± 1.42 | 0.01 | − 3.10±1.44 | 0.03 | − 2.61 ± 1.37 | 0.06 | |||
| Total cholesterol (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | 0.24 (0.93) | 4.92 (1.18) | 0.0004 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 0.004 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 4.97 ± 0.08 | 0.006 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 0.00 (1.60) | 4.72 (1.62) | 0.99 | 0.0 ± 0.16 | 0.98 | − 0.04 ± 0.18 | 4.69 ± 0.18 | 0.83 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.25 ± 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.25 ± 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.24 ± 0.19 | 0.2 | |||
| LDL-C (mmol−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 172 | 0.28 (0.83) | 2.87 (0.98) | 7.7 × 10−6 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 2.6 × 10−5 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | 2.94 ± 0.07 | 5.1 × 10−5 |
| Usual carea | 48 | − 0.28 (0.97) | 2.32 (0.8) | 0.05 | −0.28 ± 0.13 | 0.03 | − 0.28 ± 0.12 | 2.32 ± 0.12 | 0.02 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.56 ± 0.15 | 0.0003 | 0.56 ± 0.15 | 0.0002 | 0.54 ± 0.14 | 0.0001 | |||
| Apo B (g L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | − 0.01 (0.24) | 1.03 (0.29) | 0.69 | − 0.0 ± 0.02 | 0.82 | − 0.02 ± 0.02 | 1.04 ± 0.02 | 0.37 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 0.02 (0.37) | 1.07 (0.39) | 0.75 | 0.0 ± 0.04 | 0.9 | 0.0 ± 0.04 | 1.06 ± 0.04 | 0.95 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.02 (0.05) | 0.66 | − 0.01 ± 0.05 | 0.83 | − 0.02 ± 0.05 | 0.67 | |||
| HDL-C (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | 0.20 (0.31) | 1.29 (0.41) | <10−16 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | <10−16 | 0.2 ± 0.02 | 1.29 ± 0.03 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 59 | − 0.04 (0.23) | 0.92 (0.32) | 0.15 | − 0.02 ± 0.04 | 0.69 | − 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.04 | 0.41 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 1.7 × 10−10 | 0.2 ± 0.05 | 9.9 × 10−6 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 1.3 × 10−8 | |||
| Triglycerides (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | − 0.56 (1.9) | 1.71 (1.64) | <10−16 | − 0.56 ± 0.18 | 9.3 × 10−15 | − 0.54 ± 0.14 | 1.67 ± 0.13 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 0.34 (3.40) | 3.7 (5.67) | 0.22 | − 0.35 ± 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.32 ± 0.37 | 3.45 ± 0.55 | 0.43 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.9 ± 0.46 | 1.4 × 10−7 | − 0.92 ± 0.38 | 7.5 × 10−6 | − 0.86 ± 0.39 | 9.9 × 10−7 | |||
| Total/HDL-cholesterol | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 186 | − 0.47 (1.41) | 4.18 (1.71) | 4.1 × 10−6 | − 0.45 ± 0.16 | 0.005 | − 0.53 ± 0.12 | 4.19 ± 0.13 | 1.7 × 10−5 |
| Usual carea | 59 | 0.52 (3.45) | 5.96 (4.27) | 0.24 | 0.44 ± 0.29 | 0.13 | 0.42 ± 0.36 | 5.73 ± 0.43 | 0.24 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 1.00 ± 0.46 | 0.03 | − 0.89 ± 0.33 | 0.008 | − 0.95 ± 0.38 | 0.01 | |||
| hsC−reactive protein (nmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 193 | − 31.71 (127.15) | 53.81 (67.24) | <10−8 | − 29.43 ± 9.14 | <10−16 | − 34.29 ± 10.0 | 52.86 ± 5.24 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 70 | 12.48 (126.86) | 99.43 (139.91) | 0.94 | 8.48 ± 16.1 | 0.88 | 12.48 ± 14.1 | 97.72 ± 14.76 | 0.93 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 44.29 (17.14) | 1.2 × 10−6 | − 37.91 ± 18.55 | 3.0 × 10−5 | − 46.76 ± 17.24 | 9.3 × 10−7 | |||
| ALT (µkat L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 201 | − 0.16 (0.4) | 0.36 (0.19) | 9.5 × 10−9 | − 0.16 ± 0.03 | 9.4 × 10−10 | − 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 2.4 × 10−10 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.01 (0.28) | 0.47 (0.34) | 0.67 | 0.02 ± 0.05 | 0.67 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.04 | 0.77 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.18 (0.04) | 5.1 × 10−5 | − 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.0009 | − 0.16 ± 0.04 | 4.6 × 10−5 | |||
| AST (µkat L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 201 | − 0.09 (0.27) | 0.32 (0.11) | 2.8 × 10−6 | − 0.09 ± 0.02 | 1.3 × 10−5 | − 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 5.1 × 10−7 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.01 (0.32) | 0.4 (0.27) | 0.79 | 0.01 ± 0.04 | 0.69 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.72 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.1 (0.04) | 0.02 | − 0.1 ± 0.04 | 0.02 | − 0.09 ± 0.04 | 0.01 | |||
| Alkaline phosphatase (µkat L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 200 | − 0.16 (0.24) | 1.07 (0.35) | <10−8 | − 0.17 ± 0.02 | <10−16 | − 0.16 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.02 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.0 (0.22) | 1.31 (0.45) | 0.94 | 0.02 ± 0.03 | 0.61 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 1.3 ± 0.05 | 0.67 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.17 (0.03) | 6.3 × 10−8 | − 0.18 ± 0.03 | 1.4 × 10−7 | − 0.17 ± 0.03 | 3.1 × 10−8 | |||
| Serum creatinine (µmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | − 3.54 (14.14) | 73.37 (18.56) | 0.0001 | − 3.54 ± 0.88 | 0.001 | − 3.54 ± 0.88 | 74.26 ± 0.88 | 0.0001 |
| Usual carea | 71 | − 0.88 (18.56) | 77.79 (18.56) | 0.56 | − 2.65 ± 1.77 | 0.15 | − 1.77 ± 1.77 | 78.68 ± 1.77 | 0.29 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 2.65 ± 2.65 | 0.32 | − 0.88 ± 2.65 | 0.73 | − 1.77 ± 2.65 | 0.49 | |||
| BUN (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | 0.76 (2.49) | 6.82 (2.78) | 1.5 × 10−5 | 0.75 ± 0.17 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 0.79 ± 0.17 | 6.81 ± 0.19 | 5.5 × 10−6 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.07 (2.15) | 5.66 (2.11) | 0.78 | 0.06 ± 0.3 | 0.85 | − 0.01 ± 0.27 | 5.72 ± 0.26 | 0.97 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.69 (0.29) | 0.03 | 0.69 (0.32) | 0.05 | 0.8 ± 0.32 | 0.01 | |||
| eGFR (mL s−1 m−2) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | 0.03 (0.15) | 1.38 (0.2) | 0.003 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.009 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.38 ± 0.01 | 0.005 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.01 (0.19) | 1.34 (0.22) | 0.51 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.36 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 1.34 ± 0.02 | 0.48 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.61 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.51 | |||
| Anion gap (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 201 | 0.29 (2.02) | 7.08 (1.75) | 0.04 | 0.28 ± 0.15 | 0.06 | 0.28 ± 0.14 | 7.13 ± 0.12 | 0.04 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.83 (2.44) | 7.75 (1.97) | 0.004 | 0.84 ± 0.26 | 0.001 | 0.81 ± 0.26 | 7.75 ± 0.22 | 0.002 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.54 (0.3) | 0.09 | − 0.56 ± 0.31 | 0.07 | − 0.53 ± 0.3 | 0.08 | |||
| CO2 (mmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | 0.12 (2.26) | 28.06 (2.29) | 0.45 | 0.16 ± 0.18 | 0.38 | 0.18 ± 0.16 | 27.94 ± 0.16 | 0.27 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.17 (2.97) | 28.23 (2.58) | 0.63 | − 0.2 ± 0.3 | 0.51 | 0.04 ± 0.33 | 28.12 ± 0.29 | 0.9 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.05 (0.3) | 0.9 | 0.36 ± 0.36 | 0.32 | 0.14 ± 0.37 | 0.71 | |||
| Uric acid (µmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | 0.59 (70.79) | 349.18 (91.01) | 0.91 | 1.78 ± 4.76 | 0.72 | 1.78 ± 4.76 | 349.77 ± 5.95 | 0.67 |
| Usual carea | 71 | − 10.71 (64.24) | 320.03 (85.06) | 0.15 | − 16.66 ± 8.92 | 0.06 | − 11.9 ± 7.73 | 322.41 ± 10.11 | 0.13 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | 11.3 ± 8.92 | 0.21 | 18.44 ± 10.11 | 0.07 | 13.68 ± 8.92 | 0.13 | |||
| TSH (mIU L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 200 | − 0.41 (1.62) | 1.9 (1.1) | 0.0004 | − 0.4 ± 0.11 | 0.0002 | − 0.42 ± 0.1 | 1.91 ± 0.08 | 5.3 × 10−5 |
| Usual carea | 70 | − 0.09 (0.99) | 2.01 (0.99) | 0.47 | − 0.09 ± 0.19 | 0.64 | 0.0 ± 0.12 | 1.96 ± 0.12 | 0.98 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.33 ± 0.16 | 0.05 | − 0.31 ± 0.22 | 0.15 | − 0.42 ± 0.16 | 0.01 | |||
| Free T4 (pmol L−1) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 202 | 0.13 (2.32) | 11.97 (2.45) | 0.7 | 0.0 ± 0.26 | 0.83 | 0.13 ± 0.13 | 11.97 ± 0.13 | 0.58 |
| Usual carea | 71 | 0.26 (4.25) | 11.58 (2.83) | 0.7 | 0.26 ± 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.26 ± 0.39 | 11.46 ± 0.26 | 0.61 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 0.13 (0.0) | 0.8 | − 0.26 ± 0.39 | 0.43 | − 0.13 ± 0.51 | 0.78 | |||
| Any diabetes medication, e × cluding metformin (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 27.52 (49.65) | 27.98 ± 3.05 | 2.2 × 10−16 | − 27.66 ± 3.21 | <10−16 | − 27.19 ± 3.14 | 29.68 ± 2.94 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 6.85 (34.68) | 75.34 ± 5.08 | 0.09 | 7.54 ± 5.87 | 0.2 | 5.99 ± 4.31 | 72.66 ± 5.0 | 0.09 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 34.37 ± 5.27 | 7.0 × 10−11 | − 35.36 ± 6.83 | 2.3 × 10−7 | − 33.19 ± 5.34 | 9.0 × 10−9 | |||
| Sulfonylurea (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 24.31 (43.0) | 0.0 ± 0.0 | <10−16 | − 24.23 ± 2.86 | <10−16 | − 23.67 ± 2.7 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | < 10−16 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 2.74 (37.17) | 26.02 ± 5.17 | 0.53 | 2.56 ± 5.24 | 0.63 | 1.91 ± 4.23 | 26.02 ± 5.17 | 0.65 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 27.05 ± 5.23 | 2.4 × 10−7 | − 26.85 ± 6.07 | 9.7 × 10−6 | − 25.58 ± 5.02 | 3.3 × 10−7 | |||
| Insulin (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 13.3 (35.37) | 15.14 ± 2.43 | 2.8 × 10−8 | − 15.5 ± 2.0 | 9.3 × 10−15 | − 13.03 ± 2.22 | 16.74 ± 2.4 | 4.3 × 10−9 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 1.37 (31.15) | 52.05 ± 5.89 | 0.71 | 8.46 ± 3.65 | 0.02 | 3.17 ± 3.68 | 49.18 ± 5.45 | 0.39 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 14.67 ± 4.36 | 0.0008 | − 23.89 ± 4.24 | 1.8 × 10−8 | − 16.19 ± 4.3 | 0.0002 | |||
| Thiazolidinedione (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 1.38 (15.12) | 0.46 ± 0.46 | 0.18 | − 1.47 ± 0.9 | 0.1 | − 1.1 ± 0.91 | 0.42 ± 0.49 | 0.23 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 0.0 (0.0) | 1.37 ± 1.37 | 0.26 ± 1.64 | 0.87 | 0.22 ± 0.51 | 1.27 ± 1.26 | 0.67 | |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 1.38 ± 1.02 | 0.18 | − 1.78 ± 1.91 | 0.35 | − 1.31 ± 1.04 | 0.21 | |||
| SGLT−2 (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 9.63 (29.57) | 0.92 ± 0.65 | 1.5 × 10-6 | − 9.96 ± 2.04 | 1.1 × 10−6 | − 9.26 ± 1.88 | 0.92 ± 1.88 | 9.0 × 10−7 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 0.0 (28.87) | 15.07 ± 4.22 | 1 | 1.13 ± 3.72 | 0.76 | 0.87 ± 3.17 | 15.07 ± 4.21 | 0.78 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 9.63 ± 3.93 | 0.01 | − 11.0 ± 4.32 | 0.01 | − 10.13 ± 3.69 | 0.006 | |||
| DPP−4 (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 3.67 (34.42) | 6.42 ± 1.66 | 0.12 | − 3.69 ± 2.21 | 0.09 | − 3.52 ± 2.21 | 6.29 ± 1.66 | 0.11 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 2.74 (23.41) | 10.96 ± 3.68 | 0.32 | 2.97 ± 4.05 | 0.46 | 2.64 ± 2.92 | 10.74 ± 3.51 | 0.37 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 6.41 ± 3.6 | 0.07 | − 6.64 ± 4.7 | 0.16 | − 6.16 ± 3.66 | 0.09 | |||
| GLP−1 (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | 0.92 (34.6) | 13.76 ± 2.34 | 0.7 | 1.15 ± 2.31 | 0.62 | 0.98 ± 2.3 | 14.4 ± 2.29 | 0.67 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 2.74 (33.22) | 19.18 ± 4.64 | 0.48 | 2.09 ± 4.23 | 0.62 | 2.94 ± 3.84 | 17.02 ± 4.39 | 0.44 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 1.82 ± 4.54 | 0.69 | − 0.99 ± 4.91 | 0.84 | − 1.96 ± 4.48 | 0.66 | |||
| Metformin (%) | |||||||||
| CCI-all educationa | 218 | − 7.34 (46.45) | 64.22 ± 3.25 | 0.02 | − 7.14 ± 3.0 | 0.02 | − 6.34 ± 3.06 | 65.18 ± 3.14 | 0.04 |
| Usual carea | 78 | 0.0 (37.27) | 61.64 ± 5.73 | 1 | 0.83 ± 5.5 | 0.88 | − 0.08 ± 4.55 | 60.67 ± 5.61 | 0.99 |
| CCI-all vs. usual careb | − 7.34 ± 5.38 | 0.17 | − 7.95 ± 6.38 | 0.21 | − 6.26 ± 5.48 | 0.25 | |||
See Table S2 (electronic supplemental material) for CCI-web, CCI-onsite, and additional comparisons
aImputed values based on 700 iterations from multivariate normal regression
bAdjusted for sex, age, baseline BMI, baseline insulin use (user vs. non-user), and African-American race
cA significance level of P < 0.0017 ensures overall simultaneous significance of P ≤ 0.05 over the 30 variables using Bonferroni correction
dMeans (standard deviations) are presented. Sample sizes, means, and significance levels refer to subjects with baseline and 1-year measurements for completers, and to 349 subjects (262 intervention and 87 usual care) for all starters. Significance levels for completers refer to one-sample t test with or without adjustment. Untransformed triglyceride and hsC-reactive protein values are presented; however, their statistical significances were based on their log-transformed values. CCI-all refers to the CCI-web and CCI-onsite combined
eMean differences ± one standard error. Significance levels refer to two-sample t test or analysis of covariance for the differences
Results
Participant Characteristics
Table 1 presents baseline characteristics of the 262 CCI and 87 UC participants. At baseline, 88% of CCI participants were prescribed diabetes medication (57% were prescribed a diabetes medication other than metformin, 30% prescribed insulin) and 93% were obese. Eighty-seven percent of participants in UC at baseline were prescribed diabetes medication (46% prescribed insulin), and 82% were obese. Forty-four participants (16.8%) withdrew from the CCI, 22 from each education delivery mode. Baseline characteristics of CCI dropouts did not differ significantly from the 218 completers except none of the five thiazolidinedione users were dropouts (Table 1). At baseline, characteristics of CCI participants who self-selected web-based versus on-site education were not significantly different after accounting for multiple comparisons (see Table S1 in the electronic supplementary material). Compared to the 78 UC participants who completed the study, the nine that withdrew tended to be older (58 versus 52 years old), had lower TSH, and fewer were prescribed insulin, SGLT-2, DPP-4, GLP-1, or blood pressure medications (Table 1).
Effectiveness
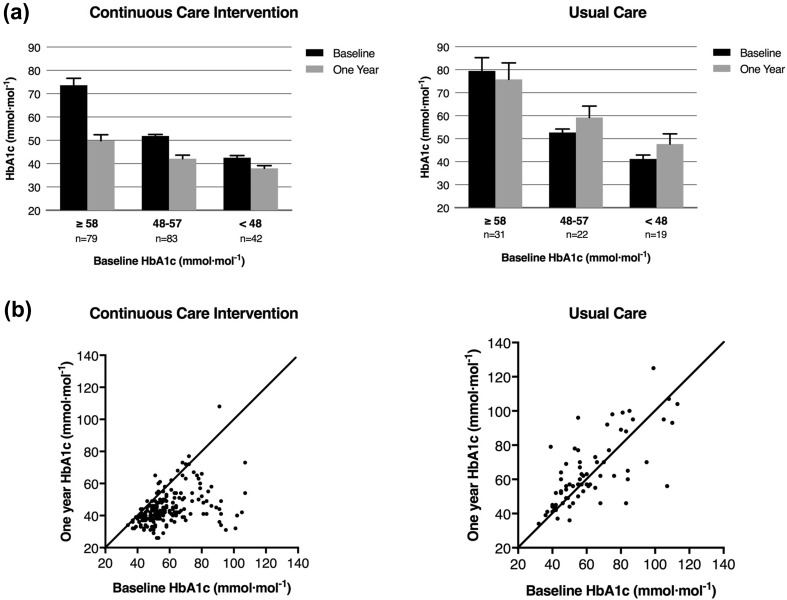
Table 2 presents mean 1-year changes in biomarkers. In the CCI, HbA1c was significantly reduced 17%, from 60 ± 1.0 mmol mol−1 (7.6 ± 0.09%) at baseline to 45 ± 0.8 mmol mol−1 (6.3 ± 0.07%) after 1 year (nominal significance P < 1.0 × 10−16; Fig. 1). Eighty-five percent (174/204) of CCI participants completing 1-year HbA1c testing observed a decline greater than 2.2 mmol mol−1 (> 0.2%) in the measure. When adjusted for multiple comparisons, significant within-CCI reductions were observed in fasting glucose (− 22%, P < 1.0 × 10−16), fasting insulin (− 43%, P = 6.7 × 10−16), C-peptide (− 23%, P = 2.2 × 10−16), HOMA-IR derived from fasting insulin excluding exogenous users (− 55%, P = 3.2 × 10−5), HOMA-IR derived from C-peptide (− 29%, P = 1.0 × 10−13), weight from clinic measurements (− 12%, P < 1.0 × 10−16), weight from home scales (− 13%, P < 1.0 × 10−16, Fig. 2), triglycerides (− 24%, P < 1.0 × 10−16), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (− 39%, P < 1.0 × 10−16), ALT (− 30%, P = 2.4 × 10−10), AST (− 21%, P = 5.1 × 10−7), and alkaline phosphatase (− 13%, P < 1.0 × 10−16). HDL-cholesterol increased 18% (P < 1.0 × 10−16) and calculated LDL-cholesterol increased 10% (P = 5.1 × 10−5) while apolipoprotein B (ApoB) concentration was unchanged (P = 0.37) for participants in the CCI. There were no significant differences in mean biomarker changes between CCI-web and CCI-onsite (see Table S2 in the electronic supplementary material). In contrast to the CCI, patients enrolled in UC for 1 year showed no Bonferroni-adjusted significant change for any of the biomarkers measured (Table 2).
Fig. 1.
Change in HbA1c over the course of 1 year for CCI and UC groups. a Mean (95% CI) in HbA1c based on starting value at baseline and 1 year for completers in both groups. b Individual changes in HbA1c over 1 year for completers in both groups
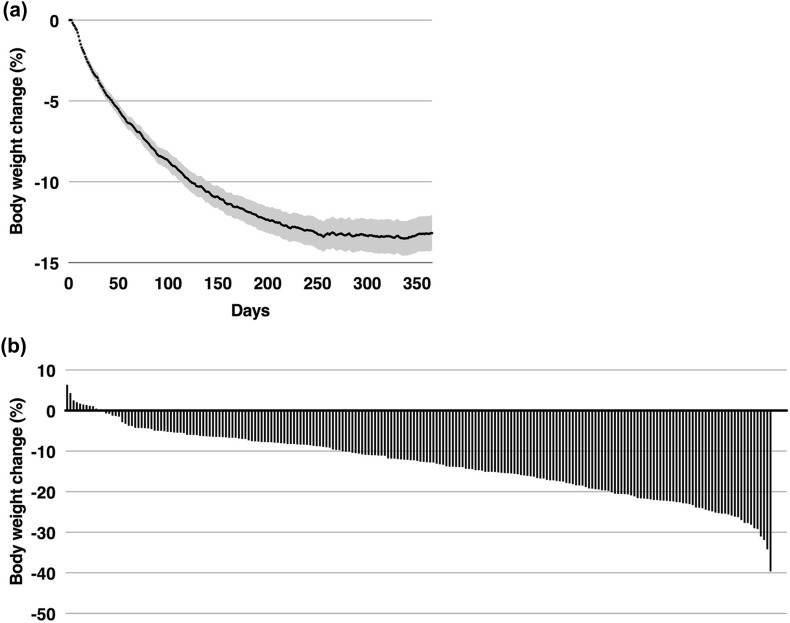
Fig. 2.
Body weight change over the course of 1 year in CCI completers. a Mean (95% CI) change in body weight for completers over the course of 1 year. For each individual, weight on a given day was computed as the 3-day trailing mean (to reduce day-to-day variation). On dates where no weights were recorded during the 3-day time window for a given participant, the most recent 3-day mean preceding the date was used. b Histogram depicting individual body weight changes at 1 year
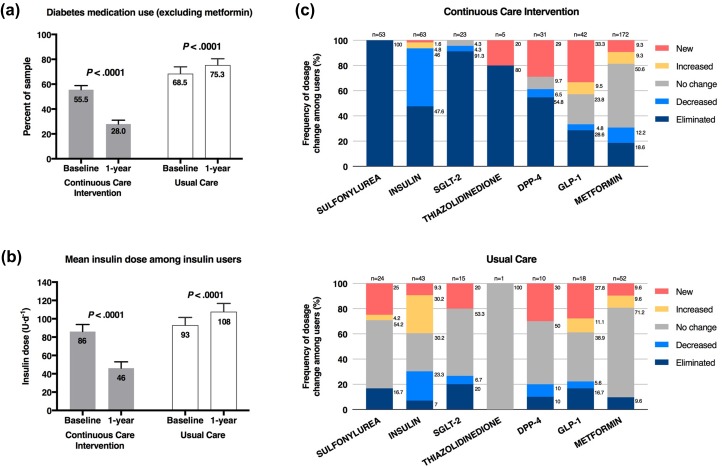
Following 1 year of CCI, usage of all diabetes medications combined (excluding metformin) was reduced significantly (56.9 ± 3.1% to 29.7 ± 3.0%, P < 1.0 × 10−16) through decreased prescriptions for DPP-4 (9.9–6.3%, P = 0.11), insulin (29.8–16.7%, P = 4.3 × 10−9), SGLT-2 inhibitors (10.3–0.9%, P = 9 × 10−7), sulfonylureas (23.7–0%, P < 1.0 × 10−16), and thiazolidinediones (1.5–0.4%, P = 0.23) (Fig. 3). GLP-1 prescriptions were statistically unchanged (13.4% at baseline to 14.4% at 1 year, P = 0.67), and metformin decreased slightly (71.4–65.0%, P = 0.04) for CCI participants. Forty percent (31/78) of CCI participants who began the study with insulin prescriptions (average dose of 64.2 units) eliminated the medication, while the remaining 60% (47/78) of insulin users reduced daily dosage from 105.2 to 53.8 units (P < 0.0001). Patients enrolled in UC for 1 year showed no Bonferroni-adjusted significant change for prescription of medication. For the 34 UC participants that continued using insulin, the average daily dose increased from 96.0 to 111.9 units.
Fig. 3.
Medication changes over the course of 1 year in completers of the CCI and UC groups. a Proportion of completers prescribed diabetes medications other than metformin. b Mean ± SE prescribed dose among insulin users. c Frequency in change of medication dosage among prescribed users by diabetes medication class in both groups
The proportion of participants in the total imputed CCI group with HbA1cbelow 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) increased from 19.5 ± 2.4% to 69.8 ± 3.1%. Of those in the CCI with HbA1c reported at 1 year, 72% (147/204) achieved HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (6.5%) and 60.3% (123/204) of participants achieved HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) while taking no diabetes medication or only metformin. Of those in the CCI with HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) at 1 year, 42.3% (52/123) were prescribed no diabetes medication and 57.7% (71/123) were prescribed metformin only. The proportion of the total imputed CCI group with fasting glucose below 6.99 mmol L−1 at 1 year increased from 34.9 ± 3.3% to 58.4 ± 3.9%, and the proportion with class III obesity decreased from 45.5 ± 3.1% to 19.6 ± 2.8%.
Compared to UC, the CCI showed significant Bonferroni-adjusted (P < 0.0017) net reductions in HbA1c (nominal significance for the two-group comparison, P < 10−16; Fig. 1), fasting glucose (P = 2.1 × 10−6), fasting insulin excluding exogenous users (P = 4.6 × 10−5), C-peptide (P = 5.3 × 10−5), HOMA-IR derived from insulin excluding exogenous users (P = 6.0 × 10−5) or derived from C-peptide (P = 3.0 × 10−5), weight (P < 10−16), triglycerides (P = 1.0 × 10−6), hsCRP (P = 9.3 × 10−7), ALT (P = 4.6 × 10−5), and alkaline phosphatase (P = 3.1 × 10−8). All of these group differences remained significant when adjusted for the baseline age, sex, insulin medication use, and body mass index (Table 2). The CCI decrease in diabetes medication use was significantly greater than the changes in the UC group for all diabetes medications (P < 10−16) and all diabetes medications excluding metformin (P = 9.0 × 10−9), including sulfonylurea (P = 3.3 × 10−7) and insulin (P = 0.0002) (Fig. 3).
The CCI-web and CC-onsite sub-cohorts provide replication of the above results. Specifically, Table S2 (see electronic supplementary material) shows that within-group Bonferroni significance was achieved separately for the mean 1-year reductions in HbA1c, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, C-peptide, HOMA-IR, triglycerides, and hsCRP, and the significant increases in HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol. The Bonferroni-adjusted significant differences from the UC cohort were also replicated by the two educational sub-cohorts for HbA1c, fasting glucose, insulin-derived HOMA-IR, weight, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, hsCRP, and alkaline phosphatase, with or without adjustment for baseline covariates.
Time Course of Biomarker Change in CCI
Over the course of the intervention at baseline, 70 days [23], and 1 year, the proportion of participants in the total imputed CCI with HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) increased from 19.5 ± 2.4 to 60.7 ± 3.1 to 69.8 ± 3.1%; the proportion with fasting glucose below 6.99 mmol L−1 (< 126 mg dL−1) increased from 34.9 ± 3.3 to 55.5 ± 3.3 to 58.4 ± 3.9%, and the proportion with class III obesity decreased from 45.5 ± 3.1, to 30.2 ± 3.1, to 19.6 ± 2.8%.
The time course of biomarker changes also differed by variable (see Table S3 in the electronic supplementary material). Most of the 1-year improvements in diabetes risk factors were achieved during the first 70 days of the intervention including 84% of the HbA1c decrease, 90% of the fasting glucose decrease, 73% of the fasting insulin decrease, 64% of the C-peptide decrease, and 87% and 74% of the decreases in HOMA-IR as estimated from fasting insulin and C-peptide concentrations, respectively. Improvements in blood pressure also mostly occurred in the initial 70 days, as did reductions in alkaline phosphatase, serum creatinine, and eGFR. Most of the plasma triglyceride decrease occurred during the first 70 days (87%), whereas essentially all the substantial increase in HDL-cholesterol occurred between the initial 70 days of the intervention and 1 year (99%). About 60% of weight loss occurred in the first 70 days.
Retention and Adherence in CCI
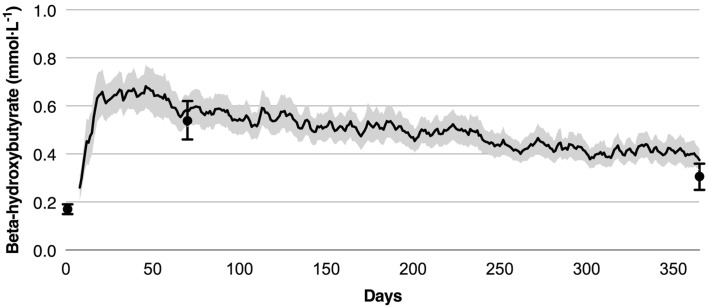
Eighty-three percent of participants remained enrolled in the CCI at 1 year. Nearly all CCI participants (96%) reported at least one BHB reading of 0.5 mmol L−1 or more by handheld measure, and among completers, the group mean at 70 days by laboratory measure was over threefold the baseline (0.54 ± 0.04 versus 0.17 ± 0.01 mmol L−1). Laboratory-measured BHB at 1 year (0.31 ± 0.03 mmol L−1) was nearly double the baseline value (Fig. 4). The intention-to-treat analysis yielded similar results, with an increase in average from baseline (0.17 ± 0.01 mmol L−1) to 70 days (0.54 ± 0.04 mmol L−1), followed by a decrease at 1 year (0.30 ± 0.02 mmol L−1), though still nearly twofold the baseline concentrations.
Fig. 4.
Beta-hydroxybutyrate concentrations of CCI completers. Note: For each individual in the graph, the BHB concentration on a given day was computed as the 3-day trailing mean (to reduce day-to-day variation). On dates where no BHB concentrations were recorded during the 3-day time window for a given participant, the most recent 3-day mean preceding the date was used. Line graph depicts mean (95% CI) over time for BHB measured at home and reported via the app. Dots and error bars represent the mean ± SE from laboratory measured BHB at baseline, 70 days, and 1 year
Safety and Adverse Events
For CCI participants, acid–base physiology was normal; no cases of metabolic acidosis were observed. One CCI patient (0.38% of starters) had a clinically significant rise in serum creatinine, but group mean declined at 1 year. Mean blood urea nitrogen increased significantly in the CCI group, possibly indicating increased dietary protein consumption although high protein intake was not recommended. Mean uric acid in the CCI rose transiently at 70 days, but was unchanged at 1 year; no new cases of gout were diagnosed. Mean free T4 level was unchanged, and TSH was significantly lower at 1 year; two new cases of subclinical hypothyroidism were observed (0.76% of starters) in the CCI [24].
Adverse events occurred in 6/262 CCI participants including one non-ST-segment myocardial infarction, one inferior myocardial ischemia by electrocardiogram, one metastatic neuroendocrine carcinoma, one malignant cancer with multiple brain lesions and lung tumor, and death from renal hemorrhage and failure and hyperkalemia. Also, one episode of hypoglycemia occurred following a motor vehicle accident and medical records indicated the patient was not taking insulin as prescribed; no other episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia requiring assistance were reported. None of the adverse events were attributed to the intervention.
Adverse events were reported in 6/87 UC participants, including one percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to left anterior descending stenosis, one PCI to right coronary artery, two carotid endarterectomies (one of which was successful), multifactorial encephalopathy, and diabetic ketoacidosis with pulmonary emboli.
Discussion
This study evaluated the effectiveness and safety of an alternative treatment model for T2D that utilized continuous remote care to provide a high level of outpatient support combined with individualized nutrition enabling long-term maintenance of behavioral and metabolic change via nutritional ketosis. This trial prospectively observed adults with T2D undergoing treatment via this novel care model and a comparison group of adults with T2D undergoing usual care treatment. Following 1 year of CCI, participants achieved a 14 mmol mol−1 (1.3 ± 0.1%) decline in HbA1c concurrent with 12% weight loss and reduction in medication use. Consistent conclusions were reached with intention-to-treat analysis and analysis of completers. A usual care group showed no change in diabetes status or related biomarkers over the year.
Effectiveness
The CCI reduced HbA1c by 14 mmol mol−1 (1.3%) at 1 year. HbA1c reductions up to 7 mmol mol−1 (0.6%) via intensive lifestyle intervention [25] and 11 mmol mol−1 (1.0%) via an energy-restricted low-carbohydrate diet with partial food provision delivered via an outpatient setting [26] were previously reported. The present intervention achieved 12% weight loss at 1 year; previously studied interventions elicited 4–9% weight loss in patients with T2D [25, 26]. The regular monitoring of weight, glucose, and BHB as biometric feedback for participant, health coach, and medical provider may have provided behavior reinforcement. Further, it seems plausible that this multicomponent care model allowed for greater improvements compared to interventions that provided a subset of components. A recent primary care-led weight management intervention utilizing a 3–5 month VLCD resulted in a 10 mmol mol−1 (0.9%) reduction in HbA1c and 10% weight loss at 1 year; 46% of participants achieved HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) while taking no medications [27]. While only 25% of participants in the present investigation achieved this measure of diabetes remission, the protocol for the present investigation discontinued metformin prescription only because of contraindication, intolerance, or patient request given its efficacy for T2D prevention and recommended use in certain populations [7]. An additional 35% of participants in the present investigation were able to attain HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) while taking only metformin. The longer duration of T2D and baseline insulin prescription to 30% of participants might be factors influencing the proportion of participants in which glycemic control medications could be discontinued in this investigation.
HbA1c improved concurrent with medication reductions prescribed for blood glucose-lowering. For each medication class, the sum percentage of eliminations and reductions of prescriptions at 1 year exceeded that observed at 70 days [23]. Improved glycemic control via a predominantly pharmaceutical approach has demonstrated paradoxical increased cardiovascular risk [28]. Tight glycemic control can elicit symptomatic hypoglycemia [29] or weight gain [30], neither of which was observed in CCI. Thus, it is likely the treatment method by which glycemic control is achieved (e.g., pharmacological, surgery, lifestyle intervention) is important to health outcomes and risk.
Most changes in HbA1c, glucose, insulin, C-peptide, and HOMA-IR occurred in the first 70 days with further improvement observed at 1 year. While the mechanism for improved insulin sensitivity in ketosis is not fully understood, early improvements in HbA1c and HOMA-IR indicate rapid restoration of liver and peripheral insulin sensitivity and are consistent with improvements observed within 2 weeks of ketosis when measured by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp [13]. Utilization of blood BHB for self-monitoring with reinforcement by clinicians may have contributed to sustained HbA1c improvement. Further, BHB acts as a signaling molecule, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress [14, 15]; therefore, mild ketonemia may benefit multiple organs and systems. With appropriate dietary formulation, benefits of nutritional ketosis are observed in mouse models of longevity and health span [31, 32]. Participant mean BHB levels are of similar magnitude to those observed with SGLT-2 inhibitor treatment (~ 0.5 mmol L−1) [33]. Recent trials [5, 34] demonstrate cardiovascular benefits to two SGLT-2 inhibitors; mild ketosis was postulated as a mechanism [33]. Nutritionally achieved ketosis may have long-term cardiovascular benefits without the pharmaceutical risk profile [34]. Further, presence of glucose and palmitate has been associated with beta cell apoptosis [35]. Given the reduced levels of glucose and palmitate observed during nutritional ketosis [36], it is plausible that ketosis might play a role in attenuating glucolipotoxicity-induced beta cell death.
Beyond achieving improved glycemic control concurrent with medication and weight reductions, the CCI had broad positive impact on blood pressure, liver enzymes, hsCRP, triglycerides, and HDL-C. Elevated ALT, AST, and ALP are associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis [37]; these enzymes were significantly reduced with intervention. Rapid reduction in triglycerides and gradual rise in HDL-C observed following CCI are consistent with previously studied carbohydrate-restricted interventions and carbohydrates are well known to increase triglycerides [38]. Of the 108 CCI completers with elevated baseline triglycerides (≥ 1.69 mmol L−1), 54% were in normal range at 1 year. Rise in LDL-C at 1 year, occurring with significant triglyceride decrease, was expected as there is less exchange via cholesteryl ester transfer protein [39]. However, this exchange would not affect particle number and ApoB was unchanged, suggesting an overall neutral impact on LDL lipoprotein-associated cardiovascular risk. In epidemiological studies, utilization of dietary saturated fat in place of carbohydrate was associated with beneficial impact on lipid profile, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality despite higher LDL-C [40, 41]. Transiently increased total and LDL cholesterol were also associated with mobilization of adipose cholesterol stores during major weight loss [42].
Consistent with population-level studies that observed very low rates of diabetes remission [43], the UC group had no change in HbA1c and other indicators of glycemic status and insulin resistance but a net increase in diabetes medication use. Laboratory tests were generally unremarkable with biomarkers not changing significantly. The same facilities and methodologies were used for both the CCI and UC participants indicating that the changes observed in CCI participants not observed in the UC participants are unlikely to be due to methodological changes in clinical or laboratory data capture.
Despite independent recruitment of the CCI and UC groups, most of their baseline characteristics including HbA1c and years since diabetes diagnosis were not significantly different. To enable a comparison between the CCI and UC groups, covariate adjustment was utilized to adjust for differences in baseline characteristics including sex, age, baseline BMI, baseline insulin use (user vs. non-user), and African-American race. With or without baseline adjustment, the change over 1 year elicited in the CC and UC groups differ in all primary outcomes—HbA1c, medication use, and weight—and most secondary outcomes including lipid profile, inflammation, and liver function. In general, the favorable changes observed in the CCI were not observed in the UC cohort. For example, of patients who obtained HbA1c measurements at 1 year, 60% of CCI participants achieved a HbA1c below 48 mmol mol−1 (< 6.5%) while taking no diabetes medications or metformin only, whereas only 10% of UC participants achieved this status.
One interpretation of these results is that the differences in observed outcomes over the year are due to advantages of the CCI over usual care. This suggests a need to incorporate carbohydrate restriction and comprehensive, continuous remote care as options in current guidelines for patients with diabetes as evidence accumulates [44]. However, alternative explanations are possible that may account for the large degree of difference observed. For instance, patients entering the CCI were recruited knowing that they were making a commitment to lifestyle change, while the UC participants were identified as recent referrals to local diabetes education programs and may not have had similar motivation or expectations of effort as the CCI participants. However, even when motivation is controlled for upon recruitment as an inclusion criterion for participation, additional factors may play a role in retention as evidenced by a recent study with randomization [45]. Also, the CCI and UC cohorts may also have differed in baseline characteristics that were not captured such as socioeconomic status.
Additionally, the treatment intensity of the two cohorts was not equal. The UC participants had one or more meetings with a registered dietitian and were under the medical supervision of their primary care provider or endocrinologist with periodic medical visits. In contrast, the CCI participants received a comprehensive and individualized continuous remote care intervention (and in one subgroup, the addition of on-site group classes). A more intensive intervention might have delivered somewhat better results than the investigation’s UC group. For instance, a recent in-person group-based intervention for weight loss in T2D adults reduced HbA1c by 3 mmol mol−1 (0.3%) and weight by 4.0% after a year and medications were reduced in 26% of participants [46]. Future research might compare interventions of similar intensity with different treatment strategies to begin to understand the contribution of each component of the intervention to the overall effect.
Adherence to CCI
Eighty-three percent of CCI participants were retained through 1 year; patient perceived benefits of favorable health outcomes, individualized continuity of care, relationship with health coach, ongoing education, biometric feedback, and peer support may have aided retention. Most participants achieved nutritional ketosis during CCI and maintained elevated BHB at 1 year, indicating sustainability and was possibly enabled by the novel use of blood BHB as daily biofeedback for adherence.
Safety of CCI
No episodes of ketoacidosis, no hypo- or hyperglycemic events requiring assistance, and no adverse events were attributable to the CCI. With improvements or no change in liver, kidney, and thyroid function, safety of the intervention appears favorable. The absence of hypoglycemic events requiring assistance despite relatively tight glucose control may be due to the careful medical provider prescription management, especially rapid downward titration of insulin and sulfonylurea preventing hypoglycemia following dietary changes. Additionally, elevated BHB may have offered protection against hypoglycemic events, as starvation-adapted humans with elevated BHB have demonstrated full preservation of central nervous system function despite profound hypoglycemia induced by exogenous insulin [47].
Study Strengths and Weaknesses
Prior studies have demonstrated favorable improvements in T2D status following carefully managed ketogenic diets as case series [48] or in small short-term randomized trials [45]. This study’s strengths include its prospective design, large cohort, high retention, duration, replication of findings between the CCI-onsite and CCI-web groups, and the collection of multiple time points in the intervention group allowing assessment of how biomarkers changed over time. This study also included participants prescribed insulin and with long-standing T2D, which were often exclusion criteria for prior studies. The means of recruitment, outpatient setting, and lack of food provision may enhance the real-world application of this study.
Weaknesses of this study include that it occurred at a single site and participants were mostly Caucasian. Socioeconomic and psychosocial status and genetics data were not collected. The study was not of sufficient size and duration to measure hard endpoints (e.g., mortality). Future trials could include a multi-site randomized controlled trial with greater racial and ethnic diversity, broader age range, and greater disease severity.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated that a T2D intervention combining technology-enabled continuous remote care with individualized care plans encouraging nutritional ketosis can significantly reduce HbA1c, medication use, and weight within 70 days [23], and that these outcomes can be maintained or improved through 1 year. Most intervention participants with HbA1c reported at 1 year achieved glycemic control in the sub-diabetes range with either no medication or the use of metformin alone. Related health parameters improved including blood pressure, lipid-lipoprotein profile, inflammation, and liver function. Ongoing research will determine the continued sustainability, effectiveness, and safety of these behavioral and metabolic changes.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the participants for their commitment to health and advancing scientific knowledge. Special thanks to IUH staff, especially Monica Keyes, Danielle Wharff, Patti McKee, Joni Anderson, and Zachary Roberts, for their excellent patient care, as well as Rachel Bolden, Sydney Rivera, and Deklin Veenhuizen, who supported study logistics. We appreciate the health coaches who worked one-on-one with participants to help them achieve their goals—Brent Creighton PhD, Theresa Link RD, Bobbie Glon RN, and Marcy Abner RD. We are grateful for Roxie McKee and her staff at Indiana University Health Arnett Laboratory Services and Dave Gibson and Jennifer L. Powers and their staff at Washington University CLCS for their roles in sample analysis, as well as Teryn Sapper and staff from the Volek Laboratory at Ohio State University for their assistance with sample storage and transportation logistics.
Funding
Sponsorship for this study and article processing charges were funded by Virta Health Corp., San Francisco, CA, USA.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published. Contributions: conceptualization and methodology, Sarah J. Hallberg, Amy L. McKenzie, Wayne W. Campbell, Tamara Hazbun, Brittanie M. Volk, James P. McCarter, Stephen D. Phinney, and Jeff S. Volek; formal analysis, Paul Williams; investigation, Sarah J. Hallberg, Amy L. McKenzie, Tamara Hazbun, Brittanie M. Volk; Writing-Original Draft, Amy L. McKenzie, Paul Williams, James P. McCarter; writing-review and editing, Sarah J. Hallberg, Amy L. McKenzie, Paul Williams, Nasir H. Bhanpuri, Anne L. Peters, Wayne W. Campbell, Tamara Hazbun, Brittanie M. Volk, James P. McCarter, Stephen D. Phinney, Jeff S. Volek; visualization, Amy L. McKenzie, Paul Williams, Nasir H. Bhanpuri, Stephen D. Phinney. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Disclosures
Virta Health Corp. funded this research study. Sarah J. Hallberg is an employee of Virta Health Corp. and has been offered stock options. Amy L. McKenzie is an employee of Virta Health Corp. and has been offered stock options. Nasir H. Bhanpuri is an employee of Virta Health Corp. and has been offered stock options. Brittanie M. Volk is an employee of Virta Health Corp. and has been offered stock options. James P. McCarter is an employee of Virta Health Corp. and has been offered stock options. Stephen D. Phinney is an employee of Virta Health Corp. and has been offered stock options. Stephen D. Phinney is a founder of Virta Health Corp. Jeff S. Volek is also a founder of Virta Health Corp. Paul Williams is a paid consultant of Virta Health Corp. Anne L. Peters has been an advisory board member or has consulted for Abbott Diabetes Care, Becton–Dickinson, Bigfoot, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Lexicon, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, sanofi, and Science 37, and has been on the Speaker’s Bureau for NovoNordisk in the last year. Wayne W. Campbell and Tamara Hazbun have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Data Availability
The data sets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Abbreviations
- ALP
Alkaline phosphatase
- ALT
Alanine aminotransferase
- ApoB
Apolipoprotein B
- AST
Aspartate aminotransferase
- BHB
Beta-hydroxybutyrate
- BUN
Blood urea nitrogen
- CBC
Complete blood count
- CCI
Continuous care intervention
- CCI-onsite
Subset of participants who selected on-site education
- CCI-web
Subset of participants who selected web-based education
- CMP
Complete metabolic panel
- DPP-4
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor
- eGFR
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- FT4
Free T4
- GLP-1
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists
- HOMA-IR
Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance
- hsCRP
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein
- PCP
Primary care provider
- SGLT-2
Sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors
- T2D
Type 2 diabetes
- TSH
Thyroid stimulating hormone
- UC
Usual care
- VLCD
Very low energy diet
Footnotes
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to 10.6084/m9.figshare.5803119.
A correction to this article is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0386-4.
Change history
3/5/2018
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake.
References
- 1.NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387(10027):1513–1530. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00618-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stokes A, Preston SH. Deaths attributable to diabetes in the united states: comparison of data sources and estimation approaches. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0170219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gregg EW, Chen H, Wagenknecht LE, et al. Association of an intensive lifestyle intervention with remission of type 2 diabetes. JAMA. 2012;308(23):2489–2496. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.67929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(4):311–322. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(22):2117–2128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP, et al. Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes—3-year outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(21):2002–2013. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1401329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Supplement 1):S1–S172. doi: 10.2337/dc18-Sint01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Handelsman Y, Henry RR, Bloomgarden ZT, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on the association of SGLT-2 inhibitors and diabetic ketoacidosis. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(6):753–762. doi: 10.4158/EP161292.PS. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mottalib A, Sakr M, Shehabeldin M, Hamdy O. Diabetes remission after nonsurgical intensive lifestyle intervention in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015(2):1–4. doi: 10.1155/2015/468704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tobias DK, Chen M, Manson JE, Ludwig DS, Willett W, Hu FB. Effect of low-fat diet interventions versus other diet interventions on long-term weight change in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(12):968–979. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00367-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chaudhry ZW, Doshi RS, Mehta AK, et al. A systematic review of commercial weight loss programmes’ effect on glycemic outcomes among overweight and obese adults with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Obes Rev. 2016;17(8):758–769. doi: 10.1111/obr.12423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bistrian BR, Blackburn GL, Flatt JP, Sizer J, Scrimshaw NS, Sherman M. Nitrogen metabolism and insulin requirements in obese diabetic adults on a protein-sparing modified fast. Diabetes. 1976;25(6):494–504. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.6.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boden G, Sargrad K, Homko C, Mozzoli M, Stein TP. Effect of a low-carbohydrate diet on appetite, blood glucose levels, and insulin resistance in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142(6):403–411. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-142-6-200503150-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, et al. Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science. 2013;339(6116):211–214. doi: 10.1126/science.1227166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Youm Y-H, Nguyen KY, Grant RW, et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome–mediated inflammatory disease. Nat Med. 2015;21(3):263–269. doi: 10.1038/nm.3804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yancy WS, Olsen MK, Guyton JR, Bakst RP, Westman EC. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140(10):769–777. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-10-200405180-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Westman EC, Yancy WS, Mavropoulos JC, Marquart M, McDuffie JR. The effect of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-glycemic index diet on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab. 2008;5(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-5-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nielsen JV, Joensson EA. Low-carbohydrate diet in type 2 diabetes: stable improvement of bodyweight and glycemic control during 44 months follow-up. Nutr Metab. 2008;5(1):14–16. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-5-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saslow LR, Kim S, Daubenmier JJ, et al. A randomized pilot trial of a moderate carbohydrate diet compared to a very low carbohydrate diet in overweight or obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus or prediabetes. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):1–11. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bazzano LA, Hu T, Reynolds K, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(5):309–318. doi: 10.7326/M14-0180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wagner EH, Austin BT, Davis C, Hindmarsh M, Schaefer J, Bonomi A. Improving chronic illness care: translating evidence into action. Health Aff. 2001;20(6):64–78. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.20.6.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Institute of Medicine . Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate. Fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein, and amino acids. Washington: The National Academies Press; 2005. pp. 1–1357. [Google Scholar]
- 23.McKenzie A, Hallberg S, Creighton BC, et al. A novel intervention including individualized nutritional recommendations reduces hemoglobin A1c level, medication use, and weight in type 2 diabetes. JMIR Diabetes. 2017;2(1):e5. doi: 10.2196/diabetes.6981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chubb SAP, Davis WA, Inman Z, Davis TME. Prevalence and progression of subclinical hypothyroidism in women with type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2005;62(4):480–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.The Look AHEAD Research Group Reduction in weight and cardiovascular disease risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes: one-year results of the look AHEAD trial. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(6):1374–1383. doi: 10.2337/dc07-0048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tay J, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Thompson CH, et al. Comparison of low- and high-carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes management: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102(4):780–790. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.112581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet. 2017. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33102-1 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.The ACCORD Study Group Long-term effects of intensive glucose lowering on cardiovascular outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(9):818–828. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1006524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC, Bigger JT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(24):2545–2559. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0802743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Henry RR, Gumbiner B, Ditzler T, Wallace P, Lyon R, Glauber HS. Intensive conventional insulin therapy for type II diabetes. Metabolic effects during a 6-mo outpatient trial. Diabetes Care. 1993;16(1):21–31. doi: 10.2337/diacare.16.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Roberts MN, Wallace MA, Tomilov AA, et al. A ketogenic diet extends longevity and healthspan in adult mice. Cell Metabolism. 2017;26(3):539–546. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Newman JC, Covarrubias AJ, Zhao M, et al. Ketogenic diet reduces midlife mortality and improves memory in aging mice. Cell Metab. 2017;26(3):547–548. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ferrannini E, Mark M, Mayoux E. CV protection in the EMPA-REG outcome trial: a “thrifty substrate” hypothesis. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(7):1108–1114. doi: 10.2337/dc16-0330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(7):644–657. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.El-Assaad W, Buteau J, Peyot M-L, et al. Saturated fatty acids synergize with elevated glucose to cause pancreatic β-cell death. Endocrinology. 2003;144(9):4154–4163. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Forsythe CE, Phinney SD, Feinman RD, et al. Limited effect of dietary saturated fat on plasma saturated fat in the context of a low carbohydrate diet. Lipids. 2010;45(10):947–962. doi: 10.1007/s11745-010-3467-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Younossi ZM, Gramlich T, Matteoni CA, Boparai N, McCullough AJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2(3):262–265. doi: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00014-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gardner CD, Kiazand A, Alhassan S, et al. Comparison of the Atkins, Zone, Ornish, and LEARN diets for change in weight and related risk factors among overweight premenopausal women. JAMA. 2007;297(9):969–977. doi: 10.1001/jama.297.9.969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Barter PJ, Brewer HB, Chapman MJ, Hennekens CH, Rader DJ, Tall AR. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein: a novel target for raising HDL and inhibiting atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23(2):160–167. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000054658.91146.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dehghan M, Mente A, Zhang X, et al. Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2017;390(10107):2050–2062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mente A, Dehghan M, Rangarajan S, et al. Association of dietary nutrients with blood lipids and blood pressure in 18 countries: a cross-sectional analysis from the PURE study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(10):774–787. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Phinney SD, Tang AB, Waggoner CR, Tezanos-Pinto RG, Davis PA. The transient hypercholesterolemia of major weight loss. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;53(6):1404–1410. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.6.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Karter AJ, Nundy S, Parker MM, Moffet HH, Huang ES. Incidence of remission in adults with type 2 diabetes: the diabetes & aging study. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(12):3188–3195. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Noakes TD, Windt J. Evidence that supports the prescription of low-carbohydrate high-fat diets: a narrative review. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(2):133–139. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-096491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Saslow LR, Mason AE, Kim S, et al. An online intervention comparing a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet and lifestyle recommendations versus a plate method diet in overweight individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. 2017;19(2):e36. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.O’Neil PM, Miller Kovach K, Tuerk PW, et al. Randomized controlled trial of a nationally available weight control program tailored for adults with type 2 diabetes. Obesity. 2016;24(11):2269–2277. doi: 10.1002/oby.21616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Drenick EJ, Alvarez LC, Tamasi GC, Brickman AS. Resistance to symptomatic insulin reactions after fasting. J Clin Invest. 1972;51(10):2757–2762. doi: 10.1172/JCI107095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dashti HM, Mathew TC, Khadada M, et al. Beneficial effects of ketogenic diet in obese diabetic subjects. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;302(1–2):249–256. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9448-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data sets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.