Abstract
Background
There is a lack of evidence to support acyclovir administration in pityriasis rosea.
Objective
To determine the efficacy of acyclovir in patients with typical pityriasis rosea.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental studies was performed in MEDLINE, SCOPUS, EMBASE and others, from January 1990 to October 2016 on acyclovir for pityriasis rosea. Random effect model was used to find the pooled Risk Ratio. Outcomes, evaluated between weeks 1 to 8, were regression of lesions, cessation of lesions, decrease of symptoms and duration of disease. Comparisons were acyclovir vs. placebo; acyclovir vs. symptomatic treatment; acyclovir vs. antibiotic; acyclovir vs. observation and combined therapy (acyclovir plus symptomatic treatment) vs. symptomatic treatment alone.
Results
Seven papers were analyzed with 324 participants, of which 159 received acyclovir and 165 were controls. Acyclovir was superior to placebo for complete regression of lesions at week 1 (Risk Ratio 5.72, CI95% 2.36-13.88). However, combined therapy was not superior to symptomatic treatment at week 4 (Risk Ratio 1.46, CI95% 0.93-2.29). Individual studies showed the superiority of acyclovir for the control of symptoms and pruritus.
Study limitations
We faced differences designs of trials and inconsistency between reports.
Conclusion
Symptomatic treatment is a reasonable option for pityriasis rosea, and the addition of acyclovir is justified for the control of symptoms and pruritus.
Keywords: Acyclovir, Histamine antagonists, Meta-analysis as topic, Pityriasis rosea, Pruritus
INTRODUCTION
Pityriasis rosea (PR) is an acute inflammatory skin disease that occurs worldwide, more often in children and young people.1,2 Typically, an exanthema of smaller patches develops across the trunk, that usually lasts 8 weeks, with moderate to severe pruritus. 3,4 The etiology is still unclear, but many features suggest a viral infectious cause: at least half of patients reports symptoms compatible with a viral upper respiratory infection, the early age of onset, the self-limited clinical course and the low rate of relapses.5, 6 Accordingly, several authors have found the presence of Human Herpes Virus type 6 and 7 (HHV-6 and HHV-7) in patients with PR, however, the evidence is not enough to confirm a direct association.4,7,8
Current treatments consist on topical and systemic therapy, mainly as symptomatic drugs, as PR is a self-limited disease.9 Yet, Drago et al,10 first described the efficacy of acyclovir for PR with promising results. Nowadays, there is still a lack of high quality evidence to support acyclovir administration in PR. Recommendations suggest its use in cases of extensive, relapsing, persistent disease or during pregnancy, mostly based on expert opinions.11 We aimed to determine the efficacy of acyclovir in comparison to other interventions in patients with typical PR, both adults and children.
METHODS
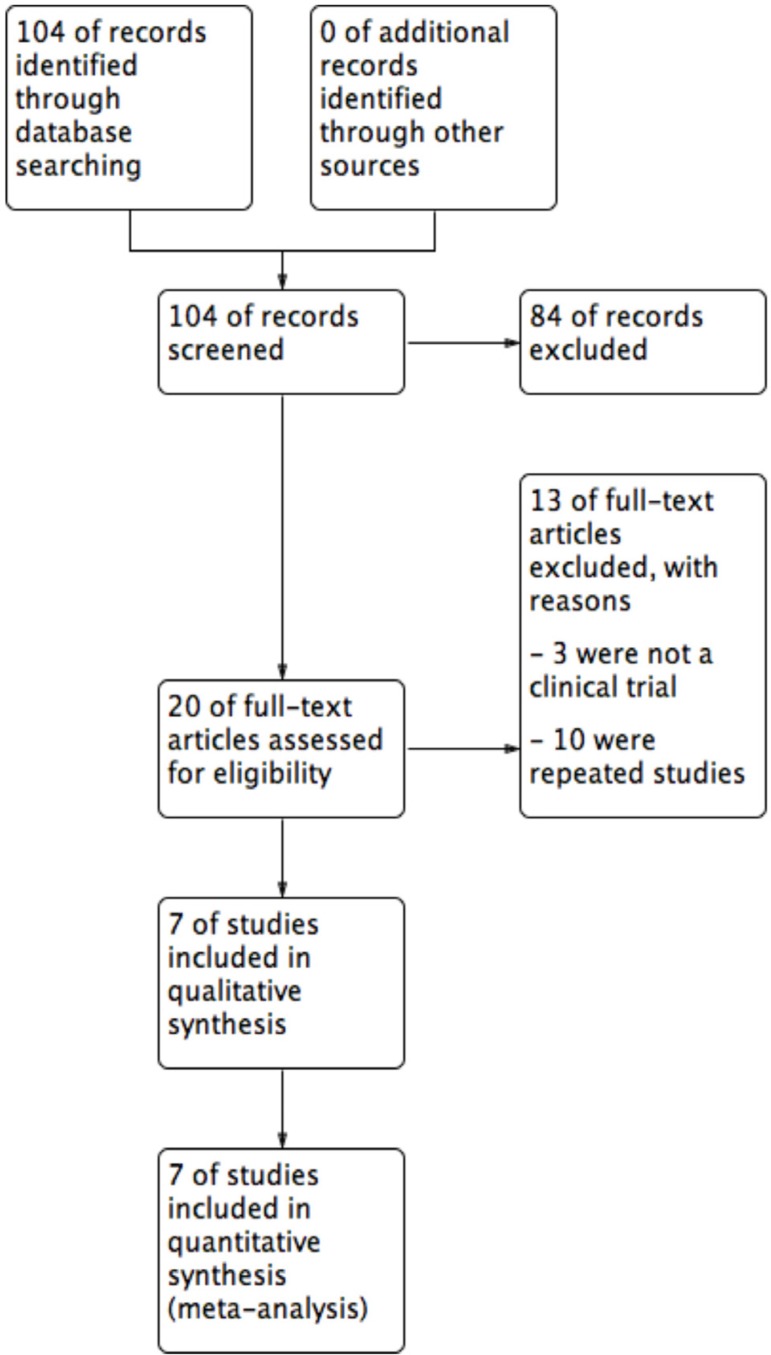
This systematic review and meta-analysis was performed according to the Cochrane Collaboration recommendations and the PRISMA guidelines (Chart 1).12-14 Protocol was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42016049318).
Chart 1:
PRISMA checklist
| Section/topic | # | Checklist item | Reported on page # |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both | 1 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Structured summary | 2 | Provide a structured summary including, as applicable: background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; systematic review registration number | 22 |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known | 4 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS) | 4 |
| METHODS | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (e.g., Web address), and, if available, provide registration information including registration number | 4 |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify study characteristics (e.g., PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (e.g., years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale | 5 |
| Information sources | 7 | Describe all information sources (e.g., databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched | 4 |
| Search | 8 | Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated | 4 |
| Study selection | 9 | State the process for selecting studies (i.e., screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis) | 5 |
| Data collection process | 10 | Describe method of data extraction from reports (e.g., piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators | 5 |
| Data items | 11 | List and define all variables for which data were sought (e.g., PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made | 5 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 12 | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis | 6 |
| Summary measures | 13 | State the principal summary measures (e.g., risk ratio, difference in means) | 6 |
| Synthesis of results | 14 | Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, if done, including measures of consistency (e.g., I2) for each meta-analysis | 6 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 15 | Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (e.g., publication bias, selective reporting within studies) | 6 |
| Additional analyses | 16 | Describe methods of additional analyses (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were pre-specified | 6 |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 17 | Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram | 6 |
| Study characteristics | 18 | For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (e.g., study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citations | 6, Table1 |
| Risk of bias within studies | 19 | Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome level assessment (see item 12) | Fig. 7 |
| Results of individual studies | 20 | For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms), present, for each study: (a) simple summary data for each intervention group (b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot | Table 1 |
| Synthesis of results | 21 | Present results of each meta-analysis done, including confidence intervals and measures of consistency | 7 |
| Risk of bias across studies | 22 | Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see Item 15). | Fig. 7 |
| Additional analysis | 23 | Give results of additional analyses, if done (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see Item 16]) | 8 |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Summary of evidence | 24 | Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (e.g., healthcare providers, users, and policy makers) | 8, 9 |
| Limitations | 25 | Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (e.g., risk of bias), and at review-level (e.g., incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias) | 11 |
| Conclusions | 26 | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence, and implications for future research | 11-12 |
| FUNDING | |||
| Funding | 27 | Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (e.g., supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review | 1 |
Source: Moher D, et al, 2009. 14
Search Strategy
A database search was independently conducted by two reviewers (MR and NT) in MEDLINE (accessed via PubMed), SCOPUS, EMBASE, SCIENCE DIRECT, LILACS and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials for the period of January 1990 until October 2016. 15,16 The search strategy was specific for each database and included a combination of the Medical Subject Heading and free text terms for ¨Acyclovir¨, "Pityriasis rosea" and "Clinical trial" (Chart 2). For unpublished studies we reviewed grey literature and experts' opinion on the topic. In addition, we scanned bibliographies of published studies by a manual search of the literature; reviewed virtual libraries of universities and theses; requested authors for papers presented at conferences and congresses of dermatology societies; and contacted the pharmaceutical industry. We also searched at ClinicalTrials.gov database to find additional studies that were not included in the initial search. There are no restrictions of language to select the studies for this review.
Chart2:
Protocol search strategy
| The search strategy was specific for each database according to the medical subject headings (MeSH) and free text terms for the key concepts. The search terms were combined as follow: "pityriasis rosea"[MeSH Terms] AND "acyclovir"[MeSH Terms] AND “clinical trial”[MeSH Terms] |
|---|
| PUBMED |
| (Pityriasis Rosea OR Pityriasis OR pityriasis rosea of gilbert OR pityriasis rosea Gilbert) AND (Acyclovir OR Acycloguanosine OR Acic* OR acyc*) No filters will be added |
| COCHRANE |
| We will search for "all text", it will be limited by "product type", indicating the point "trials". The terms will be combined as follows: (Pityriasis Rosea OR Pityriasis OR pityriasis rosea of gilbert OR pityriasis rosea Gilbert) AND (Acyclovir OR acyclovir OR Acycloguanosine OR Acic* OR acyc*) |
| SCOPUS |
| We are going to search (All words) in "All fields"
(full text) for: (Pityriasis Rosea OR Pityriasis OR pityriasis
rosea of gilbert OR pityriasis rosea Gibert) AND (Aciclovir OR
Acycloguanosine OR Acic* OR acyc*) AND (clinical trial OR clinical trials,randomized OR controlled clinical trials, randomized) |
| SCIENCEDIRECT |
| Search results: 61 results found for pub-date > 1989 and (Pityriasis Rosea OR Pityriasis) AND (Acyclovir OR Acycloguanosine) AND (clinical trial) AND LIMIT-TO(topics, "patient,treatment,acad dermatol,dermatology,skin,clinical") |
| BIREME |
| (Pityriasis Rosea OR Pityriasis OR pityriasis rosea of gilbert OR pityriasis rosea Gibert) AND (Aciclovir OR Acycloguanosine OR Acic* OR acyc*). All the studies that include one of the following terms in the tittle will be considered: limits: “humans” and main topic: “Pytiriasis rosea” |
| LILACS |
| (Pityriasis Rosea OR Pityriasis OR pityriasis rosea of gilbert OR pityriasis rosea Gibert) AND (Aciclovir OR Acycloguanosine OR Acic* OR acyc*) AND (clinical trial OR clinical trials,randomized OR controlled clinical trials,randomized) |
| Other resources |
| Clinicaltrials.gov: |
| (Pityriasis Rosea) AND (Acyclovir) |
Eligibility criteria
We included parallel-clinical trials (experimental and quasi-experimental), with open-labeled or blinded designs; studying the efficacy of acyclovir for PR. Participants included were immunocompetent and nonpregnant females and males, children and adults with PR diagnosed according to the investigator criteria and specific clinical features.
Studies should have two or more study arms, at least one arm on acyclovir (with or without symptomatic treatment), and a control group (on placebo, symptomatic treatment, antibiotics or nothing). Symptomatic treatment consists on oral or topical antihistamines, oral or topical steroids, and topical balsams.9,17
We excluded studies lacking complete data in any arm of study, after exhausting efforts to contact the authors for full data. Overlapping studies were included after discarding the one with the smaller study population.
The comparisons were (1) Acyclovir vs. placebo; (2) Acyclovir vs. symptomatic treatment; (3) Acyclovir vs. antibiotic; (4) Acyclovir vs. observation; (5) Acyclovir plus symptomatic treatment (combined therapy) vs. symptomatic treatment alone.
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the proportion of patients achieving regression of lesions after the treatment of oral acyclovir. Regression of lesions is defined as decrease or disappearance of erythema in all lesions leaving desquamation or pigmentation. Secondary outcomes were (i) The proportion of patients that achieved cessation of new lesions. (ii) The proportion of patients that had decreased systemic symptoms (pruritus). (iii) Time for complete clearance of lesions. Outcomes were measured at several weeks after treatment was initiated.
Study selection
Two reviewers (MR and NT) independently screened the titles and abstracts of all the retrieved articles, followed by the full texts of the articles considered potentially eligible for the study. They independently collected the data using a standardized data sheet. Both authors confirmed all entries and checked at least twice for completeness and accuracy. Disagreements were resolved by discussion with a third reviewer (HG). Authors were contacted by email for missing data and clarifications, in order to achieve completeness of studies.
Data analysis
The pooled relative risk (RR) was the effect measured of the primary outcome, with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI). As the heterogeneity was considerable, the pooled RR was calculated based on a random effect model, according to the 'standard approach'.18 Statistical heterogeneity was assessed with the I2 statistic.19
For secondary outcomes, dichotomous data was calculated using RR and continuous data using the standardized mean difference, with 95%CI and a random effect model.
Included trials were characterized with descriptive statistics (percentages and mean). We performed analyses with Stata13® and RevMan 5.1®.
Quality assessment
Every study was independently evaluated for `risk of bias´ by two reviewers (MR and NT), considering the domains and criteria suggested by the Cochrane Handbook v.5.1.0..12 Disagreements were discussed and resolved with a third reviewer (HG).
Other analysis
Subgroup analysis, publication bias and sensitivity analysis were not possible due to the limited number of trials in the meta-analysis.
RESULTS
The literature search yielded 104 titles and abstracts, and after eligibility criteria, 7 trials entered to systematic review and meta-analysis (Figure 1). Characteristics of included trials are detailed in table 1. There were a total of 324 participants with PR, 159 on acyclovir and 165 controls. All studies had two arms, acyclovir and control groups. Only two studies used low doses of acyclovir (400mg 5 times daily), while the rest used high doses (800mg 5 times daily).20,21 Almost all of the studies had an intervention of seven days, except one (10 days).22 All studies include male and females patients with a mean age of 26.9 years old.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of studies included in the meta-analysis
Table 1.
Systematic review of studies included
| Study | Country | Language | Centers | Blinding | N of arms | N Allocated | Acyclovir dose | Days of treatment | A scheme | C scheme | N Analyzed | S | N f | N m | Age (mean) | Age group included | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T C A | T C A | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drago 2006(10) | Italy | English | SC | SB | 2 | 87 | 45 | 42 | H | 7 | SS: Acyclovir | Placebo (vitamin C) | 87 | 45 | 42 | B | 38 | 49 | 27.4 | AD |
| Ehsani 2010(21) | Iran | English | SC | SB | 2 | 30 | 15 | 15 | H | 10 | SS: Acyclovir | Antibiotic (erythromycin) | 30 | 15 | 15 | B | 15 | 15 | 32.0 | AD |
|
Rassai
2011(20) |
Iran | English | SC | OB | 2 | 64 | NR | NR | L | 7 | SS: Acyclovir | Observation | 54 | 26 | 28 | B | NR | NR | 27.12 | B (>10yo) |
|
Amatya
2012(23) |
Nepal | English | SC | OpB | 2 | 42 | 24 | 18 | H | 7 | CS: Acyclovir + cetirizine and topical corticoid | Symptomatic (cetirizine and topical corticoid) | 42 | 24 | 18 | B | 16 | 26 | 23.0 | B (>2yo) |
|
Ganguli
2014(22) |
India | English | SC | DB | 2 | 60 | 30 | 30 | H | 7 | SS: Acyclovir | Placebo (vitamin C) | 60 | 30 | 30 | B | 27 | 33 | 24.2 | B (NR age) |
|
Das
2015(19) |
India | English | SC | OB | 2 | 24 | 12 | 12 | L | 7 | CS: Acyclovir + cetirizine and calamine lotion | Symptomatic (cetirizine and calamine lotion) | 24 | 12 | 12 | B | 10 | 14 | 33.2 | AD |
|
Singh
2016(24) |
India | English | SC | TB | 2 | 33 | NR | NR | H | 7 | SS: Acyclovir | Placebo | 27 | 13 | 14 | B | 8 | 19 | 21.35 | B (>40kg of weight) |
Abbreviations: SC: single-center; SB: single-blinded; OB: observer-blinded; OpB: open-blinded; DB: double-blinded; TB: triple-blinded; NR: no reported; N: number of patients; N allocated: number of patients allocated to each treatment; N analyzed: number of patients who completed trial and entered to analysis; T: total; C: control group; A: acyclovir group; H: high dose; L: low dose; SS: single-scheme; CS: combined-scheme; S: sex; B: both; Nf: number of females; Nm: Number of males; AD: adult (>18yo).
Main outcome analysis
324 participants entered to the meta-analysis, 159 were allocated to acyclovir, and 165 to control. Studies failed to report reasons for dropouts.
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. Placebo (two trials)
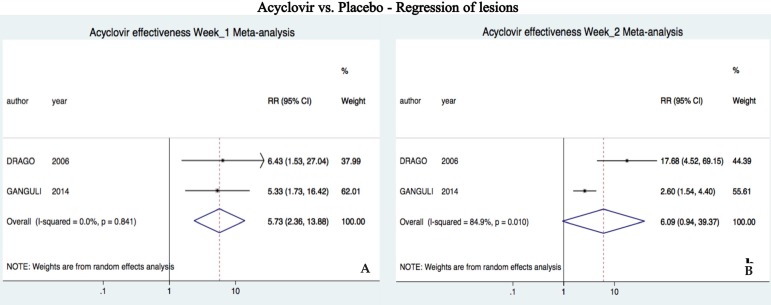
Acyclovir was superior to placebo after one week of treatment (RR 5.72, 95%CI 2.36-13.88, I2=0%); however, there was no difference at two weeks (RR 6.08, 95%CI 0.94-39.36, I2=85%) (Figure 2).10, 23
Figure 2.
Forest plots of meta-analysis for the main outcome (regression of lesions) after one A and two weeks of treatment B. Trials included compared acyclovir vs. placebo
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. antibiotic (one trial)
Acyclovir was similar to erythromycin after two weeks, but superior after four (RR 8.0 95%CI 1.13-56.33) and eight (RR 2.16 95%CI 1.13-4.15) weeks of treatment.22
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. observation (one trial)
Acyclovir was superior to observation after one (RR 3.02 95%CI 1.13-8.08), two (RR 2.92 95%CI 1.50-5.66) and four (RR 1.51 95%CI 1.10-2.08) weeks of treatment.21
Comparison: Combined therapy vs. symptomatic treatment (two trials)
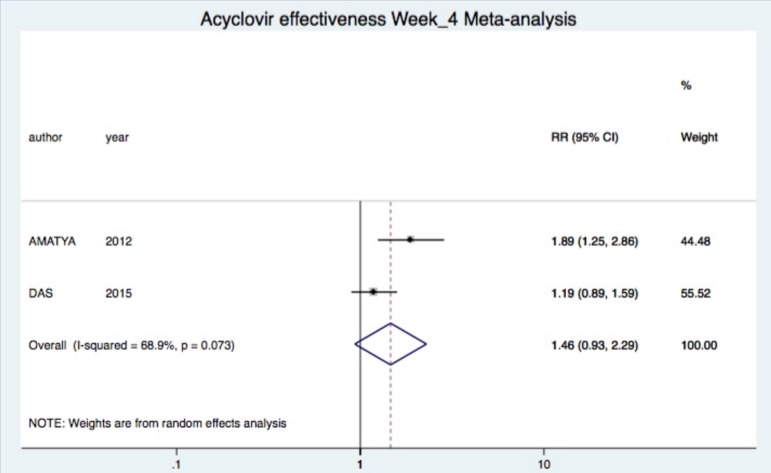
Combined treatment was not significantly superior after two (one study (23): RR 3.11 95%CI 0.93-10.39), four (two studies (19, 23): RR 1.46 95%CI 0.93-2.29, I2=69%) and eight (one study (23): RR 0.98 95%CI 0.86-1.12) weeks of treatment (Figure 3).24
Figure 3.
Forest plots of meta-analysis for the main outcome (regression of lesions) after four weeks of treatment. Trials included compared combined therapy vs. symptomatic treatment alone. Combined RR was obtained only for com parison at week 4
Secondary outcome analysis
Outcome: Cessation of new lesions
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. Placebo (two trials)
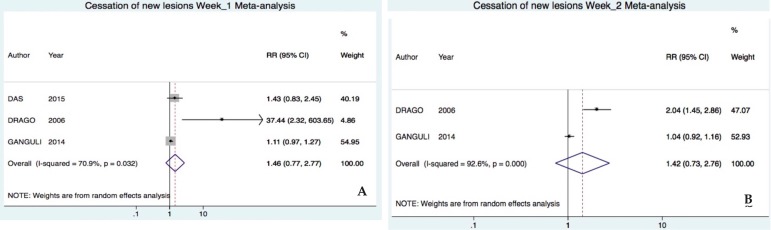
Acyclovir was not significantly superior after one (RR 4.85 95%CI 0.16-145.64, I2=83%) and two (RR 1.42 95%CI 0.73-2.75, I2=92%) weeks of treatment (Figure 4).10, 23
Figure 4.
Forest plot of the meta-analysis for secondary outcome cessation of lesions after one A and two B weeks of treatment. Trials included compared acyclovir vs. placebo
Comparison: Combined therapy vs. symptomatic treatment (one trial)
Combined therapy was not significantly superior after one week of treatment (RR 1.67, 95%CI 0.85-3.426).20
Outcome: Decrease of symptoms
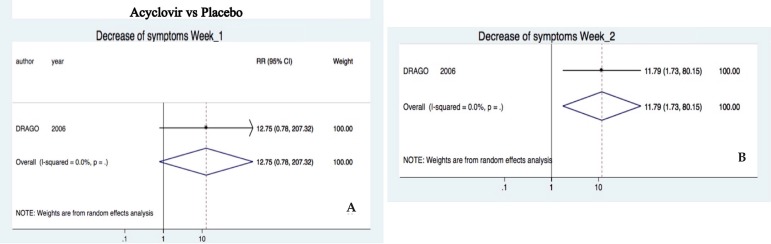
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. Placebo (one trial)
Acyclovir was not superior to decrease symptoms (e.g. fatigue, headache, sore throat, difficulty in concentrating, irritability, insomnia, and nausea) after one week (RR 12.75, 95%CI 0.78-207.32).10 Nevertheless, it was superior at two (RR 11.79, 95%CI 1.73-80.15) weeks of treatment (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Comparative diagram for decrease of symptoms analysis after one A and two B weeks of treatment. Trials included compared acyclovir vs. placebo
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. antibiotic (one trial)
Acyclovir was not significantly superior to erythromycin to decrease pruritus after two (RR 13.22, 95%CI 0.91-192.02), four (RR 1.47, 95%CI 0.83-2.61) and eight (RR 1.20, 95%CI 0.79-1.83) weeks of treatment.22
Comparison: Combined therapy vs. symptomatic treatment (one trial)
Combined therapy decreased significantly pruritus after one (SMD -1.31 95%CI -2.19, -0.41), two (SMD -1.61 95%CI -2.53, -0.68), three (SMD -1.25 95%CI-2.13, -0.27) and four (SMD -1.21 95%CI -2.10, -0.34) weeks of treatment.20
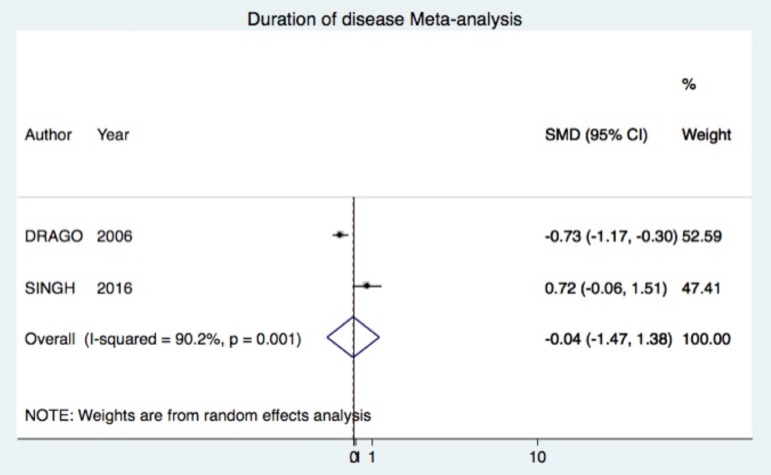
Outcome: duration of disease
Comparison: Acyclovir vs. Placebo (two trials)
Acyclovir was not superior (SMD -0.04 95%CI -1.47, 1.38) (Figure 6).10, 25
Figure 6.
Forest plot of the meta-analysis for secondary outcome duration of disease. Trials included compared acy clovir vs. placebo
The rest of analyses are not presented, as there was not data available.
DISCUSSION
Regression of lesions
This is the first meta-analysis that evaluates the efficacy of acyclovir for PR. We found that acyclovir was superior to placebo for PR at week 1 for achieving regression of lesions; but when combined with symptomatic treatment, acyclovir was not superior to control at week 4 (Figures 2 and 3). Several studies have linked PR to HHV-6 and 7 as main etiology.5, 7 However, studies are not conclusive yet, as some have proposed other etiologies, such as other viruses (e.g. HHV-8, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, etc.), association with bacterial and fungal infections, and even immunological origin.26 We believe that most of the patients responded to the antiviral when compared to placebo due to the involvement of HHV-6 and 7 (Figure 2). Still, some authors have questioned acyclovir efficacy against HHV-7, as it lacks the thymidine kinase gene.27 Nevertheless, efficacy of the antiviral is supported by the results of Watanabe et al. They found systemic active infection of both HHV-6 and 7 at the same time in PR patients, and HHV-6 does respond to acyclovir.28
When acyclovir was compared with symptomatic treatment, this superiority for regression of lesions was apparently reduced (Figure 3).20, 24 Thus, symptomatic treatment has an important role for the control of lesions in PR. Guidelines support the use of symptomatic treatment for PR with mild to moderate symptoms.9, 11 However, a prior meta-analysis found inadequate evidence for efficacy of most symptomatic treatments.17 Only a single study showed that oral antihistamine alone was superior than the combination of oral antihistamine and steroids in clearing the PR rash within two weeks.29 The symptomatic treatment used in the studies included was oral antihistamine plus topical calamine or corticoid. We suggest that oral antihistamines should be included as primary symptomatic treatment, in association with topical steroids or calamine lotion.30
Control of symptoms
One study10 demonstrated that acyclovir was superior to placebo for decreasing symptoms at week 1 and 2 (Figure 5); another study showed the significant decrease of itching from week 1 to 4 with combined treatment.20 It is important to underline that other reports had elucidated the anti-pruritic effect of acyclovir in PR.9 Other treatments, erythromycin and phototherapy, have been also proposed for pruritic management in PR with controversial results.31 Most of the guidelines suggest that, as PR is a self-limited illness, most patients do not need to be treated. Other authors propose that patients with recalcitrant symptoms, such as pruritus, are the exception: they may benefit from treatment with macrolides, phototherapy and antivirals.9
When erythromycin is compared to placebo for PR, 3 out of 4 patients on interventional group cleared completely within 2 weeks.32 Nevertheless, this study had methodological deficiencies in randomization, allocation concealment and analysis, with the adverse events inherent to macrolides.33 Other studies suggested immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of macrolides in PR due to Chlamydia, Legionella and Mycoplasma involvement, but not assertively. 34-36 Clinical trials have shown that efficacy of macrolides, such as erythromycin, clarithromycin and azithromycin has not been proven.36-38 One study compared acyclovir vs. erythromycin and showed that the antiviral was significantly superior for regression of lesions, but not significant for decrease of symptoms.22 Therefore, we recommend the use of antiviral over macrolides supported by the possible viral etiology of PR.39
Phototherapy with narrowband UVB and UVA1 has been proposed as methods to control PR severity and pruritus.40,41 Other studies have proven their efficacy in decreasing severity but failed to change itch and course of the disease.42, 43 There is inadequate evidence for phototherapy, and sessions are given thrice a week for at least one month. 27 Although it might be efficient, it may not be feasible and accessible for all patients.31
Based on the results, we think that symptomatic treatment (oral antihistamines and topical steroids/calamine) may be considered as baseline treatment for PR, and the early addition of acyclovir for pruritus control, especially in extensive, relapsing or persistent disease.11, 17, 44
Other outcomes
Acyclovir was not superior to placebo, neither combined to symptomatic treatment in cessation of new lesions at week 1 and 2 (Figure 4). In addition, acyclovir failed to decrease significantly the duration of PR compared to placebo. However, studies that entered into the meta-analysis had opposed results independently (Figure 6). 10, 25
Clinical trials included were not enough to distinguish efficacy of children from adult population. Drago et al. have found different characteristics between them.45 Children have less prevalence of systemic symptoms and less average duration of exanthema. Therefore, we believed that acyclovir in children may not be a reasonable alternative for PR, until trials demonstrate efficacy in this population.
Adverse events
Adverse events were reported in both acyclovir and control groups (Table 2). In an observer-blinded trial, 8 patients on acyclovir and antihistamines reported increased sleep, headache, nausea, vomiting and dysgeusia.20 These adverse events, although they are expected in patients on acyclovir, were not reported in the rest of trials. 46 A triple-blinded trial reported abdominal pain and diarrhea in placebo group, possibly due to nocebo effect. 25,47
Table 2.
Systematic review of adverse events
| Study | N of adverse event | List of adverse events | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | C | A | C | A | |
| Drago 2006 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Ehsani 2010 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Rassai 2011 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Amatya 2012 | 8 | 8 | 0 | Dyspepsia | None |
| Ganguli 2014 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Das 2015 | 9 | 1 | 8 | Increased sleep | Increased sleep, headache, nausea, vomiting, dysgeusia |
| Singh 2016 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Abdominal pain and diarrhea | None |
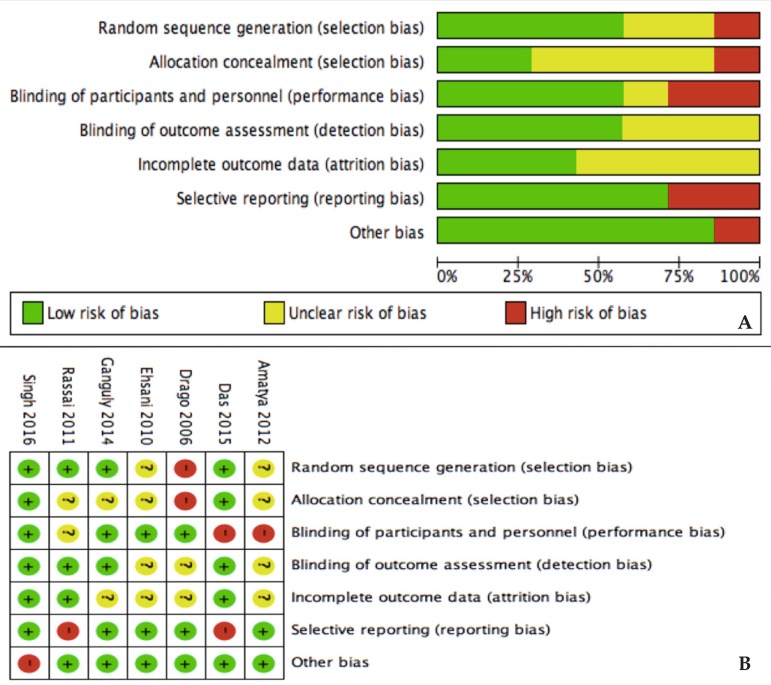
Risk of bias
Unclear risk of bias was prevalent for allocation concealment (selection bias) and incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) (Figure 7A). The rest of domains had in general low risk of bias. Drago et al,10 did not perform randomization neither allocation concealment. Two trials failed to blind participants from treatment received (Figure 7B).20, 24
Figure 7.
Risk of bias analysis. A. Between studies; B. Within studies
Limitations
We faced several limitations. First, studies did not evaluate all outcomes and they differed in temporality. Therefore, meta-analysis was not possible for all outcomes and weeks of the follow-up. Second, some studies had high risk of bias in randomization and allocation concealment. However, we decided to include all trials since they represent interventional studies with similar established outcomes. Finally, there were few trials for each comparison, thus, subgroup analysis was not possible.
CONCLUSION
Acyclovir was superior to placebo for regression of lesions of PR. However, combined therapy was not superior to symptomatic treatment for control of lesions. Individual trials indicated that acyclovir was superior to placebo and symptomatic treatment for the control of symptoms and pruritus. Finally, acyclovir failed to prevent new lesions and to shorten the duration of the disease when compared to placebo.
Our results reflect that symptomatic treatment, as oral antihistamines and topical steroids/calamine, plays an important role for PR in the regression of lesions, given that there was no difference when compared to combined treatment. We recommend the addition of acyclovir for pruritus control and it might be justified also for severe symptoms, within four weeks of the onset of PR.6
More trials need to be conducted in order to prove the efficacy of acyclovir for PR. We encourage researchers to follow similar designs and to adopt similar outcomes to unify criteria for future meta-analysis. Interventions should include acyclovir plus symptomatic treatment in therapy group. In addition, report of trials should account for randomization, allocation concealment and dropouts in order to increase quality of studies.
Footnotes
Work conducted at the Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos, Lima, Peru.
Conflict of interest: None.
AUTHORS'CONTRIBUTIONS
Milton Rodriguez-Zuniga
0000-0002-9413-2439
Statistical analysis, Approval of the final version of the manuscript, Design and planning of the study, Preparation and writing of the manuscript, Collecting, analysis and interpretation of data, Effective participation in research orientation, Intellectual participation in propaedeutic and/or therapeutic conduct of studied cases, Critical review of the literature, Critical review of the manuscript
Natalie Torres
0000-0001-8051-6426
Statistical analysis, Approval of the final version of the manuscript, Design and planning of the study, Preparation and writing of the manuscript, Collecting, analysis and interpretation of data, Effective participation in research orientation, Intellectual participation in propaedeutic and/or therapeutic conduct of studied cases, Critical review of the literature, Critical review of the manuscript
Herney Garcia-Perdomo
0000-0001-6945-8261
Statistical analysis, Approval of the final version of the manuscript, Design and planning of the study, Preparation and writing of the manuscript, Collecting, analysis and interpretation of data, Effective participation in research orientation, Intellectual participation in propaedeutic and/or therapeutic conduct of studied cases, Critical review of the literature, Critical review of the manuscript
REFERENCES
- 1.Parsons JM. Pityriasis rosea update: 1986. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;15:159–167. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(86)70151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, Broccolo F, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea: a comprehensive classification. Dermatology. 2016;232:431–437. doi: 10.1159/000445375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kilinc F, Akbas A, Sener S, Aktas A. Atypical pityriasis rosea: clinical evaluation of 27 patients. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017;36:157–162. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2016.1225217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Drago F, Broccolo F, Rebora A. Pityriasis rosea: an update with a critical appraisal of its possible herpesviral etiology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:303–318. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.07.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Canpolat Kirac B, Adisen E, Bozdayi G, Yucel A, Fidan I, Aksakal N, et al. The role of human herpesvirus 6, human herpesvirus 7, Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in the aetiology of pityriasis rosea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23:16–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mahajan K, Relhan V, Relhan AK, Garg VK. Pityriasis Rosea: An update on etiopathogenesis and management of difficult aspects. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:375–384. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.185699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Drago F, Ranieri E, Malaguti F, Battifoglio ML, Losi E, Rebora A. Human herpesvirus 7 in patients with pityriasis rosea. Electron microscopy investigations and polymerase chain reaction in mononuclear cells, plasma and skin. Dermatology. 1997;195:374–378. doi: 10.1159/000245991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chuh A, Chan H, Zawar V. Pityriasis rosea--evidence for and against an infectious aetiology. Epidemiol Infect. 2004;132:381–390. doi: 10.1017/s0950268804002304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chuh A, Zawar V, Sciallis G, Kempf W. A position statement on the management of patients with pityriasis rosea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1670–1681. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Drago F, Vecchio F, Rebora A. Use of high-dose acyclovir in pityriasis rosea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006;54:82–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.06.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ciccarese G, Drago F. Is a treatment for pityriasis rosea really needed? Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:435–435. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.190515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Handbook.cochrane.org Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions: The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. [2016 Nov 10]. [Internet] Available from: http://handbook.cochrane.org . [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Frenkel N, Schirmer EC, Wyatt LS, Katsafanas G, Roffman E, Danovich RM, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci. Vol. 87. U S: 1990. Isolation of a new herpesvirus from human CD4+ T cells; pp. 748–752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yamanishi K, Okuno T. [New human herpesvirus, human herpes virus-6] Nihon Rinsho. 1989;47:285–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chuh AA, Dofitas BL, Comisel GG, Reveiz L, Sharma V, Garner SE, et al. Interventions for pityriasis rosea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD005068. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005068.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;45:139–145. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2015.09.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Das A, Sil A, Das NK, Roy K, Das AK, Bandyopadhyay D. Acyclovir in pityriasis rosea: An observer-blind, randomized controlled trial of effectiveness, safety and tolerability. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6:181–184. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.156389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rassai S, Feily A, Sina N, Abtahian S. Low dose of acyclovir may be an effective treatment against pityriasis rosea: a random investigator-blind clinical trial on 64 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25:24–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ehsani A, Esmaily N, Noormohammadpour P, Toosi S, Hosseinpour A, Hosseini M, et al. The comparison between the efficacy of high dose acyclovir and erythromycin on the period and signs of pitiriasis rosea. 246-8Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55 doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.70672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ganguly S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of efficacy of oral acyclovir in the treatment of pityriasis rosea. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8:YC01–YC04. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8140.4360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Amatya A, Rajouria EA, Karn DK. Comparative study of effectiveness of oral acyclovir with oral erythromycin in the treatment of pityriasis rosea. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ) 2012;10:57–61. doi: 10.3126/kumj.v10i1.6916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Singh S, Anurag Tiwary NK. Acyclovir is not effective in pityriasis rosea: results of a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82:505–509. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.182791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guarneri F, Cannavo SP, Minciullo PL, Gangemi S. Pityriasis rosea of Gibert: immunological aspects. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2015;29:21–25. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chuh A. Narrow band UVB phototherapy and oral acyclovir for pityriasis rosea. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2004;20:64–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0781.2004.00072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Watanabe T, Kawamura T, Jacob SE, Aquilino EA, Orenstein JM, Black JB, et al. Pityriasis rosea is associated with systemic active infection with both human herpesvirus-7 and human herpesvirus-6. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;119:793–797. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.00200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lazaro-Medina A, Villena-Amurao C, Dy-Chua NS, Sit-Toledo MSW, Villanueva B. A clinicohistopathologic study of a randomized double-blind clinical trial using oral dexchlorpheniramine 4 mg, betamethasone 500 mcg and betamethasone 250 mcg with dexchlorpheniramine 2 mg in the treatment of pityriasis rosea: a preliminary report. Journal of the Philippine Dermatological Society. 1996;5:3–7. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stulberg DL, Wolfrey J. Pityriasis rosea. Am Fam Physician. 2004;69:87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gambichler T, Terras S, Kreuter A. Treatment regimens, protocols, dosage, and indications for UVA1 phototherapy: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:438–454. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sharma PK, Yadav TP, Gautam RK, Taneja N, Satyanarayana L. Erythromycin in pityriasis rosea: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:241–244. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(00)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bigby M. A remarkable result of a double-masked, placebo-controlled trial of erythromycin in the treatment of pityriasis rosea. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:775–776. doi: 10.1001/archderm.136.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Terraneo L, Lava SA, Camozzi P, Zgraggen L, Simonetti GD, Bianchetti MG, et al. Unusual eruptions associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory infections: review of the literature. Dermatology. 2015;231:152–157. doi: 10.1159/000430809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chuh AA, Chan HH. Prospective case-control study of chlamydia, legionella and mycoplasma infections in patients with pityriasis rosea. Eur J Dermatol. 2002;12:170–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rasi A, Tajziehchi L, Savabi-Nasab S. Oral erythromycin is ineffective in the treatment of pityriasis rosea. J Drugs Dermatol. 2008;7:35–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pandhi D, Singal A, Verma P, Sharma R. The efficacy of azithromycin in pityriasis rosea: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2014;80:36–40. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.125484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ahmed N, Iftikhar N, Bashir U, Rizvi SD, Sheikh ZI, Manzur A. Efficacy of clarithromycin in pityriasis rosea. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014;24:802–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, Parodi A. The efficacy of macrolides and acyclovir in pityriasis rosea. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2015;81:56–56. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.148572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jairath V, Mohan M, Jindal N, Gogna P, Syrty C, Monnappa PM, et al. Narrowband UVB phototherapy in pityriasis rosea. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2015;6 doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.164480. 326-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lim SH, Kim SM, Oh BH, Ko JH, Lee YW, Choe YB, et al. Low-dose ultraviolet A1 phototherapy for treating pityriasis rosea. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21:230–236. doi: 10.5021/ad.2009.21.3.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Valkova S, Trashlieva M, Christova P. UVB phototherapy for pityriasis rosea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2004;18:111–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.00803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Leenutaphong V, Jiamton S. UVB phototherapy for pityriasis rosea: a bilateral comparison study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1995;33:996–999. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(95)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Drago F, Ciccarese G, Rebora A, Parodi A. Relapsing pityriasis rosea. Dermatology. 2014;229:316–318. doi: 10.1159/000363568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Drago F, Ciccarese G, Broccolo F, Cozzani E, Parodi A. Pityriasis rosea in children: clinical features and laboratory investigations. Dermatology. 2015;231:9–14. doi: 10.1159/000381285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Heslop R, Roberts H, Flower D, Jordan V. Interventions for men and women with their first episode of genital herpes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016:CD010684. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010684.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rojas-Mirquez JC, Rodriguez-Zuniga MJ, Bonilla-Escobar FJ, Garcia-Perdomo HA, Petkov M, Becerra L, et al. Nocebo effect in randomized clinical trials of antidepressants in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:375–375. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]