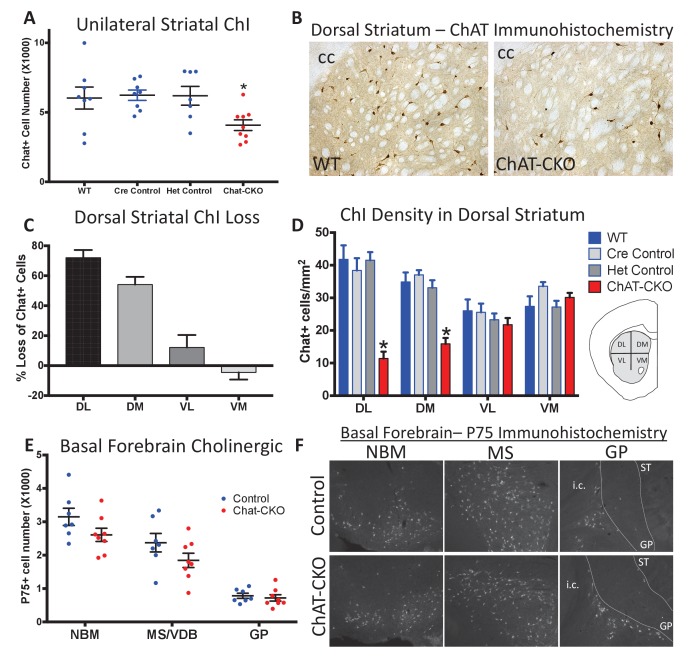
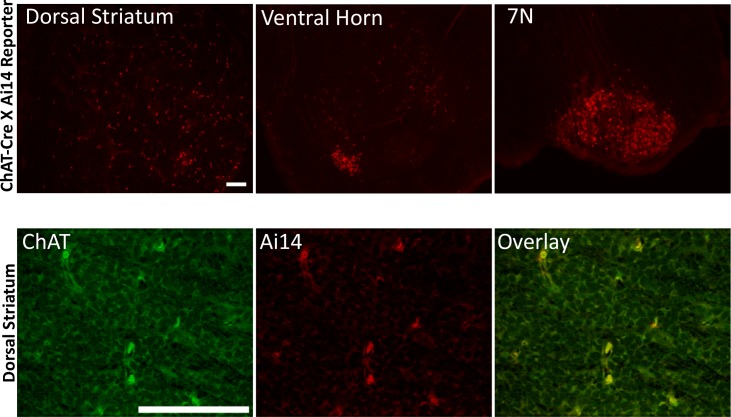
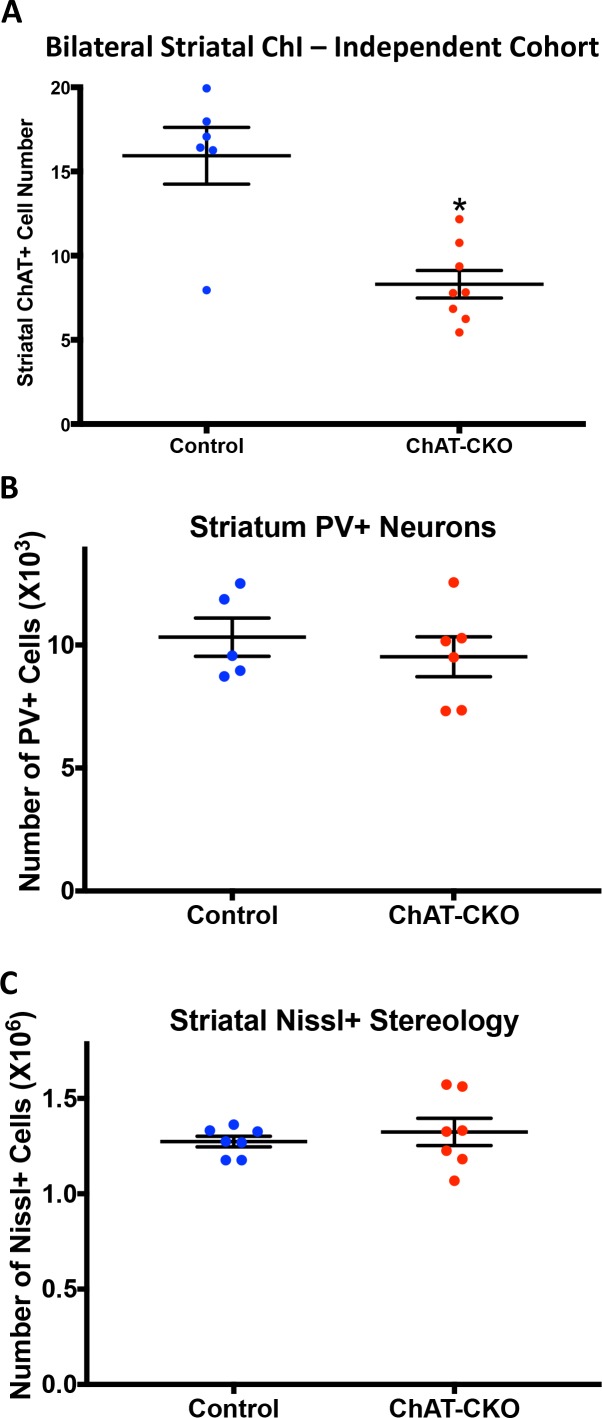
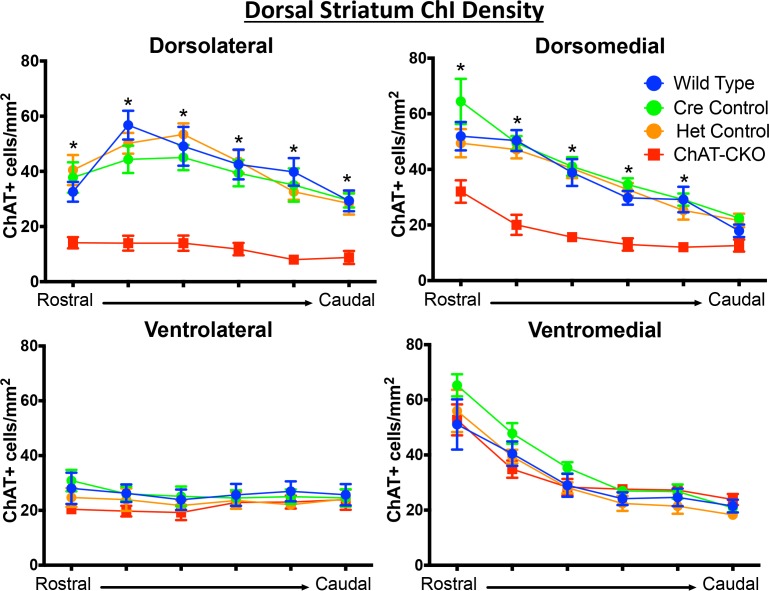
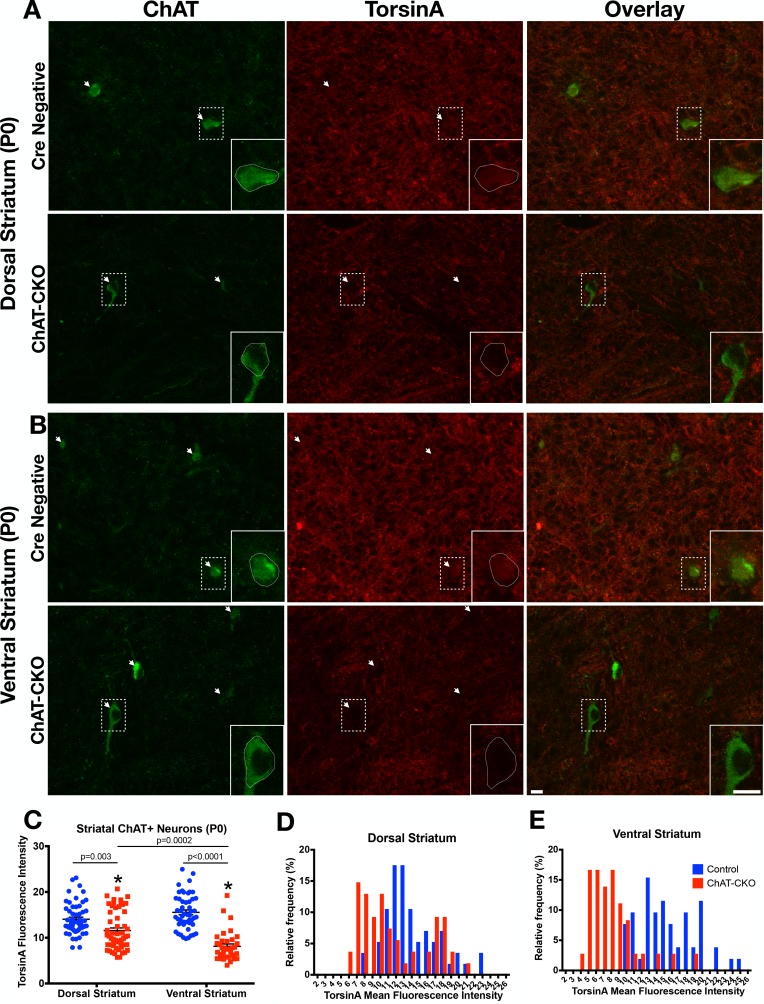
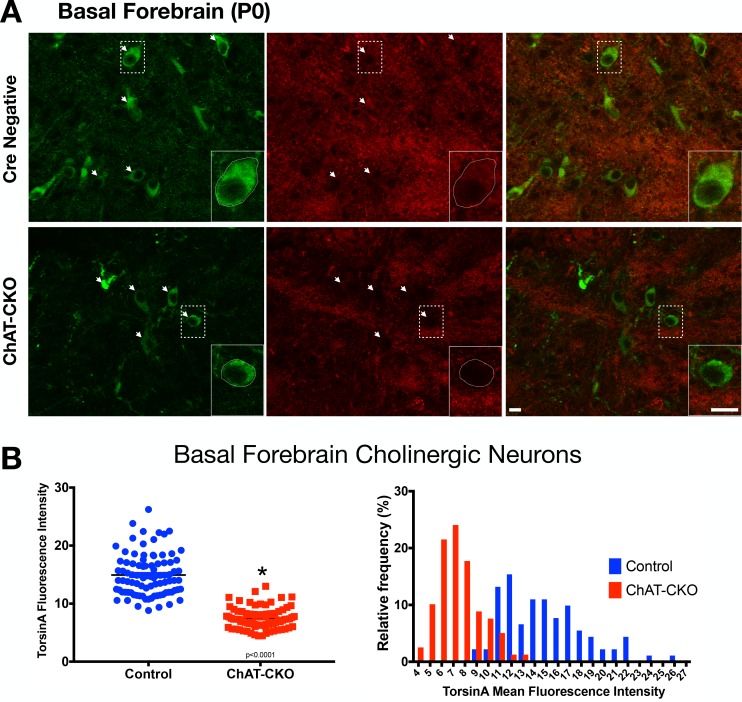
Figure 1. Conditional cholinergic neuron deletion of torsinA causes cell autonomous loss of striatal cholinergic neurons.
(A) Unilateral stereological quantification of the number of ChAT-positive neurons in the striatum of ChAT-CKO and control mice (One-way ANOVA F(3,28) = 3.589, p=0.02, Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test: adjusted p value = 0.049; ‘WT’=Tor1aFlx/+; ‘Cre Control’=ChAT-Cre+, Tor1a Flx/+; ‘Het Control’=Tor1 aFlx/-; ‘ChAT-CKO’=ChAT-Cre+, Tor1aFlx/-). (B) ChAT immunohistochemistry of coronal sections containing dorsal striatum from WT and ChAT-CKO mice (cc = corpus callosum). (C) Percent reduction in cell density by striatal quadrant (DL = dorsolateral; DM = dorsomedial, VL = ventrolateral, VM = ventromedial). (D) Significant ChI loss is selective for dorsal striatal quadrants. Cell density quantification in control and ChAT-CKO striatal quadrants (Two-way ANOVA main effect of genotype F(3,112) = 24.02, p<0.0001; main effect of quadrant F(3,112)=8.398, p<0.0001; interaction F(9,112)=8.11, p<0.0001. Post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (E) Basal forebrain neurons are spared in ChAT-CKO mice. Stereological quantification of P75-immunoreactive basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis of meynert (NBM), medial septum/nucleus of the vertical limb of the diagonal band (MS/VDB), and globus pallidus (GP). No differences in the number of cholinergic neurons was observed (NBM, t(13)=1.684, p=0.11; MS/VDB, t(13)=1.537, p=0.148; GP, t(13)=0.5, p=0.625). (F) P75 immunohistochemistry of sagittal sections containing basal forebrain cholinergic neuron populations. i.c. = internal capsule, ST = striatum.