Abstract
Background
To determine predictive factors of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) in patients undergoing enucleation (EN).
Methods
From 2005 to 2017, 47 patients underwent EN and had magnetic resonance imaging available for precise analysis of tumor location. Three pancreatic zones were delimited by the right side of the portal vein and the main pancreatic head duct (zone #3 comprising the lower head parenchyma and the uncinate process).
Results
The mortality and morbidity rates were 0% and 62%, respectively. POPF occurred in 23 patients (49%) and was graded as B or C (severe) in 15 patients (32%). Four patients (8.5%) developed a postoperative hemorrhage, and 5 patients (11%) needed a reintervention. In univariate and multivariate analyses, the pancreatic zone was the unique predictive factor of overall (P = .048) or severe POPF (P = .05). We did not observe any difference in postoperative courses when comparing the EN achieved in zones #1 and #2. We noted a longer operative duration (P = .016), higher overall (P = .017) and severe POPF (P = .01) rates, and longer hospital stays (P = .04) when comparing the EN achieved in zone #3 versus that in zones #1 and #2. Patients who underwent EN in zone #3 had a relative risk of developing a severe POPF of 3.22 compared with patients who underwent EN in the two other pancreatic zones.
Conclusion
Our study identifies the lower head parenchyma and the uncinate process as a high-risk zone of severe POPF after EN. Patients with planned EN in this zone could be selected and benefit from preoperative and/or intraoperative techniques to reduce the severe POPF rate.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12957-018-1476-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Enucleation, Pancreatic fistula, Magnetic resonance imaging
Background
Parenchyma-sparing pancreatectomies were proposed as an alternative to standard pancreatectomy for noninvasive tumors to avoid pancreatic endocrine and exocrine insufficiencies [1–4]. In this manner, enucleation (EN) was first performed in the 1960s [5]; currently, neuroendocrine tumors (particularly insulinoma) and branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) are the more frequent tumors resected by EN [6–15]. As EN induces parenchyma incision and, occasionally, deep pancreas opening, it exposes patients to postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) by unknown main pancreatic duct injury or weakening, especially if thermo-coagulation has been used too closely. Consequently, several reports have shown that EN leads to the same or a higher rate of POPF than does standard pancreatectomy, but with a “toward zero” mortality [4, 7, 10, 12, 15–17]. Predictive factors of POPF after EN have already been reported, such as age [6], body mass index [10], distance from the main pancreatic duct (≤ 2 mm) [17], cystic morphology [6], history of acute pancreatitis [6], and New York Heart Association class [14] (Table 1). These factors are not a contraindication for EN but could help pancreatic surgeons inform patients about possible prolonged postoperative courses, counterbalanced by the very low risk of developing diabetes mellitus and/or steatorrhea [1–4]. The pancreatic location of the EN (i.e., the head/uncinate process versus body/tail) seemed to be a relevant factor of POPF [9, 10, 13] (Table 1), but the head and uncinate process are usually considered a single location. Indeed, the uncinate process is defined by a portion of the head of the pancreas that hooks around posterior to the superior mesenteric vessels but is actually difficult to delimit from the proper head parenchyma on preoperative imaging and during surgery.
Table 1.
Reported risk factors of POPF after enucleation
| n | Head and uncinate together | POPF | Severe POPF | Risk factors | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turrini et al. [16] | 7 | Yes | 43% | 14% | – |
| Brient et al. [17] | 52 | Yes | 27% | 14% | Distance to MPD ≤ 2 mm |
| Jilesen et al. [10] | 60 | Yes | – | 31% | Head/uncinate BMI |
| Kaiser et al. [8] | 74 | Yes | 46% | 27% | – |
| Faitot et al. [13] | 126 | Yes | 57% | 41% | Head/uncinate |
| Song et al. [9] | 65 | Separated | 20% | 9% | Head/uncinate |
| Strobel et al. [11] | 166 | Yes | 41% | 21% | Cystic morphology |
| Wang et al. [6] | 142 | Yes | 53% | 16% | Age Acute pancreatitis Cystic morphology |
| Zhang et al. [14] | 119 | Yes | 40% | 28% | NYHA class |
| Present series | 47 | Separated | 49% | 32% | Lower head + uncinate |
BMI body mass index, POPF postoperative pancreatic fistula, NYHA New York Heart Association
The present study, based on a precise tumor location on pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), seeks to determine predictive factors of POPF in patients who underwent EN.
Methods
Initial population
From January 1, 2005, to December 31, 2017, 95 patients were eligible for EN at Institut Paoli-Calmettes (Marseille, France). All patient data were entered into a clinical database (CHIRPAN database: N°Sy50955016U) approved by both the Institut Paoli Calmettes Institutional Review/Ethical and the CNIL (“Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des Libertés” the French national board for databases) boards. Eligibility criteria for EN were (a) neuroendocrine or cystic tumor (side branch IPMN without worrying features, mucinous cystadenoma), (b) absence of main pancreatic duct dilatation, (c) absence of mural nodule or thickness of cyst wall, and (c) ability to preserve the main pancreatic duct.
Initial staging and final selected population (Fig. 1)
Fig. 1.
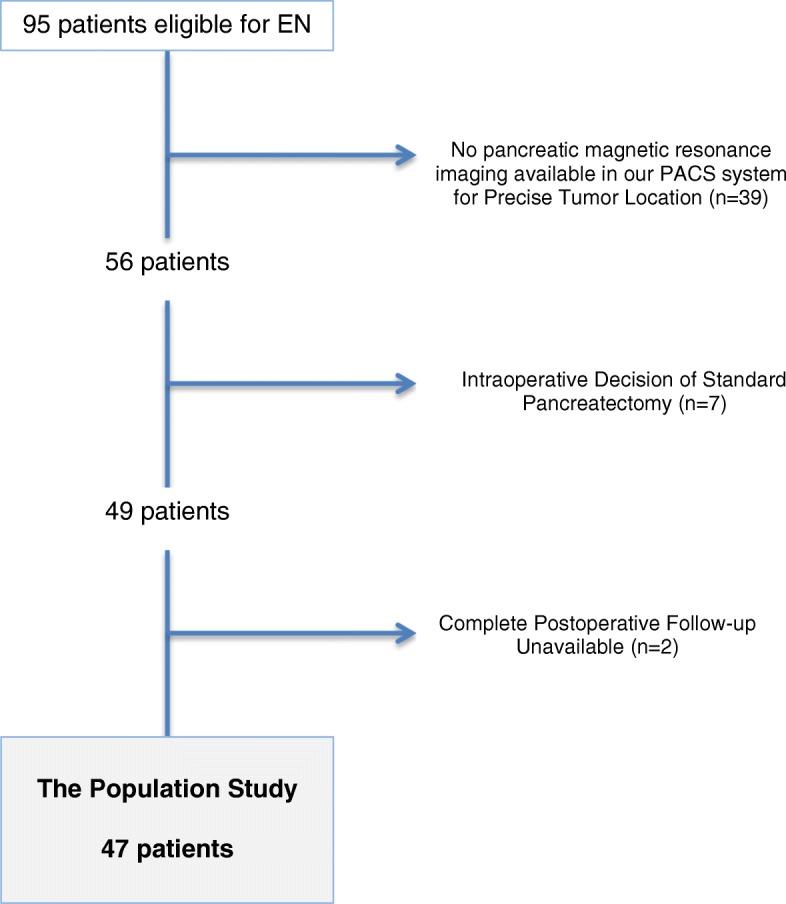
Patient selection for the present study
All patients were staged by physical examination, endoscopic ultrasound, and thin-section contrast-enhanced helical dual-phase scanning. As we supported that MRI was the most relevant imaging exam to assess pancreatic tumors [18], only patients who had a recent preoperative (within the month before surgery) MRI available on our picture archiving and communication system were included in the present study (n = 56) (Fig. 1). Consequently, for each EN, we could precisely determine the tumor location based on (a) the center of the tumor, for a spherical tumor, and (b) the crossing point between length and width, for a non-spherical tumor, as well as the tumor size (mm), and the distance to the main pancreatic duct (mm). Three pancreatic zones were arbitrarily delimited by the right side of the portal vein and the main pancreatic head duct; consequently, the pancreatic head was divided into two easily identifiable zones: zone #2, corresponding to the upper head parenchyma, and zone #3, comprising the lower head parenchyma and the uncinate process (Fig. 2). Zone #1 grouped the body and tail of the pancreas from the right side of the mesenteric vessels to the left parenchyma. Patients whose postoperative courses were not precisely known (within 90 postoperative days) were also excluded (n = 2) (Fig. 1).
Fig. 2.
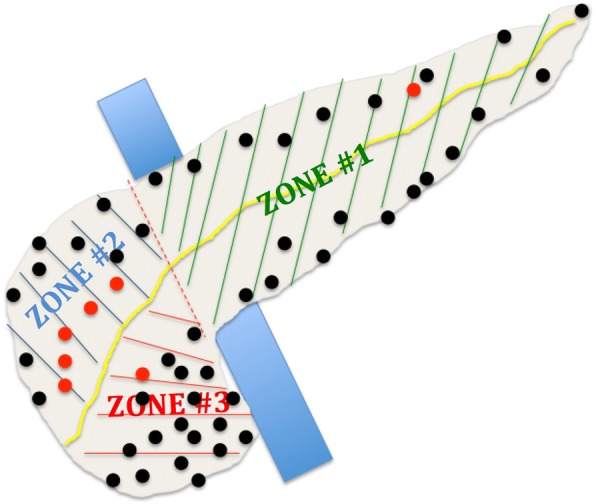
Pancreatic zones of enucleation and location of tumors (center) according to pancreatic MRI
Surgery
EN was achieved through laparotomy or laparoscopy according to surgeon preference and tumor location. Direct intraoperative ultrasound exploration was routinely performed to identify the main pancreatic duct and its distance to the tumor. Seven patients (5 in zone #2, 1 in zone #1, and 1 in zone #3) did not undergo EN because the tumor directly contacted the main pancreatic duct on intraoperative ultrasound; consequently, these patients with tumor located in zones #2 and #3 underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy and the patient with tumor located in zone #1 underwent distal pancreatectomy. Finally, 47 patients underwent EN and formed our population for the present study (Fig. 1); their tumor locations are presented in Fig. 2. The operative technique has already been described for pancreatic head IPMNs [16], and the global technical approach was not different for the body/tail or other cystic/solid tumors; coagulation was avoided to the greatest extent possible to avoid exposing the main pancreatic duct to thermal injury (Additional file 1: Figure S1). In cases of EN in zones #2 and #3, an intraoperative cholangiography with retrograde contrast back filling of the pancreatic duct was achieved to assess the integrity of both the biliary and pancreatic ducts. If the tumor was located in the “posterior” zone #3 (i.e., on the posterior face of the head of the pancreas), a larger Kocher maneuver was achieved to optimally expose the EN area. A non-aspirating drain was left in contact with the EN area, and the drain amylase level was measured on postoperative days 1 and 3. No patient had had a preventive preoperative stent inserted in the main pancreatic duct. Octreotide was not routinely used in prevention or with curative intent in the case of a POPF diagnosis.
End-points studied
The variables evaluated included age, sex, body mass index, location of the tumor (i.e., zone #1, #2, or #3), laparoscopic or open approaches, operative duration (minutes), POPF according to ISGPF grading [19] (grade A fistula was defined by a drain amylase level threefold higher than the serum amylase level; grades B and C defined severe POPF), and the overall morbidity [20] rate, including postoperative bleeding, reoperation, and perioperative red cell transfusion rates; endoscopic or radiologic drainage of a deep collection was noted, as was interventional embolization. The length of hospital stay (days) and the readmission rate were also recorded. The need of a standard pancreatectomy (salvage pancreatectomy) due to unresolved POPF was noted. Tumor morphology (i.e., cystic or solid (mixed tumors were considered as cystic type)) and exact histologic denomination (i.e., neuroendocrine tumor, IPMN, and others) were the recorded histological criteria.
Statistical analyses
The categorical factors were compared using Fisher’s exact test, and the continuous variables were compared using Student’s t test. Significance was set after a two-sided P ≤ .05. Prognostic factors with a P < .1 in univariate analysis or that were known to be relevant to predicting POPF were entered into a multivariable regression model to determine the independent predictors. Data analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software, version 5.0d (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) and SAS statistical software version 9.1 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
Patient characteristics (Table 2)
Table 2.
Patients and tumor characteristics. Intraoperative data and postoperative courses
| n or median | % or range | |
|---|---|---|
| Male gender | 12 | 26% |
| Age (years old) | 55 | 19–78 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.7 | 18–35.1 |
| Pancreatic zones | ||
| 1 | 20 | 43% |
| 2 | 9 | 19% |
| 3 | 18 | 38% |
| Distance to main duct (mm) | ||
| ≤ 2 mm | 21 | 45% |
| > 2 mm | 26 | 55% |
| Indication | ||
| Neuroendocrine tumors | 20 | 43% |
| Branch-duct IPMN | 17 | 36% |
| Others | 18 | 21% |
| Tumor morphology | ||
| Cystic | 25 | 53% |
| Solid | 22 | 47% |
| Tumor size (mm) | 20 | 4–61 |
| Operative duration (min) | 180 | 90–400 |
| POPF | ||
| Grade A | 8 | 17% |
| Grades B and C | 15 | 33% |
| Total | 23 | 50% |
| Delay surgery—POPF | 7 | 4–26 |
| Hemorrhage | 4 | 8.5% |
| Reintervention | 5 | 11% |
| Dindo morbidity | ||
| Grades 3–4 | 16 | 34% |
| Overall | 29 | 62% |
| Perioperative transfusion | 4 | 8.5% |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 15 | 6–90 |
| Readmission | 3 | 6.4% |
BMI body mass index, IPMN intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, POPF postoperative pancreatic fistula)
Patients were mainly women (74%), with a median age of 55 years (range, 19–78) and a median BMI of 22.7 (range, 18–35). Tumors were located in zone #1 in 20 patients (43%), in zone #2 in 9 patients (19%), and in zone #3 in 18 patients (38%) (Fig. 2); the most common morphology was cystic (53%), and the median size was 20 mm (range, 4–61). Twenty-one patients (45%) had a tumor distance from the main pancreatic duct ≤ 2 mm. Among patients who underwent EN in zone #3, 6 (33%) had an uncinectomy.
Surgery and postoperative course (Table 2)
The median operative duration was 180 min (range, 90–400). We detected one (2.1%) main pancreatic duct injury (in zone #3) according to intraoperative cholangiography: main pancreatic duct was electively closed with interrupted stich (Prolen 7/0) controlled by another cholangiography; a large drainage was positioned close to the suture. The mortality and overall morbidity rates were 0% and 62%, respectively. Dindo grade 3–4 complications were diagnosed in 16 patients (34%). POPF occurred in 23 patients (49%) and was severe in 15 patients (32%). The median delay between EN and POPF diagnosis was 7 days (range, 4–26). Four patients (8.5%) developed a postoperative hemorrhage in the EN zone, who all required red blood cell transfusion (range, 2–6 units). Five patients (11%) needed a reintervention for hemorrhage (n = 4) or duodenal fistula (n = 1) (cf infra). No patient required a salvage pancreatectomy. The length of hospital stay was 19 days (range, 6–90). Three patients (6.4%) needed a readmission for medical complications (urinary infection (n = 2), benign pulmonary embolism (n = 1)).
Pancreatic fistula and risk factors (Table 3a and b)
Table 3.
Univariate and multivariate analysis of risk factor for (a) all grade of postoperative pancreatic fistula and (b) grades B to C of postoperative pancreatic fistula
| a) | POPF (n = 23)% |
No POPF (n = 24)% |
Univariate P value |
Odd ratio [95% CI] |
Multivariate P value |
| Gender | – | – | |||
| Male | 8 (35) | 4 (17) | .19 | ||
| Female | 15 (65) | 20 (83) | |||
| Age (years old) | 52 | 56 | .39 | – | – |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.6 | 22 .7 | .17 | – | – |
| Pancreatic zones | .03 | 2.03 [1.01–4.07] | .048 | ||
| 1 | 8 (35) | 12 (50) | |||
| 2 | 2 (9) | 7 (29) | |||
| 3 | 13 (56) | 5 (21) | |||
| Distance to main duct (mm) | – | – | |||
| ≤ 2 mm | 10 (44) | 11 (46) | 1 | ||
| > 2 mm | 13 (46) | 13 (54) | |||
| Tumor morphology | 1 | – | – | ||
| Cystic | 13 (47) | 12 (50) | |||
| Solid | 10 (44) | 12 (50) | |||
| Tumor size (mm) | 24 | 22 | .55 | – | – |
| Laparoscopic approach | 5 (22) | 6 (25) | 1 | – | – |
| Operative duration (min) | 205 | 180 | .26 | – | – |
| b) | POPF B/C (n = 15)% |
No POPF B/C (n = 32)% |
Univariate P value |
Odd ratio [95% CI] | Multivariate P value |
| Gender | .16 | – | – | ||
| Male | 6 (40) | 6 (19) | |||
| Female | 9 (60) | 26 (81) | |||
| Age (years old) | 54 | 53 | .85 | – | – |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.6 | 23.1 | .32 | – | – |
| Pancreatic zones | .02 | 2.06 [1.01–4.3] | .05 | ||
| 1 | 3 (20) | 17 (53) | |||
| 2 | 2 (13) | 7 (22) | |||
| 3 | 10 (67) | 8 (25) | |||
| Distance to main duct (mm) | .15 | ||||
| ≤ 2 mm | 9 (60) | 12 (38) | – | – | |
| > 2 mm | 6 (40) | 20 (62) | |||
| Tumor morphology | .99 | ||||
| Cystic | 8 (53) | 17 (53) | – | – | |
| Solid | 7 (47) | 15 (47) | |||
| Tumor size (mm) | 22 | 22 | .98 | – | – |
| Laparoscopic approach | 2 (13) | 9 (28) | .27 | – | – |
| Operative duration (min) | 200 | 190 | .53 | – | – |
BMI body mass index, POPF postoperative pancreatic fistula, CI confidence interval
All patients (n = 8) with grade A POPF (of whom three patients with main pancreatic duct direct leakage (all after EN in zone #3) including the patient with main pancreatic duct injury detected intraoperatively) were managed with continuous normal alimentation and progressive drain withdrawal; the median POPF resolution delay (i.e., from POPF diagnosis) was 9 days (range, 4–16). Among the 15 patients with severe POPF, 12 (80%) required an endoscopic or radiologic drainage of a deep collection, 4 patients (27%) required a reintervention for hemorrhage, and one patient (6.7%) developed a duodenal fistula treated by conservative surgery (i.e., direct suture and drainage with progressive fistula spontaneous closure). Two patients who developed a hemorrhage needed a reintervention after an attempt at interventional embolization because the responsible artery could not be reached; another two patients underwent direct reintervention due to bleeding of the gastric wall after a transgastric drainage of a deep collection (Additional file 2: Figure S2a–e).
In the univariate and multivariate analyses, the pancreatic zone was the unique predictive factor of overall (P = .048) or severe (P = .05) POPF. Distance to the main pancreatic duct and cystic morphology was not identified as a relevant factor for predicting overall or severe POPF.
Pancreatic zones of enucleation (Table 4)
Table 4.
Patients and tumor characteristics. Intraoperative data and postoperative courses according to the pancreatic zone classification risk of POPF
| Zone #1 | Zone #2 |
P value zone#1 vs zone #2 |
Zone #3 |
P value zone#1 + 2 vs zone #3 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor located in the corresponding zone but patient underwent standard pancreatectomy according to intraoperative decision (%)* | 1 (5) | 5 (36) | .027 | 1 (5) | ns |
| n (%) | 20 (43) | 9 (19) | – | 18 (38) | – |
| Male gender (%) | 3 (15) | 1 (11) | ns | 2 (11) | ns |
| Age (years old) | 53 | 52 | ns | 56 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.8 | 21.5 | ns | 25.4 | ns |
| Distance to Wirsung (mm) | |||||
| < 2 mm (%) | 7 (35) | 4 (44) | ns | 10 (56) | ns |
| > 2 mm (%) | 13 (65) | 5 (56) | ns | 8 (44) | ns |
| Tumor morphology | |||||
| Cystic (%) | 10 (50) | 5 (56) | ns | 10 (56) | ns |
| Solid (%) | 10 (50) | 4 (44) | ns | 8 (44) | ns |
| Tumor size (mm) | 22 | 25 | ns | 22 | ns |
| Laparoscopic approach | 8 (40) | 2 (22) | ns | 1 (6) | .03 |
| Operative duration (min) | 170 | 180 | ns | 220 | .016 |
| POPF | |||||
| Grade A (%) | 5 (25) | 0 | ns | 3 (17) | ns |
| Grades B and C (%) | 3 (15) | 2 (22) | ns | 10 (56) | .01 |
| Total (%) | 8 (40) | 2 (22) | ns | 13 (72) | .017 |
| Hemorrhage (%) | 0 | 1 (11) | ns | 3 (17) | ns |
| Reintervention (%) | 0 | 1 (11) | ns | 4 (22) | ns |
| DINDO morbidity | |||||
| Grades 3–4 (%) | 3 (15) | 5 (56) | ns | 8 (44) | ns |
| Overall (%) | 8 (40) | 5 (56) | ns | 16 (89) | ns |
| Perioperative transfusion (%) | 0 | 0 | ns | 4 (22.2) | ns |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 13 | 15 | 23 | .04 | |
| Readmission (%) | 0 | 0 | ns | 3 (17) | ns |
vs versus, BMI body mass index, POPF postoperative pancreatic fistula
*These patients are not comprised in our study population
The patient and tumor characteristics were not different among the three groups defined by the three zones. Laparoscopic approach was more often used for EN in zone #1 + 2 when compared with zone #3 (P = .03). We did not observe any difference in postoperative courses when comparing the EN achieved in zones #1 and #2. We noted a longer operative duration (P = .016), higher overall (P = .017) and severe (P = .01) POPF rates, and longer hospital stay (P = .04) when comparing the EN achieved in zone #3 versus that in zone #1 + 2. Patients who underwent EN in zone #3 had a relative risk [95% confidence interval] of developing a severe POPF of 3.22 [1.31–7.91] compared with patients who underwent EN in the two other pancreatic zones (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
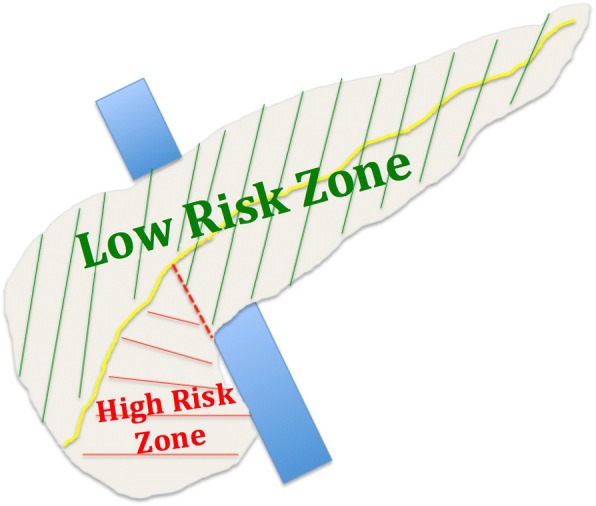
Pancreatic zones to predict overall and severe POPF according to pancreatic MRI
Discussion
Our study identified a high-risk zone (the lower head parenchyma and uncinate process) for developing a POPF after EN, with a relative risk of 3.22 compared to the rest of the cases of pancreatic parenchyma.
POPF after EN
It is now well known that EN can lead to the same POPF rate as standard pancreatectomies (Table 1); however, EN can be considered safer in terms of its mortality rate, which might increase to 10% [21, 22] after pancreatectomies. This finding completely justifies EN as a procedure of choice in patients with benign tumors. Consequently, the patient must be informed that EN is a “mini invasive” pancreatic procedure with the advantage of preserving pancreatic parenchyma but without a reduced risk of POPF and its associated morbidity. The risk factors of overall and severe POPF have already been studied: on the one hand, several factors, such as age [6], body mass index [10], distance to the main pancreatic duct [17], history of acute pancreatitis [6], and New York Heart Association class [14], were independently identified by a single publication each (Table 1); on the other hand, cystic morphology [6, 11] and tumor location [9, 10, 13] were identified in at least two independent series (Table 1). Our study confirmed that tumor location (i.e., the corresponding EN area) was relevant to predict POPF, but we improved the precision of this result by delimiting a particular zone with a higher risk than the rest of the pancreatic parenchyma. Despite the increasing trend, we did not observe any difference in terms of overall postoperative complications, postoperative hemorrhage, reintervention, perioperative transfusion, and readmission rates between patients who underwent EN in the high-risk zone and the others; however, these factors are clearly directly related to severe POPF, and the reduced sample of our series might be the cause of the non-significance of these results.
Pancreatic zones
As the head of the pancreas is a more difficult zone to expose and represents the intersection of the pancreatic, biliary, and digestive tracts, it was supposed to be at a higher risk of complication after EN. This has already been reported [9, 10, 13], but the uncinate process has never been studied separately from the rest of the head of the pancreas. Our pancreatic partition based on MRI was efficient for easily identifying patients at a high risk of developing a severe POPF after EN. We observed that patients who underwent EN of a tumor located in the upper part of the head (i.e., in zone #2) had a similar risk of experiencing severe POPF as did patients who underwent EN for a tumor located in the body or tail of the pancreas. We suppose that patients who underwent EN in zone #2 were carefully selected and that their tumors probably not deeply located in the head; in such cases, due to the high probability of bile duct injury, a pancreaticoduodenectomy may have been preferred preoperatively. This was confirmed by the lower number of patients (19% of our studied population) who underwent EN in zone #2 and by the higher rate of patients with a planned EN who ultimately had a standard pancreatectomy performed (36% in zone #2, 5% in zone #1, and 5% in zone #3). Thus, our study is limited by the absence of study of the tumor’s depth as a risk factor of POPF, even if it has never been highlighted in another study [13].
Prevention of POPF in the high-risk zone
Our study should not discourage pancreatic surgeons from performing EN in patients with tumors located in the high-risk zone because we showed that (a) it was a safe procedure, despite its high morbidity rate and (b) no patients required a salvage pancreaticoduodenectomy. Indeed, our findings permitted the identification of patients who should benefit from strict follow-up and possibly from POPF-preventive procedures. Some authors have described the usefulness of preoperative stenting in patients undergoing EN to reduce main pancreatic duct leakage [23]; a nasopancreatic drain can also be inserted preoperatively to intraoperatively contrast the back-fill of the main pancreatic duct [24] and thereby identify an unknown injury. If the main pancreatic duct stenting is reported as an interesting procedure for treating a prolonged POPF [25], it is correlated with a non-negligible risk of acute pancreatitis [26, 27] and cannot be proposed as a preoperative routine procedure. Indeed, when the EN of a deep tumor is planned in the high-risk zone, a sphincterotomy followed by the insertion of a stent in the main pancreatic duct could be discussed prior to surgery. However, three arguments must be considered before routinely adopting such a policy. First, a recent randomized study did not confirm the benefit of preoperative stenting to reduce POPF [28]. However, this series was only conducted in patients who underwent distal pancreatectomy, and no data are available concerning proximal or distal EN. Second, EN in the high-risk zone also exposes the patient to other pancreatic duct injuries such as pancreas divisum (Type IV of the Cambridge classification; 5% of the population; risk of injury of the accessory duct) [29]; ansa pancreatica (Type V; 1% of the population) [29] is another duct variation in which a loop communication is made between the main and accessory duct: stenting of the sole main duct will thus not be sufficient to prevent POPF. Third, pancreatic stenting (even after stent withdrawal) in patients diagnosed with IPMN can lead to main duct modification at imaging and impair the follow-up (modifications due to main duct IPMN or stenting). We support the idea that a careful examination of both MRI and endoscopic ultrasound could help select patients who might benefit from preoperative pancreatic stenting (the patient in the second images should have been a good candidate for preoperative stenting to avoid a lateral main duct injury despite careful ligature of the communication duct). Intraoperatively, in the case of deep EN in the high-risk zone, the pancreatic surgeon could achieve en-Roux pancreaticojejunostomy [30] or teres hepatis ligament flap plasty [31], even if such procedures have not been validated in large series to reduce POPF risk. Finally, drainage of the EN zone must be optimal to avoid pancreatic juice stagnation and favor grade A instead of severe POPF. However, drainage of the “anterior” high-risk zone is difficult (“egg cup” effect, as in the patient in the second images) and often insufficient.
Highlighted by our findings, our actual policy is to achieve a sphincterotomy with main pancreatic duct stent insertion prior to EN in the high-risk zone in patients (a) whose main pancreatic duct is found to be closer than 2 mm at MRI and/or intraoperative ultrasound and/or (b) with branch-duct IPMN consequently linked with the main pancreatic duct. Evaluation of such attitude is ongoing, and we will compare the results with those of the 18 EN achieved in the high-risk zone without preoperative stenting that we have reported in the present series.
Conclusion
Our study identifies a pancreatic zone that is at a high risk of developing a severe POPF after EN but with zero mortality. Thus, EN should be preferred to a pancreaticoduodenectomy to preserve long-term exocrine and endocrine pancreatic functions. However, we support the idea that patients who are planned for a deep EN in this zone should be selected and could benefit from some preoperative (main duct stenting) and/or intraoperative techniques (pancreaticojejunostomy and teres hepatis ligament flap plasty) to prevent severe POPF; these patients should be carefully followed up during the postoperative course, even if they have experimented with a “mini-invasive” surgery.
Additional files
Figure S1. Intraoperative picture showing the enucleation (yellow arrow) of an insulinoma in the “anterior” zone #3. Please note all ligatures (a) not to have any bleeding during the parenchyma opening that could disturb the identification of main pancreatic duct and (b) preferred to coagulation to avoid thermal damage of the main pancreatic duct. (JPEG 248 kb)
Figure S2. (a) pancreatic frontal magnetic resonance imaging showing a branch-duct intrapapillary mucinous neoplasm of zone #3 (portal vein in represented in blue, pancreatic zones are delimited by interrupted red lines); the patient underwent EN in the anterior zone #3 with elective ligature of the communicant duct; (b) drainage (yellow arrow) of a deep collection in the EN zone by two double-pigtail plastic transgastric stents; (c) 24 h after drainage, the patient presented a brutal abdominal pain with hemoglobin serum level tumbling to 6 g/dL, and the CT scan showed an hematoma (red arrow) in the enucleation area without identification of the responsible artery at arteriography; consequently the patient underwent explorative laparotomy; (d) intraoperative picture showing the hematoma in zone #3 with “egg cup” effect (main part of the hematoma descending along the right mesocolon has already been removed); (e) intraoperative picture showing the ablation of the hematoma and the two double-pigtail plastic stents. Bleeding originated from the gastric wall, which was closed by an automatic stapler application after having removed the stents. (JPEG 303 kb)
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to institutional policies but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- EN
Enucleation
- IPMN
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- POPF
Postoperative pancreatic fistula
Authors’ contributions
PD and OT contributed to the study design. OT contributed to the data collection. PD and OT contributed to the data analysis and interpretation. All authors contributed to the manuscript redaction/revising. Each author has participated sufficiently in the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patient data were entered into a clinical database (CHIRPAN database: N°Sy50955016U) approved by both the Institut Paoli Calmettes Institutional and Ethical Review and the CNIL (“Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des Libertés” the French national board for databases) boards.
Consent for publication
Consent was obtained from the patients whose intraoperative photos were used.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Pauline Duconseil, Email: pauline.duconseil@gmail.com.
Ugo Marchese, Email: marcheseu@ipc.unicancer.fr.
Jacques Ewald, Email: ewaldj@ipc.unicancer.fr.
Marc Giovannini, Email: giovanninim@ipc.unicancer.fr.
Djamel Mokart, Email: mokartj@ipc.unicancer.fr.
Jean-Robert Delpero, Email: delperojr@ipc.unicancer.fr.
Olivier Turrini, Phone: 0491223660, Email: oturrini@yahoo.fr.
References
- 1.Beger HG. Benign tumors of the pancreas-radical surgery versus parenchyma-sparing local resection—the challenge facing surgeons. J Gastrointest Surg. 2018;22(3):562–566. doi: 10.1007/s11605-017-3644-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhou Y, Zhao M, Wu L, Ye F, Si X. Short- and long-term outcomes after enucleation of pancreatic tumors: an evidence-based assessment. Pancreatology. 2016;16(6):1092–1098. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2016.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Beger HG, Siech M, Poch B, Mayer B, Schoenberg MH. Limited surgery for benign tumours of the pancreas: a systematic review. World J Surg. 2015;39(6):1557–1566. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-2976-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sauvanet A, Gaujoux S, Blanc B, Couvelard A, Dokmak S, Vullierme MP, et al. Parenchyma-sparing pancreatectomy for presumed noninvasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 2014;260(2):364–371. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Delannoy E, Combemale B. Pancreatic cystadenoma. Enucleation. Reconvery. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 1964;90:521–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang X, Tan CL, Zhang H, Chen YH, Yang M, Ke NW, et al. Short-term outcomes and risk factors for pancreatic fistula after pancreatic enucleation: a single-center experience of 142 patients. J Surg Oncol. 2018;117(2):182–190. doi: 10.1002/jso.24804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lu WJ, Cai HL, Ye MD, Wu YL, Xu B. Enucleation of non-invasive tumors in the proximal pancreas: indications and outcomes compared with standard resections. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017;18(10):906–916. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kaiser J, Fritz S, Klauss M, Bergmann F, Hinz U, Strobel O, et al. Enucleation: a treatment alternative for branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Surgery. 2017;161(3):602–610. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.09.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Song KB, Kim SC, Hwang DW, Lee JH, Lee DJ, Lee JW, et al. Enucleation for benign or low-grade malignant lesions of the pancreas: single-center experience with 65 consecutive patients. Surgery. 2015;158(5):1203–1210. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jilesen AP, van Eijck CH, Busch OR, van Gulik TM, Gouma DJ, van Dijkum EJ. Postoperative outcomes of enucleation and standard resections in patients with a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. World J Surg. 2016;40(3):715–728. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3341-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bel O, Cherrez A, Hinz U, Mayer P, Kaiser J, Fritz S, et al. Risk of pancreatic fistula after enucleation of pancreatic tumours. Br J Surg. 2015;102(10):1258–1266. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hüttner FJ, Koessler-Ebs J, Hackert T, Ulrich A, Büchler MW, Diener MK. Meta-analysis of surgical outcome after enucleation versus standard resection for pancreatic neoplasms. Br J Surg. 2015;102(9):1026–1036. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Faitot F, Gaujoux S, Barbier L, Novaes M, Dokmak S, Aussilhou B, et al. Reappraisal of pancreatic enucleations: a single-center experience of 126 procedures. Surgery. 2015;158(1):201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang T, Xu J, Wang T, Liao Q, Dai M, Zhao Y. Enucleation of pancreatic lesions: indications, outcomes, and risk factors for clinical pancreatic fistula. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013;17(12):2099–2104. doi: 10.1007/s11605-013-2355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cauley CE, Pitt HA, Ziegler KM, Nakeeb A, Schmidt CM, Zyromski NJ, et al. Pancreatic enucleation: improved outcomes compared to resection. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16(7):1347–1353. doi: 10.1007/s11605-012-1893-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Turrini O, Schmidt CM, Pitt HA, Guiramand J, Aguilar-Saavedra JR, Aboudi S, et al. Side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreatic head/uncinate: resection or enucleation? HPB (Oxford) 2011;13(2):126–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2010.00256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Brient C, Regenet N, Sulpice L, Brunaud L, Mucci-Hennekine S, Carrère N, et al. Risk factors for postoperative pancreatic fistulisation subsequent to enucleation. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16(10):1883–1887. doi: 10.1007/s11605-012-1971-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ducon Duconseil P, Turrini O, Ewald J, Soussan J, Sarran A, Gasmi M, et al. ‘Peripheric’ pancreatic cysts: performance of CT scan, MRI and endoscopy according to final pathological examination. HPB (Oxford) 2015;17(6):485–489. doi: 10.1111/hpb.12388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bassi C, Dervenis C, Butturini G, Fingerhut A, Yeo C, Izbicki J, et al. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: an international study group (ISGPF) definition. Surgery. 2005;138(1):8–13. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240(2):205–213. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000133083.54934.ae. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nimptsch U, Krautz C, Weber GF, Mansky T, Grützmann R. Nationwide in-hospital mortality following pancreatic surgery in Germany is higher than anticipated. Ann Surg. 2016;264(6):1082–1090. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Farges O, Bendersky N, Truant S, Delpero JR, Pruvot FR, Sauvanet A. The theory and practice of pancreatic surgery in France. Ann Surg. 2017;266(5):797–804. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ide S, Uchida K, Inoue M, Koike Y, Otake K, Matsushita K, et al. Tumor enucleation with preoperative endoscopic transpapillary stenting for pediatric insulinoma. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012;28(7):707–709. doi: 10.1007/s00383-012-3104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Misawa T, Imazu H, Fujiwara Y, et al. Efficacy of nasopancreatic stenting prior to laparoscopic enucleation of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2013;6(2):140–142. doi: 10.1111/ases.12006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Maire F, Ponsot P, Debove C, Dokmak S, Ruszniewski P, Sauvanet A. Endoscopic management of pancreatic fistula after enucleation of pancreatic tumors. Surg Endosc. 2015;29(11):3112–3116. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-4034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ito K, Fujita N, Kanno A, Matsubayashi H, Okaniwa S, Nakahara K, et al. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis in high risk patients who have undergone prophylactic pancreatic duct stenting: a multicenter retrospective study. Intern Med. 2011;50(24):2927–2932. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.50.6235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Matsubara H, Urano F, Kinoshita Y, Okamura S, Kawashima H, Goto H, et al. Analysis of the risk factors for severity in post endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: the indication of prophylactic treatments. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;9(4):189–195. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v9.i4.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gupta RA, Agrawal P, Doctor N, Nagral S. The effect of prophylactic transpapillary pancreatic stent insertion on clinically significant leak rate following distal pancreatectomy: results of a prospective controlled clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2015;261(3):e81. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Adibelli ZH, Adatepe M, Imamoglu C, Esen OS, Erkan N, Yildirim M. Anatomic variations of the pancreatic duct and their relevance with the Cambridge classification system: MRCP findings of 1158 consecutive patients. Radiol Oncol. 2016;50(4):370–377. doi: 10.1515/raon-2016-0041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xiao Z, Luo G, Liu Z, Jin K, Xu J, Liu C, et al. Roux-en-Y pancreaticojejunostomy reconstruction after deep enucleation of benign or borderline pancreatic lesions: a single-institution experience. HPB (Oxford) 2016;18(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2015.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hackert T, Lozanovski VJ, Werner J, Büchler MW, Schemmer P. Teres hepatis ligament flap plasty to prevent pancreatic fistula after tumor enucleation. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217(4):e29–e34. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1. Intraoperative picture showing the enucleation (yellow arrow) of an insulinoma in the “anterior” zone #3. Please note all ligatures (a) not to have any bleeding during the parenchyma opening that could disturb the identification of main pancreatic duct and (b) preferred to coagulation to avoid thermal damage of the main pancreatic duct. (JPEG 248 kb)
Figure S2. (a) pancreatic frontal magnetic resonance imaging showing a branch-duct intrapapillary mucinous neoplasm of zone #3 (portal vein in represented in blue, pancreatic zones are delimited by interrupted red lines); the patient underwent EN in the anterior zone #3 with elective ligature of the communicant duct; (b) drainage (yellow arrow) of a deep collection in the EN zone by two double-pigtail plastic transgastric stents; (c) 24 h after drainage, the patient presented a brutal abdominal pain with hemoglobin serum level tumbling to 6 g/dL, and the CT scan showed an hematoma (red arrow) in the enucleation area without identification of the responsible artery at arteriography; consequently the patient underwent explorative laparotomy; (d) intraoperative picture showing the hematoma in zone #3 with “egg cup” effect (main part of the hematoma descending along the right mesocolon has already been removed); (e) intraoperative picture showing the ablation of the hematoma and the two double-pigtail plastic stents. Bleeding originated from the gastric wall, which was closed by an automatic stapler application after having removed the stents. (JPEG 303 kb)


