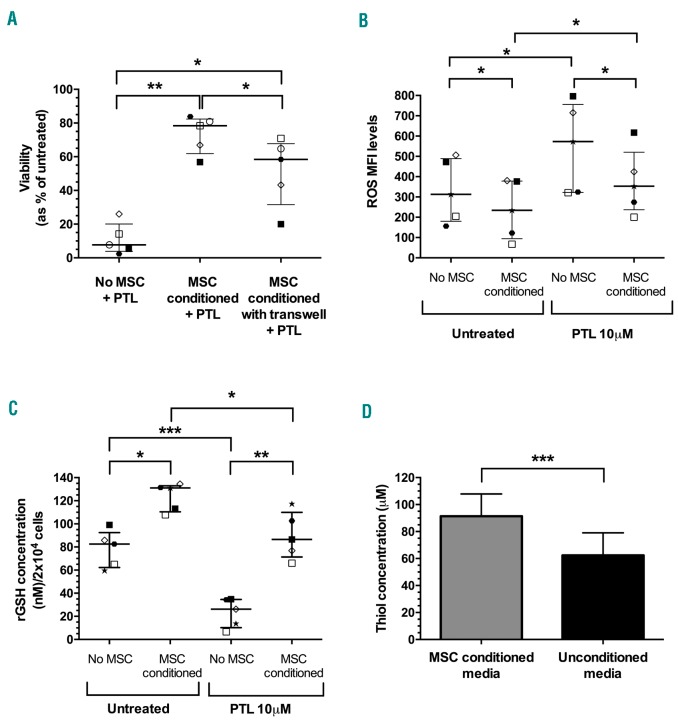
Figure 2.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) protect T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (TALL) cells from parthenolide (PTL)-induced cell death, reactive oxygen species (ROS) stress and decreased reduced glutathione (rGSH) levels. (A) The viability of T-ALL samples (patients 1, 2, 5, 6, and 10) after 24 hours (h) of PTL treatment (10 μM) with or without MSC in direct contact and in transwells. (B) ROS levels in patient samples 2, 5, 6, 9, and 10 after 1 h PTL treatment (10 μM) with or without MSC. (C) The concentration of rGSH in patient samples 2, 5, 6, 9, and 10 after 1 h PTL treatment (10 μM) with or without MSC. Symbols represent the average value in replicate samples. Each symbol represents an individual patient. Lines represent median and interquartile range. (D) Increase in thiol concentration in media from MSC culture after 24 h compared to blank media (n=6). Thiol concentrations were derived from the standard curve of known cysteine levels. Results were analyzed by one-way ANOVA (AC) or paired t-test (D). *P≤0.05,**P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001.