Hemorrhoids occur in 4% of the population and are identified in 39% to 45% of colonoscopies.1 Internal hemorrhoids have been categorized further according to the Banov classification, which has grades I to IV. Although grades III and IV have typically been managed surgically, grades I and II can be treated by endoscopic means.1, 2, 3
Numerous endoscopic methods have been described to treat internal hemorrhoids, but these techniques are fraught with high rates of postprocedural pain.3, 4, 5, 6 The described technique for hemorrhoidal therapy is a bipolar system that uses a novel anoscope with built-in illumination and a consistent compression apparatus (Figs. 1 and 2). This allows for stable energy delivery, which causes lower rates of collateral damage and, therefore, less postprocedural pain.
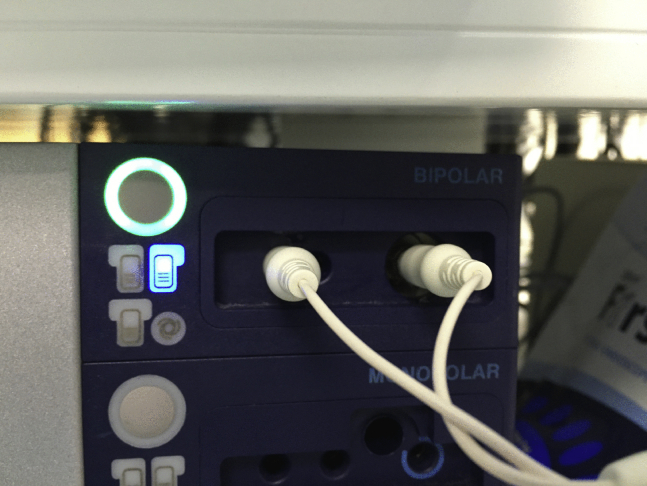
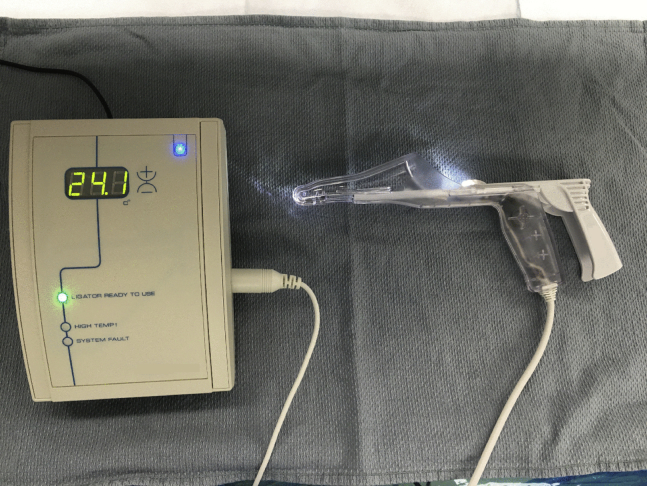
Figure 1.
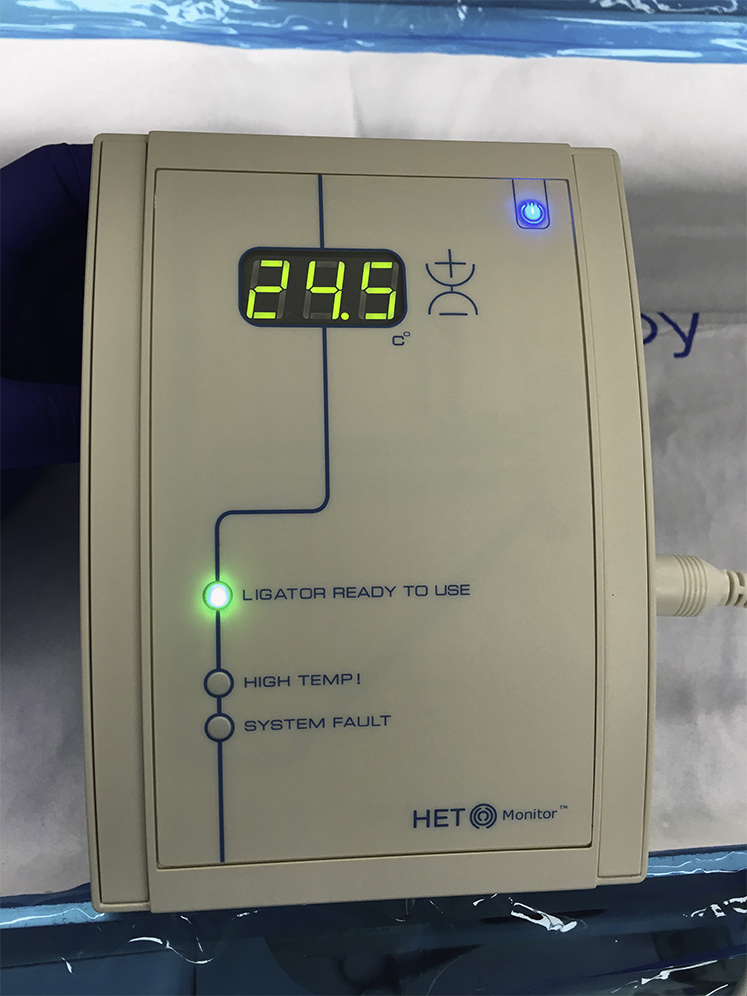
Bipolar system: visible bipolar device platform with active blue light (upper right corner), signifying power-on status and green light (mid-left), with power into electrocautery system.
Figure 2.
Speculum and bipolar system: visible bipolar system (left) and speculum with built-in illumination, bipolar energy delivery system, and handle that controls tissue approximation (right).
This video (Video 1, available online at www.VideoGIE.org) demonstrates appropriate patient selection, positioning, equipment, setup, and procedural nuances necessary for obtaining success with this bipolar system (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6). Specifically, we emphasize various techniques that can be implemented for proper tissue apposition of the hemorrhoidal cushions with the bipolar probe.
Figure 3.
Equipment: 2-inch tape (left), hemorrhoidal forceps (upper right), through-the-scope grasping forceps (lower right, left-most), surgical lubricant (lower right, right-most).
Figure 4.
Proper installation of bipolar system: cord from bipolar device placed into uppermost bipolar portion of electrocautery system.
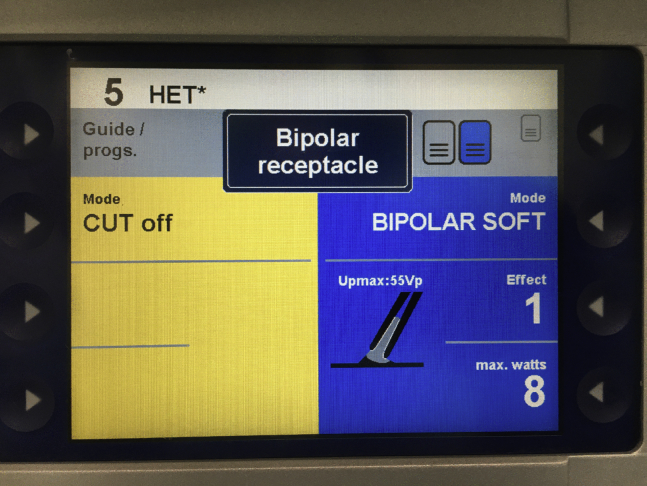
Figure 5.
Electrocautery setting for bipolar system. Visible monitor reveals bipolar setting of electrocautery system at effect 1, 8 W.
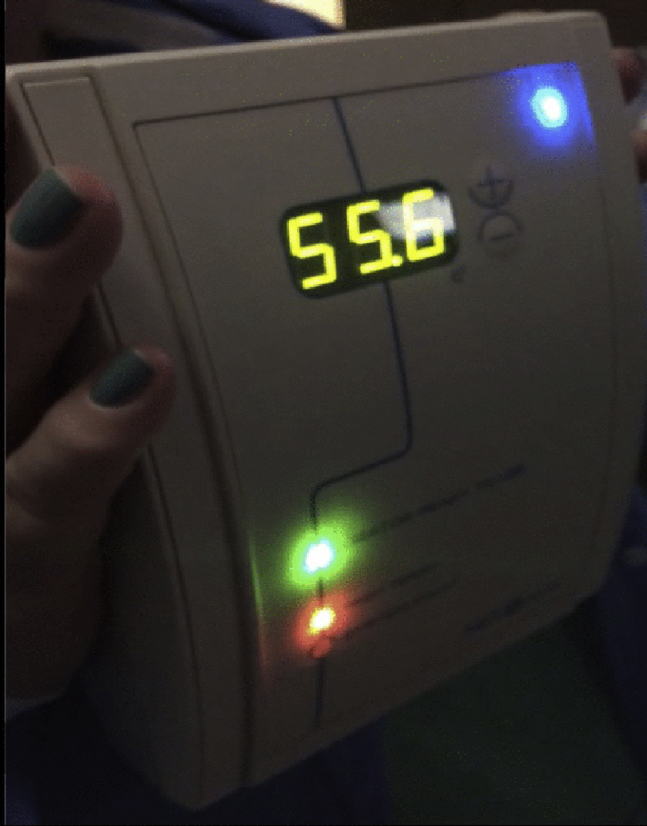
Figure 6.
Bipolar system high-temperature alarm. Visible bipolar system with red light (lower left) indicating above-target temperature reached, accompanied with audible alarm.
A 33-year-old woman presented with blood per rectum with straining. The patient underwent a colonoscopic examination, which identified 2 grade I hemorrhoids in the right anterior and posterior cushions and 1 grade II hemorrhoid in the left lateral cushion, with a hypertrophied anal papilla. No additional bleeding lesions were seen throughout the colon.
She then underwent the bipolar procedure to treat her symptomatic hemorrhoids. Using a through-the-speculum grasper to allow for tissue apposition, we delivered electrocautery energy using a bipolar current to each of the hemorrhoidal cushions (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6). Postprocedural assessment demonstrated appropriate energy delivery. Follow-up evaluation revealed absence of symptoms, and endoscopic inspection at 1 month showed resolution of hemorrhoids.
Endoscopic treatment of internal hemorrhoids with this bipolar system was safe and effective. There are numerous variations of this endoscopic technique, all of which are useful in achieving clinical success.7, 8
Disclosure
Dr Khara is a consultant for Medtronic-Covidien. Dr Johal is a consultant for Boston Scientific. Dr Diehl is a consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus. All other authors disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this publication.
Footnotes
Written transcript of the video audio is available online at www.VideoGIE.org.
Supplementary data
A video depicting a case treating hemorrhoids using this bipolar system.
References
- 1.Pfenninger J.L., Surrell J. Nonsurgical treatment options for internal hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 1995;52:821–834. 839-41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Salvati E.P. Nonoperative management of hemorrhoids: evolution of the office management of hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999;42:989–993. doi: 10.1007/BF02236687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.MacRae H.M., McLeod R.S. Comparison of hemorrhoidal treatments: a meta-analysis. Can J Surg. 1997;40:14–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Johanson J.F., Rimm A. Optimal nonsurgical treatment of hemorrhoids: a comparative analysis of infrared coagulation, rubber band ligation and injection sclerotherapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87:1600–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Iyer V.S., Shrier I., Gordon P.H. Long-term outcome of rubber band ligation for symptomatic primary and recurrent internal hemorrhoids. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004;47:1364–1370. doi: 10.1007/s10350-004-0591-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Su M.Y., Tung S.Y., Wu C.S. Long-term results of endoscopic hemorrhoidal ligation: two different devices with similar results. Endoscopy. 2003;35:416–420. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-38773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Piskun G., Tucker R. New bipolar tissue ligator combines constant tissue compression and temperature guidance: histologic study and implications for treatment of hemorrhoids. Med Devices (Auckl) 2012;5:89–96. doi: 10.2147/MDER.S34390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kantsevoy S.V., Bitner M. Nonsurgical treatment of actively bleeding internal hemorrhoids with a novel endoscopic device (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2013;78:649–653. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
A video depicting a case treating hemorrhoids using this bipolar system.