Abstract
Cytokinin is a multifaceted plant hormone that plays major roles not only in diverse plant growth and development processes, but also stress responses. We summarize knowledge of the roles of its metabolism, transport, and signalling in responses to changes in levels of both macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulphur) and micronutrients (boron, iron, silicon, selenium). We comment on cytokinin’s effects on plants’ xenobiotic resistance, and its interactions with light, temperature, drought, and salinity signals. Further, we have compiled a list of abiotic stress-related genes and demonstrate that their expression patterns overlap with those of cytokinin metabolism and signalling genes.
Keywords: cytokinin, abiotic stress, temperature, drought, nutrient, stress tolerance
1. Introduction
As sessile organisms, plants have evolved elaborate mechanisms that enable them to sense and respond to changes in environmental conditions, and are thus crucial for their adaptation and survival. These mechanisms involve abiotic stimuli triggering wide arrays of local and long-distance signals initiating developmental processes and stress responses that are regulated and coordinated by common integrative pathways. One of the key transmitted signals is cytokinin: a multifaceted plant hormone that plays major roles in diverse plant growth and development processes. Cytokinin signalling cascades are evolutionarily related to the two-component systems in unicellular organisms that participate in transduction of signals that are triggered by various environmental stimuli, for example, changes in temperature, nutrient levels, chemoattractants, or osmotic conditions [1,2,3]. In contrast to ethylene, another phytohormone that is involved in a two-component signalling pathway, cytokinin was not traditionally considered part of the primary stress response machinery. However, more recently, cytokinin crosstalk with ethylene and other so-called “stress hormones” (jasmonate, salicylic acid and abscisic acid) has been recognized (e.g., [4]), and current evidence indicates that it could be a primary perceptor in temperature or nutrient sensing. In the following text, we present an overview of cytokinin crosstalk with abiotic stimuli, as outlined in Figure 1. The presented evidence includes findings from compilation of a list of abiotic stress-related genes and analyses showing that their expression patterns overlap with those of cytokinin metabolism and signalling genes. Similarities in expression profiles mentioned here are expressed as percentages that are derived by multivariate analysis from average profiles.
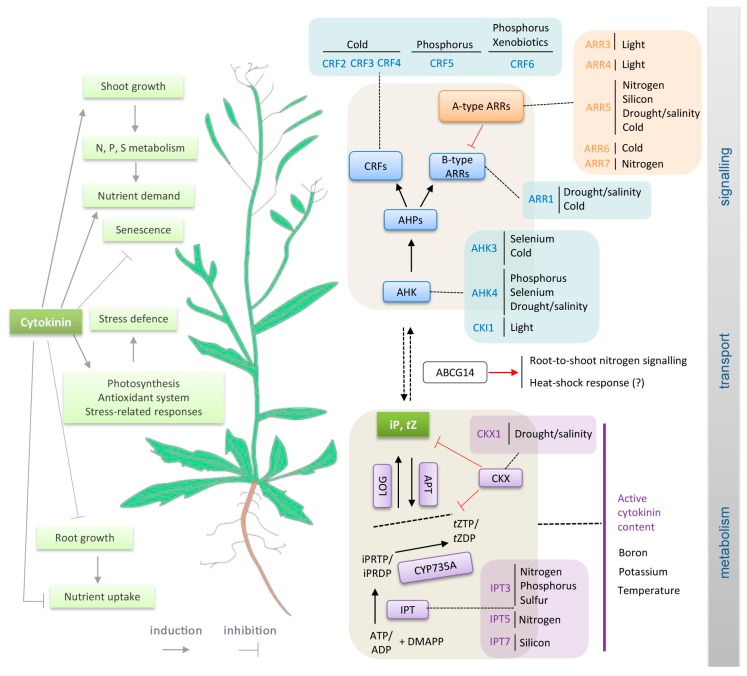
Figure 1.
Crosstalk between abiotic stress signals and cytokinin. Summary of interactive points between cytokinin metabolism and signalling pathways (as currently modelled in Arabidopsis [5]) and abiotic stress response pathways. See corresponding sections of the text for details and references.
2. Nutrient Stress
Plants require a number of elements for their growth and development. Besides carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, which are primarily obtained from carbon dioxide and water, plants actively take up at least 20 elements. These include both macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, sulphur, potassium), and micronutrients (including boron, iron, silicon and selenium). As discussed in the following text, cytokinin plays a pivotal role in plants’ uptake of these nutrients, and their responses to toxic metal(loid)s, including cadmium, aluminium, and arsenite.
2.1. Nitrogen
Nitrogen is one of the most strongly growth-limiting nutrients for plants. Thus, their internal nitrogen status and both the availability and distribution of nitrogen in their growth media are sensed by a complex network of signalling pathways that generate and regulate integrated responses to local and long-distance signals, including several phytohormones [6,7,8,9]. A well-known connection between nitrogen metabolism and cytokinin is nitrate supplementation-induced cytokinin biosynthesis in the roots. In Arabidopsis, the availability of nitrate regulates cytokinin biosynthesis rates by controlling the expression of the enzymes that catalyse the first rate-limiting step, isopentenyl transferase (IPT3, IPT5), and subsequent production of trans-Zeatin (tZ)-type cytokinins, cytochrome P450 (CYP735A2) [10,11]. In addition to these cytokinin metabolism genes, genes encoding cytokinin-responsive type-A response regulators (ARRs) and Cytokinin Response Factors (CRFs) are regulated by nitrate, but not ammonium, in Arabidopsis [12,13,14,15]. The signalling components that are involved in nitrate-upregulated cytokinin biosynthesis are the nitrate transporter-receptor NRT1 (NPF6.3) acting upstream of IPT3 [16], and the NLP-NIGT1 transcriptional cascade controlling CYP735A2 and IPT3 expression [17]. Cytokinin also participates in nitrate foraging, which involves plants’ preferential development of lateral roots in nitrate-rich areas, thereby maximizing nitrate acquisition [18,19,20]. The transcription factor TCP20, which controls the nitrate foraging response [9,21], can also bind to promoters of type-A ARR5/7, providing an additional link between nitrogen and cytokinin signalling [18,19]. Thus, the disruption of cytokinin signalling affects nitrate uptake, as demonstrated in the Arabidopsis cytokinin signalling mutant arr1,10,12. In this genotype, the nitrate-mediated induction of glutaredoxin genes (GRX) responsible for nitrate-mediated induction of primary root growth is abolished [22]. Moreover, RNA silencing of AtGRX3/4/5/7/8 has demonstrated that GRXs act downstream of cytokinin in a signal transduction pathway, which, in this case, suppresses plants’ primary root growth when nitrate supplies are sufficient [22,23]. Our meta-analysis (which included a comparison of expression patterns of all known cytokinin metabolism and signalling genes to those of 43 genes that respond to nitrogen deficiency) provided further evidence of cytokinin’s involvement in nitrate signalling. Expression patterns of seven and eight cytokinin signalling and metabolism genes, respectively, showed high similarity (>85%) to those of nitrogen deficiency genes. Overlaps were the strongest for the cytokinin biosynthetic gene APT2, which had a similar expression profile to five nitrogen-deficiency genes. For details, see Table 1 and Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Table 1.
List of all abiotic stress-related genes, with references, and their putative interactions with cytokinin according to the expression profile analysis outlined in Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. Genes in bold indicate profile similarities >85% to cytokinin-related genes, and numbers indicate the number of detected co-expressed cytokinin signalling/metabolism genes.
| Gene Name | AGI Code | UniProt Protein Name | Significant Co-Expression with Cytokinin Signalling/Metabolism Genes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NITROGEN | ||||
| NPF6.3 | AT1G12110 | Protein NRT1/PTR FAMILY 6.3 | [157] | |
| NRT2.1 | AT1G08090 | High-affinity nitrate transporter 2.1 | [158] | |
| NRT2.2 | AT1G08100 | High-affinity nitrate transporter 2.2 | [157] | |
| NRT2.4 | AT5G60770 | High affinity nitrate transporter 2.4 | [159,160] | |
| NRT2.5 | AT1G12940 | High affinity nitrate transporter 2.5 | [13,157,161] | |
| AMT1-1 | AT4G13510 | Ammonium transporter 1 member 1 | [157] | |
| AMT1-5 | AT3G24290 | Putative ammonium transporter 1 member 5 | [161,162] | |
| GDH2 | AT5G07440 | Glutamate dehydrogenase 2 | [157] | |
| GSH3 | AT3G03910 | Probable glutamate dehydrogenase 3 | [157] | |
| GLN2 | AT5G35630 | Glutamine synthetase | 2/4 | [157,158] |
| GLU2 | AT2G41220 | Ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase 2 | [163] | |
| NIA1 | AT1G77760 | Nitrate reductase [NADH] 1 | [13,158] | |
| NIA2 | AT1G37130 | Nitrate reductase [NADH] 2 | [157] | |
| NIR1 | AT2G15620 | Ferredoxin–nitrite reductase | 1/0 | [13,158] |
| UMP1 | AT5G40850 | Urophorphyrin methylase 1 | [13,157,158] | |
| GLN1-1 | AT5G37600 | Glutamine synthetase cytosolic isozyme 1-1 | [159,164] | |
| GLN1-4 | AT5G16570 | Glutamine synthetase cytosolic isozyme 1-4 | 0/1 | [157,164] |
| At3g16150 | AT3G16150 | Probable isoaspartyl peptidase/l-asparaginase 2 | [157,159] | |
| ASN2 | AT5G65010 | Asparagine synthetase [glutamine-hydrolyzing] 2 | [22,157] | |
| ASN3 | AT5G10240 | Asparagine synthetase [glutamine-hydrolyzing] 3 | 1/1 | [165] |
| At5g13110 | AT5G13110 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase 2 | 2/1 | [157,158] |
| At1g24280 | AT1G24280 | Glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase 3 | 1/2 | [22,158] |
| UPS1 | AT2G03590 | Ureide permease 1 | [159] | |
| AT4G39795 | AT4G39795 | Uncharacterized protein | [159] | |
| RFNR1 | AT4G05390 | Ferredoxin–NADP reductase | [14,158] | |
| RFNR2 | AT1G30510 | Ferredoxin–NADP reductase | 1/1 | [158] |
| GSTF14 | AT1G49860 | Glutathione S-transferase F14 | [158] | |
| BT5 | AT4G37610 | BTB/POZ and TAZ domain-containing protein 5 | [158] | |
| CCA1 | AT2G46830 | Protein CCA1 | [157] | |
| TGA1 | AT5G65210 | Transcription factor TGA1 | [166] | |
| TGA4 | AT5G10030 | Transcription factor TGA4 | [166] | |
| NLP3 | AT4G38340 | Protein NLP3 | 1/0 | [167] |
| NLP5 | AT1G76350 | Protein NLP5 | [167] | |
| NLP7 | AT4G24020 | Protein NLP7 | [167] | |
| HHO1 | AT3G25790 | Transcription factor HHO1 | 0/1 | [158,160] |
| HRS1 | AT1G13300 | Transcription factor HRS1 | [158,160] | |
| HHO3 | AT1G25550 | Transcription factor HHO3 | [22,158,160] | |
| LBD37 | AT5G67420 | LOB domain-containing protein 37 | [14,158,168] | |
| LBD38 | AT3G49940 | LOB domain-containing protein 38 | [14,158,168] | |
| LBD39 | AT4G37540 | LOB domain-containing protein 39 | 0/1 | [158,168] |
| CIPK3 | AT2G26980 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | [158] | |
| CIPK13 | AT2G34180 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 13 | [157] | |
| AO | AT5G14760 | l-aspartate oxidase | [158] | |
| PHOSPHORUS | ||||
| PHO1 | AT3G23430 | Phosphate transporter PHO1 | 0/2 | [38] |
| PHO1-H1 | AT1G68740 | Phosphate transporter PHO1 homolog 1 | 0/1 | [169] |
| PHF1 | AT3G52190 | SEC12-like protein 1 | 0/3 | [169] |
| PHT1-1 | AT5G43350 | Inorganic phosphate transporter 1-1 | [170,171] | |
| PHT1-2 | AT5G43370 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-2 | [171,172] | |
| PHT1-3 | AT5G43360 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-3 | 1/1 | [38,171] |
| PHT1-4 | AT2G38940 | Inorganic phosphate transporter 1-4 | 1/0 | [171,172] |
| PHT1-5 | AT2G32830 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-5 | 1/0 | [170,171] |
| PHT1-6 | AT5G43340 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-6 | 0/1 | [172] |
| PHT1-7 | AT3G54700 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-7 | [173] | |
| PHT1-8 | AT1G20860 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-8 | [172,173] | |
| PHT1-9 | AT1G76430 | Probable inorganic phosphate transporter 1-9 | 1/1 | [172,173] |
| PHT2-1 | AT3G26570 | Inorganic phosphate transporter 2-1 | [170,172] | |
| SPX1 | AT5G20150 | SPX domain-containing protein 1 | [169,174] | |
| SPX2 | AT2G26660 | SPX domain-containing protein 2 | 0/2 | [174] |
| SPX3 | AT2G45130 | SPX domain-containing protein 3 | [38] | |
| IPS1 | AT3G09922 | INDUCED BY PHOSPHATE STARVATION1 | [169,174] | |
| F12E4_330 | AT5G03545 | At5g03545 | [169] | |
| ACP5 | AT5G27200 | Acyl carrier protein 5 | [38] | |
| RNS1 | AT2G02990 | Ribonuclease 1 | [169,170] | |
| SQD2 | AT5G01220 | Sulfoquinovosyl transferase SQD2 | [169] | |
| PAP10 | AT2G16430 | Purple acid phosphatase 10 | [38] | |
| PAP6 | AT1G56360 | Purple acid phosphatase 6 | [38] | |
| At4g19770 | AT4G19770 | Glycosyl hydrolase family protein with chitinase insertion domain-containing protein | [38] | |
| PUB35 | AT4G25160 | U-box domain-containing protein 35 | [38] | |
| GDPD3 | AT5G43300 | Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase GDPD3 | [38] | |
| ETC3 | AT4G01060 | MYB-like transcription factor ETC3 | [38] | |
| SULPHUR | ||||
| SULTR1;1 | AT4G08620 | Sulfate transporter 1.1 | [175,176] | |
| SULTR2;1 | AT5G10180 | Sulfate transporter 2.1 | [175,176] | |
| SULTR4;1 | AT5G13550 | Sulfate transporter 4.1 | [177,178] | |
| SULTR4;2 | AT3G12520 | Probable sulfate transporter 4.2 | [178,179,180,181] | |
| APS3 | AT4G14680 | ATP-sulfurylase 3 | [176,178] | |
| APR1 | AT4G04610 | 5′-adenylylsulfate reductase 1 | [176,178] | |
| APR2 | AT1G62180 | 5′-adenylylsulfate reductase 2 | 0/1 | [178] |
| APR3 | AT4G21990 | 5′-adenylylsulfate reductase 3 | 0/1 | [178,180] |
| SAT4 | AT4G35640 | Serine acetyltransferase 4 | [181,182] | |
| BGLU28 | AT2G44460 | Beta-glucosidase 28 | [179,180] | |
| BGLU30 | AT3G60140 | Beta-glucosidase 30 | [180,182] | |
| SDI1 | AT5G48850 | Protein SULFUR DEFICIENCY-INDUCED 1 | [178,179] | |
| SDI2 | AT1G04770 | Protein SULFUR DEFICIENCY-INDUCED 2 | [176,178] | |
| SHM7 | AT1G36370 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 7 | [178,180] | |
| GGCT2;1 | AT5G26220 | Gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 2-1 | [178,180,182] | |
| LSU1 | AT3G49580 | Protein RESPONSE TO LOW SULFUR 1 | [178,180] | |
| LSU2 | AT5G24660 | Protein RESPONSE TO LOW SULFUR 2 | [178,180,182] | |
| At3g05400 | AT3G05400 | Sugar transporter ERD6-like 12 | [180,182] | |
| At4g31330 | AT4G31330 | Protein of unknown function | 0/2 | [180,182] |
| SIP1-2 | AT5G18290 | Probable aquaporin SIP1-2 | 2/1 | [180] |
| At5g40670 | AT5G40670 | Cystinosin homolog | [180] | |
| At1g75290 | AT1G75290 | NAD | [180] | |
| NSP5 | AT5G48180 | Nitrile-specifier protein 5 | [180] | |
| AVT6C | AT3G56200 | Amino acid transporter AVT6C | [178,180] | |
| NFYA2 | AT3G05690 | Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-2 | [180] | |
| BZIP1 | AT5G49450 | Basic leucine zipper 1 | [180] | |
| RVE2 | AT5G37260 | Homeodomain-like superfamily protein | [180] | |
| POTASSIUM | ||||
| POT5 | AT4G13420 | Potassium transporter 5 | [182,183] | |
| POT4 | AT3G02050 | Potassium transporter 4 | 2/2 | [183] |
| AKT1 | AT2G26650 | Potassium channel AKT1 | [184,185] | |
| RBOHC | AT5G51060 | Respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein C | [183] | |
| CIPK23 | AT1G30270 | CBL-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 23 | [183,186] | |
| TGG1 | AT5G26000 | Myrosinase 1 | [182] | |
| TGG2 | AT5G25980 | Myrosinase 2 | [182] | |
| POT6 | AT1G70300 | Potassium transporter 6 | [187] | |
| POT8 | AT5G14880 | Potassium transporter 8 | 1/2 | [184,187] |
| KEA5 | AT5G51710 | K+ efflux antiporter 5 | 0/2 | [183] |
| KAT3 | AT4G32650 | Potassium channel KAT3 | [184] | |
| SKOR | AT3G02850 | Potassium channel SKOR | [184,188,189] | |
| AKT2 | AT4G22200 | Potassium channel AKT2/3 | 0/1 | [189] |
| POT3 | AT4G23640 | Potassium transporter 3 | 2/0 | [190] |
| POT7 | AT5G09400 | Potassium transporter 7 | 2/3 | [191] |
| CBL1 | AT4G17615 | Calcineurin B-like protein 1 | [189] | |
| CBL9 | AT5G47100 | Calcineurin B-like protein 9 | 0/1 | [189] |
| CBL10 | AT4G33000 | Calcineurin B-like protein 10 | [183] | |
| TCH3 | AT2G41100 | Calcium-binding EF hand family protein | [192] | |
| ERF73 | AT1G72360 | Integrase-type DNA-binding superfamily protein | [183] | |
| IRON | ||||
| AXX17_At1g47400 | AT1G47400 | Uncharacterized protein | [182,193] | |
| At1g47395 | AT1G47395 | At1g47390 | [182] | |
| AT2G14247 | AT2G14247 | Expressed protein | [182] | |
| At1g13609 | AT1G13609 | Defensin-like | [182] | |
| IRT1 | AT4G19690 | Fe2+ transport protein 1 | [182,193,194] | |
| F17A17.6 | AT3G07720 | AT3g07720/F17A17_6 | [182,193,194] | |
| MTPA2 | AT3G58810 | Metal tolerance protein A2 | [193,194] | |
| MJM20.4 | AT3G12900 | 2-oxoglutarate | [193,194] | |
| F21F14.100 | AT3G61930 | Uncharacterized protein At3g61930/F21F14_100 | [193,194] | |
| COPT2 | AT3G46900 | Copper transporter 2 | [193,194] | |
| CYP82C4 | AT4G31940 | Cytochrome P450 82C4 | [193] | |
| GLP4 | AT1G09560 | Germin-like protein subfamily 2 member 1 | [193,194] | |
| F17A9.4 | AT3G06890 | At3g06890 | [193,194] | |
| UGT72E1 | AT3G50740 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 72E1 | [193,194] | |
| ORG3 | AT3G56980 | Transcription factor ORG3 | [182,193,194] | |
| MYB72 | AT1G56160 | Transcription factor MYB72 | [193,194] | |
| MTPC3 | AT3G58060 | Putative metal tolerance protein C3 | [193,194] | |
| FIT | AT2G28160 | Transcription factor FER-LIKE IRON DEFICIENCY-INDUCED TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR | [194,195] | |
| BHLH47 | AT3G47640 | Transcription factor bHLH47 | 2/1 | [193,195] |
| BHLH101 | AT5G04150 | Transcription factor bHLH101 | [182,193] | |
| NAS4 | AT1G56430 | Probable nicotianamine synthase 4 | [182,193] | |
| OPT3 | AT4G16370 | Oligopeptide transporter 3 | [195,196] | |
| CGLD27 | AT5G67370 | Protein CONSERVED IN THE GREEN LINEAGE AND DIATOMS 27 | [182] | |
| FRO2 | AT1G01580 | Ferric reduction oxidase 2 | [182] | |
| FRO3 | AT1G23020 | Ferric reduction oxidase 3 | [193,195] | |
| AHA2 | AT4G30190 | Plasma membrane ATPase | [195] | |
| NRAMP4 | AT5G67330 | Metal transporter Nramp4 | 1/1 | [193,195] |
| FER1 | AT5G01600 | Ferritin-1 | [193,194] | |
| ABCI8 | AT4G04770 | UPF0051 protein ABCI8 | [193,194] | |
| At2g36885 | AT2G36885 | Translation initiation factor | 0/1 | [193,194,195] |
| APXS | AT4G08390 | Stromal ascorbate peroxidase | 1/1 | [193,194] |
| LAC7 | AT3G09220 | Laccase-7 | [193,194,195] | |
| IRT3 | AT1G60960 | Fe2+ transport protein 3, chloroplastic | 1/1 | [193] |
| At4g08300 | AT4G08300 | WAT1-related protein At4g08300 | [182] | |
| FRO4 | AT5G23980 | Ferric reduction oxidase 4 | [185] | |
| BORON | ||||
| BOR1 | AT2G47160 | Boron transporter 1 | [197] | |
| BOR4 | AT1G15460 | Boron transporter 4 | 1/1 | [198] |
| TEMPERATURE/DROUGHT | ||||
| RD29A | AT5G52310 | Low-temperature-induced 78 kDa protein | [141,199,200] | |
| KIN1 | AT5G15960 | Stress-induced protein KIN1 | [201,202] | |
| KIN2 | AT5G15970 | Stress-induced protein KIN2 | [203,204] | |
| COR15A | AT2G42540 | Protein COLD-REGULATED 15A | [200,201,202] | |
| COR47 | AT1G20440 | Dehydrin COR47 | [201,202] | |
| ERD10 | AT1G20450 | Dehydrin ERD10 | [201,202] | |
| ERD7 | AT2G17840 | Protein EARLY-RESPONSIVE TO DEHYDRATION 7 | [201,202,205] | |
| At1g30790 | AT1G30790 | F-box protein At1g30790 | 0/2 | [205] |
| MKK2 | AT4G29810 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 | [206] | |
| RAB18 | AT5G66400 | Dehydrin Rab18 | [207,208,209] | |
| LTI65/RD29B | AT5G52300 | Low-temperature-induced 65 kDa protein | [129,199,200] | |
| RD22 | AT5G25610 | BURP domain protein RD22 | [207,209] | |
| HOS1 | AT2G39810 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HOS1 | 4/3 | [203,210] |
| DREB1B | AT4G25490 | Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein 1B | [201,202] | |
| DREB1C | AT4G25470 | Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein 1C | [201,202,209] | |
| DREB1A | AT4G25480 | Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein 1A | [201,202] | |
| RABC1 | AT1G43890 | Ras-related protein RABC1 | 0/2 | [202] |
| CLPD | AT5G51070 | Chaperone protein ClpD | [209,211] | |
| SWEET15 | AT5G13170 | Bidirectional sugar transporter SWEET15 | [40,209] | |
| P5CSA | AT2G39800 | Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase A | [40,209] | |
| ABI1 | AT4G26080 | Protein phosphatase 2C 56 | [209] | |
| DREB2A | AT5G05410 | Dehydration-responsive element-binding protein 2A | [209,212] | |
| NCED3 | AT3G14440 | 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase NCED3 | [200,209] | |
| ABF3 | AT4G34000 | ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 5-like protein 6 | [209,213] | |
| PP2CA | AT3G11410 | Protein phosphatase 2C 37 | 2/2 | [200,209,214] |
| PXG3/RD20 | AT2G33380 | Probable peroxygenase 3 | [200,209,211] | |
| LEA7 | AT1G52690 | Late embryogenesis abundant protein 7 | [209,215] | |
| LEA29 | AT3G15670 | Late embryogenesis abundant protein 29 | [40] | |
| At3g17520 | AT3G17520 | Late embryogenesis abundant protein | [208,209] | |
| NAC072 | AT4G27410 | NAC domain-containing protein 72 | [208,209] | |
| MBF1C | AT3G24500 | Multiprotein-bridging factor 1c | [216,217] | |
| HSFA2 | AT2G26150 | Heat stress transcription factor A-2 | [217,218,219] | |
| HSA32 | AT4G21320 | Protein HEAT-STRESS-ASSOCIATED 32 | [216,217,218] | |
| CLPB1 | AT1G74310 | Chaperone protein ClpB1 | [216,217,218] | |
| CLPB3 | AT5G15450 | Chaperone protein ClpB3 | [216,218] | |
| HSFB2A | AT5G62020 | Heat stress transcription factor B-2a | [216,219] | |
| HSFA7A | AT3G51910 | Heat stress transcription factor A-7a | [217,218,219] | |
| HSP90-1 | AT5G52640 | Heat shock protein 90-1 | [216,217,218] | |
| HSP90-2 | AT5G56030 | Heat shock protein 90-2 | [216,217] | |
| At2g20560 | AT2G20560 | At2g20560/T13C7.15 | [216,217,218] | |
| HSFB1 | AT4G36990 | Heat stress transcription factor B-1 | [216,217,218] | |
| HSP23.6 | AT4G25200 | 23.6 kDa heat shock protein | [217,218] | |
| HSP18.1 | AT5G59720 | 18.1 kDa class I heat shock protein | [217,218] | |
| HSP17.4B | AT1G54050 | 17.4 kDa class III heat shock protein | [216,217] | |
| MED37C | AT3G12580 | Probable mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 37c | [217,220] | |
| HSP70-5 | AT1G16030 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 5 | [217,218,220] | |
| HSP70-10 | AT5G09590 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 10 | [216,217] | |
| GOLS1 | AT2G47180 | Galactinol synthase 1 | [216,217,218] | |
| APX2 | AT3G09640 | L-ascorbate peroxidase 2 | [217,218] | |
| ERDJ3A | AT3G08970 | DnaJ protein ERDJ3A | [216,217] | |
| HSP90-6 | AT3G07770 | Heat shock protein 90-6 | 2/0 | [216,217] |
| HSP90-4 | AT5G56000 | Heat shock protein 90-4 | [216,217] | |
| HSP70-8 | AT2G32120 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 8 | [216,217] | |
| MED37D | AT5G02490 | Probable mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 37c | [216,217] | |
| HSP70-3 | AT3G09440 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 3 | [216,217] | |
| HSP70-15 | AT1G79920 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 15 | 0/2 | [216,217] |
| HSP90-5 | AT2G04030 | Heat shock protein 90-5 | 0/1 | [216,217] |
| XENOBIOTIC STRESS | ||||
| GSH1 | AT4G23100 | Glutamate–cysteine ligase | [221,222] | |
| GSH2 | AT5G27380 | Glutathione synthetase | [221,222] | |
| PCS1 | AT5G44070 | Glutathione gamma-glutamylcysteinyltransferase 1 | [221,222] | |
| MAN3 | AT3G10890 | Mannan endo-1 | [223] | |
| ZAT6 | AT5G04340 | Zinc finger protein ZAT6 | [223] | |
| PCR1 | AT1G14880 | Protein PLANT CADMIUM RESISTANCE 1 | [224] | |
| HMA3 | AT4G30120 | Putative inactive cadmium/zinc-transporting ATPase HMA3 | [225,226] | |
| HMA4 | AT2G19110 | Putative cadmium/zinc-transporting ATPase HMA4 | 2/1 | [227] |
| HSFA4A | AT4G18880 | Heat stress transcription factor A-4a | [228] | |
| FC1 | AT5G26030 | Ferrochelatase-1 | [222] | |
| HMT-1 | AT3G25900 | Homocysteine S-methyltransferase 1 | 2/2 | [229] |
| MT1A | AT1G07600 | Metallothionein-like protein 1A | 1/4 | [230] |
| NRAMP5 | AT4G18790 | Metal transporter Nramp5 | 2/2 | [226,231] |
| ABCG36 | AT1G59870 | ABC transporter G family member 36 | [232] | |
| ABCB25 | AT5G58270 | ABC transporter B family member 25 | 4/3 | [233] |
| ABCC1 | AT1G30400 | ABC transporter C family member 1 | 4/2 | [226,234,235] |
| ABCC2 | AT2G34660 | ABC transporter C family member 2 | 10/7 | [226,234,235] |
| HAC1 | AT2G21045 | Protein HIGH ARSENIC CONTENT 1 | 1/1 | [236] |
| ALMT1 | AT1G08430 | Aluminum-activated malate transporter 1 | [237,238] | |
| ALS3 | AT2G37330 | Protein ALUMINUM SENSITIVE 3 | 2/4 | [237,239] |
| STOP1 | AT1G34370 | Protein SENSITIVE TO PROTON RHIZOTOXICITY 1 | 0/1 | [237,239] |
| CYP81D11 | AT3G28740 | Cytochrome P450 81D11 | [240,241,242,243] | |
| CYP710A1 | AT2G34500 | Cytochrome P450 710A1 | [82,244,245] | |
| CYP81D8 | AT4G37370 | Cytochrome P450 | [81,243,244,245] | |
| UGT73B2 | AT4G34135 | UDP-glucosyl transferase 73B2 | [241,242,244] | |
| UGT73B3 | AT4G34131 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 73B3 | [242,244] | |
| UGT73B4 | AT2G15490 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 73B4 | [241,242,244] | |
| UGT73C1 | AT2G36750 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 73C1 | [241] | |
| GSTU3 | AT2G29470 | Glutathione S-transferase U3 | [241,244] | |
| GSTU10 | AT1G74590 | Glutathione S-transferase U10 | [82,243,246] | |
| GSTU19 | AT1G78380 | Glutathione S-transferase U19 | 2/3 | [243,247] |
| GSTU24 | AT1G17170 | Glutathione S-transferase U24 | [240,241,242,243] | |
| GSTU25 | AT1G17180 | Glutathione S-transferase U25 | [241,242,243,244] | |
| GSTU26 | AT1G17190 | Glutathione S-transferase U26 | [248] | |
| GGT4 | AT4G29210 | Glutathione hydrolase 3 | 1/0 | [249] |
| ABCC3 | AT3G13080 | ABC transporter C family member 3 | [244] | |
| ABCI21 | AT5G44110 | ABC transporter I family member 21 | [242,243] | |
| DTX1 | AT2G04040 | Protein DETOXIFICATION 1 | [243,245] | |
| DTX3 | AT2G04050 | Protein DETOXIFICATION 3 | [243,245] | |
| DTX4 | AT2G04070 | Protein DETOXIFICATION 4 | [241,245] | |
| CYP710A2 | AT2G34490 | Cytochrome P450 710A2 | [82] | |
| DHAR2 | AT1G75270 | Glutathione S-transferase DHAR2 | 1/0 | [243,244] |
| DHAR3 | AT5G16710 | Glutathione S-transferase DHAR3 | 2/0 | [243] |
| GSTU4 | AT2G29460 | Glutathione S-transferase U4 | [241,244] | |
| UGT74F2 | AT2G43820 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 74F2 | [244,246] | |
| UGT73C6 | AT2G36790 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 73C6 | 0/1 | [241,245] |
| UGT74E2 | AT1G05680 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 74E2 | [241,245] | |
| UGT73B5 | AT2G15480 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 73B5 | [241,244] | |
| UGT75B1 | AT1G05560 | UDP-glycosyltransferase 75B1 | [241,244] | |
| CYP81F2 | AT5G57220 | Cytochrome P450 81F2 | [241] | |
| CYP87A2 | AT1G12740 | Photosynthetic NDH subunit of lumenal location 5 | 1/1 | [240] |
| GSTF7 | AT1G02920 | Glutathione S-transferase F7 | [243] | |
| GSTF6 | AT1G02930 | Glutathione S-transferase F6 | [243,246] | |
| ABCB15 | AT3G28345 | ABC transporter B family member 15 | [242] | |
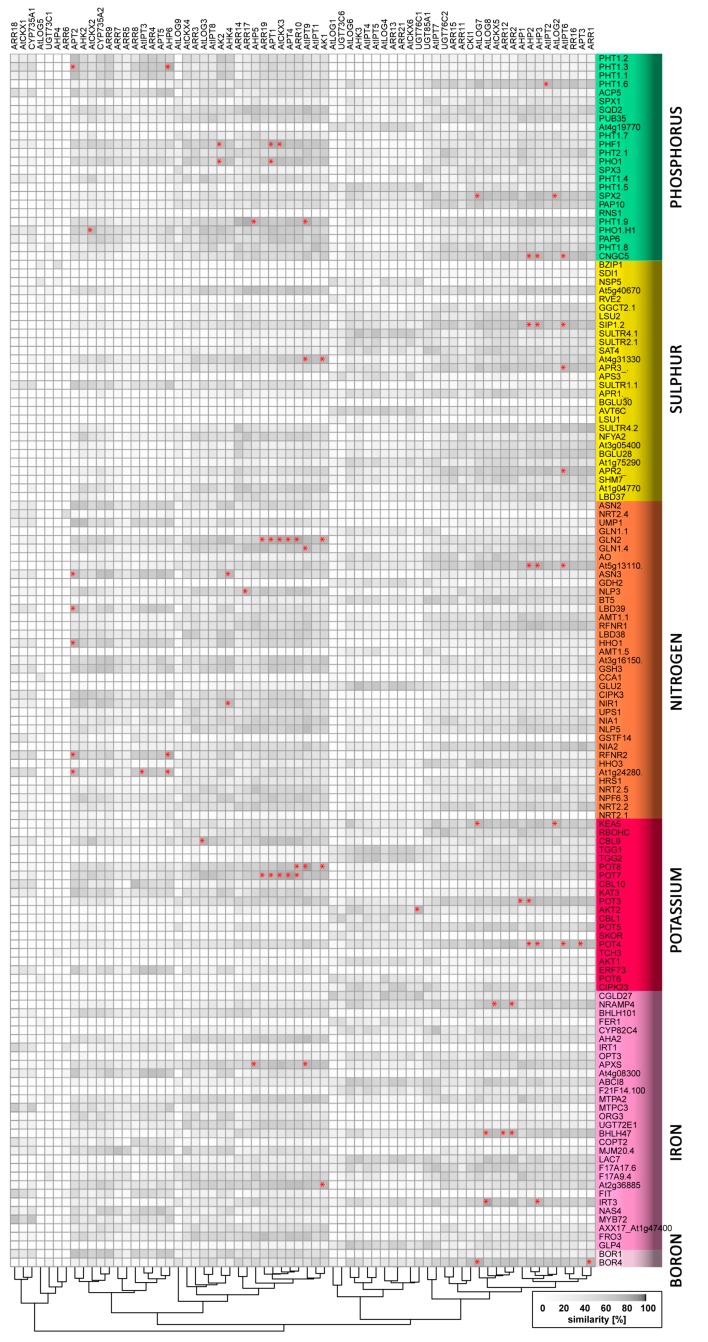
Figure 2.
Similarity of expression patterns of genes related to nutrient stress and genes involved in cytokinin metabolism or signalling. Asterisks indicate profile similarities >85%. The heatmap was generated using R software and available data from Araport [33].
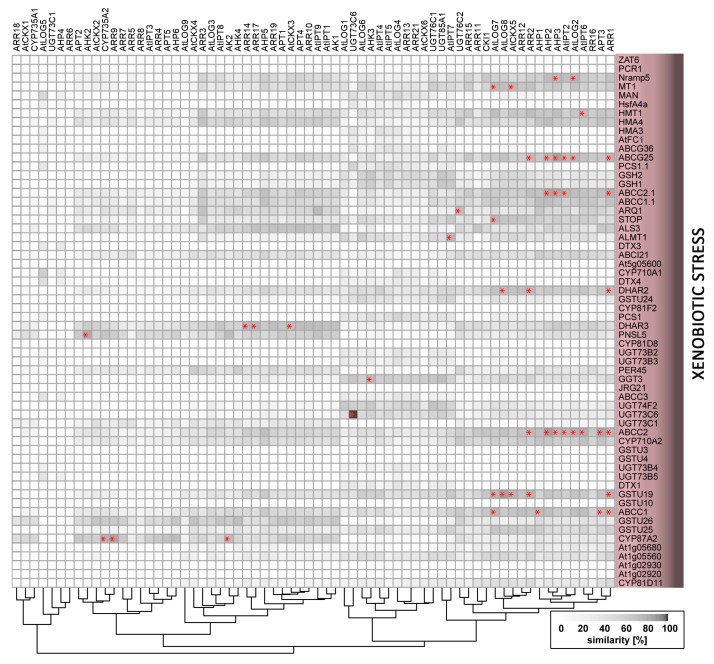
Figure 3.
Similarity of expression patterns of genes related to xenobiotic stress and genes involved in cytokinin metabolism or signalling. Asterisks indicate profile similarities >85%. The heatmap was generated using R software and available data from Araport [33].
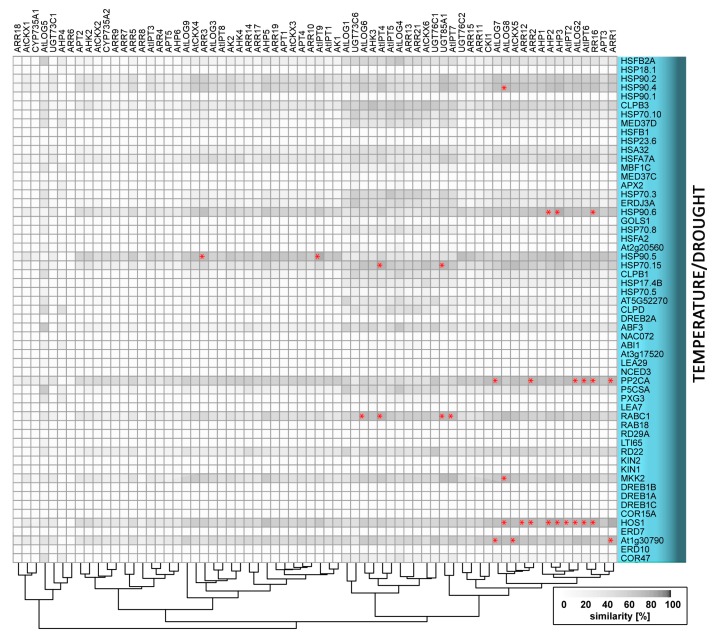
Figure 4.
Similarity of expression patterns of genes related to temperature/drought stress and genes involved in cytokinin metabolism or signalling. Asterisks indicate profile similarities >85%. The heatmap was generated using R software and available data from Araport [33].
In the shoot, root-derived cytokinins have been shown to mediate nitrate responses and modulate key traits, such as leaf size [24,25] and meristem activity-related traits [26]. Following its nitrate-induced synthesis in the root, cytokinin acts as a long-distance (systemic) signal, conveying information about the root’s nitrogen status that influences shoot metabolism and growth [12,27,28,29,30]. Cytokinin translocation via xylem in this systemic nitrogen response system is mediated by the cytokinin transporter ABCG14, and recent transcriptomic analysis indicates that its target could be the glutamate/glutamine metabolism machinery in the shoot [20,31]. Recent findings also show that long-distance transport of the cytokinin precursor tZR (which has low activity) can account for nitrate availability-mediated adjustments of shoot apical meristem size and organogenesis rates through modulating the expression of WUSCHEL [32]. Root-to-shoot cytokinin signalling operates in both directions, and, for example, lateral root growth is regulated by tZ content in the shoot [18,19,20].
2.2. Phosphorus
Like nitrogen sensing, a complex signalling system is required to maintain inorganic phosphate (Pi) homeostasis, and plants’ responses to Pi-limiting conditions involve multiple phytohormones [34,35]. As in nitrate sensing, one of the strongly affected cytokinin genes is the biosynthetic gene IPT3. Pi shortage causes the downregulation of IPT3 [36] and cytokinin signalling components, including the cytokinin receptor AHK4 [37]. Conversely, the resupply of Pi after a shortage causes upregulation of IPT3, CRF5, and CRF6 [38]. Moreover, reductions in root cytokinin levels upregulate the expression of Pi transporters [39,40,41,42] and the exogenous supply of cytokinin can suppress Pi uptake and Pi starvation responses in Arabidopsis and rice [37,43,44,45,46,47,48], presumably by mobilizing Pi from internal sources (preferentially stores in shoot tissues) [46]. This may temporarily reduce Pi starvation signalling and contribute to the relief of Pi deficiency symptoms, including the reported moderation of shoot growth inhibition of Pi-starved plants in the presence of cytokinin [49]. It has been proposed that the level of cell-cycle activity governs the magnitude of Pi demand in Pi-starved plants. This would fit well with cytokinin’s opposite effects on cell cycling in shoot and root meristems, where it, respectively, stimulates and represses cell division [50]. Further, auxin-cytokinin crosstalk via the auxin responsive factor OsARF16 regulates Pi signalling, and transport of Pi from roots to shoots [47].
2.3. Potassium
Potassium is the most abundant inorganic cation in plants, and it is one of the primary macronutrients that are generally added (together with nitrogen and phosphorus) to soil in fertilizers. Analysis of Arabidopsis plants has shown that potassium deprivation reduces cytokinin contents, and cytokinin signalling regulates root growth inhibition and potassium uptake [51]. The cited authors also found that cytokinin-deficient plants have enhanced the tolerance of potassium deficiency, which they attributed to the stimulation of ROS accumulation, root hair growth, and expression of HAK5, which encodes a potassium uptake transporter. This transporter connects multiple phytohormonal networks, as it is also regulated by ethylene [52] and participates in the modulation of the auxin transporter PIN1’s localization [53]. We found no significant similarity between expression patterns of HAK5 and any cytokinin metabolism/signalling genes. However, expression patterns of genes encoding seven potassium-deficiency-related genes (four potassium transporters, two antiporters, and a potassium channel) showed ≥85% similarity to those of candidate cytokinin genes (Table 1, Figure 2).
2.4. Sulphur
The availability of sulphur in soil is directly associated with crop yields and quality, and sulphur deficiency induces a number of adaptive responses [54]. A link between sulphur deficiency and responses in cytokinin status is indicated by IPT3 downregulation in roots of Arabidopsis plants grown on sulphur-deficient media [36], and observed changes in cytokinin contents triggered by sulphur deficiency in poplar [55]. In addition, exogenous application of cytokinin upregulates expression of sulphur-responsive genes in leaves [36]. By contrast, cytokinin downregulates the root expression of sulphate transporters (SULTR1;1 and SULTR1;2) that are involved in sulphate acquisition from the soil [39,56], and the arr1,10,12 triple mutant displays sulphur-deficiency-like gene expression patterns [57]. Thus, complex interplay between cytokinin and sulphur signalling, which is possibly mediated by independent regulatory circuits, is likely involved. The sulphur-deficiency marker gene GGCT2;1 encodes a key enzyme of glutathione degradation and it is a highly cytokinin-responsive gene [58], suggesting that cytokinin may participate in glutathione homeostasis and cytokinin-mediated glutathione decomposition may play a physiologically important role in nutrient mobilization.
2.5. Boron
Boron is an essential micronutrient for the growth of higher plants but there is a very narrow range between deficient and toxic concentrations [59]. Symptoms of severe boron deficiency include root growth inhibition, perturbances in root morphology, and reductions in vegetative and reproductive growth. Early detectable changes in boron-deficient plants include disturbances of hormonal metabolism and several lines of evidence suggest that ethylene and auxin are involved in the regulation of boron stress responses [60]. Boron deprivation induces the downregulation of cytokinin signalling genes [61,62], and our meta-analysis showed that BOR4, encoding a boron transporter, has a similar expression pattern to ARR1 and the cytokinin metabolism gene LOG7. Moreover, in oilseed rape, the shoot boron concentration reportedly correlates closely with cytokinin content, and boron enhances both cytokinin synthesis and the conversion of weakly active cytokinins to highly active forms [63]. Conversely, recent analysis indicates that boron deficiency inhibits root meristem growth via a molecular mechanism involving the cytokinin-mediated repression of cyclin CYCD3 [64].
2.6. Iron
Cytokinin suppresses expression of several genes that respond to iron deficiency in Arabidopsis [65]. This cytokinin-induced repression is mediated via AHK3 and AHK4 receptors, and it targets genes encoding components of the iron-uptake machinery (FRO2, IRT1) and the iron-deficiency induced transcription factor FIT1. The repression does not reflect the plant’s iron nutritional status, and analysis of a fit1 loss-of-function mutant indicates that it acts via a distinct, FIT1-independent signalling pathway [65]. This could be mediated by the ARF16 transcription factor, which is required for iron deficiency responses in rice [66] and participates in the auxin-cytokinin control of phosphate homeostasis [47]. Only five of 38 selected genes that are related to iron-deficiency had similar expression profiles to cytokinin regulatory genes. Moreover, the expression pattern of NRAMP4 (encoding a transporter of iron and several other metals) is similar to that of CKX (encoding a cytokinin degradation enzyme) and ARR1, but NRAMP4 expression is not reportedly upregulated by exogenous application of cytokinin [65]. Thus, this coregulation is unlikely to reflect iron status signalling.
2.7. Silicon
Silica minerals are major soil components, and high silicon uptake, boosted by root silicon transporters, promotes plants’ tolerance to many biotic and abiotic stresses. Mineralized (insoluble) silica provides structural support for many plants, but it can also enhance various defence mechanisms of plants and influence their stress responses by modulating their hormonal balance [67,68]. The beneficial effects of silicon are partially mediated by cytokinin [69]. Inter alia, silicic acid induces the cytokinin synthesis gene IPT7 and silicon accumulation delays dark-induced leaf senescence through the activation of cytokinin pathways in sorghum and Arabidopsis [70].
2.8. Selenium
At low concentrations, selenium promotes plant growth and stress resistance [71,72], but elevated levels can be toxic. Selenate and selenite, the two major forms of selenium that are found in the environment, are readily absorbed by plants via sulphate and phosphate transporters, respectively [73]. In this respect, cytokinin-regulated sulphate and Pi pathways might form a point of cross-talk between selenium and cytokinin signalling. For instance, the cytokinin-responsive sulphate transporter SULTR1;2 is a determinant of selenium tolerance in Arabidopsis [74]. Cytokinin signalling is promoted in the root tip of selenite-exposed Arabidopsis plants, and high cytokinin levels reportedly improve the performance of selenite-exposed roots, whereas reductions in cytokinin status or sensitivity enhance selenite sensitivity [75,76,77]. Recently, a selenium-tolerant Arabidopsis mutant with a loss-of-function mutation in a terpenoid synthase gene (TPS22) has been described. Observed effects of the mutation include reductions in cytokinin levels and the expression of cytokinin receptors AHK3 and AHK4, while the application of exogenous cytokinin upregulated selenocysteine methyltransferase (as well as high-affinity phosphate transporters) and decreased selenium tolerance of the mutant [42].
2.9. Xenobiotics
Strict control of processes that are involved in plants’ absorption, translocation, and storage of essential metals is crucial for the maintenance of their concentrations within physiological ranges and the avoidance of toxicity. Nevertheless, despite the transport systems’ selectivity, they may also take up toxic, non-essential metals and metalloids, such as arsenic, cadmium, chromium, lead, and mercury. Responses to these toxic xenobiotics, including cadmium [78] and aluminium [79], involve increases in cytokinin biosynthesis and signalling that inhibit root growth. Accordingly, application of substances that reduce active cytokinin contents or signalling can mitigate the adverse effects of cadmium [80]. Similarly, the cytokinin signalling component CRF6 is induced by organic xenobiotics, including the herbicide atrazine [81,82] and atrazine inhibition is weaker in the crf6 insertional mutant line than in wild-type plants [83]. Moreover, cytokinin-deficient plants grown in cadmium-contaminated soil reportedly accumulate more cadmium [39] and display enhanced arsenate tolerance [41], which is likely due to higher levels of thiol compounds [41]. Cytokinin also induces the upregulation of glutathione-S-transferase GSTU26 [84,85] and may thus play a role in glutathione conjugation.
3. Cytokinin Roles in Drought and Salinity Tolerance
Drought and salinity stress are the most frequent abiotic stresses and both impair crop production on a global scale [86]. Analysis of natural variants of Arabidopsis has shown that even mild drought can adversely affect plants if they are not evolutionarily adapted to it [87]. Plants react to water-limiting conditions by reducing their cytokinin levels, mainly through the modulation of cytokinin metabolism—as shown (inter alia) in Arabidopsis, creeping bentgrass, soybean, tobacco, and sunflower [88,89,90,91,92,93]—and/or the regulation of cytokinin receptors’ expression [94,95]. However, other mechanisms, including activation of the negative regulators of cytokinin signalling AHP6 and ARR5 also probably participate in this process [94,96,97]. Appropriate modulation of cytokinin metabolism and signalling has been known to improve drought and salt tolerance for many years [92,95,98,99], and at least five mechanisms may contribute to cytokinin-mediated enhancement of tolerance of water deficiency. These are: protection of the photosynthetic machinery, enhancement of antioxidant systems, improvement in water balance regulation, modulation of plant growth and differentiation, and modulation of activities of stress-related phytohormones.
3.1. Cytokinin Modulates Photosynthesis under Water-Limiting Conditions and Salt Stress
Changes in cytokinin status (mainly increases in cytokinin levels) reportedly enhance photosynthesis and related processes under water-deficiency or salt stress in many plant species [99,100,101,102,103,104], by increasing the expression of genes that are involved in photosynthesis, chlorophyll levels, photochemical efficiency, photochemical quenching, electron transport rates, and/or CO2 assimilation. Accordingly, in transgenic barley plants ectopically expressing the cytokinin-degradation enzyme AtCKX1, reductions in CO2 assimilation rates, accompanied by lower stomatal conductance, have been recorded [105]. Conversely, increases in CO2 assimilation have been observed in barley lines overexpressing CKX under a different promoter resulting in localization to different compartments. However, the cited authors only presented results from plants with elevated concentrations of tZ-type cytokinins [106]. It has been previously demonstrated that CKX overexpression stimulates cytokinin biosynthesis [107], so the observed positive effect on CO2 assimilation was likely due to increases in cytokinin content.
3.2. Cytokinin Enhances Capacities of Antioxidant Systems
Ectopic expression of ipt reportedly increases the capacities of plants’ antioxidant systems, including levels of antioxidants during severe drought stress [100]. This could protect their cells from excessive stress-induced ROS accumulation, thereby preserving chloroplast integrity [100,108,109] and reducing electrolyte leakage and/or rises in malondialdehyde levels [57,89,110]. On the other hand, ectopic expression of CKX in barley has been found to activate genes putatively involved in flavonoid biosynthesis [105] and flavonoids also participate in drought tolerance [111]. These effects of cytokinin in drought stress tolerance could involve indirect priming of antioxidant systems in response to manipulation of cytokinin homeostasis. In accordance with this hypothesis, significant enhancement of cytokinin biosynthesis can induce hypersensitivity-like responses and ROS-mediated cell death [112].
3.3. Cytokinin Influences Water Balance Regulation
Clearly, water management is crucial for drought tolerance, and plants with low levels of cytokinin or weak cytokinin signalling generally have higher water contents during drought stress than counterparts with higher cytokinin contents or stronger signalling [92,95,105]. This could be due to better root systems, since cytokinin is a known negative regulator of root growth and lateral root formation [106,110]. The improved water uptake in these plants is clearly complemented with reductions in transpiration rates and stomatal apertures, which could protect them from severe water losses during stress periods [57,105,110]. Ectopic expression of ipt also reduces water losses in plants that are exposed to drought, even when they have higher transpiration rates and stomatal conductance, but the mechanisms that are involved are elusive [90,102].
3.4. Cytokinin Effects on Growth
As cytokinins play key roles in root and shoot development they also participate in expression of growth and architectural traits that are required for tolerance of water-limiting conditions [113]. Cytokinins are well known to reduce root to shoot hypocotyl ratios [39,114,115], and one of the approaches for enhancing plants’ drought tolerance is to decrease cytokinin levels in order to modify root morphology and enhance root biomass [116]. Root-specific overexpression of CKX can also enhance root growth, nutrient uptake, and drought tolerance [106], as well as improving recovery after drought stress [116] without adverse effects on shoot growth. Similarly, one of the dehydration-responsive element binding factors in Malus (MdDREB6.2) activates the expression of MdCKX, mainly in roots, and overexpression of this factor can enhance drought tolerance [110]. Several studies indicate that not only quantitative features but also qualitative traits of root tissues could be important factors in cytokinin-regulated responses to water-limiting conditions, including the differentiation of vascular tissue [117] and lignification [116].
3.5. Cytokinin Crosstalk with Stress-Related Phytohormones
3.5.1. Abscisic Acid
Rapid accumulation of the phytohormone abscisic acid plays a crucial role in regulating plants’ defensive responses to drought stress, including stomatal closure, growth modulation, and synthesis of protective metabolites. It has been known for more than a decade that cytokinin and abscisic acid have antagonistic functions in diverse physiological processes, including stress tolerance, germination, and hypocotyl greening [95,118,119]. Cytokinin signalling has been shown to be dramatically inhibited by abscisic acid application [120,121] and cytokinin facilitates degradation of the abscisic acid signalling component transcription factor ABI5 [118]. It has been reported that under drought stress plants with decreased levels of cytokinin or attenuated cytokinin signalling have decreased levels of abscisic acid, but higher sensitivity to this stress-related hormone and greater drought tolerance [57,92,122]. However, elucidation of the molecular mechanism involved in this interaction has begun only recently. Experiments with a series of cytokinin and abscisic acid signalling mutants have demonstrated that cytokinin and abscisic acid interact directly through their signalling components, as plants constitutively expressing HA-Flag-ARR5 and arr5 loss-of-function mutants respectively showed increased and attenuated sensitivity to abscisic acid treatment [97]. ARR5 stability is promoted by phosphorylation catalysed by SnRK2 protein kinases that are key components of the abscisic acid signalling pathway. In contrast, type-B ARR1, 11, and 12 interact with these SnRK2s and repress their kinase activity, and the abscisic acid hypersensitivity of the triple mutant arr1,11,12 can be completely rescued by mutation of SnRK2s [97]. Interestingly, the same authors found that expression of ARR1ΔDDK (a constitutively activated form of ARR1), but not constitutive expression of ARR1-Myc, was associated with slight insensitivity to abscisic acid, suggesting that the modulation of ARR1’s phosphorylation status by cytokinin signalling may also be important. Since cytokinin is essential for normal growth of plants [10] the SnRK2-ARR regulatory module is clearly a recently discovered signalling hub that balances growth and defence in response to environmental cues.
3.5.2. Jasmonates
Jasmonic acid is known to play a role in drought tolerance [123,124]. Inter alia, drought-induced xylem differentiation is negatively and positively regulated by cytokinin and jasmonic acid, respectively, and jasmonic acid attenuates cytokinin signalling by repressing the cytokinin receptor AHK4 and stimulating expression of AHP6, a negative regulator of cytokinin signalling [117]. In addition, cytokinin may influence jasmonate metabolism. Ectopic expression of AtCKX1 in barley plants has been found to induce expression of lipoxygenases, which participate in the release of volatile compounds, including jasmonates [105], but an increase in jasmonic acid has also been observed in tobacco plants with highly increased levels of cytokinin [112].
4. Temperature and Cytokinin
Temperature is one of the most important abiotic factors influencing plants’ growth, development, productivity, and yields. Plants can only grow within taxa-specific temperature ranges, thus suboptimal temperatures cause stress, and temperature limits their geographical distributions. The mechanisms that are involved in temperature perception and signalling in plants are far from completely understood, but key aspects of associated morphological changes are clearly mediated by phytohormones.
4.1. Low Temperature Stress: Cold and Freezing
Most reported responses of cytokinin metabolism or signalling systems to low temperatures in plants are repressive [94,125,126,127,128], but there are some documented exceptions, notably cold-mediated upregulation of AHK3 [95]. However, the responses are complex, and roles of cytokinin and cytokinin signalling pathways in cold tolerance are unclear. Cold-induced attenuation of cytokinin signalling seems to impair plants’ tolerance of low temperature because the exogenous application of cytokinin significantly promotes cold tolerance in Arabidopsis [129,130,131]. Accordingly, recent hormonal analysis of Zoysia grass has shown that a genotype from relatively high latitude retained higher cytokinin levels during low-temperature treatment and exhibited higher freezing tolerance than a genotype from a lower latitude [128]. However, this seems to conflict with a reported negative role of AHK cytokinin receptors in cold tolerance [129]. The mechanisms whereby cytokinin could both promote cold tolerance and activate negative regulators of cold stress responses is unclear, but it seems to be at least partially independent of the cold-induced CBF/DREBs regulatory system [129].
Cold has also been shown to transiently activate expression of type-A ARRs in a cytokinin- and ethylene-dependent manner [129,130]. Mutation of ARR5, ARR6, and ARR7 leads to higher freezing tolerance [129], but the overexpression of ARR7 reportedly has both negative [129] and positive effects [130]. Results of overexpression studies indicate that other type-A ARRs [130] and ARR22, a cold-inducible type-C ARR [131], may also play positive roles in freezing tolerance. As shown by these conflicting results, the molecular mechanisms involved are unclear and further research is required. Besides ARRs, cytokinin response factors (CRFs) that act downstream of the primary cytokinin signalling pathway participate in responses to low temperature. More specifically, CRFs are induced by cold in Arabidopsis and tomato [130,132], and detailed analysis of Arabidopsis overexpressors and mutants has shown that CRF4 mediates freezing tolerance in non-acclimated plants [132], while CRF2 and CRF3 regulate lateral root development in response to cold stress [133]. Our meta-analysis revealed two novel candidates for interactive points in cytokinin-cold stress crosstalk: the MAP kinase MKK2, and the component of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, HOS1. The gene encoding HOS1 has a similar expression pattern to four and five genes that are involved in cytokinin metabolism and signalling, respectively (Figure 4). Cytokinin and its signalling evidently play important roles in cold stress responses, but various aspects of the molecular mechanism of their action regarding (for example) the duration of the period of cytokinin modulation prior to the stress require clarification
4.2. High Temperature and Heat Stress
Observed responses of Arabidopsis to heat stress treatments include a rapid but transient increase in active cytokinin contents [134,135]. A rapid proteomic heat-shock response that could be mimicked to some extent by cytokinin treatment at standard temperature has also been reported [136], indicating that cytokinin may play a role in temperature perception. Moreover, the accumulation of cytokinin has been observed in Pinus radiata under prolonged heat stress and in recovered plants [137,138]. Plants with increased levels of cytokinins show a higher accumulation of heat-shock proteins [107,139,140] and enhanced activity of the antioxidant system [88,112]. Accordingly, transgenic lines with inactivated components of cytokinin signalling pathways or reductions in pools of active cytokinin have displayed increased tolerance to high temperatures [141,142]. Further, analyses of temperature-induced hypocotyl growth in cytokinin-deficient transgenic plants and cytokinin receptor ahk double mutants have shown that impairment of the cytokinin pathway strongly inhibits growth at high temperatures [136]. This indicates that cytokinin could serve as a signal for thermomorphogenesis. It is also likely that a higher temperature sensitizes cytokinin signalling, which could explain why a transient increase in the active cytokinin pool is followed by its significant depletion [134,135], and downregulation in cytokinin metabolism genes and the expression of ARR-type A orthologs in strawberry (Fragaria vesca) [143,144]. It has also been proposed that heat stress-induced cytokinin depletion can promote stomatal closure, as this process is inhibited in plants with increased cytokinin levels [135].
5. Light Signalling and the Circadian Clock Interact with Cytokinin
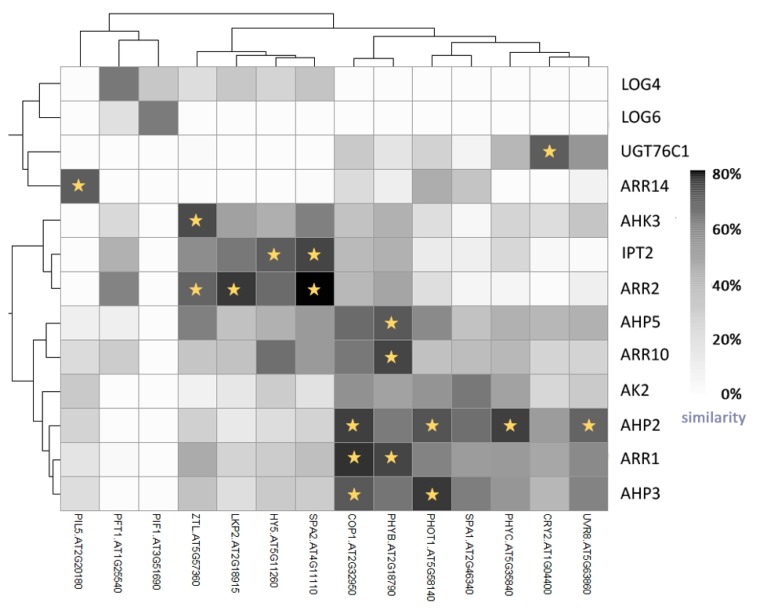
As described in a recent review [145], soon after its discovery it was found that cytokinin promotes chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development. There is increasing evidence of direct interactions between cytokinin and light via the light photoreceptor phyB [146,147]. Moreover, cytokinin-mediated development in Arabidopsis is modulated by the expression of the sensor histidine kinase CKI1 (Cytokinin Independent-1), which is regulated by phyA (and thus light) via the phyA interacting factor (PIF3) and Circadian Clock Associated 1 (CCA1) [148]. Further, levels of the cytokinin pool in tobacco leaves vary diurnally, with the main peak occurring around midday [149], and a key component of the circadian clock in plants, Late Elongated Hypocotyl (LHY), modulates cytokinin levels in Populus trees [150]. Reductions in cytokinin status or sensitivity enhance circadian stress in Arabidopsis and cytokinin-deficient plants display a highly similar expression of clock output genes to that of clock mutants [151]. Light conditions may also influence contents of specific cytokinins, as recently demonstrated in detached leaf experiments [152]. Moreover, light-cytokinin interactions are not limited to cytokinin metabolism and components of the two-component cytokinin responsive pathway. They also influence a bZIP transcription factor, Elongated Hypocotyl 5 (HY5), which participates in photomorphogenesis [94,153]. Cytokinin is also apparently involved in photoprotection mechanisms as plants with deficiencies in cytokinin receptors or cytokinin signalling are more susceptible to light stress than wild-type counterparts [154,155]. To identify new candidate participants in light-cytokinin interactions, we subjected Arabidopsis transcriptomic expression profiles to association analysis. Data were collected from the publicly available database Thalemine (available online: http://apps.araport.org/thalemine/), then normalized, and degrees of similarity between expression patterns were visualized in a heatmap (Figure 5). In total, we tested similarities in expression profiles of 70 candidate cytokinin genes and 31 genes that were putatively involved in light signalling. The analysis revealed that 10 of the latter had similar expression patterns (>70%) to candidate cytokinin genes. The results confirmed the previously described relation between ARR and COP1, but also highlighted several novel putative interactions, including a connection between the UV-B receptor UVR8 and the AHP2 component of cytokinin signalling. This is consistent with a recent finding that cytokinin regulates UV-B-induced damage in tomato seedlings [156].
Figure 5.
Heatmap showing degrees of similarity between expression profiles of cytokinin (signalling and metabolism) genes and genes involved in light perception. The heatmap was generated using R software and data available from Araport [33]. Asterisks indicate >70% similarity.
6. Summary
Generally, it can be concluded that cytokinin metabolism and signalling play important roles in abiotic stress tolerance and the manipulation of these processes in crops could be beneficial for sustainable agriculture. However, recent studies have mainly focused on global transcriptomic, proteomic and metabolomic changes in various plant species with modulated cytokinin levels [105,122,250]. Thus, further detailed analysis is required to confirm the importance of identified candidate genes/proteins and validate their roles in stress tolerance. Moreover, current models have substantial gaps. There is mounting evidence of intensive crosstalk in phytohormonal signalling, including redox and proteasome-ubiquitin pathways [251]. Thus, any disruption in a single phytohormone signalling pathway will probably affect the whole hormonome, but current limits in the sensitivity and spatiotemporal scope of analyses constrain our ability to detect all of the changes. Ongoing advances in hormonome analyses will undoubtedly improve our understanding [252], but another limitation is that most presented findings are based solely on transcriptomic analyses, in some cases supplemented with results of knocking out or overexpressing specific genes. Furthermore, posttranslational modifications play important roles in regulatory networks [253], and thus abiotic responses [254]. Thus, they must also be considered. Similarly, to fully understand phytohormonal interactions in abiotic stress responses, it will be crucial to integrate protein-protein interactions and the associated signalling hubs and networks [255].
Acknowledgments
This research was partially funded by grant AF-IGA-IP-2018/030 (Internal Grant Agency of the Faculty of AgriSciences, Mendel University in Brno), the LQ1601 (CEITEC 2020) project (which received a financial contribution from the Ministry of Education, Youths and Sports of the CR in the form of special support through the National Programme for Sustainability II funds), and by the Ministry of Education, Youths and Sports of CR from European Regional Development Fund-Project “Centre for Experimental Plant Biology”: No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000738. The authors thank Jan Zouhar for constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author Contributions
All authors (J.P., J.N., V.K., M.L., B.B., M.Č.) contributed to the analytical and systematic search of the literature. M.L. performed and interpreted results of meta analyses; J.P., J.N. and M.Č. reviewed and determined the design and structure of the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Suzuki I., Los D.A., Kanesaki Y., Mikami K., Murata N. The pathway for perception and transduction of low-temperature signals in Synechocystis. EMBO J. 2000;19:1327–1334. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hwang I., Chen H.C., Sheen J. Two-component signal transduction pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002;129:500–515. doi: 10.1104/pp.005504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wolanin P.M., Thomason P.A., Stock J.B. Histidine protein kinases: Key signal transducers outside the animal kingdom. Genome Biol. 2002;3 doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-10-reviews3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.O’Brien J.A., Benková E. Cytokinin cross-talking during biotic and abiotic stress responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2013;4:451. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kieber J.J., Schaller G.E. Cytokinin signaling in plant development. Development. 2018;145:dev149344. doi: 10.1242/dev.149344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Krapp A. Plant nitrogen assimilation and its regulation: A complex puzzle with missing pieces. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015;25:115–122. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gent L., Forde B.G. How do plants sense their nitrogen status? J. Exp. Bot. 2017;68:2531–2539. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bellegarde F., Gojon A., Martin A. Signals and players in the transcriptional regulation of root responses by local and systemic N signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2017;68:2553–2565. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Guan P., Ripoll J.J., Wang R., Vuong L., Bailey-Steinitz L.J., Ye D., Crawford N.M. Interacting TCP and NLP transcription factors control plant responses to nitrate availability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:2419–2424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1615676114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kiba T., Takei K., Kojima M., Sakakibara H. Side-chain modification of cytokinins controls shoot growth in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell. 2013;27:452–461. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kieber J.J., Schaller G.E. Cytokinins. Arabidopsis Book. 2014;12:e0168. doi: 10.1199/tab.0168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang R., Tischner R., Gutiérrez R.A., Hoffman M., Xing X., Chen M., Coruzzi G., Crawford N.M. Genomic analysis of the nitrate response using a nitrate reductase-null mutant of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004;136:2512–2522. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.044610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ramireddy E., Chang L., Schmülling T. Cytokinin as a mediator for regulating root system architecture in response to environmental cues. Plant Signal. Behav. 2014;9:e27771. doi: 10.4161/psb.27771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Menz J., Li Z., Schulze W.X., Ludewig U. Early nitrogen-deprivation responses in Arabidopsis roots reveal distinct differences on transcriptome and (phospho-) proteome levels between nitrate and ammonium nutrition. Plant J. 2016;88:717–734. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Liu K.H., Niu Y., Konishi M., Wu Y., Du H., Sun Chung H., Li L., Boudsocq M., McCormack M., Maekawa S., et al. Discovery of nitrate–CPK–NLP signalling in central nutrient–growth networks. Nature. 2017;545:311–316. doi: 10.1038/nature22077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang R., Xing X., Wang Y., Tran A., Crawford N.M. A Genetic screen for nitrate regulatory mutants captures the nitrate transporter gene NRT1.1. Plant Physiol. 2009;151:472–478. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.140434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Maeda Y., Konishi M., Kiba T., Sakuraba Y., Sawaki N., Kurai T., Ueda Y., Sakakibara H., Yanagisawa S. A NIGT1-centred transcriptional cascade regulates nitrate signalling and incorporates phosphorus starvation signals in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1376. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03832-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ruffel S., Krouk G., Ristova D., Shasha D., Birnbaum K.D., Coruzzi G.M. Nitrogen economics of root foraging: Transitive closure of the nitrate-cytokinin relay and distinct systemic signaling for N supply vs. demand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:18524–18529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1108684108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ruffel S., Poitout A., Krouk G., Coruzzi G.M., Lacombe B. Long-distance nitrate signaling displays cytokinin dependent and independent branches. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016;58:226–229. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Poitout A., Crabos A., Petřík I., Novák O., Krouk G., Lacombe B., Ruffel S. Responses to Systemic Nitrogen Signaling in Arabidopsis Roots Involve trans-Zeatin in Shoots. Plant Cell. 2018;30:1243–1257. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Guan P., Wang R., Nacry P., Breton G., Kay S.A., Pruneda-Paz J.L., Davani A., Crawford N.M. Nitrate foraging by Arabidopsis roots is mediated by the transcription factor TCP20 through the systemic signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:15267–15272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411375111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Patterson K., Walters L.A., Cooper A.M., Olvera J.G., Rosas M.A., Rasmusson A.G., Escobar M.A. Nitrate-Regulated Glutaredoxins Control Arabidopsis Primary Root Growth. Plant Physiol. 2016;170:989–999. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Walters L.A., Escobar M.A. The AtGRXS3/4/5/7/8 glutaredoxin gene cluster on Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 4 is coordinately regulated by nitrate and appears to control primary root growth. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016;11:e1171450. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2016.1171450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Walch-Liu P., Neumann G., Bangerth F., Engels C. Rapid effects of nitrogen form on leaf morphogenesis in tobacco. J. Exp. Bot. 2000;51:227–237. doi: 10.1093/jexbot/51.343.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rahayu Y.S., Walch-Liu P., Neumann G., Römheld V., von Wirén N., Bangerth F. Root-derived cytokinins as long-distance signals for NO3-induced stimulation of leaf growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2005;56:1143–1152. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Müller D., Waldie T., Miyawaki K., To J.P., Melnyk C.W., Kieber J.J., Kakimoto T., Leyser O. Cytokinin is required for escape but not release from auxin mediated apical dominance. Plant J. 2015;82:874–886. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Miyawaki K., Matsumoto-Kitano M., Kakimoto T. Expression of cytokinin biosynthetic isopentenyltransferase genes in Arabidopsis: Tissue specificity and regulation by auxin, cytokinin, and nitrate. Plant J. 2004;37:128–138. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Takei K., Ueda N., Aoki K., Kuromori T., Hirayama T., Shinozaki K., Yamaya T., Sakakibara H. AtIPT3 is a key determinant of nitrate-dependent cytokinin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004;45:1053–1062. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sakakibara H., Takei K., Hirose N. Interactions between nitrogen and cytokinin in the regulation of metabolism and development. Trends Plant Sci. 2006;11:440–448. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2006.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kiba T., Kudo T., Kojima M., Sakakibara H. Hormonal control of nitrogen acquisition: Roles of auxin, abscisic acid, and cytokinin. J. Exp. Bot. 2011;62:1399–1409. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Osugi A., Kojima M., Takebayashi Y., Ueda N., Kiba T., Sakakibara H. Systemic transport of trans-zeatin and its precursor have differing roles in Arabidopsis shoots. Nat. Plants. 2017;3:17112. doi: 10.1038/nplants.2017.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Landrein B., Formosa-Jordan P., Malivert A., Schuster C., Melnyk C.W., Yang W., Turnbull C., Meyerowitz E.M., Locke J.C.W., Jönsson H. Nitrate modulates stem cell dynamics in Arabidopsis shoot meristems through cytokinins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:1382–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718670115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Krishnakumar V., Hanlon M.R., Contrino S., Ferlanti E.S., Karamycheva S., Kim M., Rosen B.D., Cheng C.Y., Moreira W., Mock S.A., et al. Araport: The Arabidopsis Information Portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D1003–D1009. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rouached H., Arpat A.B., Poirier Y. Regulation of Phosphate Starvation Responses in Plants: Signaling Players and Cross-Talks. Mol. Plant. 2010;3:288–299. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ham B.K., Chen J., Yan Y., Lucas W.J. Insights into plant phosphate sensing and signaling. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018;49:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hirose N., Takei K., Kuroha T., Kamada-Nobusada T., Hayashi H., Sakakibara H. Regulation of cytokinin biosynthesis, compartmentalization and translocation. J. Exp. Bot. 2008;59:75–83. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Franco-Zorrilla J.M., Martin A.C., Solano R., Rubio V., Leyva A., Paz-Ares J. Mutations at CRE1 impair cytokinin-induced repression of phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2002;32:353–360. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Woo J., MacPherson C.R., Liu J., Wang H., Kiba T., Hannah M.A., Wang X.J., Bajic V.B., Chua N.H. The response and recovery of the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome to phosphate starvation. BMC Plant Biol. 2012;12:62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Werner T., Nehnevajova E., Köllmer I., Novák O., Strnad M., Krämer U., Schmülling T. Root-Specific Reduction of Cytokinin Causes Enhanced Root Growth, Drought Tolerance, and Leaf Mineral Enrichment in Arabidopsis and Tobacco. Plant Cell. 2010;22:3905–3920. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.072694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nishiyama R., Le D.T., Watanabe Y., Matsui A., Tanaka M., Seki M., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K., Tran L.S. Transcriptome analyses of a salt-tolerant cytokinin-deficient mutant reveal differential regulation of salt stress response by cytokinin deficiency. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e32124. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mohan T.C., Castrillo G., Navarro C., Zarco-Fernández S., Ramireddy E., Mateo C., Zamarreño A.M., Paz-Ares J., Muñoz R., García-Mina J.M., et al. Cytokinin Determines Thiol-Mediated Arsenic Tolerance and Accumulation. Plant Physiol. 2016;171:1418–1426. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jiang L., Cao H., Chen Z., Liu C., Cao S., Wei Z., Han Y., Gao Q., Wang W. Cytokinin is involved in TPS22-mediated selenium tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Ann. Bot. 2018 doi: 10.1093/aob/mcy093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Martín A.C., del Pozo J.C., Iglesias J., Rubio V., Solano R., de La Peña A., Leyva A., Paz-Ares J. Influence of cytokinins on the expression of phosphate starvation responsive genes in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2000;24:559–567. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Franco-Zorrilla J.M., Martín A.C., Leyva A., Paz-Ares J. Interaction between phosphate-starvation, sugar, and cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis and the roles of cytokinin receptors CRE1/AHK4 and AHK3. Plant Physiol. 2005;138:847–857. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.060517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shin H., Shin H.S., Chen R., Harrison M.J. Loss of At4 function impacts phosphate distribution between the roots and the shoots during phosphate starvation. Plant J. 2006;45:712–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang X., Yi K., Tao Y., Wang F., Wu Z., Jiang D., Chen X., Zhu L., Wu P. Cytokinin represses phosphate-starvation response through increasing of intracellular phosphate level. Plant Cell Environ. 2006;29:1924–1935. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shen C., Yue R., Yang Y., Zhang L., Sun T., Tie S., Wang H. OsARF16 Is Involved in Cytokinin-Mediated Inhibition of Phosphate Transport and Phosphate Signaling in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e112906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ribot C., Wang Y., Poirier Y. Expression analyses of three members of the AtPHO1 family reveal differential interactions between signaling pathways involved in phosphate deficiency and the responses to auxin, cytokinin, and abscisic acid. Planta. 2008;227:1025–1036. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0677-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lai F., Thacker J., Li Y., Doerner P. Cell division activity determines the magnitude of phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007;50:545–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Schaller G.E., Bishopp A., Kieber J.J. The Yin-Yang of Hormones: Cytokinin and Auxin Interactions in Plant Development. Plant Cell Online. 2015;27:44–63. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.133595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Nam Y.J., Tran L.S.P., Kojima M., Sakakibara H., Nishiyama R., Shin R. Regulatory roles of cytokinins and cytokinin signaling in response to potassium deficiency in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e47797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schachtman D.P. The Role of Ethylene in Plant Responses to K+ Deficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2015;6:1153. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rigas S., Ditengou F.A., Ljung K., Daras G., Tietz O., Palme K., Hatzopoulos P. Root gravitropism and root hair development constitute coupled developmental responses regulated by auxin homeostasis in the Arabidopsis root apex. New Phytol. 2013;197:1130–1141. doi: 10.1111/nph.12092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Koprivova A., Kopriva S. Sulfur metabolism and its manipulation in crops. J. Genet. Genom. 2016;43:623–629. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2016.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Honsel A., Kojima M., Haas R., Frank W., Sakakibara H., Herschbach C., Rennenberg H. Sulphur limitation and early sulphur deficiency responses in poplar: Significance of gene expression, metabolites, and plant hormones. J. Exp. Bot. 2012;63:1873–1893. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Maruyama-Nakashita A., Nakamura Y., Yamaya T., Takahashi H. A novel regulatory pathway of sulfate uptake in Arabidopsis roots: Implication of CRE1/WOL/AHK4-mediated cytokinin-dependent regulation. Plant J. 2004;38:779–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nguyen K.H., Ha C. Van, Nishiyama R., Watanabe Y., Leyva-González M.A., Fujita Y., Tran U.T., Li W., Tanaka M., Seki M., Schaller G.E., et al. Arabidopsis type B cytokinin response regulators ARR1, ARR10, and ARR12 negatively regulate plant responses to drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:3090–3095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600399113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bhargava A., Clabaugh I., To J.P., Maxwell B.B., Chiang Y.H., Schaller G.E., Loraine A., Kieber J.J. Identification of cytokinin-responsive genes using microarray meta-analysis and RNA-Seq in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013;162:272–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.217026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Öztürk S.E., Göktay M., Has C., Babaoğlu M., Allmer J., Doğanlar S., Frary A. Transcriptomic analysis of boron hyperaccumulation mechanisms in Puccinellia distans. Chemosphere. 2018;199:390–401. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.González-Fontes A., Herrera-Rodríguez M.B., Martín-Rejano E.M., Navarro-Gochicoa M.T., Rexach J., Camacho-Cristóbal J.J. Root Responses to Boron Deficiency Mediated by Ethylene. Front. Plant Sci. 2015;6:1103. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yang C.Q., Liu Y.Z., An J.C., Li S., Jin L.F., Zhou G.F., Wei Q.J., Yan H.Q., Wang N.N., Fu L.N., et al. Digital gene expression analysis of corky split vein caused by boron deficiency in “Newhall” Navel Orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) for selecting differentially expressed genes related to vascular hypertrophy. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e65737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Abreu I., Poza L., Bonilla I., Bolaños L. Boron deficiency results in early repression of a cytokinin receptor gene and abnormal cell differentiation in the apical root meristem of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014;77:117–121. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Eggert K., von Wirén N. Response of the plant hormone network to boron deficiency. New Phytol. 2017;216:868–881. doi: 10.1111/nph.14731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Poza-Viejo L., Abreu I., González-García M.P., Allauca P., Bonilla I., Bolaños L., Reguera M. Boron deficiency inhibits root growth by controlling meristem activity under cytokinin regulation. Plant Sci. 2018;270:176–189. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Séguéla M., Briat J.F., Vert G., Curie C. Cytokinins negatively regulate the root iron uptake machinery in Arabidopsis through a growth-dependent pathway. Plant J. 2008;55:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Shen C., Yue R., Sun T., Zhang L., Yang Y., Wang H. OsARF16, a transcription factor regulating auxin redistribution, is required for iron deficiency response in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant Sci. 2015;231:148–158. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Yin L., Wang S., Liu P., Wang W., Cao D., Deng X., Zhang S. Silicon-mediated changes in polyamine and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid are involved in silicon-induced drought resistance in Sorghum bicolor L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014;80:268–277. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kim Y.H., Khan A.L., Waqas M., Jeong H.J., Kim D.H., Shin J.S., Kim J.G., Yeon M.H., Lee I.J. Regulation of jasmonic acid biosynthesis by silicon application during physical injury to Oryza sativa L. J. Plant Res. 2014;127:525–532. doi: 10.1007/s10265-014-0641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hosseini S.A., Maillard A., Hajirezaei M.R., Ali N., Schwarzenberg A., Jamois F., Yvin J.C. Induction of Barley Silicon Transporter HvLsi1 and HvLsi2, increased silicon concentration in the shoot and regulated Starch and ABA Homeostasis under Osmotic stress and Concomitant Potassium Deficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:1359. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Markovich O., Steiner E., Kouřil Š., Tarkowski P., Aharoni A., Elbaum R. Silicon promotes cytokinin biosynthesis and delays senescence in Arabidopsis and Sorghum. Plant Cell Environ. 2017;40:1189–1196. doi: 10.1111/pce.12913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hartikainen H. Biogeochemistry of selenium and its impact on food chain quality and human health. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2005;18:309–318. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Pilon-Smits E.A., Quinn C.F., Tapken W., Malagoli M., Schiavon M. Physiological functions of beneficial elements. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009;12:267–274. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Schiavon M., Pilon-Smits E.A. The fascinating facets of plant selenium accumulation—Biochemistry, physiology, evolution and ecology. New Phytol. 2017;213:1582–1596. doi: 10.1111/nph.14378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Shibagaki N., Rose A., McDermott J.P., Fujiwara T., Hayashi H., Yoneyama T., Davies J.P. Selenate-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana identify Sultr1;2, a sulfate transporter required for efficient transport of sulfate into roots. Plant J. 2002;29:475–486. doi: 10.1046/j.0960-7412.2001.01232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Lehotai N., Kolbert Z., Peto A., Feigl G., Ördög A., Kumar D., Tari I., Erdei L. Selenite-induced hormonal and signalling mechanisms during root growth of Arabidopsis thaliana L. J. Exp. Bot. 2012;63:5677–5687. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kolbert Z., Lehotai N., Molnár Á., Feigl G. “The roots” of selenium toxicity: A new concept. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016;11:e1241935. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2016.1241935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lehotai N., Feigl G., Koós Á., Molnár Á., Ördög A., Pető A., Erdei L., Kolbert Z. Nitric oxide–cytokinin interplay influences selenite sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2016;35:2181–2195. doi: 10.1007/s00299-016-2028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bruno L., Pacenza M., Forgione I., Lamerton L.R., Greco M., Chiappetta A., Bitonti M.B. In Arabidopsis thaliana Cadmium Impact on the Growth of Primary Root by Altering SCR Expression and Auxin-Cytokinin Cross-Talk. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:1323. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Yang Z., Liu G., Liu J., Zhang B., Meng W., Müller B., Hayashi K., Zhang X., Zhao Z., De Smet I., Ding Z. Synergistic action of auxin and cytokinin mediates aluminum-induced root growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. EMBO Rep. 2017;18:1213–1230. doi: 10.15252/embr.201643806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Gemrotová M., Kulkarni M.G., Stirk W.A., Strnad M., Van Staden J., Spíchal L. Seedlings of medicinal plants treated with either a cytokinin antagonist (PI-55) or an inhibitor of cytokinin degradation (INCYDE) are protected against the negative effects of cadmium. Plant Growth Regul. 2013;71:137–145. doi: 10.1007/s10725-013-9813-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Fukudome A., Aksoy E., Wu X., Kumar K., Jeong I.S., May K., Russell W.K., Koiwa H. Arabidopsis CPL4 is an essential C-terminal domain phosphatase that suppresses xenobiotic stress responses. Plant J. 2014;80:27–39. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ramel F., Sulmon C., Cabello-Hurtado F., Taconnat L., Martin-Magniette M.L., Renou J.P., El Amrani A., Couée I., Gouesbet G. Genome-wide interacting effects of sucrose and herbicide-mediated stress in Arabidopsis thaliana: Novel insights into atrazine toxicity and sucrose-induced tolerance. BMC Genom. 2007;8:450. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ramel F., Sulmon C., Serra A.A., Gouesbet G., Couée I. Xenobiotic sensing and signalling in higher plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2012;63:3999–4014. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Brenner W.G., Schmulling T. Transcript profiling of cytokinin action in Arabidopsis roots and shoots discovers largely similar but also organ-specific responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2012;12:112. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Brenner W.G., Schmülling T. Summarizing and exploring data of a decade of cytokinin-related transcriptomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2015;6:29. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Daryanto S., Wang L., Jacinthe P.A. Global Synthesis of Drought Effects on Maize and Wheat Production. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0156362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Clauw P., Coppens F., De Beuf K., Dhondt S., Van Daele T., Maleux K., Storme V., Clement L., Gonzalez N., Inzé D. Leaf Responses to Mild Drought Stress in Natural Variants of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015;167:800–816. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.254284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Xu Y., Huang B. Effects of foliar-applied ethylene inhibitor and synthetic cytokinin on creeping bentgrass to enhance heat tolerance. Crop Sci. 2009;49:1876–1884. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2008.07.0441. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Xu S., Brockmöller T., Navarro-Quezada A., Kuhl H., Gase K., Ling Z., Zhou W., Kreitzer C., Stanke M., Tang H., et al. Wild tobacco genomes reveal the evolution of nicotine biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:6133–6138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700073114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Le D.T., Nishiyama R., Watanabe Y., Vankova R., Tanaka M., Seki M., Ham L.H., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K., Tran L.S.P. Identification and expression analysis of cytokinin metabolic genes in soybean under normal and drought conditions in relation to cytokinin levels. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e42411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Dobra J., Motyka V., Dobrev P., Malbeck J., Prasil I.T., Haisel D., Gaudinova A., Havlova M., Gubis J., Vankova R. Comparison of hormonal responses to heat, drought and combined stress in tobacco plants with elevated proline content. J. Plant Physiol. 2010;167:1360–1370. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2010.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nishiyama R., Watanabe Y., Fujita Y., Le D.T., Kojima M., Werner T., Vankova R., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K., Kakimoto T., et al. Analysis of Cytokinin Mutants and Regulation of Cytokinin Metabolic Genes Reveals Important Regulatory Roles of Cytokinins in Drought, Salt and Abscisic Acid Responses, and Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis. Plant Cell. 2011;23:2169–2183. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.087395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bano A., Dorffling K., Bettin D., Hahn H. Abscisic acid and cytokinins as possible root-to-shoot signals in xylem sap of rice plants in drying soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 1993;20:109–115. doi: 10.1071/PP9930109. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Argueso C.T., Ferreira F.J., Kieber J.J. Environmental perception avenues: The interaction of cytokinin and environmental response pathways. Plant Cell Environ. 2009;32:1147–1160. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tran L.S., Urao T., Qin F., Maruyama K., Kakimoto T., Shinozaki K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Functional analysis of AHK1/ATHK1 and cytokinin receptor histidine kinases in response to abscisic acid, drought, and salt stress in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:20623–20628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706547105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Jang G., Chang S.H., Um T.Y., Lee S., Kim J.K., Choi Y.D. Antagonistic interaction between jasmonic acid and cytokinin in xylem development. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:10212. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10634-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Huang X., Hou L., Meng J., You H., Li Z., Gong Z., Yang S., Shi Y. The Antagonistic Action of Abscisic Acid and Cytokinin Signaling Mediates Drought Stress Response in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant. 2018;11:970–982. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rivero R.M., Ruiz J.M., García P.C., López-Lefebre L.R., Sánchez E., Romero L. Resistance to cold and heat stress: Accumulation of phenolic compounds in tomato and watermelon plants. Plant Sci. 2001;160:315–321. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ghanem M.E., Albacete A., Smigocki A.C., Frébort I., Pospísilová H., Martínez-Andújar C., Acosta M., Sánchez-Bravo J., Lutts S., Dodd I.C., Pérez-Alfocea F. Root-synthesized cytokinins improve shoot growth and fruit yield in salinized tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2011;62:125–140. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Rivero R.M., Kojima M., Gepstein A., Sakakibara H., Mittler R., Gepstein S., Blumwald E. Delayed leaf senescence induces extreme drought tolerance in a flowering plant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:19631–19636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709453104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Rivero R.M., Gimeno J., Van Deynze A., Walia H., Blumwald E. Enhanced Cytokinin Synthesis in Tobacco Plants Expressing PSARK::IPT Prevents the Degradation of Photosynthetic Protein Complexes During Drought. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010;51:1929–1941. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Reguera M., Peleg Z., Abdel-Tawab Y.M., Tumimbang E.B., Delatorre C.A., Blumwald E. Stress-Induced Cytokinin Synthesis Increases Drought Tolerance through the Coordinated Regulation of Carbon and Nitrogen Assimilation in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2013;163:1609–1622. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.227702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ma X., Zhang J., Huang B. Cytokinin-mitigation of salt-induced leaf senescence in perennial ryegrass involving the activation of antioxidant systems and ionic balance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016;125:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.01.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Décima Oneto C., Otegui M.E., Baroli I., Beznec A., Faccio P., Bossio E., Blumwald E., Lewi D. Water deficit stress tolerance in maize conferred by expression of an isopentenyltransferase (IPT) gene driven by a stress- and maturation-induced promoter. J. Biotechnol. 2016;220:66–77. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Vojta P., Kokáš F., Husičková A., Grúz J., Bergougnoux V., Marchetti C.F., Jiskrová E., Ježilová E., Mik V., Ikeda Y., Galuszka P. Whole transcriptome analysis of transgenic barley with altered cytokinin homeostasis and increased tolerance to drought stress. New Biotechnol. 2016;33:676–691. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2016.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Ramireddy E., Hosseini S.A., Eggert K., Gillandt S., Gnad H., von Wirén N., Schmülling T. Root Engineering in Barley: Increasing Cytokinin Degradation Produces a Larger Root System, Mineral Enrichment in the Shoot and Improved Drought Tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2018;177:1078–1095. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Černý M., Kuklová A., Hoehenwarter W., Fragner L., Novák O., Rotková G., Jedelský P.L.P. L., Žáková K. K., Šmehilová M., Strnad M., et al. Proteome and metabolome profiling of cytokinin action in Arabidopsis identifying both distinct and similar responses to cytokinin down- and up-regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2013;64:4193–4206. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Zavaleta-Mancera H.A., López-Delgado H., Loza-Tavera H., Mora-Herrera M., Trevilla-García C., Vargas-Suárez M., Ougham H. Cytokinin promotes catalase and ascorbate peroxidase activities and preserves the chloroplast integrity during dark-senescence. J. Plant Physiol. 2007;164:1572–1582. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2007.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Ma X., Zhang J., Burgess P., Rossi S., Huang B. Interactive effects of melatonin and cytokinin on alleviating drought-induced leaf senescence in creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera) Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018;145:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2017.10.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Liao X., Guo X., Wang Q., Wang Y., Zhao D., Yao L., Wang S., Liu G., Li T. Overexpression of MsDREB6.2 results in cytokinin-deficient developmental phenotypes and enhances drought tolerance in transgenic apple plants. Plant J. 2017;89:510–526. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Nakabayashi R., Yonekura-Sakakibara K., Urano K., Suzuki M., Yamada Y., Nishizawa T., Matsuda F., Kojima M., Sakakibara H., Shinozaki K., et al. Enhancement of oxidative and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis by overaccumulation of antioxidant flavonoids. Plant J. 2014;77:367–379. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Novák J., Pavlů J., Novák O., Nožková-Hlaváčková V., Špundová M., Hlavinka J., Koukalová Š., Skalák J., Černý M., Brzobohatý B. High cytokinin levels induce a hypersensitive-like response in tobacco. Ann. Bot. 2013;112:41–55. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.White R.G., Kirkegaard J.A. The distribution and abundance of wheat roots in a dense, structured subsoil—Implications for water uptake. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33:133–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Novák J., Černý M., Pavlů J., Zemánková J., Skalák J., Plačková L., Brzobohatý B. Roles of proteome dynamics and cytokinin signaling in root to hypocotyl ratio changes induced by shading roots of Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015;56:1006–1018. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Laplaze L., Benkova E., Casimiro I., Maes L., Vanneste S., Swarup R., Weijers D., Calvo V., Parizot B., Herrera-Rodriguez M.B., et al. Cytokinins act directly on lateral root founder cells to inhibit root initiation. Plant Cell. 2007;19:3889–3900. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Pospíšilová H., Jiskrová E., Vojta P., Mrízová K., Kokáš F., Čudejková M.M., Bergougnoux V., Plíhal O., Klimešová J., Novák O., et al. Transgenic barley overexpressing a cytokinin dehydrogenase gene shows greater tolerance to drought stress. New Biotechnol. 2016;33:692–705. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2015.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Jang G., Choi Y.D. Drought stress promotes xylem differentiation by modulating the interaction between cytokinin and jasmonic acid. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018;13:e1451707. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1451707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Guan C., Wang X., Feng J., Hong S., Liang Y., Ren B., Zuo J. Cytokinin Antagonizes Abscisic Acid-Mediated Inhibition of Cotyledon Greening by Promoting the Degradation of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE5 Protein in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014;164:1515–1526. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.234740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Huang Y., Sun M.M., Ye Q., Wu X.Q., Wu W.H., Chen Y.F. Abscisic Acid Modulates Seed Germination via ABA INSENSITIVE5-Mediated PHOSPHATE1. Plant Physiol. 2017;175:1661–1668. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Yang C.Y., Huang Y.C., Ou S.L. ERF73/HRE1 is involved in H2O2 production via hypoxia-inducible Rboh gene expression in hypoxia signaling. Protoplasma. 2017;254:1705–1714. doi: 10.1007/s00709-016-1064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Nguyen T.Q., Emery R.J.N. Is ABA the earliest upstream inhibitor of apical dominance? J. Exp. Bot. 2017;68:881–884. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx028. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Prerostova S., Dobrev P.I., Gaudinova A., Knirsch V., Körber N., Pieruschka R., Fiorani F., Brzobohatý B., Černý M., Spichal L., et al. Cytokinins: Their Impact on Molecular and Growth Responses to Drought Stress and Recovery in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;9:655. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Fu J., Wu H., Ma S., Xiang D., Liu R., Xiong L. OsJAZ1 Attenuates Drought Resistance by Regulating JA and ABA Signaling in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:2108. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Ahmad P., Rasool S., Gul A., Sheikh S.A., Akram N.A., Ashraf M., Kazi A.M., Gucel S. Jasmonates: Multifunctional Roles in Stress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016;7:813. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Veselova S.V., Farhutdinov R.G., Veselov S.Y., Kudoyarova G.R., Veselov D.S., Hartung W. The effect of root cooling on hormone content, leaf conductance and root hydraulic conductivity of durum wheat seedlings (Triticum durum L.) J. Plant Physiol. 2005;162:21–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2004.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Ntatsi G., Savvas D., Papasotiropoulos V., Katsileros A., Zrenner R.M., Hincha D.K., Zuther E., Schwarz D. Rootstock Sub-Optimal Temperature Tolerance Determines Transcriptomic Responses after Long-Term Root Cooling in Rootstocks and Scions of Grafted Tomato Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:911. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Maruyama K., Urano K., Yoshiwara K., Morishita Y., Sakurai N., Suzuki H., Kojima M., Sakakibara H., Shibata D., Saito K., et al. Integrated Analysis of the Effects of Cold and Dehydration on Rice Metabolites, Phytohormones, and Gene Transcripts. Plant Physiol. 2014;164:1759–1771. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.231720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Li S., Yang Y., Zhang Q., Liu N., Xu Q., Hu L. Differential physiological and metabolic response to low temperature in two zoysiagrass genotypes native to high and low latitude. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0198885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Jeon J., Kim N.Y., Kim S., Kang N.Y., Novák O., Ku S.J., Cho C., Lee D.J., Lee E.J., Strnad M., Kim J. A subset of cytokinin two-component signaling system plays a role in cold temperature stress response in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:23371–23386. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.096644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Shi Y., Tian S., Hou L., Huang X., Zhang X., Guo H., Yang S. Ethylene signaling negatively regulates freezing tolerance by repressing expression of CBF and type-A ARR genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2012;24:2578–2595. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.098640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Kang N.Y., Cho C., Kim J. Inducible Expression of Arabidopsis Response Regulator 22 (ARR22), a Type-C ARR, in Transgenic Arabidopsis Enhances Drought and Freezing Tolerance. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e79248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Zwack P.J., Compton M.A., Adams C.I., Rashotte A.M. Cytokinin response factor 4 (CRF4) is induced by cold and involved in freezing tolerance. Plant Cell Rep. 2016;35:573–584. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1904-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Jeon J., Cho C., Lee M.R., Van Binh N., Kim J. CYTOKININ RESPONSE FACTOR2 (CRF2) and CRF3 Regulate Lateral Root Development in Response to Cold Stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2016;28:1828–1843. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Dobrá J., Černý M., Štorchová H., Dobrev P., Skalák J., Jedelský P.L., Lukšanová H., Gaudinová A., Pešek B., Malbecka J., et al. The impact of heat stress targeting on the hormonal and transcriptomic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2015;231:52–61. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Skalák J., Černý M., Jedelský P., Dobrá J., Ge E., Novák J., Hronková M., Dobrev P., Vanková R., Brzobohatý B. Stimulation of ipt overexpression as a tool to elucidate the role of cytokinins in high temperature responses of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2016;67:2861–2873. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Černý M., Jedelský P.L., Novák J., Schlosser A., Brzobohatý B. Cytokinin modulates proteomic, transcriptomic and growth responses to temperature shocks in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2014;37:1641–1655. doi: 10.1111/pce.12270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Escandón M., Cañal M.J., Pascual J., Pinto G., Correia B., Amaral J., Meijón M. Integrated physiological and hormonal profile of heat-induced thermotolerance in Pinus radiata. Tree Physiol. 2016;36:63–77. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpv127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Escandón M., Meijón M., Valledor L., Pascual J., Pinto G., Cañal M.J. Metabolome Integrated Analysis of High-Temperature Response in Pinus radiata. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;9:485. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Lochmanová G., Zdráhal Z., Konečná H., Koukalová Š., Malbeck J., Souček P., Válková M., Kiran N.S., Brzobohatý B. Cytokinin-induced photomorphogenesis in dark-grown Arabidopsis: A proteomic analysis. J. Exp. Bot. 2008;59:3705–3719. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Černý M., Dyčka F., Bobáľová J., Brzobohatý B. Early cytokinin response proteins and phosphoproteins of Arabidopsis thaliana identified by proteome and phosphoproteome profiling. J. Exp. Bot. 2011;62:921–937. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Macková H., Hronková M., Dobrá J., Turečková V., Novák O., Lubovská Z., Motyka V., Haisel D., Hájek T., Prášil I.T., et al. Enhanced drought and heat stress tolerance of tobacco plants with ectopically enhanced cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase gene expression. J. Exp. Bot. 2013;64:2805–2815. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Danilova M.N., Kudryakova N.V., Doroshenko A.S., Zabrodin D.A., Vinogradov N.S., Kuznetsov V.V. Molecular and physiological responses of Arabidopsis thaliana plants deficient in the genes responsible for ABA and cytokinin reception and metabolism to heat shock. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2016;63:308–318. doi: 10.1134/S1021443716030043. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Yang Y., Jiang Y., Mi X., Gan L., Gu T., Ding J., Li Y. Identification and expression analysis of cytokinin response regulators in Fragaria vesca. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016;38:198. doi: 10.1007/s11738-016-2213-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Mi X., Wang X., Wu H., Gan L., Ding J., Li Y. Characterization and expression analysis of cytokinin biosynthesis genes in Fragaria vesca. Plant Growth Regul. 2017;82:139–149. doi: 10.1007/s10725-016-0246-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Cortleven A., Schmülling T. Regulation of chloroplast development and function by cytokinin. J. Exp. Bot. 2015;66:4999–5013. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Sweere U., Eichenberg K., Lohrmann J., Mira-Rodado V., Bäurle I., Kudla J., Nagy F., Schafer E., Harter K. Interaction of the response regulator ARR4 with phytochrome B in modulating red light signaling. Science. 2001;294:1108–1111. doi: 10.1126/science.1065022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Chi W., Li J., He B., Chai X., Xu X., Sun X., Jiang J., Feng P., Zuo J., Lin R., et al. DEG9, a serine protease, modulates cytokinin and light signaling by regulating the level of ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATOR 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:E3568–E3576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601724113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Dobisova T., Hrdinova V., Cuesta C., Michlickova S., Urbankova I., Hejatkova R., Zadnikova P., Pernisova M., Benkova E., Hejatko J. Light Controls Cytokinin Signaling via Transcriptional Regulation of Constitutively Active Sensor Histidine Kinase CKI1. Plant Physiol. 2017;174:387–404. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Nováková M., Motyka V., Dobrev P.I., Malbeck J., Gaudinová A., Vanková R. Diurnal variation of cytokinin, auxin and abscisic acid levels in tobacco leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2005;56:2877–2883. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Edwards K.D., Takata N., Johansson M., Jurca M., Novák O., Hényková E., Liverani S., Kozarewa I., Strnad M., Millar A.J., et al. Circadian clock components control daily growth activities by modulating cytokinin levels and cell division-associated gene expression in Populus trees. Plant Cell Environ. 2018;41:1468–1482. doi: 10.1111/pce.13185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Nitschke S., Cortleven A., Iven T., Feussner I., Havaux M., Riefler M., Schmülling T. Circadian stress regimes affect the circadian clock and cause jasmonic acid-dependent cell death in cytokinin-deficient Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell. 2016;28:1616–1639. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Janečková H., Husičková A., Ferretti U., Prčina M., Pilařová E., Plačková L., Pospíšil P., Doležal K., Špundová M. The interplay between cytokinins and light during senescence in detached Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2018;41:1870–1885. doi: 10.1111/pce.13329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Vandenbussche F., Habricot Y., Condiff A.S., Maldiney R., Van der Straeten D., Ahmad M. HY5 is a point of convergence between cryptochrome and cytokinin signalling pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2007;49:428–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Cortleven A., Nitschke S., Klaumunzer M., AbdElgawad H., Asard H., Grimm B., Riefler M., Schmulling T. A Novel Protective Function for Cytokinin in the Light Stress Response Is Mediated by the ARABIDOPSIS HISTIDINE KINASE2 and ARABIDOPSIS HISTIDINE KINASE3 Receptors. Plant Physiol. 2014;164:1470–1483. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.224667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Danilova M.N., Kudryakova N.V., Voronin P.Y., Oelmüller R., Kusnetsov V.V., Kulaeva O.N. Membrane receptors of cytokinin and their regulatory role in Arabidopsis thaliana plant response to photooxidative stress under conditions of water deficit. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2014;61:434–442. doi: 10.1134/S1021443714040062. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Bashri G., Singh M., Mishra R.K., Kumar J., Singh V.P., Prasad S.M. Kinetin Regulates UV-B-Induced Damage to Growth, Photosystem II Photochemistry, and Nitrogen Metabolism in Tomato Seedlings. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018;37:233–245. doi: 10.1007/s00344-017-9721-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Patterson K., Cakmak T., Cooper A., Lager I., Rasmusson A.G., Escobar M.A. Distinct signalling pathways and transcriptome response signatures differentiate ammonium- and nitrate-supplied plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33:1486–14501. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Canales J., Moyano T.C., Villarroel E., Gutiérrez R.A. Systems analysis of transcriptome data provides new hypotheses about Arabidopsis root response to nitrate treatments. Front. Plant Sci. 2014;5:22. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Krapp A., Berthome R., Orsel M., Mercey-Boutet S., Yu A., Castaings L., Elftieh S., Major H., Renou J.-P., Daniel-Vedele F. Arabidopsis Roots and Shoots Show Distinct Temporal Adaptation Patterns toward Nitrogen Starvation. Plant Physiol. 2011;157:1255–1282. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Kiba T., Inaba J., Kudo T., Ueda N., Konishi M., Mitsuda N., Takiguchi Y., Kondou Y., Yoshizumi T., Ohme-Takagi M., et al. Repression of Nitrogen Starvation Responses by Members of the Arabidopsis GARP-Type Transcription Factor NIGT1/HRS1 Subfamily. Plant Cell. 2018;30:925–945. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Pant B.D., Musialak-Lange M., Nuc P., May P., Buhtz A., Kehr J., Walther D., Scheible W.-R. Identification of Nutrient-Responsive Arabidopsis and Rapeseed MicroRNAs by Comprehensive Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Profiling and Small RNA Sequencing. Plant Physiol. 2009;150:1541–1555. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.139139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Zhao M., Ding H., Zhu J.K., Zhang F., Li W.X. Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2011;190:906–915. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Konishi N., Ishiyama K., Matsuoka K., Maru I., Hayakawa T., Yamaya T., Kojima S. NADH-dependent glutamate synthase plays a crucial role in assimilating ammonium in the Arabidopsis root. Physiol. Plant. 2014;152:138–151. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Bi Y.M., Wang R.L., Zhu T., Rothstein S.J. Global transcription profiling reveals differential responses to chronic nitrogen stress and putative nitrogen regulatory components in Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2007;8:281. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Canales J., Rueda-López M., Craven-Bartle B., Avila C., Cánovas F.M. Novel Insights into Regulation of Asparagine Synthetase in Conifers. Front. Plant Sci. 2012;3:100. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Alvarez J.M., Riveras E., Vidal E.A., Gras D.E., Contreras-López O., Tamayo K.P., Aceituno F., Gómez I., Ruffel S., Lejay L., et al. Systems approach identifies TGA1 and TGA4 transcription factors as important regulatory components of the nitrate response of Arabidopsis thaliana roots. Plant J. 2014;80:1–13. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Konishi M., Yanagisawa S. Arabidopsis NIN-like transcription factors have a central role in nitrate signalling. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:1617. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Rubin G., Tohge T., Matsuda F., Saito K., Scheible W.R. Members of the LBD Family of Transcription Factors Repress Anthocyanin Synthesis and Affect Additional Nitrogen Responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009;21:3567–3584. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.067041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Jost R., Pharmawati M., Lapis-Gaza H.R., Rossig C., Berkowitz O., Lambers H., Finnegan P.M. Differentiating phosphate-dependent and phosphate-independent systemic phosphate-starvation response networks in Arabidopsis thaliana through the application of phosphite. J. Exp. Bot. 2015;66:2501–2514. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Hammond J.P., Bennett M.J., Bowen H.C., Broadley M.R., Eastwood D.C., May S.T., Rahn C., Swarup R., Woolaway K.E., White P.J. Changes in Gene Expression in Arabidopsis Shoots during Phosphate Starvation and the Potential for Developing Smart Plants. Plant Physiol. 2003;132:578–596. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.020941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Ayadi A., David P., Arrighi J.F., Chiarenza S., Thibaud M.C., Nussaume L., Marin E. Reducing the Genetic Redundancy of Arabidopsis PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 Transporters to Study Phosphate Uptake and Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2015;167:1511–1526. doi: 10.1104/pp.114.252338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Gu M., Chen A., Sun S., Xu G. Complex Regulation of Plant Phosphate Transporters and the Gap between Molecular Mechanisms and Practical Application: What Is Missing? Mol. Plant. 2016;9:396–416. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Lapis-Gaza H.R., Jost R., Finnegan P.M. Arabidopsis PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER1 genes PHT1;8 and PHT1;9 are involved in root-to-shoot translocation of orthophosphate. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:334. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0334-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Puga M.I., Mateos I., Charukesi R., Wang Z., Franco-Zorrilla J.M., de Lorenzo L., Irigoyen M.L., Masiero S., Bustos R., Rodriguez J., et al. SPX1 is a phosphate-dependent inhibitor of PHOSPHATE STARVATION RESPONSE 1 in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:14947–14952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404654111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Maruyama-Nakashita A., Nakamura Y., Tohge T., Saito K., Takahashi H. Arabidopsis SLIM1 is a central transcriptional regulator of plant sulfur response and metabolism. Plant Cell. 2006;18:3235–3251. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.046458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Bielecka M., Watanabe M., Morcuende R., Scheible W.R., Hawkesford M.J., Hesse H., Hoefgen R. Transcriptome and metabolome analysis of plant sulfate starvation and resupply provides novel information on transcriptional regulation of metabolism associated with sulfur, nitrogen and phosphorus nutritional responses in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2014;5:805. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Nikiforova V., Freitag J., Kempa S., Adamik M., Hesse H., Hoefgen R. Transcriptome analysis of sulfur depletion in Arabidopsis thaliana: Interlacing of biosynthetic pathways provides response specificity. Plant J. 2003;33:633–650. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Kopriva S., Calderwood A., Weckopp S.C., Koprivova A. Plant sulfur and Big Data. Plant Sci. 2015;241:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Zhang B., Pasini R., Dan H., Joshi N., Zhao Y., Leustek T., Zheng Z.L. Aberrant gene expression in the Arabidopsis SULTR1;2 mutants suggests a possible regulatory role for this sulfate transporter in response to sulfur nutrient status. Plant J. 2014;77:185–197. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Henríquez-Valencia C., Arenas-M A., Medina J., Canales J. Integrative Transcriptomic Analysis Uncovers Novel Gene Modules That Underlie the Sulfate Response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;9:470. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Kawashima C.G., Berkowitz O., Hell R., Noji M., Saito K. Characterization and expression analysis of a serine acetyltransferase gene family involved in a key step of the sulfur assimilation pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005;137:220–230. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.045377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Forieri I., Sticht C., Reichelt M., Gretz N., Hawkesford M.J., Malagoli M., Wirtz M., Hell R. System analysis of metabolism and the transcriptome in Arabidopsis thaliana roots reveals differential co-regulation upon iron, sulfur and potassium deficiency. Plant Cell Environ. 2017;40:95–107. doi: 10.1111/pce.12842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Chen D., Cao B., Wang S., Liu P., Deng X., Yin L., Zhang S. Silicon moderated the K deficiency by improving the plant-water status in sorghum. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:22882. doi: 10.1038/srep22882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Gierth M., Mäser P., Schroeder J.I. The Potassium Transporter AtHAK5 Functions in K+ Deprivation-Induced High-Affinity K+ Uptake and AKT1 K+ Channel Contribution to K+ Uptake Kinetics in Arabidopsis Roots. Plant Physiol. 2005;137:1105–1114. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.057216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Pyo Y.J., Gierth M., Schroeder J.I., Cho M.H. High-Affinity K+ Transport in Arabidopsis: AtHAK5 and AKT1 Are Vital for Seedling Establishment and Postgermination Growth under Low-Potassium Conditions. Plant Physiol. 2010;153:863–875. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.154369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Ragel P., Ródenas R., García-Martín E., Andrés Z., Villalta I., Nieves-Cordones M., Rivero R.M., Martínez V., Pardo J.M., Quintero F.J., Rubio F. CIPK23 regulates HAK5-mediated high-affinity K+ uptake in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 2015;169:01401.2015. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Osakabe Y., Arinaga N., Umezawa T., Katsura S., Nagamachi K., Tanaka H., Ohiraki H., Yamada K., Seo S.-U., Abo M., et al. Osmotic Stress Responses and Plant Growth Controlled by Potassium Transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2013;25:609–624. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.105700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Pilot G., Gaymard F., Mouline K., Chérel I., Sentenac H. Regulated expression of Arabidopsis shaker K+ channel genes involved in K+ uptake and distribution in the plant. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003;51:773–787. doi: 10.1023/A:1022597102282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Wang Y., Wu W.H. Regulation of potassium transport and signaling in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017;39:123–128. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Rigas S., Debrosses G., Haralampidis K., Vicente-Agullo F., Feldmann K.A., Grabov A., Dolan L., Hatzopoulos P. TRH1 encodes a potassium transporter required for tip growth in Arabidopsis root hairs. Plant Cell. 2001;13:139–151. doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Han M., Wu W., Wu W.-H., Wang Y. Potassium Transporter KUP7 Is Involved in K+ Acquisition and Translocation in Arabidopsis Root under K+ -Limited Conditions. Mol. Plant. 2016;9:437–446. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Armengaud P., Breitling R., Amtmann A. The Potassium-Dependent Transcriptome of Arabidopsis Reveals a Prominent Role of Jasmonic Acid in Nutrient Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2004;136:2556–2576. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.046482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Li W., Lan P. The Understanding of the Plant Iron Deficiency Responses in Strategy I Plants and the Role of Ethylene in This Process by Omic Approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 2017;8:40. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Mai H.J., Pateyron S., Bauer P. Iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana: Transcriptomic analyses reveal novel FIT-regulated genes, iron deficiency marker genes and functional gene networks. BMC Plant Biol. 2016;16:211. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0899-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Stein R.J., Waters B.M. Use of natural variation reveals core genes in the transcriptome of iron-deficient Arabidopsis thaliana roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2012;63:1039–1055. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Mendoza-Cózatl D.G., Xie Q., Akmakjian G.Z., Jobe T.O., Patel A., Stacey M.G., Song L., Demoin D.W., Jurisson S.S., Stacey G., Schroeder J.I. OPT3 Is a Component of the Iron-Signaling Network between Leaves and Roots and Misregulation of OPT3 Leads to an Over-Accumulation of Cadmium in Seeds. Mol. Plant. 2014;7:1455–1469. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Takano J., Noguchi K., Yasumori M., Kobayashi M., Gajdos Z., Miwa K., Hayashi H., Yoneyama T., Fujiwara T. Arabidopsis boron transporter for xylem loading. Nature. 2002;420:337–340. doi: 10.1038/nature01139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Miwa K., Aibara I., Fujiwara T. Arabidopsis thaliana BOR4 is upregulated under high boron conditions and confers tolerance to high boron. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014;60:349–355. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2013.866524. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Msanne J., Lin J., Stone J.M., Awada T. Characterization of abiotic stress-responsive Arabidopsis thaliana RD29A and RD29B genes and evaluation of transgenes. Planta. 2011;234:97–107. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1387-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Huang K.C., Lin W.C., Cheng W.H. Salt hypersensitive mutant 9, a nucleolar APUM23 protein, is essential for salt sensitivity in association with the ABA signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2018;18:40. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1255-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Vogel J.T., Zarka D.G., Van Buskirk H.A., Fowler S.G., Thomashow M.F. Roles of the CBF2 and ZAT12 transcription factors in configuring the low temperature transcriptome of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005;41:195–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Lee B., Henderson D.A., Zhu J.K. The Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its regulation by ICE1. Plant Cell. 2005;17:3155–3175. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.035568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Maruyama K., Sakuma Y., Kasuga M., Ito Y., Seki M., Goda H., Shimada Y., Yoshida S., Shinozaki K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Identification of cold-inducible downstream genes of the Arabidopsis DREB1A/CBF3 transcriptional factor using two microarray systems. Plant J. 2004;38:982–993. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Nakaminami K., Matsui A., Nakagami H., Minami A., Nomura Y., Tanaka M., Morosawa T., Ishida J., Takahashi S., Uemura M., et al. Analysis of differential expression patterns of mRNA and protein during cold-acclimation and de-acclimation in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014;13:3602–3611. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.039081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Janská A., Aprile A., Zámečník J., Cattivelli L., Ovesná J. Transcriptional responses of winter barley to cold indicate nucleosome remodelling as a specific feature of crown tissues. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011;11:307–325. doi: 10.1007/s10142-011-0213-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Teige M., Scheikl E., Eulgem T., Dóczi R., Ichimura K., Shinozaki K., Dangl J.L., Hirt H. The MKK2 Pathway Mediates Cold and Salt Stress Signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell. 2004;15:141–152. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Guo W.L., Chen R.-G., Du X.H., Zhang Z., Yin Y.X., Gong Z.H., Wang G.Y. Reduced tolerance to abiotic stress in transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing a Capsicum annuum multiprotein bridging factor 1. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:138. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Cho S.M., Kang B.R., Kim Y.C. Transcriptome Analysis of Induced Systemic Drought Tolerance Elicited by Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Pathol. J. 2013;29:209–220. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.SI.07.2012.0103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Rest J.S., Wilkins O., Yuan W., Purugganan M.D., Gurevitch J. Meta-analysis and meta-regression of transcriptomic responses to water stress in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2016;85:548–560. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.MacGregor D.R., Penfield S. Exploring the pleiotropy of hos1. J. Exp. Bot. 2015;66:1661–1671. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Simpson S.D., Nakashima K., Narusaka Y., Seki M., Shinozaki K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Two different novel cis-acting elements of erd1, a clpA homologous Arabidopsis gene function in induction by dehydration stress and dark-induced senescence. Plant J. 2003;33:259–270. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Sakuma Y., Maruyama K., Qin F., Osakabe Y., Shinozaki K., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Dual function of an Arabidopsis transcription factor DREB2A in water-stress-responsive and heat-stress-responsive gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:18822–18827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605639103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Baek D., Chun H.J., Kang S., Shin G., Park S.J., Hong H., Kim C., Kim D.H., Lee S.Y., Kim M.C., et al. A Role for Arabidopsis miR399f in Salt, Drought, and ABA Signaling. Mol. Cells. 2016;39:111–118. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Kuhn J.M., Boisson-Dernier A., Dizon M.B., Maktabi M.H., Schroeder J.I. The protein phosphatase AtPP2CA negatively regulates abscisic acid signal transduction in Arabidopsis, and effects of abh1 on AtPP2CA mRNA. Plant Physiol. 2006;140:127–139. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.070318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Zhang L., Zhang X., Fan S. Meta-analysis of salt-related gene expression profiles identifies common signatures of salt stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Syst. Evol. 2017;303:757–774. doi: 10.1007/s00606-017-1407-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Yamada K., Fukao Y., Hayashi M., Fukazawa M., Suzuki I., Nishimura M. Cytosolic HSP90 Regulates the Heat Shock Response That Is Responsible for Heat Acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:37794–37804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707168200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Larkindale J., Vierling E. Core genome responses involved in acclimation to high temperature. Plant Physiol. 2008;146:748–761. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.112060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Charng Y.Y., Liu H.C., Liu N.Y., Chi W.T., Wang C.N., Chang S.H., Wang T.T. A Heat-Inducible Transcription Factor, HsfA2, Is Required for Extension of Acquired Thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007;143:251–262. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.091322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Lin K.F., Tsai M.Y., Lu C.A., Wu S.J., Yeh C.H. The roles of Arabidopsis HSFA2, HSFA4a, and HSFA7a in the heat shock response and cytosolic protein response. Bot. Stud. 2018;59:15. doi: 10.1186/s40529-018-0231-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Sung D.Y., Vierling E., Guy C.L. Comprehensive expression profile analysis of the Arabidopsis Hsp70 gene family. Plant Physiol. 2001;126:789–800. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Guo J., Dai X., Xu W., Ma M. Overexpressing GSH1 and AsPCS1 simultaneously increases the tolerance and accumulation of cadmium and arsenic in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chemosphere. 2008;72:1020–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Song J., Feng S.J., Chen J., Zhao W.T., Yang Z.M. A cadmium stress-responsive gene AtFC1 confers plant tolerance to cadmium toxicity. BMC Plant Biol. 2017;17:187. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1141-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Chen J., Yang L., Yan X., Liu Y., Wang R., Fan T., Ren Y., Tang X., Xiao F., Liu Y., et al. Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor ZAT6 Positively Regulates Cadmium Tolerance through the Glutathione-Dependent Pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016;171:707–719. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Song W.Y., Martinoia E., Lee J., Kim D., Kim D.Y., Vogt E., Shim D., Choi K.S., Hwang I., Lee Y. A Novel Family of Cys-Rich Membrane Proteins Mediates Cadmium Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004;135:1027–1039. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Morel M., Crouzet J., Gravot A., Auroy P., Leonhardt N., Vavasseur A., Richaud P. AtHMA3, a P1B-ATPase Allowing Cd/Zn/Co/Pb Vacuolar Storage in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008;149:894–904. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Zhang J., Martinoia E., Lee Y. Vacuolar Transporters for Cadmium and Arsenic in Plants and their Applications in Phytoremediation and Crop Development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018;59:1317–1325. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcy006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Mills R.F., Krijger G.C., Baccarini P.J., Hall J.L., Williams L.E. Functional expression of AtHMA4, a P1B-type ATPase of the Zn/Co/Cd/Pb subclass. Plant J. 2003;35:164–176. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Van Hoewyk D., Takahashi H., Inoue E., Hess A., Tamaoki M., Pilon-Smits E.A.H. Transcriptome analyses give insights into selenium-stress responses and selenium tolerance mechanisms in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2008;132:236–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.01002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Huang J., Zhang Y., Peng J.S., Zhong C., Yi H.Y., Ow D.W., Gong J.M. Fission Yeast HMT1 Lowers Seed Cadmium through Phytochelatin-Dependent Vacuolar Sequestration in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012;158:1779–1788. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.192872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Kim Y.O., Kang H. Comparative expression analysis of genes encoding metallothioneins in response to heavy metals and abiotic stresses in rice (Oryza sativa) and Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018:1–10. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2018.1486177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Sanz-Fernández M., Rodríguez-Serrano M., Sevilla-Perea A., Pena L., Mingorance M.D., Sandalio L.M., Romero-Puertas M.C. Screening Arabidopsis mutants in genes useful for phytoremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017;335:143–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Kim D.Y., Bovet L., Maeshima M., Martinoia E., Lee Y. The ABC transporter AtPDR8 is a cadmium extrusion pump conferring heavy metal resistance. Plant J. 2007;50:207–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Kim D.Y., Bovet L., Kushnir S., Noh E.W., Martinoia E., Lee Y. AtATM3 Is Involved in Heavy Metal Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006;140:922–932. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.074146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Park J., Song W.Y., Ko D., Eom Y., Hansen T.H., Schiller M., Lee T.G., Martinoia E., Lee Y. The phytochelatin transporters AtABCC1 and AtABCC2 mediate tolerance to cadmium and mercury. Plant J. 2012;69:278–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Song W.Y., Park J., Mendoza-Cozatl D.G., Suter-Grotemeyer M., Shim D., Hortensteiner S., Geisler M., Weder B., Rea P.A., Rentsch D., et al. Arsenic tolerance in Arabidopsis is mediated by two ABCC-type phytochelatin transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:21187–21192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013964107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Sánchez-Bermejo E., Castrillo G., del Llano B., Navarro C., Zarco-Fernández S., Martinez-Herrera D.J., Leo-del Puerto Y., Muñoz R., Cámara C., Paz-Ares J., et al. Natural variation in arsenate tolerance identifies an arsenate reductase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4617. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Sawaki Y., Iuchi S., Kobayashi Y., Kobayashi Y., Ikka T., Sakurai N., Fujita M., Shinozaki K., Shibata D., Kobayashi M., et al. STOP1 regulates multiple genes that protect arabidopsis from proton and aluminum toxicities. Plant Physiol. 2009;150:281–294. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.134700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Iuchi S., Koyama H., Iuchi A., Kobayashi Y., Kitabayashi S., Kobayashi Y., Ikka T., Hirayama T., Shinozaki K., Kobayashi M. Zinc finger protein STOP1 is critical for proton tolerance in Arabidopsis and coregulates a key gene in aluminum tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:9900–9905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700117104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Larsen P.B., Geisler M.J.B., Jones C.A., Williams K.M., Cancel J.D. ALS3 encodes a phloem-localized ABC transporter-like protein that is required for aluminum tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004;41:353–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Skipsey M., Knight K.M., Brazier-Hicks M., Dixon D.P., Steel P.G., Edwards R. Xenobiotic Responsiveness of Arabidopsis thaliana to a Chemical Series Derived from a Herbicide Safener. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:32268–32276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.252726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Gandia-Herrero F., Lorenz A., Larson T., Graham I.A., Bowles D.J., Rylott E.L., Bruce N.C. Detoxification of the explosive 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in Arabidopsis: Discovery of bifunctional O- and C-glucosyltransferases. Plant J. 2008;56:963–974. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Landa P., Prerostova S., Langhansova L., Marsik P., Vanek T. Transcriptomic response of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. roots to ibuprofen. Int. J. Phytoremediation. 2017;19:695–700. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2016.1267697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Weisman D., Alkio M., Colón-Carmona A. Transcriptional responses to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-induced stress in Arabidopsis thaliana reveal the involvement of hormone and defense signaling pathways. BMC Plant Biol. 2010;10:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Behringer C., Bartsch K., Schaller A. Safeners recruit multiple signalling pathways for the orchestrated induction of the cellular xenobiotic detoxification machinery in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2011;34:1970–1985. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Manabe Y., Tinker N., Colville A., Miki B. CSR1, the Sole Target of Imidazolinone Herbicide in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007;48:1340–1358. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcm105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Subramanian S., Schnoor J.L., Van Aken B. Effects of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Their Hydroxylated Metabolites (OH-PCBs) on Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017;51:7263–7270. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b01538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.DeRidder B.P., Dixon D.P., Beussman D.J., Edwards R., Goldsbrough P.B. Induction of Glutathione S-Transferases in Arabidopsis by Herbicide Safeners. Plant Physiol. 2002;130:1497–1505. doi: 10.1104/pp.010066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Nutricati E., Miceli A., Blando F., De Bellis L. Characterization of two Arabidopsis thaliana glutathione S-transferases. Plant Cell Rep. 2006;25:997–1005. doi: 10.1007/s00299-006-0146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Grzam A., Martin M.N., Hell R., Meyer A.J. γ-Glutamyl transpeptidase GGT4 initiates vacuolar degradation of glutathione S -conjugates in Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:3131–3138. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.05.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Merewitz E. Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants. Volume 1. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2016. Chemical Priming-Induced Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants; pp. 77–103. [Google Scholar]
- 251.Černý M., Novák J., Habánová H., Cerna H., Brzobohatý B. Role of the proteome in phytohormonal signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2016;1864:1003–1015. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Šimura J., Antoniadi I., Široká J., Tarkowská D., Strnad M., Ljung K., Novák O. Plant Hormonomics: Multiple Phytohormone Profiling by Targeted Metabolomics. Plant Physiol. 2018;177:476–489. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Černý M., Skalák J., Cerna H., Brzobohatý B. Advances in purification and separation of posttranslationally modified proteins. J. Proteom. 2013;92:2–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.05.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Hsu C.C., Zhu Y., Arrington J. V, Paez J.S., Wang P., Zhu P., Chen I.H., Zhu J.K., Tao W.A. Universal plant phosphoproteomics workflow and its application to tomato signaling in response to cold stress. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018:mcp.TIR118.000702. doi: 10.1074/mcp.TIR118.000702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Vandereyken K., Van Leene J., De Coninck B., Cammue B.P.A. Hub Protein Controversy: Taking a Closer Look at Plant Stress Response Hubs. Front. Plant Sci. 2018;9:694. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]