Abstract
Background
Tobacco curly shoot virus (TbCSV) is a monopartite begomovirus associated with betasatellite (Tobacco curly shoot betasatellite, TbCSB), which causes serious leaf curl disease on tomato and tobacco in China. It is interesting that TbCSV induced severe upward leaf curling in Nicotiana benthamiana, but in the presence of TbCSB, symptoms changed to be downward leaf curling. However, the mechanism of interactions between viral pathogenicity, host defense, viral-betasatellite interactions and virus-host interactions remains unclear.
Methods
In this study, RNA-seq was used to analyze differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in N. benthamiana plants infected by TbCSV (Y35A) and TbCSV together with TbCSB (Y35AB) respectively.
Results
Through mapping to N. benthamiana reference genome, 59,814 unigenes were identified. Transcriptome analysis revealed that a total of 4081 and 3196 DEGs were identified in Y35AB vs CK (control check) and Y35A vs CK, respectively. Both GO and KEGG analyses were conducted to classify the DEGs. Ten of the top 15 GO terms were enriched in both DEGs of Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, and these enriched GO terms mainly classified into three categories including biological process, cellular component and molecular function. KEGG pathway analysis indicated that 118 and 111 pathways were identified in Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, respectively, of which nine and six pathways were significantly enriched. Three major pathways in Y35AB vs CK involved in metabolic pathways, carbon metabolism and photosynthesis, while those in Y35A vs CK were related to Ribosome, Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism and DNA replication. We observed that 8 PR genes were significantly up-regulated and 44 LRR-RLK genes were significantly differentially expressed in Y35A treatment or in Y35AB treatment. In addition, 7 and 13 genes were identified to be significantly changed in biosynthesis and signal transduction pathway of brassinosteroid (BR) and jasmonic acid (JA) respectively.
Conclusions
These results presented here would be particularly useful to further elucidate the response of the host plant against virus infection.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12985-018-1044-1) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Begomovirus, Tobacco curly shoot virus, Betasatellite, Nicotiana benthamiana, RNA-seq
Background
Tobacco curly shoot virus (TbCSV), a monopartite begomovirus (genus Begomovirus, family Geminiviridae), was isolated from tobacco in Yunnan province, China in 2002 [1]. Some TbCSV isolates were identified associating with a betasatellite molecule (Tobacco curly shoot betasatellite, TbCSB) [2]. TbCSV is one of the most important pathogens causing leaf curl disease on tomato and tobacco, and is a severe constraint to crop yields. TbCSV consists of a circular single-stranded DNA genome that encodes 6 proteins, including AV1 (coat protein, CP) and AV2 in virion-sense strand whilst AC1 (replication-related, Rep), AC2 (transcriptional activator, TrAP), AC3 (replication enhancer, REn) and AC4 in complementary-sense strand [1]. TbCSB is a small circular single-stranded DNA molecule which encodes a sole protein βC1 [2].
Viral infection is a complicated procedure involving in the interaction between viruses and host plants. Understanding host responses to viral infection is advantageous in the development of effective strategies for virus control. In recent years, the interactions between viruses and host plants were clarified through analysis of transcriptomics [3–5]. RNA-seq is a recently developed approach to transcriptome profiling via deep-sequencing technologies, which provides a far more precise measurement of levels of transcripts and their isoforms than other methods [6]. Thus, this technique was widely applied in interpretation the interaction between virus infection and host plant. The multiple resistance mechanisms against cotton leaf curl disease (CLCuD) were revealed by the transcriptome analysis based on an RNA-seq in a naturally immune cotton species (Gossypium arboreum) caused by CLCuD [7]. The technology of transcriptomics and proteomics were employed to study the differential host gene expression during Mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MYMIV) and Mungbean yellow mosaic virus (MYMV) infection under natural conditions [8]. The differential regulations of host genes revealed to be involved in cell cycle, cell-wall biogenesis, chloroplast, photosynthesis, hormone and sulphur assimilation pathways which may contribute to symptom development in soybean plants [8]. Recently, a research performed RNA-seq-based transcriptome sequencing of Jatropha curcas mosaic virus-infected and healthy leaf tissues of J. curcas, which provides a repertoire of molecular components after viral infection [9]. Similarly, several host genes were identified to be involved in different cellular and physiological processes during the infection of other viruses, including South African cassava mosaic virus (SACMV) [10], Tomato yellow leaf curl Sardinia virus (TYLCSV), Mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MYMIV) [11, 12], and Chilli leaf curl virus (ChiLCV) [13].
At present, it has been reported that the infectious clone of TbCSV induced severe upward leaf curling in N. benthamiana, but in the presence of TbCSB the symptom changed to a downward leaf curl [14]. Thus, TbCSV may represent an evolutionary intermediate between the truly monopartite begomoviruses and those that require the association of betasatellite [14]. Moreover, studies showed that AC2 and AC4 proteins of TbCSV mediate suppression of RNA silencing [15], and βC1 protein of TbCSB could bind single- and double- stranded DNA to suppress host RNA silencing activities [16]. However, it remains unclear that the molecular mechanism of viral pathogenicity, host defense and viral-host interactions. In this study, in order to get insights into the molecular mechanisms in response to TbCSV infection in N. benthamiana plants, the transcriptome analysis of N. benthamiana infected by TbCSV or TbCSV/TbCSB was performed, including differentially expressed genes, GO enrichment, KEGG enrichment, pathogenesis-related (PR) protein genes, LRR-RLK genes, brassinosteroid and jasmonic acid pathways. These data contribute to a better knowledge on the molecular mechanisms of TbCSV- and TbCSV/TbCSB- host interaction, and serve as a basis for devising new strategies to control TbCSV/TbCSB disease complex.
Methods
Virus sources and agroinoculation
The infectious clones of TbCSV isolate Y35 (pBinY35A-1.9) (Y35A) and its betasatellite (pBinY35β-2.0) (Y35B) were provided by Professor Xueping Zhou in the Biotechnology Institute of Zhejiang University. Both viral infectious clones were introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105. N. benthamiana (accession: Nb-1) plants were grown in a greenhouse under a 16 h light and 8 h dark cycle at 26 °C. The Agrobacterium with infectious clones was infiltrated into N. benthamiana leaves at 4–6 leaf stage as previously described [2].
DNA extraction and PCR detection
Leaf samples were collected at 20 days-post inoculation (dpi) and total DNA were extracted using CTAB method [17]. The TbCSV-specific primers (TbCSV-F, 5′-ATGCCTCAGCCAAGAAAACTTTT-3′; TbCSV-R, 5′-TCAACACGACGACGTCTGTTCCC-3′) and TbCSB-specific primers (TbCSB-F, 5′-ATGACAATTAAATACAACAACAAG-3′; TbCSB-R, 5′-TCATACATTAGCTATTGTCCC-3′) were designed to amplify fragments of 1086 bp and 357 bp in size, respectively. PCR reactions were performed in a 20 μL volume with reaction mixtures containing 10 μL of 2 × Taq Master Mix (Novoprotein Scientific Inc., Shanghai, China), 0.5 μL of DNA, 0.25 μM of each primer and a proper volume of ddH2O. The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation for 30 s at 94 °C, annealing for 30 s at 52 °C, extension for 30–65 s at 72 °C (depending on primer pairs used in distinct reactions), and a final extension for 10 min at 72 °C.
Materials for RNA sequencing
Leaf tissues of N. benthamiana plants were sampled at 20 dpi, and were immediately frozen and ground in liquid nitrogen and stored at − 80 °C. After PCR detection, RNA-seq was performed for stored samples. Three treatments were setting as follows: plants infected with TbCSV alone (Y35A treatment); plants infected with TbCSV and TbCSB (Y35AB treatment); uninfected plants as control (CK). There are three biological replicates per treatment respectively.
RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
Total RNA was extracted from N. benthamiana leaf tissues with RNAiso Plus (TAKARA Bio, Inc) as manufacturer’s protocol. All RNA samples were first treated with gDNA Eraser (TAKARA Bio, Inc) and reverse-transcribed using a Prime Script RT reagent Kit (Perfect Real Time) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Library preparation for transcriptome sequencing
A total amount of 3 μg RNA per sample was used as input for RNA sample preparations. Sequencing libraries were generated using NEBNext® Ultra™ RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (NEB, USA) following manufacturer’s recommendations and index codes were added to attribute sequences to each sample. Briefly, mRNA was purifed by using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads. After fragmentation, the cDNA was synthesized, and NEBNext Adaptors with hairpin loop structures were ligated to prepare for hybridization. PCR products were purifed (AMPure XP system), and library quality was assessed by Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system [18]. Finally, nine libraries were successfully constructed, and were sequenced using HiSeq™ 2500 equipment (Illumina, SanDiego, CA, USA) by 50 bp single-end (SE50) methods.
Quality control
For sequence quality control, raw data (raw reads) of fastq format were firstly processed through in-house perl scripts. In this step, clean data (clean reads) were obtained by removing reads containing adapter, reads containing ploy-N and low quality reads from raw data. Meanwhile, Q20, Q30, GC-content and sequence duplication level of clean data were calculated. All the downstream analyses were based on the clean data with high quality [19].
Reads mapping to the reference genome
The draft sequence of the N. benthamiana reference genome have been downloaded from the SGN ftp site (ftp://ftp.solgenomics.net/genomes/Nicotiana_benthamiana/assemblies) directly [20]. Index of the reference genome was built using Bowtie v2.2.3 (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA) [21] and single-end clean reads were aligned to the reference genome using TopHat v2.0.12 (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA) (mismatch = 2) [22]. The TopHat was selected as the mapping tool for that TopHat can generate a database of splice junctions based on the gene model annotation file and thus a better mapping result than other non-splice mapping tools [23].
Quantification of gene expression level
HTSeq v0.6.1 was used to count reads numbers mapped to each gene [24]. And then FPKM (Fragments per kilobase of transcript sequence per millions base pairs sequenced) of each gene was calculated based on the length of the gene and reads count mapped to this gene. FPKM, expected number of Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript sequence per Millions base pairs sequenced, considers the effect of sequencing depth and gene length for the reads count at the same time, and is currently the most commonly used method for estimating gene expression levels [25].
Differential gene expression analysis
Differential expression analysis of Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK was performed using the DESeq R package (1.18.0) (parameters: negative binomial distribution-based statistic, BH-FDR corrected p-value < 0.05) [26], which provides statistical routines for determining differential expression in digital gene expression data using a model based on the negative binomial distribution. The resulting p-values were adjusted using the Benjamini and Hochberg’s approach for controlling the false discovery rate (FDR).
GO term and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
Gene Ontology (GO; http://www.geneontology.org) enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was implemented by the GOseq R package (corrected p-value < 0.05) [27], in which gene length bias was corrected. GO terms with corrected p-value less than 0.05 were considered significantly enriched by differential expressed genes. REVIGO was used for analysis of the enriched GO terms (http://revigo.irb.hr). KEGG (http://www.genome.jp/kegg) is a database resource for understanding high-level functions and utilities of the biological system from molecular-level information, especially large-scale molecular datasets generated by genome sequencing and other high-throughput experimental technologies. And KOBAS software was used to test the statistical enrichment of differential expression genes in KEGG pathways (corrected p-value < 0.05) [28].
Quantitative real-time PCR validation
To validate the RNA-seq data, quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was conducted to examine the selected pattern of DEGs. For reverse transcription, 1 μg of total RNA was treated with gDNA Eraser (TAKARA Bio, Inc) and reverse-transcribed using a Prime Script RT reagent Kit (Perfect Real Time) and oligo (dT) as the primer according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Primer sets were designed using AlleleID software (v6.0) (Additional file 1: Table S1). RT-qPCR was conducted by using NovoStart® SYBR qPCR Super Mix Plus (Novoprotein, Shanghai, China) on CFX 96 Real-Time System (Bio-Rad). Actin was used as a reference for calculating relative abundances using the 2-△△Ct method [29]. All RT-qPCR experiments were performed in triplicate.
Results
Plants with typical viral symptoms in Y35A and Y35AB treatments
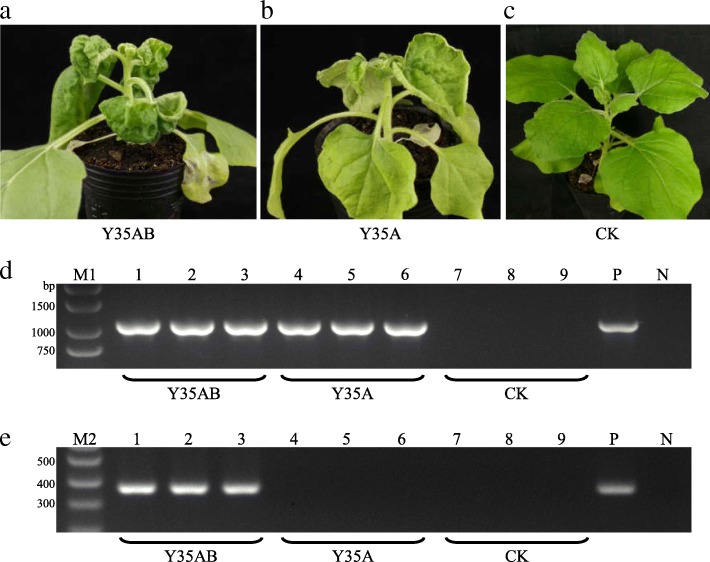
At 20 dpi, Y35A inoculated plants showed slight upward leaf curling and Y35AB inoculated plants showed severe downward leaf curl (Fig. 1a-c). PCR detection showed that they are consistent with expectations (Fig. 1d-e). Symptom observation and virus detection results showed that these plants were reliable for follow-up RNA-seq. Leaf tissues at same positions were collected from every treatment for RNA-seq.
Fig. 1.
Comparison of N. benthamiana plant symptoms of virus-infected with healthy control at 20 dpi. a Co-inoculation of TbCSV and TbCSB (Y35AB). b Solitary inoculation of TbCSV (Y35A). c Healthy control (CK). d Specific detection of TbCSV DNA-A in the nine plants for sequencing by PCR with primers TbCSV-F/TbCSV-R. e Specific detection of TbCSB in the nine plants for sequencing by PCR with primers TbCSB-F/TbCSB-R. M1: BM2000 + 1.5 kb DNA Marker; M2: DNA Marker I; 1–3: Y35AB plants; 4–6: Y35A plants; 7–9: CK plants; P: positive control; N: negative control, respectivly
Overview of transcriptome sequencing
To profile gene expression during virus infection, RNA-seq libraries were constructed for the control- and virus-inoculated N. benthamiana plants. 5.76 GB clean bases data and 59,814 unigenes were obtained from nine samples. There were 11834496–13118731, 12537134–15503750 and 11290015–12633203 clean reads in the three treatments of Y35AB, Y35A, and CK. The proportion of total reads that mapped to N. benthamiana genome of each sample was more than 96.09%, and that of uniquely mapped was above 72.69%. More than 95.58% of the clean reads had quality scores at the Q30 (an error probability for base calling of 0.1%) level [30]. Furthermore, the GC content ranges from 43.58 to 44.38%. The sequencing data are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Summary of the results of RNA-seq data
| Sample name | Y35AB-1 | Y35AB-2 | Y35AB-3 | Y35A-1 | Y35A-2 | Y35A-3 | CK-1 | CK-2 | CK-3 | mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw reads | 12166453 | 11965470 | 13272880 | 15527372 | 12560210 | 14214740 | 12646000 | 11302705 | 11794017 | 12827761 |
| Clean reads | 12032720 | 11834496 | 13118731 | 15503750 | 12537134 | 14192135 | 12633203 | 11290015 | 11782562 | 12769416 |
| Clean bases | 0.60G | 0.59G | 0.66G | 0.78G | 0.63G | 0.71G | 0.63G | 0.56G | 0.59G | 0.64 |
| Total mapped | 11620770 | 11438690 | 12605297 | 14934455 | 12075773 | 13732342 | 12346163 | 11139553 | 11524248 | 12379699 |
| 96.58% | 96.66% | 96.09% | 96.33% | 96.32% | 96.76% | 97.73% | 98.67% | 97.81% | 96.99% | |
| Uniquely mapped | 8961324 | 8847537 | 9609766 | 11389720 | 9176512 | 10320807 | 9238644 | 8316046 | 8564617 | 9380553 |
| 74.47% | 74.76% | 73.25% | 73.46% | 73.19% | 72.72% | 73.13% | 73.66% | 72.69% | 73.48% | |
| Q30 (%) | 95.74 | 95.68 | 95.58 | 96.20 | 96.08 | 96.14 | 95.76 | 95.70 | 95.80 | 95.85 |
| GC contents (%) | 43.58 | 43.75 | 44.11 | 44.15 | 44.23 | 44.38 | 43.93 | 43.80 | 43.92 | 43.98 |
Note: Clean reads: Reads from sequencing after filtering low-quality reads. Clean bases: The number of clean reads is multiplied by the length and converted to G. Q30: The percentage of bases with a Phred value >30
Analysis of DEGs
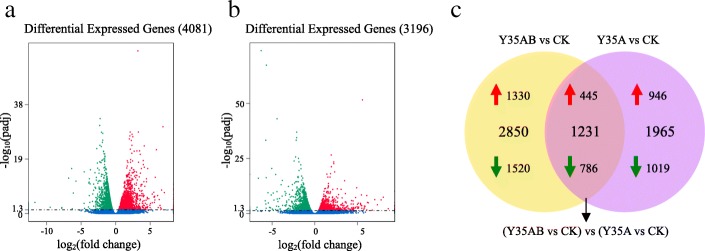
An adjusted p-value < 0.05 by DESeq was used to identify DEGs. In the Y35AB vs CK, 4081 DEGs (Fig. 2a, Additional file 2: Table S2), including 1775 up-regulated and 2306 down-regulated genes, were identified (Fig. 2c). And 3196 transcripts (1391 up-regulated and 1805 down-regulated genes) showed significant changes in Y35A vs CK (Fig. 2b, c and Additional file 3: Table S3). However, a total of 1232 DEGs in Y35AB vs CK overlap with those in Y35A vs CK, including 445 up-regulated and 786 down-regulated genes (Fig. 2c).
Fig. 2.
Volcano plots and Venn diagrams of DEGs (a-b). DEGs of Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK displayed by volcano plots. The abscissa shows the fold change difference in the expression of genes in different groups, and the vertical coordinates indicate the adjusted p-values for the differences in expression. Genes without significant differences are indicated by blue dots. The up-regulated genes are represented by red dots, and the down-regulated genes are represented by green dots. Venn diagrams showing the overlap in DEGs between Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK (c)
GO enrichment analysis
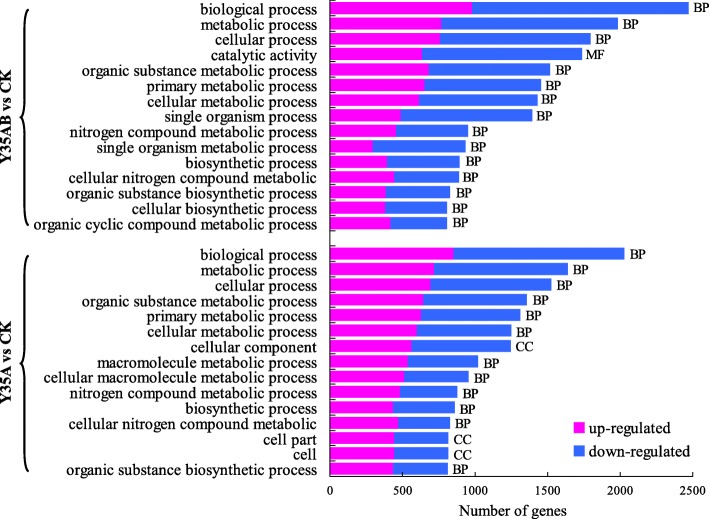
Gene Ontology, an internationally standardized gene function classification system, was used to classify the DEGs. The results were enriched in Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, and 124 and 76 of them were significantly enriched, respectively. Further, the top 15 GO functional annotation terms were listed, and 10 of them were shared between Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, associated with biological process, metabolic process, cellular process, organic substance metabolic process, primary metabolic process, cellular metabolic process, nitrogen compound metabolic process, biosynthetic process, cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process and organic substance biosynthetic process (Fig. 3, Additional files 4 and 5: Tables S4 and S5). Furthermore, it was found that these enriched GO terms mainly classified into biological process.
Fig. 3.
Most of the top 15 GO terms of three categories significantly enriched in DGEs of Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK. MF, molecular function; BP, biological process; CC, cellular component
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
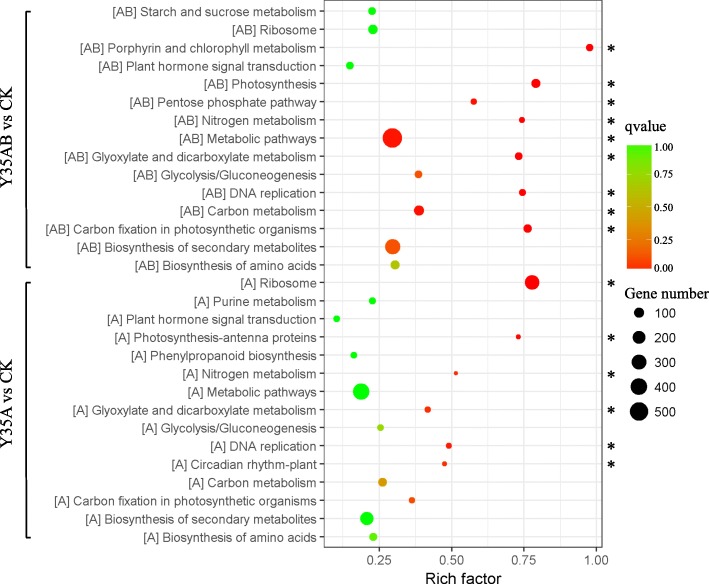
In order to further clarify molecular and biological functions of the genes, these DEGs were mapped to the KEGG database. KEGG pathway analysis indicated that 118 and 111 pathways were identified in Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, respectively, of which nine and six were significantly enriched with p-value< 0.05. The significantly enrichment analysis showed that DEGs of Y35AB vs CK involved in metabolic pathways, carbon metabolism, photosynthesis, carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, DNA replication, pentose phosphate pathway and nitrogen metabolism. While, DEGs involved in ribosome, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, DNA replication, circadian rhythm-plant, photosynthesis-antenna proteins and nitrogen metabolism were significantly enriched in Y35A vs CK (Fig. 4, Additional files 6 and 7: Tables S6 and S7).
Fig. 4.
KEGG pathways of the more or main significantly enriched in DGEs. The rich factor reflects the degree of enriched DGEs in a given pathway. The number of enriched DGEs in the pathway is indicated by the circle area, and the circle color represents the ranges of the corrected p-value
Metabolic pathway was the major pathway which contains the largest number of DEGs in both Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, but DEGs involved in metabolic pathway were not significantly different in Y35A vs CK, it further indicated that the presence of TbCSB differentially changed metabolic pathways in N. benthamiana. The rich factor of porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism pathway in Y35AB vs CK was near 1.00, the results showed that almost all genes in this pathway differentially expressed in TbCSV associated with betasatellite infected plants. Nevertheless, ribosome pathway might play an important role in response to TbCSV infection for the number of enriched DEGs in ribosome pathway wasnear to that enriched in metabolic pathways, and the rich factor was more than 0.75.
Screening of Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK common highly expressed DEGs
FPKM reflecting both the effect of sequencing depth and gene length for the read count, and is a commonly used method for estimating gene expression levels [31]. The fold change in gene expression was used to distinguish differentially expressed genes between samples because of the significance of digital gene expression profiles [32]. The intersection of highly expressed DGEs in Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK was considered. Finally, 17 DEGs were identified (|log2(Fold change)| ≥ 1 and FPKM≥50) from significantly enriched KEGG pathways, these 17 genes were shared between Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK all down-regulated, and involved in six pathways, including photosynthesis, porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, metabolic pathways, carbon metabolism, carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms, and glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism. Additionally, six DEGs that not enriched in any pathway were screened (|log2 (Fold change) | ≥ 2 and FPKM≥50), including four up-regulated and two down-regulated. In total, 23 candidate genes were screened as shown in Table 2.
Table 2.
Screened candidate genes in Y35AB and Y35A
| Gene symbol | Unigene ID | Protein properties | log2FCa | log2FCb | pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PsaFa | Niben101Scf 00271g04024 | photosystem I reaction center subunitIII, chloroplastic-like | -1.4180 | -1.1769 | Photosynthesis |
| PsaFb | Niben101Scf 02156g05001 | photosystem I reaction center subunit III, chloroplastic-like | -1.5190 | -1.6335 | Photosynthesis |
| PsaFc | Niben101Scf 04964g00002 | photosystem I reaction center subunit III, chloroplastic-like | -1.5257 | -1.2865 | Photosynthesis |
| PsaNa | Niben101Scf 17701g01020 | photosystem I reaction center subunit N, chloroplastic-like | -1.6702 | -1.5537 | Photosynthesis |
| PsaNb | Niben101Scf 35628g00001 | photosystem I reaction center subunit N, chloroplastic-like | -1.3129 | -1.0396 | Photosynthesis |
| ChlHa | Niben101Scf 04388g00011 | magnesium-chelatase subunit ChlH, chloroplastic-like | -1.6623 | -2.1794 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism |
| ChlHb | Niben101Scf 07214g00015 | magnesium-chelatase subunit ChlH, chloroplastic-like | -1.4638 | -1.8585 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism |
| BchP | Niben101Scf 06249g03002 | geranylgeranyl diphosphate reductase, chloroplastic-like | -1.8576 | -1.0521 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism |
| HemA | Niben101Scf 10063g00003 | glutamyl-tRNA reductase 1,chloroplastic-like | -1.4101 | -2.0903 | Porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism |
| DXS | Niben101Scf 00246g04005 | probable 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase, chloroplastic-like | -1.0040 | -1.0126 | Metabolic pathways |
| GME1-X1 | Niben101Scf 01696g06050 | GDP-mannose 3,5-epimerase 1-like,transcript variant X1 | -1.6022 | -1.1137 | Metabolic pathways |
| CAB3A | Niben101Scf 03961g00004 | chlorophyll a-b binding protein 50, chloroplastic-like | -1.1418 | -1.0719 | Metabolic pathways |
| GDCSa | Niben101Scf 02480g02012 | glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating), mitochondrial-like | -1.5732 | -1.1698 | Carbon metabolism |
| GDCSb | Niben101Scf 03839g04019 | glycine dehydrogenase (decarboxylating), mitochondrial-like | -1.1991 | -1.0395 | Carbon metabolism |
| rbcS | Niben101Scf 02381g04022 | ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small chain S41, chloroplastic-like | -1.2691 | 0.7603 | Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms |
| FBA1 | Niben101Scf 02864g04008 | fructose-bisphosphate aldolase 1,chloroplastic-like | -1.3167 | -1.0072 | Carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms |
| glsF | Niben101Scf 04198g01002 | ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase, chloroplastic-like | -1.1161 | -1.0704 | Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism |
| GRP | Niben101Scf 03052g00011 | glycine-rich protein-like | 2.1379 | 1.4647 | No pathway enriched |
| GRP3a | Niben101Scf 01084g05013 | glycine-rich protein 3-like | 3.9423 | 3.1735 | No pathway enriched |
| GRP3b | Niben101Scf 01084g03004 | glycine-rich protein 3-like | 2.0529 | 1.8836 | No pathway enriched |
| CAX3 | Niben101Scf 01329g00002 | vacuolar cation/proton exchanger 3-like | -2.2799 | -1.2535 | No pathway enriched |
| FSD1 | Niben101Scf 03679g03009 | Fe superoxide dismutas ,chloroplastic-like | -2.1527 | -1.9924 | No pathway enriched |
| PU | Niben101Scf 10524g02015 | putative uncharacterized protein | 2.0616 | 0.9243 | No pathway enriched |
FC Fold change
aY35AB vs. CK
bY35A vs. CK
Validation of the selected genes by RT-qPCR
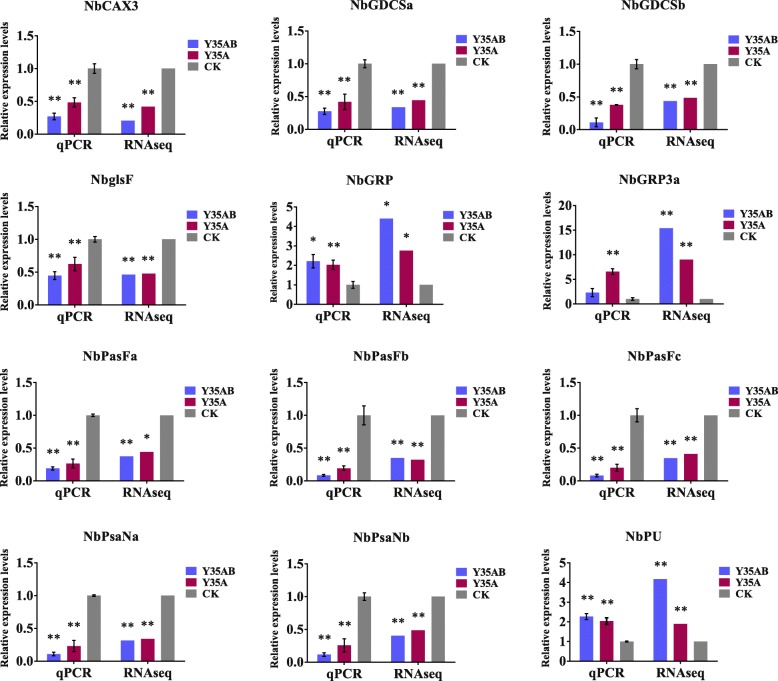
To validate the RNA-seq data, 12 genes were selected randomly for RT-qPCR analysis from the Table 2, including genes GDCSa, GDCSb, PsaFa, PsaFb, PsaFc, PsaNa, PsaNb, glsF, CAX3, GRP, GRP3a and PU. The results indicated that the genes expression patterns by RT-qPCR were consistent with that by transcriptome sequencing (Fig. 5), the fold changes between RNA-seq and RT-qPCR were different which maybe caused by the sensitive of methodology or the used samples between RNA-seq and RT-qPCR were not the same one.
Fig. 5.
Comparison of relative expression levels determined by RNA-seq and qPCR on 12 genes selected. All qPCR reactions were used three biological replica samples, repeated three times, and the data are presented as the mean ± SD. Relative expression levels are calculated from Ct values according to the 2–ΔΔCt method. Actin was the reference gene for these qPCR experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared with CK, “*” indicate significant difference (0.01 ≤ p < 0.05), “**” indicate extremely significant difference (P < 0.01)
Analysis of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes
An important feature of the plant defense in response to pathogen attack is the induction and accumulation of various PR proteins which are also a part of systematic acquired resistance (SAR). There were 29 PR genes identified by a local BLAST in RNA-seq dataset and online BLAST analysis based on reported PR family genes in N. tabacum. Among them, eight genes (27.6%) were significantly up-regulated, including PR-2 (Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like), PR-3 (Chitinase 8, glycoside hydrolase), PR-5 (Pathogenesis-related thaumatin superfamily protein), PR-11 (Chitinase-3-like protein 2), PR-17 (Plant basic secretory protein family protein), of them four genes were found in Y35AB vs CK, and five genes were observed in Y35A vs CK (Table 3).
Table 3.
Screened PRP family genes
| PR family | Unigene ID | Protein properties | log2FCa | qvaluea | log2FCb | qvalueb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR1 | Niben101Scf13926g01014 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein, allergen V5/Tpx-1-related | ||||
| Niben101Scf03376g03004 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein, allergen V5/Tpx-1-related | |||||
| Niben101Scf00107g03008 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein, allergen V5/Tpx-1-related | |||||
| Niben101Scf01999g07002 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein, allergen V5/Tpx-1-related | |||||
| PR2 | Niben101Scf01001g00005 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like, Glycoside hydrolase, family 17 | ||||
| Niben101Scf01001g00004 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like, Glycoside hydrolase, family 17 | |||||
| Niben101Scf01001g00003 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like, Glycoside hydrolase, family 17 | Inf | 0.023496 | |||
| Niben101Ctg13736g00004 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like, Glycoside hydrolase, family 17 | Inf | 1.94E-04 | |||
| Niben101Scf04869g03002 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like, Glycoside hydrolase, family 17 | 3.9490 | 0.038646 | 5.4381 | 2.14E-04 | |
| Niben101Scf01001g00006 | Glucan endo-1,3-beta-glucosidase-like, Glycoside hydrolase, family 17 | |||||
| PR3 | Niben101Scf02041g00002 | Chitinase 8, Glycoside hydrolase, family 19 | 5.1058 | 1.99E-05 | ||
| PR4 | Niben101Scf01400g00014 | Thaumatin-like protein | ||||
| Niben101Scf03436g01016 | Thaumatin-like protein | |||||
| PR5 | Niben101Scf00126g00008 | Pathogenesis-related thaumatin superfamily protein | 0.9949 | 0.027102 | ||
| Niben101Scf05554g05006 | Pathogenesis-related thaumatin superfamily protein | 1.4585 | 3.24E-08 | |||
| PR6 | Niben101Scf00953g05001 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein, allergen V5/Tpx-1-related | ||||
| Niben101Scf04053g01004 | Cysteine-rich secretory protein, allergen V5/Tpx-1-related | |||||
| PR9 | Niben101Scf03460g04004 | Peroxidase 53, Haem peroxidase | ||||
| Niben101Scf07182g05012 | Peroxidase 53, Haem peroxidase | |||||
| PR10 | Niben101Scf03526g00006 | Major pollen allergen Bet v 1-M/N, Bet v I type allergen | ||||
| Niben101Scf10735g00016 | Major pollen allergen Bet v 1-M/N, Bet v I type allergen | |||||
| Niben101Scf02474g01024 | Major pollen allergen Bet v 1-M/N, Bet v I type allergen | |||||
| Niben101Scf01938g04007 | Major pollen allergen Bet v 1-M/N, Bet v I type allergen | |||||
| PR11 | Niben101Scf06295g04023 | Chitinase-3-like protein 2, Glycoside hydrolase superfamily | 4.4843 | 0.007133 | ||
| Niben101Scf01789g04010 | Chitinase-3-like protein 2, Glycoside hydrolase superfamily | |||||
| PR17 | Niben101Scf03385g02011 | Plant basic secretory protein family protein, uncharacterised protein family | 2.7696 | 6.69E-04 | ||
| Niben101Scf03385g01006 | Plant basic secretory protein family protein, uncharacterised protein family | |||||
| Niben101Scf01341g01002 | Plant basic secretory protein family protein, uncharacterised protein family | |||||
| Niben101Ctg10643g00004 | Plant basic secretory protein family protein, uncharacterised protein family |
log2FC > 0, up-regulated, log2FC < 0, down-regulated. Inf: the readcount of control (CK) was zero. Blank lattices show genes expression has no significant difference
FC Fold change
aY35AB vs. CK
bY35A vs. CK
Analysis of LRR-RLKs genes
Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinases (LRR-RLKs) are the largest of receptor-like kinases in plants and play crucial roles in development and stress responses. In the present study, We combined RNA-seq dataset obtained LRR-RLK sequences with previously NCBI reported sequences to perform analysis, results showed that a total of 71 unigenes were identified potential LRR-RLK genes in RNA-seq dataset, however, 44 significantly different unigenes were observed. Among them, 18 unigenes were found in Y35AB vs CK with 10 unigenes down-regulated and the other 8 unigenes up-regulated, and 32 unigenes expressed in Y35A vs CK, with 20 and 12 unigenes were down-regulated and up-regulated, respectively. Five unigenes were commonly regulated in both Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, including one up-regulated and four down-regulated unigenes (Table 4).
Table 4.
Screened DEGs of LRR-RLKs
| Unigene ID | Protein properties | log2FCa | qvaluea | log2FCb | qvalueb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Niben101Scf13404g00002 | Brassinosteroid LRR receptor kinase-like; BRI1 | -0.8361 | 0.000272 | ||
| Niben101Scf07123g01015 | Elicitor-inducible leucine-rich repeats receptor-like protein | 5.5080 | 0.000289 | ||
| Niben101Scf00104g02013 | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 17-like | 0.8664 | 0.021066 | ||
| Niben101Scf04252g00009 | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 17-like | 1.8551 | 0.003213 | ||
| Niben101Scf09559g00005 | F-box/LRR-repeat MAX2 homolog A-like | 0.8581 | 0.018415 | ||
| Niben101Scf15394g00006 | F-box/LRR-repeat protein 14-like | -0.8927 | 0.013552 | ||
| Niben101Scf20268g00001 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase ERECTA | -0.7116 | 0.011214 | ||
| Niben101Scf05301g03002 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase ERL1 | -0.7516 | 0.013687 | -0.7589 | 0.013627 |
| Niben101Scf00247g01007 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase ERL1 | -0.5633 | 0.024694 | ||
| Niben101Scf11723g02003 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase ERL1 | -0.6679 | 0.026512 | -0.7100 | 0.017084 |
| Niben101Scf03619g03004 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase FEI2 | -0.5426 | 0.018415 | ||
| Niben101Scf03925g01010 | LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase GSO1 | 2.3343 | 0.007479 | 3.1551 | 0.041202 |
| Niben101Scf02203g04006 | Plant intracellular Ras-group-related LRR protein 4-like | -0.6640 | 0.048845 | ||
| Niben101Scf00206g00014 | putative F-box/LRR-repeat protein At5g02700 | 1.5307 | 0.020135 | ||
| Niben101Scf00073g04006 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g07650 | -1.4546 | 0.005161 | ||
| Niben101Scf00244g03004 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g06840 | -0.6603 | 0.021347 | ||
| Niben101Scf00418g02007 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g37250 | -0.5934 | 0.047527 | ||
| Niben101Scf00920g09027 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At5g48740 | -1.1084 | 0.000766 | ||
| Niben101Scf01061g08014 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g20940 | -1.0192 | 0.001468 | ||
| Niben101Scf01278g09008 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g56140 | 0.9239 | 0.023952 | ||
| Niben101Scf02357g08010 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g07650 | -0.6424 | 0.001803 | ||
| Niben101Scf02665g15003 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g06840 | -0.5769 | 0.044996 | ||
| Niben101Scf02827g07005 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At3g47570 | 2.3756 | 0.027087 | ||
| Niben101Scf03098g00011 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g34110 | -1.2224 | 3.35E-06 | ||
| Niben101Scf03262g02006 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g24230 | -0.6865 | 0.030882 | ||
| Niben101Scf03445g05005 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g26540 | -0.8802 | 0.000669 | ||
| Niben101Scf03735g07013 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g36180 | 2.0409 | 0.002356 | ||
| Niben101Scf05348g01026 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g12460 | -1.3373 | 3.02E-05 | ||
| Niben101Scf05405g07003 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At3g47570 | 2.0599 | 0.003076 | ||
| Niben101Scf05405g07006 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At3g47570 | 1.5589 | 0.022376 | ||
| Niben101Scf05767g05006 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g20940 | -0.8478 | 0.000497 | ||
| Niben101Scf05977g01008 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g12460 | -1.2826 | 8.11E-05 | ||
| Niben101Scf06144g00013 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g20940 | -0.9557 | 7.81E-05 | ||
| Niben101Scf06151g02014 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67720 | 0.7683 | 0.046840 | ||
| Niben101Scf06562g02013 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g26540 | -0.5968 | 0.021640 | -0.9943 | 2.01E-05 |
| Niben101Scf06789g03005 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67720 | 0.9483 | 0.042093 | 0.9711 | 0.042650 |
| Niben101Scf07034g06018 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g36180 | -0.8501 | 0.034812 | ||
| Niben101Scf07515g02006 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g56140 | 0.6846 | 0.005558 | ||
| Niben101Scf07681g01013 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g20940 | -0.7450 | 0.014076 | ||
| Niben101Scf07695g01023 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g30520 | 0.7628 | 0.001146 | ||
| Niben101Scf07736g01007 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g63430 | 0.6791 | 0.006612 | ||
| Niben101Scf08134g02008 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g37250 | -0.5193 | 0.047055 | -0.7817 | 0.000797 |
| Niben101Scf10101g00023 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At4g30520 | 0.6651 | 0.002463 | ||
| Niben101Scf11047g00001 | probable LRR receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g16250 | 0.7640 | 0.047280 |
log2FC > 0, up-regulated, log2FC < 0, down-regulated. Blank lattices show genes expression has no significant difference
FC Fold change
aY35AB vs. CK
bY35A vs. CK
Analysis of brassinosteroid and jasmonic acid pathway
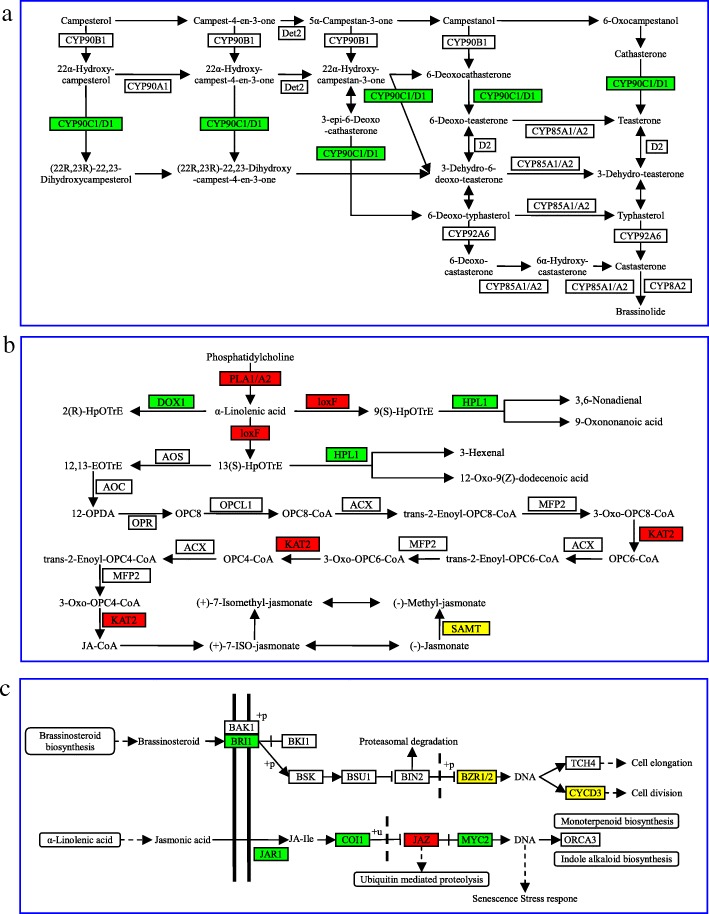
Plant hormones are not only essential for growth and development, but also play crucial roles in plant defense responses [33, 34]. The transcriptome data showed that only one brassinosteroid (BR) synthesis-related gene, 3-epi-6-deoxocathasterone 23-monooxygenase (CYP90C1/D1) was significantly decreased upon virus infection (Fig. 6a), it is likely result in a reduction of brassinosteroid. By contrast, expressions of jasmonic acid (JA) -ralated biosynthesis genes DOX1, HPL1, SAMT-X1 were decreased and PLA1/A2, loxF, KAT2, SAMT-X2 were significantly increased upon virus infection (Fig. 6b). We conjecture that the expression level of jasmonic acid might was increase. In addition, part of BR and JA signaling genes expression level were also altered, BRI1, BZR2, CYCD3-X2 were down-regulated and BZR1, CYCD3-X1 were up-regulated in BR signal transduction pathway, and JAR1, COI1, MYC2 were down- regulated and JAZ1, JAZ2 were up-regulated in JA signal transduction pathway (Fig. 6c). All synthesis- and signal transduction- related significantly difference expressed unigenes of BR and JA pathway shown in Table 5.
Fig. 6.
DEGs of BR and JA in biosynthesis and signal transduction pathway. a BR biosynthesis pathway, b JA biosynthesis pathway, c signal transduction pathway of BR and JA, respectively. Genes with red background were up-regulated, green background were down-regulated, yellow background some were up-regulated and some were down-regulated
Table 5.
Significant difference expression unigenes of BR and JA pathway
| Gene symbol | Unigene ID | Protein properties | log2FCa | qvaluea | log2FCb | qvalueb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | CYP90C1/D1 | Niben101Scf05764g04013 | 3-epi-6-deoxocathasterone 23-monooxygenase | -0.8193 | 0.019172 | ||
| BRI1 | Niben101Scf13404g00002 | Brassinosteroid LRR receptor kinase-like, BRI1 | -0.8361 | 2.72E-04 | |||
| BZR1 | Niben101Scf03110g05009 | Brassinosteroid resistant 1 | 0.5592 | 0.025611 | |||
| BZR2 | Niben101Scf06112g01006 | Brassinosteroid resistant 2 | -1.2497 | 7.36E-07 | |||
| CYCD3-X1 | Niben101Scf05643g01012 | Cyclin D3, 3 protein, plant | 1.3753 | 1.44E-07 | |||
| CYCD3-X1 | Niben101Scf02445g10017 | Cyclin D3, 3 protein, plant | 1.2863 | 0.002511 | |||
| CYCD3-X2 | Niben101Scf00107g02002 | Cyclin D3, 2 protein, plant | -0.8767 | 0.017675 | -1.2925 | 2.43E-04 | |
| JA | PLA1/A2 | Niben101Scf00711g02004 | Triacylglycerol lipase SDP1-like; Phospholipase A1/A2 | 1.8227 | 0.003036 | ||
| DOX1 | Niben101Scf07070g02002 | Alpha-dioxygenase | -3.8126 | 7.60E-13 | -3.9498 | 7.95E-14 | |
| loxF | Niben101Scf05407g00001 | Linoleate 9S-lipoxygenase-like | 0.9407 | 0.021540 | |||
| HPL1 | Niben101Scf00313g08016 | Fatty acid hydroperoxide lyase, HPL1 | -1.2170 | 1.14E-09 | -0.9629 | 7.37E-07 | |
| HPL1 | Niben101Scf02207g11009 | Fatty acid hydroperoxide lyase, HPL1 | -1.4966 | 1.06E-05 | |||
| KAT2 | Niben101Scf10189g02009 | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase 2, peroxisomal | 0.6201 | 0.007053 | |||
| SAMT-X1 | Niben101Scf05122g00005 | Salicylate carboxymethyltransferase-like | -1.4545 | 2.97E-11 | -0.8505 | 2.96E-04 | |
| SAMT-X2 | Niben101Scf01146g12006 | Salicylate carboxymethyltransferase-like | 1.6487 | 0.010833 | |||
| JAR1 | Niben101Scf01076g00005 | Jasmonic acid-amino synthetase | -0.6477 | 0.003456 | -0.8340 | 0.001705 | |
| COI1 | Niben101Scf02280g08005 | Coronatine-insensitive 1, COI1 | -0.6123 | 0.024317 | -0.8990 | 2.81E-04 | |
| JAZ1 | Niben101Scf00298g01006 | Jasmonate ZIM-domain protein 1 | 0.7577 | 0.039355 | |||
| JAZ2 | Niben101Scf07798g03026 | Jasmonate ZIM domain-containing protein | 0.7728 | 3.95E-04 | |||
| MYC2 | Niben101Scf15224g00002 | Transcription factor MYC2 | -0.6238 | 0.042856 |
log2FC > 0, up-regulated, log2FC < 0, down-regulated. Blank lattices show genes expression has no significant difference
FC Fold change
aY35AB vs. CK
bY35A vs. CK
Discussion
TbCSV is a serious threat to many crops in China. In this study, RNA-seq -based transcriptomic characterization and comparative analysis of TbCSV-infected N. benthamiana with control plants was used to shed some light on understanding the molecular interactions of this pathosystem. 4081 and 3196 DEGs were screened from Y35AB vs CK and Y35A vs CK, respectively. Among the top 15 enriched physiological pathways, the porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, photosynthesis and pentose phosphate pathway were significantly affected in Y35AB vs CK. It suggested that, the disorder of these pathways might be responsible to the more serious leaf curling symptom on Y35AB-infected N. benthamiana plants. In addition, previous reports showed that βC1, an essential pathogenicity protein encoded by betasatellite, is required for symptom induction and RNA silencing suppression [2, 16, 35–37]. Thus, βC1 protein might contribute to the specific changes of those genes or biological pathways in Y35AB-infected plants.
In our study, the DEGs expression with high levels that mainly concerned with photosynthesis-related genes including photosynthesis, porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolismand carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms were down-regulated in N. benthamiana plants infected with TbCSV. Meanwhile, the KEGG pathway analysis showed significant enrichments of the photosynthesis, and the porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism pathway in Y35AB-infected plants, with higher rich factor. It has been reported that photosynthesis-related genes could be affected upon virus infection such as Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) [38], Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) [39], Rice stripe virus (RSV) [40, 41] and Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV) [42]. And the chloroplast, one of the most dynamic organelles ofplant cell, plays an active part in the defense response and is crucial for inter organelle signaling [43]. Therefore, viruses need to suppress the chloroplast-mediated defense by employing pathogenicity factors, such as effector proteins, for successful infections [44, 45]. Furthermore, a previous study showed that a Radish leaf curl betasatellite (RaLCB) damages the structural and functional integrity of chloroplasts, leading to inhibition of photosynthesis and symptom formation [46]. Some photosynthesis-related genes were down-regulated during both Y35A and Y35AB infections, indicating that these genes might participate in the interaction between TbCSV and N. benthamiana.
An important feature of the plant defense response to pathogen attack is the induction and accumulation of various PR proteins, which are also a part of systematic acquired resistance (SAR) [47]. Previously, PR proteins were divided into five families based on their localization, isoelectric point, molecular mass, and biological activity [48]. PR proteins are currently categorized into 17 families. At present, besides PR-6 is predicted by automated computational analysis based on a genomic sequence (gene ID: LOC107768382), nine out of 17 families, including PR-1, PR-2 [49], PR-3, PR-4, PR-5 [50], PR-9 [51], PR-10 [52], PR-11 [53], PR-17 [54] families were reported that associated with the acquired resistance to pathogen infections. Among these PR proteins, PR-1 is generally considered as a marker gene of disease resistance [55]. Based on NCBI retrieval and local BLAST analysis, 29 PR genes in N. benthamiana were identified. In the present study, the expression levels of 8 PR genes were found to be significantly regulated in virus-infected N. benthamiana plants (Table 3). It was previously reported that in pathogens-infected wheat, the genes encoding peroxidase, PR-1, PR-2, PR-3, PR-4, and PR-5 were induced after 6–12 h and reached the highest levels at 36–48 h [56, 57]. In our research, leaf tissues of N. benthamiana plants for RNA-seq assays were collected at 20 dpi, and the transcript levels of some PR genes (8 out of 29) were regulated significantly. For subsequent research, the expression of PR genes can be determined in a time course study. Based on our research, we speculated that some types of PR proteins might play roles in defense response to TbCSV infection.
In plants, many cellular signaling transductions are mediated by receptor-like kinases (RLKs). Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinases (LRR-RLKs) are the largest group of receptor-like kinases in plants and play crucial roles in development and stress responses [58]. LRR-RLKs regulate a wide range of plant growth and development, including meristem development [59, 60], secondary growth [61], microsporogenesis and embryogenesis [62]. Besides, some LRR-RLKs mediated plant resistance against bacterial [63, 64] or viral pathogens [65, 66]. In this study, 71 LRR-RLKs genes were identified. Among them, 44 were differentially expressed in virus-infected N. benthamiana plants. The results showed that these LRR-RLKs genes might play important roles in N. benthamiana responses to TbCSV infection. By contrast, in the present of TbCSB, less number of LRR-RLKs genes were regulated (Table 4).
BR and JA are two important plant hormones that play crucial roles in plant growth and development [67] and also involved in plant defense responses to pathogen infections [68–70]. In the BR signaling pathway, BRASSINAZOLE RESISTANT (BZR) is a transcription factor, which orchestrating plant developmental and physiological processes by regulating BR-target gene expression [71, 72]. BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 1 (BRI1) is a brassinosteroid receptor, of which ubiquitously expresses plasma membrane-localized protein kinase [73], belonging to an LRR-RLKs subfamily [74]. For the JA signaling transduction, the perception of JA is mediated by the co-receptor CORONATINE INSENSITIVE 1 (COI1), which is an F-box protein cooperated with a family of the JASMONATE ZIM-domain (JAZ) transcriptional proteins. Upon the pathogens infection, bioactive JAs promote direct interaction between COI1 and JAZ proteins and then trigger the SCF-COI1 complex, resulting in poly-ubiquitination and degradation of the JAZ proteins. Ultimately, a variety of transcription factors could be activated for the expression of the JA-responsive genes [75]. Besides, MYC2 is a bHLH (basic helix-loop-helix) transcription factor and a positive regulator of JA responses [76]. A study has shown that rhizobacterium-mediated induction of JA reduces the symptoms of CMV infection in Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia plants [77]. In this study, BRI1, BZR1, BZR2, CYCD3, JAR1, COI1, JAZ and MYC2 genes were significantly regulated under the infection of TbCSV (Fig. 6). It suggested that BR and JA pathways played a role in response to TbCSV infection.
Conclusion
In this study, a genome-wide transcript profile was obtianed for N. benthamiana plant infected by TbCSV or plus TbCSB using RNA-seq approaches, and genes involved in plant defense system were found to be significantly regulated after TbCSV and TbCSV /TbCSB infection. The information provided in our study would be particularly useful for investigating the molecular mechanisms concerning begomovirus-host interaction and excavate resistance genes.
Additional files
Table S1. Primers used for RT-qPCR. (DOCX 18.9 kb)
Table S2. List of DEGs between Y35AB vs CK. (XLS 796 kb)
Table S3. List of DEGs between Y35A vs CK. (XLS 629 kb)
Table S4. Enriched GO terms of DEGs between Y35AB vs CK. (XLS 3.15 mb)
Table S5. Enriched GO terms of DEGs between Y35A vs CK. (XLS 2.83 mb)
Table S6. Enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs between Y35AB vs CK. (XLS 216 kb)
Table S7. Enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs between Y35A vs CK. (XLS 181 kb)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Professor Xueping Zhou in the Biotechnology Institute of Zhejiang University for providing the infectious clones of TbCSV isolate Y35 (Y35A) and its betasatellite (Y35B).
Funding
This research work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. XDJK2017A006 and XDJK2015D039), National Natural Science Founding of China (Grant No. 31772127), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015 M572431), and Chongqing Postdoctoral Science special Foundation (Xm2015120).
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials described in the manuscript are available in the Additional files 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.
Authors’ contributions
LQ conceived and designed the study and revised the paper. KL, GW, ML and MM performed the experiments and made analysis of the data. JD, MS and XS participated preparation including discussion and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Ke Li, Email: lihai8730@163.com.
Gentu Wu, Email: wugtu@163.com.
Mingjun Li, Email: lmj603@163.com.
Mingge Ma, Email: 1248289377@qq.com.
Jiang Du, Email: dujiang20080803@163.com.
Miao Sun, Email: 445879215@qq.com.
Xianchao Sun, Email: sunxianchao@163.com.
Ling Qing, Phone: 0086-023-68250695, Email: qling@swu.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Xie Y, Zhou XP, Zhang ZK, Qi YJ. Tobacco curly shoot virus isolated in Yunnan is a distinct species of Begomovirus. Chin Sci Bull. 2002;47:197–200. doi: 10.1360/02tb9047. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhou XP, Xie Y, Tao XR, Zhang ZK, Li ZH, Fauquet CM. Characterization of DNAβ associated with begomoviruses in China and evidence for co-evolution with their cognate viral DNA-A. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:237–247. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.18608-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pacheco R, Garcia-Marcos A, Manzano A, Garcia De Lacoba M, Camanes G, Garcia-Agustin P, Ramon Diaz-Ruiz J, Tenllado F. Comparative analysis of transcriptomic and hormonal responses to compatible and incompatible plant-virus interactions that lead to cell death. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012;25:709–723. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-11-11-0305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kamitani M, Nagano AJ, Honjo MN, Kudoh H, Kummerli R. RNA-Seq reveals virus-virus and virus-plant interactions in nature. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016;92:1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Miozzi L, Napoli C, Sardo L, Accotto GP. Transcriptomics of the interaction between the monopartite phloem-limited geminivirus Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Sardinia Virus and Solanum lycopersicum highlights a role for plant hormones, autophagy and plant immune system fine tuning during infection. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10:57–63. doi: 10.1038/nrg2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Naqvi RZ, Zaidi SS, Akhtar KP, Strickler S, Woldemariam M, Mishra B, Mukhtar MS, Scheffler BE, Scheffler JA, Jander G, et al. Transcriptomics reveals multiple resistance mechanisms against cotton leaf curl disease in a naturally immune cotton species, Gossypium arboreum. Sci Rep. 2017;7:15880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15963-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pavan Kumar BK, Kanakala S, Malathi VG, Gopal P, Usha R. Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of yellow mosaic diseased soybean. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol. 2016;26:224–234. doi: 10.1007/s13562-016-0385-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sood A, Chauhan RS. Comparative NGS transcriptomics unravels molecular components associated with mosaic virus infection in a bioenergy plant species, Jatropha curcas L. BioEnergy Res. 2017;10:129–145. doi: 10.1007/s12155-016-9783-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pierce EJ, Rey MEC. Assessing global transcriptome changes in response to South African Cassava Mosaic Virus [ZA-99] infection in susceptible Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS One. 2013;8:e67534. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yadav RK, Chattopadhyay D. Differential soybean gene expression during early phase of infection with Mungbean yellow mosaic India virus. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:5123–5134. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kundu A, Patel A, Paul S, Pal A. Transcript dynamics at early stages of molecular interactions of MYMIV with resistant and susceptible genotypes of the leguminous host, vigna mungo. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kushwaha N, Sahu PP, Prasad M, Chakraborty S. Chilli leaf curl virus infection highlights the differential expression of genes involved in protein homeostasis and defense in resistant chilli plants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99:4757–4770. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li ZH, Xie Y, Zhou XP. Tobacco curly shoot virus DNAβ is not necessary for infection but intensifies symptoms in a host-dependent manner. Phytopathology. 2005;95:902–908. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-95-0902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cui XF, Zhou XP. AC2 and AC4 proteins of Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus and Tobacco curly shoot virus mediate suppression of RNA silencing. Chin Sci Bull. 2004;49:2607–2612. doi: 10.1360/982004-131. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cui XF, Li GX, Wang DW, Hu DW, Zhou XP. A Begomovirus DNAβ-encoded protein binds DNA, functions as a suppressor of RNA silencing, and targets the cell nucleus. J Virol. 2005;79:10764–10775. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10764-10775.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Abarshi MM, Mohammed IU, Wasswa P, Hillocks RJ, Holt J, Legg JP, Seal SE, Maruthi MN. Optimization of diagnostic RT-PCR protocols and sampling procedures for the reliable and cost-effective detection of Cassava brown streak virus. J Virol Methods. 2010;163:353–359. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.10.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Xiong HC, Guo HJ, Xie YD, Zhao LS, Gu JY, Zhao SR, Li JH, Liu LX. RNAseq analysis reveals pathways and candidate genes associated with salinity tolerance in a spaceflight-induced wheat mutant. Sci Rep. 2017;7:2731. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03024-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen JW, Hou K, Qin P, Liu H, Bin Y, Yang WT, Wu W. RNA-Seq for gene identification and transcript profiling of three Stevia rebaudiana genotypes. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:571–581. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Deng XG, Zhu T, Peng XJ, Xi DH, Guo H, Yin Y, Zhang DW, Lin HH. Role of brassinosteroid signaling in modulating tobacco mosaic virus resistance in Nicotiana benthamiana. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20579. doi: 10.1038/srep20579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 2012;9:357. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim D, Pertea G, Trapnell C, Pimentel H, Kelley R, Salzberg SL. TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013;14:R36. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL, Pachter L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 2012;7:562–578. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:166–169. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1105–1111. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Anders S, Huber W. Differential expression of RNA-Seq data at the gene level – the DESeq package. Heidelberg: Embl; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010;11:R14. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3787–3793. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-△△Ct method. Methods. 2012;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Peng H, He XJ, Gao J, Ma HX, Zhang ZM, Shen Y, Pan GT, Lin HJ. Transcriptomic changes during maize roots development responsive to Cadmium (Cd) pollution using comparative RNAseq-based approach. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464:1040–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G, Mortazavi A, Kwan G, Van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ, Pachter L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:511–515. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Audic S, Claverie JM. The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res. 1997;7:986–995. doi: 10.1101/gr.7.10.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Whitham SA, Yang C, Goodin MM. Global impact: elucidating plant responses to viral infection. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006;19:1207. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Alazem M, Lin NS. Roles of plant hormones in the regulation of host–virus interactions. Mol Plant Pathol. 2015;16:529. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Saeed M, Behjatnia SA, Mansoor S, Zafar Y, Hasnain S, Rezaian MA. A single complementary-sense transcript of a geminiviral DNA beta satellite is determinant of pathogenicity. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2005;18:7–14. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cui X, Tao X, Xie Y, Fauquet CM, Zhou X. A DNAβ associated with Tomato yellow leaf curl China virus is required for symptom induction. J Virol. 2004;78:13966–13974. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.13966-13974.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Saunders K, Norman A, Gucciardo S, Stanley J. The DNA beta satellite component associated with ageratum yellow vein disease encodes an essential pathogenicity protein (beta C1) Virology. 2004;324:37–47. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bhat S, Folimonova SY, Cole AB, Ballard KD, Lei Z, Watson BS, Sumner LW, Nelson RS. Influence of host chloroplast proteins on Tobacco mosaic virus accumulation and intercellular movement. Plant Physiol. 2013;161:134–147. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.207860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mochizuki T, Ogata Y, Hirata Y, Ohki ST. Quantitative transcriptional changes associated with chlorosis severity in mosaic leaves of tobacco plants infected with Cucumber mosaic virus. Mol Plant Pathol. 2014;15:242–254. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Xu Y, Zhou XP. Role of rice stripe virus NSvc4 in cell-to-cell movement and symptom development in Nicotiana benthamiana. Front Plant Sci. 2012;3:269. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kong LF, Wu JX, Lu LN, Xu Y, Zhou XP. Interaction between Rice stripe virus disease-specific protein and host PsbP enhances virus symptoms. Mol Plant. 2014;7:691–708. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Balasubramaniam M, Kim BS, Hutchens-Williams HM, Loesch-Fries LS. The photosystem II oxygen-evolving complex protein PsbP interacts with the coat protein of Alfalfa mosaic virus and inhibits virus replication. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2014;27:1107–1118. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-14-0035-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bhattacharyya D, Chakraborty S. Chloroplast: the Trojan horse in plant-virus interaction. Mol Plant Pathol. 2017;19:504–18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Jelenska J, Yao N, Vinatzer BA, Wright CM, Brodsky JL, Greenberg JT. A J domain virulence effector of Pseudomonas syringae remodels host chloroplasts and suppresses defenses. Curr Biol. 2007;17:499. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.02.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Petre B, Saunders DG, Sklenar J, Lorrain C, Win J, Duplessis S, Kamoun S. Candidate effector proteins of the rust pathogen melampsora larici-populina target diverse plant cell compartments. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2015;28:689–700. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-01-15-0003-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bhattacharyya D, Gnanasekaran P, Kumar RK, Kushwaha NK, Sharma VK, Yusuf MA, Chakraborty S. A geminivirus betasatellite damages the structural and functional integrity of chloroplasts leading to symptom formation and inhibition of photosynthesis. J Exp Bot. 2015;66:5881–5895. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Van LL, Rep M, Pieterse CM. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2006;44:135–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lcvan L, Eavan S. The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities, and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 1999;55:85–97. doi: 10.1006/pmpp.1999.0213. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Antoniw JF, Ritter CE, Pierpoint WS, Loon LCV. Comparison of three pathogenesis-related proteins from plants of two cultivars of tobacco infected with TMV. J Gen Virol. 1980;47:79–87. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-1-79. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Loon LCV. Regulation of changes in proteins and enzymes associated with active defence against virus infection. In: Wood RKS, editor. Active defense mechanisms in plants. New York: Plenum Press; 1982. pp. 247–273. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lagrimini LM, Burkhart W, Moyer M, Rothstein S. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the lignin-forming peroxidase from tobacco: molecular analysis and tissue-specific expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:7542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang Y, Zhang ZL, Jiang CH, Chang AX, Yang AG, Luo CG, Wang SM, Wang YY. Cloning and expression analysis of a pathogenesis related protein gene NtPR10 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) Chin Tob Sci. 2017;38:1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Melchers LS, Apotheker-De Groot M, Van Der Knaap JA, Ponstein AP, Sela-Buurlage MB, Bol JF, Cornelissen BJC, Van Den Elzen PJM, Linthorst HJM. A new class of tobacco chitinases homologous to bacterial exo-chitinases displays antifungal activity. Plant J. 1994;5:469–480. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1994.5040469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Okushima Y, Koizumi N, Kusano T, Sano H. Secreted proteins of tobacco cultured BY2 cells: identification of a new member of pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Mol Biol. 2000;42:479–488. doi: 10.1023/A:1006393326985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ryals JA, Neuenschwander UH, Willits MG, Molina A, Steiner HY, Hunt MD. Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell. 1996;8:1809–1819. doi: 10.1105/tpc.8.10.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pritsch C, Muehlbauer GJ, Bushnell WR, Somers DA, Vance CP. Fungal development and induction of defense response genes during early infection of wheat spikes by Fusarium graminearum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2000;13:159–169. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2000.13.2.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pritsch C, Vance CP, Bushnell WR, Somers DA, Hohn TM, Muehlbauer GJ. Systemic expression of defense response genes in wheat spikes as a response to Fusarium graminearum infection. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 2001;58:1–12. doi: 10.1006/pmpp.2000.0308. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Shiu SH, Bleecker AB. Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.181141598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Clark SE, Williams RW, Meyerowitz EM. The CLAVATA1 gene encodes a putative receptor kinase that controls shoot and floral meristem size in Arabidopsis. Cell. 1997;89:575–585. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schoof H, Lenhard M, Haecker A, Mayer KF, Jürgens G, Laux T. The stem cell population of Arabidopsis shoot meristems in maintained by a regulatory loop between the CLAVATA and WUSCHEL genes. Cell. 2000;100:635. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80700-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Agusti J, Lichtenberger R, Schwarz M, Nehlin L, Greb T. Characterization of transcriptome remodeling during cambium formation identifies MOL1 and RUL1 as opposing regulators of secondary growth. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1001312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Albrecht C, Russinova E, Hecht V, Baaijens E, De Vries S. The Arabidopsis thaliana SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASES1 and 2 control male gametogenesis. Plant Cell. 2005;17:3337–3349. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.036814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gómezgómez L, Boller T. FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell. 2000;5:1003. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D, Caniard A, Jones JD, Boller T, Felix G. Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell. 2006;125:749. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Elizabeth PBF, Santos AA, Luz DF, Waclawovsky AJ, Chory J. The geminivirus nuclear shuttle protein is a virulence factor that suppresses transmembrane receptor kinase activity. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2545–2556. doi: 10.1101/gad.1245904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Santos AA, Lopes KV, Apfata JA, Fontes EP. NSP-interacting kinase, NIK: a transducer of plant defence signalling. J Exp Bot. 2010;61:3839. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kim TW, Wang ZY. Brassinosteroid signal transduction from receptor kinases to transcription factors. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2010;61:681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.092057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.De Vleesschauwer D, Xu J, Hofte M. Making sense of hormone-mediated defense networking: from rice to Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:611. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bruyne LD, Hfte M, Vleesschauwer DD. Connecting growth and defense: the emerging roles of brassinosteroids and gibberellins in plant innate immunity. Mol Plant. 2014;7:943–959. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nakashita H, Yasuda M, Nitta T, Asami T, Fujioka S, Arai Y, Sekimata K, Takatsuto S, Yamaguchi I, Yoshida S. Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J. 2003;33:887–898. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Clouse SD. Brassinosteroid signal transduction: from receptor kinase activation to transcriptional networks regulating plant development. Plant Cell. 2011;23:1219–1230. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.084475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Wang WF, Bai MY, Wang ZY. The brassinosteroid signaling network - a paradigm of signal integration. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2014;21:147. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2014.07.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Schumacher K, Chory J. Brassinosteroid signal transduction: still casting the actors. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2000;3:79. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(99)00038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Li J, Chory J. A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involved in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell. 1997;90:929–938. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kim H, Park D, Hahn Y. Identification of novel RNA viruses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa): an Alphapartitivirus, a Deltapartitivirus, and a Marafivirus. Gene. 2017;638:7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chini A, Fonseca S, Fernández G, Adie B, Chico JM, Lorenzo O, Garcíacasado G, Lópezvidriero I, Lozano FM, Ponce MR. The JAZ family of repressors is the missing link in jasmonate signalling. Nature. 2007;448:666. doi: 10.1038/nature06006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ryu CM, Murphy JF, Mysore KS, Kloepper JW. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria systemically protect Arabidopsis thaliana against Cucumber mosaic virus by a salicylic acid and NPR1-independent and jasmonic acid-dependent signaling pathway. Plant J. 2004;39:381–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Primers used for RT-qPCR. (DOCX 18.9 kb)
Table S2. List of DEGs between Y35AB vs CK. (XLS 796 kb)
Table S3. List of DEGs between Y35A vs CK. (XLS 629 kb)
Table S4. Enriched GO terms of DEGs between Y35AB vs CK. (XLS 3.15 mb)
Table S5. Enriched GO terms of DEGs between Y35A vs CK. (XLS 2.83 mb)
Table S6. Enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs between Y35AB vs CK. (XLS 216 kb)
Table S7. Enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs between Y35A vs CK. (XLS 181 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data and materials described in the manuscript are available in the Additional files 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7.