Abstract
Viral encephalitis by definition is the result of human virus affecting the brain and sparing the meninges. The other nervous system manifestations are meningitis, meningoencephalitis, encephalomyelitis, and encephalomyeloradiculitis. Encephalitis can involve any age group from children to old people. The severity of the disease depends on the viral agent and the host immune system. The patient can present with fever, headache, seizure, neurological deficit, or altered sensorium. Laboratory investigations, imaging, and cerebrospinal fluid analysis are crucial in the diagnosis of encephalitis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings may be nonspecific or specific and plays a major role in the diagnosis of encephalitis and predicting the possible cause. This pictorial essay reviews the MRI findings of common types of viral encephalitis.
KEYWORDS: Encephalitis, magnetic resonance imaging, meningoencephalitis, viral encephalitis
INTRODUCTION
Viral encephalitis is the result of human virus affecting the central nervous system (CNS). There are two types of encephalitis – primary and secondary. Primary encephalitis is when the virus involves the brain and the spinal cord directly, while secondary encephalitis also called postinfectious encephalitis occurs when infection spreads to brain from another part of the body. The diagnosis is usually obtained based on laboratory investigations. However, imaging plays an important role in early diagnosis and for follow-up. Imaging can show nonspecific findings such as focal or diffuse cerebral altered signal intensity, cerebral edema, diffusion restriction, hemorrhages, necrosis, and enhancement. In some conditions, specific diagnosis can be obtained based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. In this pictorial essay, we reviewed the MRI findings of patients with encephalitis referred to our hospital between January 2012 and January 2017 and subsequently proved on serology or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests. The clinical, radiological features, and course are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Summary of magnetic resonance imaging and clinical findings in various common viral encephalitis
DISCUSSION
Herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE) Types 1 and 2:
HSE is the most common cause of fatal sporadic necrotizing viral encephalitis. The incidence is two cases per million people per year. They are associated with high mortality and morbidity without proper treatment. There are two types described as follows: neonatal HSE and adult type. In adults and older children, HSE commonly involves temporal and frontal lobes and is caused by Type 1 herpes simplex virus (HSV). In neonates, it is commonly caused by Type 2 HSV, being acquired during delivery and there is diffuse brain involvement. CSF and PCR values are usually gold standard for diagnosis; however, MRI findings are considered important for aiding to diagnosis.
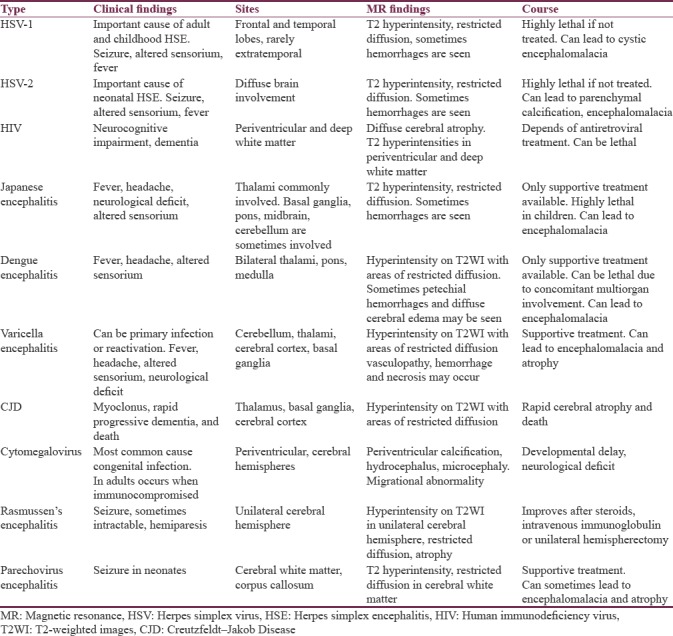
Over 95% of the cases of HSE is caused by (HSV)–1. The infection is caused by gaining access through the nasopharyngeal mucosa and reaches brain along the branches of trigeminal nerve. The viral gene remains latent within until any triggering event occurs such as trauma, stress, immune suppression status, or sometimes may occur spontaneously. Patients commonly present with fever, headache, photophobia, generalized weakness, and seizures.[1] MR imaging shows hypersensitivity involving the cortical and the subcortical regions of bilateral temporal, frontal lobes, and insula on T2-weighted images (WI). There may be associated restricted diffusion, gyral swelling, loss of gray-white matter interface, and mild or no enhancement [Figure 1a–c]. Petechial hemorrhages are usually seen after 48 h. Involvement of extratemporal regions, cingulated gyrus can also be sometimes seen. Atrophy and encephalomalacia of the corresponding regions may occur as sequelae. Early diagnosis and treatment with acyclovir is crucial. Common differential diagnoses to be considered are infarcts and status epilepticus.[2] Status epileptics present unilaterally and typically involves mainly the cortex. Postictal edema usually is more widespread and predominantly affects the entire hemispheric cortex.[3]
Figure 1.
A 40-year-old male patient with herpes simplex virus encephalitis presented with altered sensorium. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery coronal image (a) shows hyperintensity in the right perisylvian and temporal regions (arrows). Diffusion-weighted imaging image (b) shows restricted diffusion in the right temporal region (arrowhead). Postcontrast T1-weighted images (c) shows mild enhancement in the right temporal cortex (open arrow)
HSV 2 infection is common in neonates and is due to transplacental transmission or infection from birth canal. It commonly causes diffuse brain edema seen as hyperintensity on T2WI. Associated diffusion restriction and hemorrhages may be also be seen.
Human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is infection that has direct and indirect effect on CNS. HIV initially affects the dendritic cells in the skin and mucosa. It then binds to CD4 receptors in the Langerhans cells, then infects, and destroys the CD4 positive T-cells leading to a burst of viremia which causes a widespread tissue dissemination. The HIV-infected cells can pass across the blood-brain barrier and penetrate the brain.
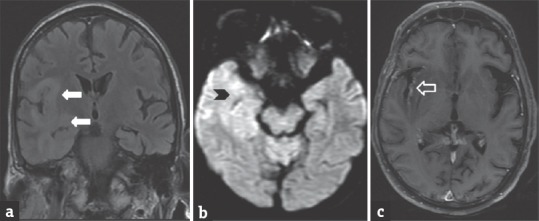
MRI shows volume loss with widening of the ventricle and sulci. Reduced gray-white matter volume is seen in the medial frontal gyri. White matter is near to normal on T1W Images and shows patchy bilateral symmetrical hyperintensity on T2WI/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequence [Figure 2a–c]. HIV lesions do not usually enhance on contrast or show restricted diffusion.[4] Differential diagnosis includes progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML is an opportunistic infection caused by John Cunningham virus. On imaging, PML shows multifocal lesions commonly involving the posterior fossa white matter (more specifically the middle cerebellar peduncle). Solitary lesions tend to present in the subcortical U fibers.[5]
Figure 2.
A 34-year-old male patient, positive for human immunodeficiency virus with low CD4 count presented with seizure. Coronal T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery image (a) shows hyperintensity in cortex and subcortical white matter of the right temporal region (arrows). Diffusion-weighted imaging (b) shows mild restricted diffusion in the right temporal region (arrowhead). TIW sagittal image (c) shows diffuse cerebral atrophy (open arrow)
Japanese encephalitis
The causative virus is spread by a mosquito and the disease is commonly found in the South-Asian population; humans are accidental host in the disease. Patients present with symptoms such as fever, rigors, headache, focal neurological deficit, and sometimes may be fatal. Patients who survive may be left with permanent neurological or psychotic sequelae.
MRI characteristics are T2/FLAIR hyperintensity in bilateral thalami [Figure 3a–c]. Unilateral involvement has also been reported, however, to a far less extent. Other regions of involvement are basal ganglia, substantia nigra, red nucleus, pons, hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and cerebellum. In some patients, hemorrhagic transformation may occur, especially in thalami. There is usually no enhancement following contrast administration.[6] Differential diagnosis to be considered is HSV encephalitis.
Figure 3.
A 15-year-old female patient with Japanese encephalitis presented with bilateral visual disturbances. T2W (a), T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (b) images shows hyperintensity in bilateral posterior thalami (arrows). Postcontrast T1W image (c) shows no contrast enhancement
Dengue encephalitis
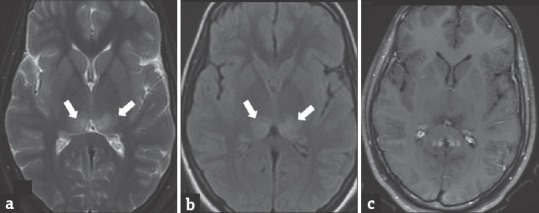
Dengue is a single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the flavivirus genus. This causes dengue fever and dengue hemorrhagic fever. Although dengue is not clinically a neurotropic virus, dengue encephalitis occurs due to neural infection by the virus. Analysis must be done whenever possible to isolate the virus or the antibody from the serum. Studies show that MRI after serology plays a major role in the diagnosis. MRI shows hyperintensity in bilateral thalami and globus pallidus on T2WI. Other sites that may be involved are hippocampus, temporal lobe, and the pons [Figure 4a].[7] There may be restricted diffusion and variable contrast enhancement [Figure 4b and c].
Figure 4.
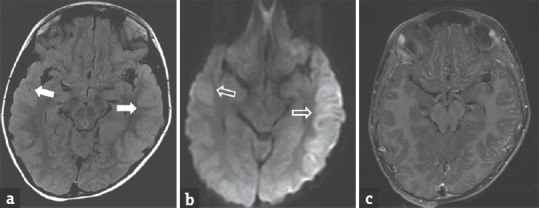
A 6-year-old male child with dengue encephalitis presenting with fever and seizure. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery image (a) shows hyperintensity in the bilateral temporal regions, better seen on left side (arrows). Diffusion-weighted image (b) shows restricted diffusion (open arrows). Postcontrast T1 image (c) shows no enhancement
Varicella zoster encephalitis
The incidence of varicella-zoster has reduced since the introduction of varicella zoster vaccine in 1995. Despite the widespread use of the vaccine, varicella-zoster continues to cause CNS disease. Varicella-zoster encephalitis has a median age of 40–50 years at diagnosis and 30% of the cases are under 15 years. It is commonly seen in immunocompetent patients.[8] Symptoms are commonly seen 10 days after chickenpox rash or after varicella vaccination. Meningitis is seen in >50% and encephalitis is seen in 40% of the affected patients.
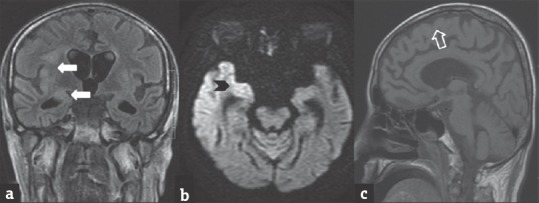
MRI findings include cerebellitis, myelitis with hyperintensities seen on T2W/FLAIR sequences. Restriction is usually seen on diffusion-weighted images (DWI). In varicella-zoster vasculopathy with stroke, T2 hyperintensities may be seen in cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, and deep white matter [Figure 5a and b]. Sometimes associated hemorrhages and necrosis may be present [Figure 5c]. Contrast enhancement is patchy and mild in varicella-zoster encephalitis.
Figure 5.
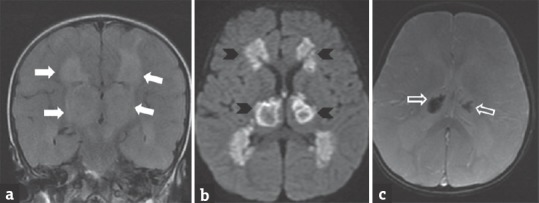
A 2-year-old male child with varicella zoster encephalitis presenting with fever, altered sensorium and later developed prolonged spasticity. Coronal fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (a) image shows hyperintensity in bilateral thalami and periventricular white region (arrows). Diffusion-weighted image (b) shows restricted diffusion (arrowheads). Gradient image (c) shows hemorrhage within bilateral thalami (open arrow)
Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease
Prion diseases are a spectrum of neuro-degenerative disease that includes Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease (CJD), Kuru, Gerstmann-Straussler-Schenker syndrome, and fatal familial insomnia. Out of these, CJD is the most common to affect the humans (90%), caused by proteinaceous infectious particles that are devoid of both DNA and RNA. They are four types of CJD, namely sporadic, familial, iatrogenic and variant. Clinical symptoms include dementia, cerebral atrophy, myoclonic jerks, sensory and psychiatric symptoms, Brownell Oppenheimer variant (cerebellar syndrome), and Heidenhain variant (cortical blindness). CJD affects the gray matter, more than the white matter. MR imaging shows T2/T2 FLAIR hyperintensities in the basal ganglia, posterior thalamus (Pulvinar sign), posterior medial thalamus (Hockey stick sign), and cerebral cortex [Figure 6a–c].[9]
Figure 6.
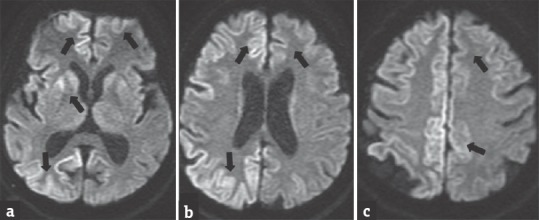
A 65-year-old male with Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease presenting with progressive weakness of limbs and reduced sensorium. Diffusion-weighted images (a-c) showing restricted diffusion in the right cerebral cortex, basal ganglia and left frontoparietal cortex (arrows). The patient deteriorated over a period of two months
Rasmussen's encephalitis
Although it is not part of the acute spectrum discussed, it shows more of a chronic infection picture. It is focal or localized encephalitis that shows clinical symptoms such as epilepsy, hemiparesis, and altered sensorium. Patients affected are between 14 months and 14 years with peak incidence at 6 years of age. Exact etiology of Rasmussen encephalitis is unknown. Viral infection and glutamate toxicity are the two possible etiologies. Although the initial MRI images do not show any finding, with passage of time hypersensitivity on T2W/FLAIR images are noted in the cortical and the subcortical white matter of the affected hemisphere [Figure 7a–c]. Minimal or no enhancement is seen. There may be other areas affected like basal ganglia. Cortical atrophy is noted in late stages.[10]
Figure 7.
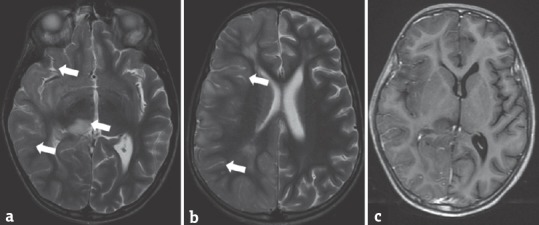
A 9-year-old boy with Rasmussen's encephalitis presented with fever and altered sensorium of 1-month duration. T2-weighted image (a and b) shows hyperintensities in the right thalamus and cerebral cortex (arrows). Postcontrast T1 W (c) image shows no significant enhancement
Cytomegalovirus encephalitis
Cytomegalovirus is one of the major causes of congenital infection in children. Out of these affected newborns, only 10% develop CNS manifestations. Clinically asymptomatic infants may show normal developmental milestones, whereas infants with clinical manifestations such as hepatosplenomegaly, petechiae, and jaundice have worse prognosis. Hearing loss and delayed development are associated long-term risk factors, starting with a general rule that the earlier the presentation, the more grave are the findings.
Imaging findings include microcephaly with ventriculomegaly, white matter volume loss, delayed myelination, and periventricular cysts. The abnormality in the cortex can extend from dysgenesis to lissencephalic pattern. T2/FLAIR images show myelin delay or destruction and white matter volume loss. There may be associated T2 hyperintensities with restricted diffusion [Figure 8a–c]. Periventricular calcifications/cysts with enlarged ventricles may also occur.
Figure 8.
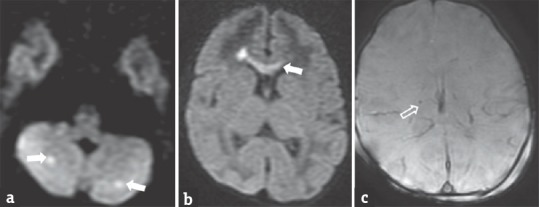
Neonate with cytomegalovirus encephalitis presented with irritable cry and worsening sensorium. Diffusion-weighted images (a and b) show restricted diffusion in the genu of the corpus callosum and bilateral cerebellar hemispheres (arrows). Gradient image (c) shows blooming in bilateral periventricular regions (open arrows), suggesting calcifications
Human parechovirus encephalitis
It can manifest in several forms – encephalitis, meningitis, sepsis, respiratory illness, and gastroenteritis. It is an important cause of seizure in the neonatal period. On MRI, T2/FLAIR hyperintensities with restricted diffusion may be seen in the white matter and corpus callosum [Figure 9a–c]. DWI is more sensitive in depicting these findings. Associated petechial hemorrhages may be present.[11]
Figure 9.
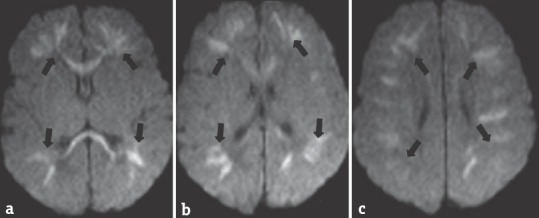
A 7-day-old neonate with parechovirus encephalitis presented with seizure and feeding difficulties. Diffusion-weighted images (a-c) showing restricted diffusion in bilateral cerebral white matter and corpus callosum (arrows). The neonate was symptomatically treated and improved
CONCLUSION
Each of the above-discussed encephalitis has its own typical clinical presentation and MRI characteristics. Knowledge about them helps not only in the diagnosis but also in the management.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Egdell R, Darren E, Solomon T. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis. BMJ. 2012;344:e3630. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e3630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.McCabe K, Tyler K, Tanabe J. Diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities as a clue to the diagnosis of herpes simplex encephalitis. Neurology. 2003;61:1015–6. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000082387.97051.f5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kramer RE, Lüders H, Lesser RP, Weinstein MR, Dinner DS, Morris HH, et al. Transient focal abnormalities of neuroimaging studies during focal status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 1987;28:528–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb03683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Becker JT, Maruca V, Kingsley LA, Sanders JM, Alger JR, Barker PB, et al. Factors affecting brain structure in men with HIV disease in the post-HAART era. Neuroradiology. 2012;54:113–21. doi: 10.1007/s00234-011-0854-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shah R, Bag AK, Chapman PR, Curé JK. Imaging manifestations of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Radiol. 2010;65:431–9. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2010.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Siu JC, Chan CY, Wong YC, Yuen MK. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of Japanese encephalitis. J Hong Kong Coll Radiol. 2004;7:76. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Varatharaj A. Encephalitis in the clinical spectrum of dengue infection. Neurol India. 2010;58:585–91. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.68655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pahud BA, Glaser CA, Dekker CL, Arvin AM, Schmid DS. Varicella zoster disease of the central nervous system: Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory features 10 years after the introduction of the varicella vaccine. J Infect Dis. 2011;203:316–23. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Finkenstaedt M, Szudra A, Zerr I, Poser S, Hise JH, Stoebner JM, et al. MR imaging of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Radiology. 1996;199:793–8. doi: 10.1148/radiology.199.3.8638007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cece H, Tokay L, Yildiz S, Karakas O, Karakas E, Iscan A, et al. Epidemiological findings and clinical and magnetic resonance presentations in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Int Med Res. 2011;39:594–602. doi: 10.1177/147323001103900228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gupta RK, Soni N, Kumar S, Khandelwal N. Imaging of central nervous system viral diseases. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35:477–91. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


