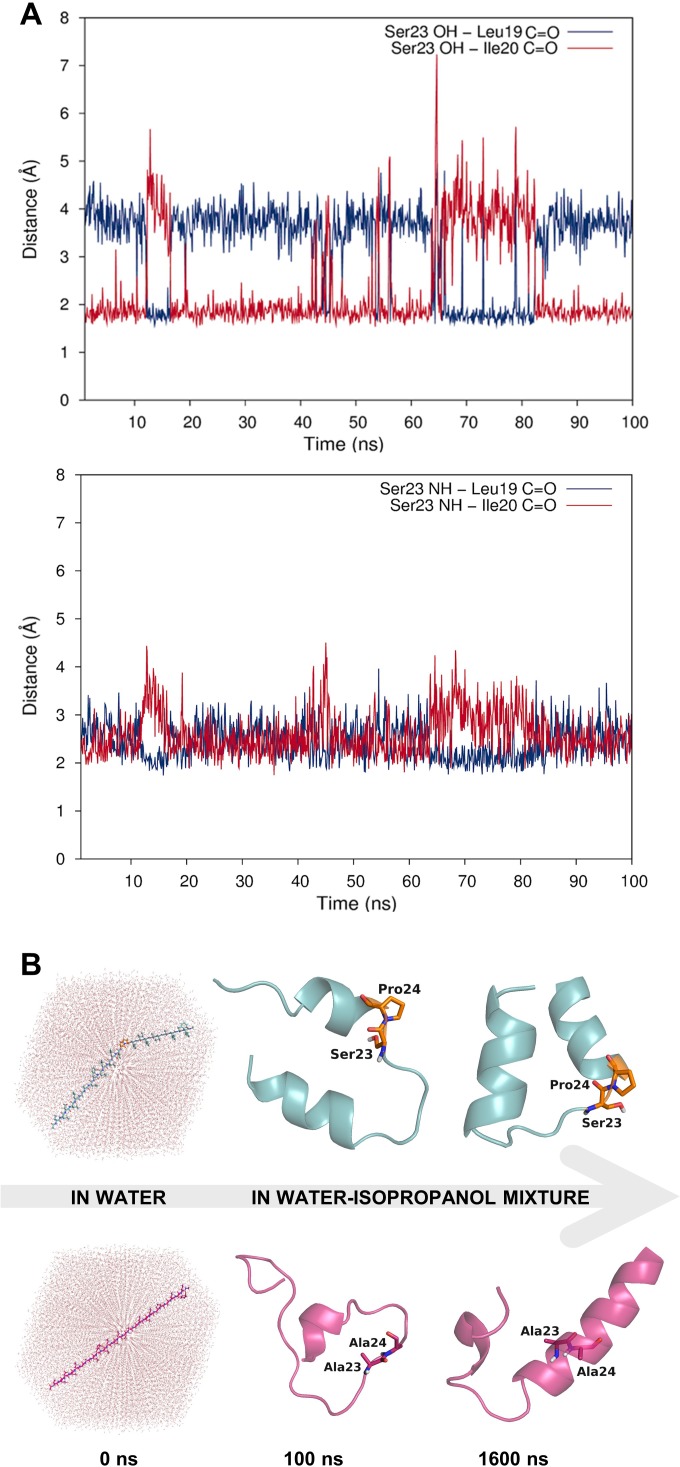
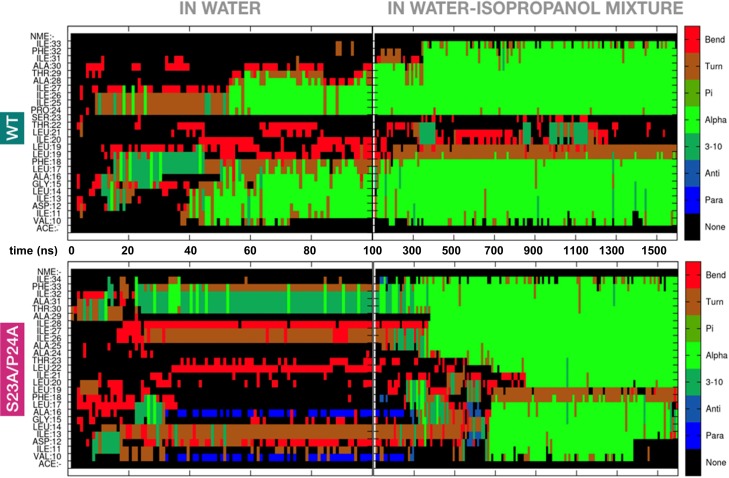
Figure 3. Dynamic hydrogen bonding around the Ser-Pro motif facilitates early folding of the RMH domain.
(A) Dynamic hydrogen bonding between the side chain hydroxyl (top panel) or backbone amide-NH (bottom panel) of Ser23 and the backbone amide-C=O of Leu19 and Ile20 measured during MD simulations of PglC in a POPE lipid bilayer. (B) Peptides corresponding to the RMH domains of wild-type (top) and S23A/P24A PglC (bottom) were folded from an extended conformation (left panel) for 100 ns in water (middle panel), followed by an additional 1500 ns in 20% isopropanol/water (right panel).