Abstract
The spontaneous rhythmic action potentials generated by the sinoatrial node (SAN), the primary pacemaker in the heart, dictate the regular and optimal cardiac contractions that pump blood around the body. Although the heart rate of humans is substantially slower than that of smaller experimental animals, current perspectives on the biophysical mechanisms underlying the automaticity of sinoatrial nodal pacemaker cells (SANCs) have been gleaned largely from studies of animal hearts. Using human SANCs, we demonstrated that spontaneous rhythmic local Ca2+ releases generated by a Ca2+ clock were coupled to electrogenic surface membrane molecules (the M clock) to trigger rhythmic action potentials, and that Ca2+–cAMP–protein kinase A (PKA) signaling regulated clock coupling. When these clocks became uncoupled, SANCs failed to generate spontaneous action potentials, showing a depolarized membrane potential and disorganized local Ca2+ releases that failed to activate the M clock. β-Adrenergic receptor (β-AR) stimulation, which increases cAMP concentrations and clock coupling in other species, restored spontaneous, rhythmic action potentials in some nonbeating “arrested” human SANCs by increasing intracellular Ca2+ concentrations and synchronizing diastolic local Ca2+ releases. When β-AR stimulation was withdrawn, the clocks again became uncoupled, and SANCs reverted to a nonbeating arrested state. Thus, automaticity of human pacemaker cells is driven by a coupled-clock system driven by Ca2+-cAMP-PKA signaling. Extreme clock uncoupling led to failure of spontaneous action potential generation, which was restored by recoupling of the clocks. Clock coupling and action potential firing in some of these arrested cells can be restored by β-AR stimulation–induced augmentation of Ca2+-cAMP-PKA signaling.
INTRODUCTION
Cells within the sinoatrial node (SAN), the heart’s pacemaker, generate spontaneous rhythmic action potentials that excite cardiac muscle to contract, enabling the heart to pump blood around the body. In pacemaker cells that reside within the SAN (SANCs), an ensemble of surface membrane–bound, voltage- and time-dependent ion channels, the so-called membrane or M clock [including hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels and the electrogenic Na+-Ca2+ exchanger (NCX)], is coupled to a “Ca2+ clock.” The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) that generates spontaneous local Ca2+ releases prompts the M clock to generate action potentials (1–9). Functions within each of these clocks (or “biological oscillators”) are driven by constitutively active Ca2+–adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cAMP)-protein kinase A (PKA) signaling that is intrinsic to SANCs (5). Clock functions are highly interdependent. The degree of coupling between the clocks dynamically varies and is an important factor in the regulation of normal SANC automaticity (10, 11). Whether a Ca2+ clock or coupled-clock system is actually involved in the automaticity of human SANCs, however, is currently unknown. We studied freshly isolated SANCs from human hearts to test two hypotheses: (i) that normal human SANC automaticity is regulated by intrinsic cAMP-dependent coupling of Ca2+ clock to M clocks, and (ii) that failure of automaticity in human SANCs can result from clock uncoupling that can be restored by activation of Ca2+-cAMP signaling intrinsic to SANCs by β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR) stimulation.
RESULTS
Ca2+ and membrane potential measurements at baseline and in response to β-AR stimulation
We isolated and studied morphologically healthy-appearing single SANCs from SAN tissue of donor human hearts (Fig. 1, A and B, and movie S1). The donors were both male and female, ranging in age from 26 to 65 years, and were free from major cardiovascular diseases (table S1). Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence staining and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analyses confirmed that single SANCs isolated from a region of SAN tissue close to the SAN artery (Fig. 1C) were positive for HCN4 protein (Fig. 1D) and HCN4 mRNA (Fig. 1E), a SANC-specific marker that underlies the SANC funny current, If.
Fig. 1. Single SANC isolation from a human heart.
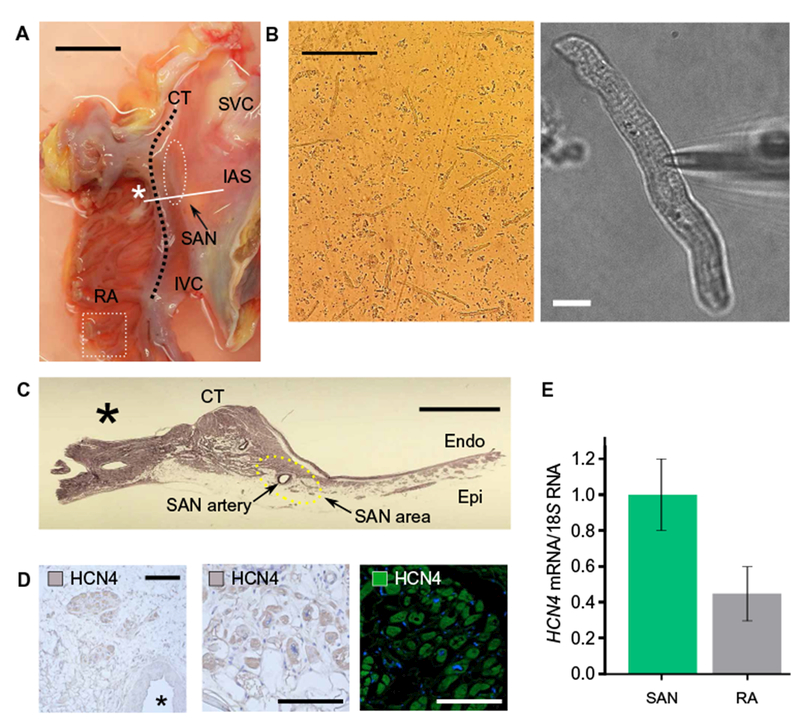
(A) A posterior right atrial (RA) tissue including SAN region was removed from the rest of the heart. The SAN region was identified anatomically (white dashed lines), from which small strips were excised for subsequent enzymatic digestion. IAS, intra-atrial septum; IVC, inferior vena cava; CT, crista terminalis. Scale bar, 2 cm. (B) Examples of isolated single human SANCs under low power (left scale bar, 200 μm) and high power (right scale bar, 10 μm). An example is also shown in movie S1. (C) A cross section of the SAN region marked with a solid line and an asterisk in (A) shows SAN tissue surrounding the SAN artery. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Immunohistochemical (right and middle) and immunofluorescence staining (left) for the SANC marker HCN4. Left scale bar, 30 μm. Middle and right scale bars, 20 μm. (E) HCN4 expression normalized to 185 ribosomal RNA as determined by qPCR was ~2.2-fold higher in SAN than in right atria. Data were from three independent experiments.
Visualization of intracellular Ca2+ within SANCs by Fluo-4 AM fluorescence revealed action potential–induced cytosolic Ca2+ transients and spontaneous diastolic local Ca2+ releases, the hallmark diastolic Ca2+ signal of the Ca2+ clock (Fig. 2, A and B, and movie S2). An increase in the ensemble Ca2+ signal of local diastolic Ca2+ releases gradually built during diastolic depolarization, peaking during late diastole and leading to an increase in the mean global cytosolic diastolic Ca2+ level that ultimately merged into the rapid upstroke of the ensuing action potential–induced whole-cell Ca2+ transient (Fig. 2C). β-AR stimulation reduced the local Ca2+ release period and the ensemble Ca2+ signal of local Ca2+ releases, and this was accompanied by a concurrent reduction in the action potential–induced Ca2+ transient cycle length (Table 1, “Firing SANCs”).
Fig. 2. 2D Ca2+ signal and membrane potential measurements in single isolated human SANCs that fired spontaneous action potentials at baseline.
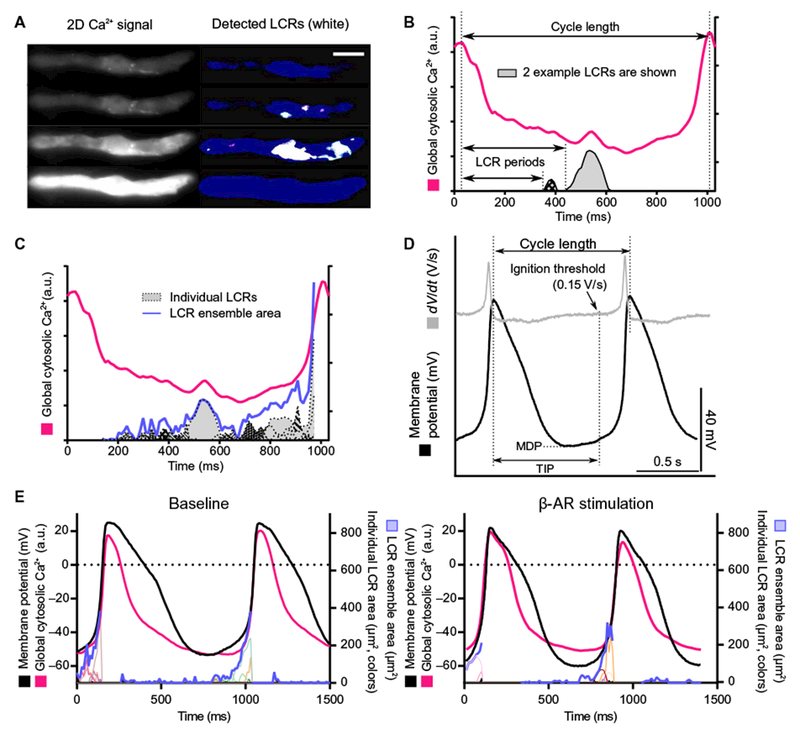
Local Ca2+ releases (LCRs) were observed in all human SANCs studied (22 cells from 4 hearts; 16 from female, 6 from male). (A) 2D high-speed Ca2+ recording of a typical human SANC. Left and right: 2D original data and local Ca2+ release detection through our custom program (white), respectively (28). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Local Ca2+ release period is defined as the time that elapses between the peak of the prior action potential–induced global cytosolic Ca2+ transient and the onset of each local Ca2+ releases. a.u., arbitrary units. (C) Action potential-induced Ca2+ transients (magenta), individual local Ca2+ releases (plotted in gray-black), and local Ca2+ release ensemble area (blue). The ensemble area for local Ca2+ releases sums the total area for all local Ca2+ releases. A dynamic example of events is presented in movie S2. (D) Example of membrane potential measured from 1 of 4 of the 12 human SANCs in which Ca2+ signals were measured (12). MDP, maximum diastolic potential; TIP, time to ignition phase. (E) Effect of β-AR stimulation on action potential, local Ca2+ releases, and global cytosolic Ca2+ transient. Membrane potential (black), global cytosolic Ca2+ transient (magenta), individual local Ca2+ releases (plotted in colors), and local Ca2+ release ensemble (blue) in a human SANC that generated spontaneous action potentials at baseline (left) and during β-AR stimulation (right) are illustrated. See Tables 1 and 2 for quantitative data.
Table 1. Action potential–induced global cytosolic Ca2+ transient cycle lengths and local Ca2+ release characteristics in human SANCs.
Data were from 20 single SANCs isolated from four hearts (three male, one female).
| n | CaT CL (ms) |
LCR ensemble (μm2/10 ms) |
LCR period (ms) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | β-AR stimulation | Baseline | β-AR stimulation | Baseline | β-AR stimulation | ||
| Firing SANCs | 12 | 1676 ± 241 | 971 ± 234* | 15.9 ± 4.2 | 28.1 ± 3.7* | 870± 126 | 530± 129* |
| Arrested SANCs (responder) | 4 | NA | 3328 ± 1110 | 22 ± 3 | 39 ± 10* | NA | 1432 ± 528 |
| Arrested SANCs (nonresponder) | 4 | NA | NA | 11 ± 5 | 3 ± 3 | NA | NA |
P < 0.05, compared to baseline by two-tailed paired t test. CaT CL, Ca2+ transient cycle length; NA, not applicable.
Membrane potential measurements and action potential cycle length at baseline and in response to β-AR stimulation
Membrane potential was measured by perforated patch clamp in a part of SANCs in which Ca2+ was measured (Table 1 and Fig. 2D), at baseline and during β-AR stimulation. β-AR stimulation shortened action potential cycle length and reduced the time to ignition phase (Table 2), a parameter that reflects the initiation of the feed-forward, nonlinear growth of the ensemble local diastolic Ca2+ release signal in late diastole (12).
Table 2. Action potential characteristics of single isolated firing human SANCs.
Data were from 11 single SANCs isolated from two hearts (one female, one male).
| n | Arrested potential |
AP CL (ms) |
MDP (mV) |
TIP (ms) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Baseline | β-AR stimulation | Baseline | β-AR stimulation | Baseline | β-AR stimulation | ||
| Firing SANCs | 4 | NA | 1698 ± 482 | 1211 ± 374* | −50.1 ± 2.3 | −55.3 ± 5.4 | 1582 ± 483 | 958 ± 357* |
| Arrested SANCs (responder) | 4 | −39.7 ± 3.3 | NA | 2936 ± 608 | NA | −56.2 ± 4.2 | NA | 2302 ± 616 |
| Arrested SANCs (nonresponder) | 3 | −31.3 ± 8.8 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
P < 0.05, compared to baseline by two-tailed paired t test. AP CL, action potential cycle length; MDP, maximum diastolic potential; TIP, time to ignition phase.
Simultaneous measurement of membrane potential and twodimensional (2D) Ca2+ signals in these four cells demonstrated a direct relationship between local Ca2+ releases and action potential firing (Fig. 2E). A reduction in action potential cycle length in response to β-AR stimulation was accompanied with earlier occurrence of local Ca2+ releases (Fig. 2E and Tables 1 and 2).
cAMP effects on local Ca2+ releases in human SANCs
To determine the role of cAMP on Ca2+ clock–generated local Ca2+ releases during β-AR stimulation, we applied cAMP to permeabilized SANCs, of which intracellular free Ca2+ concentration was fixed at 50 nM (Fig. 3A). cAMP augmented local Ca2+ release characteristics, shifting the distribution of the sizes (Fig. 3B), durations (Fig. 3C), and Ca2+ signal of individual local Ca2+ releases (Fig. 3D) to higher values, similar to the effects of β-AR stimulation on intact human SANCs that fire spontaneous action potentials (Fig. 2E and Table 1). Because cAMP does not directly affect Ca2+ cycling of the Ca2+ clock, its augmenting effect on local Ca2+ release characteristics in permeabilized SANCs must be modulated by cAMP-mediated, PKA-dependent phosphorylation of SR Ca2+ cycling proteins, including phospholamban and ryanodine receptor, as previously shown in SANCs isolated from animal hearts (5).
Fig. 3. The effect of cAMP in skinned isolated human SANCs.
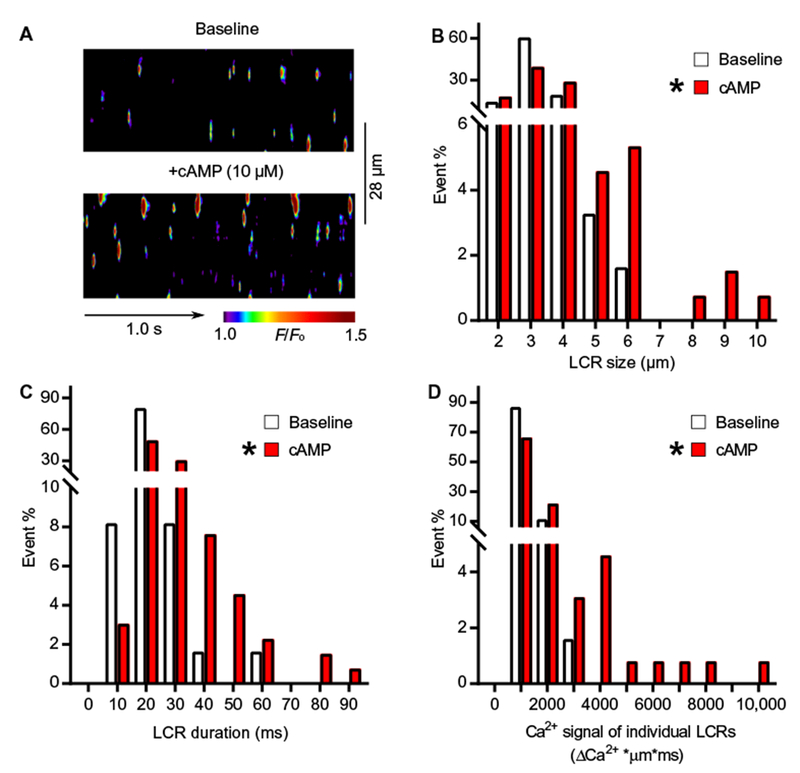
(A) Representative examples of confocal line-scan images of permeabilized human SANCs bathed in 50 nM free [Ca2+] under baseline conditions (upper panel) and in response to cAMP (10 μM) in the same cell (lower panel). (B to D) Histogram distributions of local Ca2+ release characteristics in permeabilized human SANCs under baseline conditions (white bars, 61 local Ca2+ releases from three cells) and in response to 10 μM cAMP (red bars, 131 local Ca2+ releases from three cells): (B) size, (C) duration, and (D) Ca2+ signals of individual local Ca2+ releases. Data are from three independent experiments. Fisher’s exact test was used to determine the statistical significance of a shift in the distribution of local Ca2+ release in permeabilized SANCs in response to β-AR stimulation. The asterisk indicates a significant shift in the distribution of local Ca2+ release parameters toward higher values (>50% percentile) in response to cAMP.
Nonbeating or “arrested” isolated human SANCs
We also studied some isolated SANCs that were arrested and did not generate action potential–induced global cytosolic Ca2+ transients, indicating the absence of spontaneous action potentials. Local Ca2+ releases, however, were present in such arrested cells (Fig. 4A). The resting membrane potential of arrested SANCs was relatively depolarized at −35.5 ± 4.2 mV. In response to superfusion of the β-AR agonist isoproterenol, 50% of arrested cells began to generate action potential–induced global cytosolic Ca2+ transients (Fig. 4A, a “responder”; Fig. 4B, a “nonresponder”). On average, there was no difference between the responders and nonresponders in ensemble Ca2+ signals of local Ca releases during the arrested phase (Table 1). However, in response to β-AR stimulation, the local Ca2+ release ensemble signals were increased in responders but not in nonresponders (Table 1). The membrane potentials of arrested SANCs did not differ between responders and nonresponders (Table 2).
Fig. 4. Local Ca2+ releases in the absence of action potential-induced Ca2+ transients in arrested isolated human SANCs.
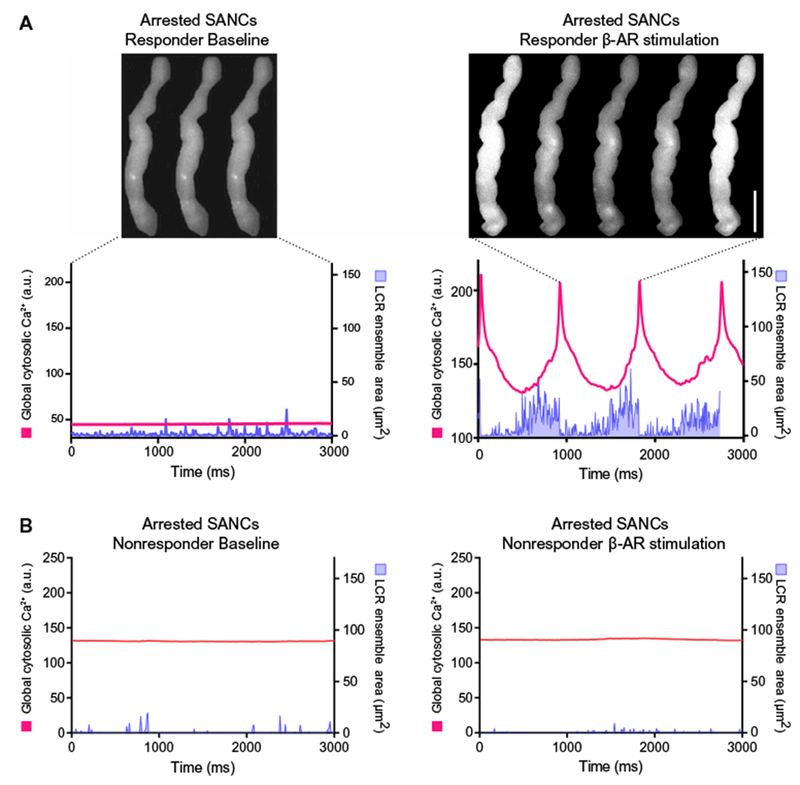
Local Ca2+ releases were present in human SANCs that were devoid of spontaneous action potential-induced global cytosolic Ca2+ transients at baseline (Table 1). Local Ca2+ release characteristics in arrested responder cells (n = 4) and nonresponder cells (n = 4) to β-AR stimulation are listed in Table 1. (A) Example of an arrested responder (left) that began to fire action potential-induced Ca2+ transients in response to β-AR stimulation (right). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Example of nonresponder or a cell that did not fire action potential-induced Ca2+ transients in the presence of β-AR stimulation. Local Ca2+ releases are present in the arrested state and did not became augmented by β-AR stimulation.
Membrane potential and Ca2+ recordings during the transition from the arrested to the beating state
Simultaneous recordings of membrane potential and 2D Ca2+ signal at critical stages of the transition from the arrested to the beating state during β-AR stimulation in a SANC are shown in Fig. 5. Although membrane potential could be recorded for long periods, Ca2+ signals could be recorded only for short time periods (Fig. 5A, orange highlight) to minimize both phototoxicity and bleaching of the Ca2+ indicator. Before β-AR stimulation, membrane potential was relatively depolarized at −38 mV, and the average global cytosolic Ca2+ signal and local Ca2+ release ensemble were small and disorganized (Fig. 5A, a, and movie S3). Shortly after initiation of β-AR stimulation (within ~30 s), the membrane potential began to hyperpolarize, and self-organized oscillations in membrane potential emerged (Fig. 5A, b; simultaneous Ca2+ imaging was not performed at that time). A brief return to the arrested state then occurred (Fig. 5A, c), followed by a series ofbona fide action potential generation (Fig. 5A, d). Action potential cycle length and time to ignition point progressively shortened during this transition state (table S2).
Fig. 5. The evolution of automaticity in arrested isolated human SANCs in response to β-AR stimulation.
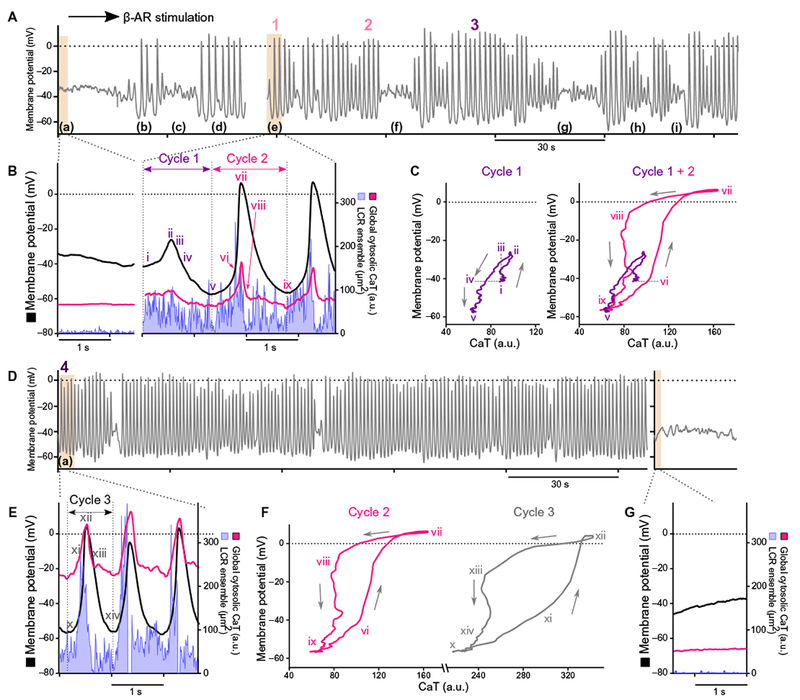
(A) Membrane potential from a typical arrested responder human SANCs before and during early β-AR stimulation. (B) Simultaneous recordings of membrane potential (black), global cytosolic Ca2+ signal (magenta), and local Ca2+ release ensemble (LCR ensemble, blue area) in an arrested SANC before and during action potential firing in response to β-AR stimulation at times from sections indicated by (a) and (e) in (A). (C) Phase plane diagrams of membrane potential and Ca2+ from sections indicated as “Cycle 1” and “Cycle 2” in (B). Roman numerals i to ix in (C) correspond to time points i to ix indicated in (B). (D) Membrane potential at a later stage of β-AR stimulation. (E) Simultaneous recordings of membrane potential (black), global cytosolic Ca2+ transient (magenta), and local Ca2+ release ensemble (blue) from a section marked as (a) in (D). (F) Phase plane plot diagrams of membrane potential and Ca2+ from sections indicated as “Cycle 2” in (B) and “Cycle 3” in (C). Roman numerals x to xiv correspond to time points x to xiv in (C), and Roman numerals vi to ix correspond to time points vi to ix in (B). (G) Simultaneous recordings of membrane potential (black), global cytosolic Ca2+ signal (magenta), and local Ca2+ release ensemble (LCR ensemble, blue area) in an arrested SANC after washout of β-AR stimulation.
Ca2+ measurements were made simultaneously with membrane potential at the indicated periods (Fig. 5A, a and e, and movie S3) and during the initial small oscillations (Fig. 5B, i and ii, and movie S3). The global cytosolic Ca2+ level increased, and the membrane potential depolarized simultaneously. Membrane potential then hyperpolarized to a maximum diastolic potential of −55 mV, and both average global cytosolic Ca2+ and local Ca2+ releases declined, reaching nadirs near the time of the maximum diastolic potential (Fig. 5B, iii to v). Thereafter, local Ca2+ releases began to increase in magnitude, producing a robust increase in the ensemble Ca2+ signal, which was accompanied by depolarization of the diastolic membrane potential (Fig. 5B, v and vi), ultimately merging into the action potential and action potential–mediated global cytosolic Ca2+ transient (Fig. 5B, cycle 2). The changes in Ca2+ and membrane potential during this transition state behavior are similar to those of steady-state response (Fig. 4A and Table 2).
The early transition from arrest to spontaneous action potential firing in response to β-AR stimulation was characterized by an intermittent series of action potentials punctuated by brief periods of arrest (Fig. 5A, f to i) and variable cycle lengths (fig. S1A). With continued exposure to β-AR stimulation, however, dropped beats due to repolarization failure became rare, whereas the average action potential cycle length and cycle-to-cycle interval variability decreased (fig. S1B). That is, β-AR stimulation entrained the Ca2+ and M clocks in a time-dependent manner, leading to the firing of rhythmic spontaneous action potentials.
Detailed Ca2+-Vm interactions during the transition from arrest to spontaneous action potential firing
Phase plane diagrams of cycles 1 and 2 (Fig. 5B) permit closer inspection of simultaneous time-dependent changes that occurred in membrane potential and Ca2+ during the early responses to β-AR stimulation (Fig. 5C). In cycle 1, Ca2+ increased and membrane potential simultaneously depolarized to a peak (Fig. 5C, i and ii) and then both decayed together (Fig. 5C, iii and iv), initially over the same range of Ca2+ encountered during the initial Ca2+ upstroke but at a more depolarized membrane potential than that during the initial upstroke of the voltage oscillation (Fig. 5C, iii). Ca2+ then continued to decline, and membrane potential simultaneously hyperpolarized (Fig. 5C, iv and v) to levels below their initial values (Fig. 5C, i) at the start of their small initial oscillations. Maximum diastolic potential was ultimately established at −55 mV (Fig. 5C). Achievement of this membrane hyperpolarization may have been driven by the effects of the initial depolarization of membrane potential or Ca2+ increase on Ca2+-activated K+ channels (13–15), although this speculation warrants further investigation.
Figure 5C (right) superimposes the Ca2+ membrane potential phase plane diagram for the initial Ca2+ and membrane potential oscillation (Fig. 5B, cycle 1) and for the subsequent bona fide action potential and action potential–induced global cytosolic Ca2+ transient (Fig. 5B, cycle 2). Note that both membrane potential and Ca2+ at the point at which acceleration of membrane potential depolarization induces rapid upstroke of the Ca2+ transient at the start of cycle 1 were the same (Fig. 5C, vi). That is, the Ca2+ membrane potential phase plane trajectory achieved at the initial bona fide action potential upstroke (Fig. 5C, cycle 2) was the same that ofthe prior, initial oscillation (Fig. 5C, i) as those values at the start of the small Ca2+ and membrane potential oscillations in the previous cycle (Fig. 5C, Cycle 1 + 2, vi). Acceleration of the membrane depolarization at this point likely resulted from Ca2+-mediated activation of L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels occurring during prior Ca2+ oscillations. The rapid increase in cytosolic Ca2+ caused by the membrane potential depolarization of the action potential (Fig. 5C, vi and vii) likely occurred through Ca2+-induced Ca2+ releases involving L-type Ca2+ channels and ryanodine receptors.
Simultaneous Ca2+ and membrane potential recordings made at a later stage of β-AR stimulation (Fig. 5, D, a, and E) illustrate how coupled-clock function continued to evolve with time during the transition to steady-state beating. As a result of several action potentials that generated Ca2+ influx, the average diastolic global cytosolic Ca2+ substantially increased from 50 during early β-AR stimulation to 220 arbitrary units during late β-AR stimulation (Fig. 5F, ix compared to x). This effect of action potential firing has been observed previously in rabbit SANCs initially arrested by voltage clamp, but which subsequently begins to fire action potentials after removal of the clamp, as the SR Ca2+ load increases during the resumption of action potential firing (4). This increase in global diastolic Ca2+ was accompanied by more rapid action potential repolarization. Otherwise, the general shapes of the phase plane diagrams of Ca2+ and membrane potential in early and late β-AR stimulation were similar (Fig. 5F). When β-AR stimulation was discontinued (Fig. 5G), the individual and averaged local Ca2+ release signals returned to pre–β-AR stimulation levels, the membrane potential depolarized to around −40 mV, and the cell returned to the pre–β-AR stimulation nonbeating arrested state (Fig. 5, F compared to G). Ca2+ recordings at points indicated in Fig. 5 (B and E) are shown with simultaneous membrane recordings (Fig. 6A). A reduction in action potential cycle length was accompanied by early local Ca2+ release (Fig. 6B).
Fig. 6. A unique continuum of clock coupling in human SANCs, which fire spontaneous action potentials over a wide range of rates.
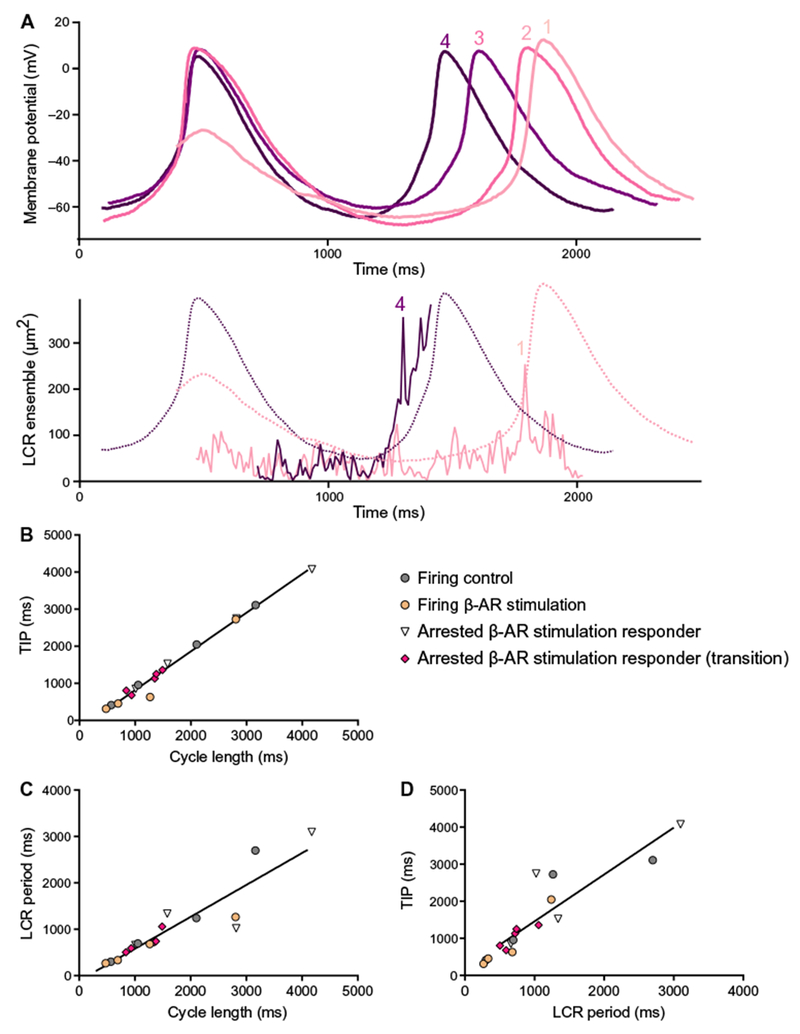
(A) Evolution of membrane potential and local Ca2+ release ensemble during the transition from arrested state to action potential firing. Detail of high-resolution action potential recordings during transition phase from arrested state to action potential firing (upper panel) and local Ca2+ release ensemble measured simultaneously during early and late stages of the β-AR stimulation response in critical stages in Fig. 5 (lower panel). Corresponding action potential tracings from upper panel are overlaid as dashed lines. Color-coded numbers 1 to 4 in each panel corresponds to numbers 1 to 3 in Fig. 5A and number 4 in Fig. 5D. (B to D) Correlations between cycle length, local Ca2+ release period, and time to ignition phase observed across SANCs over a wide range of action potential firing rates. Color codes of points are as follows: gray, steady-state firing at baseline (Fig. 2E, left, and Table 1; n = 4 cells); orange, those during β-AR stimulation (Fig. 2E, right, and Table 1; n = 4 cells); white, steady state (Fig. 4A, right; n = 4); magenta, transition state (Fig. 5 and table S2; n = 5 cells) of initially arrested responder SANCs that generated spontaneous action potential in response to β-AR stimulation. Correlations between cycle length and time to ignition phase (B), cycle length and local Ca2+ release period (C), and local Ca2+ release period and time to ignition phase (D) in each group of cells tested separately did not statistically differ from each other. Therefore, all points in each panel conform to common line: cycle length compared to time to ignition phase, Y = 1.073*X + 241.1, R2 = 0.96 (B); cycle length compared to local Ca2+ release period, Y = 0.718*X − 136, R2 = 0.85 (C); local Ca2+ release period compared to time to ignition phase, 1.264*X + 196, R2 = 0.82 (D).
Clock coupling across a broad range of action potential cycle lengths
Action potential cycle length in cells labeled varied over a 10-fold range (Fig. 6, B and C). The relationship of local Ca2+ release periods and time to ignition point to action potential cycle length over this broad range informs clock coupling across a broad range of action potential cycle lengths. The color-coded points in this figure on clock coupling over a broad range of action potential firing rates indicated the human SANC subpopulations studied, namely, those that fire spontaneous action potentials at baseline (Fig. 2E, gray) and in response to β-AR stimulation (Fig. 2E, yellow, and Tables 1 and 2), initially arrested responder SANCs in the steady state (Fig. 4A, right, white, and Tables 1 and 2), and arrested responder to β-AR stimulation in transient state (Fig. 5, B and E, magenta). The positive correlations between cycle length and time to ignition point (Fig. 6B), cycle length and local Ca2+ release period (Fig. 6C), and local Ca2+ release period and time to ignition phase (Fig. 6D) confirmed a continuum of clock coupling in human SANCs that fire spontaneous action potentials over a wide range of rates.
DISCUSSION
We demonstrated that human SANCs had a functioning Ca2+ clock that was coupled to a membrane clock, and that this coupled-clock system underlies spontaneous action potential generation (Figs. 2 to 6). Furthermore, a reduction in local Ca2+ release period within a given action potential cycle was accompanied by a concurrent reduction in action potential cycle length and vice versa (Fig. 6). These discoveries in human SANCs concur with the current paradigm of SANC automaticity established in animal models (2–7). Previously, Verkerk et al. (16) have characterized action potential characteristics and ion currents interpreted as If and INa (17) from three SANCs from excised SAN tissue from a patient with refractory inappropriate sinus tachycardia (16). These authors have also recorded action potential–induced Ca2+ transients from SANCs from the same patient (18). Our observations indicate that a Ca2+ clock operates in human SANCs and generates local Ca2+ releases and that a coupled-clock system drives human SANC automaticity.
How the coupled clock works
Numerous internal and external signals regulate each clock: voltage, time, intrinsic cAMP signaling, PKA- and CaMKII-dependent clock protein phosphorylation, and the intracellular concentration of Ca2+, which functions as the clock oscillatory substrate (11). Local Ca2+ releases, NCX, If, IK, and ICa play key roles in clock coupling (12). Feed-forward signaling originating from the action potential firing rate or cycle length in a given steady state also regulates clock molecules by regulating cellular Ca2+ load. M clock ion channels are both voltage-, time-, and transmembrane ion concentration gradient–dependent, and some are regulated by Ca2+ and are also modulated by phosphorylation; the NCX and Na-K-ATPase (adenosine triphosphatase) are also voltage- and transmembrane gradient-dependent but are not time-dependent as ion channels. The SR Ca2+ clock operates as a Ca2+ capacitor: Its Ca2+ charge is regulated by SERCA2, which pumps Ca2+ into the SR lumen, and by ryanodine receptors, which dissipate the Ca2+ charge by releasing Ca2+ beneath the cell surface membrane. SR Ca2+ cycling is modulated by phosphorylation of phospholamban and ryanodine receptors. Ion pumps within each clock are energy-dependent. Because both clocks either directly or indirectly regulate both surface membrane potential and intracellular Ca2+, clock functions do not operate independently of each other but operate as a bidirectionally coupled system (3).
β-AR stimulation effects on clock coupling
Stimulation of autonomic receptors modulates the functions of the clock molecules to increase their coupling. Specifically, β-AR stimulation increases Ca2+ influx and phosphorylation of clock proteins, modulating Ca2+ and phosphorylation-dependent clock functions: Both Ca pumping into SR and activation of ryanodine receptors accelerate, and the kinetics of Ca2+ flux into and from the SR accelerate, thereby regulating local Ca2+ release periodicity (3). β-AR stimulation augments the interplay between L-type Ca2+ channels and SR Ca2+ cycling by enhancing the coupling between Ca2+ and M clocks (12). Enhanced Ca2+ influx is accompanied by concomitant acceleration of action potential repolarization, possibly due to Ca2+-activated K+ channels (13–15).
Effect of clock coupling in human SANCs
Here, the spontaneous diastolic local Ca2+ release ensemble signal was increased through synchronization of individual local Ca2+ releases and occurred earlier, during diastolic depolarization. Increased cAMP or increased Ca2+ and phosphorylation of M clock molecules (such as L-type Ca2+ channels, Kv channels, HCN channels, and Na-K-ATPase) also modulated their functions.
As Ca2+ was cleared from the cytosol and from beneath the surface membrane, the local Ca2+ release ensemble signal reached a nadir and the membrane potential hyperpolarized (Fig. 2E). When the maximum diastolic potential was achieved, robust local Ca2+ releases begin to occur, initiating diastolic depolarization of the membrane potential (Fig. 2E). The exponential-like growth of the late local Ca2+ release ensemble signal accelerated during β-AR stimulation and was accompanied by concurrent increases in the rate of diastolic depolarization and reduction of the action potential cycle length (Fig. 2E, right). These effects reflected improved clock coupling by Ca2+-cAMP-PKA–dependent mechanisms, including increased If activation by cAMP and synchronization of spontaneous local ryanodine receptor activation after the maximum diastolic polarization (3). Thus, hyperpolarization of membrane potential that increases activation of both INCX and If, phosphorylation-dependent synchronization of ryanodine receptors that gives rise to synchronization of local Ca2+ release production, activation of INCX, and increased cell Ca2+ due to the reduction in average action potential cycle length are putative critical factors in improving clock coupling in response to β-AR stimulation. The net result of β-AR stimulation-induced enhancement of clock coupling is an increase in the spontaneous action potential firing rate.
Arrested SANCs
We encountered different degrees of clock coupling in our experiments in human SANCs (fig. S2, A to C). Nonbeating, arrested human SANCs, or those that did not generate spontaneous action potentials or action potential–induced Ca2+ transients under baseline conditions, exhibited extreme clock uncoupling, being relatively depolarized yet still continuing to generate local Ca2+ releases (fig. S2A). One possible explanation for this action potential arrest seen in some human SANCs is that, at the depolarized membrane potential characteristic of arrested SANCs (Fig. 5B and Table 2), INCX is closer to its reversal potential (4), favoring the nonelectrogenic SERCA-driven return of Ca2+ derived from local Ca2+ releases out of the cytoplasm and back to the SR, rather than electrogenic extrusion through NCX. When local Ca2+ releases fail to optimally activate NCX, partial uncoupling of the Ca2+ and M clocks occurs, resulting in substantially slower, dysrhythmic action potential firing or even action potential failure (fig. S2A), compared to optimal clock coupling (fig. S2, B and C) (19,20). Another possibility is a reduction in cell and SR Ca2+ loading due to the absence of action potentials and resulting Ca2+ transients (4).
β-AR stimulation, however, restored automaticity in only half of the arrested SANCs in our study, and when the stimulation was removed, these cells returned to the arrested state with a depolarized membrane potential of the arrested state before the β-AR stimulation (Fig. 5G). This raises the possibility that some cells within SAN tissue may not participate in basal action potential firing but can be recruited during sympathetic stimulation, which is consistent with previous studies (21). Conversely, arrested cells in which automaticity could not be restored by β-AR stimulation may represent SANCs that have lost functional clock coupling, possibly because of the cell isolation procedure.
In conclusion, our study provides evidence that clock coupling is a critical component of the cellular-molecular physiology operational in human SANCs. Because action potential failure in some human SANCs is a manifestation of severe clock uncoupling, dysfunctional clock coupling, in addition to SAN fibrosis and impaired cell-to-cell interactions (22, 23), may contribute to SAN dysfunction in pathological states. Further work in human SANCs, an infrequently used but relevant platform for the study of SAN clinical diseases, will be critical to establish definitive details of the workings of the coupled-clock system in human cardiac pacemaker health and disease. In this context, the findings of our study offer the potential to stimulate the development of therapies that target pacemaker cell clock uncoupling.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
Adult human hearts not required for transplantation were procured from Washington Regional Transplant Community. Experimental protocols were approved by the George Washington University Institutional Review Board. Informed donor consents were obtained for all tissue used in this study. All methods described in this section were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health guidelines on human research.
Human SAN and SANC isolation
Explanted hearts were cardioplegically arrested in University of Wisconsin solution [containing 100 mM potassium lactobionate, 25 mM KH2PO4, 5 mM MgSO4, 30 mM raffinose, 5 mM adenosine, 3 mM glutathione,1 mM allopurinol, and hydroxyethyl starch (50 g/liter)](24) and were cooled to +4°C in the operating room after aortic crossclamp. Donor hearts were perfused systemically before removal from the chest. The heart was maintained at this low temperature to preserve tissue during the transportation time from the operating room to the research laboratory. The SAN region was cut into small strips (~1.0 mm wide) perpendicular to the crista terminalis and excised. The final SAN preparation consisted of SAN strips attached to the small portion of crista terminalis. The SAN preparation was washed twice in Ca2+-free solution containing 140 mM NaCl, 5.4 mM KCl, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 0.33 mM NaH2PO4, 5 mM Hepes, and 5.5 mM glucose (pH 6.9) and incubated at 35.5°C for 30 min in the same solution with addition of elastase type IIA (0.6 mg/ml; Sigma Chemical Co.), collagenase type 2 (0.6 mg/ml; Worthington), and 0.1% bovine serum albumin (Sigma Chemical Co.). The SAN preparation was washed in modified Kraftbruhe (KB) solution containing 70 mM potassium glutamate, 30 mM KCl, 10 mM KH2PO4, 1 mM MgCl2, 20 mM taurine, 10 mM glucose, 0.3 mM EGTA, and 10 mM Hepes (titrated to pH 7.4 with KOH) and kept at 4°C for 1 hour in KB solution containing polyvinylpyrrolidone (50 mg/ml; Sigma Chemical Co.). Finally, cells were dispersed from the SAN preparation by gentle pipetting in the KB solution and stored at 4°C. After dispersion, we studied cells with the typical morphology of a SANC [as described by Verheijck et al. (25)]. Details of individual human hearts used for this work, including patient age and cause of death, are given in table S1.
Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescent staining
Samples were dissected from the central part of the SAN tissue, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, paraffin-embedded, and sectioned at 5 μm thickness for the following immunostaining methods. To immunolabel HCN4, we used mouse monoclonal antibody to HCN4 (S114– 10, ab85023, Abcam) added at a dilution of 1:1500 at 4°C overnight after deparaffinization with xylene. For immunohistostaining, the sections were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at room temperature followed by addition of biotinylated “ready-to-use” secondary antibody, having enzyme conjugated at room temperature for 60 min (catalog no. 95–9943-B; Histostain Bulk Kit, Invitrogen). Chromogen DAB (3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride) was then added for 5 min (catalog no. 00–2014; DAB Kit, Invitrogen). Finally, the sections were counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated, transparentized, and mounted. Sections were washed with PBS at room temperature, followed by addition of anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 antibody at a dilution of1:50 (A-11029, Invitrogen) at room temperature for 1 hour. The sections were washed, stained with 4′ ,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), and sealed with glycerol before observation under a microscope.
RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, RT-qPCR, and data analysis
RNA was extracted from human SAN and right atria tissue with the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) using deoxyribonuclease on column digestion according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Two micrograms of total RNA was used for complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis in 50-μl reaction volume with MMLV reverse transcriptase (Life Technologies) with poly-T primers. For synthesis of each cDNA, template control for the detection of possible contamination and RT control for tracing of possible genomic DNA presence were not used. RT-qPCR was performed on QuantStudio 6 Detection System (Applied Biosystems) with 384-well platform. The reaction was performed with FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master Mix with ROX (Roche) using the manufacturer’s recommended conditions. The size of the amplicon was verified, and a dissociation curve was obtained. Each well contained 0.5 μl of cDNA solution and 10 μl of reaction mixture. Each sample was quadruplicated and repeated twice using de novo synthesized cDNA sets. RT-qPCR analysis was performed using ΔΔCt method. Expression levels of HCN4 transcript were normalized to expression of S18. Primers for HCN4 amplification were as follows: ACGTGTGCGGTCTAGTTTAATCC (forward) and AGAACGTCCCTAGACCATGCA (reverse); for RPS18, CAGCCAGGTCCTAGCCAATG (forward) and CCTCTATGGGCCCGAATCTT (reverse).
2D high-speed Ca2+ signal recording
Ca2+ dynamics within isolated single human SANCs were measured by 2D imaging of the fluorescent Ca2+ indicator Fluo-4. Cells were loaded with 2.5 μM Fluo-4 AM (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 15 min at room temperature. Fluo-4 AM was subsequently washed out of the chamber with bathing solution containing the following: 140 mM NaCl, 5 mM Hepes, 0.33 mM NaH2PO4∙H2O, 5.4 mM KCl, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 5.5 mM glucose, and 1.8 mM CaCl2 (titrated to pH 7.35 with NaOH). Ca2+ signals were measured within the ensuing 60 min at 36° ± 0.1°C. Temperature was controlled by an Analog TC2BIP 2/3Ch bipolar temperature controller from Cell MicroControls. This heated both the glass bottom of the perfusion chamber and the solution entering the chamber (via a preheater). Fluo-4 fluorescence was detected using a high-speed Hamamatsu C9100–12 CCD camera (100 frames/s, with an 8.192-mm2 sensor of 512 × 512 pixel resolution) or a pco. edge 4.2 CMOS camera (100 frames/s, with a 13.2-mm2 sensor of 2048 × 2048 pixel resolution) mounted on a Zeiss inverted microscope (Carl Zeiss Inc.) with a ×63 oil immersion lens and a fluorescence excitation light source (CoolLED pE-300-W, BioVision Technologies Inc.) (4). Fluo-4 fluorescence excitation (blue light, 470/40 nm) and emission light collection (green light, 525/50 nm) were performed using the Zeiss filter set 38 HE. To avoid phototoxicity, Fluo-4 was excited only for short periods of time (<30 s). Data acquisition was performed using Simple PCI (Hamamatsu Corporation) or pco.camware 64 (PCO AG). The 2D Ca2+ signals were obtained before, during, and after washout of β-AR stimulation induced by 1 μM isoproterenol (Sigma-Aldrich).
Local Ca2+ releases in permeabilized human SANCs
A subset of SANCs isolated from human SAN tissue was permeabilized with saponin (0.01%) in a solution containing 100 mM C4H6NO4K (dl-aspartic acid potassium salt), 25 mM KCl, 10 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgATP, 0.81 mM MgCl2 (~1 mM free Mg2+), 20 mM Hepes, 0.5 mM EGTA, 10 mM phosphocreatine, and creatine phosphokinase (5 U/ml) (pH 7.2). After washing out saponin, 0.03 mM Fluo-4 pentapotassium salt and a desired amount of CaCl2 were added to the same solution as above. The cytosolic free [Ca2+]i at given total Ca2+, Mg2+, ATP, and EGTA concentrations was calculated using a computer program (WinMAXC 2.50, Stanford University). We recorded local Ca2+ releases, bathed in 50 nM free [Ca2+]i at 35° ± 0.5°C by confocal microscopy in the line-scan mode before and during cAMP application. The line-scan was set along the long axis of the cell close to the sarcolemmal membrane, as previously described for rabbit SANCs (26).
Analysis of Fluo-4 intensity recorded in permeabilized human SANCs
Fluo-4 measurements of local Ca2+ release amplitude in permeabilized human SANCs are presented as F/F0 (normalized Ca2+ signal). Local Ca2+ release spatial size (in micrometers) was indexed as the full width at half maximum amplitude (FWHM), and its duration (in milliseconds) was characterized as the full duration at half maximum amplitude (FDHM). The numbers of local Ca2+ release events detected per cell were normalized per 100 μm of the line-scan image during a 1-s time interval. The Ca2+ signal of an individual local Ca2+ release was estimated as follows: local Ca2+ releases = FWHM × FDHM × 1/2ΔCa2. Absolute free [Ca2+] change (ΔCa2+; in nanomole per liter) was estimated from F/F0, as previously described (27). The Ca2+ signal of the local Ca2+ release ensemble within a cell was calculated as the sum of all Ca2+ signals of individual local Ca2+ releases and normalized per 100 μm of the line-scan image during a 1-s time interval.
Measurement of membrane potential
In some experiments, we also simultaneously recorded membrane potentials in addition to 2D Ca2+ signals by using perforated patch clamp, as previously described (28). Membrane potential was measured in the current clamp configuration using an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Molecular Devices). Patch pipette resistances ranged between 3 and 5 megohms, and pipettes were filled with a solution containing 120 mM K+ gluconate, 5 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgATP, 5 mM Hepes, and 20 mM KCl (titrated to pH 7.2 with KOH). Amphotericin B (320 μM, Sigma-Aldrich, A-4888) was added into the pipette solution as the pore-forming agent. Liquid junction potential was calculated using pClamp software (Molecular Devices) and adjusted accordingly. The membrane potential and Ca2+ recordings were electronically synchronized. Time to ignition phase is a time interval between the prior peak of action potential and the point when dV/dt exceeds “ignition threshold” (0.15 V/s) during diastolic depolarization (Fig. 2D) (12).
Computational analysis of local Ca2+ releases
We used an in-house program (“XYT Event Detector”) to objectively, automatically, and rapidly analyze the individual and ensemble behavior of the local Ca2+ releases (29). This program yields detailed information about the number, timing [“local Ca2+ release period”: the length of time between the peak of the prior action potential–induced Ca2+ transient and the onset of the local Ca2+ release (28)], area, amplitude, duration, and travel information of individual local Ca2+ releases and the local Ca2+ release ensemble (namely, the summation of all local Ca2+ release areas in a given time). This was then analyzed in association with the whole-cell Ca2+ transient trace and the membrane potential to yield insights into local Ca2+ release contribution to membrane potential, that is, spontaneous firing behavior (Fig. 2, B and C) (29).
Statistics
Values are expressed as means ± SE. Two-tailed paired Student’s t test was used to compare Vm and Ca2+ signal characteristics between those in baseline and during β-AR stimulation, and Ca2+ signals between responder and nonresponder arrested SANCs in baseline condition in Tables 1 and 2. Fisher’s exact test was used to detect statistical significance for a shift in the distribution of local Ca2+ release in permeabilized SANCs in response to increased cAMP in Fig. 3. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Supplementary Material
Movie S1. A freshly isolated single spontaneously beating human SANC from heart 3.
Movie S2. LCR detection software on a spontaneously beating human SANC from heart 4.
Movie S3. Simultaneous measurements of membrane potential and a 2D Ca2+ signal.
Fig. S1. Action potential repolarization failure in the transition from arrest to spontaneous action potential firing in response to β-AR stimulation.
Fig. S2. A schematic of the clock coupling in SANCs.
Table S1. Characteristics of the donor hearts used in the present study.
Table S2. Time-dependent evolution of action potential parameters in the transition state of an initially arrested human SANC.
Acknowledgments:
We would like to thank R. Wilders and A. O. Verkerk for sharing their experience and detailed protocol for isolating human single SANCs.
Funding: This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program, National Institute on Aging, NIH; Leducq Foundation Transatlantic Network of Excellence “RHYTHM”; NIH R21EB023106, “Near-infrared optogenetic control of the human heart”; NIH R01 HL126802, “Exploration of arrhythmogenic triggers and substrates in heart failure”; and NIH R01 HL114395, “Arrhythmogenic remodeling in human heart failure.” K.T. was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Research Fellowship for Japanese Biomedical and Behavioral Researchers at NIH. O.J.M. was supported by the National Institute for Health Research in the UK.
Footnotes
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Data and materials availability: All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper or the Supplementary Materials.
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Hüser J, Blatter LA, Lipsius SL, Intracellular Ca2+ release contributes to automaticity in cat atrial pacemaker cells. J. Physiol 524 (Pt. 2), 415–422 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bogdanov KY, Vinogradova TM, Lakatta EG, Sinoatrial nodal cell ryanodine receptor and Na+-Ca2+ exchanger: Molecular partners in pacemaker regulation. Circ. Res 88, 1254–1258 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lakatta EG, Maltsev VA, Vinogradova TM, A coupled SYSTEM of intracellular Ca2+ clocks and surface membrane voltage clocks controls the timekeeping mechanism of the heart’s pacemaker. Circ. Res 106, 659–673 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vinogradova TM, Zhou Y-Y, Maltsev V, Lyashkov A, Stern M, Lakatta EG, Rhythmic ryanodine receptor Ca2+ releases during diastolic depolarization of sinoatrial pacemaker cells do not require membrane depolarization. Circ. Res 94, 802–809 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vinogradova TM, Lyashkov AE, Zhu W, Ruknudin AM, Sirenko S, Yang D, Deo S, Barlow M, Johnson S, Caffrey JL, Zhou Y-Y, Xiao R-P, Cheng H, Stern MD, Maltsev VA, Lakatta EG, High basal protein kinase A–dependent phosphorylation drives rhythmic internal Ca2+ store oscillations and spontaneous beating of cardiac pacemaker cells. Circ. Res 98, 505–514 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Monfredi O, Maltsev VA, Lakatta EG, Modern concepts concerning the origin of the heartbeat. Physiology 28, 74–92 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tsutsui K, Monfredi JO, Lakatta EG, A general theory to explain heart rate and cardiac contractility changes with age. Physiol. Mini Rev 9, 9–25 (2016). [Google Scholar]
- 8.Capel RA, Terrar DA, The importance of Ca2+-dependent mechanisms for the initiation of the heartbeat. Front. Physiol 6, 80 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sanders L, Rakovic S, Lowe M, Mattick PAD, Terrar DA, Fundamental importance of Na+–Ca2+ exchange for the pacemaking mechanism in guinea-pig sino-atrial node. J. Physiol 571,639–649 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maltsev VA, Lakatta EG, Synergism of coupled subsarcolemmal Ca2+ clocks and sarcolemmal voltage clocks confers robust and flexible pacemaker function in a novel pacemaker cell model. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 296, H594–H615 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sirenko SG, Maltsev VA, Yaniv Y, Bychkov R, Yaeger D, Vinogradova TM, Spurgeon HA, Lakatta EG, Electrochemical Na+ and Ca2+ gradients drive coupled-clock regulation of automaticity of isolated rabbit sinoatrial nodal pacemaker cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 311, H251–H267 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lyashkov AE, Behar J, Lakatta EG, Yaniv Y, Maltsev VA, Positive feedback mechanisms among local Ca releases, NCX, & ICaL ignite pacemaker action potentials. Biophys. J 114, 1176–1189 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Weisbrod D, Peretz A, Ziskind A, Menaker N, Oz S, Barad L, Eliyahu S, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Dascal N, Khananshvili D, Binah O, Attali B, SK4 Ca2+ activated K+ channel is a critical player in cardiac pacemaker derived from human embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 110, E1685–E1694 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhang X-D, Lieu DK, Chiamvimonvat N, Small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels and cardiac arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm 12, 1845–1851 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lai MH, Wu Y, Gao Z, Anderson ME, Dalziel JE, Meredith AL, BK channels regulate sinoatrial node firing rate and cardiac pacing in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 307, H1327–H1338 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Verkerk AO, Wilders R, van Borren MMGJ, Peters RJG, Broekhuis E, Lam K, Coronel R, de Bakker JMT, Tan HL, Pacemaker current (If) in the human sinoatrial node. Eur. Heart J 28, 2472–2478 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Verkerk AO, Wilders R, van Borren MMGJ, Tan HL, Is sodium current present in human sinoatrial node cells? Int. J. Biol. Sci 5, 201–204 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Verkerk AO, van Borren MMGJ, Wilders R, Calcium transient and sodium-calcium exchange current in human versus rabbit sinoatrial node pacemaker cells. ScientificWorldJournai 2013, 507872 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Maltsev VA, Yaniv Y, Maltsev AV, Stern MD, Lakatta EG, Modern perspectives on numerical modeling of cardiac pacemaker cell. J. Pharmacol. Sci 125, 6–38 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lakatta EG, DiFrancesco D, What keeps us ticking: A funny current, a calcium clock, or both? J. Moi. Ceii. Cardioi 47, 157–170 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Opthof T, VanGinneken ACG, Bouman LN, Jongsma HJ, The intrinsic cycle length in small pieces isolated from the rabbit sinoatrial node. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol 19, 923–934 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Csepe TA, Kalyanasundaram A, Hansen BJ, Zhao J, Fedorov VV, Fibrosis: A structural modulator of sinoatrial node physiology and dysfunction. Front. Physioi 6, 37 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Monfredi O, Boyett MR, Sick sinus syndrome and atrial fibrillation in older persons—A view from the sinoatrial nodal myocyte. J. Moi. Cell. Cardioi 83, 88–100 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Southard JH, van Gulik TM, Ametani MS, Vreugdenhil PK, Lindell SL, Pienaar BL, Belzer FO, Important components of the UW solution. Transpiantation 49, 251–257 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Verheijck EE, Wessels A, van Ginneken ACG, Bourier J, Markman MWM, Vermeulen JLM, de Bakker JMT, Lamers WH, Opthof T, Bouman LN, Distribution of atrial and nodal cells within the rabbit sinoatrial node: Models of sinoatrial transition. Circuiation 97, 1623–1631 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sirenko S, Yang D, Li Y, Lyashkov AE, Lukyanenko YO, Lakatta EG, Vinogradova TM, Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of Ca2+ cycling proteins generates robust rhythmic local Ca2+ releases in cardiac pacemaker cells. Sci. Signal 6, ra6 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sirenko S, Maltsev VA, Maltseva LA, Yang D, Lukyanenko Y, Vinogradova TM, Jones L, Lakatta EG, Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ cycling protein phosphorylation in a physiologic Ca2+ milieu unleashes a high-power, rhythmic Ca2+ clock in ventricular myocytes: Relevance to arrhythmias and bio-pacemaker design. J. Moi. Ceii. Cardioi 66, 106–115 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Monfredi O, Maltseva LA, Spurgeon HA, Boyett MR, Lakatta EG, Maltsev VA, Beat-to-beat variation in periodicity of local calcium releases contributes to intrinsic variations of spontaneous cycle length in isolated single sinoatrial node cells. PLOS ONE 8, e67247 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Maltsev AV, Parsons SP, Kim MS, Tsutsui K, Stern MD, Lakatta EG, Maltsev VA, Monfredi O, Computer algorithms for automated detection and analysis of local Ca2+ releases in spontaneously beating cardiac pacemaker cells. PLOS ONE 12, e0179419 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Movie S1. A freshly isolated single spontaneously beating human SANC from heart 3.
Movie S2. LCR detection software on a spontaneously beating human SANC from heart 4.
Movie S3. Simultaneous measurements of membrane potential and a 2D Ca2+ signal.
Fig. S1. Action potential repolarization failure in the transition from arrest to spontaneous action potential firing in response to β-AR stimulation.
Fig. S2. A schematic of the clock coupling in SANCs.
Table S1. Characteristics of the donor hearts used in the present study.
Table S2. Time-dependent evolution of action potential parameters in the transition state of an initially arrested human SANC.


