Abstract
Bats play key ecological roles, also hosting many zoonotic pathogens. Neotropical bat microbiota is still poorly known. We speculate that their dietary habits strongly influence their microbiota richness and antibiotic-resistance patterns, which represent growing and serious public health and environmental issue. Here we describe the aerobic microbiota richness of bats from an Atlantic Forest remnant in Southeastern Brazil, and the antibiotic-resistance patterns of bacteria of clinical importance. Oral and rectal cavities of 113 bats from Carlos Botelho State Park were swabbed. Samples were plated on 5% sheep blood and MacConkey agar and identified by the MALDI-TOF technique. Antibiotic susceptibility tests were performed using Kirby-Bauer’s antibiotic disc diffusion technique.We identified 596 isolates at the genus level and tentatively to the species level. Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum in all the dietary guilds, representing 87% of the total identified samples. The most common bacteria within bat individuals were Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca and Serratia marcescens, and within bat species were Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas sp. and Staphylococcus sp. Frugivores presented the most diverse microbiota. In general, the antibiogram results indicated a low occurrence of resistance on eigth potentially pathogenic bacteria species. The resistance to antibiotics found on our samples was related mostly to the intrinsic resistance of the tested species.The low occurrence of resistant bacteria in our samples could be related to the well preserved environment where bats were caught. Once the major causes of resistance-acquiring are related to anthropic activites, the controlled access of tourists on certain regions of the Park seems to be effectively protecting the environment.
Introduction
Bats as a group are distributed worldwide, with more than 1300 species, representing ca. 20% of the world mammals [1]. They are highly diversified ecologically, bringing together the most diversified feeding strategies among terrestrial vertebrates. Dietary strategies include frugivory, hematophagy, insectivory, nectarivory, carnivory, piscivory and omnivory [1, 2]. Some species allocated in one of these categories include different food sources in their diet [1, 2]. Due to this diversified diet they provide important ecosystem services such as seed dispersal, pollination and pest control, but also carry many pathogens, some of them of zoonotic potential [3, 4]. Little is known about Neotropical bat microbiota, which is in great part studied for Old World species and mostly related to the gastrointestinal diversity [5–11];. Also, studies focused on the interaction, influence and ecologic role of bats oral and rectal microbiota are scarce, despite their importance on the digestion, vitamin synthesis, protection against harmful microorganisms and also public health [12–17].
Previous studies of bat gut microbiota showed that the bacteria diversity is in part related to the host diet, with a partial overlap between species in different dietary guilds, once these species can compensate the lack of some requirements with different food sources during resources shortages [9, 18]. Besides the microbiota diversity, the bacteria antibiotic-resistance patterns could be also modulated by dietary habits [19–21]. Among the major causes of resistance acquiring is the contact with anthropic environments [21, 22]. Antimicrobial resistant bacteria are a growing and serious problem to the public health and environment, and are reported to be present even on remote habitats [17, 23]. The presence of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife brings implications, as it can drive animals to become potential reservoirs of resistant bacteria, and also impose limits to the efficiency of antibiotics used on the control of human and wildlife diseases [17, 21].
Against that background, we aimed (1) to describe the oral and rectal aerobic microbiota richness of bats in five dietary guilds from the Carlos Botelho State Park (CBSP), a protected area on the Atlantic Forest of Southeastern Brazil, focusing bacteria of clinical importance; (2) to identify the antibiotic-resistance profile of eight potentially pathogenic bacteria for those bats; and (3) to evaluate whether the protected area is preserving the wildlife from antibiotic resistant bacteria.
Material and methods
Sampling
Fieldwork was conducted monthly from October 2016 to September 2017 on the Carlos Botelho State Park (CBSP; 24°12'–24°4'S, 47°47'–48°7'W), which is a protected area in the Brazilian Southeastern Atlantic Forest, created in 1982. The phytophysiognomy is mostly represented by the ombrophilous forest, with ca. 23,300 ha composed by pristine forests [24]. Bats were captured using with mist-nets and during searches for roosts, under the permits SISBIO/ICMBIO 54.381-1/2016 and COTEC/SMA-IF 260108006.479/2016. Monthly, oral and rectal cavities of one bat of each species captured were swabbed with sterile cotton swabs, which were then separately transported in Stuart’s transport medium and refrigerated. Samples used in this study were collected from 113 bats of 33 species, divided into five dietary guilds (frugivores [FRU]; insectivores [INS]; nectarivores [NEC]; sanguivores [SAN]; and carnivores [CAR]).
Isolation and identification of the microbiota
Samples collected in fieldwork were plated on 5% sheep blood agar and MacConkey agar, and incubated aerobically at 36°C for 24h. Colonies were further isolated by morphotype and preserved in Tryptic Soy Broth and 20% glycerol at -80°C; all the isolates are stocked at the Culture Collection of the Fundação Parque Zoológico de São Paulo. The isolates were later identified by the matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) technique, using MALDI Biotyper System in collaboration with the Proteomics Laboratory at Universidade Federal de São Paulo [25]. The database of this technique is mostly composed by pathogenic species, therefore a great part of the identifications tend to result on pathogenic bacteria species. Isolates were analyzed using a formic acid-based direct, on-plate preparation method. Small amounts of a single colony were smeared directly onto a spot of the MALDI-TOF MS steel anchor plate. Each spot was then overlaid with one microliter of 70% formic acid and allowed to dry. The dried mixture was overlain with 1 μl of matrix solution (α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid [HCCA]) dissolved in 50% acetonitrile, 47.5% water, and 2.5% trifluoroacetic acid and allowed to dry prior to analysis using the MALDI Biotyper. An Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) isolate was used for instrument calibration. Two positive controls (Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923) were included with each run [26].
Antibiotic sensitivity
Antibiotic susceptibility tests were performed on Mueller Hinton agar using Kirby-Bauer’s antibiotic disc diffusion technique [27]. The tests were performed for the most potentially pathogenic bacteria species Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella sp., Serratia marcescens, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Stenotrophomonas sp. The antibiotics used on the tests were selected according to the bacteria characteristics [28], and the discs were firmly placed on the seeded plates, which were incubated at 36°C for 24h. The susceptibility of each isolate for different antibiotics was evaluated by the zones of inhibition, which were measured and compared with the susceptibility pattern of each antibiotic defined by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [28].
The antibiotics tested for Acinetobacter baumannii were: amikacin (AMI, 30 μg), ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg), ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), chloramphenicol (CLO, 30 μg), gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg), imipenem (IPM, 10 μg) and norfloxacin (NOR, 10 μg). The antibiotics tested for Pseudomonas aeruginosa were: ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg), ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg), imipenem (IPM, 10 μg) and norfloxacin (NOR, 10 μg). The antibiotics tested for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Stenotrophomonas sp. were: ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg), ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg), imipenem (IPM, 10 μg), norfloxacin (NOR, 10 μg) and trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole (SUT, 1.25/23.75 μg). The antibiotics tested for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, Salmonella sp. and Serratia marcescens were: amikacin (AMI, 30 μg), ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg), ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), chloramphenicol (CLO, 30 μg), gentamicin (GEN, 10 μg), imipenem (IPM, 10 μg), doxycycline (DOX, 30 μg), ampicillin (AMP, 10 μg), amoxicillin-clavulanate (AMC, 20/10 μg) and cephalexin (CFL, 30 μg).
Results
Oral and rectal microbiota
We isolated 830 morphotypes of bacteria from bats in five different dietary guilds (carnivores, frugivores, insectivores, nectarivores and sanguivores). A total of 596 morphotypes were identified at the genus level and tentatively to the species level by the MALDI-TOF methodology, including 243 from the oral cavity and 353 from the rectal cavity. Successfully identified isolates from the oral cavity are represented by: 14 isolates from two species of carnivores; 15 isolates from two species of sanguivores; 25 isolates from three species of nectarivores; 75 isolates from 14 species of insectivores; and 113 isolates from 10 species of frugivores (Table 1). Successfully identified isolates from the rectal cavity are represented by: 11 isolates from two species of carnivores; 27 isolates from two species of sanguivores; 60 isolates from two species of nectarivores; 90 isolates from 15 species of insectivores; and 165 isolates from 11 species of frugivores (Table 2).
Table 1. Successfully identified oral microbiota from bats of Carlos Botelho State Park, São Paulo State.
| Species (Number of specimens) | Diet | Oral Microbiota (Number of isolates) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Phyllostomidae | ||||
| Subfamily Micronycterinae | ||||
| Micronycteris microtis(2) | Insectivore | Hafnia alvei (2); Serratia marcescens (1); Streptococcus gallinaceus (1) | ||
| Micronycteris schimdtorum(1) | Insectivore | - | ||
| Subfamily Desmodontinae | ||||
| Desmodus rotundus(6) | Sanguivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Arthrobacter sp. (1); Klebsiella sp. (1); Kluyvera sp. (1); Pantoea sp. (1); Pseudomonas stutzeri (2); Raoultella sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (2); Serratia sp. (1); Staphylococcus aureus (1); Streptococcus gallinaceus (1) | ||
| Diphylla ecaudata(3) | Sanguivore | Staphylococcus sp. (2) | ||
| Subfamily Phyllostominae | ||||
| Mimon bennetti(1) | Carnivore | Citrobacter freundii (1); Enterobacter sp. (2); Klebsiella sp. (1); Lactococcus lactis (1); Serratia marcescens (1) | ||
| Trachops cirrhosus(2) | Carnivore | Aeromonas hydrophila (2); Kluyvera ascorbata (2); Lactococcus lactis (1); Serratia marcescens (3) | ||
| Subfamily Glossophaginae | ||||
| Anoura caudifer(9) | Nectarivore | Arthrobacter sp.(1); Cedecea lapagei (1); Lactococcus lactis (1); Microbacterium sp. (1); Pseudomonas fulva (1); Pseudomonas koreensis (1); Pseudomonas sp.(1); Rahnella sp. (2); Serratia marcescens (6); Staphylococcus aureus (1); Streptococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Anoura geoffroyi(7) | Nectarivore | Arthrobacter sp. (1); Enterobacter cloacae (1); Pantoea agglomerans (1); Pantoea sp. (1); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Staphylococcus aureus (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Glossophaga soricina(1) | Nectarivore | Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Subfamily Carolliinae | ||||
| Carollia perspicillata(8) | Frugivore | Escherichia sp. (1); Escherichia vulneris (1); Neisseria sp. (1); Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1); Pseudomonas extremorientalis (2); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Serratia liquefaciens (1); Serratia marcescens (5); Staphylococcus sp. (1); Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (1) | ||
| Subfamily Glyphonycterinae | ||||
| Glyphonycteris sylvestris(2) | Insectivore | Serratia sp. (4) | ||
| Subfamily Stenodermatinae | ||||
| Artibeus fimbriatus(9) | Frugivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Arthrobacter sp. (1); Burkholderia sp. (1);Enterobacter cloacae (2); Enterobacter sp. (3); Klebsiella oxytoca (2); Pseudomonas sp. (3); Raoultella ornithinolytica (1); Raoultella terrigena (4); Serratia marcescens (3); Serratia sp. (2); Stenotrophomonas sp.(1) | ||
| Artibeus lituratus(5) | Frugivore | Acinetobacter sp. (2); Lactococcus sp. (1); Leclercia adecarboxylata (1); Leclercia sp. (1); Pantoea agglomerans (1); Pantoea sp. (1); Salmonella sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (2); Serratia sp. (1); Staphylococcus saprophyticus (1); Streptococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Artibeus obscurus(8) | Frugivore | Enterobacter sp. (1); Leclercia adecarboxylata (1); Ochrobactrum intermedium (1); Ochrobactrum sp. (1); Pantoea agglomerans (6); Pseudomonas koreensis (2); Pseudomonas sp. (6); Serratia marcescens (5); Serratia sp. (1); Stenotrophomonas sp. (1) | ||
| Dermanura cinerea(2) | Frugivore | Pantoea sp. (3); Serratia marcescens (1); Serratia sp.(2) | ||
| Platyrrhinus lineatus(1) | Frugivore | Enterobacter asburiae (1); Klebsiella oxytoca (1); Klebsiella sp. (1) | ||
| Platyrrhinus recifinus(1) | Frugivore | Enterobacter sp. (2); Serratia marcescens (2) | ||
| Pygoderma bilabiatum(2) | Frugivore | - | ||
| Sturnira lilium(8) | Frugivore | Acinetobacter lwoffii (1); Escherichia coli (2); Hafnia sp. (2); Lactococcus lactis (1); Pantoea agglomerans (1); Pantoea ananatis (2); Pseudomonas sp. (3); Streptococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Sturnira tildae(5) | Frugivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Bacillus thuringiensis (1); Enterobacter sp. (1); Escherichia coli (2); Leclercia sp. (1); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Stenotrophomonas sp. (1) | ||
| Vampyressa pusilla(1) | Frugivore | Enterobacter sp. (2) | ||
| Family Molossidae | ||||
| Subfamily Molossinae | ||||
| Cynomops abrasus(1) | Insectivore | Acinetobacter pittii (2); Enterobacter cloacae (1) | ||
| Molossops neglectus(1) | Insectivore | Enterobacter sp. (1); Escherichia coli (1); Serratia marcescens (2); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Molossus currentium(1) | Insectivore | Hafnia sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (4) | ||
| Molossus molossus(4) | Insectivore | Cedecea lapagei (1); Citrobacter sp. (1); Ochrobactrum sp. (1); Ochrobactrum tritici (1); Serratia marcescens (2); Serratia sp. (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Molossus rufus(2) | Insectivore | Acinetobacter baumannii (1); Acinetobacter sp. (1); Escherichia coli (1); Proteus vulgaris (1); Salmonella sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (2) | ||
| Family Vespertilionidae | ||||
| Subfamily Vespertilioninae | ||||
| Eptesicus taddeii(1) | Insectivore | Serratia sp. (2) | ||
| Lasiurus ebenus(1) | Insectivore | Enterobacter cloacae (1); Pseudomonas aeruginosa (2); Serratia marcescens (3) | ||
| Histiotus velatus(3) | Insectivore | Enterobacter sp. (1); Erwinia persicina (1); Hafnia alvei (2); Pseudomonas sp.(1); Serratia marcescens (2); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Subfamily Myotinae | ||||
| Myotis albescens(1) | Insectivore | Staphylococcus sp. (2) | ||
| Myotis nigricans(6) | Insectivore | Aeromonas hydrophila (1); Enterobacter sp. (2); Lactococcus lactis (1); Pantoea agglomerans (1); Pantoea sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (3); Serratia sp. (2); Yokenella regensburgei (1) | ||
| Myotis riparius(2) | Insectivore | Serratia marcescens (2) | ||
| Myotis ruber(2) | Insectivore | Enterococcus faecalis (1); Ewingella americana (2); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (2); Serratia sp. (1) | ||
Table 2. Successfully identified rectal microbiota from bats of Carlos Botelho State Park, São Paulo State.
| Species (Number of specimens) | Diet | Rectal Microbiota (Number of isolates) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family Phyllostomidae | ||||
| Subfamily Micronycterinae | ||||
| Micronycteris microtis(2) | Insectivore | Citrobacter koseri (1); Citrobacter sp. (1); Enterobacter cloacae (1); Hafnia alvei (2) | ||
| Micronycteris schimdtorum(1) | Insectivore | Staphylococcus sp. (2) | ||
| Subfamily Desmodontinae | ||||
| Desmodus rotundus(6) | Sanguivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Brevundimonas sp. (1); Citrobacter sp. (2); Edwardsiella sp. (1); Escherichia coli (3); Klebsiella oxytoca (4); Klebsiella sp. (2); Pantoea sp. (2); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Staphylococcus aureus (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Diphylla ecaudata(3) | Sanguivore | Enterobacter cloacae (1); Enterobacter sp. (1); Escherichia sp. (3); Klebsiella oxytoca (1); Serratia marcescens (2) | ||
| Subfamily Phyllostominae | ||||
| Mimon bennetti(1) | Carnivore | Citrobacter freundii (1); Hafnia alvei (1); Klebsiella oxytoca (1); Kluyvera ascorbata (1); Vagococcus fluvialis (1) | ||
| Trachops cirrhosus(2) | Carnivore | Escherichia coli (2); Kluyvera ascorbata (3); Serratia marcescens (1) | ||
| Subfamily Glossophaginae | ||||
| Anoura caudifer(9) | Nectarivore | Acinetobacter baylyi (1); Acinetobacter sp. (2); Bacillus sp. (2); Cedecea lapagei (3); Enterobacter radicincitans (1); Enterobacter sp. (1); Erwinia sp. (4); Ewingella sp. (1); Klebsiella oxytoca (2); Klebsiella sp. (1); Kluyvera sp. (1); Pantoea agglomerans (1); Pantoea ananatis (1); Pantoea sp. (2); Pseudomonas sp. (4); Pseudomonas taetrolens (1); Raoultella terrigena (1); Serratia marcescens (3); Staphylococcus aureus (3); Staphylococcus sp. (1); Streptococcus agalactiae (1); Streptococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Anoura geoffroyi(7) | Nectarivore | Citrobacter freundii (1); Enterobacter sp. (5); Hafnia alvei (1); Hafnia sp. (2); Klebsiella sp. (1); Kluyvera ascorbata (1); Kluyvera sp. (1); Pantoea ananatis (1); Pantoea sp. (1); Raoultella terrigena (1); Serratia sp. (1); Staphylococcus capitis (1); Staphylococcus epidermidis (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1); Stenotrophomonas sp. (1); Streptococcus agalactiae (1) | ||
| Glossophaga soricina(1) | Nectarivore | - | ||
| Subfamily Carolliinae | ||||
| Carollia perspicillata(8) | Frugivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Bacillus sp. (1); Enterobacter sp. (4); Escherichia sp. (1); Ewingella sp. (1); Leclercia adecarboxylata (2); Pantoea sp. (2); Pseudomonas putida (2); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Raoultella terrigena (1); Serratia marcescens (4); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Subfamily Glyphonycterinae | ||||
| Glyphonycteris sylvestris(2) | Insectivore | Serratia marcescens (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Subfamily Stenodermatinae | ||||
| Artibeus fimbriatus(9) | Frugivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Enterobacter asburiae (1); Enterobacter cloacae (2); Enterobacter sp. (5); Erwinia sp. (1); Escherichia coli (4); Klebsiella sp. (1); Lactococcus sp. (2); Leclercia adecarboxylata (1); Raoultella ornithinolytica (1); Raoultella sp. (1); Raoultella terrigena (2); Serratia marcescens (2) | ||
| Artibeus lituratus(5) | Frugivore | Bacillus megaterium (1); Citrobacter freundii (1); Enterobacter cloacae (1); Enterobacter sp. (2); Escherichia coli (2); Klebsiella oxytoca (1); Lactococcus lactis (2); Lactococcus sp. (1); Pantoea agglomerans (1); Pantoea sp. (2); Serratia marcescens (2); Serratia sp. (1) | ||
| Artibeus obscurus(8) | Frugivore | Enterobacter aerogenes (1); Enterobacter ludwigii (1); Enterobacter sp. (6); Enterococcus sp. (1); Erwinia sp. (1); Escherichia coli (6); Escherichia sp. (4); Hafnia sp. (1); Klebsiella oxytoca (2); Klebsiella sp. (1); Raoultella planticola (1); Raoultella terrigena (1); Serratia marcescens (4); Serratia sp. (1);Sphingobacterium sp. (1) | ||
| Dermanura cinerea(2) | Frugivore | Citrobacter sp. (1); Enterobacter sp. (3); Klebsiella sp. (1); Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (1) | ||
| Platyrrhinus lineatus(1) | Frugivore | Enterobacter sp. (4); Kluyvera ascorbata (1) | ||
| Platyrrhinus recifinus(1) | Frugivore | Enterobacter sp. (1); Raoultella sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (1) | ||
| Pygoderma bilabiatum(2) | Frugivore | Enterobacter cloacae (2); Leclercia adecarboxylata (2); Leclercia sp. (1); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (2); Stenotrophomonas sp. (1) | ||
| Sturnira lilium(8) | Frugivore | Citrobacter freundii (2); Citrobacter sp. (2); Enterobacter sp. (1); Escherichia coli (8); Escherichia sp. (5); Klebsiella sp. (2); Kluyvera ascorbata (1); Kluyvera sp. (1); Pantoea sp. (1); Pseudomonas sp. (2); Serratia marcescens (2) | ||
| Sturnira tildae(5) | Frugivore | Aeromonas sp. (1); Cedecea sp. (1); Citrobacter freundii (1); Citrobacter sp. (1); Enterobacter sp. (2); Escherichia coli (1); Escherichia sp. (3); Kluyvera sp. (1); Providencia alcalifaciens (3); Pseudomonas sp. (2); Streptococcus gallolyticus (1) | ||
| Vampyressa pusilla(1) | Frugivore | Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Family Molossidae | ||||
| Subfamily Molossinae | ||||
| Cynomops abrasus(1) | Insectivore | Providencia rettgeri (2); Providencia sp. (1) | ||
| Molossops neglectus(1) | Insectivore | Enterococcus sp. (1); Providencia rettgeri (2) | ||
| Molossus currentium(1) | Insectivore | Lactococcus sp. (1); Proteus sp. (1); Proteus vulgaris (1) | ||
| Molossus molossus(4) | Insectivore | Enterococcus faecalis (2); Enterococcus sp. (2); Escherichia coli (3); Hafnia alvei (2); Hafnia sp. (2);Klebsiella oxytoca (2); Lactococcus sp. (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1); | ||
| Molossus rufus(2) | Insectivore | Escherichia albertii (1); Escherichia coli (1); Proteus vulgaris (3); Salmonella sp. (1) | ||
| Family Vespertilionidae | ||||
| Subfamily Vespertilioninae | ||||
| Eptesicus taddeii(2) | Insectivore | Enterococcus sp. (1); Escherichia coli (1); Escherichia sp. (1); Hafnia alvei (1); Providencia sp. (2); Serratia sp. (1) | ||
| Lasiurus ebenus(1) | Insectivore | Acinetobacter sp. (1); Enterobacter asburiae (1); Enterobacter cloacae (1); Escherichia vulneris (1); Klebsiella sp. (1); Leclercia sp. (1); Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1); Staphylococcus sp. (1) | ||
| Histiotus velatus(3) | Insectivore | Ewingella sp. (1); Hafnia alvei (3); Hafnia sp. (3);Sphingobacterium sp. (1) | ||
| Subfamily Myotinae | ||||
| Myotis albescens(1) | Insectivore | Plesiomonas shigelloides (1); Plesiomonas sp. (1) | ||
| Myotis nigricans(6) | Insectivore | Hafnia alvei (2); Lactococcus garvieae (2); Lactococcus lactis (1); Serratia marcescens (1); Serratia sp. (2); Staphylococcus hominis (1); Staphylococcus xylosus (1) | ||
| Myotis riparius(2) | Insectivore | Enterococcus faecalis (1); Hafnia alvei (2); Raoultella sp. (1); Raoultella terrigena (1); Serratia marcescens (4) | ||
| Myotis ruber(2) | Insectivore | Cedecea sp. (1); Enterococcus faecalis (1); Ewingella americana (2); Hafnia alvei (1); Lactococcus lactis (1); Pseudomonas sp. (1); Serratia marcescens (1) | ||
Isolates belong to four bacteria phyla, divided into 15 families. Proteobacteria was the most abundant phylum in all the dietary guilds, representing 87% of the total samples, followed by Firmicutes with 12%, and Actinobacteria and Bacteriodetes counting together 1% of the total identified samples. The family Enterobacteriaceae represented 73% of the samples, followed by Pseudomonadaceae, with 7%, and the other 20% are composed by small sums of the families Aeromonadaceae, Bacillaceae, Brucellaceae, Burkholderiaceae, Caulobacteraceae, Enterococcaceae, Lysobacteraceae, Microbacteriaceae, Micrococcaceae, Moraxellaceae, Neisseriaceae, Sphingobacteriaceae, Staphylococcaceae and Streptococcaceae. The phylum Actinobacteria, represented by Arthrobacter sp. and Microbacterium sp. was found only in the oral cavity, while the phylum Bacteroidetes is represented only by Sphingobacterium sp. in the rectal cavity.
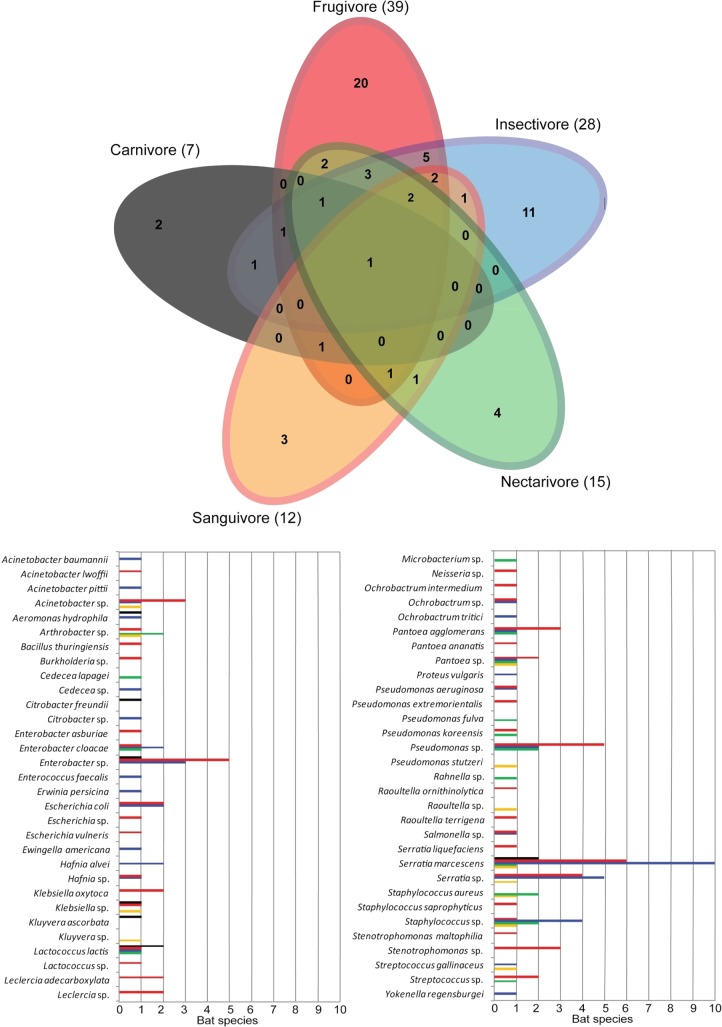
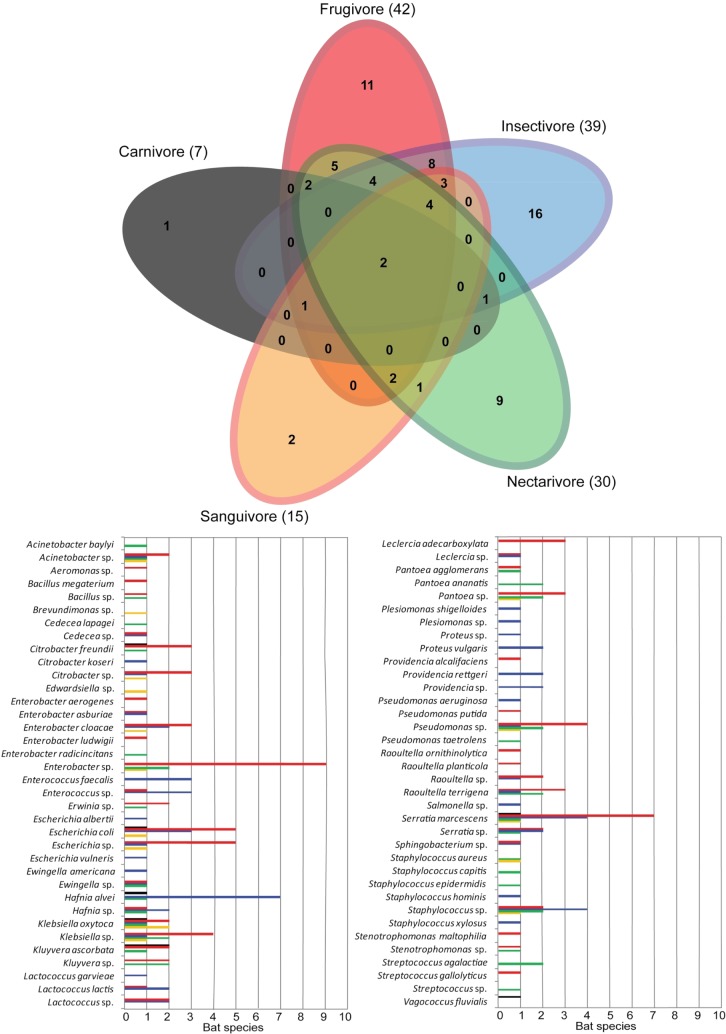
Sixty-two taxa of bacteria were identified in the oral cavity and 72 in rectal cavity of the bats. The Venn diagram analysis (Figs 1 and 2) indicates that the major proportion of the bacteria within the dietary guilds is shared between two or more guilds. The oral richness shared between guilds varies from 49% to 75%, whereas the rectal richness varies from 59% to 87% of bacteria taxa shared with at least one other guild. However, only the species S. marcescens is shared between all five guilds when the oral richness is analyzed alone, and only the species K. oxytoca and S. marcescens are shared between all the guilds when considered the rectal richness. Comparing the dietary guilds, higher richness was found on frugivores (58 taxa), followed by insectivores (50 taxa), nectarivores (37 taxa), sanguivores (21 taxa) and carnivores (11 taxa).
Fig 1. Venn-diagram showing the distribution of bacterial taxa from oral swabs of five dietary guilds of bats on Carlos Botelho State Park, São Paulo State.
The number of taxa within each guild is represented in parenthesis. The abundance of each taxa on bat species is presented in the graph, and separated by dietary guilds.
Fig 2. Venn-diagram showing the distribution of bacterial taxa from rectal swabs of five dietary guilds of bats on Carlos Botelho State Park, São Paulo State.
The number of taxa within each guild is represented in parenthesis. The abundance of each taxa on bat species is presented in the graph, and separated by dietary guilds.
Antibiotic sensitivity
Strains of one A. baumannii, 20 E. coli, 13 K. oxytoca, two P. aeruginosa, two Salmonella sp., 36 S. marcescens, two S. maltophilia and five Stenotrophomonas sp. were selected as the most potentially pathogenic isolates and tested for their susceptibility for antibiotics. The A. baumannii isolate was resistant only to ciprofloxacin, intermediate to ceftriaxone and sensible to all the other tested antibiotics. The two P. aeruginosa isolates were sensible to all the antibiotics tested. The two Salmonella sp. isolates exhibited different sensitivity, with one sensible to all the antibiotics tested, and the other resistant to the antibiotics ampicillin and cephalexin. Two S. maltophilia and five Stenotrophomonas sp. isolates also exhibited differences in sensitivity, with all the isolates resistant to the antibiotics ceftriaxone and imipenem, only one isolate sensible to the antibiotic gentamicin, and with variable sensitivity to the antibiotic ceftazidime (Table 3).
Table 3. Antibiotic-resistance patterns of Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella sp., Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Stenotrophomonas sp. from swabs of bats on Carlos Botelho State Park, Brazil.
The resistance patterns are classified as Sensitive (S), Intermediate (I) and Resistant (R). See Materials and Methods section for description of diet and antibiotics.
| Bat species | Diet | Bacteria | Cavity | SUT | AMI | CAZ | CRO | CIP | CLO | DOX | GEN | IPM | NOR | AMC | AMP | CFL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molossus rufus | INS | Acinetobacter baumannii | Oral | - | S | S | I | R | S | - | S | S | S | - | - | - |
| Carollia perspicillata | FRU | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Oral | - | - | S | S | S | - | - | S | S | S | - | - | - |
| Lasiurus ebenus | INS | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Oral | - | - | S | S | S | - | - | S | S | S | - | - | - |
| Artibeus lituratus | FRU | Salmonella sp. | Oral | - | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | S | R | R |
| Molossus rufus | INS | Salmonella sp. | Rectal | - | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | - | S | S | S |
| Carollia perspicillata | FRU | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | Oral | S | - | S | R | S | - | - | R | R | S | - | - | - |
| Dermanura cinerea | FRU | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | Rectal | S | - | S | R | S | - | - | R | R | S | - | - | - |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Stenotrophomonas sp. | Oral | S | - | R | R | S | - | - | R | R | S | - | - | - |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Stenotrophomonas sp. | Oral | S | - | R | R | S | - | - | R | R | S | - | - | - |
| Pygoderma bilabiatum | FRU | Stenotrophomonas sp. | Rectal | S | - | R | R | S | - | - | S | R | S | - | - | - |
| Sturnira tildae | FRU | Stenotrophomonas sp. | Oral | S | - | S | R | S | - | - | R | R | S | - | - | - |
| Anoura geoffroyi | NEC | Stenotrophomonas sp. | Rectal | S | - | S | R | S | - | - | R | R | S | - | - | - |
The 20 E. coli isolates responses to the antibiotics tested were variable. Resistance to the antibiotics was absent for 16 of the isolates (80% of E. coli isolates), one isolate (5% of E. coli isolates) was resistant to ampicillin, one isolate (5% of E. coli isolates) was resistant to ampicillin and cephalexin, and two (10% of E. coli isolates) were resistant to amoxicillin-clavulanate, ampicillin and cephalexin (Table 4). From the 13 K. oxytoca isolates, seven (54% of K. oxytoca isolates) showed resistance to ampicillin, five (38% of K. oxytoca isolates) were intermediate to ampicillin, and one (8% of K. oxytoca isolates) was resistant to amoxicillin-clavulanate, ampicillin and cephalexin (Table 5). From the 36 S. marcescens isolates, 34 (95% of S. marcescens isolates) presented resistance to the antibiotics amoxicillin-clavulanate, ampicillin and cephalexin, and only two isolates (5% of S. marcescens isolates) were not resistant to amoxicillin-clavulanate and ampicillin (Table 6).
Table 4. Antibiotic-resistance patterns of Escherichia coli from swabs of bats on Carlos Botelho State Park, Brazil.
The resistance patterns are classified as Sensitive (S), Intermediate (I) and Resistant (R). See Materials and Methods section for description of diet and antibiotics.
| Bat species | Diet | Bacteria | Cavity | AMI | CAZ | CRO | CIP | CLO | DOX | GEN | IPM | AMC | AMP | CFL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trachops cirrhosus | CAR | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I |
| Artibeus lituratus | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Escherichia coli | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Sturnira lilium | FRU | Escherichia coli | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Sturnira lilium | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Sturnira lilium | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Sturnira lilium | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Sturnira lilium | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Sturnira tildae | FRU | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Eptesicus taddeii | INS | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Molossops neglectus | INS | Escherichia coli | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Molossus molossus | INS | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
| Molossus rufus | INS | Escherichia coli | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R |
| Molossus rufus | INS | Escherichia coli | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S |
Table 5. Antibiotic-resistance patterns of Klebsiella oxytoca from swabs of bats on Carlos Botelho State Park, Brazil.
The resistance patterns are classified as Sensitive (S), Intermediate (I) and Resistant (R). See Materials and Methods section for description of diet and antibiotics.
| Bat species | Diet | Bacteria | Cavity | AMI | CAZ | CRO | CIP | CLO | DOX | GEN | IPM | AMC | AMP | CFL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mimon bennetti | CAR | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Klebsiella oxytoca | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Klebsiella oxytoca | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Artibeus lituratus | FRU | Klebsiella oxytoca | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Platyrrhinus lineatus | FRU | Klebsiella oxytoca | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Diphylla ecaudata | SAN | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S |
| Molossus molossus | INS | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
| Anoura caudifer | NEC | Klebsiella oxytoca | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | S |
Table 6. Antibiotic-resistance patterns of Serratia marcescens from swabs of bats on Carlos Botelho State Park, Brazil.
The resistance patterns are classified as Sensitive (S), Intermediate (I) and Resistant (R). See Materials and Methods section for description of diet and antibiotics.
| Bat species | Diet | Bacteria | Cavity | AMI | CAZ | CRO | CIP | CLO | DOX | GEN | IPM | AMC | AMP | CFL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mimon bennetti | CAR | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Trachops cirrhosus | CAR | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Artibeus fimbriatus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Artibeus lituratus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Artibeus obscurus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Carollia perspicillata | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Carollia perspicillata | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Dermanura cinerea | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Platyrrhinus recifinus | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Pygoderma bilabiatum | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Pygoderma bilabiatum | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Sturnira lilium | FRU | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Glyphonycteris sylvestris | INS | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Histiotus velatus | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Lasiurus ebenus | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Micronycteris microtis | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Molossops neglectus | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | I | S | R |
| Molossus cf. currentium | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Molossus molossus | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Molossus molossus | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Molossus rufus | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | I | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Myotis nigricans | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Myotis nigricans | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Myotis nigricans | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Myotis riparius | INS | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Myotis ruber | INS | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Myotis ruber | INS | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Anoura caudifer | NEC | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Anoura caudifer | NEC | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Anoura caudifer | NEC | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
| Desmodus rotundus | SAN | Serratia marcescens | Oral | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R |
| Diphylla ecaudata | SAN | Serratia marcescens | Rectal | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | S | R | R | R |
Discussion
Bacteria richness
Gram-negative bacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria seems to be common in bat microbiota on studies based both on culture protocols and DNA sequencing, being isolated from oral and rectal cavities [8], intestine [9, 18] and saliva [10]. The phyla Actinobacteria, Bacteriodetes and Firmicutes were also previously reported as common on bats [10, 11, 18].
The mammalian gut microbiota diversity is related to the host diet, and should increase from animal-based diets to omnivorous to herbivore diets [29]. In our results, the frugivores microbiota was the most diverse among the five analyzed dietary guilds, and agrees to the mammalian gut microbiota theory. The less diverse microbiota in our survey was found in carnivores, which is also in agreement to the mammal microbiota theory. However, insectivores also showed high microbiota richness, and diverge from the expected, which could be explained by the inclusion of different alimentary items, rather than insects, on the diet of many species classified as insectivores. Species such as Glyphonycteris sylvestris, Lampronycteris brachyotis, Micronycteris microtis and Myotis nigricans analyzed in this study are reported to complement their diet with fruits and/or pollen [30–32], which could increase the general microbiota richness of the insectivore bats guild analyzed here.
Another possible explanation for the richness observed in the different bat guilds lies within the number of bats sampled for each guild, whereas the most diverse guilds are also the ones with more bat captures.Though most of the results are in agreement to other studies based on DNA sequencing, the general bacteria richness of bats from CBSP may be biased by the identification technique and the culture step. On the other hand, some bacteria genera, including pathogenic ones, are hard to speciate using DNA sequencing techniques [11], making comparisons even harder.
Some bacteria genera, such as Arthrobacter, Burkholderia, Microbacterium, Neisseria and Rahnella were found only in the oral cavity. Arthrobacter is composed by soil bacteria, and was also found on bats’ wing sacs, chin and axillae by other authors [33–35]; strains of Arthrobacter and Rahnella were identified as effective inhibitory antagonists of the growth of Pseudogymnoascus destructans, the fungus that causes white-nose syndrome, a letal bat disease [36]. Burkholderia and Microbacterium were previously found on bats’ saliva, urine, faeces, and intestine [9, 10]. Neisseria was previously found on bat saliva samples [10], and is closely related to mucosal and dental surfaces, being a consistent component of human oral microbiota and also found in different mammals [37]. The rectal cavity exclusive genus Enterococcus was also isolated from bats’ wings [35]. Brevundimonas, found only on the rectal cavity, was originally isolated from water and hospital-related material. This bacterium has been previously reported for marine mammals and is not common in bats [38, 39].
Bacteria genera observed within different dietary guilds were also divergent, with some exclusive occurrences. Edwardsiella was found only in sanguivores. This bacterium was previously isolated from bovine faeces and latter from cattle meat, wild mammals and birds [40, 41]. Thus, the occurrence of this bacterium only in this guild appears to be related to the feeding habit, which is based on blood from domestic and wild mammals and birds [42]. Plesiomonas, Proteus and Yokenella were identified only in insectivores. The genus Proteus, however, was also found in sanguivores and frugivores in other studies [8, 43]. The genus Plesiomonas is reported to be isolated from freshwater and surface water samples [44], and many species of insectivores are associated to these environments [45–47], where they forage and could be exposed to bacteria. Yokenella was previously isolated from the intestinal tracts of insects and faeces of insect-feeding animals, including bats [48, 49]; therefore it is probably related to this kind of diet. Vagococcus, here observed only in carnivores, has been recovered from animals, water, soil and human sources [50]. S.marcescens and K. oxytoca were found on all five dietary guilds. S.marcescens was reported in other studies and various dietary guilds, including frugivores [7], sanguivores [8, 43], and insectivores[11, 35]. K. oxytoca was previously reported in frugivores [7, 51] and insectivores[14, 52]; however, K. oxytoca was highly related to vespertilionid (insectivores) bats rather than to any other Australian mammal on previous studies [53].
Antibiotic sensitivity
Generally, the resistance to antibiotics found on our samples was related to the intrinsic resistance of the tested species [54] and independent of dietary guilds of the bats. The species P. aeruginosa and S. maltophilia did not show any resistance besides their expected intrinsic resistance patterns. The species A. baumannii and Stenotrophomonas sp. showed resistance to the antibiotics ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime, respectively; those resistances are not intrinsic and could be acquired from both clinical or environmental antibiotic resistance genes sources, disseminated on the environment. A. baumannii is one of the most important pathogens in hospitals, and the development of multidrug-resistant strains has become of great concern for antibiotic therapies. Ciprofloxacin is a very potent antibiotic used as first line agaist A. baumannii infections [55–57] and previous studies have isolated high rates of ciprofloxacin resistant strains of A. baumannii [58–60]. The development of resistance on A. baumannii strains has been previously related to mutations in the quinolone resistance determining regions and efflux pump mechanisms [58, 59]. The only strain of A. baumannii was isolated from an insectivore bat that was found during the day on the floor of a Visitors Center on CBSP, and the possible contact of the bat with human leavings could have influenced on the acquiring of resistant strains. The Stenotrophomonas sp. resistant strains were found on frugivorous and nectarivorous and could outcome from the contact with water or fruits and even casual ingestion of insects [19–21].
Additionally, once the contact with anthropic and agricultural environments is one of the major sources of acquired resistance, the activity pattern and diet of carnivores, insectivores and sanguivores bats would make them more susceptible to exposure to antimicrobials [21, 61, 62]. Therefore, it could be expected that carnivore, insectivore and sanguivore bats would present a higher rate of antibiotic resistant strains, when compared to frugivores and nectarivores. However, this pattern is not clear when we analyse the results obtained for the antibiograms of the abundant bacteria species E. coli, K. oxytoca and S. marcescens to compare the dietary guilds. A larger number of samples and complementary analysis could help to better evaluate this question.
The tested K. oxytoca isolates presented only one resistant strain (5%) and none of the S. marcescens isolates presented any resistance besides the intrinsic ones. The small rates of resistant bacteria observed on CBSP in consistently different from those observed in other studies conducted on areas influenced by anthropic activities [17, 20, 63, 64]. A study conducted on Krakatau Islands found a great number of resistant bacteria on local bats and rats, which they correlated, in part, to anthropic influence on the local islands [20]. The antibiotic-resistance pattern found for E. coli isolates from Nigerian bats also showed a great number of resistant isolates; the resistance was attributed to the use of antibiotics on poultry feed or on poultry itself [17]. Analyzing all of our tested isolates, 71 out of 81 (87%) did not present any resistance besides the expected from the intrinsic pattern, which could be related to the effectiveness of CBSP on the conservation of the wildlife and environment present on the preserved area of the Park. Once some of the sampling sites were close to the Park limits and some Brazilian bats are know to forage on distances of 0.5 to 15 km [65–67], it seens that bats from CBSP prefer to forage on the pristine environments rather than anthropized surroundings. Moreover, the restriction of the contact to antibiotics would not lead to the decline of acquired resistances; therefore, it is reasonable to expect that resistance patterns on CBSP were always similar to the results presented here and no previous chronic exposures existed [68]. This result is in agreement to previous studies [22, 69], which reported a lack of human-acquired antibiotic resistance on environments with minimal anthropic influence and no chronic exposure to antibiotics.
Besides direct exposure to antibiotics, bacterial resistance can be originated through horizontally mobile elements such as conjugative plasmids, integrons and transposons [21]. Therefore, the low rate of resistance found on the Enterobacteriaceae from CBSP also suggests a small probability of the diffusion of acquired resistance on the Park. Many authors reported that bacteria from remote areas could work as sentinels and help to evaluate the impact of anthropic pressure on wildlife and the role of wild-species and natural environments on the process of resistance acquiring, which includes not only the exposure to antibiotics but also horizontal transference [21–23]. Our findings reinforce the need of monitoring antimicrobial resistance in wildlife from remote areas, appearing to be an effective tool to evaluate the environment responses to anthropic pressures. On this way, more efforts should be carried out on the Park to better evaluate local resistance patterns, the impact that the human activites of the surroundings on the Park environment and the role of wildlife as reservoirs of resistant bacteria.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the staff of Parque Estadual Carlos Botelho for the logistical support, and to the Proteomics Laboratory from the Universidade Federal de São Paulo (UNIFESP) to provide the MALDI Biotyper for this research.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Fundação Parque Zoológico de São Paulo. The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Fenton MB, Simmons N. Bats: A World of Science and Mystery. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Herrera GL, Gutierrez E, Hobson KA, Altube B, Díaz WG, Sánchez-Cordero V. Sources of assimilated protein in five species of New World frugivorous bats. Oecologia. 2002;133: 280–287. 10.1007/s00442-002-1036-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19: 531–545. 10.1128/CMR.00017-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Peracchi AL, Lima IP, Reis NR, Nogueira MR, Ortencio Filho H. Ordem Chiroptera In: Reis NR, Peracchi AL, Pedro WA, Lima IP, editors. Mamíferos do Brasil. Londrina: Editora Universidade Estadual de Londrina; 2006. pp. 153–230. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Souza V, Rocha M, Valera A, Eguiarte LE. Genetic structure of natural populations of Escherichia coli in wild hosts on different continents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65: 3373–3385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Costa LP, Leite YLR, Mendes SL, Ditchfield AD. Mammal Conservation in Brazil. Conserv Biol. 2005;19: 672–679. 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2005.00666.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Daniel DS, Ng YK, Chua EL, Arumugam Y, Wong WL, Kumaran JV. Isolation and identification of gastrointestinal microbiota from the short-nosed fruit bat Cynopterus brachyotis brachyotis. Microbiol Res. 2013;168: 485–496. 10.1016/j.micres.2013.04.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Galicia J, Marcela M, Buenorostro SA, García GJ. Diversidad específica bacteriana en murciélagos de distintos gremios alimenticios en la sierra sur de Oaxaca, México. Rev Biol Trop. 2014;62: 1673–1681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Banskar S, Mourya DT, Shouche YS. Bacterial diversity indicates dietary overlap amoung bats of different feeding habits. Microbiol Res. 2016;182: 99–108. 10.1016/j.micres.2015.10.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dietrich M, Kearney T, Seamark EC, Markotter W. The excreted microbiota of bats: evidence of niche specialisation based on multiple body habitats. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017;364: 1–7. 10.1093/femsle/fnw284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vengust M, Knapic T, Weese JS. The fecal bacterial microbiota of bats; Slovenia. PLoS ONE 2018;13: e0196728 10.1371/journal.pone.0196728 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Klite PD. Intestinal bacteria flora and transit time of three neotropical bat species. J Bacteriol. 1965;90: 375–379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pinus M, Müller HE. Enterobacteria of bats (Chiroptera). Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1980;247: 315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Di Bella C, Piraino C, Caracappa S, Fornasari L, Violani C, Zava B. Enteric microflora in Italian Chiroptera. J Mt Ecol. 2003;7: 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Whitaker JO, Dannelly HK Jr., Prentice DA. Chitinase in insectivorous bats. J Mammal. 2004;85: 15–18. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mühldorfer K, Wibbelt G, Haensel J, Riehm J, Speck SY. Species isolated from bats, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis J. 2010;16: 578–580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Oluduro AO. Antibiotic-resistant commensal Escherichia coli in faecal droplets from bats and poultry in Nigeria. Vet Ital. 2012;48: 297–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Carrillo-Araujo M, Taş N, Alcántara-Hernández RJ, Gaona O, Schondube JE, Medellín RA, et al. Phyllostomid bat microbiome composition is associated to host phylogeny and feeding strategies. Front Microbiol. 2015;6: 1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Remington JS, Schimpff SC. Please don’t eat the salads. N Engl J Med. 1981;304: 433–435. 10.1056/NEJM198102123040730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Graves SR, Kennelly-Merrit SA, Tidermann CR, Rawlinson PA, Harvey KJ, Thornton IWB. Antibiotic-resistance patterns of enteric bacteria of wild mammals on the Krakatau Islands and West Java, Indonesia. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B. 1988;322: 339–353. 10.1098/rstb.1988.0129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Radhouani H, Silva N, Poeta P, Torres C, Correia S, Igrejas G. Potential impact of antimicrobial resistance in wildlife, environment and human health. Front Microbiol. 2014;5: 1–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Thaller MC, Migliore L, Marquez C, Tapia W, Cedeno V, Rossolini GM, et al. Tracking acquired antibiotic resistance in commensal bacteria of Galapagos land iguanas: no man, no resistance. PLoS ONE 2010;5: e8989 10.1371/journal.pone.0008989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smith S, Wang J, Fanning S, McMahon BJ. Antimicrobial resistant bacteria in wild mammals and birds: a coincidence or cause for concern? Ir Vet J. 2014;67: 1–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Paulo São (State). Plano de Manejo do Parque Estadual Carlos Botelho. São Paulo: Secretaria do Meio Ambiente/Instituto Florestal; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Veen SQ, Claas ECJ, Kuijper EJ. High-Through put Identification of Bacteria and Yeast by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry in Conventional Medical Microbiology Laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48: 900–907. 10.1128/JCM.02071-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schmitt BH, Cunningham SA, Dailey AL, Gustafson DR, Patel R. Identification of anaerobic bacteria by Bruker Biotyper matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry with on-plate formic acid preparation. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51: 782–786. 10.1128/JCM.02420-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bauer AW, Kirby WMM, Sherris JC, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966;45: 493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.NCCLS. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Approved Standard, 2nd Ed NCCLS document M31-A2. Pennsylvania: NCCLS; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ley RE, Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Knight R, Gordon JG. Worlds within worlds: evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6: 776–788. 10.1038/nrmicro1978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Giannini NP, Kalko EKV. The guild structure of animalivorous leaf–nosed bat of Barro Colorado Island, Panama, revisited. Acta Chiropt. 2005;7: 131–146. 10.3161/1733-5329(2005)7[131:TGSOAL]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Williams SL, Genoways HH. Subfamily Phyllostominae In: Gardner AL, editor. Mammals of South America, Volume I. Marsupials, Xenarthrans, Shrews, and Bats. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2008. pp. 255–300. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Novaes RLM, Souza RF, Ribeiro EA, Siqueira AC, Greco AV, Moratelli R. First evidence of frugivory in Myotis (Chiroptera, Vespertilionidae, Myotinae). Biodivers Data Journal. 2015;3: 1–5. 10.3897/BDJ.3.e6841 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Conn HJ, Dimmick I. Soil bacteria similar in morphology to Mycobacterium and Corynebacterium. J Bacteriol. 1947;54: 291–303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Studier EH, Lavoie KH. Microbial involvement in scent production in noctilionid bats. J Mammal. 1984;65: 711–714. 10.2307/1380864 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Voigt CC, Caspers B, Speck S. Bats, bacteria, and bat smell: sex-specific diversity of microbes in a sexually selected scent organ. J Mammal. 2005;86: 745–749. 10.1644/1545-1542(2005)086[0745:BBABSS]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Micalizzi EW, Mack JN, White GP, Avis TJ, Smith ML. Microbial inhibitors of the fungus Pseudogymnoascus destructans, the causal agent of white-nose syndrome in bats. PloS ONE. 2017;12: e0179770 10.1371/journal.pone.0179770 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bennett JS, Bratcher HB, Brehony C, Harrison OB, Maiden MC. The Genus Neisseria In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F, editors. The Prokaryotes. Berlin: Springer; 2014. pp. 881–900. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Segers P, Vancanneyt M, Pot B, Torck U, Hoste B, Dewettinck D, et al. Classification of Pseudomonas diminuta Leifson and Hugh 1954 and Pseudomonas vesicularis Büsing, Döll, and Freytag 1953 in Brevundimonas gen. nov. as Brevundimonas diminuta comb. nov. and Brevundimonas vesicularis comb. nov., respectively. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 1994;44: 499–510. 10.1099/00207713-44-3-499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wallace CC, Yund PO, Ford TE, Matassa KA, Bass AL. Increase in antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from stranded marine mammals of the Northwest Atlantic. Ecohealth. 2013;10: 201–210. 10.1007/s10393-013-0842-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ewing WH, McWhorter AC, Escobar MR, Lubin AH. Edwardsiella, a new genus of Enterobacteriaceae based on a new species, E. tarda. Int J Syst EvolMicrobioly. 1965;15:33–38. 10.1099/00207713-15-1-33 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Van Damme LR, Vandepitte J. Isolation of Edwardsiella tarda and Plesiomonas shigelloides from mammals and birds in Zaire. Rev Elev Med Vet Pays Trop. 1984;37: 145–151. doi: 10.19182/remvt.8429 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Oliveira GR, Porto GS, Lima IP. Subfamília Desmodotinae Wagner 1840 In: Reis NR, Peracchi AP, Batista CB, Lima IP, Pereira AD, editors. História Natural dos Morcegos Brasileiros: Chave de Identificação de Espécies. Rio de Janeiro: Technical Books Editora; 2017. pp. 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chaverri G. Flora bacteriana aeróbica del tracto digestivo del vampiro común, Desmodus rotundus (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae). Rev Biol Trop. 2006;54: 717–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Niedziela T, Lukasiewicz J, Jachymek W, Dzieciatkowska M, Lugowski C, Kenne L. Core Oligosaccharides of Plesiomonas shigelloides O54: H2 (Strain CNCTC 113/92) Structural and serological analysis of the lipopolysaccharide core region, the o-antigen biological repeating unit, and the linkage between them. J Biol Chem. 2002;277: 11653–11663. 10.1074/jbc.M111885200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Handley CO Jr.. Mammals of the Smithsonian Venezuelan Project. Brigham Young Univ Sci Bull. 1976;20: 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- 46.López-González C, Presley SJ, Owen RD, Willig MR.Taxonomic status of Myotis (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) in Paraguay. J Mammal. 2001;82: 138–160. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Meyer CFJ, Weinbeer M, Kalko EKV. Home–range size and spacing patterns of Macrophyllum macrophyllum (Phyllostomidae) foraging over water. J Mammal. 2005;86: 587–598. 10.1644/1545-1542(2005)86[587:HSASPO]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cassel-Beraud AM, Richard C. The aerobic intestinal flora of the microchiropteran bat Chaerephon pumila in Madagascar. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1988;81: 806–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Oliveira SMP, Morais BA, Gonçalves CA, Giordano-Dias CM, Vilela ML, Brazil RP, et al. Digestive tract microbiota in female Lutzomyia longipalpis (Lutz & Neiva, 1912) (Diptera: Psychodidae) feeding on blood meal and sucrose plus blood meal. Cad Saude Publica. 2001;17: 229–232. 10.1590/S0102-311X2001000100024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lawson PA. The genus Vagococcus In: Holzapfel WH, Wood BJB, editors. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Biodiversity and Taxonomy. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2014. pp. 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Anand AAP, Sripathi K. Digestion of cellulose and xylan by symbiotic bacteria in the intestine of the Indian flying fox (Pteropus giganteus). Comp Biochem Physiol AMol Integr Physiol. 2004;139: 65–69. 10.1016/j.cbpb.2004.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gordon DM, Lee J. The genetic structure of enteric bacteria from Australian mammals. Microbiol. 1999;145: 2673–2682. 10.1099/00221287-145-10-2673 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gordon DM. Geographical structure and host specificity in bacteria and the implications for tracing the source of coliform contamination. Microbiol. 2001;147: 1079–1085. 10.1099/00221287-147-5-1079 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Leclercq R, Cantón R, Brown DF, Giske CG, Heisig P, MacGowan AP, et al. EUCAST expert rules in antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;19: 141–160. 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03703.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Higgins PG, Wisplinghoff H, Stefanik D, Seifert H. Selection of topoisomerase mutations and overexpression of adeB mRNA transcripts during an outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother 2004;54:821–3. 10.1093/jac/dkh427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Meric M, Kasap M, Gacar G, Budak F, Dundar D, Kolayli F, et al. Emergence and spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a tertiary care hospital in Turkey. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008;282: 214–218. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01129.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Benjamin AE, Ahmed H, Sebastian GBA. The Rise of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19: 223–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ardebili A, Lari AR, Talebi M. Correlation of ciprofloxacin resistance with the AdeABC efflux system in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. AnnLab Med. 2014;34: 433–438. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.6.433 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Maleki MH, Jalilian FA, Khayat H, Mohammadi M, Pourahmad F, Asadollahi K, et al. Detection of highly ciprofloxacin resistance Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from patients with burn wound infections in presence and absence of efflux pump inhibitor. Mædica (Burchar), 2014;9: 162–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chen LK, Kuo SC, Chang KC, Cheng CC, Yu PY, Chang CH, et al. Clinical Antibiotic-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains with higher susceptibility to environmental phages than antibiotic-sensitive strains. Sci Rep. 2017;7: 6319 10.1038/s41598-017-06688-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Alonso CA, González-Barrio D, Tenorio C, Ruiz-Fons F, Torres C. Antimicrobial resistance in faecal Escherichia coli isolates from farmed red deer and wild small mammals. Detection of a multiresistant E. coli producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016;45: 34–39. 10.1016/j.cimid.2016.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Reis NR, Peracchi AL, Batista CB, Lima IP, Pereira AD. História Natural dos Morcegos Brasileiros: Chave de Identificação de Espécies,1st ed. Rio de Janeiro: Technical Books; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sherley M, Gordon DM, Collignon PJ. Variations in antibiotic resistance profile in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from wild Australian mammals. Environ Microbiol. 2000;2: 620–631. 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2000.00145.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Costa D, Poeta P, Sáenz Y, Vinué L, Coelho AC, Matos M, et al. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli isolates recovered from wild animals. Microb Drug Resist. 2008;14: 71–77. 10.1089/mdr.2008.0795 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Mello MAR, Kalko EKV, Silva WR. Movements of the bat Sturnira lilium and its role as a seed disperser of Solanaceae in the Brazilian Atlantic forest. J Trop Ecol. 2008;24: 225–228. 10.1017/S026646740800480X [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Peracchi AL, Lima IP, Reis NR, Nogueira MR, Ortencio Filho H. Ordem Chiroptera In: Reis NR, Peracchi AL, Pedro WA, Lima IP, editors. Mamíferos do Brasil, 2nd ed. Londrina: Editora Universidade Estadual de Londrina; 2011. pp. 155–234. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sekiama ML, Rocha VJ, Peracchi AL. Subfamília Carolliinae In: Reis NR, Fregonezi MN, Peracchi AL, Shibatta OA. Morcegos do Brasil: guia de campo. Rio de Janeiro: Technical Books Editora; 2013. pp. 109–133. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gilliver MA, Bennett M, Begon M, Hazel SM, Hart CA. Enterobacteria: antibiotic resistance found in wild rodents. Nature. 1999;401: 233 10.1038/45724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Österblad M, Norrdahl K, Korpimaki E, Huovinen P. How wild are wild mammals? Nature. 2001;409: 37–38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript.