FIGURE 1.
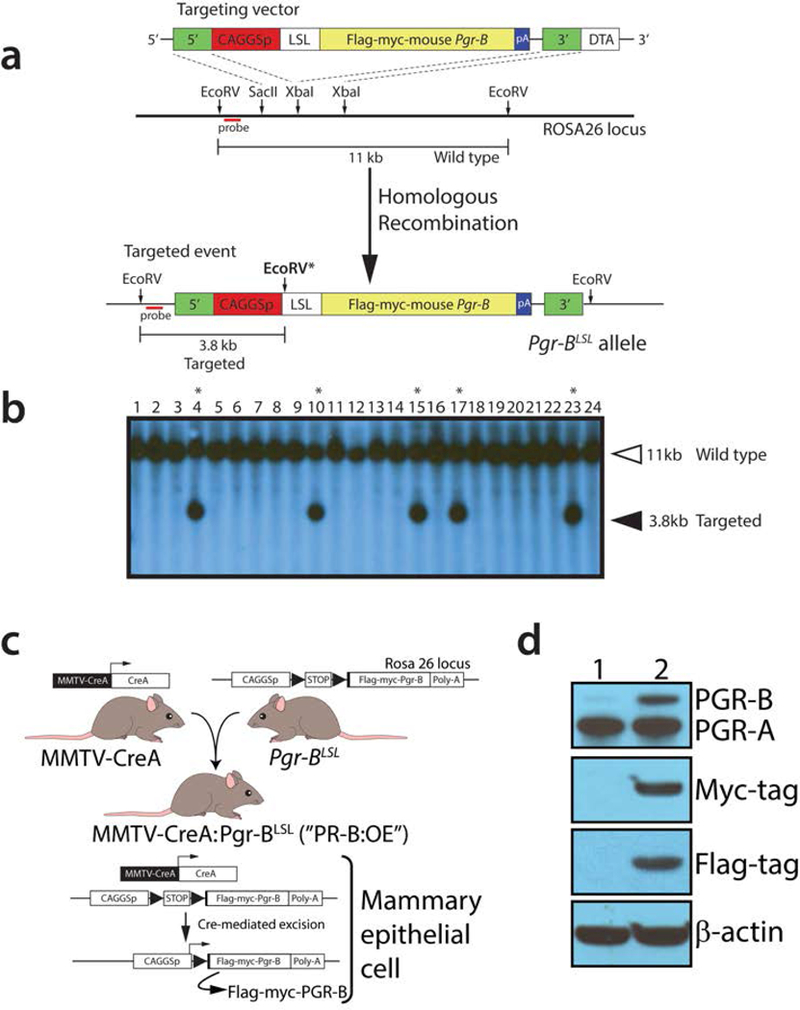
Generation of the Pgr-BLSL mouse. (a) Schematic (not to scale) of the targeting strategy in AB2.2 ES cells to generate the Pgr-BLSL allele in the Rosa26 locus. The location of the probe used for Southern analysis of targeted events is shown in red. With EcoRV digestion, the wild type allele is predicted to yield a 11kb hybridization band using this probe. Following homologous recombination with the targeting vector, a positive targeted event is predicated to display a 3.8kb hybridizing band due to an additional EcoRV site (EcoRV*) within the targeting vector (Wu et al., 2010). The 5’ and 3’ homology arms of the targeting vector are indicated in green. The constitutively active promoter is CAGGSp; LSL denotes the LoxP-STOP-LoxP cassette. The epitope-tagged murine Pgr-B cDNA insert is shown in yellow with its strong polyadenylation signal in blue. The targeting vector also contains the diphtheria toxin A gene for negative selection, which was not used in these studies. (b) Typical Southern result using the targeting strategy detailed in (a) above. Lanes 4, 10, 15, 17, and 23 represent positive targeted ES cell clones. Mouse lines were generated from ES cell clones: 4, 10, and 17; mice derived from ES cell clone 17 were analyzed in these studies. (c) Breeding strategy to generate the PR-B:OE by crossing the MMTV-CREA transgenic with mice harboring the Pgr-BLSL targeted allele. (d) Western analysis of mammary epithelial cell protein isolates derived from virgin control (lane 1) and PR-B:OE (lane 2) mice using primary antibodies against PGR, the myc-tag, and FLAG-tag; β-actin served as a loading control.
