Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the groundwater quality Indices of Groundwater resource for Agricultural Use in jolfa city (Iran) during one decade (2003–2013). Data showed in the first and end year of the study period, the Mean±SD of Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) and Sodium Percentage (Na%) indices 5455.77±3878.02, 3638.69±3565.19 and 51.49±15.65, 41.58±17.69, respectively. The data indicate that the, in terms of sodium percentage and sodium adsorption ratio, the water quality in this area is not suitable for irrigation.
Keywords: Groundwater, Indices changes, SAR, Na%, Jolfa
Specifications Table
| Subject area | Chemistry |
|---|---|
| More specific subject area | Chemistry of groundwater |
| Type of data | Table, Figures |
| How data was acquired | Data collected from Iran Water Resources Management Organization during the years 2003– 2013 |
| Data format | Raw, analyzed |
| Experimental factors | All water samples were stored in a polyethylene bottles at room temperature in dark place. |
| Data source location | Jolfa, East Azerbaijan province, Iran |
| Data accessibility | The data are available with this article |
Value of the data
-
•
Determination of the physical and chemical quality of the groundwater resources of the city of Jolfa, East Azerbaijan province, Iran.
-
•
Determine the indices changes in the quality of water resources in the city quality and management of water resources to prevent significant risks to human health [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9].
-
•
The result of data analysis shows that ground water in this some area is not suitable for agricultural according to calculated indices.
-
•
The data of this study can help to better understand the quality of groundwater in the area and provide further studies.
1. Data
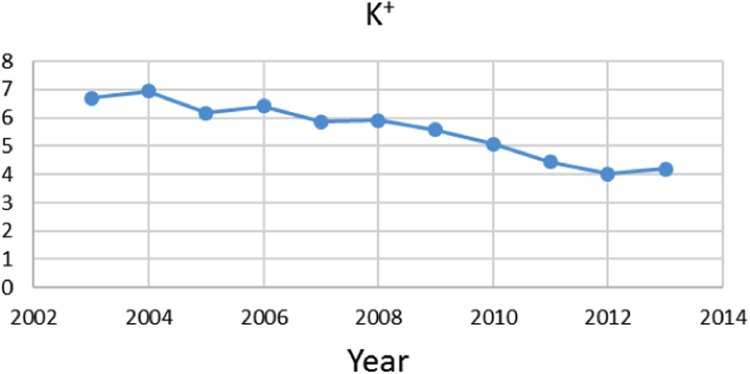
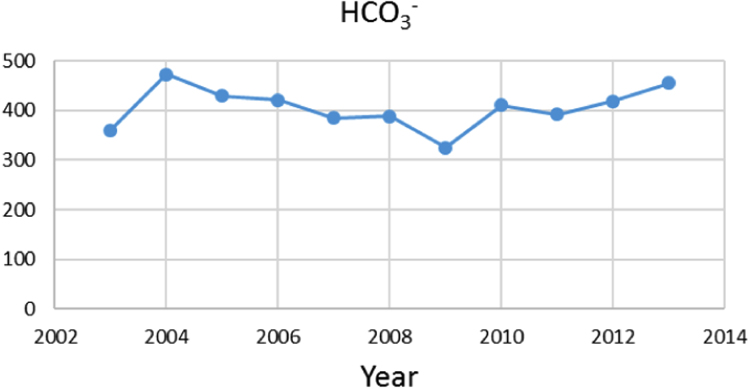
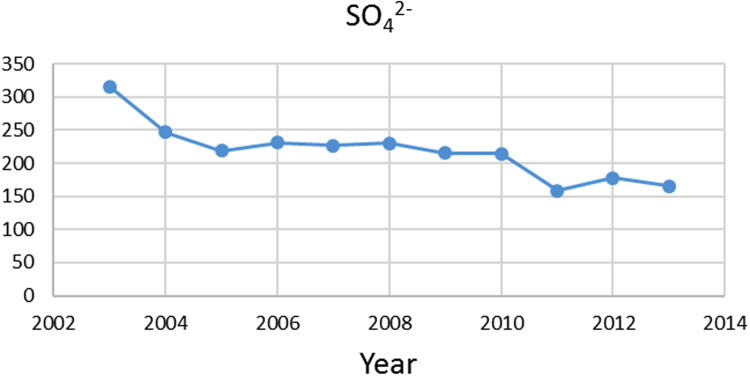
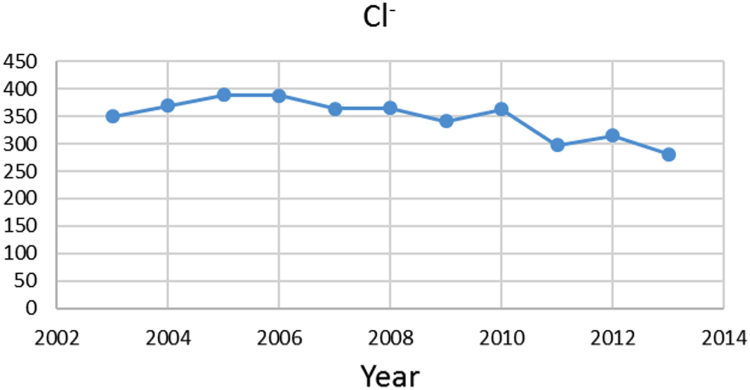
Data presented here deal with monitoring of physical and chemical including pH, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, EC, TDS, , , Cl−, and TH as shown in Table 2. Results of water Na% and SAR indices calculations samples obtained from Jolfa city shown in Table 3. Summary of water quality indices in present study presented in Table 1.
Table 2.
Chemical analysis report of water quality of drinking water resource of Jolfa city.
| Year | pH | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | Cl− | TDS | EC | TH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L | mg/L as CaCO3 | ||
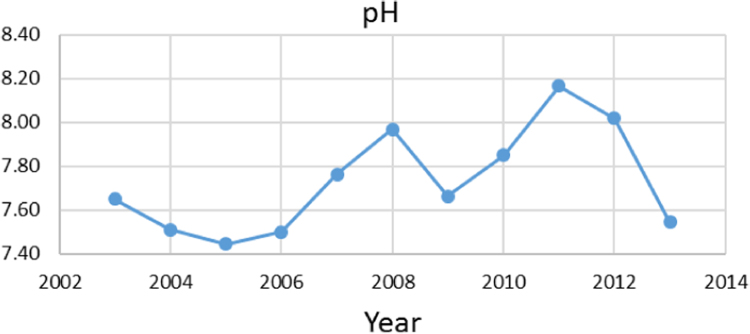
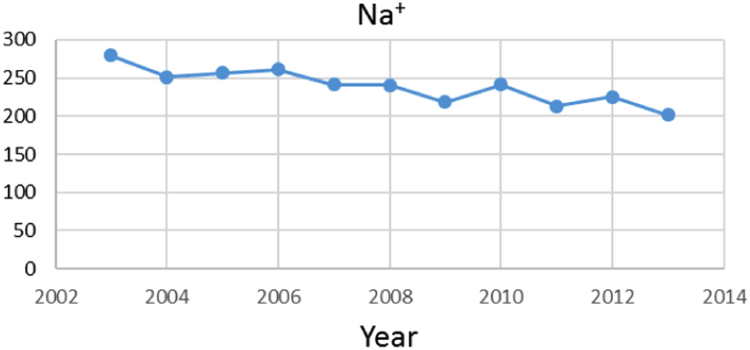
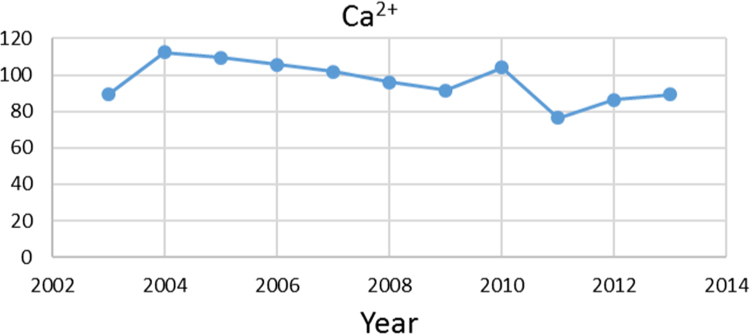
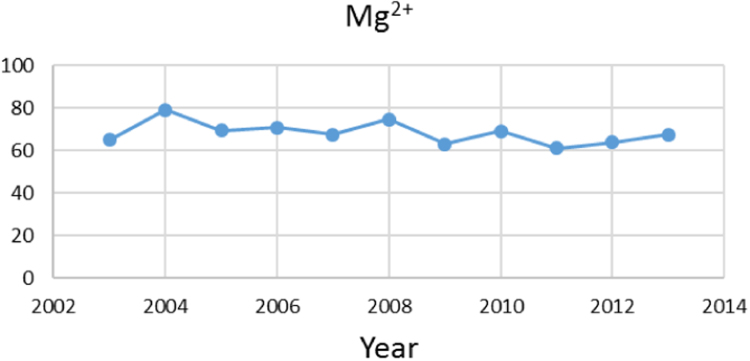
| 2003 | 7.65 | 279.78 | 89.21 | 64.88 | 6.70 | 359.86 | 315.77 | 349.44 | 733.25 | 1126.85 | 491.12 |
| 2004 | 7.51 | 251.46 | 112.54 | 79.19 | 6.94 | 472.36 | 246.67 | 369.61 | 754.67 | 1166.38 | 608.56 |
| 2005 | 7.45 | 256.88 | 109.40 | 69.47 | 6.18 | 428.84 | 218.68 | 388.51 | 715.25 | 1128.45 | 554.80 |
| 2006 | 7.50 | 260.85 | 105.63 | 70.76 | 6.42 | 421.63 | 230.63 | 387.46 | 679.75 | 1132.92 | 556.45 |
| 2007 | 7.76 | 241.64 | 101.90 | 67.52 | 5.87 | 384.53 | 226.32 | 363.52 | 640.77 | 1067.95 | 533.78 |
| 2008 | 7.97 | 240.87 | 96.13 | 74.69 | 5.90 | 388.32 | 230.52 | 365.23 | 648.78 | 1081.31 | 548.97 |
| 2009 | 7.66 | 218.20 | 91.55 | 63.11 | 5.59 | 325.27 | 215.00 | 340.96 | 583.66 | 972.76 | 489.65 |
| 2010 | 7.85 | 240.98 | 104.06 | 69.12 | 5.07 | 410.53 | 214.80 | 363.10 | 646.60 | 1077.67 | 545.75 |
| 2011 | 8.17 | 213.20 | 76.45 | 61.04 | 4.44 | 391.75 | 158.44 | 297.13 | 548.92 | 1023.81 | 443.35 |
| 2012 | 8.02 | 225.44 | 86.45 | 64.00 | 4.03 | 418.44 | 177.93 | 314.34 | 588.97 | 978.00 | 480.60 |
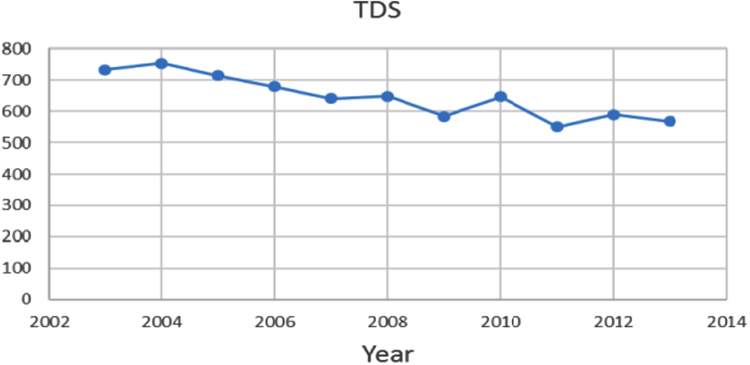
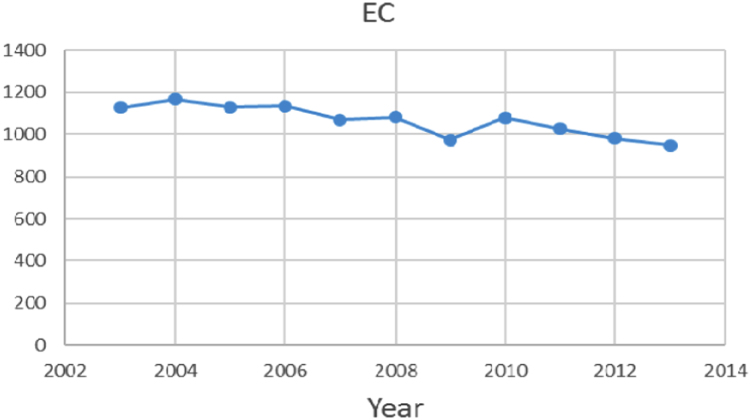
| 2013 | 7.55 | 201.48 | 89.11 | 67.41 | 4.19 | 455.27 | 165.32 | 281.20 | 567.43 | 945.71 | 501.31 |
| Mean | 7.74 | 241.44 | 97.87 | 68.55 | 5.61 | 405.33 | 220.80 | 351.86 | 651.77 | 1071.98 | 527.42 |
| Max | 9.10 | 825.50 | 417.00 | 191.18 | 12.62 | 947.12 | 873.60 | 843.00 | 1062.20 | 1770.00 | 905.40 |
| Min | 6.30 | 115.00 | 12.40 | 17.55 | 2.80 | 131.15 | 48.00 | 99.40 | 124.80 | 208.00 | 275.00 |
| SD | 0.49 | 234.49 | 90.60 | 38.76 | 3.70 | 174.42 | 203.18 | 387.84 | 461.71 | 762.93 | 339.81 |
| WHO Guide Line | 6.5–8.5 | 400 | 250 | 150 | – | – | 200 | 200 | 500.00 | – | 200.00 |
| 1053IR Standard | 6.5–8.6 | 200 | 300 | 30 | – | – | 250 | 250 | 1000.00 | – | 200.00 |
Table 3.
Results of water Na% and SAR indices calculations samples obtained from Jolfa city.
| Year | SAR | Na% |
|---|---|---|
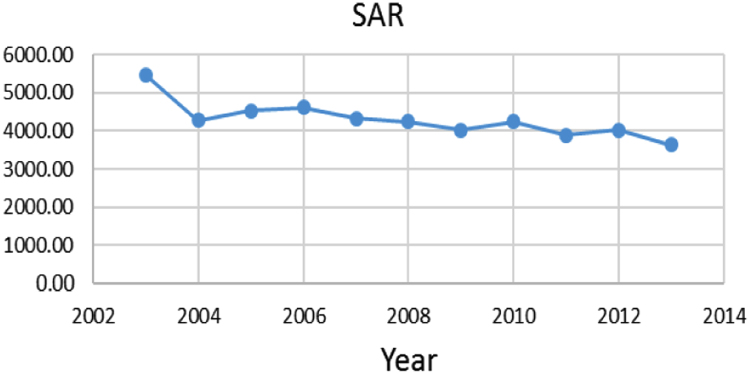
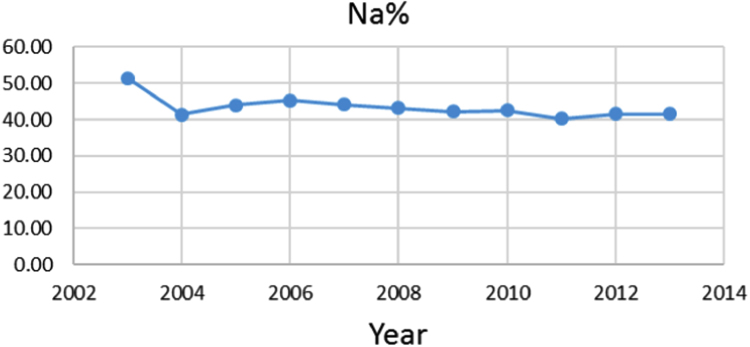
| 2003 | 5455.77 | 51.49 |
| 2004 | 4273.21 | 41.38 |
| 2005 | 4532.03 | 43.96 |
| 2006 | 4615.19 | 45.21 |
| 2007 | 4330.70 | 44.07 |
| 2008 | 4248.65 | 43.22 |
| 2009 | 4019.50 | 42.18 |
| 2010 | 4237.66 | 42.56 |
| 2011 | 3887.75 | 40.20 |
| 2012 | 4028.86 | 41.60 |
| 2013 | 3638.69 | 41.58 |
| Mean | 4328.59 | 43.48 |
Table 1.
| Indices | Formula |
|---|---|
| Sodium percentage (Na %) | |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) |
Na% and SAR indices in groundwater resources, also physical and chemical parameters in the city of Jolfa in the years (2003–2013) shown in Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4, Fig. 5, Fig. 6, Fig. 7, Fig. 8, Fig. 9, Fig. 10, Fig. 11, Fig. 12, Fig. 13.
Fig. 2.
pH parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 3.
Na+ parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 4.
Ca2+ parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 5.
Mg2+ parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 6.
K+ parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 7.
parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 8.
parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 9.
Cl− parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 10.
TDS parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 11.
EC parameter for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 12.
SAR index for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
Fig. 13.
Na% index for ground water in Jolfa city (During 2003–2013).
The maximum and minimum Na% and SAR indices are 83.27, 20622 and 5.27, 0.25 respectively.
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
2.1. Study area description
Jolfa city is one of the cities of East Azerbaijan province in Iran. Jolfa city is located in East Azerbaijan province at UTM coordinates of X=45.17 −46.31 east longitude and Y=38.39 −39.2 north latitude [15]. Summer jolfa rayon is hot and dry, but winter is cold [15], [16]. Average temperature in January is between –10 and −3 °C and in July between +19 and +28 °C. Amount of annual precipitation is 200–600 mm [Fig. 1] [15], [17].
Fig. 1.
Location of the study area in Jolfa city, East Azerbaijan, Iran.
2.2. Data collection
The required data were collected from the results recorded in the water in the Iran Water resources management Company during the years 2003–2013. A total of 460 samples were analyzed over 11 years. Physical and chemical parameters of Jolfa city water samples were analyzed following a standard method [18], [19], [20], [21], [22], [23], [24]. Number of samples in years studied (2003–2013) presented in Table 4.
Table 4.
Number of samples in years studied (2003–2013).
| Year | Number of samples |
|---|---|
| 2003 | 42 |
| 2004 | 41 |
| 2005 | 43 |
| 2006 | 42 |
| 2007 | 40 |
| 2008 | 39 |
| 2009 | 34 |
| 2010 | 80 |
| 2011 | 37 |
| 2012 | 36 |
| 2013 | 26 |
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank the respected management of Iran׳s water resources for their supports from authors.
Footnotes
Transparency data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2018.06.017.
Contributor Information
Hossein Najafi Saleh, Email: najafi.saleh@gmail.com.
Hossein Faraji, Email: faraji_hoseyn@yahoo.com.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
.
References
- 1.Abbasnia A., Alimohammadi M., Mahvi A.H., Nabizadeh R., Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Pasalari H., Mirzabeigi H.,M. Assessment of groundwater quality and evaluation of scaling and corrosiveness potential of drinking water samples in villages of Chabahr city, Sistan and Baluchistan province in Iran. Data Brief. 2018;16:182–192. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kazemi Moghadam V., Yousefi M., Khosravi A., Yaseri M., Mahvi A.H., Hadei M., Mohammadi A.A., Robati Z., Mokamel A. High concentration of fluoride can be increased risk of abortion. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018 doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1250-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yousefi M., Yaseri M., Nabizadeh R., Hooshmand E., Jalilzadeh M., Mahvi A.H., Mohammadi A.A. Association of hypertension, body mass index and waist circumference with fluoride intake; water drinking in residents of fluoride endemic areas, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018 doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Yaseri M., Mahvi A.H. Epidemiology of fluoride and its contribution to fertility, infertility, and abortion: an ecological study in West Azerbaijan Province, Poldasht County, Iran. Fluoride. 2017;50:343–353. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mohammadi A.A., Yousefi M., Yaseri M., Jalilzadeh M., Mahvi A.H. Skeletal fluorosis in relation to drinking water in rural areas of West Azerbaijan, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:17300. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17328-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Asghari F.B., Jaafari J., Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Dehghanzadeh R. Evaluation of water corrosion, scaling extent and heterotrophic plate count bacteria in asbestos and polyethylene pipes in drinking water distribution system. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess.: Int. J. 2018;24:1138–1149. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yousefi M., Ghoochani M., Mahvi A.H. Health risk assessment to fluoride in drinking water of rural residents living in the Poldasht city, Northwest of Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018;148:426–430. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Abbasnia A., Yousefi N., Mahvi A.H., Nabizadeh R., Radfard M., Yousefi M., Alimohammadi M. Evaluation of groundwater quality using water quality index and its suitability for assessing water for drinking and irrigation purposes; case study of Sistan and Baluchistan province (Iran) Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess.: Int. J. 2018 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Radfard M., Yunesian M., Nabizadeh Nodehi R., Biglari H., Hadi M., Yosefi N., Yousefi M., Abbasnia A., Mahvi A.H. Drinking water quality and Arsenic health risk assessment in Sistan-and-Baluchestan, Southeastern province Iran. Human. Ecol. Risk Assess.: Int. J. 2018 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Soleimani H., Abbasnia A., Yousefi M., Mohammadi A.A., Khorasgani F.C. Data on assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation in rural area Sarpol-e Zahab city, Kermanshah province, Iran. Data Brief. 2018;17:148–156. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.12.061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yousefi M., Najafi Saleh H., Mohammad A.A., Mahvi A.H., Ghadrpoori M., Suleimani H. Data on water quality index for the groundwater in rural area Neyshabur County, Razavi province, Iran. Data Brief. 2017;15:901–907. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.10.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mohammadi A.A., Yaghmaeian K., Faraji H., Nabizadeh R., Dehghani M.H., Khaili J.K. Temporal and spatial variation of chemical parameter concentration in drinking water resources of Bandar-e Gaz City using geographic information system. Desalination Water Treat. 2017;68:170–176. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yousefi M., Saleh H.N., Yaseri M., Mahvi A.H., Soleimani H., Saeedi Z. Data on microbiological quality assessment of rural drinking water supplies in Poldasht county. Data Brief. 2018;17:763–769. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mohammadi A.A., Najafi Saleh H., Mahvi A.H., Alimohammadi M., Nabizadeh R., Yousefi M. Data on corrosion and scaling potential of drinking water resources using stability indices in Jolfa, East Azerbaijan, Iran. Data Brief. 2018;16:724–731. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Asghari F.B., Mohammadi A.A., Aboosaedi Z., Yaseri M., Yousefi M. Data on fluoride concentration levels in cold and warm season in rural area of Shout (West Azerbaijan, Iran) Data Brief. 2017;15:528–531. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mohammadi A.A., Yousefi M., Mahvi A.H. Fluoride concentration level in rural area in Poldasht city and daily fluoride intake based on drinking water consumption with temperature. Data Brief. 2017;13:312–315. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.05.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Amouei A.I., Mahvi A.H., Mohammadi A.A., Asgharnia H.A., Fallah S.H., Khafajeh A.A. Physical and chemical quality assessment of potable groundwater in rural areas of Khaf, Iran. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012;18:693–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Asghari F.B., Mohammadi A.A., Dehghani M.H. Data on assessment of groundwater quality with application of ArcGIS in Zanjan, Iran. Data Brief. 2018;18:375–379. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.03.059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yousefi M., Dehghani M.H., Nasab S.M., Taghavimanesh V., Nazmara S., Mohammadi A.A. Data on trend changes of drinking groundwater resources quality: a case study in Abhar. Data Brief. 2018;17:424–430. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Assadi A., Dehghani M.H., Rastkari N., Nasseri S., Mahvi A.H. Photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solutions with zinc oxide nanoparticles and hydrogen peroxide. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2012;38:5–16. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Saleh H.N., Dehghani M.H., Nabizadeh R., Mahvi A.H., Hossein F., Ghaderpoori M. Data on the acid black 1 dye adsorbtion from aqueous solutions by low-cost adsorbent-Cerastoderma lamarcki shell collected from the northern coast of Caspian Sea. Data Brief. 2018;17(2018):774–780. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Amouei A., Mohammadi A., Koshki Z., Asgharnia H., Fallah S., Tabarinia H. Nitrate and Nitrite in available bottled water in babol (Mazandaran; Iran) in Summer 2010. J. Babol Univ. Med. Sci. 2012;14:64–70. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Takdastana A., Mirzabeygi (Radfard) M., Yousefi M., Abbasnia A., Khodadadia R., Mahvi A.H., Naghan D.Jalili. Neuro-fuzzy inference system Prediction of stability indices and Sodium absorption ratio in Lordegan rural drinking water resources in west Iran. Data Brief. 2018;18:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.02.075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mirzabeygi M., Yousefi M., Soleimani H., Mohammadi A.A., Mahvi A.H., Abbasnia A. The concentration data of fluoride and health risk assessment in drinking water in the Ardakan city of Yazd province, Iran. Data Brief. 2018;18:40–46. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.02.069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material