Figure 1.
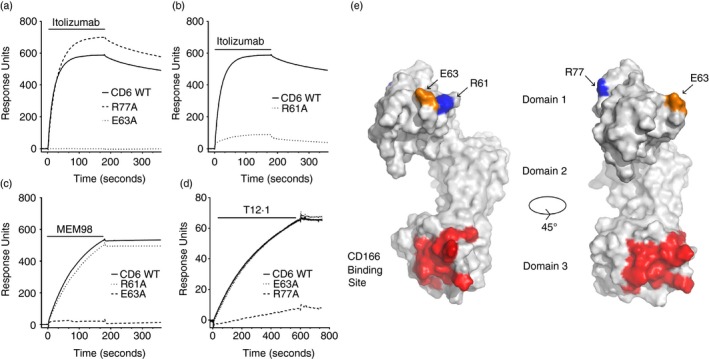
CD6 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) bind epitopes on different faces of CD6 domain 1. (a–d) Surface plasmon resonance sensograms show binding traces for itolizumab, MEM98 and T12.1 injection (bars) over wild‐type or mutated CD6–CD4d3+4 chimeric proteins immobilized via a CD4d3+4 mAb at 25°. The background signal over CD4d3+4 (control surface) is subtracted from each trace. Conformation of CD6 was confirmed by OX126 binding or reactivity with the other domain 1 mAbs (data not shown). Mutants and their effects on antibody binding are summarized in Table 1. (e) Residues that affect MEM98 (E63, in orange), MT605 (R77, in blue) or itolizumab (E63 and R61, in blue) binding are highlighted on the structure of CD6 shown as a solvent‐excluded surface, as is the CD166 binding site (in red) in the third domain. A second orientation rotated through 45° with respect to the first is shown for clarity.
