Key Points
Question
Is repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation an efficacious treatment for treatment-resistant major depression in patients who are veterans?
Findings
In this randomized clinical trial of 164 US veterans with depression, the overall remission rate was 39%, with no significant difference between the active and sham groups. Patients with comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder showed the least improvement.
Meaning
These findings may reflect the importance of close clinical surveillance, rigorous monitoring of concomitant medication, and regular interaction with clinic staff in bringing about significant improvement in this treatment-resistant population.
Abstract
Importance
Treatment-resistant major depression (TRMD) in veterans is a major clinical challenge given the high risk for suicidality in these patients. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) offers the potential for a novel treatment modality for these veterans.
Objective
To determine the efficacy of rTMS in the treatment of TRMD in veterans.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A double-blind, sham-controlled randomized clinical trial was conducted from September 1, 2012, to December 31, 2016, in 9 Veterans Affairs medical centers. A total of 164 veterans with TRD participated.
Interventions
Participants were randomized to either left prefrontal rTMS treatment (10 Hz, 120% motor threshold, 4000 pulses/session) or to sham (control) rTMS treatment for up to 30 treatment sessions.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary dependent measure of the intention-to-treat analysis was remission rate (Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression score ≤10, indicating that depression is in remission and not a clinically significant burden), and secondary analyses were conducted on other indices of posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, hopelessness, suicidality, and quality of life.
Results
The 164 participants had a mean (SD) age of 55.2 (12.4) years, 132 (80.5%) were men, and 126 (76.8%) were of white race. Of these, 81 were randomized to receive active rTMS and 83 to receive sham. For the primary analysis of remission, there was no significant effect of treatment (odds ratio, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.59-2.26; P = .67). At the end of the acute treatment phase, 33 of 81 (40.7%) of those in the active treatment group achieved remission of depressive symptoms compared with 31 of 83 (37.4%) of those in the sham treatment group. Overall, 64 of 164 (39.0%) of the participants achieved remission.
Conclusions and Relevance
A total of 39.0% of the veterans who participated in this trial experienced clinically significant improvement resulting in remission of depressive symptoms; however, there was no evidence of difference in remission rates between the active and sham treatments. These findings may reflect the importance of close clinical surveillance, rigorous monitoring of concomitant medication, and regular interaction with clinic staff in bringing about significant improvement in this treatment-resistant population.
Trial Registration
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01191333
This randomized clinical trial evaluates the efficacy of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation vs sham stimulation for treatment of depression in veterans.
Introduction
In any given year, major depressive disorder (MDD) occurs in 1 in 20 adults.1 Traditional treatments for MDD include a mix of pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic interventions, although up to 20% of patients fail to respond to these traditional treatments.2,3 Nonresponders can be classified as having treatment-resistant MDD (TRMD). Management of TRMD is complex and involves treatments such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Although such approaches may be reasonable for patients with severe depression or patients with suicidality, for most patients with moderate TRMD symptoms, the decision to escalate treatments is more difficult because these treatments come with increased risks and associated costs. New TRMD treatments are needed, preferably without major safety concerns or adverse effects as seen with aggressive polypharmacy or ECT.
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a noninvasive method of delivering brain stimulation using an electromagnetic coil that is positioned on the head near the brain region of interest. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies shows efficacy in TRMD4 with effect sizes comparable to those in studies of contemporary antidepressant medications. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation has fewer of the risks associated with ECT or the potential adverse effects and risks of monoamine oxidase inhibitors and is less expensive to administer than ECT.5 Thus, there is the potential for a significant advance in Veterans Affairs (VA) mental health care, with associated cost savings, if rTMS were to be shown as effective in the treatment of TRMD in VA patients.
To our knowledge, no other large-scale clinical trial has examined the efficacy of rTMS in VA patients with depression. This trial is an important next step because veterans may experience a different treatment response compared with civilians. This differential treatment response is well documented in studies of treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), in which veterans did not show the same treatment gains seen in civilians in both pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic trials.6,7 Veterans experience medical and psychiatric comorbidities that complicate their clinical presentation and can reduce their treatment response.8 Clinical trials in civilians often include a narrow subset of the patient population that is free from medical and psychiatric comorbidities; thus, it is unknown if these positive findings seen in civilian populations would translate into similar effects in VA practice settings. To address this question, we conducted a double-blind, sham-controlled trial of rTMS in veterans with TRMD.
Methods
Study participants were veterans with TRMD who received care in the VA health care system. Diagnosis of TRMD required both the classification of MDD as determined by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV and the failure of at least 2 prior pharmacologic interventions rated as adequate by a modified version of the Antidepressant Treatment History Form.9 The Antidepressant Treatment History Form findings are described in eTables 1 and 2 in Supplement 1. Veterans with comorbid PTSD and a history of substance use disorders were not excluded from study participation. Veterans had to be stable while receiving psychotropic medications for 4 weeks prior to randomization and continue receiving concomitant medications throughout rTMS treatment. Detailed inclusion/exclusion criteria can be found in the Box and drug screen results are in eTable 3 in Supplement 1. Study participants were recruited from a variety of settings where veterans receive mental health services in the VA health care system. These settings include traditional outpatient mental health clinics, primary care clinics, residential treatment programs, and inpatient settings at VA medical centers in Waco, Texas; Charleston, South Carolina; Cincinnati, Ohio; Palo Alto, California; Philadelphia, Pennsylvania; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; San Francisco, California; Salt Lake City, Utah; and White River Junction, Vermont. The protocol is available in Supplement 2.
Box. rTMS Trial Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria.
Inclusion Criteria
Between ages 18 and 80 y
Per the SCID for DSM-IV-TR, patients have an MDD diagnosis. HRSD score ≥20 no more than 7 days prior to randomization
Exhibit moderate level of resistance to antidepressant treatment defined, using the ATHF, as failure of ≥2 adequate medication trials
Duration of current episode of MDD, ≤10 y
Ability to obtain a motor threshold (should be determined at the end of the screening process)
Currently under the care of a VA psychiatrist
If receiving a psychotropic medication regimen, that regimen will be stable for ≥4 weeks prior to randomization and patient will be willing to continue receiving a stable regimen during the acute treatment phase
Has an adequately stable condition and environment to enable attendance at scheduled clinic visits
Women agree to use 1 of the following acceptable methods of birth control listed in the protocol: complete abstinence; oral contraceptive; levonorgestrel implant; medroxyprogesterone acetate; condom with spermicide; cervical cap with spermicide; diaphragm with spermicide; intrauterine device; surgical sterilization
Able to read, verbalize understanding, and voluntarily sign the informed consent form prior to performance of any study-specific procedures or assessments
Exclusion Criteria
Pregnancy or lactationa
Unable to be safely withdrawn, at least 2 wk before treatment commencement, from medications that substantially increase the risk of having seizures
Cardiac pacemaker
Implanted device (deep brain stimulation) or metal in the brain
Cochlear implant
Mass lesion, cerebral infarct, increased intracranial pressure, or other active central nervous system disease, including a seizure disorder
Known current psychosis as determined by DSM-IV or SCID (Axis I, psychotic disorder, schizophrenia) or a history of a nonmood psychotic disorder
Known current bipolar I disorder as determined by SCID or a history of bipolar I disorder
Current amnestic disorders, dementia, Blessed Orientation-Memory-Concentration score >10,10,b delirium, or other cognitive disorders
Current substance abuse (not including caffeine or nicotine) as determined by positive toxicology screen, or by history via SCID, within 3 months prior to screening
Elevated risk of seizure due to TBI
Participation in concurrent clinical trial
Prior exposure to rTMS
Active current suicidal intent or plan as evidenced by a score of 4 or 5 on the suicidal ideation portion of the CSSRS11 or the endorsement of an actual attempt, interrupted attempt, or an aborted attempt in the past 6 months; all patients will be required to establish a written safety plan involving their primary VA psychiatrist and the treatment team before entering the clinical trial
Unstable cardiac disease or recent (<3 months previous) myocardial infarction
Refusal to sign consent for participation in the study
All 9 participating medical centers were reviewed and approved by the VA Central Institutional Review Board. Data were processed, managed, and analyzed by the VA Cooperative Studies Program Coordinating Center, Perry Point, Maryland. An independent data safety and monitoring board reviewed safety issues and study progress. All participants provided written informed consent; those who completed the study received financial compensation. Furthermore, all participants remained under the care of the primary mental health clinician and continued to receive stable doses of psychotropic medications throughout their participation in this trial.
Interventions
Study participants were randomized to either left prefrontal rTMS treatment (10 Hz, 120% motor threshold, 4000 pulses/session) or to sham (control) rTMS treatment for up to 30 treatment sessions. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation was administered using a modified MagPro R30 (MagVenture) device with Cool-B65-A/P coil. The A (active) side of the unmarked coil delivered active treatment and the P (placebo) delivered sham treatment. For both groups, treatment was delivered in 5 session blocks over a period of 5 to 12 calendar days. Approximately 4000 stimulation pulses were delivered in each treatment session. Participants received between 20 and 30 sessions of rTMS. Participants who experienced remission after the initial 20 to 30 sessions received another 6 additional taper sessions that were delivered over a 3-week period.
Randomization to Treatment and Blinding
Study participants were randomized to either active or sham treatment using an adaptive randomization scheme (biased coin procedure). On-site study staff (including site investigators, study coordinators, treaters, and raters) and participants were blinded to treatment group assignment. Each participant was assigned a number that was associated with a treatment group. Before each treatment session, study staff key-entered this number into the rTMS device to deliver the appropriate treatment (active or sham) for each participant. Detailed information on these measures and frequency of assessments is available in the full protocol (Supplement 2).12
Primary and Secondary Outcomes
The primary outcome of this intention-to-treat study was remission in depressive symptoms, which was defined as a score of 10 or less, indicating that depression is in remission and not a clinically significant burden, on the 24-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) (score range, 0-75; from not clinically significant to very severe depression) at the end of the acute treatment phase. Secondary outcomes included improvements in measures of depression (Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale [score range, 0-50; from no symptoms to severe depression], Beck Depression Inventory-II [score range, 0-63; from minimal to severe depression]), PTSD (PTSD Checklist–Military [score range, 17-85; higher scores indicate more severe symptoms] and Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-IV [score range, 0-136; from asymptomatic/few symptoms to extreme PTSD symptoms]), suicidal ideation (Beck Scale for Suicide Ideation [score range, 0-38; higher scores indicate great suicidality] and Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale [score range, 2-25; higher scores indicate higher intensity), and quality of life (Veterans RAND 36-item Health Survey [higher scores indicate better functioning]).
Statistical Analysis
Primary analyses were performed using intent-to-treat principles on the 164 randomized patients. We performed logistic regression analyses to evaluate treatment efficacy that were adjusted for PTSD diagnosis, history of substance use disorder, and study site at the end of acute treatment and 24-week follow-up. Baseline characteristics between the 2 groups were compared using the Pearson χ2 test or Fisher exact test for categorical variables and analysis of variance or Wilcoxon signed rank test for continuous variables. For secondary analyses, the general linear model and logistic regression were used for the continuous and binary end points analyses, and a mixed linear model and generalized estimating equations were used to analyze the continuous and binary longitudinal measurements, respectively. All of the hypotheses were tested at the significance level of .05, using unpaired, 2-tailed tests. SAS, version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc) was used for statistical analysis.
Results
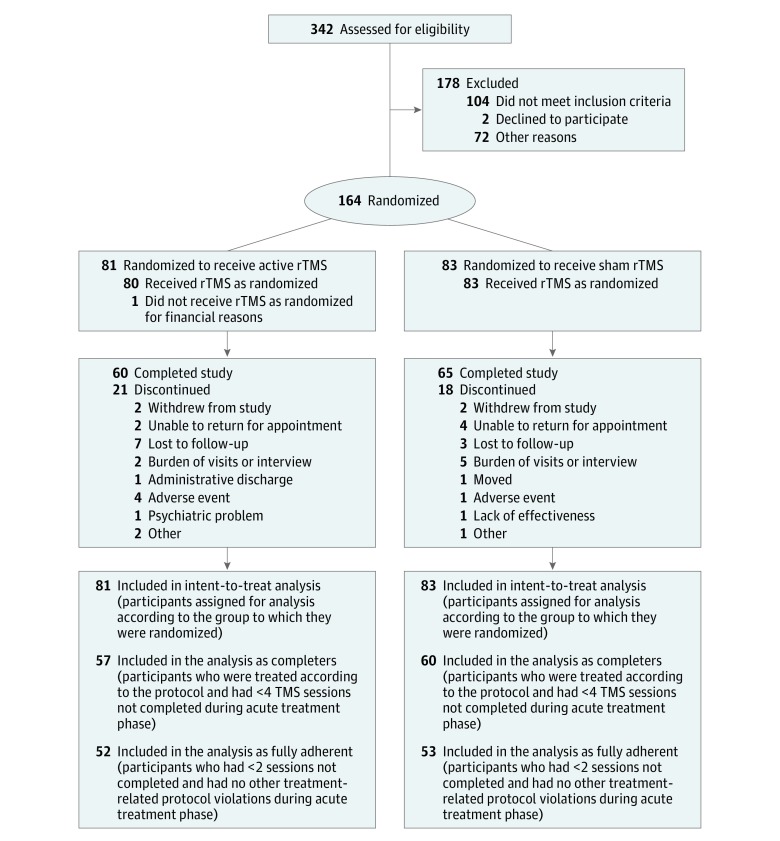
Participants were enrolled at 9 VA medical centers over a 4-year period with active enrollment extending from September 1, 2012, to May 31, 2016, and with data collection completed on December 31, 2016. We screened 342 patients and randomized 164 (Figure 1).
Figure 1. CONSORT Diagram.
rTMS indicates repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Of the 81 participants who were randomized to the active treatment group, 60 completed the study, 9 terminated during the treatment phase, and 12 withdrew during the follow-up phase. Of the 83 participants randomized to the sham treatment group, 65 completed the study, 9 terminated during the treatment phase, and 9 withdrew during the follow-up phase. The 5 main reasons for discontinuation included lost to follow-up/unable to contact, burden of visits/interviews, unable to return to clinic, adverse medical event, and withdrew from study. The groups did not significantly differ in terms of attrition, reasons for discontinuation, or number of adverse events.
Baseline demographic and clinical features of study participants by treatment group are reported in Table 1. Demographic characteristics did not differ significantly between the groups. There were no significant differences at baseline between the 2 groups other than on the Beck Depression Inventory in which the sham group rated themselves as being more depressed than the active treatment group.
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics.
| Characteristic | Active rTMS (n = 81) |
Sham rTMS (n = 83) |
Total (N = 164) |
P Valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD), y | 55.6 (12.2) | 54.8 (12.6) | 55.2 (12.4) | .66 |
| Men, No. (%) | 67 (82.7) | 65 (78.3) | 132 (80.5) | .48 |
| Married, No. (%) | 29 (35.8) | 33 (39.8) | 62 (37.8) | .60 |
| Education above high school, No. (%) | 40 (49.4) | 49 (59.0) | 89 (54.3) | .22 |
| Work history (past 4 wk), No. (%) | 17 (21.0) | 22 (26.5) | 39 (23.8) | .41 |
| White, No. (%) | 63 (77.8) | 63 (76.8) | 126 (77.3) | .78 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 30.8 (6.2) | 30.4 (5.1) | 30.6 (5.7) | .71 |
| PTSD (SCID), No. (%) | 40 (49.4) | 41 (49.4) | 81 (49.4) | .99 |
| Substance abuse, No. (%) | 45 (55.6) | 43 (51.8) | 88 (53.7) | .63 |
| HRSD-24 score, mean (SD)b | 26.2 (4.9) | 27.5 (5.1) | 26.9 (5.0) | .10 |
| MADRS score, mean (SD)c | 24.7 (7.6) | 26.2 (6.9) | 25.5 (7.3) | .19 |
| BDI-II score, mean (SD)d | 22.6 (10.3) | 26.5 (10.0) | 24.5 (10.3) | .04e |
| CAPS (life time), mean (SD)f | 45.4 (37.8) | 44.1 (37.5) | 44.8 (37.6) | .83 |
| CAPS (current), mean (SD)f | 32.0 (31.3) | 34.1 (32.2) | 33.1 (31.7) | .67 |
| PCL-M, mean (SD)g | 42.2 (17.5) | 43.3 (18.8) | 42.8 (18.1) | .69 |
| VR-36 (PCS), mean (SD)h | 42.4 (11.5) | 40.2 (10.0) | 41.3 (10.8) | .20 |
| VR-36 (MCS), mean (SD)i | 27.2 (11.6) | 25.1 (10.0) | 26.2 (10.8) | .22 |
| BSI mean (SD)j | 3.7 (6.0) | 5.6 (6.7) | 4.7 (6.5) | .06 |
| BHS, mean (SD)k | 9.8 (6.6) | 11.2 (5.5) | 10.5 (6.1) | .16 |
| CSSRS l | ||||
| Ideation intensity, mean (SD) | 7.4 (6.6) | 7.8 (6.9) | 7.6 (6.7) | .67 |
| Ideation, No. (%) | 49 (60.5) | 51 (61.5) | 100 (61.0) | .90 |
| Behavior, No. (%) | 1.0 (1.2) | 0.0 (0.0) | 1.0 (0.6) | .49m |
| Suicidality, No. (%) | 49 (60.5) | 51 (61.5) | 100 (61.0) | .90 |
| Medical history (neurologic disorder), No. (%) | 42 (51.9) | 39 (47.0) | 81 (49.4) | .53 |
| Medical history (psychiatric disorder), No. (%) | 79 (97.5) | 82 (98.8) | 161 (98.2) | .55 |
| Medical history (traumatic brain injury), No. (%) | 5 (6.2) | 5 (6.0) | 10 (6.1) | .97 |
Abbreviations: BDI-II, Beck Depression Inventory II; BHS, Beck Hopelessness Scale; BMI, body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared); BSI, Beck Scale for Suicide Ideation; CAPS, Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-IV; CSSRS, Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale; HRSD-24, 24-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale; MCS, mental component scale; PCL-M, PTSD Checklist–Military; PCS, physical component scale; PTSD, posttraumatic stress disorder; rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; SCID, Structured Clinical Interview for DSM Disorders; VR-36, Veterans RAND 36-item Health Survey.
P values based on χ2 tests for categorical variables and analysis of variance tests for continuous variables.
Score range, 0 to 75; scores indicate from not clinically significant to very severe depression.
Score range, 0 to 50; from no symptoms to severe depression.
Score range, 0 to 63; from minimal to severe depression.
P value based on Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Score range, 0 to 136; from asymptomatic/few symptoms to extreme PTSD symptoms.
Score range, 17 to 85; higher scores indicate more severe symptoms.
Higher scores indicate better physical functioning.
Higher scores indicate better mental health functioning.
Score range, 0 to 38; higher scores indicate great suicidality.
Score range, 0 to 20; from none/minimal to severe hopelessness.
Score range, 2 to 25; higher scores indicate higher intensity.
P value based on Fisher exact test.
Primary Outcome: Remission of Depressive Symptoms
The effects of rTMS treatment on primary and secondary outcomes are reported in Table 2. For the primary analysis of remission in the intention-to-treat sample (n = 164), there was no significant effect of treatment (odds ratio [OR], 1.16; 95% CI, 0.59-2.26; P = .67). Among the predefined covariates (substance abuse, PTSD status, and sites) in the logistic model, PTSD status was significantly related to the remission rate (OR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.24-0.94; P = .03). At the end of the acute treatment phase, 33 of 81 participants (40.7%) in the active treatment group who finished the rTMS treatment achieved remission of depressive symptoms compared with 31 of 83 (37.4%) of those in the sham treatment group. Overall, 64 of 164 (39.0%) of the participants achieved remission. At the end of the follow-up phase, 16 (19.8%) of the active treatment group evidenced sustained remission compared with 13 (15.7%) of the sham treatment group.
Table 2. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Major Study Outcomes Using the Intention-to-Treat Sample.
| Outcome | Baseline | End of rTMS Treatment | End of 24-Wk Follow-up | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active (n = 81) | Sham (n = 83) | Active (n = 73) | Sham (n = 77) | Adjusted Effect Estimate (95% CI)a | P Value | Active (n = 60) | Sham (n = 65) | Adjusted Effect Estimate (95% CI)a | P Value | |
| Depression symptom remission rate, No. (%) | ||||||||||
| HRSD Remission rateb | NA | NA | 33 (40.7) | 31 (37.4) | 1.16 (0.59 to 2.26) |
.67 | 16 (19.8) | 13 (15.7) | 1.55 (0.62 to 3.86) |
.35 |
| HRSD remission rateb for MDD without PTSD | NA | NA | 20 (48.8) | 18 (42.9) | 1.82 (0.68 to 4.93) |
.23 | 14 (34.2) | 10 (23.8) | 2.69 (0.86 to 8.4) |
.09 |
| HRSD Remission rateb for MDD with PTSD | NA | NA | 13 (32.5) | 13 (31.7) | 0.73 (0.25 to 2.16) |
.56 | 2 (5.0) | 3 (7.3) | 0.73 (0.09 to 5.7) |
.76 |
| Depression symptoms severity, mean (SD) | ||||||||||
| HRSD score | 26.2 (4.9) | 27.5 (5.1) | 14.8 (9.1) | 14.4 (8.6) | 1.28 (−1.42 to 3.97) |
.34 | 16.3 (9.5) | 17.1 (8.9) | 0.67 (−2.59 to 3.94) |
.68 |
| MADRS score | 24.7 (7.6) | 26.2 (6.9) | 14.3 (11.1) | 13.1 (10.5) | 2.26 (−0.91 to 5.44) |
.16 | 13.7 (10.2) | 15.0 (9.7) | − 0.03 (−3.45 to 3.39) |
.99 |
| BDI score | 22.6 (10.3) | 26.5 (10.0) | 14.2 (10.9) | 13.0 (9.5) | 2.22 (−0.64 to 5.08) |
.12 | 9.0 (8.3) | 12.8 (10.8) | − 1.59 (−6.08 to 2.89) |
.48 |
| Suicidality | ||||||||||
| BSI score, mean (SD) | 3.7 (6.0) | 5.6 (6.7) | 2.0 (4.6) | 2.7 (4.9) | 0.08 (−1.46 to 1.62) |
.91 | 1.5 (4.2) | 2.5 (4.9) | − 0.54 (−2.25 to 1.17) |
.53 |
| Suicidal ideation based on CSSRS, No. (%) | 49 (60.5) | 51 (61.5) | 18 (25.7) | 21 (28.8) | 0.90 (0.40 to 2.00) |
.79 | 14 (24.6) | 15 (23.8) | 1.02 (0.43 to 2.46) |
.96 |
| PTSD symptom severity, mean (SD) | ||||||||||
| CAPS score | 32.0 (31.3) | 34.1 (32.2) | 26.9 (28.2) | 23.3 (27.6) | 5.20 (−0.49 to 10.89) |
.07 | 26.7 (28.6) | 21.3 (23.9) | 4.47 (−0.69 to 9.64) |
.09 |
| PCL-M score | 42.2 (17.4) | 43.3 (18.8) | 37.0 (16.9) | 35.2 (16.7) | 2.68 (−0.84 to 6.19) |
.13 | 37.4 (17.4) | 35.2 (16.0) | 2.68 (−1.49 to 6.85) |
.21 |
| Quality of life, mean (SD) | ||||||||||
| VR-36 standardized PCS | 42.4 (11.5) | 40.2 (10.0) | 41.9 (10.9) | 41.2 (11.9) | −1.32 (−3.61 to 0.97) |
.27 | 42.8 (10.8) | 40.1 (12.3) | 0.08 (−2.67 to 2.83) |
.96 |
| VR-36 standardized MCS | 27.2 (11.6) | 25.1 (10.0) | 35.1 (14.3) | 36.0 (14.7) | −1.76 (−5.91 to 2.39) |
.40 | 34.5 (12.8) | 34.8 (13.4) | −0.12 (−4.48 to 4.24) |
.96 |
Abbreviations: BDI, Beck Depression Inventory; BSI, Beck Scale for Suicide Ideation; CAPS, Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-IV; CSSRS, Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale; HRSD, Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale; MCS, mental component scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; NA, not applicable; PCL-M, PTSD Checklist–Military; PCS, physical component scale; PTSD, posttraumatic stress disorder; rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; VR-36, Veterans RAND 36-item Health Survey.
Treatment effects of rTMS estimated from logistic regressions for binary outcomes adjusted for PTSD, substance use, and site; estimated from general linear regressions for continuous outcomes adjusted for baseline; and presented in the Table as odds ratios (95% CI from the logistic regressions and treatment coefficients (95% CI) from the general linear regressions.
The HRSD remission rates were calculated based on 164 randomized participants. If the HRSD score was missing, the participant was considered as not achieving remission based on the protocol.
Secondary Outcomes: PTSD, Suicidality, and Quality of Life
When we examined the effects of the rTMS treatment on PTSD symptoms, there was no significant effect of treatment at the end of the acute treatment phase in either the Clinician Administered PTSD Scale for DSM-IV (treatment coefficient, 5.20; 95% CI, −0.49 to 10.89; P = .07) or the PTSD Checklist–Military (treatment coefficient, 2.68; 95% CI, −0.84 to 6.19; P = .13). Secondary outcomes are described in eTable 6 and eTable 7 in Supplement 1. These nonsignificant findings were also observed at the end of the follow-up phase. Furthermore, a similar pattern of nonsignificant findings was seen in measures of suicidality and quality of life at both the end of acute treatment and follow-up phases. A similar pattern of results was seen in both the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale and the Beck Depression Inventory (eTable 4 in Supplement 1).
Moderators of Treatment Effect
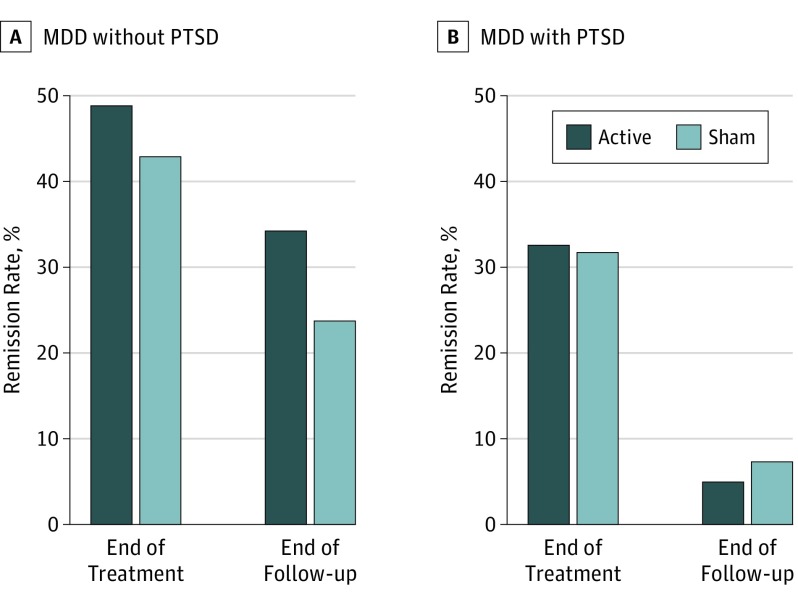
Figure 2 highlights a potential treatment-moderating effect of PTSD diagnosis. When stratifying by presence or absence of PTSD comorbidity, 20 of 41 participants (48.8%) without PTSD achieved remission (a rate higher than the overall mean); only 13 of 40 participants with MDD (32.5%) with PTSD demonstrated remission (a rate lower than the overall mean). In the sham control condition, 18 participants (42.9%) with MDD without PTSD achieved remission compared with 13 participants (31.7%) with PTSD. Thus, rates of remission were higher for MDD (without PTSD) for active compared with sham conditions, whereas there was little difference for MDD with PTSD, and rates of remission were also lower in this comorbid group. Comorbidity also had a moderating effect on maintenance of remission. At the end of the follow-up phase, 14 participants (34.2%) with MDD (without PTSD) in the active treatment group maintained remission, compared with only 2 participants (5.0%) with MDD and PTSD. In the sham treatment condition, 3 participants (7.3%) with PTSD maintained remission, compared with 10 participants (23.8%) in the same treatment group without PTSD.
Figure 2. Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression Remission Rates Stratified by Presence or Absence of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).
Remission in patients without (A) and with (B) PTSD. Discussion of the effects of PTSD is provided in the Moderators of Treatment Effect section. MDD indicates major depressive disorder.
Additional Analyses
We also used a linear mixed-model approach to examine whether the lack of a significant difference between active and sham groups might have reflected missing data. The results of our primary and secondary analyses did not change. Also, to examine whether the lack of a significant difference between the active and sham groups reflected any attenuation in power due to our inclusion of covariates in our model (substance abuse, PTSD, and site), we conducted the primary analyses without these covariates included, and again, our findings remained unchanged.
Safety
Treatment-emergent adverse events did not differ significantly between treatment groups and were generally consistent with expected background medical issues in this population. The most common nonserious adverse events included nasopharyngitis (8 participants in both groups), depression (8 active and 3 sham participants), and falls (3 active and 7 sham participants). Headache, an adverse event commonly associated with rTMS, occurred in 15 active and 16 sham participants. There were 18 patients with abnormal results of hearing tests in each group, but this was believed to be an artifact of frequent, imprecise testing. The most common serious adverse event was suicidal ideation (3 active and 4 sham participants). No suicides or seizures occurred during the study and there were no deaths.
Discussion
In this study of veterans with TRMD, we found that the delivery of rTMS while the participants were receiving other antidepressants was safe and well tolerated, with remission in 39.0% of all patients by the end of acute treatment. This finding is consistent with the observation that placebo response has been increasing over time in clinical trials of antidepressant medication.13 This remission rate is high compared with other studies of veterans with TRMD. A recent study of 3 pharmacologic augmentation strategies for veterans who did not respond to 1 antidepressant showed remission rates at 12 weeks that ranged from 22% to 29%.14 The higher remission rates seen in our rTMS study are even better because the patients undergoing rTMS were documented to have 2 failed trials of antidepressants, whereas the pharmacologic augmentation clinical trial required only 1 failed prior trial. Furthermore, this rTMS study showed that 16 of 33 (48.5%) of active rTMS participants with acute remission were still in remission 24 weeks later, as were 13 of 31 (41.9%) of those in the sham group.
Differences With the OPT-TMS Study
We did not observe a significant difference in remission rates between the active rTMS and sham groups, which differs from previous rTMS trials in civilians. Specifically, the OPT-TMS trial reported remission rates in which 14% of participants who received active rTMS treatment achieved remission compared with 5% of those in the sham group (OR, 4.2; 95% CI, 1.32-13.24; P = .02).15 It is not surprising to find that these veterans had a differential treatment response as this is consistent with prior pharmacologic and psychotherapeutic trials in which veterans did not show the same treatment gains seen in civilians.6,7 Although the veterans in the present study are fairly representative of the veterans with TRMD seen in the VA, they are significantly more complex than participants recruited in civilian trials of rTMS on several factors. First, this study differed from most rTMS studies in the high proportion of men (80.5%), which is notable because women may have a better response rate to rTMS than men.16 The small number of female participants precluded formal statistical analyses of differential response; however, in our small sample, women generally had higher remission rates (eTable 5 in Supplement 1). Furthermore, compared with participants in the OPT-TMS trial, the veterans in the present trial were on average 8 years older (55.2 vs 47.1 years), had not responded to at least 2 prior antidepressant trials in their current depressive episode (compared with 1.51 on average), had numerous comorbid psychiatric disorders, including 49.4% with PTSD and 53.7% with a substance use disorder (compared with no comorbid Axis I disorders). These comorbidities increased the complexity of the patients, and thus their need for heightened clinical surveillance. Although the OPT-TMS researchers met with their participants with a similar frequency, the visits in the present study were almost twice the length of those in the OPT-TMS trial.
Possible Causes of High Remission Rates
Our findings also differ from those of prior rTMS research in terms of the high rate of remission seen in both the active and sham groups. These high remission rates suggest that veterans’ expectations of improvement and extensive attention provided by the rTMS treatment team may have played a large role in the significant clinical improvements they experienced. As with other trials of rTMS, veterans in this study had daily meetings over 20 to 30 days with mental health professionals. However, unlike past trials of rTMS, veterans in this study were evaluated for medication adherence before each treatment session to confirm their adherence to a stable regimen of psychotropic medication, as this was a requirement for participation in the trial. Complementing the daily queries regarding medication adherence were the extensive evaluations of mood, suicidality, and substance use at the end of each treatment block and follow-up visit. Although all participants were followed up by mental health clinicians in the VA system, the regular contact with study staff was more extensive than is typically provided in outpatient mental health settings. This added attention may have interacted with the fact that this study was, to our knowledge, the first large rTMS clinical trial in which medications were included and contributed to enhanced adherence to pharmacologic treatments. Furthermore, 76.2% of the participants were unemployed and thus potentially socially isolated and/or inactive. This raises the possibility that the high remission rate may be in part due to the increased activity and contact with study staff, which is consistent with the substantial effects seen in trials of behavioral activation.17,18
PTSD as a Potential Moderator for Veterans With TRMD
Although prior studies of veterans suggested that they would have a response to psychiatric treatment different from civilians, we did not anticipate the differences in remission rates at follow-up seen in patients with TRMD with and without PTSD. In the active treatment, only 5.0% of patients with MDD and PTSD remained in remission at follow-up compared with 34.2% in those with MDD without PTSD. Similarly, in the sham condition, only 7.3% of patients with MDD and PTSD remained in remission at follow-up compared with 23.8% of those with MDD but without PTSD. Our ability to detect significant differences between these subgroups is limited by the sample size. Thus, futures studies should examine if such differences might be real. Furthermore, it is not known if the PTSD symptoms predated the current MDD episode, and thus would be the primary problem that is contributing to or exacerbating the depressive symptoms. Although PTSD is not a common comorbidity in rTMS studies of depressed civilians, anxiety disorder comorbidity has been found to be an indicator of poor outcome with rTMS.19 Treatment of PTSD may be more effective if targeting dysfunctional neural circuitry in this condition. For example, although studies has shown single-pulse TMS stimulation of the right ventrolateral prefrontal cortex during concurrent functional magnetic resonance imaging inhibited amygdala activity in PTSD, greater ability of right dorsolateral, prefrontal, single-pulse TMS/functional magnetic resonance imaging to inhibit amygdala activity in patients with PTSD is an indicator of better outcome with subsequent exposure therapy.20 Ultimately, we anticipate that overall outcomes will be improved by better aligning in future work particular aspects of rTMS interventions (eg, brain location, stimulation protocol including theta burst, TMS coil type) with biological and clinical heterogeneity, as exemplified here by PTSD comorbidity. Finally, we note that results of a recent study of ECT in veterans with MDD and PTSD showed a positive effect on both MDD and PTSD symptoms.21 Thus, the effects of rTMS and ECT appear to be quite different in this population of veterans.
Given this widespread use of rTMS in civilian populations and the high overall remission rates observed in this study, it would seem to be reasonable to use rTMS treatment in veterans. This is occurring in many sites across the nation. Like the present study, VA clinical use of rTMS involves a comprehensive approach to the patients, including pharmacotherapy, psychotherapy, and psychosocial support. The fact that there appears to be a positive response to ECT in veterans with MDD and PTSD suggests that such patients would do best with ECT.
Limitations
The participants in this study are representative of patients seen in VA mental health care. These participants had multiple comorbidities, including PTSD and substance abuse. Given the complexity of our participants, a primary limitation of the project is that larger sample sizes are needed to discern subgroup effects. Furthermore, many advances have been made in the technical administration of rTMS in both MDD and PTSD since this study was conceived and the treatment would be done differently today.
Conclusions
This study supports the clinical observation that a combination of interventions including rTMS is effective for achieving symptom remission in 39.0% of veterans with MDD who were previously treatment resistant. This finding was particularly the case for the subset of veterans who did not have current PTSD as 1 of their comorbid characteristics where remission rate was 45.8%, whereas those with PTSD remission rate was 32.1%.
Achieving remission rates of 40% and over in treatment-resistant veterans is a clinically meaningful result warranting evaluation of such comprehensive approaches to treatment of patients with difficult-to-treat MDD within the VA. Future work with rTMS may show an enhanced effect when newer coil models, better stimulus targeting, biological markers of response, higher frequency rates of stimulation, and longer duration of treatment are implemented.
eTable 1. Adequacy of Antipsychotic and Antidepressant Trial by Treatment Group before Randomization
eTable 2. Adequacy of Antipsychotic and Antidepressant Trial by Treatment Group at End of Active Treatment
eTable 3. Urine Drug Screen Results
eTable 4. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Secondary Outcomes (Intention to Treat)
eTable 5. Effect of rTMS Treatment by Gender
eTable 6. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Secondary Outcomes (Intention to Treat) by PTSD Status, End of rTMS Treatment
eTable 7. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Secondary Outcomes (Intention to Treat) by PTSD Status, End of 24-Week Follow-up
Protocol
Footnotes
Abbreviations: ATHF, Antidepressant Treatment History Form; CSSRS, Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale; HRSD, Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression; MDD, major depressive disorder; rTMS, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; SCID, Structured Clinical Interview for DSM Disorders; TBI, traumatic brain injury; VA, Veterans Affairs.
This is a US Food and Drug Administration–required exclusion. In the future, if rTMS becomes a proven treatment for major depression, its safety in the context of pregnancy should be studied separately.
Scores of 10 or greater are indicative of clinically significant cognitive impairment.
References
- 1.Hasin DS, Goodwin RD, Stinson FS, Grant BF. Epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcoholism and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(10):1097-1106. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.62.10.1097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thase ME. Therapeutic alternatives for difficult-to-treat depression: a narrative review of the state of the evidence. CNS Spectr. 2004;9(11):808-816, 818-821. doi: 10.1017/S1092852900002236 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Keller MBLP, Lavori PW, Mueller TI, et al. Time to recovery, chronicity, and levels of psychopathology in major depression: a 5-year prospective follow-up of 431 subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;49(10):809-816. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820100053010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.George MS, Taylor JJ, Short EB. The expanding evidence base for rTMS treatment of depression. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2013;26(1):13-18. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0b013e32835ab46d [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kozel FAGM, George MS, Simpson KN. Decision analysis of the cost-effectiveness of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation versus electroconvulsive therapy for treatment of nonpsychotic severe depression. CNS Spectr. 2004;9(6):476-482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Friedman MJ, Marmar CR, Baker DG, Sikes CR, Farfel GM. Randomized, double-blind comparison of sertraline and placebo for posttraumatic stress disorder in a Department of Veterans Affairs setting. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68(5):711-720. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v68n0508 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hundt NE, Barrera TL, Robinson A, Cully JA. A systematic review of cognitive behavioral therapy for depression in veterans. Mil Med. 2014;179(9):942-949. doi: 10.7205/MILMED-D-14-00128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Agha Z, Lofgren RP, VanRuiswyk JV, Layde PM. Are patients at Veterans Affairs medical centers sicker? a comparative analysis of health status and medical resource use. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(21):3252-3257. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.21.3252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sackeim HAPJ, Prudic J, Devanand DP, Decina P, Kerr B, Malitz S. The impact of medication resistance and continuation pharmacotherapy on relapse following response to electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1990;10(2):96-104. doi: 10.1097/00004714-199004000-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Katzman R, Brown T, Fuld P, Peck A, Schechter R, Schimmel H. Validation of a short Orientation-Memory-Concentration Test of cognitive impairment. Am J Psychiatry. 1983;140(6):734-739. doi: 10.1176/ajp.140.6.734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Posner K, Brown GK, Stanley B, et al. The Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale: initial validity and internal consistency findings from three multisite studies with adolescents and adults. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(12):1266-1277. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.10111704 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mi Z, Biswas K, Fairchild JK, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for treatment-resistant major depression (TRMD) veteran patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2125-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Khan A, Detke M, Khan SR, Mallinckrodt C. Placebo response and antidepressant clinical trial outcome. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2003;191(4):211-218. doi: 10.1097/01.NMD.0000061144.16176.38 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mohamed S, Johnson GR, Chen P, et al. ; and the VAST-D Investigators . Effect of antidepressant switching vs augmentation on remission among patients with major depressive disorder unresponsive to antidepressant treatment: the VAST-D randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(2):132-145. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.8036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.George MS, Lisanby SH, Avery D, et al. Daily left prefrontal transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy for major depressive disorder: a sham-controlled randomized trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67(5):507-516. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Malik AM, Haque Z, Ide G, Farley A. Gender and age as factors in response and remission of depression treated with transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Stimulation. 2016;9(5):e7. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2016.06.022 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ekers D, Webster L, Van Straten A, Cuijpers P, Richards D, Gilbody S. Behavioural activation for depression; an update of meta-analysis of effectiveness and sub group analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dobson KS, Hollon SD, Dimidjian S, et al. Randomized trial of behavioral activation, cognitive therapy, and antidepressant medication in the prevention of relapse and recurrence in major depression. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2008;76(3):468-477. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.76.3.468 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lisanby SH, Husain MM, Rosenquist PB, et al. Daily left prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the acute treatment of major depression: clinical predictors of outcome in a multisite, randomized controlled clinical trial. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34(2):522-534. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fonzo GA, Goodkind MS, Oathes DJ, et al. PTSD psychotherapy outcome predicted by brain activation during emotional reactivity and regulation. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174(12):1163-1174. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.16091072 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ahmadi N, Moss L, Simon E, Nemeroff CB, Atre-Vaidya N. Efficacy and long-term clinical outcome of comorbid posttraumatic stress disorder and major depressive disorder after electroconvulsive therapy. Depress Anxiety. 2016;33(7):640-647. doi: 10.1002/da.22451 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eTable 1. Adequacy of Antipsychotic and Antidepressant Trial by Treatment Group before Randomization
eTable 2. Adequacy of Antipsychotic and Antidepressant Trial by Treatment Group at End of Active Treatment
eTable 3. Urine Drug Screen Results
eTable 4. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Secondary Outcomes (Intention to Treat)
eTable 5. Effect of rTMS Treatment by Gender
eTable 6. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Secondary Outcomes (Intention to Treat) by PTSD Status, End of rTMS Treatment
eTable 7. Effect of rTMS Treatment on Secondary Outcomes (Intention to Treat) by PTSD Status, End of 24-Week Follow-up
Protocol