Abstract
This study estimates the total costs associated with administering chimeric antigen receptor T-cell treatment.
In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the drugs tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah; Novartis) and axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta; Kite Pharma) as the first chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) immunotherapies. Treatment with tisagenlecleucel has been priced at $475 000 and axicabtagene ciloleucel at $373 000; however, these prices are for the drug products alone and do not account for the costs associated with leukapheresis, lymphodepletion therapy, and the adverse effects of CAR-T immunotherapy. These costs are not negligible as 43 patients (44%) who received tisagenlecleucel in clinical trials required stays in the intensive care unit for cytokine release syndrome (CRS).1 In this study, we estimated the total costs of CAR-T immunotherapy, including nondrug costs, using publicly available data.
Methods
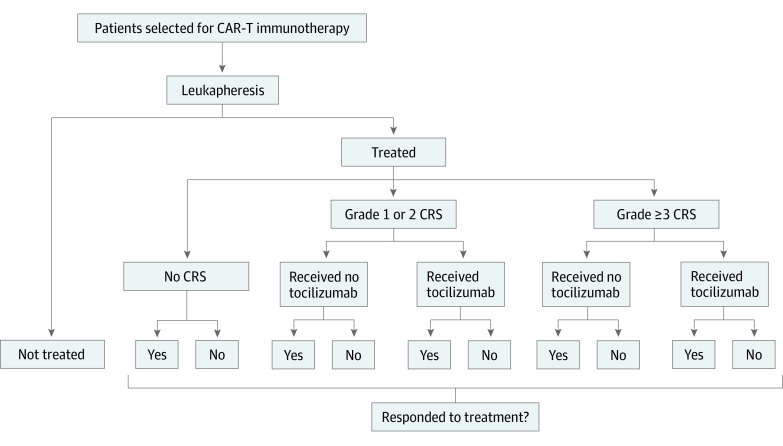
The institutional review board at the University of Pittsburgh deemed this study exempt. We divided the potential outcomes of patients selected for CAR-T immunotherapy into 11 scenarios, accounting for the receipt of treatment, development of CRS, and response to CAR-T immunotherapy (Figure). We calculated the probabilities of each scenario using input probabilities from the Food and Drug Administration Advisory Committee briefing document for tisagenlecleucel,1 the preliminary results of the Determine Efficacy and Safety of CTL019 in Pediatric Patients With Relapsed and Refractory B-cell ALL (Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia) (ELIANA) trial,2 and the Food and Drug Administration–approved label for axicabtagene ciloleucel.3 To calculate the physician costs for leukapheresis and for administration of lymphodepletion therapy and CAR-T immunotherapy, we used the 2017 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule rates; facility costs were calculated using the 2017 Medicare Hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System amounts. Costs of drugs other than CAR-T drugs were based on 2017 Medicare Part B payment limits. To calculate the facility costs of hospitalizations for CRS, we used estimates from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project and from published studies4; physician costs were calculated as 26% of facility costs.5 All estimates were inflated to 2017 US dollars using the Consumer Price Index for Medical Care.
Figure. Overview of 11 Hypothetical Scenarios for Patients Selected for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell (CAR-T) Immunotherapy.
The expected probabilities of each scenario with the drugs tisagenlecleucel and axicabtagene ciloleucel were calculated using input probabilities from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Advisory Committee briefing document for tisagenlecleucel,1 the preliminary results of the Determine Efficacy and Safety of CTL019 in Pediatric Patients With Relapsed and Refractory B-cell ALL (Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia) (ELIANA) trial,2 and the FDA-approved label for axicabtagene ciloleucel.3 CRS indicates cytokine release syndrome.
To estimate the mean expected cost per patient treated, we added up the expected costs of the drug product in each scenario and its expected probability and then divided the sum by the probability of being treated. Because Novartis, the manufacturer of tisagenlecleucel, offered to waive the costs of the drug for patients who do not demonstrate a response to treatment after 1 month, we estimated the costs of tisagenlecleucel with and without refunds for individuals with no treatment response.
Results
As the Table shows, the total costs of treatment with tisagenlecleucel per patient treated range from $478 777 for those without CRS to $531 823 for those with severe CRS (CRS grade ≥3). The mean expected cost is $510 963, which decreases to $432 131 under the outcomes-based pricing arrangement. The mean expected cost of axicabtagene ciloleucel per patient treated is $402 647. With approximately 600 US patients eligible for tisagenlecleucel every year, the $432 131 estimate would translate into annual expenditures of $259 million. With 7500 US patients annually eligible for axicabtagene ciloleucel, the total expenditures would be more than $3 billion.
Table. Estimated Total Costs and Mean Expected Costs per Patient for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Immunotherapies .
| Treatment Scenario | Total Cost, $a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tisagenlecleucel | Axicabtagene Ciloleucel | ||
| Base-Case Pricing | Outcomes-Based Pricingb | ||
| Not treated | 1207 | 1207 | 1207 |
| Treated | |||
| No CRS | |||
| Response | 478 777 | 478 777 | 377 253 |
| No response | 478 777 | 3777 | 377 253 |
| Grade 1-2 CRS, received no tocilizumabc | |||
| Response | 502 464 | 502 464 | 400 940 |
| No response | 502 464 | 27 464 | 400 940 |
| Grade 1-2 CRS, received tocilizumabc | |||
| Response | 504 276 | 504 276 | 404 564 |
| No response | 504 276 | 29 276 | 404 564 |
| Grade ≥3 CRS, received no tocilizumabc | |||
| Response | 530 011 | 530 011 | 411 429 |
| No response | 530 011 | 55 010 | 411 429 |
| Grade ≥3 CRS, received tocilizumabc | |||
| Response | 531 823 | 531 823 | 415 053 |
| No response | 531 823 | 56 823 | 415 053 |
| Mean expected costs per patient treated | 510 963 | 432 131 | 402 647 |
Abbreviation: CRS, cytokine release syndrome.
All costs are expressed in 2017 US dollars.
Under the outcomes-based pricing agreement announced by Novartis, the manufacturer of tisagenlecleucel, drug costs would be waived for those patients who do not respond to treatment within 1 month of administration.
A CRS grade of 3 or greater represents severe CRS.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this study provides the first estimates of the total costs of CAR-T immunotherapy in the United States; these estimates are consistent with those previously calculated for the United Kingdom.6 Although our study did not examine the benefits associated with CAR-T immunotherapy and hence does not provide estimates of cost-effectiveness, it nevertheless has important implications.
One could argue that the nondrug costs associated with CAR-T immunotherapy are negligible when compared with drug costs, as the former represent 7% of total costs. However, in absolute terms, these nondrug costs are $30 000 to $36 000 for the average patient and as high as $56 000 for those with severe CRS; these costs are equivalent to the costs of many of today’s most expensive medications. Moreover, under the proposed outcomes-based pricing arrangement, nondrug costs are not refunded for patients who do not demonstrate a response to treatment. Payers and the public must understand that only the costs borne by the manufacturer, but not the total costs of CAR-T immunotherapy, will be reimbursed for those who display no treatment response.
As the number of patients eligible for CAR-T immunotherapy and other expensive therapies increase, accurately measuring and accounting for the associated nondrug costs will be important when assessing the treatment’s true costs and value and when negotiating pricing arrangements.
References
- 1.Novartis . Tisagenlecleucel (CTL019) for the treatment of pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee briefing document. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/advisorycommittees/committeesmeetingmaterials/drugs/oncologicdrugsadvisorycommittee/ucm566168.pdf. Published July 12, 2017. Accessed September 5, 2017.
- 2.Novartis . Novartis pivotal CTL019 6-month follow-up data show durable remission rates in children, young adults with r/r B-cell ALL. https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-pivotal-ctl019-6-month-follow-data-show-durable-remission-rates. Published June 23, 2017. Accessed October 10, 2017.
- 3.US Food and Drug Administration . Prescribing information for Yescarta. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/CellularGeneTherapyProducts/ApprovedProducts/UCM581226.pdf. Accessed October 20, 2017.
- 4.Hsu BS, Brazelton TB III. A comparison of costs between medical and surgical patients in an academic pediatric intensive care unit. WMJ. 2015;114(6):236-239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Peterson C, Xu L, Florence C, Grosse SD, Annest JL. Professional fee ratios for US hospital discharge data [published correction appears in Med Care. 2016;54(2):218]. Med Care. 2015;53(10):840-849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hettle R, Corbett M, Hinde S, et al. The assessment and appraisal of regenerative medicines and cell therapy products: an exploration of methods for review, economic evaluation and appraisal. Health Technol Assess. 2017;21(7):1-204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]