Abstract
Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is an inflammatory disease of unknown causes, characterized by recurrent inflammation in cartilaginous tissues of the whole body. Recently, researchers have reported that, in mouse experiments, altered gut microbe-dependent T cell differentiation occurred in gut associated lymphoid tissues. Here, we investigated whether gut microbe alteration existed, and if so, the alteration affected peripheral T cell differentiation in patients with RP. In an analysis of gut microbiota, we found increased annotated species numbers in RP patients compared with normal individuals. In the RP gut microbiota, we observed several predominant species, namely Veillonella parvula, Bacteroides eggerthii, Bacteroides fragilis, Ruminococcus bromii, and Eubacterium dolichum, all species of which were reported to associate with propionate production in human intestine. Propionate is a short-chain fatty acid and is suggested to associate with interleukin (IL)10-producing regulatory T (Treg) cell differentiation in gut associated lymphoid tissues. IL10 gene expressions were moderately higher in freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of RP patients than those of normal individuals. Six hours after the initiation of the cell culture, regardless of the presence and absence of mitogen stimulation, IL10 gene expressions were significantly lower in RP patients than those in normal individuals. It is well known that PBMC of patients with autoimmune and inflammatory diseases show hyporesponsiveness to mitogen stimulation. We suggest that, in RP patients, continuous stimulation of intestinal T cells by excessive propionate leads to the spontaneous IL10 production and a subsequent refractory period of T cells in patients with RP. The hyporesponsiveness of Treg cells upon activation may associate with inflammatory cytokine production of PBMC and subsequently relate to chondritis in RP patients.
Introduction
Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is an uncommon systemic connective tissue disorder characterized by recurrent and episodic inflammation of cartilaginous tissues, such as ear, nose, joint, and respiratory tract [1]. RP often affects other proteoglycan rich organs, namely eye, inner ear, heart, blood vessels, and kidney [1]. In our survey [2], half of RP patients suffered from laryngotracheal involvement which was generally considered as a major cause of RP morbidity and mortality through infection, tracheomalacia, and so on.
There are no specific laboratory tests for the diagnosis and assessment of disease activity in RP. In our study of Japanese RP patients [2], elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rates and increased serum C-reactive protein concentrations were observed in 68.2% and 86.2% of the patients, respectively.
The initial investigation of autoantibodies against type II collagen reported that the recognition manners to the antigens were disease (RP)-specific and the serum levels were correlated with disease severity [3]. Autoantibodies to matrilin, another cartilage protein, were observed in RP patients and had affinity to tracheolaryngeal and nasal cartilage [4].
T helper type 1 (Th1)-skewed responses were found in the serum cytokine concentrations of RP patients [5]. As an inflammatory disease with enhanced Th1 responses, anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α antibody administration was suggested to be a choice of treatment in patients with refractory RP [6]. Th1-skewed responses were observed in natural killer T cells, a subset of innate-like lymphocytes, in RP patients [7].
Recent studies demonstrated that Th17 cells and regulatory T (Treg) cells play a crucial role in human diseases [8]. Th17 cells and Treg cells exhibited proinflammatory and antiinflammatory effects, respectively, on the other types of immunocompetent cells [8]. Both of the Th cell subpopulations were reported to differentiate in gut associated lymphoid tissues and need several specified gut microbes for their differentiation [9,10]. Researchers suggested that gut microbes were able to modulate the balance between Th17 cells and Treg cells through the metabolites, short-chain fatty acids [11–18]. Depletion of short-chain fatty acids, such as propionate and butyrate, was thought to cause various human diseases, such as type 1 diabetes, asthma, and multiple sclerosis through the unbalance of Th17 and Treg cells [16–18]. Actually, we previously demonstrated that compositional alteration of gut microbes and skewed responses of T cells in the peripheral blood occurred in patients with RP [19].
Here, we obtained 16S rRNA metagenomic data of RP patients and compared the data with those of normal individuals. We analyzed gene expressions of inflammation associated cytokines in freshly isolated and cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in RP patients and normal individuals for comparison.
Materials and methods
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the institutional review boards of St. Marianna University School of Medicine and was registered with the University Hospital Medical Information Network-Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN000018937). We conducted our research according to the principles expressed in the Declaration of Helsinki. We obtained written informed consent from each individual prior to enrolment in the study.
16S rRNA metagenomic data
We analyzed the feces of 25 RP patients and 27 normal individuals to obtain 16S rRNA metagenomic data. Mean age (years) of the patients was 54.8 ± 2.8 (standard error of the means) and that of normal individuals was 52.8 ± 2.8. The male to female ratios were 7:18 in RP patients and 12:15 in normal individuals. In patients, mean age of disease onset was 44.8 ± 3.4 and mean disease duration (years) was 10.0 ± 1.6. The clinical data of the 25 RP patients were summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Clinical characteristics of patients with relapsing polychondritis.
| % Organ involvement | ||||
|
Metagenomic analysisa (n = 25) |
Gene expression analysisa (n = 22) | |||
| At onset | Cumulative | At onset | Cumulative | |
| Ear | 60.0 | 60.0 | 68.2 | 68.2 |
| Nose | 44.0 | 44.0 | 59.1 | 59.1 |
| Airway | 48.0 | 48.0 | 40.9 | 40.9 |
| Inner ear | 8.0 | 20.0 | 4.6 | 13.6 |
| Joint | 24.0 | 32.0 | 18.2 | 36.4 |
| Eye | 36.0 | 52.0 | 40.9 | 54.6 |
| Skin | 0 | 4.0 | 0 | 4.6 |
| Cardiovascular | 0 | 8.0 | 0 | 13.6 |
| Central nervous system | 0 | 4.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Renal | 0 | 8.0 | 0 | 9.1 |
| Medications at the time of sample collection, % | ||||
| Metagenomic analysisa (n = 25) | Gene expression analysisa (n = 22) | |||
| Steroid | 88.0 | 86.3 | ||
| Methotrexate | 28.0 | 36.4 | ||
| Cyclophosphamide | 0 | 0 | ||
| Cyclosporine | 24.0 | 18.2 | ||
| Tacrolimus | 16.0 | 18.2 | ||
| Azathioprine | 4.0 | 4.6 | ||
| Mizoribine | 8.0 | 4.6 | ||
| Biologic agents | 20.0 | 31.8 | ||
a18 patients were evaluated with both the metagenomic analysis and the gene expression analysis.
We described here the study methods briefly. We extracted genomic DNA from fecal samples by treating them with achromopeptidase (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Tokyo, Japan) [20]. We amplified the V1–V2 16S rRNA gene region by primers according to a procedure reported previously [21]. We purified (AMPure XP magnetic purification beads, Beckman Coulter, Tokyo, Japan), quantified (Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer, Agilent Technologies Japan, Tokyo, Japan), and sequenced the amplicon libraries (Ion Torrent PGM, Life Technologies Japan, Tokyo, Japan).
Sequence analysis
We filtered the output file using QIIME software (version 1.9.1) with the default settings. After calculation of an operational taxonomic unit (OTU) table, we estimated microbial α and β diversity using QIIME software.
At the same time, we obtained another OTU table by QIIME software with a Greengenes-formatted database. We modified and predicted the file by using PICRUSt software and obtained a taxonomy file and a bacterial gene function file. We have uploaded the files to the Galaxy (http://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/galaxy) [22].
Statistical analysis of the sequenced data
Uploaded files were analyzed statistically with LEfSe (linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size) software [23]. LEfSe was an algorithm to find significant differences in genomic features (genes, pathways, or taxa) among groups, using nonparametric factorial Kruskal-Wallis sum-rank test and Wilcoxon rank-sum test. In LEfSe software, linear discriminant analysis was used to estimate the effect size of each differentially abundant feature. Those features that showed higher log LDA scores than 2.0 were chosen for subsequent plotting of output charts. Consequently, LEfSe indicated those features that better discriminated among groups with the log LDA scores.
Cell culture, gene expression analyses, and an Elisa assay
We obtained PBMC of 22 RP patients and 11 normal individuals. 18 patients were evaluated with both the metagenomic analysis and the gene expression analysis. Mean age (years) of the patients was 53.3 ± 3.4 (standard error of the means) and that of normal individuals was 43.3 ± 2.8. The male to female ratios were 8:14 in RP patients and 5:6 in normal individuals. In patients, mean age of disease onset was 42.5 ± 4.2 and mean disease duration (years) was 10.5 ± 1.6. The clinical data of the 22 RP patients were summarized in Table 1.
PBMC were cultured for 24 hours with and without 1 μg/ml phytohemagglutinin (PHA, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and a low concentration of phorbol myristate acetate (PMA, Sigma-Aldrich, 4 ng/ml). We harvested the cells and extracted total RNA from freshly isolated, 6-hour-cultured, and 24-hour-cultured PBMC. We studied 5 combinations of TaqMan primers and probes from Life Technologies Japan Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) as follows: interleukin (IL)10, forkhead box P3 (Foxp3), IL1β, IL6, and TNFα. Gene expressions of RP patients were estimated by the ΔΔCt method, followed by normalization of the titers relative to 2-ΔΔCt of normal individuals. The gene expression levels of normal individuals were defined as 1.000.
We measured fecal secretory IgA (sIgA) of 25 RP patients and 24 normal individuals using an Elisa kit (Eagle Biosciences, Nashua, NH).
Statistical analysis of demographical, gene expression, Elisa assay, and metagenomic data
We compared demographical data of patients with those of normal individuals by using Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Fisher’s exact test. We compared OTU numbers, α diversity index scores, relative gene expressions, and Elisa titers by using Wilcoxon rank-sum test with statistical software JMP 13.0.0 (SAS Institute Japan, Tokyo, Japan).
Results
Increased relative abundance of propionate-producing bacteria in patients with RP
We analyzed the feces of 25 RP patients and 27 normal individuals to obtain 16S rRNA metagenomic data. We compared the data of RP patients with those of age- and gender-matched normal individuals.
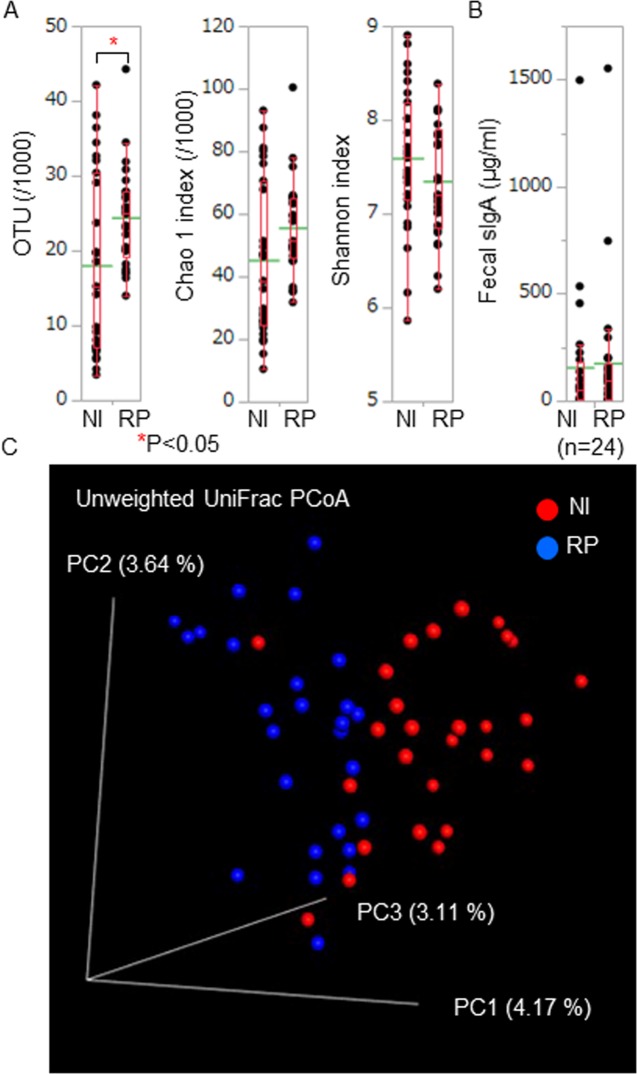
We estimated OTU numbers (annotated species numbers) and α diversity (Chao 1 and Shannon indexes) using QIIME software. α diversity was defined as the diversity within a community and Chao 1 and Shannon indexes were species richness and evenness estimators, respectively. OTU numbers were significantly high in RP patients compared with those in normal individuals (Fig 1A). Chao 1 and Shannon index scores were comparable between RP patients and normal individuals (Fig 1A). Fecal sIgA concentrations, which may suggest activation of intestinal immunity, were comparable between RP patients and normal individuals (Fig 1B).
Fig 1. Bacterial numbers and diversity of RP gut microbiota.
(A) We estimated OTU numbers (annotated species numbers) and α diversity scores (Chao 1 and Shannon indexes) of each sample. OTU numbers of RP patients (RP) were significantly higher than those of normal individuals (NI). Chao 1 and Shannon index scores were comparable between RP patients and normal individuals. (B) We measured fecal sIgA concentrations and compared the data between RP patients and normal individuals. Fecal sIgA concentrations were comparable between RP patients and normal individuals. These biological parameters of RP patients and normal individuals were displayed with dot plots. A box-plot and a mean level (green line) of each group of RP patients and normal individuals were indicated. (C) We estimated β diversity between RP patients and normal individuals. We showed the PCoA plots in a three dimensional structure where three axes and each contribution ratio were depicted. We exploratory evaluated the distance between the distribution of RP patients and that of normal individuals using two-sided Student's two-sample t-test and Monte Carlo permutations. We obtained a significant P value of the β diversity between RP patients and normal individuals in unweighted UniFrac PCoA (P = 0.01).
We exploratory estimated β diversity between RP patients and normal individuals. β diversity was defined as the diversity between communities. We obtained a figure of principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) plots using a linear conversion formula (Fig 1C).
We evaluated the distance between the distribution of RP patients and that of normal individuals using two-sided Student's two-sample t-test and Monte Carlo permutations of QIIME software. We obtained a significant P value of the β diversity between RP patients and normal individuals in unweighted UniFrac PCoA (P = 0.01), suggesting that the gut microbe compositional difference was obvious between RP patients and normal individuals.
We analyzed the metagenomic data of bacterial taxa using LEfSe analytic method to detect major taxon differences between RP patients and normal individuals. There were significant differences in relative abundance of 25 bacterial species between RP patients and normal individuals (Table 2, S1 and S2 Figs).
Table 2. Abundant bacterial species in RP patients and normal individuals.
| Abundant species in RP patients | Abundant species in normal individuals |
|---|---|
| Eubacterium dolichum★ | Serratia species |
| Staphylococcus species | Leuconostoc species |
| Coprobacillus cateniformis | Salmonella enterica |
| Bifidobacterium bifidum | Roseburia faecis |
| Ruminococcus bromii★ | Pseudomonas species |
| Acidaminococcus species★ | |
| Blautia product | |
| Lactobacillus vaginalis | |
| Christensenella species★ | |
| Bifidobacterium animalis | |
| Proteus species | |
| Gardnerella species | |
| Anaerofustis species | |
| Bacteroides eggerthii★ | |
| Finegoldia species | |
| Kocuria rhizohila | |
| Bacteroides fragilis★ | |
| Veillonella parvula★ | |
| Scardovia species | |
| Lactobacillus salivarius |
★, These species were reported to associate with propionate production in the intestine.
Relative abundance of (in the phylum Firmicutes) Eubacterium dolichum, Staphylococcus species, Coprobacillus cateniformis, Ruminococcus bromii, Acidaminococcus species, Blautia producta, Lactobacillus vaginalis, Christensenella species, Anaerofustis species, Finegoldia species, Veillonella parvula, Lactobacillus salivarius, (in the phylum Actinobacteria) Bifidobacterium bifidum, Bifidobacterium animalis, Gardnerella species, Kocuria rhizohila, (in the phylum Bacteroidetes) Bacteroides fragilis, Scardovia species, Bacteroides eggerthii, and (in the phylum Proteobacteria) Proteus species increased significantly in patients with RP.
In the RP predominant bacteria, several species (indicated in Table 2 using asterisks) were reported to associate with propionate production in the intestine (details were described in the Discussion section) [24–31].
Relative abundance of (in the phylum Firmicutes) Leuconostoc species, Roseburia faecis, (in the phylum Proteobacteria) Serratia species, Salmonella enterica, and Pseudomonas species increased significantly in normal individuals.
Abundant Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) modules for the citrate cycle in patients with RP
We assigned predicted gene functions of the metagenomic data according to the KEGG module database and identified predominant modules in RP patients and normal individuals (Tables 3 and 4 and S3 Fig). A KEGG module was a collection of manually defined functional units and was utilized for the annotation and biological interpretation of sequenced genomes.
Table 3. Abundant KEGG modules in RP patients.
| KEGG module identifiers | KEGG module names |
|---|---|
| M00096 | C5 isoprenoid biosynthesis, non-mevalonate pathway |
| M00048 | Inosine monophosphate biosynthesis, PRPP + glutamine = > IMP |
| M00016 | Lysine biosynthesis, succinyl-DAP pathway, aspartate = > lysine |
| M00019 | Valine/isoleucine biosynthesis, pyruvate = > valine / 2-oxobutanoate = > isoleucine |
| M00121 | Heme biosynthesis, glutamate = > protoheme/siroheme |
| M00011 | Citrate cycle, second carbon oxidation, 2-oxoglutarate = > oxaloacetate |
| M00009 | Citrate cycle |
| M00060 | Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis, KDO2-lipid A |
| M00335 | Sec (secretion) system |
| M00324 | Dipeptide transport system |
| M00012 | Glyoxylate cycle |
| M00008 | Entner-Doudoroff pathway, glucose-6P = > glyceraldehyde-3P + pyruvate |
| M00117 | Ubiquinone biosynthesis, prokaryotes, chorismate = > ubiquinone |
| M00149 | Succinate dehydrogenase, prokaryotes |
| M00229 | Arginine transport system |
| M00150 | Fumarate reductase, prokaryotes |
| M00124 | Pyridoxal biosynthesis, erythrose-4P = > pyridoxal-5P |
| M00260 | DNA polymerase III complex, bacteria |
| M00045 | Histidine degradation, histidine = > N-formiminoglutamate = > glutamate |
| M00198 | Putative sn-glycerol-phosphate transport system |
Table 4. Abundant KEGG modules in normal individuals.
| KEGG module identifiers | KEGG module names |
|---|---|
| M00125 | Riboflavin biosynthesis, GTP = > riboflavin/FMN/FAD |
| M00119 | Pantothenate biosynthesis, valine/L-aspartate = > pantothenate |
| M00185 | Sulfate transport system |
| M00157 | F-type ATPase, prokaryotes and chloroplasts |
| M00164 | ATP synthase |
| M00003 | Gluconeogenesis, oxaloacetate = > fructose-6P |
| M00018 | Threonine biosynthesis, aspartate = > homoserine = > threonine |
| M00115 | NAD biosynthesis, aspartate = > NAD |
| M00026 | Histidine biosynthesis, PRPP = > histidine |
| M00200 | Putative sorbitol/mannitol transport system |
| M00349 | Microcin C transport system |
| M00225 | Lysine/arginine/ornithine transport system |
| M00136 | GABA biosynthesis, prokaryotes, putrescine = > GABA |
| M00144 | NADH:quinone oxidoreductase, prokaryotes |
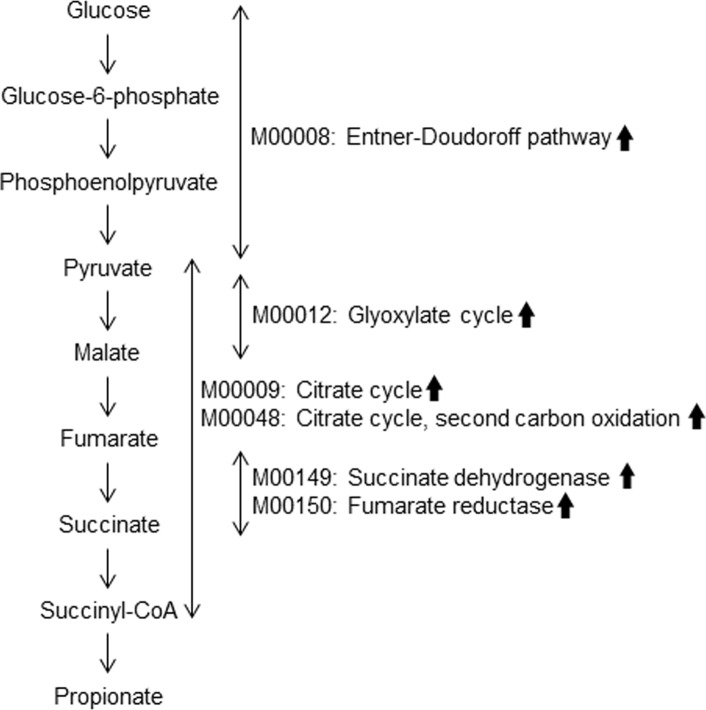
In the abundant KEGG modules of RP patients, we observed gene functions for glycolysis (M00008), citrate cycle (M00009, M00011, M00012, M00149, M00150), and amino acid biosynthesis and transport (M00016, M00019, M00229).
Fig 2 indicates RP predominant gene functions associated with succinate-propionate pathway [24,26], suggesting greater capacity for propionate production in the intestine of RP patients than that of normal individuals.
Fig 2. Schematic representation of succinate-propionate pathway and its alterations in patients with RP.
Several predominant gene functions of RP gut microbiota of this study (arrows) corresponded to several components of the succinate-propionate pathway. Veillonella species, Bacteroides species, and Acidaminococcus species utilize the pathway for the propionate production.
In the abundant KEGG modules of normal individuals, we observed gene functions for electron transport system (M00115, M00157, M00164, M00144) and vitamin B biosynthesis (M00125, M00119).
RP PBMC exhibited marked alterations in IL10 gene expressions
Several RP predominant species were reported to associate with propionate production in the intestine [24–31]. It was suggested that propionate promoted IL10-producing Treg cell differentiation in the intestine with gene expressions of Foxp3 [11,13–15]. We analyzed cytokine gene expressions in PBMC of 22 RP patients and 11 normal individuals to assess whether skewed IL10-producing Treg cell responses existed in patients with RP. PBMC were cultured with and without mitogen stimulation and we extracted messenger RNA from freshly isolated, 6-hour-cultured, and 24-hour-cultured PBMC.
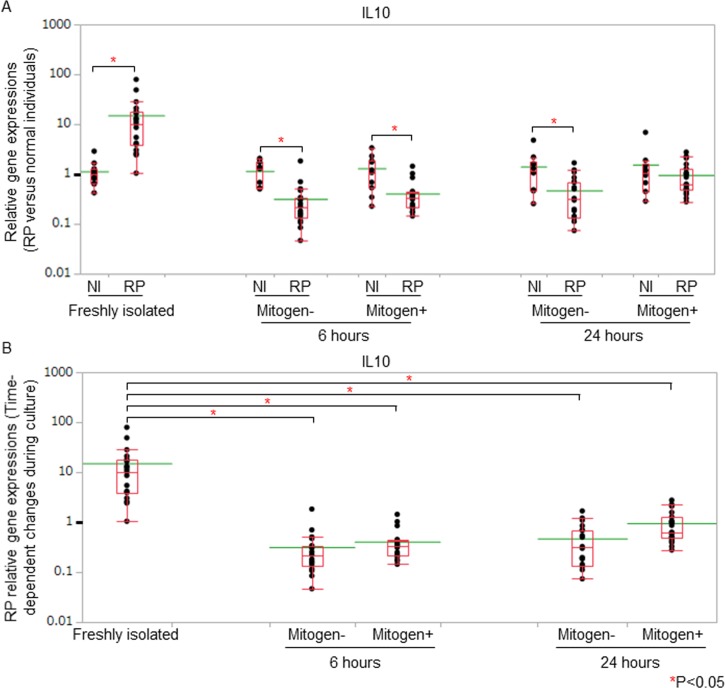
Freshly isolated PBMC elicited excessive responses with regard to IL10 production in RP patients compared with normal individuals. IL10 gene expressions of freshly isolated PBMC were significantly higher in RP patients than those in normal individuals even though the expression levels were moderate (Fig 3A). These data suggested that IL10-producing T cells were activated substantially in vivo in patients with RP. IL10 gene expressions were significantly lower in RP patients than those in normal individuals 6 hours after the initiation of the cell culture regardless of the presence and absence of mitogen stimulation (Fig 3A). When we compared the data of the freshly isolated PBMC with those of cultured PBMC in patients with RP, IL10 gene expressions decreased significantly regardless of the presence and absence of mitogen stimulation after the initiation of the cell culture (Fig 3B).
Fig 3. IL10 gene expressions on PBMC of RP patients.
(A) IL10 gene expressions of RP PBMC compared with those of normal PBMC. We measured IL10 gene expressions of freshly isolated, 6-hour-cultured, and 24-hour-cultured PBMC in RP patients (RP) and normal individuals (NI). Gene expressions of RP patients were estimated by the ΔΔCt method, followed by normalization of the titers relative to 2-ΔΔCt of normal individuals. The gene expression levels of normal individuals were defined as 1.000. IL10 gene expressions of freshly isolated PBMC were significantly higher in RP patients than those in normal individuals. IL10 gene expressions were significantly lower in RP patients than those of normal individuals 6 hours after the initiation of the cell culture, regardless of the presence and absence of mitogen stimulation. (B) Time-dependent changes of IL10 gene expressions of RP PBMC. We compared the gene expression data of the freshly isolated PBMC with those of cultured PBMC in patients with RP. IL10 gene expressions decreased significantly regardless of the presence and absence of mitogen stimulation in RP patients after the initiation of the cell culture. Relative gene expressions of RP patients against those of normal individuals were displayed with dot plots. A box-plot and a mean level (green line) of each group of RP patients and normal individuals were indicated.
Foxp3 gene expressions of RP freshly isolated PBMC were significantly lower than those of normal individuals (Fig 4A). When we compared the gene expression data of the freshly isolated PBMC with those of cultured PBMC in patients with RP, Foxp3 gene expressions increased significantly in the presence of mitogen stimulation 24 hours after the initiation of the cell culture (Fig 4B).
Fig 4. Foxp3 gene expressions in PBMC of RP patients.
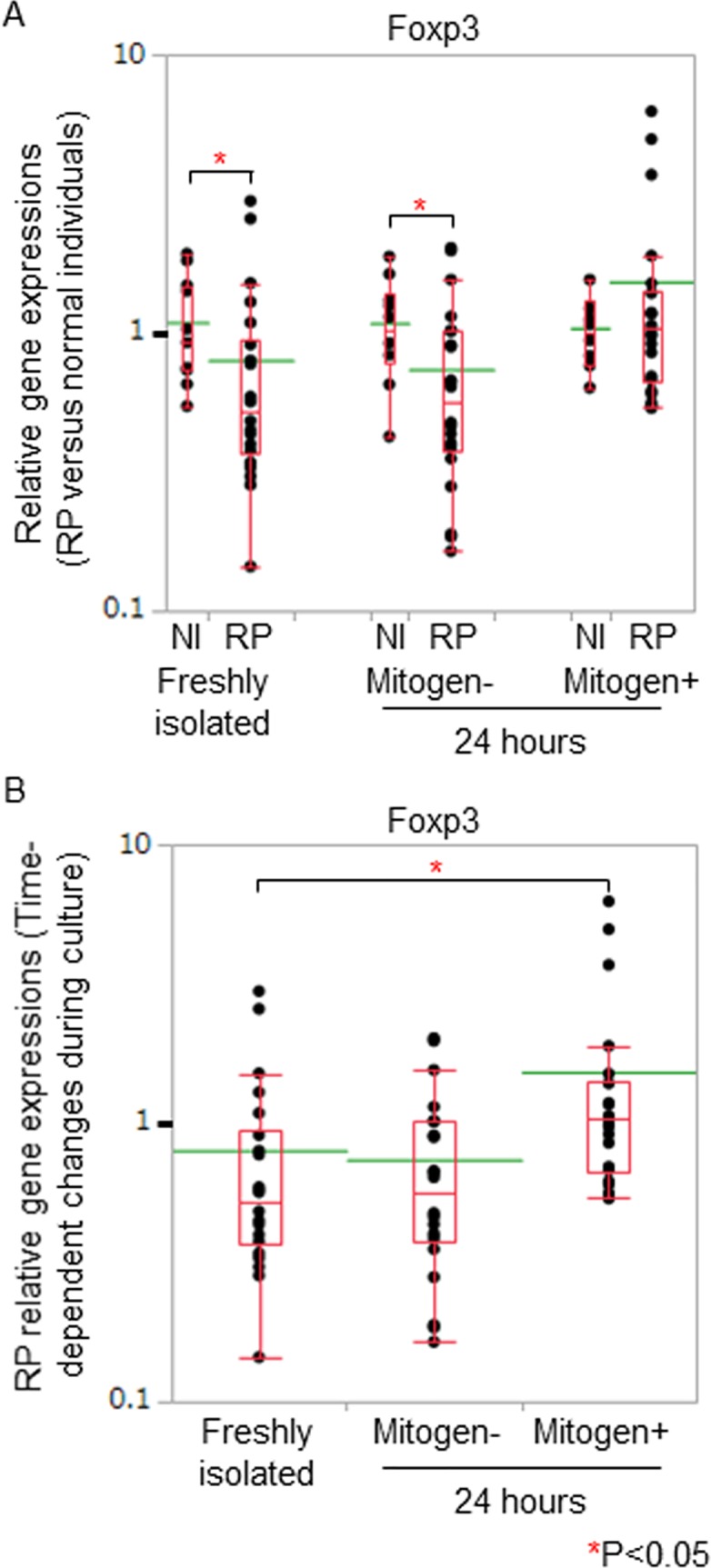
(A) We assessed RP relative gene expressions of Foxp3 by normalizing the titers to 2-ΔΔCt of normal individuals. The gene expression levels of normal individuals were defined as 1.000. Foxp3 gene expressions of RP freshly isolated PBMC were significantly lower than those of normal individuals. (B) We compared the gene expression data of the freshly isolated PBMC with those of cultured PBMC in patients with RP. Foxp3 gene expressions increased significantly in the presence of mitogen stimulation 24 hours after the initiation of the cell culture. Relative gene expressions of RP patients against those of normal individuals were displayed with dot plots. A box-plot and a mean level (green line) of each group of RP patients and normal individuals were indicated.
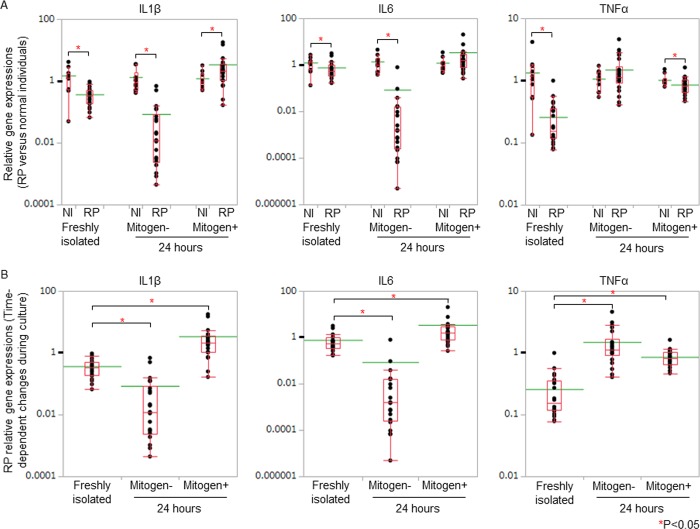
IL1β gene expressions of RP patients were significantly higher than those of normal individuals in the presence of mitogen stimulation, 24 hours after the initiation of the cell culture (Fig 5A). We compared the gene expression data of the freshly isolated PBMC with those of cultured PBMC in patients with RP. After the initiation of the cell culture, in the absence of mitogen stimulation, TNFα gene expressions increased significantly in RP patients (Fig 5B). With the stimulation, IL1β, IL6, and TNFα gene expressions increased significantly in RP patients (Fig 5B).
Fig 5. Inflammatory cytokine gene expressions in PBMC of RP patients.
(A) We assessed RP relative gene expressions of inflammatory cytokines by normalizing the titers to 2-ΔΔCt of normal individuals. The gene expression levels of normal individuals were defined as 1.000. IL1β gene expressions of RP patients were significantly higher than those of normal individuals in the presence of mitogen stimulation, 24 hours after the initiation of the cell culture. (B) We compared the gene expression data of the freshly isolated PBMC with those of cultured PBMC in patients with RP. After the initiation of the cell culture, in the absence of mitogen stimulation, TNFα gene expressions increased significantly in RP patients. With the stimulation, IL1β, IL6, and TNFα gene expressions increased significantly in RP patients. Relative gene expressions of RP patients against those of normal individuals were displayed with dot plots. A box-plot and a mean level (green line) of each group of RP patients and normal individuals were indicated.
Discussion
Here, we observed increased relative abundance of propionate-producing species in the intestine of RP patients. We found skewed Treg cell responses in patients with RP.
Veillonella parvula, Bacteroides eggerthii, Bacteroides fragilis (Table 2) were major propionate-producing bacteria in human intestine [24–28].
The most abundant species of this study in patients with RP, Eubacteria dolichum and Christensenella species, showed positive correlations with increased propionate concentrations in the human intestine on a resistant starch diet [29]. In other studies, resistant starch feeding significantly elevated fecal propionate concentrations with increased abundance of Ruminococcus bromii in the intestine of rats [30] and humans [31]. These data suggested that high concentrations of intestinal propionate produced by RP gut microbes modified the intestinal immune functions.
The gut derived propionate was reported to be metabolized in the host liver and the concentrations in the peripheral blood were low [32,33]. In the intestine, propionate induced IL10-producing Treg cells [11,13–15], but not TGFβ-producing Treg cells [11], through the epigenetic modification [11,12,14,15]. The intestinal propionate did not affect [11] and reduced [13] Th1 and Th17 cell populations of the intestine. Production of inflammatory cytokines, namely IL6 and IL12, by dendritic cells, was reduced by propionate [34] and propionate-treated dendritic cells increased Treg cells in in vitro experiments [12,35]. These findings seemed to share several common characteristics with gene expression analysis of this study.
IL10 enhanced gene expression of and protein production of type II collagen in injured cartilage grafts [36]. IL10 increased tibial length in the organ culture of IL10 gene-deficient mouse [37]. Thus inappropriate production of IL10 may bring about degeneration of cartilaginous tissues. Refractory phase in IL10 gene expression of PBMC in the cell culture may promote degeneration of chondrocyte in RP patients with inflammatory conditions. T cell hyporesponsiveness against mitogen stimulation was well known in patients with inflammatory diseases [38,39].
Increased gene expressions of inflammatory cytokines in response to mitogen stimulation became evident (Fig 5B). Mitogen or (auto)antigen may be important for provoking inflammatory cytokine production in patients with RP. In the absence of mitogen stimulation, TNFα gene expressions increased significantly in the 24-hour-culture (Fig 5B). It is known that several lactic acid-producing bacteria, including Bifidobacterium species and Lactobacillus species [40,41], and the bacterial cell surface components [42] increased TNFα production of human PBMC. Gut microbes of RP patients may associate with increased TNFα production by some means. Further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
In addition, IL10 hyporesponsiveness of Treg cells in response to mitogen stimulation may associate with TNFα overproduction of PBMC in patients with RP [43]. In regard to the efficiency of anti-TNFα antibody treatment in RP patients [6], TNFα seems to play a crucial role in the development of chondritis.
We observed characteristic alteration of 34 bacterial gene functions in patients with RP and normal individuals (Tables 3, 4, and S3 Fig). In RP patients, we observed abundant gene functions for glycolysis and citrate cycle, several functions of which were important for succinate-propionate pathway (Fig 2) [24]. Veillonella species, Bacteroides species, and Acidaminococcus species utilize the pathway for the propionate production [24–26] and the data support our hypothesis of a possible relationship between RP gut microbiota and T cell dysfunctions in patients with RP.
In normal individuals, we observed abundant gene functions for several proteins of electron transport chain, including ATP. Bacterial ATP was shown to increase Th17 cells in the intestine through the activation of antigen presenting cells which expressed TNFα gene [44]. It is possible that reduced ATP synthesis of RP gut microbes brings about Th17/Treg cell imbalance in the intestine.
Calcineurin inhibitors, namely cyclosporine and tacrolimus, negatively regulate T cell receptor signaling pathway and inhibit Th cell activation [45]. The compounds directly reduced the frequencies and functions of Treg cells, but not Th17 cells [46], in several in vitro and in vivo assays [46–49]. It may be important to assess peripheral T cell and the host responses to the inhibitors and elucidate the relationships between them in RP patients.
In conclusion, our findings suggested that propionate-producing gut microbes became predominant, leading to defective Treg cell function upon activation in patients with RP. Decreased production of IL10 by Treg cells and increased production of TNFα by PBMC may lead to chondritis in RP patients.
Supporting information
We analyzed metagenomic data of bacterial taxa using PICRUSt/LEfSe to assess major taxon differences between RP patients (RP) and normal individuals (NI). PICRUSt/LEfSe provided us with bar plots of prevalent biological features with the log LDA scores (effect sizes).
In this chart, significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from RP patients were exhibited by green bars. Significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from normal individuals were exhibited by red bars. “p__”, “c__”, “o__”, “f__”, “g__”, and “s__” indicated phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species, respectively.
Predominant species in RP patients and normal individuals were listed in Table 2.
(TIF)
PICRUSt/LEfSe provided us with a cladogram of seven levels (from kingdom to species) from the same OTU table of S1 Fig. Circles ranged from the phylum (the innermost) to the species.
Significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from RP patients (RP) were exhibited by small green circles and green shadings. Significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from normal individuals (NI) were exhibited by small red circles and red shadings. The circle sizes corresponded to the log LDA scores (effect sizes).
This cladogram demonstrated that the class Bacilli, the order Actinomycetales, and several genera and species were abundant in RP patients.
(TIF)
We assigned predicted gene functions according to the KEGG module database to identify predominant modules in RP patients (RP) and normal individuals (NI).
Predominant KEGG modules in RP patients and normal individuals were listed in Tables 3 and 4, respectively.
(TIF)
Data Availability
QIIME software is available from QIIME organization homepage at http://qiime.org/. PICRUSt software is available from PICRUSt tutorial homepage at http://picrust.github.io/picrust/install.html#install. Greengene database is available at http://greengenes.secondgenome.com/downloads/database/13_5.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Grant Number 17K10009) of Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (http://www.jsps.go.jp/english/e-grants/index.html). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Letko E, Zafirakis P, Baltatzis S, Voudouri A, Livir-Rallatos C, Foster CS. Relapsing polychondritis: a clinical review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002; 31: 384–395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Oka H, Yamano Y, Shimizu J, Yudoh K, Suzuki N. A large-scale survey of patients with relapsing polychondritis in Japan. Inflamm Regen. 2014; 34: 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Foidart JM, Abe S, Martin GR, Zizic TM, Barnett EV, Lawley TJ, et al. Antibodies to type II collagen in relapsing polychondritis. N Engl J Med. 1978; 299: 1203–1207. 10.1056/NEJM197811302992202 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hansson AS, Heinegård D, Piette JC, Burkhardt H, Holmdahl R. The occurrence of autoantibodies to matrilin 1 reflects a tissue-specific response to cartilage of the respiratory tract in patients with relapsing polychondritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001; 44: 2402–2412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sato T, Yamano Y, Tomaru U, Shimizu Y, Ando H, Okazaki T, et al. Serum level of soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 as a biomarker of disease activity in relapsing polychondritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2014; 24: 129–136. 10.3109/14397595.2013.852854 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kingdon J, Roscamp J, Sangle S, D'Cruz D. Relapsing polychondritis: a clinical review for rheumatologists. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017. November 6 10.1093/rheumatology/kex406 [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Takagi D, Iwabuchi K, Iwabuchi C, Nakamaru Y, Maguchi S, Ohwatari R, et al. Immunoregulatory defects of V alpha 24V+ beta 11+ NKT cells in development of Wegener's granulomatosis and relapsing polychondritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004; 136: 591–600. 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02471.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Noack M, Miossec P. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2014; 13: 668–677. 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ivanov II, Atarashi K, Manel N, Brodie EL, Shima T, Karaoz U, et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell. 2009; 139: 485–498. 10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Oshima K, Suda W, Nagano Y, Nishikawa H, et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature. 2013; 500: 232–236. 10.1038/nature12331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly-Y M, et al. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science. 2013; 341: 569–573. 10.1126/science.1241165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van der Veeken J, deRoos P, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 2013; 504: 451–455. 10.1038/nature12726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Haghikia A, Jörg S, Duscha A, Berg J, Manzel A, Waschbisch A, et al. Dietary fatty acids directly impact central nervous system autoimmunity via the small intestine. Immunity. 2015; 43: 817–829. 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Furusawa Y, Obata Y, Fukuda S, Endo TA, Nakato G, Takahashi D, et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature. 2013; 504: 446–450. 10.1038/nature12721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Park J, Kim M, Kang SG, Jannasch AH, Cooper B, Patterson J, et al. Short-chain fatty acids induce both effector and regulatory T cells by suppression of histone deacetylases and regulation of the mTOR-S6K pathway. Mucosal Immunol. 2015; 8: 80–93. 10.1038/mi.2014.44 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Levy M, Kolodziejczyk AA, Thaiss CA, Elinav E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017; 17: 219–232. 10.1038/nri.2017.7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Byndloss MX, Bäumler AJ. The germ-organ theory of non-communicable diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018; 16: 103–110. 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.158 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, et al. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science. 2012; 336: 1262–1267. 10.1126/science.1223813 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shimizu J, Kubota T, Suzuki N. An abundance of butyrate-producing bacterium in the intestine and increased Foxp3 gene expression of T cells in patients with relapsing polychondritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 Suppl 10: 2477–2478. 10.1002/art.40321 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Morita H, Kuwahara T, Ohshima K, Sasamoto H, Itoh K, Hattori M, et al. An improved DNA isolation method for metagenomic analysis of the microbial flora of the human intestine. Microbes Environ. 2007; 22: 214–222. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim SW, Suda W, Kim S, Oshima K, Fukuda S, Ohno H, et al. Robustness of gut microbiota of healthy adults in response to probiotic intervention revealed by high-throughput pyrosequencing. DNA Res. 2013; 20: 241–253. 10.1093/dnares/dst006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol. 2013; 31: 814–821. 10.1038/nbt.2676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, et al. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011; 12: R60 10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Reichardt N, Duncan SH, Young P, Belenguer A, McWilliam Leitch C, Scott KP, et al. Phylogenetic distribution of three pathways for propionate production within the human gut microbiota. ISME J. 2014; 8: 1323–1335. 10.1038/ismej.2014.14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Marchandin H, Teyssier C, Campos J, Jean-Pierre H, Roger F, Gay B, et al. Negativicoccus succinicivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human clinical samples, emended description of the family Veillonellaceae and description of Negativicutes classis nov., Selenomonadales ord. nov. and Acidaminococcaceae fam. nov. in the bacterial phylum Firmicutes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010; 60: 1271–1279. 10.1099/ijs.0.013102-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Macy JM, Probst I. The biology of gastrointestinal Bacteroides. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979; 33: 561–594. 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rios-Covian D, Sánchez B, Salazar N, Martínez N, Redruello B, Gueimonde M, et al. Different metabolic features of Bacteroides fragilis growing in the presence of glucose and exopolysaccharides of bifidobacteria. Front Microbiol. 2015; 6: 825 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00825 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hidalgo-Cantabrana C, Sánchez B, Milani C, Ventura M, Margolles A, Ruas-Madiedo P. Genomic overview and biological functions of exopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Bifidobacterium spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014; 80: 9–18. 10.1128/AEM.02977-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Upadhyaya B, McCormack L, Fardin-Kia AR, Juenemann R, Nichenametla S, Clapper J, et al. Impact of dietary resistant starch type 4 on human gut microbiota and immunometabolic functions. Sci Rep. 2016; 6: 28797 10.1038/srep28797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kalmokoff M, Zwicker B, O'Hara M, Matias F, Green J, Shastri P, et al. Temporal change in the gut community of rats fed high amylose cornstarch is driven by endogenous urea rather than strictly on carbohydrate availability. J Appl Microbiol. 2013; 114: 1516–1528. 10.1111/jam.12157 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Abell GC, Cooke CM, Bennett CN, Conlon MA, McOrist AL. Phylotypes related to Ruminococcus bromii are abundant in the large bowel of humans and increase in response to a diet high in resistant starch. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2008; 66: 505–515. 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00527.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Morrison DJ, Preston T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes. 2016; 7: 189–200. 10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bloemen JG, Venema K, van de Poll MC, Olde Damink SW, Buurman WA, Dejong CH. Short chain fatty acids exchange across the gut and liver in humans measured at surgery. Clin Nutr. 2009; 28: 657–661. 10.1016/j.clnu.2009.05.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nastasi C, Candela M, Bonefeld CM, Geisler C, Hansen M, Krejsgaard T, et al. The effect of short-chain fatty acids on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Sci Rep. 2015; 5: 16148 10.1038/srep16148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kaisar MMM, Pelgrom LR, van der Ham AJ, Yazdanbakhsh M, Everts B. Butyrate conditions human dendritic cells to prime type 1 regulatory T cells via both histone deacetylase inhibition and G protein-coupled receptor 109A signaling. Front Immunol. 2017; 8: 1429 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01429 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Behrendt P, Feldheim M, Preusse-Prange A, Weitkamp JT, Haake M, Eglin D, et al. Chondrogenic potential of IL-10 in mechanically injured cartilage and cellularized collagen ACI grafts. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018; 26: 264–275. 10.1016/j.joca.2017.11.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jung YK, Kim GW, Park HR, Lee EJ, Choi JY, Beier F, et al. Role of interleukin-10 in endochondral bone formation in mice: anabolic effect via the bone morphogenetic protein/Smad pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65: 3153–3164. 10.1002/art.38181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Crucian B, Dunne P, Friedman H, Ragsdale R, Pross S, Widen R. Detection of altered T helper 1 and T helper 2 cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with multiple sclerosis utilizing intracellular cytokine detection by flow cytometry and surface marker analysis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1996; 3: 411–416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Victorino RM, Hodgson HJ. Alteration in T lymphocyte subpopulations in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980; 41: 156–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sheikhi A, Shakerian M, Giti H, Baghaeifar M, Jafarzadeh A, Ghaed V, et al. Probiotic yogurt culture Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 modulate the cytokine secretion by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with ulcerative colitis. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2016; 66: 300–305. 10.1055/s-0035-1569414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Djaldetti M, Bessler H. Probiotic strains modulate cytokine production and the immune interplay between human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and colon cancer cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2017; 364: fnx014 10.1093/femsle/fnx014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ashraf R, Vasiljevic T, Smith SC, Donkor ON. Effect of cell-surface components and metabolites of lactic acid bacteria and probiotic organisms on cytokine production and induction of CD25 expression in human peripheral mononuclear cells. J Dairy Sci. 2014; 97: 2542–2558. 10.3168/jds.2013-7459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Levitz SM, Tabuni A, Nong SH, Golenbock DT. Effects of interleukin-10 on human peripheral blood mononuclear cell responses to Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans, and lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1996; 64: 945–951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Atarashi K, Nishimura J, Shima T, Umesaki Y, Yamamoto M, Onoue M, et al. ATP drives lamina propria T(H)17 cell differentiation. Nature. 2008; 455: 808–812. 10.1038/nature07240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hermann-Kleiter N, Baier G. NFAT pulls the strings during CD4+ T helper cell effector functions. Blood. 2010; 115: 2989–2997. 10.1182/blood-2009-10-233585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chiasson VL, Talreja D, Young KJ, Chatterjee P, Banes-Berceli AK, Mitchell BM. FK506 binding protein 12 deficiency in endothelial and hematopoietic cells decreases regulatory T cells and causes hypertension. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 1167–1175. 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.162917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li X, Liang Y, LeBlanc M, Benner C, Zheng Y. Function of a Foxp3 cis-element in protecting regulatory T cell identity. Cell. 2014; 158: 734–748. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Akimova T, Kamath BM, Goebel JW, Meyers KE, Rand EB, Hawkins A, et al. Differing effects of rapamycin or calcineurin inhibitor on T-regulatory cells in pediatric liver and kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2012; 12: 3449–3461. 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04269.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Whitehouse G, Gray E, Mastoridis S, Merritt E, Kodela E, Yang JHM, et al. IL-2 therapy restores regulatory T-cell dysfunction induced by calcineurin inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114: 7083–7088. 10.1073/pnas.1620835114 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
We analyzed metagenomic data of bacterial taxa using PICRUSt/LEfSe to assess major taxon differences between RP patients (RP) and normal individuals (NI). PICRUSt/LEfSe provided us with bar plots of prevalent biological features with the log LDA scores (effect sizes).
In this chart, significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from RP patients were exhibited by green bars. Significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from normal individuals were exhibited by red bars. “p__”, “c__”, “o__”, “f__”, “g__”, and “s__” indicated phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species, respectively.
Predominant species in RP patients and normal individuals were listed in Table 2.
(TIF)
PICRUSt/LEfSe provided us with a cladogram of seven levels (from kingdom to species) from the same OTU table of S1 Fig. Circles ranged from the phylum (the innermost) to the species.
Significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from RP patients (RP) were exhibited by small green circles and green shadings. Significantly enriched bacterial taxa in samples obtained from normal individuals (NI) were exhibited by small red circles and red shadings. The circle sizes corresponded to the log LDA scores (effect sizes).
This cladogram demonstrated that the class Bacilli, the order Actinomycetales, and several genera and species were abundant in RP patients.
(TIF)
We assigned predicted gene functions according to the KEGG module database to identify predominant modules in RP patients (RP) and normal individuals (NI).
Predominant KEGG modules in RP patients and normal individuals were listed in Tables 3 and 4, respectively.
(TIF)
Data Availability Statement
QIIME software is available from QIIME organization homepage at http://qiime.org/. PICRUSt software is available from PICRUSt tutorial homepage at http://picrust.github.io/picrust/install.html#install. Greengene database is available at http://greengenes.secondgenome.com/downloads/database/13_5.