Abstract
Background
The distribution of Taenia saginata in the Americas is unclear. Establishing the distribution, economic burden, and potentials for control of bovine cysticercosis is increasingly important due to the growing demand for beef. This paper aims to take the first step and reviews the recent distribution of T. saginata taeniosis and bovine cysticercosis on a national level within the Americas.
Methods
We undertook a systematic review of published and grey literature for information on the occurrence, prevalence, and geographical distribution of bovine cysticercosis and human taeniosis in the 54 countries and territories of the Americas between January 1st, 1990 and December 31st, 2017. Data on bovine cysticercosis from OIE reports from 1994 to 2005 were also included.
Results
We identified 66 papers from the Americas with data on the occurrence of taeniosis or bovine cysticercosis and an additional 19 OIE country reports on bovine cysticercosis. Taeniosis was reported from 13 countries, with nine of these countries reporting specifically T. saginata taeniosis, and four countries reporting non-species specific taeniosis. The reported prevalence of taeniosis ranged between 0.04–8.8%. Bovine cysticercosis was reported from 19 countries, nine identified through the literature search, and an additional 10 identified through the OIE country reports for notifiable diseases. The reported prevalence of bovine cysticercosis ranged between 0.1–19%. Disease occurrence was restricted to 21 countries within the Americas, the majority from the mainland, with the only island nations reporting either bovine cysticercosis or taeniosis being Cuba, Haiti, and the US Virgin Islands.
Conclusions
Taenia saginata is widely distributed across 21 of the 54 countries in the Americas, but insufficient epidemiological data are available to estimate the subnational spatial distribution, prevalence, incidence and intensity of infections. This needs to be addressed through active surveillance and disease detection programmes. Such programmes would improve the data quantity and quality, and may enable estimation of the economic burden due to bovine cysticercosis in the region in turn determining the requirement for and cost-effectiveness of control measures.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13071-018-3079-y) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Taenia saginata, Cestoda, Beef tapeworm, Taeniosis, Bovine cysticercosis, North and South America, Caribbean
Background
Taenia saginata is a zoonotic tapeworm that is of economic importance in countries where cattle are kept. The parasite is transmitted from human tapeworm carriers (taeniosis) to bovines (cysticercosis) by excretion of eggs or proglottids containing eggs into the environment via the stool. Bovines can then ingest the eggs through contaminated feed or water. After ingestion, the eggs hatch and release oncospheres in the small intestines, where the oncospheres penetrate the intestinal wall to reach the blood circulation. This distributes them throughout the body, but primarily to muscle tissue, where they develop into cysticerci. For humans to become infected with T. saginata, raw or undercooked bovine meat or offal containing infective cysts must be consumed. Bovine cysticercosis has been associated with various environmental factors related to water sources, such as animals having access to surface water, flooding of pastures and proximity to wastewater sources [1].
Taeniosis causes only a few, if any, mild symptoms in humans [2], and bovine cysticercosis is usually asymptomatic. The primary burden of the parasite is therefore the economic burden imposed on the cattle industry. Economic losses occur when infected carcasses are identified during routine meat inspection at slaughter facilities, causing total economic loss if the carcass is condemned due to high intensity infection, or partial economic loss if extra-processing of the carcass is required due to low intensity infection. Additional costs may include increased labour costs due to extra-handling and transport of infected carcasses to appropriate facilities, in addition to, potential freezing, transport and processing of the meat. However, the current economic burden due to bovine cysticercosis in the Americas has not been estimated.
Post-mortem inspection procedures of carcasses for pathogens vary from country to country, and even from facility to facility in some countries. In general, however, this diagnostic method has low sensitivity for detection of bovine cysticercosis [3–5]. Nevertheless, routine meat inspection remains the preferred tool for T. saginata detection in bovines. There is currently no ante-mortem test that performs with high sensitivity and high specificity, regardless of infection intensity. The sensitivities of existing serological tests are highly dependent on the infection intensity within the host [6], with the tests becoming increasingly unreliable as infection intensity decreases. The lack of a ‘gold standard’, combined with the non-specific symptomatic/asymptomatic nature of the diseases caused by the parasite in humans and bovines, and the prolonged survival of T. saginata eggs in the environment [7], makes T. saginata difficult to control.
Taenia saginata is thought to be widely distributed throughout the world, and to a larger degree in low-income countries where hygiene and sanitation standards are below average and routine meat inspection not always enforced. Nonetheless, in countries where standards of hygiene and sanitation are considered high and routine meat inspection enforced, such as within Europe, bovine cysticercosis still remains widely distributed [8]. There is no clear overview of the distribution of this zoonotic cestode in the Americas, and with a growing demand for beef, establishing the distribution, prevalence, economic burden, and potentials for control is more important than ever. This paper aims to take the first step, and reviews the distribution of T. saginata taeniosis and bovine cysticercosis on a national level within the Americas between 1990 and 2017.
Methods
Search strategy
We undertook a systematic review of published literature for information on the occurrence, prevalence, and geographical distribution of bovine cysticercosis and human taeniosis in the Americas between January 1st, 1990 and December 31st, 2017, using an approach that followed PRISMA guidelines [9]. The protocol and the PRISMA checklist for this review can be found in Additional file 1. The Americas for the purpose of this review included the following 54 countries or territories: Anguilla, Antigua & Barbuda, Argentina, Aruba, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, Bolivia, Brazil, British Virgin Islands, Canada, Caribbean Netherlands, Cayman Islands, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Curacao, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Falkland Islands, French Guiana, Greenland, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Martinique, Mexico, Montserrat, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Puerto Rico, Saint Barthélemy, Saint Kitts & Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Martin, Saint Pierre & Miquelon, Saint Vincent & the Grenadines, Suriname, Trinidad & Tobago, Turks & Caicos Islands, Uruguay, US Virgin Islands, USA and Venezuela.
The first search was done in PubMed (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed), using the following search phrase: (cysticerc* OR cisticerc* OR "C. bovis" OR taenia* OR tenia* OR saginata OR taeniosis OR teniosis OR taeniasis OR ténia OR taeniid OR cysticerque OR Taeniarhynchus) AND (America OR USA OR Brazil OR Argentina OR Canada OR Peru OR Chile OR Ecuador OR Bolivia OR Paraguay OR Costa Rica OR Uruguay OR Bermuda OR Greenland OR Caribbean Netherlands OR Saint Barts OR Saint Pierre and Miquelon OR Falkland Islands OR Anguilla OR Antigua and Barbuda OR Aruba OR Bahamas OR Barbados OR Belize OR Bonaire OR British Virgin Islands OR Bermuda OR Cayman Islands OR Colombia OR Costa Rica OR Cuba OR Curaçao OR Dominica OR Dominican Republic OR El Salvador OR French Guiana OR Grenada OR Guadeloupe OR Guatemala OR Guyana OR Haiti OR Honduras OR Jamaica OR Martinique OR Mexico OR Montserrat OR Netherlands Antilles OR Nicaragua OR Panama OR Puerto Rico OR Saba OR Saint Kitts and Nevis OR Saint Lucia OR Saint Vincent and the Grenadines OR Saint Eustatius OR Sint Maarten OR Saint Martin OR Suriname OR Trinidad and Tobago OR Turks and Caicos Islands OR US Virgin Islands OR Venezuela). The following databases were also searched using keywords from the above search phrase: Web of Science (www.webofknowledge.com), OpenGrey (http://www.opengrey.eu/), and CABDirect (http://www.cabdirect.org/).
Selection criteria
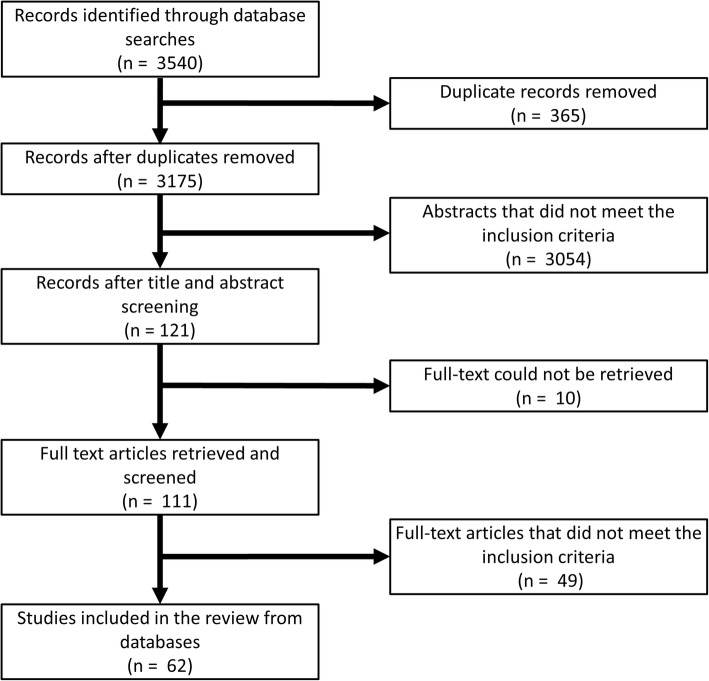
Outputs from the databases searches were compiled and screened for duplicates. Thereafter, titles and abstracts were screened for eligibility and were excluded on the following grounds: (i) studies concerning a parasite other than T. saginata; (ii) studies reporting data from countries different from those listed above; (iii) studies published prior to January 1st, 1990 or after December 31st, 2017; (iv) studies reporting results outside the scope of the review question (e.g. laboratory experiments, environmental studies and general reviews); and (v) duplicated data. If the same data had been published more than once, the oldest article was included and all others omitted. Full text manuscripts were then retrieved where possible and assessed by the same criteria as above (Fig. 1). The citations in identified reports were also screened for relevant literature.
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of the database searches
Data on bovine cysticercosis from OIE reports from 1994 to 2005 were also obtained [10, 11]. Additionally, we sought to obtain data from known articles not captured in the literature database searches, as well as unpublished work (i.e. masters’ theses) and these were included if they confirmed presence of T. saginata from a country where no disease report had been identified in the literature search, or if prevalence data were presented at a higher geographical resolution to that in the published literature.
Data extraction and generation
From the included literature and reports, data were extracted into predefined tables that can be found in Additional file 2: Tables S1-S3. Prevalence data were only extracted if both the numerator and the denominator were provided, and 95% confidence intervals using the Clopper-Pearson method, were calculated, if not already stated within the paper. All maps were generated using ArcGIS 10.3.1 (ESRI Inc., USA).
Results
Search results
The database searches yielded 62 articles presenting data on taeniosis or bovine cysticercosis in the Americas. An additional four articles were identified from other sources and confirmed occurrence of taeniosis in Venezuela, and occurrence of bovine cysticercosis in the USA and the US Virgin Islands. Of the 66 articles identified, 31 reported occurrences of taeniosis, 33 reported occurrences of bovine cysticercosis, and two papers reported occurrences of both diseases. A total of 19 OIE country reports were also identified. All eligible references are listed within the tables of this paper.
Taeniosis and bovine cysticercosis occurrence
In the period 1990–2017, taeniosis or bovine cysticercosis has been reported within all mainland countries in the Americas except for Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, Panama and Suriname. The only island nations within the region to report any disease occurrence during the study period were Cuba, Haiti and the US Virgin Islands, contributing to occurrence of the parasite in a total of 21 countries within the Americas.
Human taeniosis occurrence
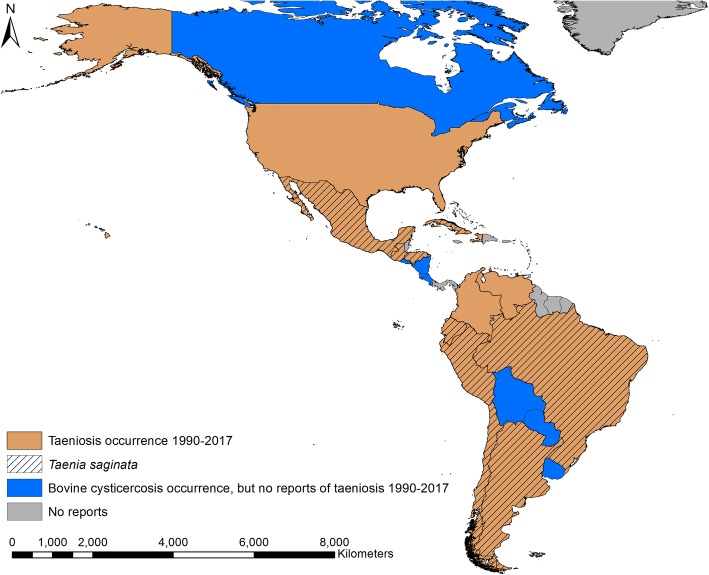
In the period 1990–2017, taeniosis was reported in 13 countries in the Americas, with T. saginata taeniosis reported in nine of those countries (Fig. 2). Colombia, Haiti, Venezuela and the USA reported taeniosis, but the specific tapeworm species were not confirmed in any of the reports. In seven countries there were reports of bovine cysticercosis, but no reports of taeniosis. In total, 33 papers reporting the occurrence of taeniosis within the Americas were identified in the search strategy. Of the 33 papers, there were three case reports of taeniosis, with species identification done in two of these cases, Chile and Mexico (Table 1). In the case reports from Brazil and Chile, it was unclear exactly when the infection had been discovered.
Fig. 2.
Countries with reports of taeniosis due to Taenia saginata and Taenia spp. in the period 1990–2017
Table 1.
Individual cases of human taeniosis (published case studies)
| Country | Year | Nationality | Speciesa | Diagnostic technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | na | Brazilian | Taenia spp. | Proglottid identification | [27] |
| Chile | na | na | T. saginata | Proglottid identification | [28] |
| Mexico | 2006 | na | T. saginata | Proglottid identification | [29] |
Abbreviation: na information not provided
aIf confirmed
Of the 33 papers, seven contained insufficient data, or the data were of insufficient quality to yield prevalence estimations (Table 2). In the majority of these studies, species identification was performed, but the diagnostic method was not always described.
Table 2.
Aggregated cases of human taeniosis (hospital/laboratory/field records without prevalence data)
| Country | Year | No. of cases | Speciesa | Diagnostic technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | na | na | Taenia spp. | Ritchie technique | [30] |
| Colombia | 2009–2013 | na | T. saginata | na | [31] |
| Honduras | na | 4 | T. saginata | Worm expulsion | [32] |
| Peru | 2004–2007 | 16 | T. saginata | Worm expulsion | [33] |
| Peru | 1998–2000 | 11 | T. saginata | Worm expulsion | [34] |
| Venezuela | na | 1 | Taenia spp. | Ritchie technique | [35] |
| Venezuela | 2004 | 18 | Taenia spp. | na | [36] |
Abbreviation: na information not provided
aIf confirmed
In 23 papers, the methodology and data were sufficiently described to enable prevalence and confidence interval calculations (Table 3). In the majority, disease confirmation was based on various microscopic methods. Prevalence reports ranged from between 0.04–8.8%. All 23 studies reported data that could be georeferenced to first-level administration.
Table 3.
Prevalence of human taeniosis (published data)
| Country | Year | Location of studya | Time frame | Prevalence (%) (95% CI) | Species | Diagnostic technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 1993 | Corrientes | Apr-Oct | 0.48 (0.01–2.66) | T. saginata b | Microscopy | [37] |
| Argentina | 2005 | Corrientes | Mar-Dec | 1.77 (0.22–6.25) | Taenia spp. | Graham tests | [38] |
| Brazil | na | Minas Gerais | na | 0.18 (0.13–0.26) | Taenia spp. | Kato-Katz | [39] |
| Brazil | 2000–2001 | Minas Gerais | na | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) | T. saginata | Worm expulsion | [40] |
| Brazil | na | Mato Grosso do Sul | na | 2.24 (0.46–6.40) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [41] |
| Brazil | 2004–2006 | Paraná | Jun-May | 0.23 (0.00–0.28) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [42] |
| Brazil | 1992–1993 | Minas Gerais | Jan-Dec | 2.22 (1.43–3.29) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [43] |
| Brazil | 1992 | Minas Gerais | na | 0.72 (0.46–1.07) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [44] |
| Chile | 2005–2008 | Maule | Jan-Dec | 0.13 (0.07–0.21) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [45] |
| Colombia | 2004 | Bolívar | Feb-Jun | 0.79 (0.16–2.28) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [46] |
| Ecuador | 2000 | Imbabura | Jan-May | 0.40 (0.13–0.94) | T. saginata | Ritchie technique & worm expulsion | [47] |
| Pichincha | 2.30 (1.32–3.71) | ||||||
| Guatemala | na | Jutiapa | na | 0.06 (0.010.33) | T. saginata | Worm expulsion | [48] |
| Guatemala | 1991–1995 | Jutiapa | Oct-Jan | 0.03 (0.01–0.16) | T. saginata b | Copro-antigen ELISA | [49] |
| Haiti | 2002 | Nationwide | na | 0.31 (0.18–0.49) | Taenia spp. | Ritchie technique | [50] |
| Honduras | na | Francisco Morazán | na | 0.25 (0.01–1.37) | Taenia spp. | Ritchie technique | [51] |
| Mexico | 2004 | Chihuahua | Aug-Dec | 1.02 (0.21–2.96) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy & Copro-antigen ELISA | [52] |
| Mexico | 1992 | Baja California | Feb-Jul | 6.5 (2.43–13.66) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [53] |
| Mexico | 1998 | Guerrero | na | 0.74 (0.15–2.16) | Taenia spp. | Copro-antigen ELISA | [54] |
| Mexico | 1996 | Morelos | na | 0.50 (0.10–1.44) | Taenia spp. | Copro-antigen ELISA & Ritchie technique | [55] |
| Peru | 2008 | Ayacucho | na | 1.4 (0.44–3.14) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy | [56] |
| Peru | na | Tumbes | na | 1.5 (0.55–3.22) | Taenia spp. | Copro-antigen ELISA | [57] |
| USA | 2004 | Texas | Aug-Dec | 8.8 (4.11–16.09) | Taenia spp. | Microscopy & Copro-antigen ELISA | [52] |
| Venezuela | na | Tachira | na | 0.8 (0.02–4.31) | Taenia spp. | Ritchie technique | [58] |
Abbreviations: CI confidence interval, na information not provided
aFirst-level administration
bNo description of species confirmation
Bovine cysticercosis
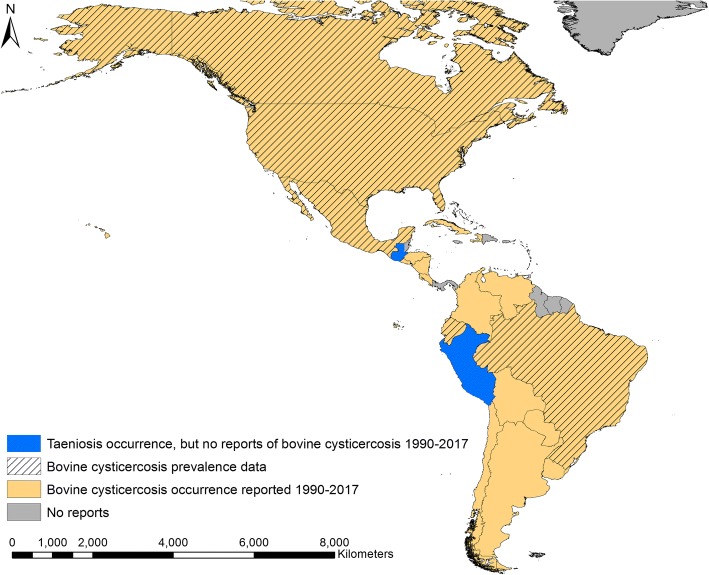
Bovine cysticercosis was reported from 19 countries within the Americas during the period 1990–2017. The literature search identified nine countries with bovine cysticercosis, and an additional 10 countries were identified through the 1994 and 2005 OIE country reports for notifiable diseases [10, 11]. Taenia saginata was reported from humans in both Guatemala and Peru during 1990–2017, but no reports of bovine cysticercosis could be obtained from these two countries (Fig. 3). Cuba, Haiti and the US Virgin Islands were the only island nations/territories to report bovine cysticercosis during the study period. On the mainland most countries reported bovine cysticercosis, but no reports could be found from Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname and Panama. Of the 35 papers identified that reported occurrence of bovine cysticercosis, seven did not contain sufficient data for prevalence calculations. All seven papers reported results of official meat inspections in Brazil, Chile, Cuba, the USA and the US Virgin Islands, respectively (Table 4).
Fig. 3.
Bovine cysticercosis occurrence and countries with studies reporting prevalence in the period 1990–2017
Table 4.
Reported occurrence of bovine cysticercosis (case studies/published data without full prevalence or incidence data) based on meat inspection
| Country | Year | Location of studya | Cases | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | na | Minas Gerais | na | [59] |
| Brazil | 2005–2006 | Goias | na | [60] |
| Brazil | 2009–2010 | Minas Gerais | 2019 | [61] |
| Brazil | 2008–2010 | Espírito Santo | na | [62] |
| Chile | 2010 | na | 148 | [63] |
| Cuba | 1998–2001 | Villa Clara | na | [64] |
| USA | 1985–1994 | Nationwide | na | [23] |
| US Virgin Islands | 1992 | na | na | [23] |
Abbreviation: na information not provided
aFirst-level administration
In total, 28 papers contained sufficient information to calculate prevalence and 95% confidence intervals (Table 5). Most of the studies (82%) originated from Brazil, where reported prevalence ranged between 0.1–19%, with both ends of this range obtained by routine meat inspection. Overall, the majority of the studies reported official meat inspection data, but antibody detection (by Ab-ELISA or immunoblot, studies in Brazil) and antigen detection (Ag-ELISA, study in Ecuador) were also used as diagnostic techniques.
Table 5.
Prevalence of bovine cysticercosis (published data)
| Country | Year | Location of studya | Time frame | Prevalence (95% CI) | Diagnostic technique | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 2013 | Minas Gerais | Jan-Jun | 2.1 (2.01–2.22) | Meat inspection | [65] |
| Brazil | 2006–2007 | Bahia | na | 0.7 (0.64–0.67) | Meat inspection | [66] |
| Brazil | 2004 | Minas Gerais | na | 3.2 (3.00–3.48) | Meat inspection | [67] |
| Brazil | na | Mato Grosso do Sul | na | 18.8 (11.51–28.00) | Meat inspection | [68] |
| Brazil | 2000 | Paraná | Jul-Dec | 3.8 (3.60–4.07) | Meat inspection | [69] |
| Brazil | 2013 | Minas Gerais | Jul-Aug | 15.1 (12.91–17.44) | Ab-ELISA | [70] |
| 4.7 (3.47–6.19) | Immunoblot | |||||
| Brazil | 2007–2010 | Nationwide | Jan-Apr | 1.1 (1.05–1.05) | Meat inspection | [71] |
| Brazil | 2010–2015 | Nationwide | Jan-Dec | 0.6 (0.62–0.62) | Meat inspection | [72] |
| Brazil | 2004 | Paraná | Jan-Dec | 9.3 (6.57–12.58) | Meat inspection | [73] |
| Brazil | 2010–2011 | São Paulo | Oct-Aug | 4.8 (4.58–5.04) | Meat inspection | [74] |
| Brazil | 2003–2004 | Rio de Janeiro | Jan-Dec | 2.3 (2.07–2.45) | Meat inspection | [75] |
| Brazil | na | Minas Gerais | na | 10.6 (7.55–14.40) | Ab-ELISA | [76] |
| 4.1 (2.28–6.83) | Immunoblot | |||||
| Brazil | 2004–2008 | Paraná | Jan-Dec | 2.2 (2.22–2.24) | Meat inspection | [77] |
| Brazil | 1997–2003 | Rio de Janeiro | Jan-Dec | 2.0 (1.91–1.99) | Meat inspection | [78] |
| Brazil | 2012 | São Paulo | Jan-Dec | 2.9 (2.83–3.03) | Meat inspection | [79] |
| Minas Gerais | 1.8 (1.71–1.93) | |||||
| Goias | 0.7 (0.61–0.82) | |||||
| Mato Grosso do Sul | 1.1 (0.77–1.58) | |||||
| Brazil | 2013–2014 | Mato Grosso | Jan-Dec | 0.1 (0.09–0.09) | Meat inspection | [80] |
| Brazil | 2009 | Minas Gerais | na | 2.5 (0.92–5.36) | Ab-ELISA | [81] |
| Brazil | 2009–2010 | Bahia | Jan-Jan | 3.6 (3.43–3.69) | Meat inspection | [82] |
| Brazil | 2008 | Goiás | Jan-Dec | 0.7 (0.67–0.73) | Meat inspection | [83] |
| Brazil | 2000 | Parana | Jul-Dec | 3.8 (3.60–4.07) | Meat inspection | [84] |
| Brazil | 2009–2013 | Rio Grande do Sul | Jan-Dec | 2.5 (2.28–2.78) | Meat inspection | [85] |
| Brazil | 2011–2013 | Rio Grande do Sul & Tocantins | Jan-Apr | 5.0 (2.80–8.03) | Meat inspection | [86] |
| Brazil | na | Paraíba | na | 2.7 (2.11–3.46) | Ab-ELISA | [87] |
| Canada | 1992 | Ontario | Oct; Dec | 5.8 (4.81–6.82) | Meat inspection | [88] |
| Canada | 2000 | Alberta | Apr | 7.9 (4.02–13.72) | Meat inspection | [89] |
| Ecuador | 2000–2001 | Imbabura; Pichincha | Dec-Jan | 5.8 (3.71–8.57) | Ag-ELISA | [47] |
| 0.3 (0.01–1.48) | Meat inspection | |||||
| 2.5 (1.32–4.40) | Ag-ELISA | |||||
| 0.5 (0.06–1.66) | Meat inspection | |||||
| Mexico | 2008–2009 | Nationwide | Oct-Jul | 0.2 (0.17–0.25) | Meat inspection | [90] |
| USA | 1992–1993 | Idaho | May-May | 8.9 (8.09–9.66) | Meat inspection | [91] |
Abbreviations: CI confidence interval, na information not provided
aFirst-level administration
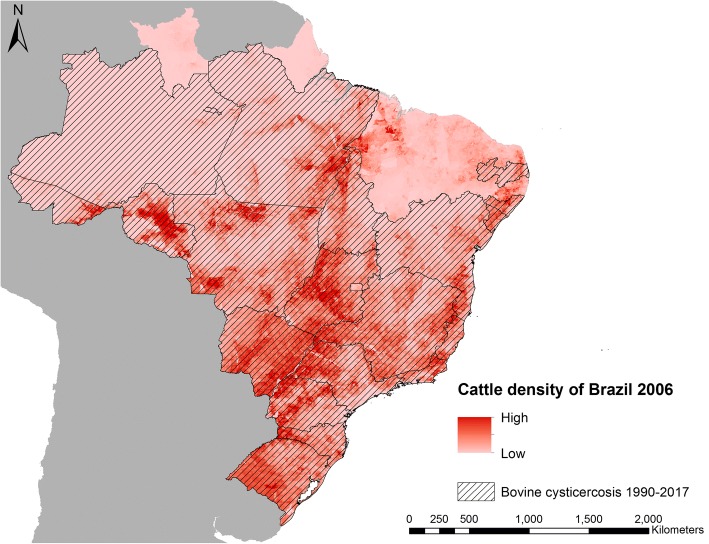
Brazil was the only country, where data on bovine cysticercosis could be obtained from several regions of the country. In the period 1990–2017, bovine cysticercosis was reported in 70% (19/27) of the states (first-level administration) in Brazil. As an illustration of risk of bovine cysticercosis, Fig. 4 shows the 2006 modelled density of cattle in Brazil [12], overlaid with the 19 states from where bovine cysticercosis was reported during 1990–2017.
Fig. 4.
States in Brazil with bovine cysticercosis during 1990–2017 and the modelled cattle density for Brazil in 2006 [12]
Discussion
This review shows that T. saginata is widely distributed across the Americas. Taeniosis was widely reported, but not always at the species level. The estimation of the distribution and the prevalence of taeniosis is severely complicated by the lack of specific symptoms in tapeworm carriers [2], and the fact that the disease is not commonly notifiable. Some studies differentiated between T. saginata taeniosis and the much more dangerous infection, T. solium taeniosis. This was usually done in studies with a research objective where the study outcome was dependent on the species differentiation. In health care and routine screening, this information is seen to be of less importance to the physicians attending as the anthelminthic treatments prescribed to patients will be effective against either parasite species [13, 14], despite the risk of cysticercosis transmission to either the carrier or their family members if T. solium is present.
The majority of the taeniosis infections reported had been identified by microscopic examination for the presence of Taenia spp. eggs, which has low sensitivity [15], and cannot be used for determining the diagnosis to species level. Prevalence of taeniosis ranged from very low levels to almost 9%, which is very similar to previous reports of taeniosis prevalence (0.01–10%) from Europe [16]. However, a direct comparison between studies is not appropriate, as variables such as study duration, recruitment criteria, diagnostic methods and standards of randomisation differ across studies. Clinical investigators should be encouraged to adopt a consensus protocol for collecting and analysing data for apparent taeniosis prevalence estimation, which would make comparison between studies and areas less biased.
It is clear from this review that bovine cysticercosis is widely distributed across the mainland of the Americas. It also indicates, however, a scarcity of recent data from the region. Taenia saginata taeniosis was reported from both Guatemala and Peru, but we were unable to identify any reports of bovine cysticercosis from either country. More than half of countries found to have bovine cysticercosis were found through the OIE databases [10, 11]. However, bovine cysticercosis is no longer notifiable to the OIE, and the reporting, if any, is not standardised across the countries in the region. The occurrence of bovine cysticercosis could only be georeferenced to a first-level administration in five countries. This illustrates that for most of the countries where T. saginata is endemic, more data are needed to pinpoint areas of risk and areas with high transmission rates. Presence of bovine cysticercosis seems to be related to the number of animals within a farm [17], spatial modelling of livestock density could therefore be considered as a first step in estimating areas of risk, such as previously done for T. solium [18]. Detailed mapping studies with prevalence of bovine cysticercosis are warranted for all endemic countries; however, such studies only seem to have been performed in Brazil. Bovine cysticercosis prevalence based on meat inspection ranged from very low levels to almost 19%, which is a higher range than recent reports from Europe (< 5%) [8], the Middle East (3%) [19] and Africa (< 4%) [20, 21].
Only five countries on the mainland (Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname and Panama) did not have reports of taeniosis or bovine cysticercosis. All five countries have cattle industries and in 2016 had an estimated number of cattle: 110,024 in Belize, 18,945 in French Guiana, 10,115 in Guyana, 36,138 in Suriname, and 1,554,200 in Panama [22]. Due to reports of bovine cysticercosis from neighbouring countries, the missing reports could be a result of underreporting rather than absence of the parasite in these populations. Epidemiological surveys should be performed in these five countries in order to confirm or refute the absence of T. saginata. The lack of reports of T. saginata from the smaller Caribbean islands, except for one case from the US Virgin Islands in 1994 [23], could suggest that infection pressure is insufficient to sustain transmission on these islands and reports are a result of small self-limiting outbreaks resulting from imported taeniosis cases. Cattle populations are relatively small on the Caribbean islands with many islands slaughtering less than 1000 cattle annually [22], which would likely mitigate any potential outbreak to burn out quickly. However, bovine cysticercosis was found on the two largest Caribbean islands (Cuba and Hispaniola). On Hispaniola, bovine cysticercosis was only reported in Haiti (Fig. 4); thus, investigations to explore the situation in the Dominican Republic are highly warranted.
There are clear diagnostic issues in terms of both taeniosis and bovine cysticercosis. The sensitivity of meat inspection for bovine cysticercosis can be increased to some extent by making more incisions into organs and muscles of the carcass. However, the risk of contaminating the carcass with microbes that pose a risk to food safety is correlated with the number of incisions made [24]. Since the health risk in T. saginata infections are minimal, compared to those of bacterial pathogens for example, an increase of the number of incisions might be unwise or should perhaps be completely avoided under certain circumstances. However, more incisions in the heart has been shown to increase the sensitivity for the diagnosis of bovine cysticercosis compared to the EU-approved routine meat inspection [25]. Still, more research is required to determine whether meat inspection procedures should be changed and what consequences it will have for areas of low and high bovine cysticercosis endemicity, respectively. Another approach to reduce transmission risk could be risk-based meat inspection in countries where appropriate herd level data is obtainable [26].
Taenia saginata is prevalent in countries where sanitation standards are high [8], suggesting that elimination of this parasite is extremely difficult. Epidemiological surveys and mapping studies should be performed in all endemic countries in order to evaluate the distribution and the economic burden of T. saginata and to assess whether cost-effective intervention measures can be implemented. Standard goals should be put forward in terms of describing a protocol for estimating the distribution, prevalence, incidence and the economic burden of bovine cysticercosis. Based on the economic analyses, cost-effective measures can then be implemented, if appropriate, in the efforts to control T. saginata.
Conclusions
Taenia saginata is widely distributed across the Americas, but the epidemiological data available are insufficient to estimate the subnational spatial distribution, prevalence, incidence and intensity of infections. This needs to be addressed through active surveillance and disease detection programmes. Such programmes would ameliorate the lack of data needed to quantify the economic burden bovine cysticercosis imposes on the region. These issues should be addressed in order to assess the need and advocate for implementation of cost-effective control measures against T. saginata if necessary.
Additional files
Review protocol and PRISMA checklist. (PDF 527 kb)
Table S1. Identified literature supporting the presence of Taenia saginata in the Americas during 1990-2017. Table S2. States in Brazil with bovine cysticercosis in 1990–2017. Table S3. Countries in the Americas with Taenia saginata occurrence in 1990-2017. (XLSX 37 kb)
Acknowledgments
This work was a collaboration within the framework of CYSTINET, the European network on taeniasis/cysticercosis, COST ACTION TD1302 and members of the T. saginata working group: Branko Bobic, Paul Torgerson and Ramon Eichenberger.
Availability of data and materials
All references found eligible in our literature review are included in the article.
Abbreviation
- CI
Confidence interval
Authors’ contributions
UCB conducted the systematic review of literature, extracted and analysed the data and drafted the first version of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the design of the study, interpretation of the data, and writing the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Uffe Christian Braae, Email: UBraae@rossvet.edu.kn.
Lian F. Thomas, Email: lian.thomas@zoonotic-diseases.org
Lucy J. Robertson, Email: lucy.robertson@nmbu.no
Veronique Dermauw, Email: vdermauw@itg.be.
Pierre Dorny, Email: pdorny@itg.be.
Arve Lee Willingham, Email: awillingham@rossvet.edu.kn.
Anastasios Saratsis, Email: saratsis@vri.gr.
Brecht Devleesschauwer, Email: brechtdv@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Boone I, Thys E, Marcotty T, de Borchgrave J, Ducheyne E, Dorny P. Distribution and risk factors of bovine cysticercosis in Belgian dairy and mixed herds. Prev Vet Med. 2007;82:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2007.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tembo A, Craig PS. Taenia saginata taeniosis: copro-antigen time-course in a voluntary self-infection. J Helminthol. 2015;89:612–619. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X14000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jansen F, Dorny P, Berkvens D, Van Hul A, Van den Broeck N, Makay C, et al. High prevalence of bovine cysticercosis found during evaluation of different post-mortem detection techniques in Belgian slaughterhouses. Vet Parasitol. 2017;244:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dorny P, Vercammen F, Brandt J, Vansteenkiste W, Berkvens D, Geerts S. Sero-epidemiological study of Taenia saginata cysticercosis in Belgian cattle. Vet Parasitol. 2000;88:43–49. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4017(99)00196-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kyvsgaard N, Ilsoe B, Henriksen SA, Nansen P. Distribution of Taenia saginata cysts in carcases of experimentally infected calves and its significance for routine meat inspection. Res Vet Sci. 1990;49:29–33. doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(18)31041-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Eichenberger R, Lewis F, Gabriël S, Dorny P, Torgerson P, Deplazes P. Multi-test analysis and model-based estimation of the prevalence of Taenia saginata cysticercus infection in naturally infected dairy cows in the absence of a ‘gold standard’reference test. Int J Parasitol. 2013;43:853–859. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ilsoe B, Kyvsgaard NC, Nansen P, Henriksen SA. A study on the survival of Taenia saginata eggs on soil in Denmark. Acta Vet Scand. 1990;31:153–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Laranjo-Gonzalez M, Devleesschauwer B, Gabriel S, Dorny P, Allepuz A. Epidemiology, impact and control of bovine cysticercosis in Europe: a systematic review. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:81. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1362-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.OIE . World Animal Health Information Database (WAHID) Interface. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 11.OIE . World Animal Health in 1995. Paris: Office International des Epizooties; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Robinson TP, Wint GR, Conchedda G, Van Boeckel TP, Ercoli V, Palamara E, et al. Mapping the global distribution of livestock. PLoS One. 2014;9:e96084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gherman I. Observations on treatment of taeniasis by N-(2'-chloro-4'-nitrophenyl)-5-chlorosalicylamide. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1968;61:432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pawłowski ZS. Efficacy of low doses of praziquantel in taeniasis. Acta Trop. 1990;48:83–88. doi: 10.1016/0001-706X(90)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Praet N, Verweij JJ, Mwape KE, Phiri IK, Muma JB, Zulu G, et al. Bayesian modelling to estimate the test characteristics of coprology, coproantigen ELISA and a novel real-time PCR for the diagnosis of taeniasis. Tropical Med Int Health. 2013;18:608–614. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dorny P, Praet N. Taenia saginata in Europe. Vet Parasitol. 2007;149:22–24. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Allepuz A., Napp S., Picado A., Alba A., Panades J., Domingo M., Casal J. Descriptive and spatial epidemiology of bovine cysticercosis in North-Eastern Spain (Catalonia) Veterinary Parasitology. 2009;159(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.09.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Braae UC, Devleesschauwer B, Sithole F, Wang Z, Willingham AL. Mapping occurrence of Taenia solium taeniosis/cysticercosis and areas at risk of porcine cysticercosis in Central America and the Caribbean basin. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10:424. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2362-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Garedaghi Y, Saber AR, Khosroshahi MS. Prevalence of bovine cysticercosis of slaughtered cattle in Meshkinshahr Abattoir. Am J Anim Vet Sci. 2011;6:121–124. doi: 10.3844/ajavsp.2011.121.124. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Asaava LL, Kitala PM, Gathura PB, Nanyingi MO, Muchemi G, Schelling E. A survey of bovine cysticercosis/human taeniosis in Northern Turkana District, Kenya. Prev Vet Med. 2009;89:197–204. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2009.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ibrahim N, Zerihun F. Prevalence of Tania saginata cysticercosis in cattle slaughtered in Addis Ababa Municipal Abattoir, Ethiopia. Glob Vet. 2012;8:467–471. [Google Scholar]
- 22.FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations statistical databases http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QL. Accessed 9 Sept 2018.
- 23.Saini PK, Webert DW, McCaskey PC. Food safety and regulatory aspects of cattle and swine cysticercosis. J Food Prot. 1997;60:447–453. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-60.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Buncic S, Nychas G-J, Lee MR, Koutsoumanis K, Hébraud M, Desvaux M, et al. Microbial pathogen control in the beef chain: recent research advances. Meat Sci. 2014;97:288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.04.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Eichenberger RM, Stephan R, Deplazes P. Increased sensitivity for the diagnosis of Taenia saginata cysticercus infection by additional heart examination compared to the EU-approved routine meat inspection. Food Control. 2011;22:989–992. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.11.033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Blagojevic B, Robertson LJ, Vieira-Pinto M, Johansen MV, Laranjo-González M, Gabriël S. Bovine cysticercosis in the European Union: impact and current regulations, and an approach towards risk-based control. Food Control. 2017;78:64–71. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.02.052. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sartorelli AC, da Silva MG, Rodrigues MA, da Silva RJ. Appendiceal taeniasis presenting like acute appendicitis. Parasitol Res. 2005;97:171–172. doi: 10.1007/s00436-005-1408-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schenone H, Schenone S, Arriagada J. Eliminacion oral de segmentos de estrobila de Taenia saginata. Bol Chil Parasitol. 1992;47:33–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marquez-Navarro A, Cornejo-Coria Mdel C, Cebada-Lopez F, Sanchez-Manzano RM, Diaz-Chiguer DL, Nogueda-Torres B. Taenia saginata: failure treatment in a child with 5-year long-lasting infection. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2012;35:125–127. doi: 10.1097/SGA.0b013e31824eb933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jeske S, Bianchi TF, Moura MQ, Baccega B, Pinto NB, Berne MEA, Villela MM. Intestinal parasites in cancer patients in the South of Brazil. Braz J Biol. 2017;78:574–578. doi: 10.1590/1519-6984.175364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rodríguez-Morales Alfonso J., Yepes-Echeverri María Camila, Acevedo-Mendoza Wilmer F., Marín-Rincón Hamilton A., Culquichicón Carlos, Parra-Valencia Esteban, Cardona-Ospina Jaime A., Flisser Ana. Mapping the residual incidence of taeniasis and cysticercosis in Colombia, 2009–2013, using geographical information systems: Implications for public health and travel medicine. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2018;22:51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2017.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.de Kaminsky RG. Albendazole treatment in human taeniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991;85:648–650. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90378-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bustos JA, Rodriguez S, Jimenez JA, Moyano LM, Castillo Y, Ayvar V, et al. Detection of Taenia solium taeniasis coproantigen is an early indicator of treatment failure for taeniasis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2012;19:570–573. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05428-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jeri C, Gilman RH, Lescano AG, Mayta H, Ramirez ME, Gonzalez AE, et al. Species identification after treatment for human taeniasis. Lancet. 2004;363:949–950. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15791-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Acurero E, Diaz I, Diaz N, Bracho A, Ferrer M, Matheus A. Prevalence of enteroparasitism in pregnant women at the “Dr. Armando Castillo Plaza” Maternity Center, Maracaibo, Venezuela. Kasmera. 2008;36:148–58.
- 36.Benitez JA, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Vivas P, Plaz J. Burden of zoonotic diseases in Venezuela during 2004 and 2005. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1149:315–317. doi: 10.1196/annals.1428.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Borda CE, Rea MJ, Rosa JR, Maidana C. Intestinal parasitism in San Cayetano, Corrientes, Argentina. Bull Pan Am Health Organ. 1996;30:227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Milano AM, Oscherov EB, Palladino AC, Bar AR. Enteroparasitosis infantil en un area urbana del nordeste Argentino. Medicina. 2007;67:238–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Carvalho Odos S, Guerra HL, Campos YR, Caldeira RL, Massara CL. Prevalencia de helmintos intestinais em tres mesorregioes do Estado de Minas Gerais. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2002;35:597–600. doi: 10.1590/S0037-86822002000600009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Esteves FM, Silva-Vergara ML, Carvalho AC. Inquerito epidemiologico sobre teniase em populacao do Programa Saude da Familia no municipio de Uberaba, MG. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2005;38:5301. doi: 10.1590/S0037-86822005000600017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Neres-Norberg A, Guerra-Sanches F, Blanco Moreira-Norberg PR, Madeira-Oliveira JT, Santa-Helena AA, Serra-Freire NM. Enteroparasitismo en indigenas terena en el Estado de Mato Grosso do Sul, Brasil. Rev Salud Publica. 2014;16:859–870. doi: 10.15446/rsap.v16n6.40031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Santos SA, Merlini LS. Prevalencia de enteroparasitoses na populacao do municipio de Maria Helena, Parana. Cien Saude Colet. 2010;15:899–905. doi: 10.1590/S1413-81232010000300033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Silva-Vergara ML, Prata A, Netto HV, Vieira Cde O, Castro JH, Micheletti LG, et al. Risk factors associated with taeniasis-cysticercosis in Lagamar, Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1998;31:65–71. doi: 10.1590/S0037-86821998000100009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Silva-Vergara ML, Prata A, Vieira Cde O, Castro JH, Micheletti LG, Otano AS, Franquini J., Jr Aspectos epidemiologicos da teniase-cisticercose na area endemica de Lagamar, MG. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 1995;28:345–349. doi: 10.1590/S0037-86821995000400007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vidal S, Toloza L, Cancino B. Evolution of the prevalence the enteroparasitoses in Talca - Chile. Rev Chil Infectol. 2010;27:336–40. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Agudelo-Lopez S, Gomez-Rodriguez L, Coronado X, Orozco A, Valencia-Gutierrez CA, Restrepo-Betancur LF, et al. Prevalencia de parasitosis intestinales y factores asociados en un corregimiento de la Costa Atlantica Colombiana. Rev Salud Publica. 2008;10:633–642. doi: 10.1590/S0124-00642008000400013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rodriguez-Hidalgo R, Benitez-Ortiz W, Dorny P, Geerts S, Geysen D, Ron-Roman J, et al. Taeniosis-cysticercosis in man and animals in the Sierra of northern Ecuador. Vet Parasitol. 2003;118:51–60. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Allan J. C., Mencos F., Garcia-Noval J., Sarti E., Flisser A., Wang Y., Liu D., Craig P. S. Dipstick dot ELISA for the detection of Taenia coproantigens in humans. Parasitology. 1993;107(01):79. doi: 10.1017/S0031182000079439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Allan JC, Velasquez-Tohom M, Garcia-Noval J, Torres-Alvarez R, Yurrita P, Fletes C, et al. Epidemiology of intestinal taeniasis in four, rural, Guatemalan communities. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1996;90:157–165. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1996.11813039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Champetier de Ribes G, Fline M, Desormeaux AM, Eyma E, Montagut P, Champagne C, et al. Helminthoses intestinales en milieu scolaire en Haiti en 2002. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2005;98:127–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sanchez AL, Medina MT, Ljungstrom I. Prevalence of taeniasis and cysticercosis in a population of urban residence in Honduras. Acta Trop. 1998;69:141–149. doi: 10.1016/S0001-706X(97)00132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Behravesh CB, Mayberry LF, Bristol JR, Cardenas VM, Mena KD, Martinez-Ocana J, et al. Population-based survey of taeniasis along the United States-Mexico border. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2008;102:325–333. doi: 10.1179/136485908X300788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Huh S, Ahn C, Chai JY. Intestinal parasitic infections in the residents of an emigration camp in Tijuana, Mexico. Korean J Parasitol. 1995;33:65–67. doi: 10.3347/kjp.1995.33.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Martinez-Maya JJ, de Aluja AS, Avila-Ramirez G, Aguilar-Vega L, Plancarte-Crespo A, Jaramillo-Arango CJ. Taeniosis and detection of antibodies against cysticerci among inhabitants of a rural community in Guerrero State, Mexico. Salud Publica Mex. 2003;45:84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sarti E, Schantz PM, Avila G, Ambrosio J, Medina-Santillan R, Flisser A. Mass treatment against human taeniasis for the control of cysticercosis: a population-based intervention study. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000;94:85–89. doi: 10.1016/S0035-9203(00)90451-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cordero A, Miranda E, Segovia G, Cantoral V, Huarcaya I. Prevalencia de teniosis y seroprevalencia de cisticercosis humana en Pampa Cangallo, Ayacucho, Peru 2008. Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica. 2010;27:562–568. doi: 10.1590/S1726-46342010000400011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.O'Neal SE, Moyano LM, Ayvar V, Gonzalvez G, Diaz A, Rodriguez S, et al. Geographic correlation between tapeworm carriers and heavily infected cysticercotic pigs. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:e1953. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Meza NW, Rossi NE, Galeazzi TN, Sanchez NM, Colmenares FI, Medina OD, et al. Cysticercosis in chronic psychiatric inpatients from a Venezuelan community. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:504–509. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2005.73.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Goncalves FD, Machado GA, Oliveira HB, Rezende M, Mineo JR, Costa-Cruz JM. Hydrophobic fraction of Taenia saginata metacestodes, rather than hydrophilic fraction, contains immunodominant markers for diagnosing human neurocysticercosis. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2010;43:254–259. doi: 10.1590/S0037-86822010000300008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.EAGdV J, VBL M, Vinaud MC, RdS LJ, GFC L. Molecular identification of Cysticercus bovis at different stages of the host-parasite interaction process. Rev Patol Trop. 2011;40:331–340. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Morais HR, Pirtouscheg A, Moreira MD, Tavares M. Interrelation between viability of Cysticercus bovis and organs of encystment in bovine cattle from Triângulo Mineiro. PUBVET. 2011;5:1037.
- 62.Vieira NP, Faria PB, Mattos MR, Pereira AA. Condemnation of bovine liver in the southern region of the State Espirito Santo, Brazil. Arq Bras Med Vet Zoo. 2011;63:1605–1608. doi: 10.1590/S0102-09352011000600047. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cayo F, Valenzuela G, Paredes E, Ruiz V, Gallo C. Distribution and viability of cyticerci of Taenia saginata in meat cuts from naturally infected beef. Arch Med Vet. 2013;45:207–212. doi: 10.4067/S0301-732X2013000200014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.PFdl R, Alberto EB, Alonso LR, MdC Q. Considerations on the cycle of Taenia saginata in humans and bovines of the province Villa Clara, Cuba. REDVET. 2006;7:040607.
- 65.Assunção EF, Ferreira IM, Braga HF. Bovine cysticercosis and tuberculosis prevalence in an exporter slaughterhouse of Campina Verde, MG. PUBVET. 2014;8:1783. doi: 10.22256/pubvet.v8n19.1783. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bavia ME, Carneiro D, Cardim LL, Silva MMN, Martins MS. Spatial scan statistic in the detection of risk areas for bovine cysticercosis in the state of Bahia. Arq Bras Med Vet Zoo. 2012;64:1200–1208. doi: 10.1590/S0102-09352012000500018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Costa RFR, Santos IF, Santana AP, Tortelly R, Nascimento ER, Fukuda RT, et al. Characterization of Cysticercus bovis lesions at postmortem inspection of cattle by gross examination, histopathology and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Pesqui Vet Bras. 2012;32:477–484. doi: 10.1590/S0100-736X2012000600002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.de Aragao SC, Biondi GF, Lima LGF, Nunes CM. Animal cysticercosis in indigenous Brazilian villages. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2010;19:132–134. doi: 10.1590/S1984-29612010000200014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.de Souza VK, Pessoa-Silva Mdo C, Kowalczuk M, Marty S, Thomaz-Soccol V. Regioes anatomicas de major ocorrencia de Cysticercus bovis em bovinos submetidos a inspecao federal em matadouro-frigorifico no municipio de Sao Jose dos Pinhais, Parana, de Julho a Dezembro de 2000. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2007;16:92–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Duarte CTD, Pinto PSA, Silva LF, Santos TO, Acevedo-Nieto EC, Almeida LP. Transmission and prevalence profile of bovine cysticercosis in rural properties of Triangulo Mineiro, Brazil. Pesqui Vet Bras. 2016;36:793–797. doi: 10.1590/s0100-736x2016000900001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Dutra LH, Girotto A, RFdC V, TSWJ V, Zangirolamo AF, FAC M, et al. The prevalence and spatial epidemiology of cysticercosis in slaughtered cattle from Brazil. Semin Cienc Agrar. 2012;33:1887–1896. doi: 10.5433/1679-0359.2012v33n5p1887. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Rossi Gabriel Augusto Marques, Martins Isabella Vilhena Freire, Campos Rafael Ferraço de, Soares Luiz Filippe Simão, Almeida Henrique Meiroz de Souza, Mathias Luis Antonio. Spatial distribution of bovine cysticercosis—A retrospective study in Brazil from 2010 through 2015. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2017;145:145–149. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2017.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Falavigna-Guilherme AL, Silva K, Araújo SM, Tobias ML, Falavigna DLM. Cisticercose em animais abatidos em Sabáudia, Estado do Paraná. Arq Bras Med Vet Zoo. 2006;58:950–951. doi: 10.1590/S0102-09352006000500036. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ferreira MM, Revoredo TB, Ragazzi JP, Soares VE, Ferraldo AS, RPd M, WDZ L. Prevalence, spatial distribution and risk factors for cattle cysticercosis in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Pesqui Vet Bras. 2014;34:1181–1185. doi: 10.1590/S0100-736X2014001200006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Garcia LN, Pereira MA, Miranda FJ, Gomes FF, Resende MA, Lira BR. Cysticercus bovis em bovinos abatidos sob servico de inspecao federalna regiao serrana do Estado do Rio de Janeiro em 2003 e 2004. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet. 2008;17(Suppl. 1):170–1. [PubMed]
- 76.Garro FL, Santos TM, Assis DCS, Heneine LGD, Ornellas CBD, Pinto PSA, Santos WLM. Diagnosis of bovine taeniasis-cysticercosis complex in Sao Joao Evangelista, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Arq Bras Med Vet Zoo. 2015;67:1063–1069. doi: 10.1590/1678-4162-8196. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Guimaraes-Peixoto RPM, Souza VK, Pinto PSA, Santos TO. Distribution and identification of risk areas for bovine cysticercosis in the State of Parana, Brazil. Pesqui Vet Bras. 2012;32:975–9.
- 78.Pereira MAVC, Schwanz VS, Barbosa CG. Prevalence of cysticercosis in bovine carcasses in slaughterhouses and cold stores in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil, submitted to the federal surveillance service (SIF-RJ) from 1997 to 2003. Arq Inst Biol (Sao Paulo) 2006;73:83–87. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Rossi GA, Hoppe EG, Mathias LA, Martins AM, Mussi LA, Prata LF. Bovine cysticercosis in slaughtered cattle as an indicator of Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) and epidemiological risk factors. Prev Vet Med. 2015;118:504–508. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2015.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Rossi GAM, HASd S, WDZ L, HMdS A, Soares VE, AMC V, et al. Prevalence and geospatial distribution of bovine cysticercosis in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Prev Vet Med. 2016;130:94–98. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2016.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Santos TO, Pinto PSA, Iasbik AF, Silva LF, Nieto ECA, Guimaraes-Peixoto RPM. Epidemiological survey of the taeniasis/cysticercosis complex in cattle farms in Vicosa County, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Pesqui Vet Bras. 2013;33:449–452. doi: 10.1590/S0100-736X2013000400006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Silva DR, Albuquerque GR. Cysticercosis in cattle slaughtered under State Inspection in the municipality of Vitoria da Conquista, BA. Rev Bras Med Vet. 2010;32:225–228. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Silveira Neto OJd, Oliveira RRd, Pereira FdO, Basile ÂLdC, Taveira RZ. Occurrence and location of Cysticercus bovis in cattle submitted to Federal Inspection in slaughterhouse in Goias, Brazil. PUBVET. 2011;5:21.
- 84.Souza VK, Pessoa-Silva MD, Minozzo JC, Thomaz-Soccol V. Bovine cysticercosis prevalence in Parana State, southern of Brazil, in animals slaughtered under the SIF 1710. Semin Cienc Agrar. 2007;28:675–83.
- 85.Teixeira JLR, Recuero ALC, Brod CS. Ambispective cohort study of bovine cysticercosis from slaughterhouses with Municipal Inspection Service (SIM) in the southern Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Rev Patol Trop. 2015;44:146–154. doi: 10.5216/rpt.v44i2.36644. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Tessele B, Brum JS, Barros CSL. Parasitic lesions observed in cattle slaughtered for human consumption. Pesqui Vet Bras. 2013;33:873–89.
- 87.Maia Amanda R.A., Fernandes Leise G., Pinto Paulo S.A., Guimarães-Peixoto Rafaella P.M., Silva Letícia F., Santos Carolina S.A.B., Alves Clebert J., Clementino Inácio J., Azevedo Sérgio S. Herd-level seroprevalence and associated risk factors for bovine cysticercosis in the State of Paraíba, Northeastern Brazil. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2017;142:51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2017.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Borman-Eby HA, Ayim DS, Small C. Cysticercus bovis in cattle in two beef feedlots in southern Ontario. Can Vet J. 1994;35:711–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 89.Lees W, Nightingale J, Brown D, Scandrett B, Gajadhar A. Outbreak of Cysticercus bovis (Taenia saginata) in feedlot cattle in Alberta. Can Vet J. 2002;43:227–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Gonzalez SAC, Castillo JLR, Valencia GL, Hurtado RMB, Robles ESH, Navarro FJM. Prevalence of Taenia saginata larvae (Cysticercus bovis) in feedlot cattle slaughtered in a federal inspection type abattoir in northwest Mexico. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2015;12:462–5. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 91.Yoder DR, Ebel ED, Hancock DD, Combs BA. Epidemiologic findings from an outbreak of cysticercosis in feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1994;205:45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Review protocol and PRISMA checklist. (PDF 527 kb)
Table S1. Identified literature supporting the presence of Taenia saginata in the Americas during 1990-2017. Table S2. States in Brazil with bovine cysticercosis in 1990–2017. Table S3. Countries in the Americas with Taenia saginata occurrence in 1990-2017. (XLSX 37 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All references found eligible in our literature review are included in the article.