Abstract
How fast can a cell locate a specific chromosomal DNA sequence specified by a single stranded oligonucleotide? To address this question we investigate the intracellular search processes of the CRISPR-associated protein Cas9, which can be programmed by a guide RNA to bind essentially any DNA sequence. This targeting flexibility requires Cas9 to unwind the DNA double helix to test for correct base pairing to the guide RNA. Here we study the search mechanisms of the catalytically inactive dCas9 in living Escherichia coli by combining single molecule fluorescence microscopy and bulk restriction protection assays. We find that it takes a single fluorescently labeled dCas9 six hours to find the correct target sequence, which implies that each potential target is bound for less than 30 ms. Once bound, dCas9 remains associated until replication. To achieve fast targeting, both Cas9 and its guide RNA have to be present at high concentrations.
Cells have evolved two strategies to search their genome for specific information. Transcription factors and restriction enzymes recognize a specific DNA sequence through interactions in double stranded DNA (dsDNA) grooves, whereas other proteins are dynamically programmed by an RNA or single stranded DNA (ssDNA) to recognize complementary nucleic acid sequences through base pairing. Examples of the latter are Argonaute(1) and Hfq(2) programmed by small RNAs to target and regulate mRNA; the homologous repair machinery primed by ssDNA(3), and CRISPR-Cas programmed by guide RNA to target dsDNA(4–7). How transcription factors search and bind DNA is well understood(8) and in vivo kinetics have been studied for Hfq mediated targeting by small RNAs(9), but very little is known about how the factors that are dynamically programmed for base pairing specific sequences in dsDNA find their targets in the context of myriad similar sequences.
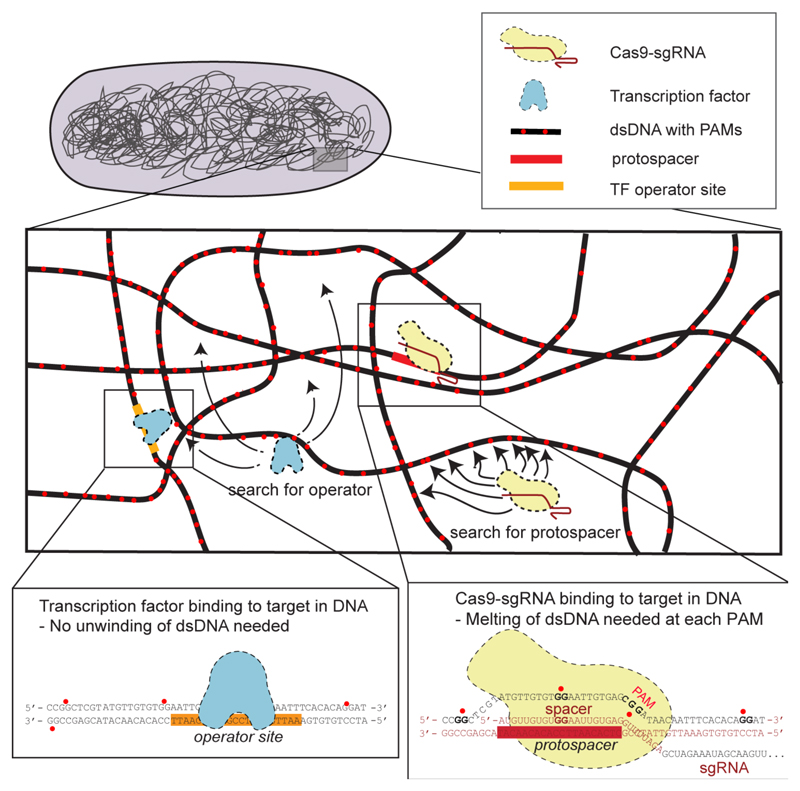
CRISPR-Cas targeting and homologous recombination depend on unwinding dsDNA throughout the genome to test for complementarity (Fig. 1)(10, 11). In the case of CRISPR-Cas the search problem is simplified by requiring a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) as a prerequisite for unwinding the dsDNA(4, 7, 12–14). For Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9, which has a GG-dinucleotide PAM, this still implies that every eighth base pair in a genome has to to be interrogated (Fig. 1). Here we investigate how long it takes Cas9 to find a specific target sequence in E. coli and what insight this gives into possible search mechanisms.
Fig. 1. Comparison of Cas9 and transcription factor search.
Cas9 (in yellow) must unwind dsDNA at every PAM (red dots) to test for sgRNA complementarity to the protospacer (detail, lower right). In contrast, a transcription factor (in blue) scans the dsDNA by sliding in the grooves (detail, lower left).
To measure the time required for Cas9 to locate a specific target, we fused the nuclease deficient dCas9 to the fluorescent protein YPet (fig. S1, S6) and expressed it at a few (~5) molecules per cell from the chromosome. At this expression level and a 5s image acquisition time, non-bound molecules contribute to the diffuse fluorescence background, whereas DNA-bound fluorophores are detectable as individual diffraction limited spots (15). dCas9-YPet was programmed by a single-guide RNA (sgRNA-a; see fig. S8C)(5) targeted against the lacO1 operator sequence. This allows us to trigger the accessibility of the target sequence by IPTG, because IPTG induces dissociation of LacI repressor from lacO1 (8, 16) (Fig. 2A). In the absence of sgRNA or target sites very few spots are observed (fig. S2). Throughout the rest of the experiments all sgRNA were present at saturating concentrations at which every dCas9-YPet is in complex with sgRNA (fig. S3). We used an array of 36 lacO1 sites cloned in a bacterial artificial chromosome (pSMART, 2.1 copies per cell, fig. S4) as the search target (see table S1 for array sequence). The array was used to speed up the first binding event, while maintaining a low copy number of dCas9-YPet such that individual bound molecules can be detected over the fluorescent background.
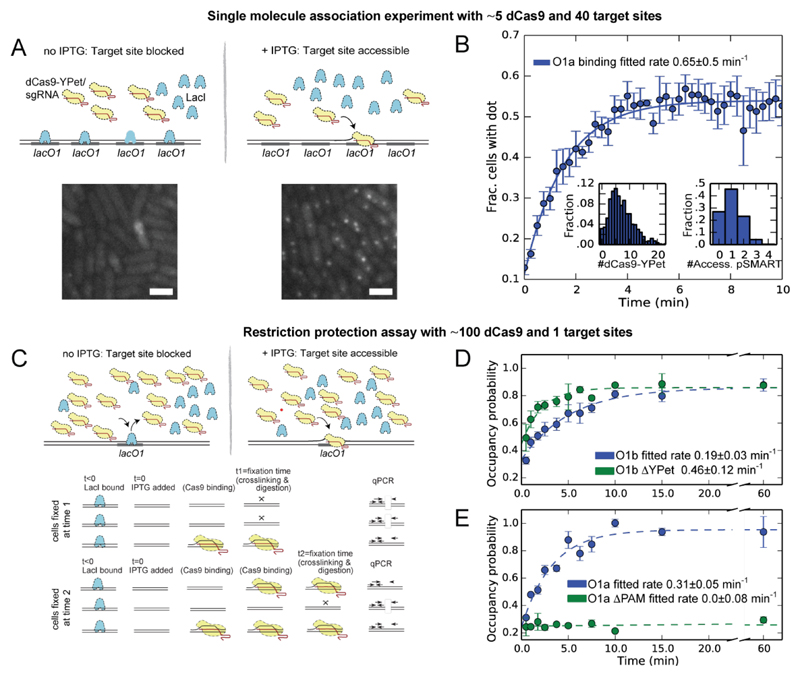
Fig. 2. Association.
(A) Upper: Schematic illustration of the single molecule assay, where dCas9-YPet is expressed at low copy number in a strain containing pSMART plasmids each with 36 lacO1-binding sites. In the absence of IPTG, lacO1 sites are occupied by LacI, preventing dCas9-YPet from binding. LacI dissociates after addition of IPTG, and subsequently dCas9-YPet binds lacO1, enabling specific fluorescent spots to be detected using exposure times of 5 s. Lower: fluorescence images acquired before (left) and 10 min after (right) addition of IPTG (strain PL42F9). Scale-bar 2µm. (B) Fraction of cells containing at least one spot (y-axis) as a function of time after addition of IPTG (x-axis). The curve is fitted to a single exponential function. Left inset distributions of number of fluorescent dCas-YPet (strain PL42F2) Right inset Distribution of accessible pSMART (strain PL41D2) per cell, which is based on the pSMART copy number distribution (fig. S4) corrected for the fact that 50% of the pSMARTs are available for binding (fig. S5). In total 63382 cells are analyzed. (C) Upper: Schematic illustration of the bulk assay, in which dCas9 or dCas9-YPet is expressed at a high copy number in the presence of only one target site per chromosome. LacI dissociates from lacO1 after addition of IPTG, permitting dCas9-YPet to bind. Lower: Schematic of experimental procedure. IPTG is added at t=0, freeing the lacO1 site. At later times, here time 1 or time 2, different batches of cells are fixed and bound dCas9 are cross-linked to DNA; the chromatin is subsequently purified and digested with BsrBI. The fraction of cut and uncut DNA is quantified by qPCR with two sets of primers, one upstream and one amplifying across the cut site. (D) Measured bulk association to lacO1-b in the intC locus for dCas9-YPet (strain DJ3F6) is compared to dCas9 (strain DJ3I3) (see table S1 for sequences). Please note that the concentrations are slightly different in the two strains which is why the rates should not be directly compared (see main text and supplementary text section 2.1.3.) (E) Measured bulk association to lacO1-a in the intC locus for dCas9-YPet with (strain DJ3F5) or without (strain DJ3F8) a PAM adjacent to the protospacer. (D+E) Each data point is derived from three biological replicates (each consisting of three technical replicates). r represents the rate at which any of the dCas9 proteins binds to the single target site. See fig. S6 and table S1 for strains and sequences.
We measure the association rate based on the time-dependent appearance of fluorescence spots, corresponding to immobile dCas9-YPet, after making the target sites accessible by IPTG addition (Fig. 2A). Different sets of ~200 cells are imaged at each time point to avoid the complications of photobleaching in time-lapse measurements(15). The rate of dCas9-YPet binding to any target site is determined by an exponential fit to the experimental data for the first binding event per cell (Fig. 2B). When we in addition account for the number of plasmids (fig. S4), that only 50% of the plasmids are accessible to binding (fig. S5, Fig. 2B, left inset, supplementary text section 2.2.4), and also the number of fluorescent dCas9-Ypet and its uncertainty due to non-full length bands on western blot (6±1, supplementary text, section 2.1.5) we obtain the association rate 2.7x10-3±0.6x10-3 min-1 molecule-1 (for details see supplementary text section 2.1.1). Fig 2B does not plateau at one mainly because of cell to cell variation in the number of accessible pSMART per cell (Fig. 2B left inset) and the distribution of fluorescent dCas9-YPet per cell (Fig. 2B right inset). The possible sources of error in the association rate determination due to the maturation of YPet (fig. S7) and potential sliding of dCas9 (fig. S8B) across the array are found to be small (supplementary text, sections 2.2.1 and 2.2.2) and are not included in the rate estimate. In summary, an individual sgRNA-programmed dCas9-YPet protein requires on average 6 hours to find and bind its target site.
To test how the activity of the fluorescent fusion protein compares to the native protein, we developed a bulk restriction protection assay (Fig. 2C) where a single lacO1 site, introduced in the intC position of the E. coli chromosome, is targeted by dCas9 (sgRNA-b; see fig. S8C), which is expressed at a 15.1±6.5 fold higher concentration than in the fluorescence assay (fig. S1, supplementary text, section 2.1.2). The lacO1 site contains a cleavage site for the restriction enzyme BsrBI, and therefore binding of dCas9 can be measured as protection from BsrBI cleavage. After adding IPTG at time zero, which renders the target site accessible for dCas9, we determined the fraction of protected cleavage sites at multiple time points using qPCR (Fig. 2C). The association in the dCas9-YPet strain was 1.7±0.3 times slower than in the dCas9 strain after we adjusted for the difference in abundance and account for uncertainty due to non-full length bands on western blot (Fig. 2D, fig. S1, supplementary text 2.1.3). This suggests that the fusion protein is partly impaired, although the absolute in vivo activity of the fusion protein is hard to assess due to the presence of a non-full length band in the western blot (fig. S1). Nevertheless the restriction protection estimate for the non-fusion dCas9 association rate falls in the range 2.9x10-3±1.5x10-3 min-1 molecule-1 (supplementary text, section 2.1.2).
We also used the restriction protection assay with dCas9-YPet for a number of pairwise comparisons: (i) When there is no PAM sequence, we detect no binding (Fig. 2E). (ii) When we target the same target sequence introduced at different positions at the chromosome, the rate of binding changes by about 40% which may be due to a difference in accessibility for dCas9 binding, a difference in the amount of genomic DNA per target site, or a difference in the efficiency in crosslinking (fig. S8A). (iii) When we change the sgRNA and target another part of lacO at the same chromosome position the rate of binding changes by about 40% (Fig. 2D,E), which may be due to how the different sgRNA seed-regions interact with DNA at non-target PAM sequences or influence the probability of binding at the target sequence.
Next we measured how long dCas9-YPet stays bound at the target by reversing the single molecule association experiment. Thus, cells were initially grown with IPTG to permit dCas9-YPet to bind specifically to the lacO1 array. IPTG was removed at time zero and dissociation was monitored as the decrease in the mean number of spots per cell (Fig. 3A, B; Fig S10). The procedure was repeated under various growth conditions. We observe a strong correlation between generation time and the time taken for all molecules to dissociate (Fig. 3C). This agrees well with the in vitro observation that dCas9 enters an irreversibly bound state once the spacer sequence has hybridized (11) and the very slow dissociation measured in eucaryotic cells (17), considering that dCas9 necessarily dissociates at replication.
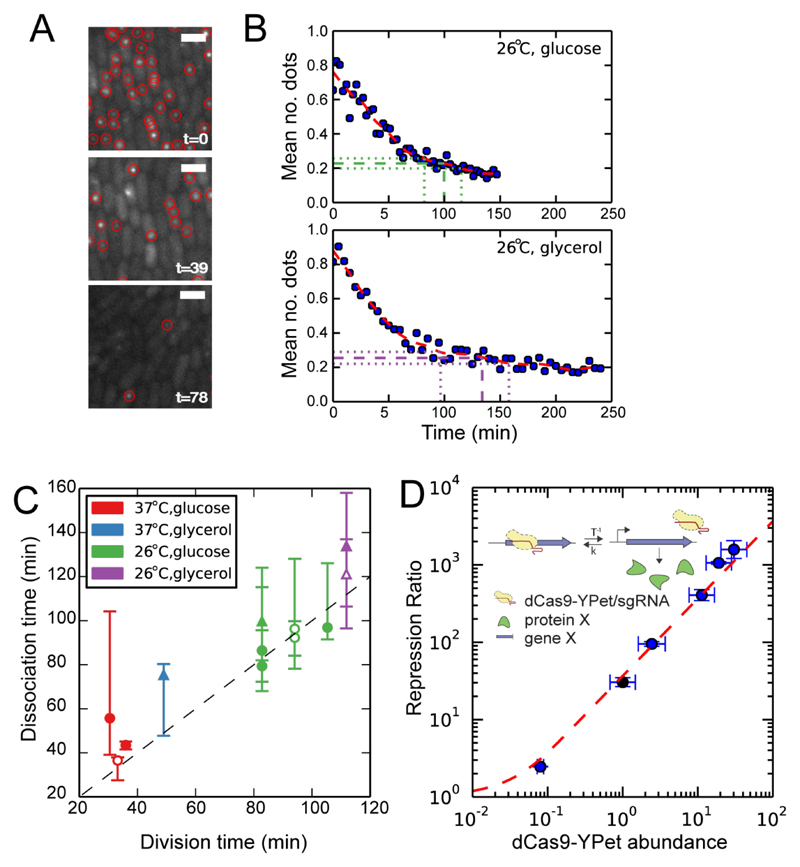
Fig. 3. Dissociation and repression.
(A) Fluorescence images of cells with dCas9-YPet at three different time points (t in min) after removing IPTG. Scale bar: 2µm. (B) Two examples from a set of dissociation curves acquired at different growth rates resulting from different carbon sources and temperatures. The red dashed lines are a smoothed versions of the curves. The time range when the curve has dropped to within 5%-15% of the plateau is indicated by horizontal dashed lines. (C) The time for dissociation (defined as reaching 10% from the plateau) is plotted (y-axis) as a function of generation time (x-axis) for individual experiments. The error bars represent the 5%-15% range shown in B. Different colors represent different growth conditions (legend), in which only the temperature or the carbon source of the M9 media is changing (see supplementary material and methods section 1.6.3.2 for details). The generation times for data points with filled symbols are estimated in the same microfluidic experiment as the corresponding dissociation time estimates. The generation times for the data points with open symbols are averages of other experiments (filled symbols) under the same growth conditions. Strains: PL42F9 (circles) PL42H2 (triangles). All individual dissociation curves are shown in fig. S10 (D) The repression ratio (red dashed line) as predicted by Eq. 1 using the measured binding rate (rC=0.34 min-1, strain DJ3D5) and the generation time (T=107 min) is compared to the measured repression ratio of the regulated lacZ gene (markers). If the binding rate instead would be calculated from the repression ratio for DJ3D5 it would be rC=0.29 min-1. The expression level of dCas9-YPet is measured using Western blots (fig. S1) and plotted relative to the strain DJ3D5 (black marker). The other strains are, in order of increasing expression, PL41E1, PL42B6, PL42C1, and PL42C9. X-axis error bars are based on three different Western blots; y-axis error bars on at least three repression ratio measurements.
The dissociation rate measurement offers an opportunity to test the consistency of our association rate estimates based on the steady state target site occupancy. We targeted the native lacO1 site in the lacZ promoter with sgRNA-b such that lacZ expression is off when dCas9 is bound (Fig. 3D inset). The predicted repression ratio (RR) is
| (1) |
where r is the rate of binding per dCas9-YPet, C is the number of dCas9-YPet and T is the generation time (see supplementary material and methods section 1.5.2 for derivation). The bulk association rate assay gives rC=0.34 min-1 for this strain (fig. S8A). We constructed 5 variants of the lacZ targeting strains that constitutively express different levels of dCas9-YPet (table S1, fig. S1). The repression ratio was determined as the ratio of lacZ expression in the absence of the cognate sgRNA to lacZ expression in its presence. In Fig. 3D we plot the repression ratio against the expression level of dCas9-YPet. The data agrees with the prediction (Eq. 1) based on the association rate measurement, the dCas9-YPet expression levels and the generation time.
Given that it takes dCas9 6h to test the 106 PAMs (5.4x105PAM/genome x ~2 genome/cell), it can only spend ~20ms per PAM unwinding the DNA and testing for hybridization if it binds irreversibly the first time it reaches the cognate target. This is much faster than the 750ms reported for Eukaryotic cells (18) and the ~10s measured in vitro (11). To investigate whether all PAMs are sampled, we imaged dCas9-YPet at exposure times ranging from 2ms to 1s in cells which do not have a specific target site (Fig. 4A). At each exposure time we selectively observe the fraction of molecules that are immobile and thus bound for at least the length of the exposure (Fig. 4B). To translate this into a distribution of non-target PAM residence times we scaled the corresponding density function by 1/t and renormalized (supplementary materials and methods, section 1.7.2.4). This results in a broad distribution with an average of 30ms (Fig. 4C). This is an upper limit for the average non-specific residence time, since transiently bound (<5ms) molecules are indistinguishable from freely diffusing molecules. The <30ms non-specific residence time is clearly compatible with a search mechanism that explores all PAMs.
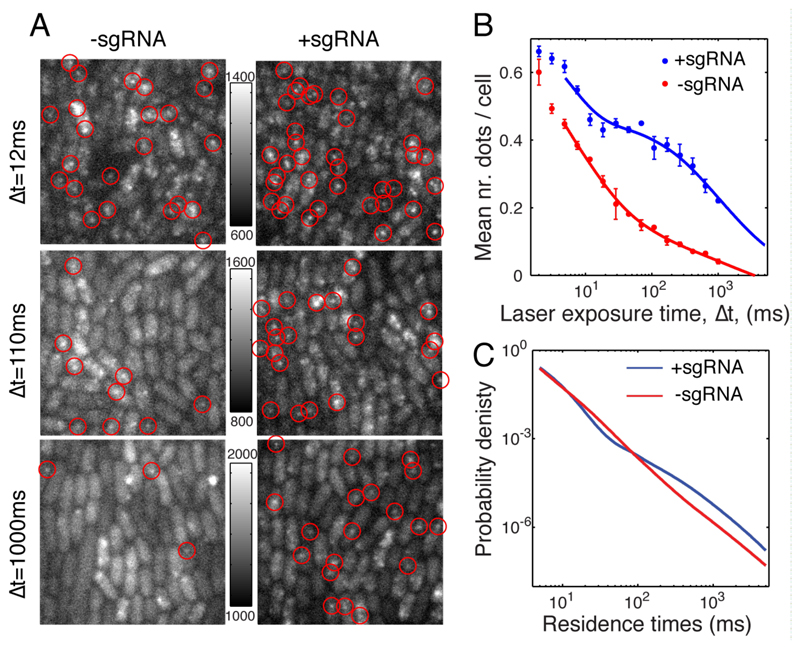
Fig. 4. Non-specific Binding.
Cells containing dCas9-YPet but no specific chromosomal target are imaged in the presence (strain:PL42H9) or absence (strain:PL42H8) of sgRNA-a, using exposure times ranging from 2ms to 1s while keeping the laser power times exposure-time constant. A. Examples of fluorescence images for different laser exposure times in absence (-sgRNA) and presence (+sgRNA) sgRNA-a. Automatically detected fluorescent dots are indicated by red circles. Each row has the same camera counts to grayscale mapping as indicated by the scale bar in between the example images. B. The average number of dots detected per cell as function of laser exposure time (dots). Error bars are the standard error of the mean of three technical repeats using the same microfluidic device. Solid lines are smoothing spline fits, which are extrapolated until 5 seconds laser exposure time. C. Distribution of residence times estimated using the fitted lines, <N(t)>, in (A). The distribution is given by p(t) = - D (1/t) d<N(t)>/dt, where D is chosen such that integral of p(t) = 1 and t is the laser exposure time. (see SI for details on calculation). The average residence times are <30ms in presence of sgRNA-a and <20 ms in absence of sgRNA-a.
Given the search time of 6 hours per molecule, we may ask if Cas9 could be effective as an adaptive immune system in S. pyogenes (19). We determined the abundance of Cas9 in S. pyogenes by Western blotting to be almost twice that of the non-fused dCas9 strain (fig. S1) where the time to bind a single target is 2 min (Fig. 2D), suggesting a search time of 1 min in S. pyogenes. Furthermore, the frequency (GG bp-1) of PAMs in pyogenes is 2/3 of that of E. coli, which can be expected to reduce the search time to 40s. Thus, the targeting time in pyogenes could be as little as a few minutes depending on which fraction of the Cas9s are programmed by the relevant spacer RNA. This suggests that no additional rate enhancing factors are needed for Cas9 search in pyogenes. Overall dCas9 kinetics is slow due to the flexible targeting mechanism, but association can be made fast for a few selected targets using high copy numbers.
Supplementary Material
One Sentence Summary.
The price Cas9 pays for being able to target any DNA sequence is time.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Katharine Abruzzi for supplying the plasmid pAFS52, and Ines Fonfara and Emmanuelle Charpentier for help with making S.pyogenes protein lysates. This work was supported by the European Research Council (ERC), the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (KAW), and Vetenskapsrådet (VR).
Footnotes
Author contributions: J.E, C.U. conceived the project, J.E, C.U., D.L.J., D.F, M.L. and P.L. designed study; D.L.J., C.U., M.L, D.F and P.L. conducted the experiments; D.L.J, P.L., D.F. and V.C. performed the analysis; C.U., P.L. and D.L.J. made the bacterial strains and plasmids; D.L.J., D.F. and J.E. derived the theory; and J.E., D.L.J., P.L., and D.F. wrote the paper.
References
- 1.Hutvagner G, Simard MJ. Argonaute proteins: key players in RNA silencing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:22–32. doi: 10.1038/nrm2321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vogel J, Luisi BF. Hfq and its constellation of RNA. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:578–589. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen Z, Yang H, Pavletich NP. Mechanism of homologous recombination from the RecA–ssDNA/dsDNA structures. Nature. 2008;453:489–494. doi: 10.1038/nature06971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deltcheva E, et al. CRISPR RNA maturation by trans-encoded small RNA and host factor RNase III. Nature. 2011;471:602–607. doi: 10.1038/nature09886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jinek M, et al. A Programmable Dual-RNA–Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. Science. 2012;337:816–821. doi: 10.1126/science.1225829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Barrangou R, et al. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science. 2007;315:1709–1712. doi: 10.1126/science.1138140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Semenova E, et al. Interference by clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) RNA is governed by a seed sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:10098–10103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104144108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hammar P, et al. The lac repressor displays facilitated diffusion in living cells. Science. 2012;336:1595–1598. doi: 10.1126/science.1221648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fei J, et al. RNA biochemistry. Determination of in vivo target search kinetics of regulatory noncoding RNA. Science. 2015;347:1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1258849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Greene EC. DNA Sequence Alignment during Homologous Recombination. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:11572–11580. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R116.724807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sternberg SH, Redding S, Jinek M, Greene EC, Doudna JA. DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9. Nature. 2014;507:62–67. doi: 10.1038/nature13011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sternberg SH, LaFrance B, Kaplan M, Doudna JA. Conformational control of DNA target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas9. Nature. 2015;527:110–113. doi: 10.1038/nature15544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mojica FJM, Díez-Villaseñor C, García-Martínez J, Almendros C. Short motif sequences determine the targets of the prokaryotic CRISPR defence system. Microbiology. 2009;155:733–740. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.023960-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Marraffini LA, Sontheimer EJ. Self versus non-self discrimination during CRISPR RNA-directed immunity. Nature. 2010;463:568–571. doi: 10.1038/nature08703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hammar P, et al. Direct measurement of transcription factor dissociation excludes a simple operator occupancy model for gene regulation. Nat Genet. 2014;46:405–408. doi: 10.1038/ng.2905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gilbert W, Müller-Hill B. Isolation of the lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966;56:1891–1898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ma H, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 nuclear dynamics and target recognition in living cells. J Cell Biol. 2016;214:529–537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Knight SC, et al. Dynamics of CRISPR-Cas9 genome interrogation in living cells. Science. 2015;350:823–826. doi: 10.1126/science.aac6572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Marraffini LA. In: Streptococcus pyogenes : Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations. Ferretti JJ, Stevens DL, Fischetti VA, editors. University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center; Oklahoma City (OK): 2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.