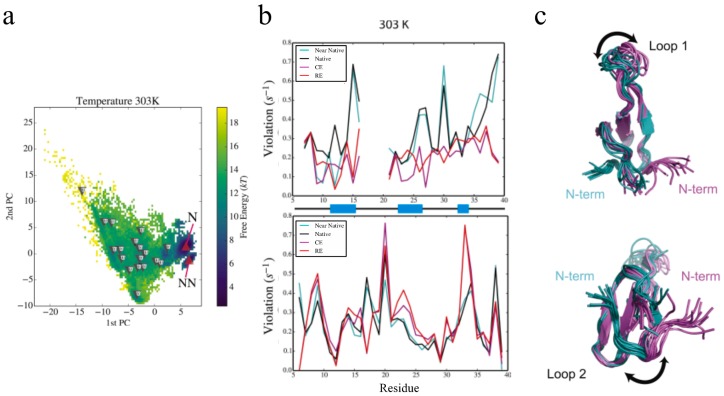
Figure 7.
The eNOE is sensitive to minor populated states in the Pin1 WW domain. (a) Free-energy landscapes and cluster populations from replica-exchange molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and maximum entropy-based chemical shift reweighing carried out at 303 K are shown. The upward facing red triangles indicate cluster centroids that have a higher population in the reweighed ensemble (RE) than the canonical ensemble. The downward pointing triangles indicate clusters that have a lower population. For more information, see reference [35]; (b) Root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) violations of cross-relaxation rate constants from bidirectional (top) and unidirectional (bottom) eNOEs from REs and canonical ensembles (CEs), as well as from the native and near-native conformational clusters at 303 K. RMSD violations of 0.1–0.2 s—1 translate into distance errors of approximately 0.3–0.4 Å. Secondary structure by residue (black lines indicate loops and coiled regions, and blue blocks indicate β strands) are shown on x-axis; (c) The conformational changes inherent to the native and near-native states are depicted by calculated structural ensembles. The change in loop 1 (residues 17–20, top) of the WW domain and the topological rearrangement of the N and C termini (bottom) are especially prevalent. Ten conformers are shown in each cluster. This figure was adapted from [35], Copyright (2016), with permission from Cell Press.