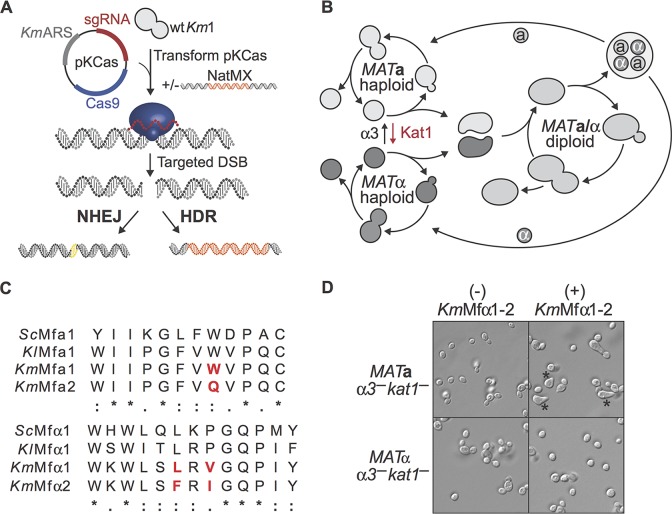
FIG 1.
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing and mating-type switching in K. marxianus. (A) CRISPRNHEJ and CRISPRHDR systems. K. marxianus transformed with the pKCas plasmid generates small indels near the cut site, a common product of nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) repair of the DNA double-strand break. When transformed with both the pKCas plasmid and a donor DNA, homologous recombination products are seen in the target site. (B) Yeast life cycle. Haploid MATa and MATα switch mating type by transposases α3 and Kat1 in K. lactis. Haploid cells conjugate to form MATa/MATα diploids. Diploids undergo meiosis to form haploid spores that germinate to complete the life cycle. (C) Mature a- and α-pheromones from K. marxianus aligned with the S. cerevisiae and K. lactis sequences. Red indicates nonconserved amino acids between K. marxianus a- and α-factors. Amino acids are marked as identical (*), with similar polarity (:), or with different polarity (.). (D) Incubation of putative heterothallic MATa and MATα strains with a cocktail of both mature α-factor pheromones (KmMfα1 and -2) results in mating projections from the MATa strain only (*).