Abstract
Objective: To determine the neuroprotective effects and underpinning mechanisms of thrombopoietin (TPO), Matrix Metalloproteinase-9(MMP-9) and Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats.
Methods: Male rats underwent 2 hours of right middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) followed by 22 hours of reperfusion. PBS or TPO (0.1ug/kg) was administered from caudal vein before reperfusion. Neurologic deficits, brain edema, Evans blue (EB) extravasation, NF-κB and MMP-9 expression were subsequently examined.
Results: Ischemia-reperfusion injury produced a large area of edema. TPO significantly reduced edema and alleviated neurologic deficits after ischemia-reperfusion. Ischemia-induced increases of NF-κB, MMP-9 and Evans blue extravasation were reduced by TPO intervention.
Conclusion: TPO improved neurological function and ameliorated brain edema after stroke, partly by reducing the ischemia-induced increase of NF-κB and MMP-9.
Keywords: Thrombopoietin (TPO), Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), Ischemia-Reperfusion (IR)
1. Introduction
The most effective treatment for ischemic stroke is thrombolytic intervention. However, the process of thrombolytic intervention is accompanied with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, leading to increased permeability of blood-brain barrier (BBB) and brain edema 1. Reperfusion injury is attributed to various factors, including inflammation, oxidative stress and proteolytic enzyme, which result in damage of BBB integrity and hemorrhagic transformation 2. It has to be noted that recombinant tissue plasminogen activator(r-tPA) can only be administered within 3 hours after stroke 3. Therefore, it is important to look for alternative therapy for ischemic stroke, especially for the cases with brain ischemia longer than 3 hours.
Increasing evidence has suggested that hematopoietic growth factors are a new treatment strategy for stroke. Hematopoietic growth factors are proteins that regulate the production of blood cells. However, these factors can manifest additional functions beyond their hematopoietic action. Thrombopoietin (TPO) is a primary hematopoietic growth factor for platelet production, participating in the process of hematopoietic cell's proliferation, differentiation and maturation 4. TPO is successfully used for thrombocytopenia. In addition to the hematopoietic system, TPO and its receptors (i.e. c-MPL) are expressed in various organs including heart and nervous system which indicates that TPO may have hematopoiesis-independent effects 5. TPO can augment angiogenic response 6, improve ventricular function and present protection against myocardial ischemia 7. Besides its expression in hematopoietic system, TPO receptor (c-MPL) also located in the central nervous system, and can inhibit the apoptosis of nerve cells, through the activation of the PI-3K/AKT signal pathway 8. In contrast, Balcik showed that increased TPO level may multiply both platelet count and size, contributing to the progress of ischemic stroke 9. Research has also shown that during moderate hypoxia ischemia, TPO promotes the apoptosis of nerve cell, whereas under severe hypoxia ischemia condition, TPO inhibits the apoptosis of nerve cell 10. Therefore, how ischemia alters the expression of TPO still remain debatable and its roles during ischemia-reperfusion are far from clear.
Inflammation plays an important role in the damage of blood brain barrier after ischemic-reperfusion injury 11, 12. NF-κB is a vital regulator of inflammation response and nerve cell apoptosis. Interestingly, TPO has been demonstrated to regulate PI-3K signal pathway and phosphorylation of PI-3K signal pathway could activate NF-κB and MMP-9 13-15. Inhibition of stroke-induced increase of NF-κB could protect brain from cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury 16. MMP-9 is an independent factor of BBB damage. Several studies showed that up-regulated expression of MMP-9 could degrade extracellular matrix and intercellular tight junction, leading to increased permeability of BBB and subsequent brain edema and hemorrhagic transformation after ischemia-reperfusion 17.
It is still unknown whether TPO could protect against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury or not, therefore, the purpose of our study is to investigate the action and mechanism of TPO in model of stroke. We propose that TPO regulates the expression of NF-κB and MMP-9 and thus modulates the permeability of BBB after ischemia-reperfusion injury.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Animal model and groups
The research was conducted in accordance with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals by the United National Institutes of Health. All experimental protocols were approved by the Second Xiangya Hospital Animal Care Committee of Central South University. Male rats weighing from 250g to 300g were divided randomly into three groups: the sham operation group, ischemia-reperfusion model (IR) group and TPO intervention group.
The model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion was established in Sprague-Dawley rats as per the Longa's suture method 18. A silicone-coated nylon monofilament was passed through the bifurcation of the common carotid artery to the internal carotid artery, advancing along the internal carotid artery to approximately 18-22 mm from the bifurcation until a proximal occlusion of the right middle cerebral artery was established. After 2 hours of occlusion, the filament was withdrawn slowly to allow blood supply in the middle cerebral artery for 22 hours. Room temperature was maintained at 25°C during the operation. The body temperature was maintained until recovery.
Sham operation group only received the internal carotid artery separation, whilst IR group and TPO intervention group received 2 hours of MCAO followed by 22 hours of reperfusion, PBS (0.1ug/kg) or TPO (0.1ug/kg) was injected via tail vein respectively prior to reperfusion. Each group was randomly divided into subgroups, for TTC staining, brain water content measuring, Evans blue dyeing, HE and immunohistochemistry staining, Western blot and RT-PCR.
2.2 Neurological deficits score
The neurological deficits were evaluated by an examiner blind to the experimental groups, after 2 hours of MCAO and 22 hours of reperfusion 18. Details were as follows: 0, no symptoms of neural damage; 1, failure to extend left forepaws; 2, circling to the left; 3, falling down to the left; 4, no spontaneous walking with a loss of consciousness. Rats received 1 to 3 score were selected as observational objectives.
2.3 Triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining
Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC; Sigma) staining was used for confirming the success of the MCAO model. After 22 hours of reperfusion, the rats were deeply re-anesthetized by 10% chloral hydrate. The brain tissue were quickly removed on ice and placed in an environment of -20°C for half an hour. Then the brain tissue were sliced into 6 coronal sections of 2 mm thickness and immersed in 2% TTC solution in the dark at 37°C for 30min and kept in 4% paraformaldehyde at 4°C overnight.
2.4 Brain water content
Rats were killed after 22 hours of reperfusion under deeply anesthetized. Brain tissues were split into right and left hemispheres without olfactory bulb, cerebellum and brain stem, the right hemispheres were evaluated wet weights (ww) on a balance immediately, and then dried in the oven at 110°C for 24 hours to get the dry weights (dw). The brain water content was calculated with the following formula: brain water content =(ww-dw)/ww× 100%.
2.5 Evans Blue extravasation
Rats were injected with Evans blue (2% in saline, 4 mL/kg; Sigma) via the tail vein 1 hour prior to sacrifice. Before decollation, rats were perfused with saline to remove the intravascular dye. Then the brain tissue were homogenized in 2mL 50% trichloroacetic acid and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 30 minutes. The supernatant liquid (50 uL) were mixed with ethanol (150ul) and measured absorbance (at 632nm) by spectrophotometry. The content of Evans blue was quantified with a standard curve and expressed as ug Evans blue /g brain tissue.
2.6 HE and Immunohistochemistry staining
After 22 hours of reperfusion, the brains were removed after cardiac perfusion with saline and paraformaldehyde (4%). Then the brains were post-fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 hours, embedded in paraffin and cut into 4 µm thick serial co ronal sections after the optic chiasm. Sections were baked in the oven at 60°C for 90 minutes, dewaxed in xylene and hydrated in graded ethanol. HE staining was used for observing the profile of cerebral cortex tissue and immunohistochemical staining was used to examine the expression of MMP-9 (1:100) and NF-κB (1:50) in the ischemic hemisphere. Five different visual fields were chosen randomly from each slice and three slices were used from each sample. Images were taken under an objective lens of 40x and were collected by microscope-digital photographic system (DP12 SZX7, Olympus Inc., Japan).
2.7 Western Blot
Ischemic and control brain tissues were homogenized with RIPA buffer (Applygen, China) which contained a mixture of protease inhibitors, and the protein concentration of extracts were determined by BCA protein analysis kit (Pierce, Rockford, USA). Protein extracts (50μg of total protein) were seperated in 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, then transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were incubated with TBS-T (tris-buffered saline and 0.1% Tween-20, Sigma, USA) containing 5% non-fat milk at room temperature for 1 hour, then with primary antibodies against NF-κB (1:200 dilution, Santa Cruz) and MMP-9(1:1000 dilution, Abcam) at 4°C for a whole night. Membranes loaded with primary antibodies were washed with TBS-T for 3 times, and then incubated for 1 hour at room temperature with horseradish peroxidase conjugate secondary antibodies (1:3000 dilution, Santa Cruz). The membranes were then developed with the SuperEnhanced chemiluminescence detection kit (Thermo pierce, USA). The membranes were incubated with β-actin primary antibodies (1:4000 dilution, Sigma) as control. Protein expression was standardized with an equivalent β-actin protein. The bands were detected using X-ray film and quantified using Quantity-one Analysis software.
2.8 Real-Time PCR
Frozen brain tissues were homogenized with Trizol reagent at the ratio of 100mg/5ml. Total RNA was extracted following technical manual of Trizol RNA kit (Invitrogen, USA). The content and purity of extracted RNA were determined by nucleic acid protein spectrophotometer, the ratio of 260/280nm absorbance was 1.8-2.0. Extracted RNA was electrophoresed with 1% of agarose gel to display clear rRNA bands for the template quality and purity control, and then reversely transcribed in accordance with instructions of the SuperRT First-strand cDNA synthesis kit (ComWin, China). Reverse transcription products were amplified by SYBER® Green PCR Master Mix system (Invitrogen, USA) in 10ul final reaction volume. Relative abundance of mRNA was calculated after normalization with β-actin. RT-PCR was used for analyzing the levels of NF-κB and MMP-9 mRNA after 22 hours of reperfusion. The mean Ct values were normalized by the internal control β-actin. The difference of ΔCt values of the control sample was calculated and defined as ΔΔCt. The relative value of mRNA expression level was expressed as 2-ΔΔCt.
The primers were as follows: NF-κB: F5'-GGTGGAGTTTGGGAAGGATTTG-3', R5'-TTTTCTCCGAAGCTGAACAAACAC-3'; MMP-9:F5'-GGCACCATCATAACATCACCTA-3', R5'-GACACCAAACTGGATGACAATG-3'; β-actin: F5'-CATCCTGCGTCTGGACCTGG-3', R5'-TAATGTCACGCACGATTTCC-3'.
2.9 Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 19.0. Data were expressed as mean ± SD, and analyzed with ANOVA, followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test, but neurological deficit assessment was tested by Mann-Whitney U test between two groups. The significance level was set at P<0.05.
3. Results
3.1 TTC staining
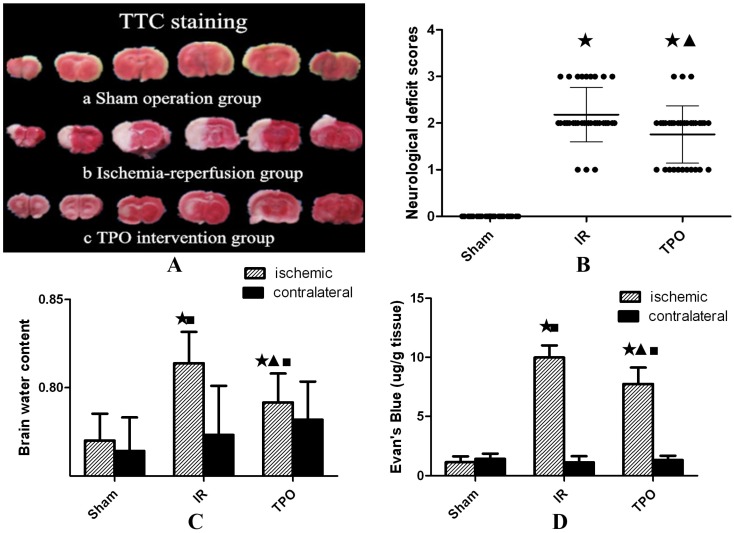
No infarction was observed in the sham operation group, while white infarct lesion appeared in the IR group and TPO intervention group, verifying successful establishment of MCAO model in rats (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
Effect of thrombopoietin in ischemia-reperfusion rats' brains. (A) TTC staining of brain slices after ischemia- reperfusion. Uniformly red region in Sham operation group (a) vs. white infarct lesion in IR group (b) and TPO intervention group(c). (B) Compared with sham operation group, the neurological deficit scores were significantly increased in IR and TPO intervention group, and TPO intervention decreased neurological deficit at 24h after MCAO. (C) The brain water content of ischemic hemispheres was significantly increased after MCAO, and TPO intervention reduced ischemia-induced increase of brain water content, whereas no difference was found in contralateral hemispheres. (D) The Evan's blue extravasation of ischemic hemispheres is significantly higher than that of sham group and contralateral hemispheres in IR and TPO intervention group, and TPO intervention reduced Evan's blue content significantly compared with the IR group. (★Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ▲Compared with the IR group, P<0.05; ■Compared with the contralateral brain, P<0.05)
3.2 Neurological deficit score
Neurological deficits were assessed and scored within 24 hours after ischemia. There were no symptoms of neurological deficit in the sham operation group. Compared with IR group, the neurological deficit scores were significantly reduced in TPO intervention group (Table 1, Figure 1B).
Table 1.
Neurological deficit score of each group (n=33,‾X ±S)
| Group | Grade |
|---|---|
| Sham operation group | 0 |
| IR group | 2.18±0.58★ |
| TPO intervention group | 1.76±0.61★▲ |
★Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ▲Compared with the IR group, P<0.05
3.3 TPO reduced brain edema and BBB damage
The brain water content of IR group was higher than that in sham operation group, TPO intervention could reduce the increase of brain water content caused by IR injury (Table 2, Figure 1C).
Table 2.
The brain water content of each group (n=6, ‾X ±S)
| Group | Ischemic hemisphere | Contralateral hemisphere |
|---|---|---|
| Sham operation group | 0.77±0.015 | 0.76±0.019 |
| IR group | 0.81±0.018 ★■ | 0.77±0.028 |
| TPO intervention group | 0.79±0.016 ★▲■ | 0.78±0.022 |
★Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ▲Compared with the IR group, P<0.05.
■Compared with the contralateral brain, P<0.05
BBB disruption following 2 hours ischemia and 22 hours reperfusion was assessed by measuring the content of Evan's blue in brain tissue. The content of Evan's blue in ischemic hemisphere is significantly higher than that in the contralateral hemisphere in IR group. Compared with the IR group, TPO intervention group showed significantly less Evan's blue content (Table 3, Figure 1D).
Table 3.
The Evan's blue content of each group (n=6, ‾X ±S, ug/g)
| Group | Ischemic hemisphere | Contralateral hemisphere |
|---|---|---|
| Sham operation group | 1.15±0.49 | 1.42±0.44 |
| IR group | 9.98±1.02★■ | 1.13±0.51 |
| TPO intervention group | 7.74±1.39★▲■ | 1.32±0.36 |
★Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ▲Compared with the IR group, P<0.05
■Compared with the contralateral brain, P<0.05
3.4 TPO attenuated ischemia-induced neuronal cell damage
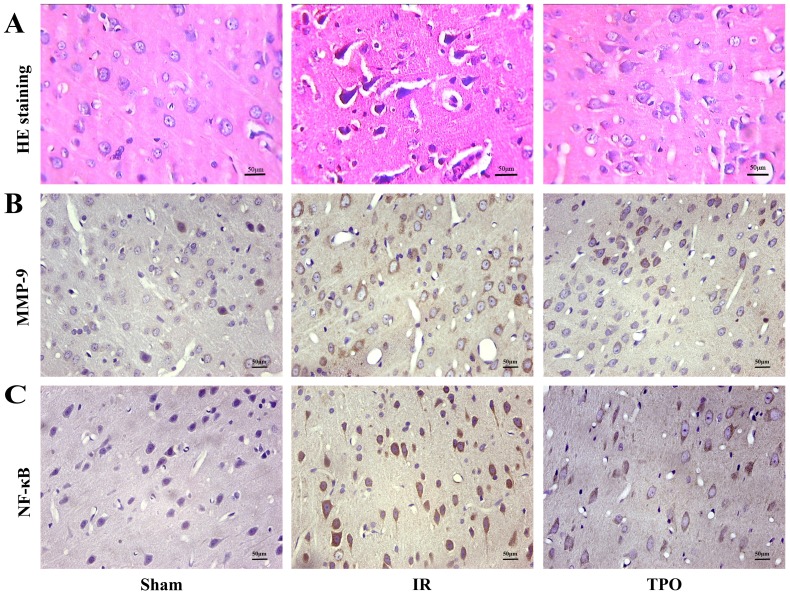
The cell morphology and structure were normal in sham operation group, but presented obvious changes in IR and TPO intervention group. In the ischemia and infarction region of brain tissue, the gross brain structures disappeared with the neuronal numbers decreased. Some neurons presented karyopyknosis. TPO intervention could reduce neuronal damage comparing with IR group (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
Hematoxylin-Eosin staining (A) and Immunohistochemical staining of MMP-9 (B) and NF-κB (C) in the cerebral cortex. Scale bar, 50μm. (400×magnification) There was increased MMP-9, NF-κB immunoreactivity after Ischemia-reperfusion. TPO intervention reduced MMP-9, NF-κB immunoreactivity significantly.
3.5 TPO suppressed the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB
We further performed immunohistochemistry in order to determine the expressing levels of MMP-9 and NF- κB in the cerebral cortex infarction region. MMP-9 and NF-κB positive staining were mainly distributed in neurons, endothelial cells and neutrophils. MMP-9 protein was located in cytoplasm, while NF-κB was located both at cytoplasm and nucleus. Five fields were chosen randomly from each slice ,then the average positive cell number were calculated by the sum divided by five, then the average cell number was calculated from the three slices. Few positive cells were found in sham operation group, but there was a considerable increase in the number of positive cells in IR group, TPO intervention could reduce the increased expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB caused by ischemia (Figure 2B, 2C, 3C and Table 4).
Table 4.
Number of MMP-9 and NF-κB positive cells in each group (n=6, ‾X ±S)
| Group | MMP-9 | NF-κB |
|---|---|---|
| Sham operation group | 9.31±2.96 | 7.17 ± 1.98 |
| IR group | 30.78±5.79▲ | 40.82 ± 8.73▲ |
| TPO intervention group | 22.41±4.58▲■ | 24.67 ± 6.33▲■ |
▲Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ■Compared with the IR group, P<0.05
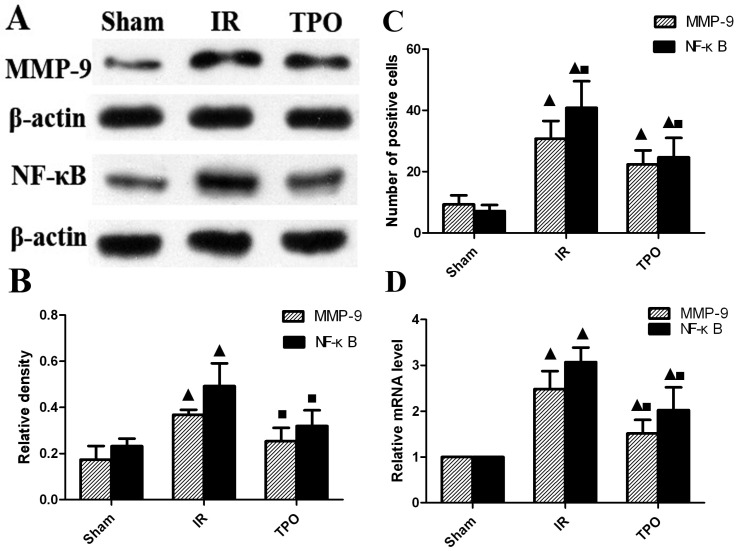
We further quantified the protein level of MMP-9 and NF-κB with western blot. The expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins were up-regulated after ischemia-reperfusion. TPO intervention significantly decreased the MMP-9 and NF-κB protein levels (Figure 3A, 3B and Table 5). In line with the results of immunohistochemistry and Western blot, the mRNA expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB was up-regulated after ischemia-reperfusion. The augmented expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB was remarkably attenuated in TPO intervention group (Figure 3D and Table 6).
Figure 3.
TPO suppressed the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB. (A, B) Western blot results showing the expressing levels of MMP-9 and NF-κB protein; (C) Number of MMP-9 and NF-κB positive cells assessed by immunohistochemistry; (D) RT-PCR results displaying the mRNA expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB. The expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB was massively increased in IR group, and TPO intervention effectively blocked the increase caused by ischemia-reperfusion. (▲Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ■Compared with the IR group, P<0.05)
Table 5.
Relative protein level of MMP-9 and NF-κB in each group (n=6, ‾X ±S)
| Group | MMP-9 | NF-κB |
|---|---|---|
| Sham operation group | 0.17±0.059 | 0.23 ± 0.033 |
| IR group | 0.37±0.021▲ | 0.49 ± 0.099▲ |
| TPO intervention group | 0.25±0.058▲■ | 0.32 ± 0.068▲■ |
▲Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ■Compared with the IR group, P<0.05
Table 6.
Relative mRNA expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB in each group (n=6, ‾X ±S)
| Group | MMP-9 | NF-κB |
|---|---|---|
| Sham operation group | 1 | 1 |
| IR group | 2.49±0.39▲ | 3.07 ± 0.32▲ |
| TPO intervention group | 1.52±0.30▲■ | 2.03 ± 0.49▲■ |
▲Compared with the sham operation group, P<0.05; ■Compared with the IR group, P<0.05
4. Discussion
Thrombopoietin, the main regulator in the generation of megakaryocyte and platelet production, used to be a common treatment for thrombocytopenia 19. In recent years, a large number of studies have also found that TPO participates in some important physiological processes beyond the hematopoietic system, especially in nervous system. Whether it is beneficial or harmful after ischemia is unknown. Previous study has shown that TPO and mean platelet volume were increased significantly in stroke patients, leading to better hemostatic tendency, which might contribute to the progress of ischemia stroke 9. Decreased platelet count caused by TPO inhibitor could reduce experimental occlusive thrombogenesis, suggesting that suppressing platelet production with TPO inhibitor may prevent stroke and heart attack 20. However, other studies had opposite outcomes. Baker et al. showed that TPO treatment could reduce myocardial infarct size and apoptosis following ischemia-reperfusion through multiple signaling pathways including JAK-2 and p42/44 MAPK as well as K (ATP) channels 21. TPO also enhanced the correction of ischemia via promoting angiogenic response mediated by the increased platelet level 6. The present study shows that after 2 hours ischemia followed by 22 hours reperfusion, the BBB permeability was massively increased, leading to severe brain edema and neurologic deficit, TPO intervention significantly reduced brain edema and neurologic deficit caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury. These results suggest that TPO could protect brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury, and hopefully be a new therapeutic method in stroke.
The MMP family members, especially MMP-9, have been shown significantly up-regulated after stroke, degrading tight-junction proteins and leading to damage of BBB 22. Higher activity and expression of MMP-9 were closely related to brain edema 23. Inhibition of MMP-9 expression can relieve cerebral edema after stroke 24. Zhou et al. showed that TPO could reduce ischemic brain injury by inhibiting the stroke-induced increase in MMP-925. They found that TPO significantly inhibited the stroke-induced increase in MMP-9 mRNA expression, active-MMP-9 protein expression, and MMP-9 enzymatic activity. In stroke, the MMP-9 activation was of multi-factorial origins including inflammation 26. NF-κB promoted inflammation process and activated inflammatory cytokines, resulting in inflammation cascade amplification 14, 27. NF-κB phosphorylation induced by TNF-α or PI3K-γ could damage endothelial cell, leading to BBB damage and brain edema 27, 28. Guan et al. found that Ruscogenin protected against brain ischemia by inhibiting NF-κB p65 expression 16, which also meant inhibition of NF-kB expression could protect brain tissue from IR injury. There was NF-κB transcriptional regulation binding site before TATA box of the gene regulation sequence of MMP-9. Activated NF-κB could increase the transcription of MMP-929. Annabi found that inhibiting the NF-κB phosphorylation by resveratrol could decrease MMP-9 expression and BBB damage 30. Therefore, we hypothesize that TPO could regulate NF-κB/MMP-9 to protect brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury. The present study shows that the expression of NF-κB and MMP-9 was significantly increased in brain tissue after ischemia reperfusion, which is in line with their mRNA expression, TPO treatment obviously reduced the stroke-induced increase of NF-κB and MMP-9.
Ehrenreich et al. showed that TPO and its receptor were down-regulated upon hypoxia, could cause death of cultured hippocampal neurons at low concentration, and lost its death-promoting function at high concentration 31. In this study, the TPO intervention was at the dose of 0.1ug/kg, in accordance with Zhou's results, which demonstrated that 0.1ug/kg is most effective to reverse ischemia-reperfusion injury 25. Additionally, decreasing the platelet production, but remaining at a physiological range and without interfering by the hemostatic function of platelets, has been suggested as a safe alternative to platelet inhibitors for thromboprophylaxis 20.
Besides, our research had some limitations. Firstly, we didn't conduct detection of active form of NF-kB. Secondly, we didn't perform matrix metalloproteinase zymography to determine whether the activity of MMP-9 has altered by TPO intervention. We will conduct relevant activity testing of NF-kB and MMP-9 in the further study. Thirdly, As the present study didn't measure the count and the function of platelet in blood, future studies shall focus on the balance between brain protective and platelet promoting function.
5. Conclusion
In summary, this study shows that the intervention of TPO can significantly reduce neurologic deficit, improve the BBB permeability and relieve cerebral edema, suggesting that the TPO might have the neuro-protective effects in ischemia reperfusion injury via decreasing the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB. This experiment reveals that the NF-κB /MMP-9 signaling pathway may be involved in the BBB damage after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury and thus provides a new treatment strategy for stroke.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no.81271298), the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department in China (Grant no.2011SK3236).
References
- 1.Zhang Q, Gao T, Luo Y. et al. Transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induces early and chronic axonal changes in rats: its importance for the risk of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tu Q, Cao H, Zhong W. et al. Atorvastatin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9:268–275. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.128220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boudreau DM, Guzauskas GF, Chen E. et al. Cost-effectiveness of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator within 3 hours of acute ischemic stroke: current evidence. Stroke. 2014;45:3032–3039. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.005852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vainchenker W, Besancenot R, Favale F. Megakaryopoiesis: regulation of platelet production by thrombopoietin. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2013;197:395–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alvarez RM, Fernandez BI, Arias-Salgado EG. et al. Effects of thrombopoietin receptor agonists on procoagulant state in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 2014;112:65–72. doi: 10.1160/TH13-10-0873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kawamoto T, Sasajima J, Sugiyama Y. et al. Ex vivo activation of angiogenic property in human peripheral blood-derived monocytes by thrombopoietin. Int J Hematol. 2013;98:417–429. doi: 10.1007/s12185-013-1423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chan KY, Zhou L, Xiang P. et al. Thrombopoietin improved ventricular function and regulated remodeling genes in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167:2546–2554. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.06.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yang M, Shu LL, Cui Y. The role of PDGF/PDGFR in the regulation of platelet formation. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2011;19:1097–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Balcik OS, Bilen S, Ulusoy EK. et al. Thrombopoietin and mean platelet volume in patients with ischemic stroke. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2013;19:92–95. doi: 10.1177/1076029611434528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu XM, Feng Y, Li AM. Effect of G-CSF and TPO on HIBD in neonatal rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015;8:132–136. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60303-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yadav VR, Prasad S, Gupta SC. et al. 3-Formylchromone interacts with cysteine 38 in p65 protein and with cysteine 179 in IkappaBalpha kinase, leading to down-regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)-regulated gene products and sensitization of tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:245–256. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.274613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 12.Huang L, Wong S, Snyder EY. et al. Human neural stem cells rapidly ameliorate symptomatic inflammation in early-stage ischemic-reperfusion cerebral injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5:129. doi: 10.1186/scrt519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Monzen S, Tashiro E, Kashiwakura I. Megakaryocytopoiesis and thrombopoiesis in hematopoietic stem cells exposed to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 2011;176:716–724. doi: 10.1667/rr2725.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhuang R, Lin MX, Song QY. et al. Effects of curcumin on the expression of nuclear factor-kappaB and intercellular adhesion molecular 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009;29:1153–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shih RH, Wang CY, Yang CM. NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in Neurological Inflammation: A Mini Review. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015;8:77. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guan T, Liu Q, Qian Y. et al. Ruscogenin reduces cerebral ischemic injury via NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory pathway in the mouse model of experimental stroke. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;714:303–311. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.07.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Takata F, Dohgu S, Matsumoto J. et al. Brain pericytes among cells constituting the blood-brain barrier are highly sensitive to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, releasing matrix metalloproteinase-9 and migrating in vitro. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:106. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S. et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20:84–91. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Arai Y, Jo T, Matsui H. et al. Comparison of up-front treatments for newly diagnosed immune thrombocytopenia -a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Haematologica. 2018;103:163–171. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.174615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tucker EI, Marzec UM, Berny MA. et al. Safety and antithrombotic efficacy of moderate platelet count reduction by thrombopoietin inhibition in primates. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2:37r–45r. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Baker JE, Su J, Hsu A. et al. Human thrombopoietin reduces myocardial infarct size, apoptosis, and stunning following ischaemia/reperfusion in rats. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;77:44–53. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tang X, Zhong W, Tu Q. et al. NADPH oxidase mediates the expression of MMP-9 in cerebral tissue after ischemia-reperfusion damage. Neurol Res. 2014;36:118–125. doi: 10.1179/1743132813Y.0000000266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bauer AT, Burgers HF, Rabie T. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 mediates hypoxia-induced vascular leakage in the brain via tight junction rearrangement. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010;30:837–848. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lee K, Lee JS, Jang HJ. et al. Chlorogenic acid ameliorates brain damage and edema by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9 in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;689:89–95. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhou J, Li J, Rosenbaum DM. et al. Thrombopoietin protects the brain and improves sensorimotor functions: reduction of stroke-induced MMP-9 upregulation and blood-brain barrier injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011;31:924–933. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ludewig P, Sedlacik J, Gelderblom M. et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 inhibits MMP-9-mediated blood-brain-barrier breakdown in a mouse model for ischemic stroke. Circ Res. 2013;113:1013–1022. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.He W, Chen W, Zhou Y. et al. Xanthotoxol exerts neuroprotective effects via suppression of the inflammatory response in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2013;33:715–722. doi: 10.1007/s10571-013-9939-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jin R, Song Z, Yu S. et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase gamma plays a central role in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute experimental stroke. Stroke. 2011;42:2033–2044. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.601369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chiu PS, Lai SC. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 leads to claudin-5 degradation via the NF-kappaB pathway in BALB/c mice with eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Annabi B, Lord-Dufour S, Vezina A. et al. Resveratrol Targeting of Carcinogen-Induced Brain Endothelial Cell Inflammation Biomarkers MMP-9 and COX-2 is Sirt1-Independent. Drug Target Insights. 2012;6:1–11. doi: 10.4137/DTI.S9442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ehrenreich H, Hasselblatt M, Knerlich F. et al. A hematopoietic growth factor, thrombopoietin, has a proapoptotic role in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:862–867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406008102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]