Abstract
Interrupting T cell costimulatory signals as a strategy to control undesired immune responses, such as occur in autoimmunity or transplantation, has the potential to alleviate many of the unwanted side effects associated with current immunosuppressive therapies. Belatacept, a high-affinity version of CTLA4-Ig that blocks ligand ligation to CD28, has been approved for use in kidney transplant recipients. Despite the long-term benefits associated with its use, such as improved renal function and lower cardiovascular risk, a subset of patients treated with belatacept experience elevated rates of acute T cell–mediated rejection, tempering enthusiasm for its use. Here we demonstrate that costimulation-independent T cell alloreactivity relies on signaling through CD122, the shared IL-2 and IL-15 receptor β-chain. Combined costimulatory and CD122 blockade improved survival of transplanted tissue in mice and nonhuman primates by controlling proliferation and effector function of CD8+ T cells. The high-affinity IL-2 receptor was dispensable for memory CD8+ T cell responses, whereas signaling through CD122 as a component of the high-affinity IL-15 receptor was critical for costimulation-independent memory CD8+ T cell recall, distinguishing specific roles for IL-2 and IL-15 in T cell activation. These studies outline a novel approach for clinical optimization of costimulatory blockade strategies in transplantation by targeting CD122.
Keywords: Immunology, Transplantation
Keywords: Costimulation, Cytokines, T cells
Introduction
Blockade of key T cell costimulatory pathways represents a more targeted strategy to prevent unwanted immune responses such as rejection in transplant recipients. Recently, belatacept, a high-affinity variant of the CTLA4-Ig fusion protein, became the first approved alternative to conventional nonspecific immunosuppression for kidney transplant recipients (1, 2). Compared with patients receiving cyclosporine, transplant patients treated with belatacept enjoyed superior function of their transplanted kidney with fewer off-target toxicities and a 43% risk reduction of death or graft loss in a 7-year follow-up (3–5). Despite these improvements, a significant subset of patients experienced elevated rates and grades of acute allograft rejection during belatacept therapy (6, 7). Belatacept specifically interrupts T cell costimulatory signals mediated by CD28-CD80/CD86 interactions. Memory CD8+ T cells are capable of mounting alloimmune responses despite blockade of CD28 and CD154 costimulatory molecules (8–11). We recently demonstrated that a critical threshold of T cell memory can effectively predict belatacept resistance in patients and nonhuman primates (NHPs) and that belatacept-resistant rejection is uniquely characterized by allograft infiltrate that is more fully differentiated, with a unique proinflammatory cytokine signature (12, 13). There are subsets of memory CD8+ T cells in humans and NHPs that lack CD28 expression altogether and rely on alternative signals for activation (14, 15). One such signal is provided by the shared IL-2 and IL-15 cytokine signaling complex.
IL-2 and IL-15 signals depend on the assembly of high-affinity heterotrimeric receptors which share a β-chain (CD122) and common γ-chain (γc) (16). The unique contributions of these cytokines to host protection and alloimmunity, while described, are not fully elucidated. Interestingly, IL-2/IL-2Rα knockout animals exhibit autoimmunity, whereas IL-15/IL-15Rα knockout animals have diminished CD8, IELS, NK, and NKT cells, suggesting that these 2 cytokines have unique biological roles despite a shared signaling complex (17–20). Blocking the shared IL-2/IL-15Rβ has ameliorated disease in a murine model of IL-15–dependent autoimmunity (21). Additionally, we know that IL-15 signaling is critical for memory CD8+ T cell homeostasis and survival (22–24). Exogenous IL-15 has been shown to induce expansion of memory CD8+ T cells in rhesus monkeys (25). Inflammation may drive IL-15 production, leading to enhanced trafficking and proliferation of memory T cells following viral infection, but it is unclear what role IL-15 signaling has in transplant rejection, including its role in costimulation-independent T cell responses (26). We and others have demonstrated that IL-2 and IL-15 signaling induces the loss of CD28 while providing other activation signals (27, 28). Thus, signaling through the IL-2/IL-15 receptor complex may activate alloreactive T cells while making them increasingly resistant to belatacept due to loss of CD28. In support of this, recent studies by Traitanon et al demonstrate that IL-15 uniquely drives the proliferation of human alloreactive memory CD8+ T cells, despite costimulatory blockade (CoB) with CTLA4-Ig (29). Here we demonstrate that blockade of the shared IL-2 and IL-15 receptor β-chain, CD122, synergizes with CoB to abrogate both primary and memory CD8+ T cell responses to transplanted tissue and results in prolonged transplant survival in mice and NHPs. Interestingly, blockade of the high-affinity IL-2 receptor failed to inhibit T cell recall and graft rejection, whereas blockade of CD122 controlled CD8+ memory T cells, suggesting recall responses uniquely require IL-15, but can dispense with IL-2. This data supports a role for IL-15 not only in memory T cell homeostasis but also in memory T cell activation, proliferation, and acquisition of effector function. In contrast, the high-affinity IL-2 receptor in combination with CoB is sufficient to prevent primary allo-specific T cell responses. CD122-directed therapy allows for blockade of 2 pathways involved in T cell activation, IL-2 and IL-15, which possess distinct functions as signal 3 cytokines in primary and recall responses, respectively.
We translated these findings into a preclinical, NHP renal transplant model where we characterized the expression of CD122 as a marker of antigen-experienced memory CD8+ T cells, and found that IL-15 augments effector function of T cells, more so than IL-2, across the spectrum of memory T cell differentiation. Belatacept-resistant allograft infiltrate was characterized by high expression of CD122, but not CD25. The addition of a novel humanized CD122 blocking antibody synergized with belatacept to abrogate alloreactivity in vitro and markedly prolong survival of NHP renal transplant recipients. These data offer a novel strategy for the optimization of CoB in transplantation and define a critical role for CD122 in both primary and secondary immune responses, as part of the IL-2 and IL-15 receptor systems, respectively. Our studies suggest that signaling through IL-2/IL-15R (CD122) directly contributes to costimulation independence. The translation of CD122-directed therapy for transplantation may be superior to currently approved therapies targeting CD25, which may also deplete regulatory T cells (30). Furthermore, CD122-directed therapy has the benefit of interrupting the IL-2 receptor and the IL-15 receptor, inhibiting both primary and secondary alloreactive T cell responses. These data improve our understanding of the basic signaling requirements of T cells, and highlight the distinctive role of IL-15R in graft-specific memory responses.
Results
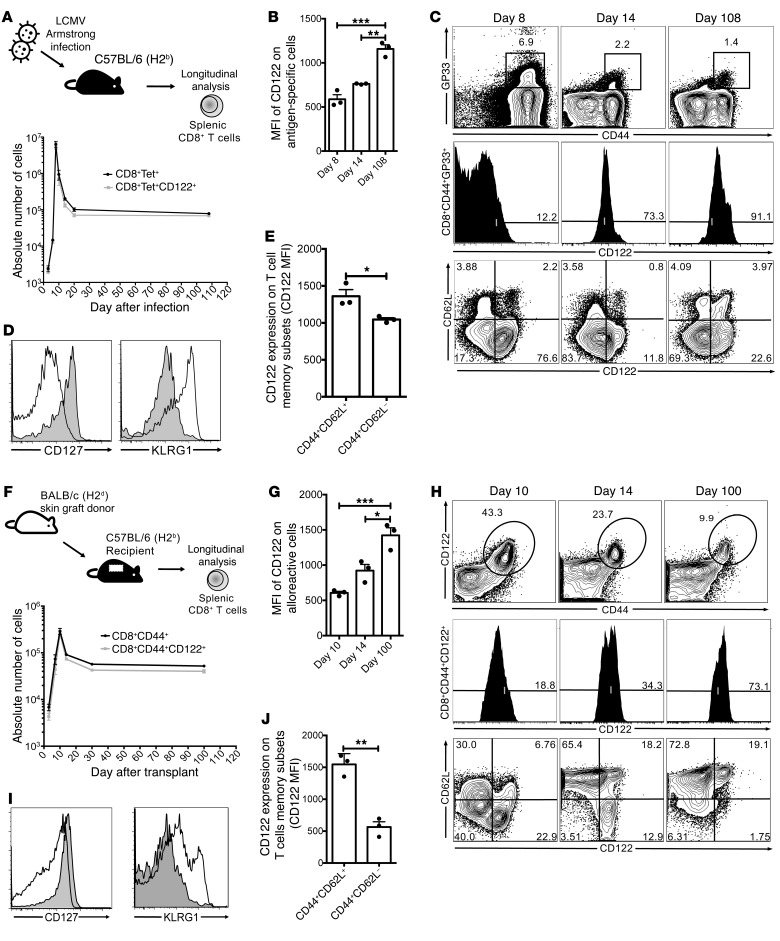
CD122 is highly expressed on antigen-specific memory CD8+ T cells.
High levels of CD122 expression distinguish memory CD8+ T cells and NK cells (31). Consistent with previous reports, we observed elevated CD122 expression on nearly all activated (CD44+) CD8+ T cells following viral infection (32). In a well-described model of acute viral infection with the Armstrong strain of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), we found CD122 to be expressed on more than 95% of viral antigen-specific cells tracked with GP33 tetramer (Figure 1A, corresponding FACS plot Figure 1C). Virus-specific CD8+ T cells not only maintained CD122 expression over time but the CD122 MFI increased as the population of antigen-specific T cells matured to a memory phenotype (Figure 1B, corresponding FACS plot Figure 1C). We observed that IL-2/IL-15Rβ (CD122) is expressed on both short-lived effector cells at the peak of response to infection (KLRG1hiCD127lo CD8+ T cells) as well as memory T cells (KLRG1loCD127hi CD8+ T cells, Figure 1D). Antigen-specific central memory CD44+CD62L+ CD8+ T cells exhibited the highest expression of CD122 when compared with effector memory CD44+CD62L– CD8+ T cells at 3 months after infection (Figure 1E, corresponding FACS plot Figure 1C). Phenotypically, CD122 expression on antigen-specific cells suggests an important role for CD122 during acute responses and in memory.
Figure 1. Kinetics of CD122 expression on CD8 T cells in acute viral infection and allograft rejection.
(A) C57BL/6 mice were infected with LCMV Armstrong strain. The frequency and phenotype of antigen-specific (CD44+GP33 tetramer+) splenic CD8+ T cells were assessed longitudinally, and more than 95% of all antigen-specific T cells (black circles) expressed CD122 (gray squares). (B) The MFI of CD122 on antigen-specific T cells was highest at day 108 compared with day 8, P = 0.0002. (C) Representative FACS plot of data shown in A (top row) and B (middle row). Bottom row depicts changing phenotype of CD122+ cells after infection. (D) Representative histogram demonstrating that antigen-specific T cells are phenotypically CD127loKLRG1hi on day 8 after infection (unshaded) compared with a memory time point (day 108), when cells were CD127hiKLRG1lo (shaded). (E) CD122 is more highly expressed on antigen-specific TCM (CD44+CD62L+) CD8+ T cells compared with TEM (CD44+CD62L–) CD8+ T cells (P = 0.0274). (F) C57BL/6 (H2b) mice received BALB/c (H2d) skin grafts and were assessed longitudinally, similar to A. The majority of alloreactive CD8+CD44+ T cells (black circles) expressed CD122 (gray squares). (G) CD122 MFI was highest 100 days after transplant (P = 0.0011). (H) Representative FACS plot of data shown in F (top row) and G (middle row). Bottom row depicts phenotypic changes after transplant. (I) CD122+ cells demonstrate similar CD127 and KLRG1 expression at the peak of rejection (unshaded) and memory (shaded) compared with infection (D). (J) Alloreactive CD8+ TCM cells express higher levels of CD122 compared with TEM CD8+ T cells (P = 0.0016). P values generated by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B, G). Student’s t test, 2-tailed. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of 3 mice per group (E, J). All results, including FACS plots, represent 3 independent experiments (n = 3 mice/group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
Virus-specific and alloreactive CD8+ T cells demonstrate similar expression of CD122.
We translated these findings to a model of transplantation to characterize CD122 expression on alloreactive CD8+ T cells during a primary challenge with an allograft. We characterized CD122 expression on alloreactive CD44+ CD8+ T cells (Figure 1, F–J). The expansion, contraction, and homeostasis of alloreactive CD8+ T cells in a BALB/c (H-2d) to C57BL/6 (H-2b) skin transplant model was similar to LCMV acute infection as previously described (9). CD122 expression on alloreactive CD8+ T cells was comparable to the LCMV-specific response and was similarly highest on central memory CD8+ T cells (TCM) compared with effector memory CD8+ T cells (TEM) (CD122 MFI TCM = 1,545 vs. TEM = 564, P = 0.0016, Figure 1J). CD122 expression was increased at distant memory time points where CD122+ T cells are increasingly of a TCM phenotype (Figure 1H). These findings suggest an important role for CD122 signaling in alloimmunity and potentially a distinctive role in alloreactive CD8+ T cell memory.
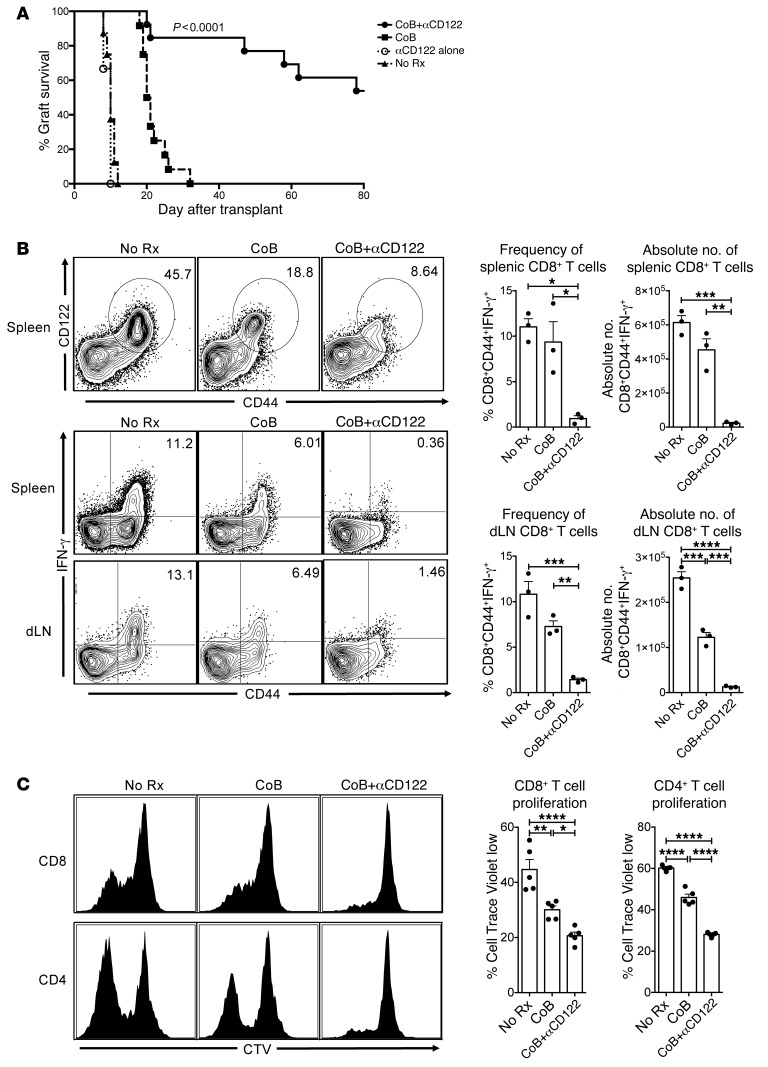
CD122 signaling underlies costimulation-independent rejection.
Immunosuppressive strategies employing CoB have already shown promise in kidney transplant recipients, but wider adoption has been limited in part due to significantly elevated rates of T cell–mediated acute rejection (5–7, 33). We sought to investigate the role of CD122 signaling in costimulation-independent rejection. C57BL/6 (H-2b) recipients of BALB/c (H-2d) skin allografts undergo vigorous CoB-resistant rejection during primary challenges (median survival time [MST] = 21 days with CoB vs. MST = 10 days without treatment, Figure 2A). Mice receiving anti-CD122 alone rejected with similar kinetics to untreated mice (MST = 10 days, Figure 2A). CoB extended graft survival modestly compared with control animals (21 days vs. 10 days, Figure 2A), but combined CD122 and CoB prevented costimulation-independent rejection and prolonged allograft survival significantly (MST > 80 days, P < 0.0001, Figure 2A). These data suggest that signaling through CD122 as part of either the IL-2 and/or the IL-15 receptor is critical for costimulation-independent rejection. We investigated the mechanisms underlying the survival benefit observed in animals treated with CoB+anti-CD122. CoB alone fails to completely suppress alloreactive CD8+ T cells, but the addition of CD122 blockade efficiently mitigates the generation of an alloimmune response (Figure 2, B and C). Combination therapy reduced both the expansion and effector function of alloreactive T cells by nearly 10-fold compared with CoB, and 20-fold compared with unmodified rejection (absolute number of dLN CD8+CD44+IFN-γ+ = 2.54 × 105 in no treatment [No Rx] vs. 1.23 × 105 in CoB vs. 1.27 × 104 in CoB + anti-CD122, P < 0.0001, Figure 2B). In a model of graft-versus-host disease we found similar effects of combined CoB and anti-CD122 on alloreactive T cell proliferation and effector function (Figure 2C). These data suggest that in the absence of traditional costimulatory signals such as CD28 and CD154, signaling through CD122 supports the expansion, activation, and effector function of naive alloreactive T cells through the effects of IL-2 and/or IL-15.
Figure 2. CD122 signaling underlies costimulation-independent rejection.
(A) Median survival time (MST) of BALB/c skin allografts on C57BL/6 recipients without treatment was 10 days (black triangles, No Rx). Anti-CD122 alone failed to improve graft survival (open circles, MST = 10 days). Mice treated with CoB (CTLA4-Ig+αCD40L) succumb to costimulation-independent rejection (black squares, MST = 21 days). Combination CoB+αCD122 prolongs survival to greater than 80 days, preventing costimulation-independent rejection in the majority of recipients (n = 6–13 per group, representative of 3 independent experiments, P < 0.0001, Mantel-Cox log-rank test). (B) Mice were sacrificed at day 10 after transplant. Representative FACS plots of splenocytes from untreated (No Rx), CoB, and CoB+αCD122-treated animals. CoB+αCD122 resulted in reduced frequency of alloreactive CD44+CD122+ CD8+ T cells. Correspondingly, there is marked decrease in frequency of CD44+IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells in both the spleen (P = 0.0048) and dLN (P = 0.0009), as well as a reduction in absolute numbers of alloreactive CD44+IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells in the spleen (P = 0.0002) and dLN (P < 0.0001). (C) In a model of acute graft-versus-host disease, C57BL/6 splenocytes were labeled with CTV and transferred into sublethally irradiated BALB/c recipients, which were either untreated (No Rx), treated with CoB, or treated with CoB+αCD122. After 72 hours, splenocytes were harvested and assessed for CTV-labeled cell division as depicted in representative histograms. Both CD8+ (P < 0.0001) and CD4+ (P < 0.0001) alloproliferation was significantly constrained with combination CoB+αCD122 treatment. P values were generated by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; bars represent the mean ± SEM of 3–5 mice per group (B–C). Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
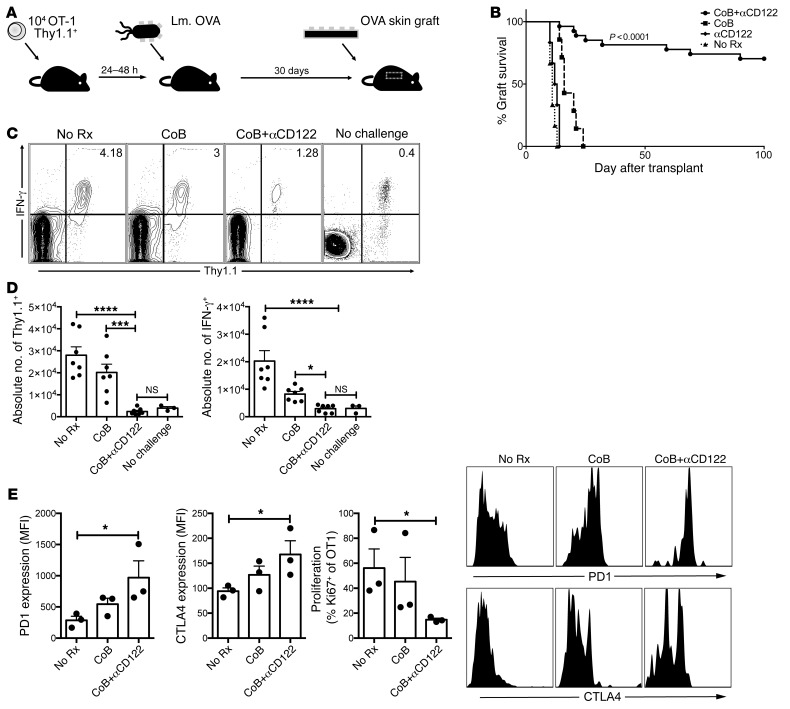
CD122 signaling supports costimulation-independent memory responses.
Immune memory can significantly contribute to transplant rejection (34, 35). Memory T cells can readily function without the requirement of traditional costimulatory signals, resulting in allograft rejection despite CoB (9, 36–38). Previous studies outlined an important role for IL-15 in memory T cell homeostasis, but the role of IL-2 and IL-15 in the generation of effective memory T cell responses remains unclear, with some groups demonstrating a critical role for IL-2 in the generation of effective recall responses, whereas others have shown an important role for IL-15 signaling in recall (22, 26, 32, 39–43). Further confounding efforts to understand the respective contribution of these cytokines in generating memory responses is the role of costimulatory signals, particularly the CD40-CD154 pathways, which can support recall responses (44, 45). Thus, we investigated the role of IL-2R and IL-15R signaling in CD8+ T cell recall in the setting of CoB. OVA-specific CD8+ T cells (OT-I) were transferred into naive C57BL/6 recipients and immunized with Listeria monocytogenes engineered to express chicken ovalbumin (Lm-OVA). After 30 days, mice were rechallenged with OVA-expressing skin grafts (Figure 3A). In the context of memory CD8+ T cell–mediated transplant rejection, anti-CD122 synergized with CoB to prolong graft survival indefinitely (MST > 100 days, P < 0.0001, Figure 3B). CoB alone fails to significantly prolong graft survival (MST = 16 days). Animals treated with anti-CD122 alone rejected with similar kinetics to animals who received no therapy (MST = 11 days). We investigated the phenotypic and functional effects underlying prolonged graft survival in a model of memory CD8+ T cell–mediated acute graft rejection. CoB alone did not significantly reduce the frequency of graft-reactive CD8+ memory T cells compared with untreated mice (Figure 3, C and D). The addition of anti-CD122 to CoB dramatically constrained the expansion and effector function of graft-reactive cells (Figure 3, C and D). Further, we observed a change in phenotype, where the combination of anti-CD122 and CoB induced a PD-1hiCTLA4hi exhausted phenotype on antigen-specific CD8+ T cells (Figure 3E). CoB+anti-CD122 reduced Ki67 expression in graft-reactive memory CD8+ T cells as well, suggesting that the difference in numbers was due at least in part to decreased expansion/proliferation (Figure 3E). These data suggest that signaling through the shared IL-2/IL-15Rβ chain during recall responses is critical for memory CD8+ T cell proliferation and effector function; however, the relative importance of IL-2R versus the IL-15R remained undetermined.
Figure 3. CD122 signaling supports costimulation-independent recall responses.
(A) In a model of memory CD8+ T cell–mediated graft rejection, OVA-specific CD8+ T cells (Thy1.1+OT-1) were transferred into naive C57BL/6 mice. Mice were immunized 24–48 hours later with Listeria monocytogenes expressing ovalbumin (Lm.OVA). After 30 days, mice were challenged with an OVA-expressing skin graft. (B) Untreated mice experienced rapid acute rejection (black triangles, No Rx, MST = 11). Mice treated with αCD122 rejected their skin grafts with similar kinetics to untreated mice (black diamonds, αCD122, MST = 13). CoB treated mice experienced memory CD8+ T cell mediated costimulation independent rejection shortly after (black squares, CoB, MST=16). Addition of αCD122 synergized with CoB to prolong graft survival indefinitely (black circles, CoB+αCD122, MST > 100 days, n = 6–13/group, P < 0.0001 Mantel-Cox log-rank test). (C) We investigated the impact of CoB+αCD122 by examining the frequency and function of graft specific CD8+ T cells in the draining lymph nodes 5 days after transplantation. Addition of αCD122 constrains the expansion of graft specific CD8+ T cells as demonstrated in representative FACS plots. (D) Both absolute number of graft specific (Thy1.1+) cells (P < 0.0001) and IFN-γ+ cells (P < 0.0001) were diminished with the addition of αCD122. (E) CoB+αCD122 therapy resulted in increased coinhibitory receptor expression on remaining graft specific CD8+ T cells. Thy1.1+ cells demonstrated increased PD-1 (P = 0.0303) and CTLA4 (P = 0.0065) expression. Additionally, decreased Ki67 expression (P = 0.0250) indicated reduced cell-cycle entry. (C–E) P values were generated by 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of 3–7 mice per group. Results are representative of 5 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
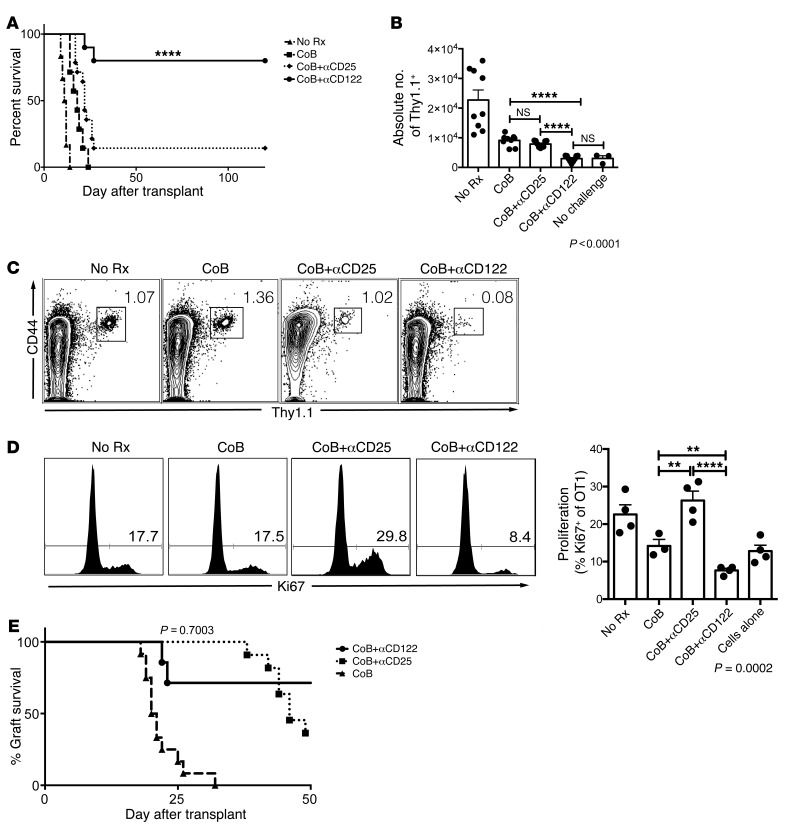
Antigen-specific memory T cells do not require the high-affinity IL-2R to mediate CoB-resistant rejection.
Currently approved immunosuppressive strategies for transplant recipients include the use of anti-CD25 therapies (46, 47). The role of IL-2 and IL-15 in the generation of recall responses is the subject of great interest for vaccine development, cancer immunotherapy, autoimmunity, and transplantation (31). We investigated the impact of the addition of a short course of anti-CD25 mAb as an adjuvant therapy to CoB in this memory T cell–mediated model of graft rejection. The addition of anti-CD25 failed to prolong graft survival (MST = 22 days, Figure 4A), whereas the addition of anti-CD122 therapy, which blocks IL-15 and IL-2 signaling, prolonged graft survival indefinitely and controlled the expansion of graft-reactive memory T cells, relative to CoB or CoB+anti-CD25 (Figure 4, B and C). Mice who received OT-1 adoptive transfer and Lm.OVA immunization but no skin graft challenge were labeled “No Challenge” and utilized as controls. Combined CoB+anti-CD25 failed to control the frequency of cells entering the cell cycle compared with the significant reduction in animals treated with CoB+anti-CD122, as measured by the frequency of cells expressing Ki67 (mean frequency ± SEM of Ki67+ of Thy1.1+ = 22.58 ± 2.58 in No Rx vs. 14.2 ± 1.71 in CoB vs. 7.66 ± 0.55 in CoB+anti-CD122 vs. 26.28 ± 2.52 in CoB+anti-CD25 vs. 12.81 ± 1.59 in No Challenge, P < 0.0001, Figure 4D). This increased cell cycle entry may be due to inhibition or reduction of Tregs in CoB+anti-CD25–treated mice.
Figure 4. Antigen-specific memory T cells do not require high-affinity IL-2R to mediate CoB resistant rejection.
(A) Utilizing the same model of memory CD8+ T cell mediated graft rejection as modeled in Figure 3, we evaluated the relative importance of the high-affinity IL-2 receptor by blocking CD25, compared with blocking CD122, which interrupts both the IL-2R and IL-15R. Untreated mice rejected rapidly (black triangle, MST = 11 days). CoB alone led to costimulation-independent rejection (black squares, MST = 16 days). Combined CoB+αCD25 (black diamonds, MST = 23 days) failed to prevent memory CD8+ T cell–mediated CoB-resistant rejection, whereas combined CoB+αCD122 resulted in indefinite graft survival in the majority of transplant recipients (black circles, MST > 100 days, P < 0.0001, n = 6–13 per group, Mantel-Cox log-rank test). (B) CoB+αCD122 synergistically controlled the expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells during recall responses more effectively than CoB or CoB+αCD25 (P < 0.0001). (C) Representative FACS plot demonstrate reduced frequency of antigen-specific cells in CoB+αCD122-treated animals compared with CoB or CoB+αCD25. (D) CoB+αCD122 therapy resulted in a significant reduction of antigen-specific cells entering cell cycle, demonstrated by reduced Ki67 expression in representative histograms and the corresponding graph comparing CoB+αCD122 versus CoB or CoB+αCD25 (P = 0.0002). (E) In the BALB/c to C57BL/6 skin transplant model, a primary alloimmune challenge, the addition of αCD25 therapy (black squares), which interrupts the high-affinity IL-2R, demonstrated similar efficacy in prolonging allograft survival as the addition of αCD122 (black circles), which blocks both the IL-2R and IL-15R complexes. P values were generated by 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of 3–9 mice per group. Results are representative of 5 independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.
Previous studies underscored the importance of the high-affinity IL-2 receptor in costimulation-independent rejection during a primary allo-immune response (48). Our studies confirmed these results, demonstrating that both anti-CD25 and anti-CD122 synergize with CoB to prolong graft survival during a primary response (Figure 4E). These data suggest that the IL-15R receptor is necessary for costimulation-independent memory T cell responses, whereas the high-affinity IL-2R receptor is dispensable. In the setting of a primary allo-immune challenge, costimulation-independent cells rely on the high-affinity IL-2 receptor. Targeting CD122 interrupts both the IL-2 and IL-15 receptors, without the potential unwanted effects of anti-CD25 therapies on Tregs.
CD122 phenotype and function in rhesus macaques.
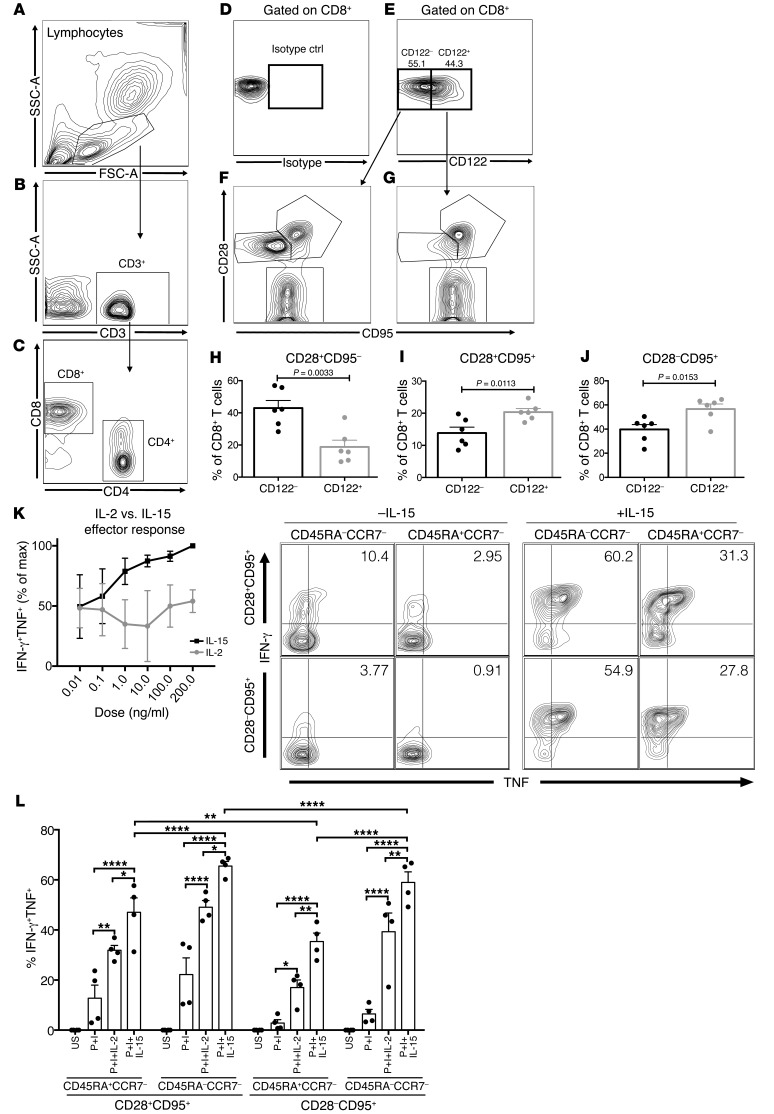
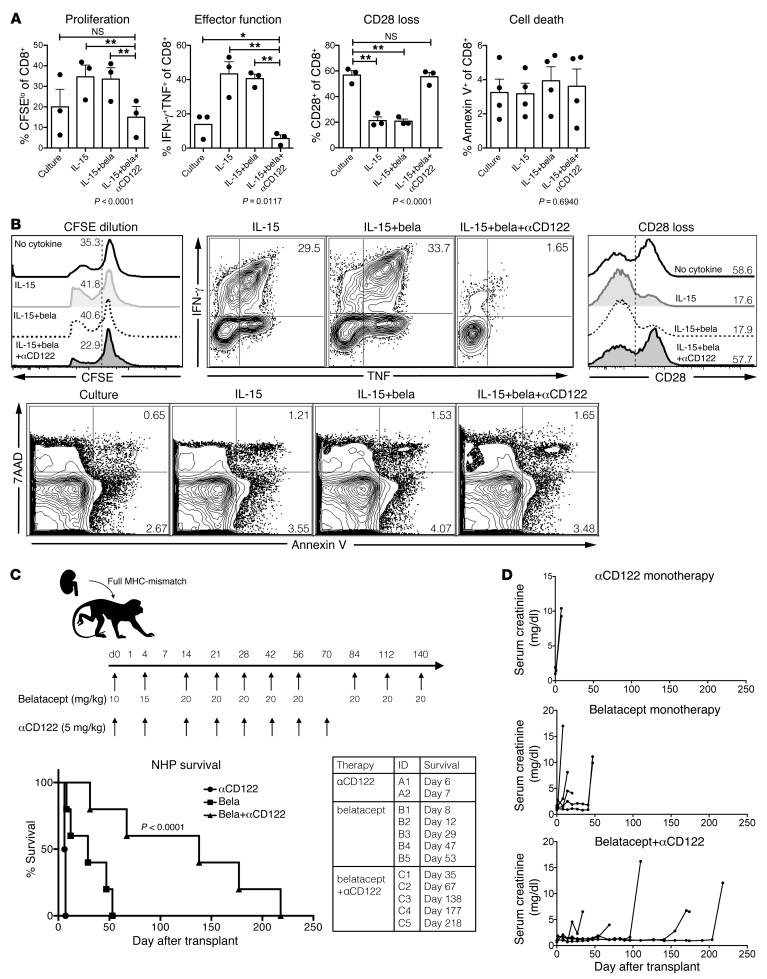
In an effort to evaluate whether these findings were potentially translatable to patients we sought to characterize the phenotype and function of CD122 on CD8+ T cells in a preclinical model using rhesus macaques. We first characterized CD122 expression on CD8 T cells using an appropriate isotype control (Figure 5, A–E). CD122 is highly expressed on TCM (CD28+CD95+) and TEM (CD28–CD95+) but not naive (CD28+CD95–) CD8+ T cells (Figure 5, F–J). Next, we assessed the effector function of CD8+ memory T cell subsets and the relative effects of exogenous IL-2 and IL-15. The addition of IL-15 for 5 hours dramatically increased effector cytokine production by CD8+ T cells, more so than IL-2 (Figure 5, K and L). Analysis of intergroup differences revealed that in all memory subsets, IL-15 was more potent at recruiting cells into an effector response when compared with IL-2 (Figure 5L). Increasing, albeit supra-therapeutic, concentrations of IL-2 may elicit similar responses (Figure 5K). We have previously reported that CD28+ memory T cells in rhesus monkeys and humans predict CoB-resistant rejection (12, 13). We found CD28+ memory T cells more responsive to exogenous IL-15 than CD28– memory T cell subsets (Figure 5L). To better understand the mechanism(s) by which CD122 signaling contributes to alloreactivity, we utilized an ex vivo mixed lymphocyte reaction with NHP PBMCs. We found that IL-15 augmented alloreactivity, specifically by increasing proliferation and effector function, and IL-15 induced a loss of CD28 expression in CD8+ T cells (Figure 6, A and B). Belatacept fails to inhibit alloreactivity in vitro, but the addition of a humanized CD122-specific monoclonal antibody (HuABC2) synergistically inhibits proliferation, effector function, and CD28 downregulation in CD8+ T cells without evidence of increased cell death (Figure 6, A and B). These data suggest CD122 signaling, particularly via IL-15, in primate CD8+ T cells is sufficient to support costimulation-independent responses, and in fact CD122 signaling drives the loss of the costimulatory molecule CD28 while augmenting proliferation and effector function, potentiating therapeutic resistance to CD28-directed therapies, such as belatacept.
Figure 5. CD122 phenotype and function on rhesus macaque CD8 T cells.
(A) Rhesus PBMCs were analyzed by FACS. Gates based on lymphocytes were defined by forward and side-scatter, (B) further gated on CD3+ T cells and then (C) CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells. (D) Gating on CD8+ T cells, an isotype control was utilized to define (E) CD122– versus CD122+ CD8+ T cells. (F) CD122– cells demonstrated higher frequencies of CD28+CD95– naive CD8+ T cells in contrast to (G) CD122+ cells which were predominantly TEM CD28–CD95+ or TCM CD28+CD95+ CD8+ T cells. (H–J) The increased memory phenotype of CD122+ (gray bars) CD8+ T cells versus the more naive phenotype of CD122– (black bars) CD8+ T cells is depicted graphically. (K) The addition of IL-15 in vitro increased frequencies of CD8+ T cells recruited into the effector response as measured by dual IFN-γ and TNF production. IL-15 augments effector function across the spectrum of memory differentiation, as defined by CD28, CD95, CD45RA, and CCR7 expression. (L) IL-15 was superior to IL-2 in recruiting CD8+ T cells into an effector response. IL-15 augments cytokine production by CD28+CD95+ cells compared with CD28–CD95+ cells (P < 0.0001). (H–J) P values were generated by Student’s t test, 2-tailed. (L) P values were generated by 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; bars represent the mean ± SEM of 3–6 rhesus macaques. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001.
Figure 6. Humanized αCD122 synergizes with belatacept to inhibit alloreactivity and prolong NHP transplant survival.
(A) MLR of NHP PBMCs between fully MHC-mismatched pairs. CFSE-labeled responder lymphocytes were incubated for 96 hours with irradiated stimulators (culture), with IL-15, IL-15+bela (belatacept), or IL-15+bela+αCD122. The addition of belatacept alone did not suppress proliferation, effector function, or loss of CD28 expression. The combination of bela+αCD122 reduced proliferation (P < 0.0001), diminished effector function (P = 0.0117), and restored CD28 expression on CD8+ T cells to similar levels as culture conditions without IL-15 (P = 0.8011). (B) Representative FACS plots of CD8+ T cell expansion by CFSE dilution, effector function as measured by dual IFN-γ and TNF production, and apoptosis and cell death as measured by 7-AAD and Annexin V staining (corresponds to graphs in A). (C) NHPs underwent bilateral nephrectomy and life-sustaining renal transplantation from a fully MHC-mismatched NHP donor. Animals were treated with humanized αCD122 alone (5 mg/kg, black circles, n = 2, MST = 7 days), belatacept alone (black squares, n = 5, MST = 29 days), or bela+αCD122 (black triangles, n = 5, MST = 138 days, P < 0.0001, Mantel-Cox log-rank test). Combination bela+αCD122 synergized to prolong NHP survival compared with belatacept monotherapy, or αCD122 monotherapy. (D) Corresponding serum creatinine curves of NHPs and demonstrated rejection were preceded by declining graft function. (A–B) P values were generated by repeat measures 1-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; bars represent the mean ± SEM of 3 NHPs per group. In vitro results are representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
A humanized anti-CD122 mAb synergizes with belatacept to significantly prolong allograft survival in NHPs.
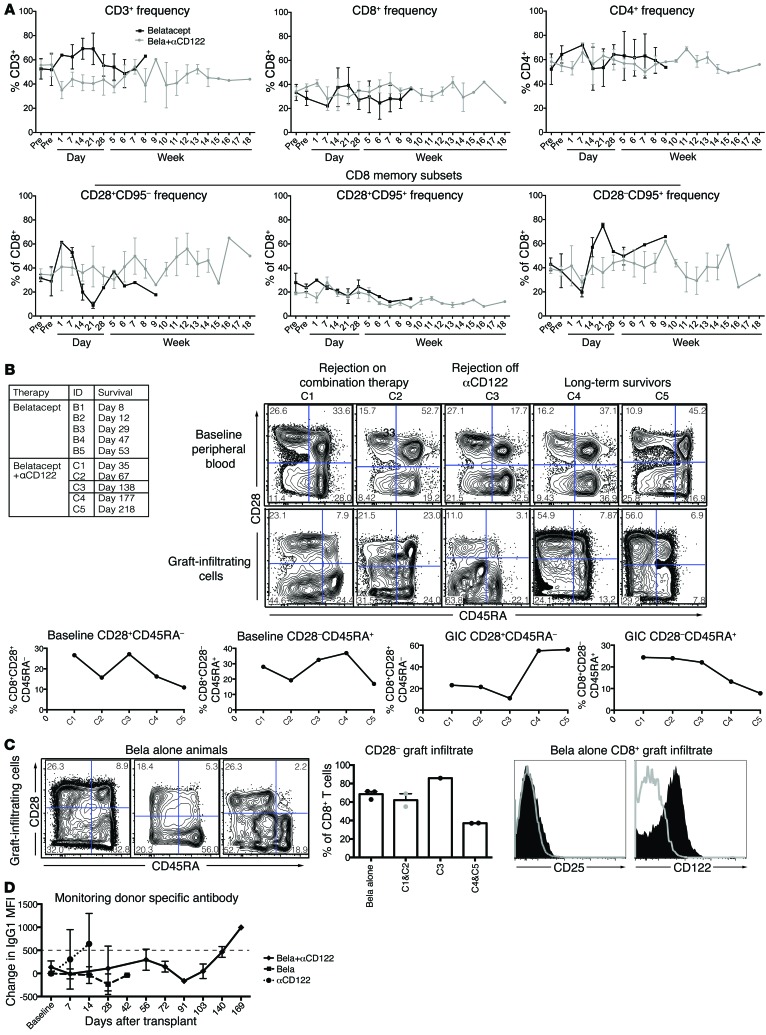
We next tested whether treatment with a humanized anti-CD122 antibody would impact CoB-resistant rejection in a NHP kidney transplant model (Figure 6C). This rigorous model gives rise to allograft rejection that is resistant to CoB with belatacept monotherapy (1). We observed no survival benefit in animals treated with anti-CD122 monotherapy (n = 2, MST = 7 days, Figure 6C). The combination of CoB using belatacept and anti-CD122 significantly prolonged kidney transplant survival in NHPs (n = 5, MST = 138 days, P < 0.0001, Figure 6C). We did not observe a marked increase in viral reactivation, confirming an absence of overt over-immunosuppression (Supplemental Figure 1; supplemental material available online with this article; https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI95914DS1). These data indicate that belatacept-resistant rejection relies on CD122 signaling. We assessed the impact of combined belatacept plus anti-CD122 as compared with belatacept alone and found no significant impact on T cell subsets (Figure 7A). Belatacept+anti-CD122 improved survival compared with belatacept alone; however, the kinetics of rejection on combination therapy allowed for further intragroup comparison. Two animals, C1 and C2, rejected on combination therapy (day 35 and day 67) whereas one animal rejected after cessation of anti-CD122 (C3, day 148), and 2 animals rejected after withdrawal of both anti-CD122 and belatacept (C4, day 177 and C5, day 218). Further analysis revealed no significant differences in pretransplant memory T cell immunophenotype; however, graft-infiltrating CD8+ T cells in animals that rejected after withdrawal of all therapy (C4 and C5) demonstrated a similar phenotype with increased CD28+ memory T cells. This is in contrast to animals that rejected on combination therapy (C1 and C2), in which there were higher frequencies of CD28– infiltrate (C1 69% and C2 55% vs. C4 37.3% and C5 37%, Figure 7C). While there were no significant pretransplant differences in T cell immunophenotype between belatacept or belatacept+anti-CD122–treated animals, only 3 belatacept monotherapy animals had sufficient graft infiltrate to analyze with FACS and interestingly, all demonstrated a marked CD28– allograft infiltrate (Figure 7, A–C). Flow cytometric characterization of belatacept-resistant rejectors revealed uniform upregulation of CD122, but not CD25, on all graft-infiltrating T cells at the time of rejection (Figure 7C). Importantly, both belatacept and belatacept+anti-CD122–treated animals did not develop donor-specific antibody (DSA) while on combination therapy (Figure 7D).
Figure 7. Immunologic impact of combined belatacept+αCD122 therapy in NHP kidney transplant recipients.
(A) Longitudinal analysis of CD3+ T cell frequencies did not reveal significant differences in CD4+ or CD8+ subsets, nor were there significant changes in memory subsets between belatacept (black squares) and belatacept+αCD122 (gray circles) treated animals. (B) Comparison of pretransplant CD8+ memory subsets did not discriminate between animals which rejected on combination therapy (C1 and C2) versus those which rejected after withdrawal of anti-CD122 (C3) versus animals with prolonged survival (C4 and C5). However, graft infiltrating CD8+ T cells in animals which experienced prolonged survival demonstrated a marked increase in CD28+CD45RA– T cells. Data represented by FACS plots and corresponding graphs depicting memory subset frequencies. (C) Characterization of graft infiltrate from 3 animals treated with belatacept alone demonstrating similar graft infiltrate phenotype to C1 and C2, combination therapy–resistant animals. Sample FACS plot of one belatacept alone animal demonstrating no increased expression of CD25 in graft infiltrating CD8+ T cells (solid black histogram) compared with peripheral blood (gray histogram, no fill) at the time of rejection. In contrast graft infiltrating CD8+ T cells (solid black histogram) had increased expression of CD122. (D) Combination belatacept+αCD122 (black diamonds) and belatacept monotherapy (black squares) treated animals did not develop donor-specific antibody during treatment. Animals receiving αCD122 monotherapy (black circles) demonstrated a positive DSA at the time of sacrifice. DSA greater than 500 MFI was positive.
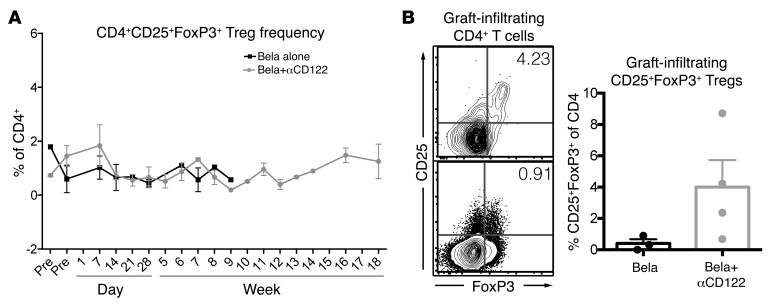
Regulatory T cells play a key role in graft tolerance, and may be adversely impacted with current CD25-directed therapies. We assessed the longitudinal peripheral blood frequencies of Tregs (CD4+CD25+FoxP3+) and found no significant impact on the frequency of Tregs with either belatacept monotherapy or the combination of anti-CD122 and belatacept (Figure 8A). We did, however, measure the frequency of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ cells within graft infiltrate and found a trend toward an increased frequency of Tregs in the combination belatacept+anti-CD122–treated animals (Figure 8B).
Figure 8. Increased graft infiltrating Tregs in combination belatacept+αCD122.
(A) Longitudinal analysis of Tregs in the peripheral blood of animals treated with belatacept monotherapy (black squares) compared with belatacept+αCD122 (gray circles) revealed no significant differences between the treatment groups. (B) Sample FACS plot of combination belatacept+αCD122 (top) treated animal compared with belatacept monotherapy (bottom). Graphical representation demonstrating a trend toward increased graft infiltrating Tregs in combination bela+αCD122 (gray circles, mean ± SEM, 4.001% ± 1.732%) compared with belatacept monotherapy (black circles, 0.4043% ± 0.2462%, P = 0.1414, Student’s t test).
Discussion
The introduction of potent, nonspecific immunosuppression with calcineurin inhibitors dramatically improved short-term outcomes in solid organ transplantation. Despite excellent improvements early after transplantation, the late outcomes remain essentially unchanged and represent the greatest challenge for transplant recipients (49). Unfortunately, most transplant patients eventually lose their allograft from rejection or die as the result of increased cardiovascular complications or infections. The advent of CoB as a more targeted strategy for transplant immunosuppression has demonstrated the first evidence of improved long-term outcomes and graft function in the setting of clinical trials and in posttrial use (5, 7). However, a significant number of patients treated with belatacept experienced elevated rates and grades of acute rejection within the first 6 months of transplantation (6, 7). Studies that investigate T cell reactivity in the setting of CoB improve our understanding of the dynamic signaling requirements of T cells while addressing a pressing clinical need for safer, more specific forms of immunosuppression. Signal 2 (costimulation) and signal 3 (provided by cytokines) are synergistic and in some respects redundant; in the absence of signal 2, signal 3 cytokines can support robust responses. Here we focused our investigation on the ability of signal 3 cytokines IL-2 and IL-15 to support costimulation-independent rejection. We evaluated a strategy to block both IL-2 and IL-15 signaling with a single, CD122-directed reagent in mice, and then translated our findings into a preclinical model utilizing NHPs in order to optimize CoB strategies in the setting of transplantation. The addition of anti-CD122 offered several key advantages to current transplant immunosuppression strategies: (a) abrogation of the primary immune response, (b) superior attenuation of memory CD8+ T cell recall compared with strategies targeting the high-affinity IL-2R, and (c) sparing of Tregs, which are targeted by current CD25-directed therapies in transplant, with a possible increase in the frequency of intragraft Tregs in NHPs.
IL-2 and IL-15 are structurally and genetically distinct cytokines, sharing little sequence similarity. Though these cytokines share 2 signaling subunits, CD122, the shared IL-2 and IL-15 receptor β-chain, and CD132 the common γ-chain (γc), they have distinct contact residues with CD122 and CD132 (50). Their nonredundant roles are highlighted by the divergent phenotypes of IL-2/IL-2Rα–/– mice, which suffer from autoimmunity due to CD4+CD25+ Treg deficiency, and IL-15/IL-15Rα knockout mice, which have decreased CD8+ T cells, intraepithelial lymphocytes, NK cells, and NK T cells (17–20, 51). Saturating doses of IL-2 and IL-15 give rise to nearly identical CD8+ T cell transcriptomes (50). Thus, the temporal and spatial differences in receptor subunit expression (CD25 vs. CD122) may underlie the unique roles of IL-2 and IL-15 in the generation and maintenance of adequate adaptive immune responses as opposed to unique intrinsic signaling properties of IL-2/IL-2Rα and IL-15/IL-15Rα (50, 52). IL-2 is readily taken up by CD4+CD25+ Tregs, which rapidly express the high-affinity IL-2R as predicted by high expression of CD25. On the other hand, CD122 expression is highest on CD8+ memory T cells and NK cells, allowing for formation of the high-affinity IL-15R. IL-15Rα is expressed in trans by antigen presenting cells, as well as by a number of peripheral tissue cell types, notably in renal epithelium (53). IL-15Rα presents IL-15 in complex and binds with 150 times greater affinity than circulating IL-15 to cells expressing CD122 and the common γ-chain (50, 53, 54).
The current body of knowledge emphasizes a critical role for IL-2 in the generation of effective primary immune responses, memory differentiation, and recall, whereas IL-15 is conceptualized as providing homeostatic proliferative signals for memory T cells, and recently, potentially providing inflammatory signals to increase memory T cell cycling (26, 41, 43, 55–57). The type of immune challenge used in these studies, the chronicity and antigen load, as well as the strength and duration of cytokine signaling, influences the quality of CD8+ T cell memory development and recall responses (58–61). It is likely that costimulation confounds studies of the individual contributions of either IL-2 or IL-15 (45, 62, 63). Costimulation provides a set of redundant activation signals that may obscure the unique contribution of either IL-2 or IL-15 in recall in studies utilizing IL-2/IL-2Rα or IL-15/IL-15Rα mice (42, 63). In our studies, the use of CoB revealed distinct roles for IL-2R compared with IL-15R. The high-affinity IL-2R was dispensable for effective memory CD8+ T cell recall responses, whereas blockade of CD122, which interrupts both IL-2R and IL-15R, abrogated memory CD8+ T cell–dependent graft rejection. The source and sequence of events leading to IL-15R–mediated costimulation-independent recall responses in graft rejection requires further investigation.
Targeting CD122 provides the opportunity to block 2 distinct pathways that support T cell responses with a single reagent. Both allograft rejection and autoimmune disease are characterized by naive and memory T cell recruitment into a pathogenic response, thus there is a need to address both primary and recall responses in order to ameliorate disease. Previous studies have underscored the potential of the IL-15 pathway to mediate autoimmune disease and allograft rejection. Interruption of IL-15 signaling alleviated autoimmunity and prevented islet allograft rejection (21, 64–68). Current, clinically approved therapeutics in transplantation are designed to solely interrupt the high-affinity IL-2R in order to promote allograft acceptance (46, 47). Our data suggest that targeting both the IL-2 and IL-15 pathways with a single agent, anti-CD122, may be a superior strategy for limiting pathogenic T cell responses.
Beyond its role as a signaling receptor subunit for both IL-2 and IL-15, recent studies have identified CD122 expression as a marker of stem cell memory T cells (TSCM) (69–71). These cells have superior proliferative capacity compared with conventional TCM or TEM and in a model of graft-versus-host disease these cells required CD28 and IL-15 signaling (72). Studies aimed at assessing the role of TSCM in alloimmunity and autoimmunity, and the role of CD122 as a phenotypic or functional marker, may aid in the development of therapeutic strategies. Others have defined a role for CD122+ CD8+ T cells as a potent regulator of the immune response (73, 74). In both mice and NHPs, we found that the addition of CD122 blockade prolonged allograft survival. Current, clinically approved CD25-directed therapy is thought to have a detrimental impact on conventional Tregs, which support allograft tolerance. Adoption of a strategy that targets CD122 rather than CD25 may spare CD4+CD25+ Tregs, as we found that addition of CD122 blockade may lead to increased intragraft Tregs. The physiologic impact of CD122+CD8+ regulatory T cells, and any potential detrimental impact of CD122-directed therapy on this tolerogenic subset, warrant further study.
In this report we outline a new strategy for the optimization of clinical CoB, built on a finer mechanistic understanding of the role of IL-2R and IL-15R. We translated these findings from the murine to NHP model of kidney transplantation utilizing a humanized antibody directed at CD122. Costimulation-independent responses highlight the unique role of IL-2 and IL-15, and together with emerging data regarding the capacity of IL-15 to uniquely support costimulation-independent responses of human memory CD8+ T cells, these studies provide the basis to explore potential future clinical translation (29).
Methods
Mice
C57BL/6 (H-2b) and BALB/c (H-2d) mice were obtained from the National Cancer Institute (Frederick, MD). OT-I (75) transgenic mice, purchased from Taconic Farms, were bred to Thy1.1+ background at Emory University. mOVA mice (C57BL/6 background, H-2b) (76) were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. All animals were maintained in accordance with Emory University IACUC guidelines. All animals were housed in pathogen-free animal facilities at Emory University.
Viral infection and kinetic analysis
To induce acute infection, mice were inoculated with 2 × 105 PFU LCMV acute Armstrong strain (i.p. injection). Virus-specific CD8+ T cells were monitored with APC-conjugated gp33-41 tetramer.
Donor-reactive T cell adoptive transfers and memory generation
To generate OVA-specific memory T cells, splenocytes from Thy1.1+ OT-I mice were resuspended in PBS and 1.0 × 104 Thy1.1+ OT-I T cells were injected i.v. 24–48 hours prior to inoculation with 104 CFU Lm.OVA (77) by i.p. injection. After 30 days, peripheral frequencies of Thy1.1 OT-I T cells were assessed and mice were given recall challenge with OVA-expressing skin graft from mOVA donors.
Skin transplantation and antibody treatment
Full-thickness tail or ear skin was transplanted onto the dorsal thorax of recipient mice and secured with adhesive bandages. Where indicated, mice were treated with 250 μg CTLA4-Ig (Bristol Myers Squibb), 250 μg hamster monoclonal anti-mouse CD154 (MR-1, BioXcell), 200 μg anti-CD122 (ChMBC7, JN Biosciences), or 200 μg anti-CD25 (PC61, BioXcell) i.p. on days 0, 2, 4, and 6 after transplantation. ChMBC7 is available from JN Biosciences via material transfer agreement.
Acute graft-versus-host disease model
C57BL/6 splenocytes were labeled with 10 μM Cell Trace Violet (CTV, C34571, Invitrogen). C57BL/6 CTV-labeled splenocytes (3 × 107) were transferred i.v. into sublethally irradiated (800 rads) BALB/c recipients, and selected groups received therapy on days 0 and 2 as described above. Splenocytes were harvested on day 3 and analyzed by flow cytometry to assess CTV-labeled cell division. Experiments involved 3–5 mice per group, and were verified in 3 independent repeats.
Donor-recipient pair selection and kidney transplantation
All experiments described herein were performed in compliance with the principles set forth in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources, National Research Council, DHHS). Outbred rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) ranging between 3 and 5 years old were obtained from AlphaGenesis, Inc., and Yerkes National Primate Research Center. Donor-recipient pairs were chosen to maximize genetic disparity at both MHC class I and class II alleles based on 454 deep-sequencing analysis (University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI). Animals were heparinized (100 U/kg) during organ procurement and implantation. Left native nephrectomy was performed at least 3 weeks prior to transplantation, and a completion right native nephrectomy was performed at the time of transplantation. All transplanted animals were monitored with daily clinical assessment and serial laboratory evaluations, including complete blood count and serum chemistry. Animals demonstrated excellent graft function postoperatively and were sacrificed at the time of allograft rejection, defined by graft dysfunction. Depressed renal function pursuant to allograft rejection was determined by 2 consecutive measurements of Cr greater than 5 or BUN greater than 120.
NHP experimental groups and immunomodulation
Rhesus macaques underwent bilateral nephrectomy and life-sustaining renal allograft transplantation. All donor-recipient pairs were MHC defined and maximally mismatched. Five animals received belatacept (Bristol Myers Squibb) as follows: d0, 10 mg/kg; d4, 15 mg/kg; d14–d28, 20 mg/kg weekly; d42, 20 mg/kg; d56, 20 mg/kg; d84, 20 mg/kg; d112, 20 mg/kg; d140, 20 mg/kg. Two animals received 5 mg/kg anti-CD122 alone (HuABC2, JN Biosciences) on d0, d4, d7, d14, d21, d28, d42, d56, and d70. HuABC2 is available from JN Biosciences via material transfer agreement. Five animals received combination belatacept and anti-CD122 as described (Figure 6C).
Antibodies and flow cytometric analysis
Nonhuman primates.
Flow cytometric analysis was performed up to 3 times before transplantation and serially after transplantation to characterize peripheral blood immune cell phenotypes. Total T cells and T cell subsets were quantified by complete blood cell count and flow cytometry. Fresh PBMCs were isolated by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation (BD Biosciences). PBMCs were stained with the following mAbs: CD3 PacBlue, CD95 V450, CD3 Alexa 700, CD4 PerCP-Cy5.5, CD8 V500, CD28 PE-Cy7, CD25 PE-Cy7, IFN-γ PE-Cy7, CD28 APC, TNF APC, CD122 (both clones Mik2 and Mikβ3) (all from BD Biosciences). PE human IgG1 isotype control clone QA16A12 was utilized to define CD122 expression in Figure 5 (Biolegend). PBMCs (1.5 × 106) were incubated with appropriately titered antibodies for 15 minutes at 4°C and washed twice. For intracellular staining, cells were fixed and permeabilized using the BD Cytofix/Cytoperm kit (BD Biosciences) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Intracellular staining was performed with FoxP3 V450 (Biolegend) to detect Tregs. Samples were acquired immediately on a BD LSR II multicolor flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and data were analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree Star). For mixed lymphocyte reactions, 1 × 106 PBMCs were labeled with CFSE labeling dye, and incubated with CTV-labeled and irradiated MHC mismatched stimulator PBMCs (1 × 106). For the stimulation assay, 1.5 × 106 PBMCs were cultured in RPMI 1640 (Corning Cellgro) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and stimulated with 10 μM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and 200 nM ionomycin (Sigma-Aldrich) for 5 hours. IL-2 (100 ng/ml) and/or IL-15 (10 ng/ml) were utilized in both 4–5 hour stimulations (Figure 5) and in mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) (Figure 6) as described (Peprotech). PBMCs were washed twice prior to antibody staining and data acquisition.
Murine
Surface stains and flow cytometry.
Spleens or draining axillary and brachial LNs were stained for CD4, CD8, Thy1.1, CTLA4, PD-1, KLRG1, CD127, CD62L, CD122 (clone 5H4, different regional binding site than ChMBC7), and CD44 (Biolegend). Samples were analyzed using an LSRII FACS machine (BD Biosciences). Data were analyzed using FlowJo software (Treestar).
Intracellular cytokine staining.
Where indicated, responder lymphocytes or splenocytes were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin or 10 nM OVA257–264 (Genscript) in the presence of 10 μg/ml Brefeldin A for 4–5 hours. An intracellular staining kit was used to detect TNF, IFN-γ (Biolegend), and IL-2 (BD Biosciences) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistics
Survival statistics were calculated using a log-rank test. T cell frequencies, absolute numbers, and MFI were compared using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, or unpaired t test (comparison between 2 groups). Data were analyzed using Prism 6 (GraphPad Software). P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Study approval
Both murine and NHP experimental subjects received humane care and treatment in accordance with Emory University IACUC guidelines, and all experimental protocols utilizing animals were conducted with approval by Emory University’s institutional review board.
Author contributions
DVM and ABA designed the study and experiments. DVM conducted the murine infection and skin graft experiments, primate experiments, and data analysis, and wrote the manuscript. YD helped with murine skin graft experiments. DVM, ABA, LBH, and SCK performed primate kidney transplants. CPB assisted with primate flow cytometry. JYT developed murine and humanized anti-CD122 mAbs. EAS and JJ provided veterinary care and supervision of primate experiments. CPL provided help with experimental design. ABA conceived of many experiments, assisted with analysis, and helped write the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
DVM was supported by the NIH Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award Individual Predoctoral MD/PhD Fellowship (F30 DK109665). The primate experiments were also supported by the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases Nonhuman Primate Transplantation Tolerance Cooperative Study Group grant AI051731 from NIH. Primate experiments were also supported by the Yerkes National Primate Research Center base grant RR00165.
Version 1. 09/17/2018
Electronic publication
Version 2. 10/01/2018
Print issue publication
Funding Statement
Nonhuman Primate Transplantation Tolerance Cooperative Study Group (NHPCSG)Opportunity Pool Supplement
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: ABA has received research funding and consulting fees from BMS. JYT is an employee and managing partner of JN Biosciences LLC.
Reference information: J Clin Invest. 2018;128(10):4557–4572.https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI95914.
Contributor Information
David V. Mathews, Email: david.mathews@emory.edu.
Ying Dong, Email: ydong@emory.edu.
Christian P. Larsen, Email: clarsen@emory.edu.
Andrew B. Adams, Email: Andrew.b.adams@emory.edu.
References
- 1.Larsen CP, et al. Rational development of LEA29Y (belatacept), a high-affinity variant of CTLA4-Ig with potent immunosuppressive properties. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(3):443–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.00749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vincenti F, et al. Costimulation blockade with belatacept in renal transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(8):770–781. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vanrenterghem Y, et al. Belatacept-based regimens are associated with improved cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors compared with cyclosporine in kidney transplant recipients (BENEFIT and BENEFIT-EXT studies) Transplantation. 2011;91(9):976–983. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31820c10eb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rostaing L, et al. Long-term belatacept exposure maintains efficacy and safety at 5 years: results from the long-term extension of the BENEFIT study. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(11):2875–2883. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vincenti F, et al. Belatacept and long-term outcomes in kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(4):333–343. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1506027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vincenti F, et al. A phase III study of belatacept-based immunosuppression regimens versus cyclosporine in renal transplant recipients (BENEFIT study) Am J Transplant. 2010;10(3):535–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.03005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Adams AB, et al. Belatacept combined with transient calcineurin inhibitor therapy prevents rejection and promotes improved long-term renal allograft function. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(11):2922–2936. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bingaman AW, Farber DL. Memory T cells in transplantation: generation, function, and potential role in rejection. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(6):846–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Adams AB, et al. Heterologous immunity provides a potent barrier to transplantation tolerance. J Clin Invest. 2003;111(12):1887–1895. doi: 10.1172/JCI17477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Floyd TL, et al. Limiting the amount and duration of antigen exposure during priming increases memory T cell requirement for costimulation during recall. J Immunol. 2011;186(4):2033–2041. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Trambley J, et al. Asialo GM1+ CD8+ T cells play a critical role in costimulation blockade-resistant allograft rejection. J Clin Invest. 1999;104(12):1715–1722. doi: 10.1172/JCI8082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mathews DV, et al. Belatacept-resistant rejection is associated with CD28+ memory CD8 T cells. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(9):2285–2299. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cortes-Cerisuelo M, et al. Increased pretransplant frequency of CD28+ CD4+ TEM predicts Belatacept-resistant rejection in human renal transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2017;17(9):2350–2362. doi: 10.1111/ajt.14350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Appay V, van Lier RA, Sallusto F, Roederer M. Phenotype and function of human T lymphocyte subsets: consensus and issues. Cytometry A. 2008;73(11):975–983. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mahnke YD, Brodie TM, Sallusto F, Roederer M, Lugli E. The who’s who of T-cell differentiation: human memory T-cell subsets. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(11):2797–2809. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ikemizu S, Chirifu M, Davis SJ. IL-2 and IL-15 signaling complexes: different but the same. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(12):1141–1142. doi: 10.1038/ni.2472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sadlack B, Kühn R, Schorle H, Rajewsky K, Müller W, Horak I. Development and proliferation of lymphocytes in mice deficient for both interleukins-2 and -4. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24(1):281–284. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lodolce JP, et al. IL-15 receptor maintains lymphoid homeostasis by supporting lymphocyte homing and proliferation. Immunity. 1998;9(5):669–676. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80664-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kennedy MK, et al. Reversible defects in natural killer and memory CD8 T cell lineages in interleukin 15-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 2000;191(5):771–780. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.5.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, Schimpl A, Feller AC, Horak I. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell. 1993;75(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80067-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yokoyama S, et al. Antibody-mediated blockade of IL-15 reverses the autoimmune intestinal damage in transgenic mice that overexpress IL-15 in enterocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(37):15849–15854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908834106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Becker TC, et al. Interleukin 15 is required for proliferative renewal of virus-specific memory CD8 T cells. J Exp Med. 2002;195(12):1541–1548. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Judge AD, Zhang X, Fujii H, Surh CD, Sprent J. Interleukin 15 controls both proliferation and survival of a subset of memory-phenotype CD8(+) T cells. J Exp Med. 2002;196(7):935–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Surh CD, Sprent J. Homeostasis of naive and memory T cells. Immunity. 2008;29(6):848–862. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sneller MC, et al. IL-15 administered by continuous infusion to rhesus macaques induces massive expansion of CD8+ T effector memory population in peripheral blood. Blood. 2011;118(26):6845–6848. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-377804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Richer MJ, Pewe LL, Hancox LS, Hartwig SM, Varga SM, Harty JT. Inflammatory IL-15 is required for optimal memory T cell responses. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(9):3477–3490. doi: 10.1172/JCI81261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chiu WK, Fann M, Weng NP. Generation and growth of CD28nullCD8+ memory T cells mediated by IL-15 and its induced cytokines. J Immunol. 2006;177(11):7802–7810. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Miyagawa F, et al. IL-15 serves as a costimulator in determining the activity of autoreactive CD8 T cells in an experimental mouse model of graft-versus-host-like disease. J Immunol. 2008;181(2):1109–1119. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.2.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Traitanon O, et al. IL-15 induces alloreactive CD28(-) memory CD8 T cell proliferation and CTLA4-Ig resistant memory CD8 T cell activation. Am J Transplant. 2014;14(6):1277–1289. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bluestone JA, et al. The effect of costimulatory and interleukin 2 receptor blockade on regulatory T cells in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2008;8(10):2086–2096. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02377.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Waldmann TA. The biology of interleukin-2 and interleukin-15: implications for cancer therapy and vaccine design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(8):595–601. doi: 10.1038/nri1901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ku CC, Murakami M, Sakamoto A, Kappler J, Marrack P. Control of homeostasis of CD8+ memory T cells by opposing cytokines. Science. 2000;288(5466):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5466.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kaplan B. Belatacept: the promises and challenges of belatacept and costimulatory blockade. Am J Transplant. 2010;10(3):441–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Valujskikh A, Lakkis FG. In remembrance of things past: memory T cells and transplant rejection. Immunol Rev. 2003;196:65–74. doi: 10.1046/j.1600-065X.2003.00087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ford ML, Larsen CP. Transplantation tolerance: memories that haunt us. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(86):86ps22. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brook MO, Wood KJ, Jones ND. The impact of memory T cells on rejection and the induction of tolerance. Transplantation. 2006;82(1):1–9. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000226082.17507.da. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Valujskikh A, Pantenburg B, Heeger PS. Primed allospecific T cells prevent the effects of costimulatory blockade on prolonged cardiac allograft survival in mice. Am J Transplant. 2002;2(6):501–509. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-6143.2002.20603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Croft M, Bradley LM, Swain SL. Naive versus memory CD4 T cell response to antigen. Memory cells are less dependent on accessory cell costimulation and can respond to many antigen-presenting cell types including resting B cells. J Immunol. 1994;152(6):2675–2685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Goldrath AW, et al. Cytokine requirements for acute and Basal homeostatic proliferation of naive and memory CD8+ T cells. J Exp Med. 2002;195(12):1515–1522. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tan JT, Ernst B, Kieper WC, LeRoy E, Sprent J, Surh CD. Interleukin (IL)-15 and IL-7 jointly regulate homeostatic proliferation of memory phenotype CD8+ cells but are not required for memory phenotype CD4+ cells. J Exp Med. 2002;195(12):1523–1532. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mitchell DM, Ravkov EV, Williams MA. Distinct roles for IL-2 and IL-15 in the differentiation and survival of CD8+ effector and memory T cells. J Immunol. 2010;184(12):6719–6730. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mathieu C, et al. IL-2 and IL-15 regulate CD8+ memory T-cell differentiation but are dispensable for protective recall responses. Eur J Immunol. 2015;45(12):3324–3338. doi: 10.1002/eji.201546000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schluns KS, Williams K, Ma A, Zheng XX, Lefrançois L. Cutting edge: requirement for IL-15 in the generation of primary and memory antigen-specific CD8 T cells. J Immunol. 2002;168(10):4827–4831. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.10.4827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bevan MJ. Helping the CD8(+) T-cell response. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(8):595–602. doi: 10.1038/nri1413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hernandez MG, Shen L, Rock KL. CD40 on APCs is needed for optimal programming, maintenance, and recall of CD8+ T cell memory even in the absence of CD4+ T cell help. J Immunol. 2008;180(7):4382–4390. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.7.4382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nashan B, Moore R, Amlot P, Schmidt AG, Abeywickrama K, Soulillou JP. Randomised trial of basiliximab versus placebo for control of acute cellular rejection in renal allograft recipients. CHIB 201 International Study Group. Lancet. 1997;350(9086):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)09278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vincenti F, et al. Interleukin-2-receptor blockade with daclizumab to prevent acute rejection in renal transplantation. Daclizumab Triple Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(3):161–165. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199801153380304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jones TR, et al. The role of the IL-2 pathway in costimulation blockade-resistant rejection of allografts. J Immunol. 2002;168(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.3.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lamb KE, Lodhi S, Meier-Kriesche HU. Long-term renal allograft survival in the United States: a critical reappraisal. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(3):450–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ring AM, et al. Mechanistic and structural insight into the functional dichotomy between IL-2 and IL-15. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(12):1187–1195. doi: 10.1038/ni.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sadlack B, et al. Generalized autoimmune disease in interleukin-2-deficient mice is triggered by an uncontrolled activation and proliferation of CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25(11):3053–3059. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Malek TR, Castro I. Interleukin-2 receptor signaling: at the interface between tolerance and immunity. Immunity. 2010;33(2):153–165. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Giron-Michel J, et al. Interleukin-15 plays a central role in human kidney physiology and cancer through the γc signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(2):e31624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chirifu M, et al. Crystal structure of the IL-15-IL-15Ralpha complex, a cytokine-receptor unit presented in trans. Nat Immunol. 2007;8(9):1001–1007. doi: 10.1038/ni1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Williams MA, Tyznik AJ, Bevan MJ. Interleukin-2 signals during priming are required for secondary expansion of CD8+ memory T cells. Nature. 2006;441(7095):890–893. doi: 10.1038/nature04790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Obar JJ, et al. CD4+ T cell regulation of CD25 expression controls development of short-lived effector CD8+ T cells in primary and secondary responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(1):193–198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909945107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sandau MM, Kohlmeier JE, Woodland DL, Jameson SC. IL-15 regulates both quantitative and qualitative features of the memory CD8 T cell pool. J Immunol. 2010;184(1):35–44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Castro I, Yu A, Dee MJ, Malek TR. The basis of distinctive IL-2- and IL-15-dependent signaling: weak CD122-dependent signaling favors CD8+ T central-memory cell survival but not T effector-memory cell development. J Immunol. 2011;187(10):5170–5182. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kalia V, Sarkar S, Subramaniam S, Haining WN, Smith KA, Ahmed R. Prolonged interleukin-2Ralpha expression on virus-specific CD8+ T cells favors terminal-effector differentiation in vivo. Immunity. 2010;32(1):91–103. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Castro I, Dee MJ, Malek TR. Transient enhanced IL-2R signaling early during priming rapidly amplifies development of functional CD8+ T effector-memory cells. J Immunol. 2012;189(9):4321–4330. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pipkin ME, Sacks JA, Cruz-Guilloty F, Lichtenheld MG, Bevan MJ, Rao A. Interleukin-2 and inflammation induce distinct transcriptional programs that promote the differentiation of effector cytolytic T cells. Immunity. 2010;32(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Welten SP, et al. The viral context instructs the redundancy of costimulatory pathways in driving CD8(+) T cell expansion. Elife. 2015;4:e07846. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fuse S, Zhang W, Usherwood EJ. Control of memory CD8+ T cell differentiation by CD80/CD86-CD28 costimulation and restoration by IL-2 during the recall response. J Immunol. 2008;180(2):1148–1157. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.2.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chen J, et al. Insulin-dependent diabetes induced by pancreatic beta cell expression of IL-15 and IL-15Rα. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(33):13534–13539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312911110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ferrari-Lacraz S, et al. Targeting IL-15 receptor-bearing cells with an antagonist mutant IL-15/Fc protein prevents disease development and progression in murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2004;173(9):5818–5826. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.9.5818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ferrari-Lacraz S, Zheng XX, Fueyo AS, Maslinski W, Moll T, Strom TB. CD8(+) T cells resistant to costimulatory blockade are controlled by an antagonist interleukin-15/Fc protein. Transplantation. 2006;82(11):1510–1517. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000243168.53126.d2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ferrari-Lacraz S, et al. An antagonist IL-15/Fc protein prevents costimulation blockade-resistant rejection. J Immunol. 2001;167(6):3478–3485. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.6.3478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ferrari-Lacraz S, Zheng XX, Kim YS, Maslinski W, Strom TB. Addition of an IL-15 mutant/FCgamma2A antagonist protein protects islet allografts from rejection overriding costimulation blockade. Transplant Proc. 2002;34(3):745–747. doi: 10.1016/S0041-1345(01)02900-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lugli E, et al. Superior T memory stem cell persistence supports long-lived T cell memory. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(2):594–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI66327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gattinoni L, Klebanoff CA, Restifo NP. Paths to stemness: building the ultimate antitumour T cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(10):671–684. doi: 10.1038/nrc3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Flynn JK, Gorry PR. Stem memory T cells (TSCM)—their role in cancer and HIV immunotherapies. Clin Transl Immunology. 2014;3(7):e20. doi: 10.1038/cti.2014.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Cieri N, et al. IL-7 and IL-15 instruct the generation of human memory stem T cells from naive precursors. Blood. 2013;121(4):573–584. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-431718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Dai H, Wan N, Zhang S, Moore Y, Wan F, Dai Z. Cutting edge: programmed death-1 defines CD8+CD122+ T cells as regulatory versus memory T cells. J Immunol. 2010;185(2):803–807. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Dai Z, et al. Natural CD8+CD122+ T cells are more potent in suppression of allograft rejection than CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Am J Transplant. 2014;14(1):39–48. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hogquist KA, Gavin MA, Bevan MJ. Positive selection of CD8+ T cells induced by major histocompatibility complex binding peptides in fetal thymic organ culture. J Exp Med. 1993;177(5):1469–1473. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ehst BD, Ingulli E, Jenkins MK. Development of a novel transgenic mouse for the study of interactions between CD4 and CD8 T cells during graft rejection. Am J Transplant. 2003;3(11):1355–1362. doi: 10.1046/j.1600-6135.2003.00246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Shen H, Miller JF, Fan X, Kolwyck D, Ahmed R, Harty JT. Compartmentalization of bacterial antigens: differential effects on priming of CD8 T cells and protective immunity. Cell. 1998;92(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80946-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.