Abstract
Background
The data from individual observational studies included in meta-analyses of drug effects are collected either from ad hoc methods (i.e. “primary data”) or databases that were established for non-research purposes (i.e. “secondary data”). The use of secondary sources may be prone to measurement bias and confounding due to over-the-counter and out-of-pocket drug consumption, or non-adherence to treatment. In fact, it has been noted that failing to consider the origin of the data as a potential cause of heterogeneity may change the conclusions of a meta-analysis. We aimed to assess to what extent the origin of data is explored as a source of heterogeneity in meta-analyses of observational studies.
Methods
We searched for meta-analyses of drugs effects published between 2012 and 2018 in general and internal medicine journals with an impact factor > 15. We evaluated, when reported, the type of data source (primary vs secondary) used in the individual observational studies included in each meta-analysis, and the exposure- and outcome-related variables included in sensitivity, subgroup or meta-regression analyses.
Results
We found 217 articles, 23 of which fulfilled our eligibility criteria. Eight meta-analyses (8/23, 34.8%) reported the source of data. Three meta-analyses (3/23, 13.0%) included the method of outcome assessment as a variable in the analysis of heterogeneity, and only one compared and discussed the results considering the different sources of data (primary vs secondary).
Conclusions
In meta-analyses of drug effects published in seven high impact general medicine journals, the origin of the data, either primary or secondary, is underexplored as a source of heterogeneity.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12874-018-0561-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Observational studies, Meta-analysis, Source of data, Heterogeneity, Drug, Over-the-counter, Out-of-pocket
Background
Specific research questions are ideally answered through tailor-made studies. Although these ad hoc studies provide more accurate and updated data, designing a completely new project may not represent a feasible strategy [1, 2]. On the other hand, clinical and administrative databases used for billing and other fiscal purposes (i.e. “secondary data”) are a valuable resource as an alternative to ad hoc methods (i.e. “primary data”) since it is easier and less costly to reuse the information than collecting it anew [3]. The potential of secondary automated databases for observational epidemiological studies is widely acknowledged; however, their use is not without challenges, and many quality requirements and methodological pitfalls must be considered [4].
Meta-analysis represents one of the most valuable tools for assessing drug effects as it may lead to the best evidence possible in epidemiology [5]. Consequently, its use for making relevant clinical and regulatory decisions on the safety and efficacy of drugs is dramatically increasing [6]. Existence of heterogeneity in a given meta-analysis is a feature that needs to be carefully described by analyzing the possible factors responsible for generating it [7]. In this regard, the results of a recent study [8] show that whether the origin of the data (primary vs secondary) is explored as a potential cause of heterogeneity may change the conclusions of a meta-analysis due to an effect modification [9]. Thus, considering the source of data as a variable in sensitivity and subgroup analyses, or meta-regression analyses, seems crucial to avoid misleading conclusions in meta-analyses of drug effects.
Given the evidence noted [8, 9], we surveyed published meta-analyses in a selection of high-impact journals over a 6-year period, to assess to what extent the origin of the data, either primary or secondary, is explored as a source of heterogeneity in meta-analyses of observational studies.
Methods
Meta-analysis selection and data collection process
General and internal medicine journals with an impact factor > 15 according to the Web of Science were included in the survey [10]. This method has been widely used to assess quality as well as publication trends in medical journals [11–13]. The rationale is that meta-analyses published in high impact journals: (1) are likely to be rigorously performed and reported due to the exhaustive editorial process [12, 14]; and, (2) in general, exert a higher influence on medical practice due to the major role played by these journals in the dissemination of the new medical evidence [14, 15]. We searched MEDLINE on May 2018 using the search terms “meta-analysis” as publication type and “drug” in any field between January 1, 2012 and May 7, 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), Lancet, Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), British Medical Journal (BMJ), JAMA Internal Medicine (JAMA Intern Med), Annals of Internal Medicine (Ann Intern Med), and Nature Reviews Disease Primers (Nat Rev Dis Primers).
Two investigators (GP-R, FR) independently assessed publications for eligibility. Abstracts were screened and if deemed potentially relevant, full text articles were retrieved. Articles were excluded if they met any of the following conditions: (1) were not a meta-analysis of published studies, (2) no drug effects were evaluated, (3) only randomized clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis (in order to consider observational studies), (4) less than two observational studies were included in the meta-analysis (since with a single study it would not have been possible to calculate a pooled measure). When a meta-analysis included both observational studies and clinical trials, only observational studies were considered.
A data extraction form was developed previously to extract information from articles. Two investigators (GP-R, FR) independently extracted and recorded the information and resolved discrepancies by referring to the original report. If necessary, a third author (AF) was asked to resolve disagreements between the investigators.
When available we extracted the following data from each eligible meta-analysis: first author, publication year, journal, drug(s) exposure and outcome(s); number of individual studies included in the meta-analysis based on each type of data source used (primary vs secondary), for both exposure and outcome assessment; and exposure- and outcome-related variables included in sensitivity, subgroup or meta-regression analyses. We extracted data directly from the tables, figures, text, and supplementary material of the meta-analyses, not from the individual studies.
Assessment of exposure and outcome
We considered “primary data” the information on drug exposure collected directly by the researchers using interviews –personal or by telephone– or self-administered questionnaires. The origin of the data was also considered primary when objective diagnostic methods were used for the determination of drug exposure (e.g. blood test). “Secondary data” are data that were formerly collected for other purposes than that of the study at hand and that were included in databases on drug prescription (e.g. prescription registers, medical records/charts) and dispensing (e.g. computerized pharmacy records, insurance claims databases). Regarding the outcome assessment, we considered primary data when an objective confirmation is available that endorses them (e.g. confirmed by individual medical ad hoc diagnosis, lab test or imaging results). These criteria are based on those commonly used in the risk assessment of bias for observational studies [16–19].
Results
MEDLINE search results yielded 217 articles from the major general medical journals (3 from NEJM, 46 from Lancet, 26 from JAMA, 85 from BMJ, 19 from JAMA Intern Med, 38 from Ann Intern Med, and 0 from Nat Rev Dis Primers) (see Fig. 1). A total of 194 articles were excluded (see list of excluded articles with reasons for exclusion in Additional file 1) leaving 23 articles to be examined [20–42]. General characteristics of the 23 included meta-analyses are outlined in Table 1.
Fig. 1.
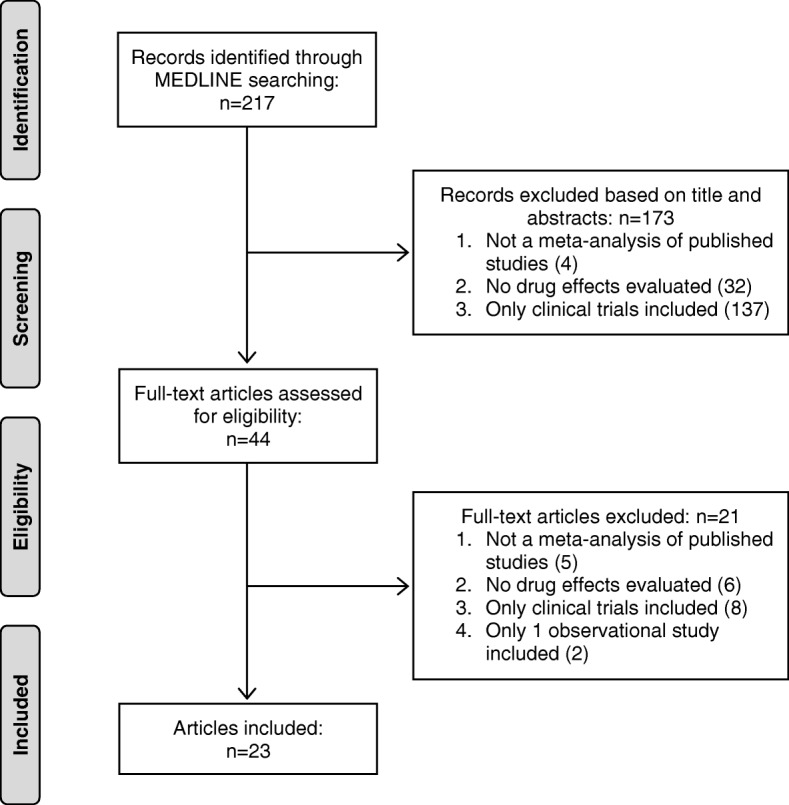
Flow diagram of literature search results
Table 1.
Characteristics of the 23 included meta-analyses
| Meta-analysis | Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author | Year | Journal | Drug exposure | Outcome |
| Weiss J [20] | 2017 | Ann Intern Med | Antihypertensive drugs | Harms outcomes: Cognitive impairment, quality of life, falls, fractures, syncope, functional status, hypotension, acute kidney injury, medication burden, withdrawal due to adverse events |
| Bally M [21] | 2017 | BMJ | NSAIDs | Myocardial infarction |
| Sordo L [22] | 2017 | BMJ | Opioid substitution treatment (methadone, buprenorphine) | All cause and overdose mortality |
| Tariq R [23] | 2017 | JAMA Intern Med | Gastric acid suppressants | Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection |
| Maruthur NM [24] | 2016 | Ann Intern Med | Diabetes monotherapy (thiazolidinediones, metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists) or metformin-based combinations | All-cause mortality, macrovascular and microvascular outcomes, intermediate outcomes (hemoglobin A1c, body weight, systolic blood pressure, heart rate), hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal side effects, genital mycotic infections, congestive heart failure |
| Paul S [25] | 2016 | Ann Intern Med | Antiviral prophylaxis | Primary outcome: Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) reactivation Secondary outcomes: HBV-related hepatitis, interrupted chemotherapy, acute liver failure, mortality |
| Li L [26] | 2016 | BMJ | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors | Heart failure |
| Hospital admissions for heart failure | ||||
| Molnar AO [27] | 2015 | BMJ | Generic immunosuppressive drugs | Patient survival, allograft survival, acute rejection, adverse events, bioequivalence |
| Ziff OJ [28] | 2015 | BMJ | Digoxin | Primary outcome: All-cause mortality |
| Secondary outcomes: Cardiovascular mortality; admission to hospital for any cause, cardiovascular causes and heart failure; incident stroke, incident myocardial infarction | ||||
| CGESOC [29] | 2015 | Lancet | Hormone therapy (oestrogen, progestagen) | Ovarian cancer |
| Bellemain- Appaix A [30] | 2014 | BMJ | Tienopyridines (clopidogrel) | Primary outcome: All-cause mortality, major bleeding Secondary outcomes: Major cardiovascular events and myocardial infarction, stroke, urgent revascularization, stent thrombosis |
| Grigoriadis S [31] | 2014 | BMJ | Antidepressants (SSRIs) | Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn |
| Li L [32] | 2014 | BMJ | Incretin-based treatments | Pancreatitis |
| Kalil AC [33] | 2014 | JAMA | Vancomycin MIC | All-cause mortality |
| Stegeman BH [34] | 2013 | BMJ | Combined oral contraceptives | Venous thrombosis |
| Maneiro JR [35] | 2013 | JAMA Intern Med | Biologic agents (abatacept, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, infliximab, rituximab) | Influence of AABs: on efficacy in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or other spondyloarthropathies), in hypersensitivity reactions, and on the concentration of biological drugs; effect of concomitant treatment in development of AAB |
| Hartling L [36] | 2012 | Ann Intern Med | Antipsychotics | Primary outcomes: Improved core symptoms of illness (positive and negative symptoms and general psychopathology), adverse events: diabetes mellitus, death, tardive dyskinesia, major metabolic syndrome |
| Secondary outcomes: Functional outcomes, health care system use; response, remission and relapse rates; medication adherence, health-related quality of life, other patient-oriented outcomes (e.g. patient satisfaction), other adverse events: extrapyramidal symptoms, weight gain | ||||
| Hsu J [37] | 2012 | Ann Intern Med | Antivirals (oseltamivir, zanamivir, amantadine, rimantadine) | Mortality, hospitalization, intensive care unit admission, mechanical ventilation and respiratory failure, duration of hospitalization, duration of signs and symptoms, time to return to normal activity, complications, critical adverse events: major psychotic disorders, encephalitis, stroke, seizure; important adverse events: pain in extremities, clonic twitching, body weakness, dermatologic changes (urticaria or rash); influenza viral shedding, emergence of antiviral resistance |
| Caldeira D [38] | 2012 | BMJ | ACEIs and ARBs | Incidence of pneumonia |
| Pneumonia related mortality | ||||
| MacArthur GJ [39] | 2012 | BMJ | Opiate substitution, methadone detoxification | HIV infection among people who inject drugs |
| Mantha S [40] | 2012 | BMJ | Progestin-only contaception | Venous thromboembolic events |
| Silvain J [41] | 2012 | BMJ | Enoxaparin, unfractioned heparin | Primary outcome: Mortality, major bleeding Secondary outcomes: Composite ischaemic end point (death or myocardial infarction), complications of myocardial infarction, minor bleeding |
| McKnight RF [42] | 2012 | Lancet | Lithium | Renal function, thyroid function, parathyroid function, hair disorders, skin disorders, bodyweight, teratogenicity |
Abbreviations: AABs antibodies against biologic agents, ACEIs, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, Ann Intern Med Annals of Internal Medicine, ARBs angiotensin receptor blockers, BMJ British Medical Journal, DPP-4 Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4, GLP-1 glucagon like peptide-1, JAMA Journal of the American Medical Association, MIC minimum inhibitory concentration, NSAIDs non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, SGLT-2 sodium–glucose cotransporter 2, SSRIs selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Source of exposure and outcome data
Table 2 summarizes the evidence regarding the type of data source included in each meta-analysis, according to the information presented in the data extraction tables of the article. The information was evaluated taking the study design into account. Only eight meta-analyses [21, 24, 26, 31, 32, 34, 38, 41] reported the source of data, three of them [31, 34, 38] reporting mixed sources for both the exposure and outcome assessment. Five meta-analyses [21, 24, 26, 32, 41] reported only secondary sources for the exposure assessment, three of them [21, 24, 41] reporting as well only secondary sources for the outcome assessment, while in the other two [26, 32] only primary and mixed sources for the outcome assessment were reported respectively.
Table 2.
Reporting of the data source in the data extraction tables of the included meta-analyses
| Meta-analysis (MA) | Exposure assessment | Outcome assessment | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data source presented in MA | Cohort studies (n) | Case-control studies (n) | Data source presented in MA | Cohort studies (n) | Case-control studies (n) | |||||||||
| 1ry | 2ry | NR | 1ry | 2ry | NR | 1ry | 2ry | NR | 1ry | 2ry | NR | |||
| Weiss J [20] Harms outcomes |
No | . | . | . | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Bally M [21] | Yes | 0 | 3b | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Yes | 0 | 3b | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Sordo L [22] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Tariq R [23] | Noac | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Maruthur NM [24] | Yesd | 0 | 3 | 0 | . | . | . | Yesd | 0 | 3 | 0 | . | . | . |
| Paul S [25] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Li L [26] Heart failure |
Yes | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | Yes | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Li L [26] Hospital admissions for heart failure |
Yes | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 | Yes | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Molnar AO [27] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Ziff OJ [28] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| CGESOC [29] | No | . | . | . | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Bellemain-Appaix A [30] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Grigoriadis S [31] | Yes | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Yes | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Li L [32] | Yes | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | Yes | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Kalil AC [33] | No | . | . | . | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Stegeman BH [34] | Yes | 0 | 9 | 0 | 8 | 8 | 1 | Yes | 4 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 12 | 0 |
| Maneiro JR [35] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Hartling L [36] | No | . | . | . | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Hsu J [37] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Caldeira D [38] | Yes | 2 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 1 | Yes | 0 | 1 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| MacArthur GJ [39] | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . | Noa | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Mantha S [40] | No | . | . | . | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Silvain J [41] | Yes | 0 | 7 | 0 | . | . | . | Yes | 0 | 7 | 0 | . | . | . |
| McKnight RF [42] | No | . | . | . | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | . | . | . |
Abbreviations: 1ry number of individual studies in each MA based on primary data sources, 2ry number of individual studies in each MA based on secondary data sources, NR number of individual studies in each MA with not reported data source
aAlthough the meta-analysis shows the results of methodological quality assessment based on a standardized scale, it does not indicate the type of data source used for each individual observational study included in the meta-analysis
bCohort with nested case-control analysis
cThe meta-analysis reports that most of the included observational studies assessed medication exposure through a review of medical records
dThe meta-analysis reports only data from high-quality observational studies
Source of data in the analysis of heterogeneity
All but two [20, 42] of the meta-analyses performed subgroup and/or sensitivity analyses. Although three of them [23, 34, 36] considered the methods of outcome assessment – type of diagnostic assay used for Clostridium difficile infection, method of venous thrombosis diagnosis confirmation, and type of scale for psychosis symptoms assessment respectively– as stratification variables, only the second referred to the origin of the data. Only five meta-analyses [22, 28, 33, 35, 39] included meta-regression analyses to describe heterogeneity, none of which considered the source of data as an explanatory variable. Other findings for the inclusion of the data source as a variable in the analysis of heterogeneity are presented in Table 3.
Table 3.
Inclusion of the data source as a variable in the analysis of heterogeneity of the included meta-analyses
| Meta-analysis | Subgroup/ sensitivity analysis | Meta-regression analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure-related variables | Outcome-related variables | Other variables | Type of data source included | Exposure-related variables | Outcome-related variables | Other variables | Type of data source included | |
| Weiss J [20] Harms outcomes |
. | . | . | No | . | . | . | No |
| Bally M [21] | Timing of exposure to NSAIDs, dosage and duration of treatment, concomitant drug treatment | Comorbidities | Alternative statistical model, reason for exclusion | No | . | . | . | No |
| Sordo L [22] | Time interval in and out of opioid substitution treatment | . | Alternative statistical model | No | Treatment provider, prevalence of opioid injection, average methadone dose | . | Mean age, percentage of men, location, percentage of inpatient induction, percentage loss to follow-up, midpoint follow-up period | No |
| Tariq R [23] | Type of gastric acid suppressant (PPI and H2B reported together, PPI alone, or H2B alone) | Case definition (time interval of recurrence: within 60 days vs within 90 days), type of diagnostic assay used for Clostridium difficile infection | Study design, study setting (inpatients vs outpatients), data adjustment | No | . | . | . | No |
| Maruthur NM [24] | Mode of therapy | . | . | No | . | . | . | No |
| Paul S [25] Primary outcome |
. | Chronic or resolved hepatitis B virus infection | Tumor and chemotherapy subtype, alternative statistical model, quality of design | No | . | . | . | No |
| Paul S [25] Secondary outcomes |
. | . | Alternative statistical model, quality of design | No | . | . | . | No |
| Li L [26] | Type of control, mode of therapy, individual drugs | . | Length of follow up, type of design | No | . | . | . | No |
| Molnar AO [27] | . | . | Type of design | No | . | . | . | No |
| Ziff OJ [28] Primary outcome |
. | . | Data adjustment, population type | No | Difference between digoxin and control arms at baseline: Diabetes, hypertension, diuretics, anti-arrhythmic drugs | . | Summary bias score, baseline study level variable: Year of publication, age, sex, previous myocardial infarction | No |
| Ziff OJ [28] Secondary outcomes |
. | . | . | No | . | . | . | No |
| CGESOC [29] | Duration of use in current and past users of hormone therapy, types of hormone therapy | Tumour histology and malignant potential of the tumour | Study design, geographical region, age at first use of hormone therapy, age at menarche, parity, oral contraceptive use, height, bosy mass index, alcohol use, tobacco use, mother or sister with ovarian/breast cancer, histerectomy | No | . | . | . | No |
| Bellemain-Appaix A [30] | Clopidogrel dose | Types of percutaneous coronary intervention | Type of design | No | . | . | . | No |
| Grigoriadis S [31] | Timing of exposure to SSRIs | . | Study design, congenital malformations, control, meconium aspiration | No | . | . | . | No |
| Li L [32] | Type of incretin agents, type of control, mode of therapy, individual incretin agents | . | Length of follow-up, alternative effect measure, alternative statistical model | No | . | . | . | No |
| Kalil AC [33] | Different MIC cutoffs, assay type | Hospital or 30-d mortality | Publication year, quality of design | No | Vancomycin MIC cut-off, vancomycin exposure in the previous 6 months, vancomycin trough levels, proportion of patients who received vancomycin treatment | Control mortality, APACHE II score, Charlson score, duration of bacteremia, proportion of patients with endocarditis, proportion of patients located in the intensive care unit | Age | No |
| Stegeman BH [34] | Generation of progestogen used in combined oral contraceptives, combined oral contraceptive pill | Method of diagnosis confirmation | Funding source, study design | Yes (outcome) | . | . | . | No |
| Maneiro JR [35] | Type of biologic agent, concomitant treatment (monotherapy vs combined therapy), prior use of TNF inhibitors | Type of disease | Length of follow-up, data quality, study design, level of evidence of studies | No | Type of biologic agent, prior use of TNF inhibitors, method of measurement of antibodies, type of the anti-TNF monoclonal antibody |
Type of disease, time of disease duration, time to assess response | Age and sex of patients, number of participants, length of follow-up, data quality, study design, level of evidence of studies | No |
| Hartling L [36] Primary outcomes |
Type of drug-comparison | Type of scale for the assessment of symptoms and quality of life | . | No | . | . | . | No |
| Hartling L [36] Secondary outcomes |
. | . | . | No | . | . | . | No |
| Hsu J [37] | Individual drugs, dosage of antiviral, timing of treatment | . | Data adjustment, confirmed influenza, type of influenza A vs B, pandemic versus seasonal influenza, severity of influenza, age, pregnancy, baseline risk (e.g. immune-compromised), setting, funding conflict | No | . | . | . | No |
| Caldeira D [38] Incidence of pneumonia |
. | . | Study design, previous stroke, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, non-Asian patients | No | . | . | . | No |
| Caldeira D [38] Pneumonia related mortality |
. | . | Study design | No | . | . | . | No |
| MacArthur GJ [39] | Duration of exposure to opiate substitution treatment | . | Data adjustment, geographical region, site of recruitment, monetary incentives, percentage of female participants, percentage of individuals from ethnic minorities | No | Exposure to methadone maintenance treatment at baseline only | . | Inclusion only of studies at lower risk of bias, inclusion only of studies that measured an incidence rate ratio, exclusion of studies that did not adjust for confounders | No |
| Mantha S [40] | Route of administration | . | Data adjustment | No | . | . | . | No |
| Silvain J [41] | Route of administration | . | Types of percutaneous coronary intervention, study publication, study size, quality of design | No | . | . | . | No |
| McKnight RF [42] | . | . | . | No | . | . | . | No |
Abbreviations: APACHE acute physiology and chronic health evaluation, MIC minimum inhibitory concentration, SSRIs selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, TNF tumor necrosis factor
We finally assessed if the influence of the data origin on the conclusions of the meta-analyses was discussed by their respective authors. We found that only four meta-analyses [21, 31, 32, 34] noted limitations derived from the type of data source used.
Discussion
The findings of this research suggest that the origin of the data, either primary or secondary, is underexplored as a source of heterogeneity and an effect modifier in meta-analyses of drug effects published in general medicine journals with high impact. Few meta-analyses reported the source of data and only one [34] of the articles included in our survey compared and discussed the meta-analysis results considering the different sources of data.
Although it is usual to consider the design of the individual studies (i.e. case-control, cohort or experimental studies) in the analysis of the heterogeneity of a meta-analysis [43, 44], the type of data source (primary vs secondary) is still rarely used for this purpose [9, 45]. In fact, the current reporting guidelines for meta-analyses, such as MOOSE (Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) [18] or PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) [46, 47], do not recommend that authors specifically report the origin of the data. This is probably due to the close relationship that exists between the study design and the type of data source used, despite the fact that each criterion has its own basis. Performing this additional analysis is a simple task that involves no additional cost. Failure to do so may lead to diverging conclusions [8].
Conclusions about the effects of a drug that are derived from studies based exclusively on data from secondary sources may be dicey, among other reasons, because no information is collected on consumption of over-the-counter drugs (i.e. drugs that individuals can buy without a prescription) [48] and/or out-of-pocket expenses for prescription drugs (i.e. costs that individuals pay out of their own cash reserves) [49]. In the health care and insurance context, out-of-pocket expenses usually refer to deductibles, co-payments or co-insurance. Figure 2 shows the model that we propose to describe the relationship between the different data records according to their origin, including the possible loss of information (susceptible to be registered only through primary research).
Fig. 2.
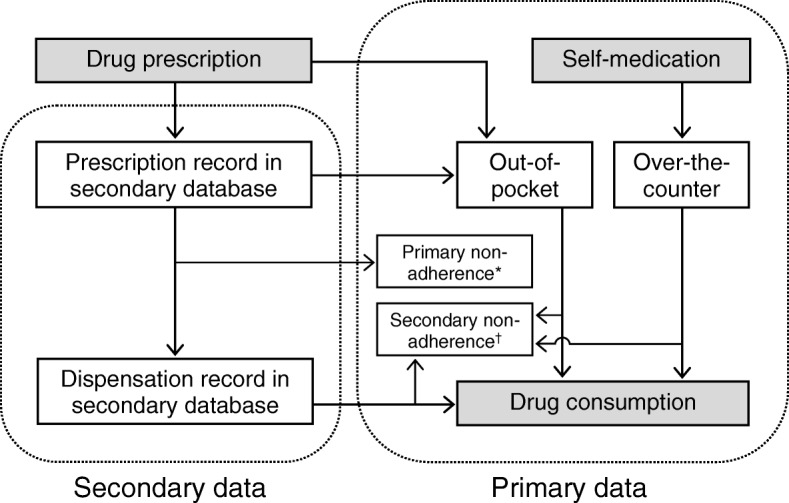
Conceptual model of individual data recording. * Never dispensed. † Absence of dispensing of successive prescriptions (or self-medication) among patients with primary adherence, or inadequate secondary adherence
Failure to take these situations into account may lead to exposure measurement bias [48, 49]. Consumption of a drug may be underestimated when only prescription data is used as secondary source without additionally considering unregistered consumption, such as over-the-counter consumption (e.g. oral contraceptives [34, 50]), that may only be available from a primary database. Alternatively, this may occur when dispensing data for billing purposes (reimbursement) are used for clinical research, if out-of-pocket expenses are not considered (see Fig. 2). The portion of the medical bill that the insurance company does not cover, and that the individual must pay on his own, is unlikely to be recorded. Data on the sale of over-the-counter drugs will also not be available in this scenario.
The reverse situation may also occur and consumption may be overestimated when only prescription data is used, if the prescribed drug is not dispensed by the pharmacist; or when dispensing data is used, if the drug is not really consumed by the patient. While primary non-adherence occurs when the patient does not pick up the medication after the first prescription, secondary non-adherence refers to the absence of dispensing of successive prescriptions among patients with primary adherence, or to inadequate secondary adherence (i.e. ≥20% of time without adequate medication) [51] (see Fig. 2). In some diseases the medication adherence is very low [52–55], with percentages of primary non-adherence (never dispensed) that exceed 30% [56]. It should be noted that the impact of non-adherence varies from medication to medication. Therefore, it must be defined and measured in the context of a particular therapy [57].
Moreover, failing to take into consideration the portion of consumption due to over-the-counter and/or out-of-pocket expenses may lead to confounding, as that variable may be related to the socio-economic level and/or to the potential of access to the health system [58], which are independent risk factors of adverse outcomes of some medications (e.g. myocardial infarction [21, 28, 30, 41]). Given the presence of high-deductible health plans and the high co-insurance rate for some drugs, cost-sharing may deter clinically vulnerable patients from initiating essential medications, thus negatively affecting patient adherence [59, 60].
Outcome misclassification may also give rise to measurement bias and heterogeneity [61]. This occurs, for example, in the meta-analysis that evaluates the relationship between combined oral contraceptives and the risk of venous thrombosis [34]. In the studies without objective confirmation of the outcome, the women were classified erroneously regardless of the use of contraceptives. This led to a non-differential misclassification that may have underestimated the drug–outcome relationship, especially when the third generation of progestogen is analysed: Risk ratio (RR) primary data = 6.2 (95% confidence interval (CI) 5.2–7.4), RR secondary data = 3.0 (95% CI 1.7–5.4) [34].
On the one hand, medical records are often considered as being the best information source for outcome variables. However, they present important limitations in the recording of medications taken by patients [62]. On the other hand, dispensing records show more detailed data on the measurement of drug exposure. However, they do not record the over-the-counter or out-of-pocket drug consumption at an individual level [48, 49], apart from offering unreliable data on outcome variables [62, 63].
Limitations
The first limitation of this research is that its findings may not be applicable to journals not included in our survey such as journals with low impact factor. Despite the widespread use of the impact factor metric [64], this method has inherent weaknesses [65, 66]. However, meta-analyses published in high impact general medicine journals are likely to be most rigorously performed and reported due to their greater availability of resources and procedures [12, 14]. It is then expected that the overall reporting quality of articles published in other lesser-known journals will be similar. Another limitation would be related to the limited search period. In this sense, and given that the general tendency is the improvement of the methodology of published meta-analyses [67, 68], we find no reason to suspect that the adverse conclusions could be different before the period from 2012 to 2018. Although it exceeds the objective of this research, one last limitation may be the inability to reanalyse the included meta-analyses stratifying by the type of data source since our study design restricts the conclusions to the published data of the meta-analyses, which were insufficiently reported, or the number of individual studies in each stratum was insufficient to calculate a pooled measure (see Table 2).
Conclusions
Owing to automated capture of data on drug prescription and dispensing that are used for billing and other administration purposes, as well as to the implementation of electronic medical records, secondary databases have generated enormous possibilities. However, neither their limitations, nor the risk of bias that they pose should be overlooked [69]. Thus, researchers should consider the link between administrative databases and medical records, as well as the advisability of combining secondary and primary data in order to minimize the occurrence of biases due to the use of any of these databases.
No source of heterogeneity in a meta-analysis should ever be considered alone but always as part of an interconnected set of potential questions to be addressed. In particular, the origin of the data, either primary or secondary, is insufficiently explored as a source of heterogeneity in meta-analyses of drug effects, even in those published in high impact general medicine journals. Thus, we believe that authors should systematically include the source of data as an additional variable in subgroup and sensitivity analyses, or meta-regression analyses, and discuss its influence on the meta-analysis results. Likewise, reviewers, editors and future guidelines should also consider the origin of the data as a potential cause of heterogeneity in meta-analyses of observational studies that include both primary and secondary data. Failure to do this may lead to misleading conclusions, with negative effects on clinical and regulatory decisions.
Additional file
Excluded articles. List of articles excluded with reasons for exclusion. (PDF 247 kb)
Acknowledgments
Funding
This study received no funding from the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- Ann Intern Med
Annals of Internal Medicine
- BMJ
British Medical Journal
- CI
Confidence Interval
- JAMA Intern Med
JAMA Internal Medicine
- JAMA
Journal of the American Medical Association
- MOOSE
Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology
- Nat Rev Dis Primers
Nature Reviews Disease Primers
- NEJM
New England Journal of Medicine
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses
- RR
Risk ratio
- VS
Versus
Authors’ contributions
AF and GP-R contributed to study conception and design. GP-R, FR and AF contributed to searching, screening, data collection and analyses. GP-R was responsible for drafting the manuscript. FR, MTH, BT and AF provided comments and made several revisions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Guillermo Prada-Ramallal, Email: guillermoj.prada@rai.usc.es.
Fatima Roque, Email: froque@ipg.pt.
Maria Teresa Herdeiro, Email: teresaherdeiro@ua.pt.
Bahi Takkouche, Email: bahi.takkouche@usc.es.
Adolfo Figueiras, Phone: (+34) 981 95 11 92, Email: adolfo.figueiras@usc.es.
References
- 1.Terris DD, Litaker DG, Koroukian SM. Health state information derived from secondary databases is affected by multiple sources of bias. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:734–741. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schneeweiss S. Understanding secondary databases: a commentary on “sources of bias for health state characteristics in secondary databases”. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:648–650. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.10.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schneeweiss S, Avorn J. A review of uses of health care utilization databases for epidemiologic research on therapeutics. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58:323–337. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Knottnerus JA, Tugwell P. Requirements for utilizing health care-based data sources for research. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:1051–1053. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Berlin JA, Golub RM. Meta-analysis as evidence: building a better pyramid. JAMA. 2014;312:603–606. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.8167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blettner M, Schlattmann P. Meta-analysis in epidemiology. In: Ahrens W, Pigeot I, editors. Handbook of epidemiology. Berlin: Springer; 2005. pp. 829–859. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Higgins JPT. Heterogeneity in meta-analysis should be expected and appropriately quantified. Int J Epidemiol. 2008;37:1158–1160. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Prada-Ramallal G, Takkouche B, Figueiras A. Diverging conclusions from the same meta-analysis in drug safety: source of data (primary versus secondary) takes a toll. Drug Saf. 2017;40:351–358. doi: 10.1007/s40264-016-0492-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Madigan D, Ryan PB, Schuemie M, Stang PE, Overhage JM, Hartzema AG, et al. Evaluating the impact of database heterogeneity on observational study results. Am J Epidemiol. 2013;178:645–651. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwt010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.InCites Journal Citation Reports. Science citation index expanded - medicine. General & Internal Thomson Reuters. https://jcr.incites.thomsonreuters.com. Accessed 10 Sept 2018.
- 11.Faggion CM, Jr, Bakas NP, Wasiak J. A survey of prevalence of narrative and systematic reviews in five major medical journals. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2017;17:176. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0453-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hopewell S, Ravaud P, Baron G, Boutron I. Effect of editors' implementation of CONSORT guidelines on the reporting of abstracts in high impact medical journals: interrupted time series analysis. BMJ. 2012;344:e4178. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e4178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Blanc X, Collet TH, Auer R, Fischer R, Locatelli I, Iriarte P, et al. Publication trends of shared decision making in 15 high impact medical journals: a full-text review with bibliometric analysis. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2014;14:71. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-14-71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rehal S, Morris TP, Fielding K, Carpenter JR, Phillips PP. Non-inferiority trials: are they inferior? A systematic review of reporting in major medical journals. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e012594. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Callaham M, Wears RL, Weber E. Journal prestige, publication bias, and other characteristics associated with citation of published studies in peer-reviewed journals. JAMA. 2002;287:2847–2850. doi: 10.1001/jama.287.21.2847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kim SY, Park JE, Lee YJ, Seo HJ, Sheen SS, Hahn S, et al. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66:408–414. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.09.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa: Univ of Ottawa; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA. 2000;283:2008–2012. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, et al. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Epidemiology. 2007;18:800–804. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181577654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weiss J, Freeman M, Low A, Fu R, Kerfoot A, Paynter R, et al. Benefits and harms of intensive blood pressure treatment in adults aged 60 years or older: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:419–429. doi: 10.7326/M16-1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bally M, Dendukuri N, Rich B, Nadeau L, Helin-Salmivaara A, Garbe E, et al. Risk of acute myocardial infarction with NSAIDs in real world use: bayesian meta-analysis of individual patient data. BMJ. 2017;357:j1909. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sordo L, Barrio G, Bravo MJ, Indave BI, Degenhardt L, Wiessing L, et al. Mortality risk during and after opioid substitution treatment: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;357:j1550. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tariq R, Singh S, Gupta A, Pardi DS, Khanna S. Association of Gastric Acid Suppression with Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177:784–791. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maruthur NM, Tseng E, Hutfless S, Wilson LM, Suarez-Cuervo C, Berger Z, et al. Diabetes medications as monotherapy or metformin-based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164:740–751. doi: 10.7326/M15-2650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Paul S, Saxena A, Terrin N, Viveiros K, Balk EM, Wong JB. Hepatitis B virus reactivation and prophylaxis during solid tumor chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164:30–40. doi: 10.7326/M15-1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li L, Li S, Deng K, Liu J, Vandvik PO, Zhao P, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and observational studies. BMJ. 2016;352:i610. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Molnar AO, Fergusson D, Tsampalieros AK, Bennett A, Fergusson N, Ramsay T, et al. Generic immunosuppression in solid organ transplantation: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2015;350:h3163. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h3163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ziff OJ, Lane DA, Samra M, Griffith M, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, et al. Safety and efficacy of digoxin: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational and controlled trial data. BMJ. 2015;351 h4451. Erratum in: BMJ 2015;351:h4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Collaborative Group On Epidemiological Studies Of Ovarian Cancer. Beral V, Gaitskell K, Hermon C, Moser K, Reeves G, et al. Menopausal hormone use and ovarian cancer risk: individual participant meta-analysis of 52 epidemiological studies. Lancet. 2015;385:1835–1842. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61687-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bellemain-Appaix A, Kerneis M, O'Connor SA, Silvain J, Cucherat M, Beygui F, et al. Reappraisal of thienopyridine pretreatment in patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014;349:g6269. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grigoriadis S, Vonderporten EH, Mamisashvili L, Tomlinson G, Dennis CL, Koren G, et al. Prenatal exposure to antidepressants and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014;348:f6932. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li L, Shen J, Bala MM, Busse JW, Ebrahim S, Vandvik PO, et al. Incretin treatment and risk of pancreatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised studies. BMJ. 2014;348:g2366. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g2366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kalil AC, Van Schooneveld TC, Fey PD, Rupp ME. Association between vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration and mortality among patients with Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2014;312:1552–1564. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.6364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stegeman BH, de Bastos M, Rosendaal FR, van Hylckama Vlieg A, Helmerhorst FM, Stijnen T, et al. Different combined oral contraceptives and the risk of venous thrombosis: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013;347:f5298. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Maneiro JR, Salgado E, Gomez-Reino JJ. Immunogenicity of monoclonal antibodies against tumor necrosis factor used in chronic immune-mediated inflammatory conditions: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173:1416–1428. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.7430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hartling L, Abou-Setta AM, Dursun S, Mousavi SS, Pasichnyk D, Newton AS. Antipsychotics in adults with schizophrenia: comparative effectiveness of first-generation versus second-generation medications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2012;157:498–511. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-7-201210020-00525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hsu J, Santesso N, Mustafa R, Brozek J, Chen YL, Hopkins JP, et al. Antivirals for treatment of influenza: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Intern Med. 2012;156:512–524. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-7-201204030-00411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Caldeira D, Alarcão J, Vaz-Carneiro A, Costa J. Risk of pneumonia associated with use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e4260. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e4260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.MacArthur GJ, Minozzi S, Martin N, Vickerman P, Deren S, Bruneau J, et al. Opiate substitution treatment and HIV transmission in people who inject drugs: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e5945. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e5945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Mantha S, Karp R, Raghavan V, Terrin N, Bauer KA, Zwicker JI. Assessing the risk of venous thromboembolic events in women taking progestin-only contraception: a meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;345:e4944. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Silvain J, Beygui F, Barthélémy O, Pollack C, Jr, Cohen M, Zeymer U, et al. Efficacy and safety of enoxaparin versus unfractionated heparin during percutaneous coronary intervention: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2012;344:e553. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McKnight Rebecca F, Adida Marc, Budge Katie, Stockton Sarah, Goodwin Guy M, Geddes John R. Lithium toxicity profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet. 2012;379(9817):721–728. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61516-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M. Systematic reviews of observational studies. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG, editors. Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in context. 2. London: BMJ Publishing Group; 2001. pp. 211–227. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Glasziou PP, Sanders SL. Investigating causes of heterogeneity in systematic reviews. Stat Med. 2002;21:1503–1511. doi: 10.1002/sim.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Seeger John, Daniel Gregory W. Pharmacoepidemiology. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2012. Commercial Insurance Databases; pp. 189–208. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zorzela L, Loke YK, Ioannidis JP, Golder S, Santaguida P, Altman DG, et al. PRISMA harms checklist: improving harms reporting in systematic reviews. BMJ. 2016;352:i157. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Cohen JM, Wood ME, Hernandez-Diaz S, Nordeng H. Agreement between paternal self-reported medication use and records from a national prescription database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2018;27:413–421. doi: 10.1002/pds.4411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gamble JM, McAlister FA, Johnson JA, Eurich DT. Quantifying the impact of drug exposure misclassification due to restrictive drug coverage in administrative databases: a simulation cohort study. Value Health. 2012;15:191–197. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2011.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Upadhya KK, Santelli JS, Raine-Bennett TR, Kottke MJ, Grossman D. Over-the-counter access to oral contraceptives for adolescents. J Adolesc Health. 2017;60:634–640. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Raebel MA, Schmittdiel J, Karter AJ, Konieczny JL, Steiner JF. Standardizing terminology and definitions of medication adherence and persistence in research employing electronic databases. Med Care. 2013;51(Suppl 3):S11–S21. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31829b1d2a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wu AC, Butler MG, Li L, Fung V, Kharbanda EO, Larkin EK, et al. Primary adherence to controller medications for asthma is poor. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12:161–166. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201410-459OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fallis BA, Dhalla IA, Klemensberg J, Bell CM. Primary medication non-adherence after discharge from a general internal medicine service. PLoS One. 2013;8:e61735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Anderson KL, Dothard EH, Huang KE, Feldman SR. Frequency of primary nonadherence to acne treatment. JAMA Dermatol. 2015;151:623–626. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2014.5254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fischer MA, Stedman MR, Lii J, Vogeli C, Shrank WH, Brookhart MA, et al. Primary medication non-adherence: analysis of 195,930 electronic prescriptions. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25:284–290. doi: 10.1007/s11606-010-1253-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Tamblyn R, Eguale T, Huang A, Winslade N, Doran P. The incidence and determinants of primary nonadherence with prescribed medication in primary care: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160:441–450. doi: 10.7326/M13-1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kolandaivelu K, Leiden BB, O'Gara PT, Bhatt DL. Non-adherence to cardiovascular medications. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:3267–3276. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kirkeby MJ, Hansen CD, Andersen JH. Socio-economic differences in use of prescribed and over-the-counter medicine for pain and psychological problems among Danish adolescents--a longitudinal study. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:1147–1155. doi: 10.1007/s00431-014-2294-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mukherjee K, Kamal KM. Sociodemographic determinants of out-of-pocket expenditures for patients using prescription drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2017;10:7–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Karter AJ, Parker MM, Solomon MD, Lyles CR, Adams AS, Moffet HH, et al. Effect of out-of-pocket cost on medication initiation, adherence, and persistence among patients with type 2 diabetes: The Diabetes Study of Northern California (DISTANCE) Health Serv Res. 2018;53:1227–1247. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.12700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Leong A, Dasgupta K, Bernatsky S, Lacaille D, Avina-Zubieta A, Rahme E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of validation studies on a diabetes case definition from health administrative records. PLoS One. 2013;8:e75256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Takahashi Y, Nishida Y, Asai S. Utilization of health care databases for pharmacoepidemiology. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;68:123–129. doi: 10.1007/s00228-011-1088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Prada-Ramallal G, Takkouche B, Figueiras A. Summarising the evidence for drug safety: a methodological discussion of different meta-analysis approaches. Drug Saf. 2017;40:547–558. doi: 10.1007/s40264-017-0518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Garfield E. The history and meaning of the journal impact factor. JAMA. 2006;295:90–93. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Seglen PO. Why the impact factor of journals should not be used for evaluating research. BMJ. 1997;314:498–502. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7079.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Brown H. How impact factors changed medical publishing–and science. BMJ. 2007;334:561–564. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39142.454086.AD. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gerber S, Tallon D, Trelle S, Schneider M, Jüni P, Egger M. Bibliographic study showed improving methodology of meta-analyses published in leading journals 1993-2002. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60:773–780. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Petropoulou M, Nikolakopoulou A, Veroniki AA, Rios P, Vafaei A, Zarin W, et al. Bibliographic study showed improving statistical methodology of network meta-analyses published between 1999 and 2015. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017;82:20–28. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ray WA. Improving automated database studies. Epidemiology. 2011;22:302–304. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31820f31e1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Excluded articles. List of articles excluded with reasons for exclusion. (PDF 247 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.


