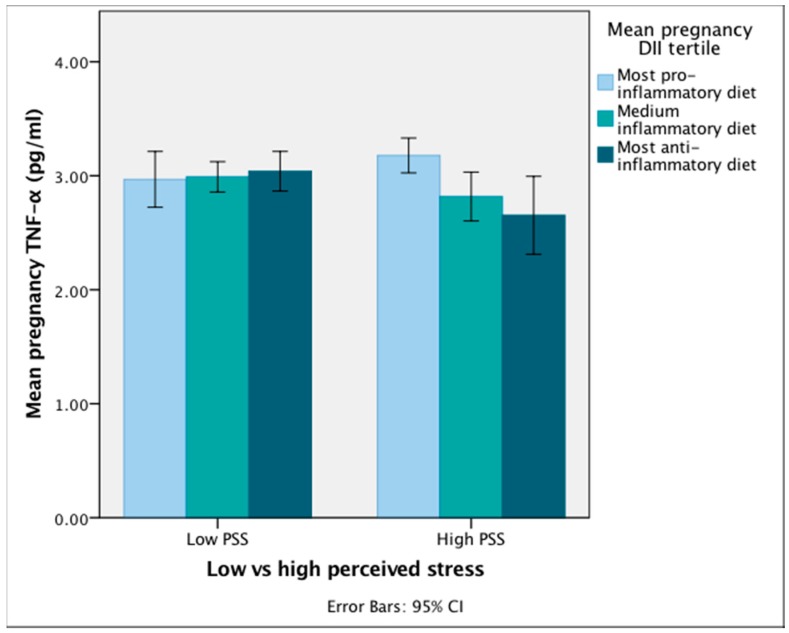
Figure 4.
Mean pregnancy TNF-α levels among pregnant women with high and low perceived stress scores, according to DII tertile. CI: Confidence Interval. Caption: DII, dietary inflammatory index; PSS, perceived stress score; TNF, tumor necrosis factor. Although DII, PSS, and TNF-α were entered to regression models as continuous variables, for the purpose of graphically depicting the effect of the DII*PSS interaction term on TNF-α, mean pregnancy DII was divided into tertiles and mean pregnancy PSS was dichotomized by the median value. A pro-inflammatory diet influences higher TNF-α levels only among women reporting higher perceived stress scores across pregnancy. Women who report lower perceived stress levels do not experience any difference in TNF-α levels, regardless of the inflammatory potential of their diet.