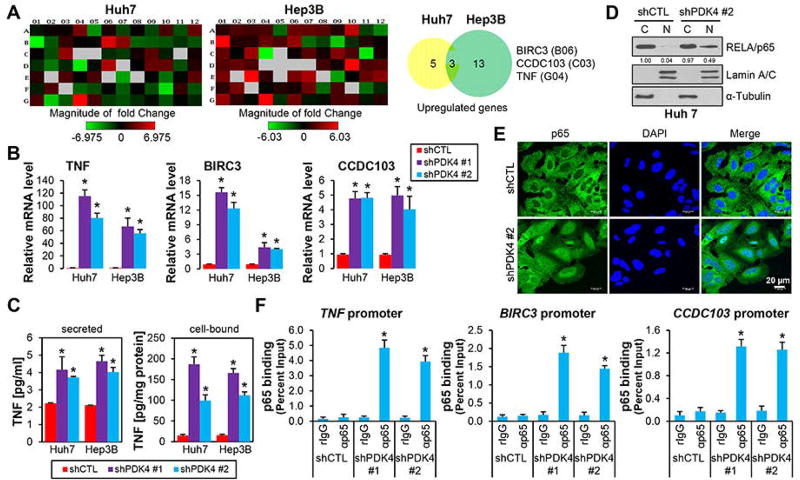
Figure 2.
PDK4-deficiency induced p65 nuclear translocation and its activation of TNF expression. (A) PCR array profile. Total RNAs from shCTL and shPDK4 Huh7 and Hep3B cell were extracted and subjected to Human Cell Death PathwayFinder PCR Array analysis. The fold changes of individual genes were represented in heat map (left) and the upregulated genes (fold > 2.0) were shown in pie charts (right). (B) qPCR of TNF, BIRC3 and CCDC103 mRNAs in shCTL and shPDK4 Huh7 and Hep3B cells. (C) ELISA assay of secreted or cellular TNF proteins in shCTL and shPDK4 Huh7 and Hep3B cells. (D) WB of cytoplasmic (C) and nuclear (N) NF-κB/p65 proteins in shCTL and shPDK4 Huh7 cells. Lamin A/C, nuclear marker; α-tubulin, cytoplasmic marker. (E) Immunofluorescence of nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of NF-κB/p65 in shCTL and shPDK4 Huh7 cells. Nucleus was counter-stained with DAPI. (F) ChIP assays of NF-κB/p65 occupancy on TNF, BIRC3 and CCDC103 promoters in shCTL and shPDK4 Huh7 cells. B, C, F: Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments with triplicate assays. *P < .01 vs shCTL.