Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to explore whether bone marrow- (BM-) derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) contributing to monocrotaline- (MCT-) induced pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in rats via modulating store-operated Ca2+ channels (SOC).
Methods
Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were assigned into MCT group (n = 30) and control group (n = 20). Rats in MCT group were subcutaneously administered with 60 mg/kg MCT solution, and rats in control group were injected with equal amount of vehicle. After 3 weeks of treatment, right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and right ventricular hypertrophy index (RVHI) of two groups were measured, and BM-derived EPCs were isolated. Immunochemistry identification and vasculogenesis detection of EPCs were then performed. [Ca2+]cyt measurement was performed to detect store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) in two groups, followed by determination of Orai and canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) channels expression.
Results
After 3 weeks of treatment, there were significant increases in RVSP and RVHI in MCT group compared with control group, indicating that MCT successfully induced PAH in rats. Moreover, the SOCE ([Ca2+]cyt rise) in BM-derived EPCs of MCT group was lower than that of control group. Furthermore, the expression levels of Orai3, TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC6 in BM-derived EPCs were decreased in MCT group in comparison with control group.
Conclusions
The SOC activities were inhibited in BM-derived EPCs of MCT-treated rats. These results may be associated with the depressed expression of Orai3, TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC6, which are major mediators of SOC.
1. Introduction
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a fatal disorder characterized by an increase in pulmonary vascular resistance [1, 2]. It always leads to right ventricular (RV) failure and death [3, 4]. Despite advances in therapeutic options, this disease represents an incurable disease due to progressive clinical deterioration and an unacceptably high early mortality [5, 6]. Therefore, elucidation of key pathological mechanism underlying PAH development is still imperative.
Accumulating evidences have confirmed that excessive pulmonary vascular remodeling is responsible for the elevated pulmonary vascular resistance in PAH [7–9]. In pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), the rise in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) is identified as a key trigger for promoting the proliferation of PASMCs and pulmonary vasoconstriction, both leading to pulmonary vascular remodeling [10–13]. Moreover, the profound pulmonary vascular remodeling and alterations in Ca2+ homeostasis in PASMCs may result in the development of PAH [14]. These findings support the pathogenic role of Ca2+ signaling in PAH.
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are considered to be important in maintaining vascular homeostasis, which can be mobilized from the bone marrow (BM) and resident locally in the lung [15]. EPCs are found to have a key role in the endothelial repair [16, 17]. It is reported that BM-derived EPCs can repair the monocrotaline- (MCT-) damaged lung in the rat MCT model of PAH [18]. Moreover, EPCs can induce neovascularization, suggesting the promising clinical application of the EPCs cell therapy to PAH [19]. However, the possible mechanism of EPCs in regulating pulmonary vascular remodeling during PAH development is largely unknown.
Notably, store-operated Ca2+ channels (SOC) is expressed in human EPCs [20]. Given the pathogenic role of Ca2+ signaling in PAH, the present study investigated whether BM-derived EPCs contributed to PAH in the MCT rat model via modulating SOC. To study this, we established the MCT rat model that was widely used to investigate PAH in rodents [20–22]. Then BM-derived EPCs were isolated. [Ca2+]cyt measurement was performed to detect store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) in BM-derived EPCs of MCT rat model and controls, followed by determination of SOC regulators, Orai, and canonical transient receptor potential channel (TRPC) expression. Our findings will provide a new insight for better understanding of PAH pathogenesis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatment
A total of 50 male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats (weighing 150-180 g) were obtained from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Rats were divided into MCT group (n = 30) and control group (n = 20). Rats in MCT group were subcutaneously administered with 60 mg/kg MCT solution 25 mg/ml diluted in vehicle (1:4 mixture of dehydrated ethanol-normal saline). Rats in control group were injected with equal amount of vehicle. This study was approved by the institutional ethical committee for animal care and use. During the treatment period, the behavior and general status were observed daily.
2.2. Measurement of Pulmonary Hemodynamic and Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
After 3 weeks of treatment, the rats were intraperitoneally anesthetized with 35mg/kg pentobarbital sodium (Abbott Laboratories, Montreal, Canada). Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) of rats in each group was measured by inserting a Millar catheter (Millar, Inc., TX, USA) into RV. Moreover, the RV was separated from the left ventricle (LV) and septum (S) for further detection of RV hypertrophy. The right heart hypertrophy index (RVHI) [RV/(LV+S)] was calculated as the ratio of RV weight to (LV+S) weight.
2.3. Isolation of Rat BM-Derived EPCs
Rats in each group were sacrificed by exsanguination, and BM was then aspirated from bilateral femurs and tibias of rats aseptically. Using density gradient centrifugation Histopaque®-1083 solution (Sigma-Aldrich, MS, USA), mononuclear cells (MNCs) were isolated from BM. To produce EPCs, BM-isolated MNCs were then resuspended in EGM-2 MV medium (Lonza, MD, USA), seeded into fibronectin (5 μg/cm2) coated six-well plates at a density of 3 × 106/cm2 and maintained at a 37°C incubator for 8 days. EGM-2 MV medium was replaced every two days.
2.4. Immunochemistry Identification
After 8 days of incubation, the fibronectin-adherent EPCs were identified by incubation with 10 μg/ml of fluorescently labeled acetylated-low-density lipoprotein (Dil-ac-LDL; Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) overnight and 10 μg/ml of fluorescently FITC-labeled Ulex europaeus agglutinin 1 (UEA-1; Sigma-Aldrich, MS, USA) for 4 h at room temperature using an immunochemistry method [4, 23]. The images were captured by Leica-SP5 confocal microscopy (Leica, Germany), and both FITC-UEA-1 and Dil-ac-LDL positive cells were considered as EPCs.
2.5. Detection of Vasculogenesis
To mimic vasculogenesis of EPCs, the vascular network formation was observed. Briefly, 24-well plates were presolidified Matrigel (BD Biosciences, MA, USA) for 30 minutes. EPCs were seeded into 24-well plates containing 500 μl EGM-2-MV medium at a density of 7.5 × 104 cells/2cm2 Matrigel. After incubation for 5 h, the developing vascular network in 10 fields was observed under a microscope (Nikon, Japan). The length of vascular network per field was calculated.
2.6. [Ca2+]cyt Measurement
According to the protocols described previously [24, 25], [Ca2+]cyt, defined as the ratio of fluorescence intensities of 340 to 380 nm wavelengths (F340/F380), was monitored using fura-2 acetoxymethyl ester (Invitrogen-Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) and then imaged with NIS Elements 3.2 software (Nikon).
To determine whether the different amplitude of [Ca2+]cyt increase between MCT and control groups was caused by SOCE, 10 μM CPA was extracellularly applied, which is a sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase inhibitor that induces Ca2+ influx. The [Ca2+]cyt rise (ΔRatio) of MCT and control groups was then detected.
2.7. Real-Time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from EPCs in MCT and control groups using TRIzol® reagent (Invitrogen, Burlington, ON, Canada). The quality and concentration of total RNA were then determined with a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop 2000, Thermo Scientific, USA). Reverse transcription into cDNA was conducted using the PrimeScriptTM RT Master Mix Kit (Takara, Japan). The expression levels of Orai and TRPC channel were then detected by real-time PCR on the Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR System 7500 Fast (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The primers (forward and reverse, 5'- 3') for amplification of genes were as follows: Orai 1: AAGTTCTTACCGCTCAAGAGGCAG and AGCGGTAGAAGTGAACGGCAAAGA; Orai 2: TGTGGGTCTCATCTTCGTGGTCTT and TGAGCTTGTGCAGTTCCTCGATCT; Orai 3: TAGTGCCTGCACCACTGTGTTAGT and ATTGTGGATGTTGCTCACGGCTTC; TRPC7: AGACACGGAAGAGGTGGAAGCAAT and AGTTAGGGTGGGCAACGAACTTCT; TRPC6: TCTGGCTGCTCATTGCCAGGAATA and AGAGTGGCTGAAGGAGTCATGCTT; TRPC5: AGTTCACACCAGACATCACACCCA and TGAACTGGACACACACTCCACACA; TRPC4: AGTTTATCTGCCACACAGCCTCCT and AGTCCGCCATCCCACATCTGTTTA; TRPC3: TCTTCCTGGGTCTGCTTGTGTTCA and TGTCCATGTGAACTGGGTGGTCTT; TRPC2: TCCTGTGAAGATCAGCCATGTGGT and TGTCTGGGTTCAGCAAGTTCTCCA; and TRPC1: ACAGAAGATGCAGAGCACAGACCA and AAGTCCGAAAGCCAAGCAAATCCC. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate. Cycling parameters were set as follows: 50°C for 2 min and 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s, 60°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 30 s.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were independently repeated three times. All measurement data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) and analyzed for significant difference by using an unpaired Student's t-test Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). A value of P < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant result.
3. Results
3.1. The General Status of Animals
During the animal experiment, 2 and 3 rats in MCT group died in the third and fourth weeks after MCT injection, respectively. As a result, 45 rats were enrolled in this study. After 3 weeks of treatment, rats in MCT group appeared to obviously have asarcia, dyspnea, and chest and ascites formation, together with liver congestion and swelling, heart enlargement, right ventricular hypertrophy, and other heart failure manifestations. Rats in control group did not exhibit any abnormities.
3.2. MCT-Induced PAH in Rats
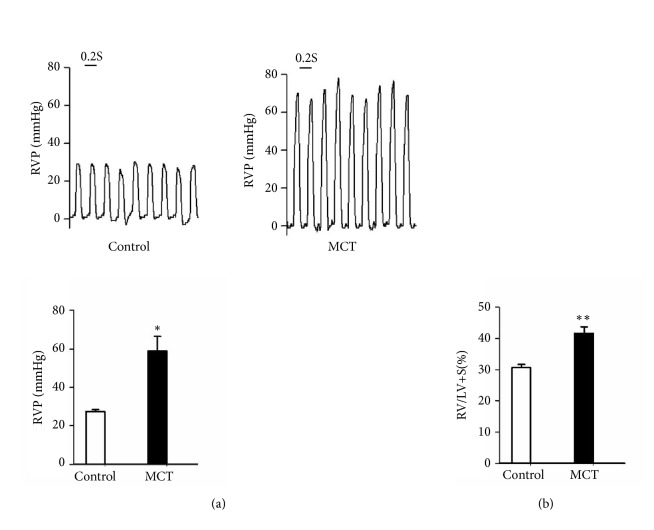
MCT was used to induce PAH in rats in this study. The results showed that rats in MCT group developed PAH after 3 weeks of MCT treatment as reflected by a remarkable increase in RVSP: 59.40 ± 8.13 mmHg in MCT rats versus 27.45 ± 0.89 mmHg in control rats (P< 0.05, Figure 1(a)). Moreover, the RVHI in MCT group (41.69 ± 2.00%) was significantly increased compared with that in the control group (31.00 ± 1.00%) (P< 0.01, Figure 1(b)). These data indicated that MCT successfully induced PAH in rats.
Figure 1.
Monocrotaline (MCT) induced pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in rats after 4 weeks of MCT treatment. (a) RVSP of rats in each group. (b) The RVHI of rats in each group. RVSP: right ventricular systolic pressure; RVHI: right ventricular hypertrophy index. ∗ P < 0.05 and ∗∗ P < 0.01 compared with control group.
3.3. Identification of BM-Derived EPCs
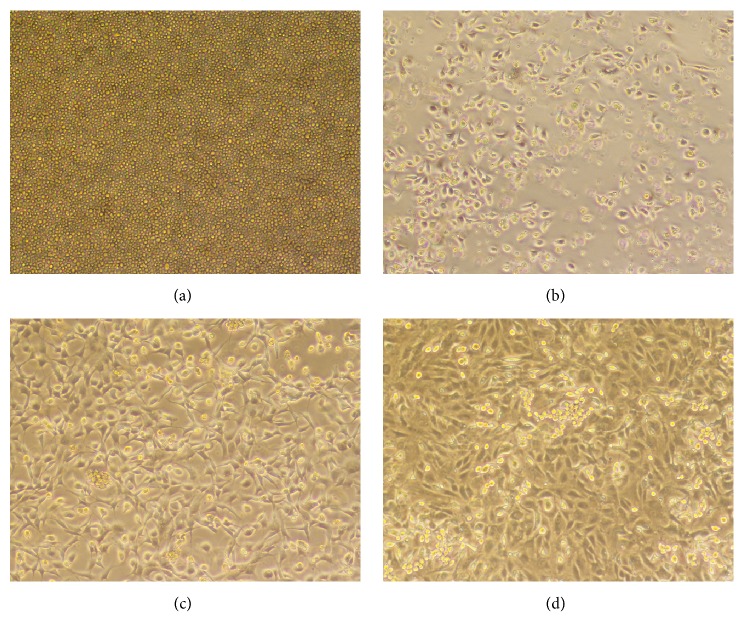
The morphological changes of EPCs were observed after culture for 1, 4, 6, and 8 days in the selective medium. After 1 day of culture, cells were adhered to the wall, but their morphology was not uniform and most of these cells were round (Figure 2(a)); some cells were polygonal or spindle-shaped after 4 days (Figure 2(b)); the majority of cells were polygonal or spindle-shaped after 6 days (Figure 2(c)); spindle-shaped or polygonal cells showed dominant growth after 8 days, paving stone-like arrangement and clear cell gaps (Figure 2(d)).
Figure 2.
The morphological changes of bone marrow- (BM-) derived endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) after culture for 1 (a), 4 (b), 6 (c), and 8 (d) days in the selective medium.
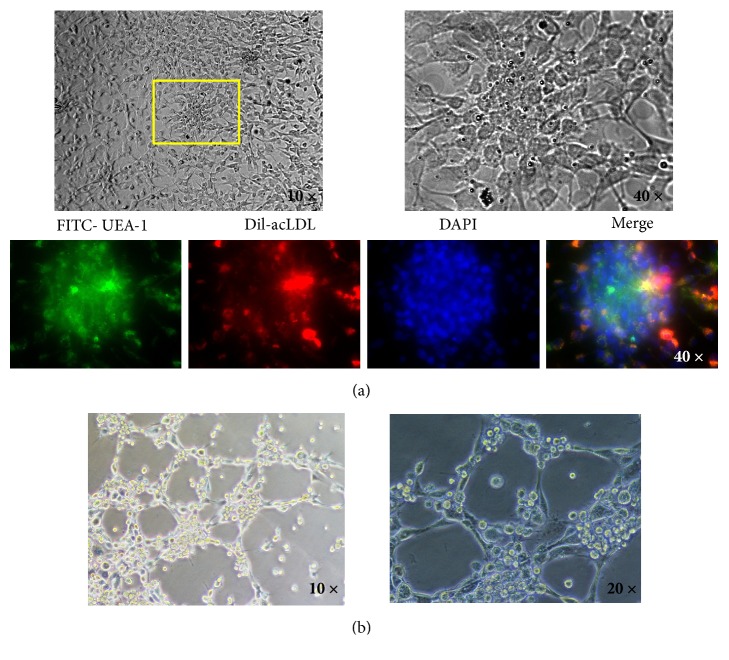
Furthermore, immunochemistry identification was performed after culture for 8 days in the selective medium. Double stained with FITC-UEA-1 and Dil-ac-LDL, EPCs in the adherent MNCs were identified (Figure 3(a)). Moreover, the results showed that 84.40 ± 8.06% of adherent MNCs were identified as double-positive EPCs, confirming that highly purified BM-derived EPCs were successfully isolated.
Figure 3.
BM-derived EPCs identification with immunochemistry (a), as well as the vascular network formation test (b).
3.4. Functional Analysis of BM-Derived EPCs by Detection of Vasculogenesis
To further confirm the function of BM-derived EPCs, the vasculogenic potential of EPCs was detected by the vascular network formation test. EPCs were seeded onto the Matrigel for incubation for 5 h. The results showed that the average length of vascular network per field of view was 9.78 ± 0.67 mm (Figure 3(b)).
3.5. MCT Decreased CPA-Induced SOCE in BM-Derived EPCs
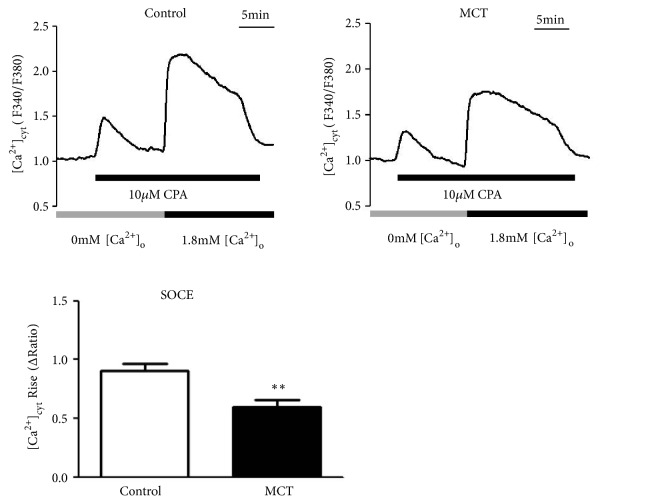
To determine whether MCT could regulate SOC in BM-derived EPCs, 10 μM CPA was extracellularly applied to detect the effects of MCT on SOCE. As shown in Figure 4, the [Ca2+]cyt rise (ΔRatio) of MCT group (0.60±0.21) was significantly lower than that in control group (0.91±0.23) (P< 0.01), indicating that MCT decreased CPA-induced SOCE.
Figure 4.
The [Ca2+]cyt rise (SOCE) of MCT and control group. ∗∗ P < 0.01 compared with control group.
3.6. The Effects of MCT on the Expression of Orai and TRPC Channel
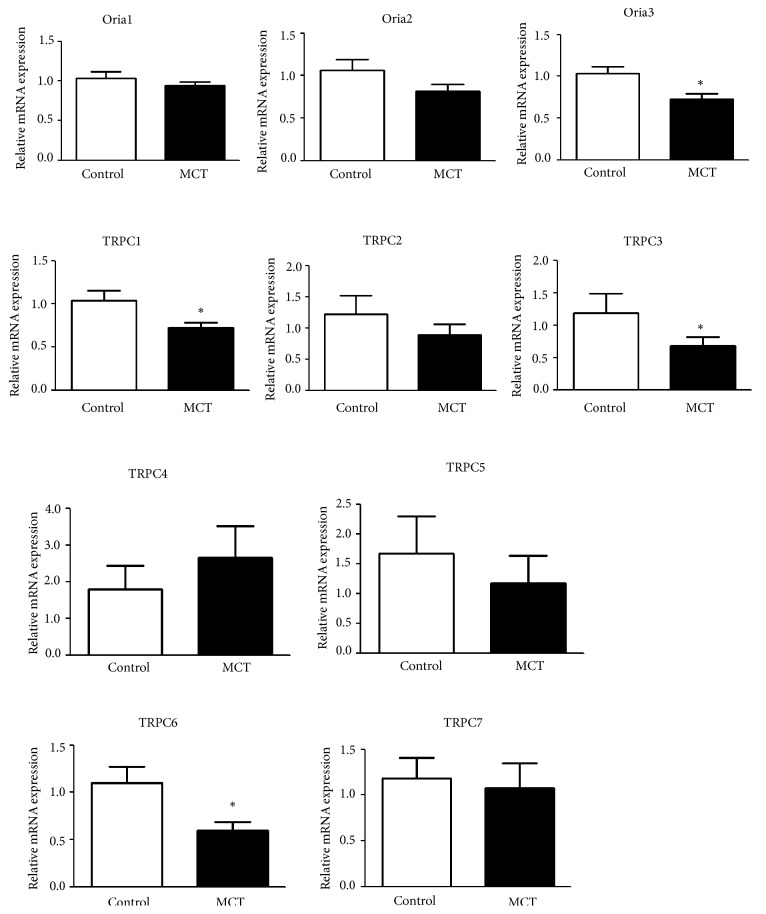
To further investigate the regulatory mechanism of MCT on SOC, we detected the Orai and TRPC channel expressions, including Orai1-3 and TRPC1-7. In comparison with control group, the expression levels of Orai3, TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC6 in BM-derived EPCs were significantly downregulated in MCT group (all P < 0.05, Figure 5), indicating that MCT decreased SOCE possible via decreasing the expression of these channel molecules.
Figure 5.
The expression of Orai and TRPC channels, including Orai1, Orai2, Orai3, TRPC1, TRPC2, TRPC3, TRPC4, TRPC5, TRPC6, and TRPC7, in MCT and control group. ∗ P < 0.05 compared with control group.
4. Discussion
PAH is a degenerating and devastating disease with limited treatment options [26]. Elucidation of the key mechanism underlying PAH will facilitate the development of effective therapeutic strategy for this disease. In this study, the MCT rat model of PAH was successfully established as reflected by a remarkable increase in RVSP and RVHI. Moreover, the delightful results were obtained that the SOCE ([Ca2+]cyt) rise in BM-derived EPCs of MCT rat model was significantly inhibited. Furthermore, the expression levels of Orai3, TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC6 were markedly decreased in BM-derived EPCs of MCT rat model. These data imply that BM-derived EPCs could be involved in MCT-induced PAH in rats via inhibiting SOCE and related channel expression.
Intracellular Ca2+ signaling, as an important second messenger for cell proliferation, is found to play an important role in numerous physiological and pathophysiological processes in PASMCs, like proliferation and hypertrophy [27]. SOCE is a ubiquitous Ca2+ entry pathway that is involved in the control of various physiological functions in various cell types [28]. When intracellular Ca2+ stores are depleted, SOC can mediate Ca2+ influx and increase [Ca2+]cyt [29]. Moreover, TRPC-dependent SOC is confirmed as an important pathway to mediate the development of MCT-induced PAH [14]. Lin et al. revealed that the enhanced SOCE is responsible for the chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats [30]. Zhou et al. demonstrated that SOC regulated endothelial hyperpermeability in severe PAH [31]. These data confirm the pathological role of SOC in PASMCs during PAH development. However, SOC may play a dual role in different cell types. A previous study has shown that SOCE is an important factor in regulating the functions of EPCs and the SOCE inhibition reduces the proliferation and migration of EPCs during atherosclerosis [32]. Wang et al. indicated that SOC inhibition could prevent H2O2-induced apoptosis, thus exerting a protective effect on EPCs [33]. Lodola et al. demonstrated that SOC was remodeled and subsequently regulated in vitro angiogenesis in EPCs isolated from tumoral patients [34]. In our study, SOC was inhibited by MCT in BM-derived EPCs of MCT-treated rats. Given the key role of SOC in EPCs, we speculate that BM-derived EPCs may prevent MCT-induced PAH in rats possible via activation of SOC.
Furthermore, both Orai and TRPC proteins are proposed to form SOC [35]. Increasing evidence has suggested the important roles of Orai and TRPC channels in PAH. Orai1, Orai12, and Orai3 can promote SOCE in PASMCs and may serve as potential therapeutic targets for chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension [36]. Dragoni et al. suggested that Orai3 is overexpressed in primary myelofibrosis-endothelial colony forming cells (ECFCs) that are EPC subset and thus resulted in the upregulation of SOCE [37]. In this study, Orai3 expression was markedly decreased in BM-derived EPCs of MCT rat model. Considering the key role SOC in PAH, we speculate that inhibition of SOCE due to the downregulation of Orai3 in BM-derived EPCs may play a key role in MCT-induced PAH. In addition, TRPC1 is a major constituent of SOCE and overexpression of TRPC1 can promote SOCE-induced vasoconstriction in rat pulmonary artery [38]. TRPC1 deficiency is found to impair the functions of EPCs on regulating angiogenesis [39]. Moreover, TRPC3 channels are found to be involved in the development of hypertension and its related complications [40]. Poteser et al. indicated that TRPC3 could regulate Ca2+ signaling in somatic EPCs [41]. TRPC3-mediated Ca2+ signaling in ECFCs is developed as a promising strategy for improving therapeutic angiogenesis in failing hearts [42]. Furthermore, TRPC6 is shown to be critically involved in the disease states of pulmonary vasculature [43]. Yu et al. revealed that a unique genetic variant of the TRPC6 gene promoter might result in pulmonary vascular abnormality in idiopathic PAH by linking abnormal TRPC6 transcription to nuclear factor-κB activity [44]. Additionally, functional interaction between TRPC1 and TRPC6 can mediate Ca2+ entry in endothelial cells to promote lung vascular permeability [45]. Blockade of TRPC3 and TRPC6 could be a promising therapeutic strategy for PAH treatment [46]. In this study, the expression of the store-operated TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC6 channels was decreased in BM-derived EPCs of MCT rat model, suggesting that BM-derived EPCs may be implicated in MCT-induced PAH via decreasing the expression of these channel molecules.
In conclusion, The SOC activities were inhibited in BM-derived EPCs of MCT-treated rats. These results may be associated with and the depressed expression of Orai3, TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC6, which are major mediators of SOC. Our findings may provide a physiological basis for the potential clinical application of the EPCs cell therapy to PAH.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270117, 81300044), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7162069), the Fund of The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0905600).
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Additional Points
Highlights. (1) MCT-induced PAH in rats successfully. (2) SOCE was decreased by MCT in BM-derived EPCs of MCT-treated rats. (3) The expressions of Orai3 and TRPC1, 3 and 6, were decreased in EPCs of MCT rats.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors' Contributions
Ran Miao and Jun Wan contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Naderi N., Boobejame P., Bakhshandeh H., Amin A., Taghavi S., Maleki M. Insulin resistance in pulmonary arterial hypertension, is it a novel disease modifier? Research in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2014;3(3):p. 8. doi: 10.5812/cardiovascmed.19710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Karpuz D., Hallioglu O., Buyukakilli B., et al. Clinical and histopathological relationship of sildenafil and bosentan treatments in rats with monocrotaline induced pulmonary hypertension. Bratislava Medical Journal. 2017;118(9):544–551. doi: 10.4149/BLL_2017_104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Frumkin L. R. The pharmacological treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pharmacological Reviews. 2012;64(3):583–620. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.005587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Asahara T., Murohara T., Sullivan A., et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302):964–967. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5302.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lau E. M. T., Humbert M., Celermajer D. S. Early detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nature Reviews Cardiology. 2015;12(3):143–155. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kaiser A., Malik F., Haque T., et al. The Right Ventricular Diameter can Predict the Presence of Pulmonary Hypertension. Bangladesh Heart Journal. 2016;30(2):p. 48. doi: 10.3329/bhj.v30i2.28810. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yamamura A., Yamamura H., Yuan J. X. Enhanced Ca2+-sensing Receptor Function in Pulmonary Hypertension. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(12):1351–1359. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wu K., Zhang Q., Wu X., et al. Chloroquine is a potent pulmonary vasodilator that attenuates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2017;174(22):4155–4172. doi: 10.1111/bph.13990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rothman A., Arnold N., Abou Hanna J., et al. P612Feasibility and safety of a wireless pulmonary artery pressure monitoring system in chronic porcine models of pulmonary hypertension. European Heart Journal. 2017;38(suppl_1) doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx501.P612. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Smith K. A., Ayon R. J., Tang H., Makino A., Yuan J. X.-J. Calcium-sensing receptor regulates cytosolic [Ca2+] and plays a major role in the development of pulmonary hypertension. Frontiers in Physiology. 2016;7 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fernandez R. A., Sundivakkam P., Smith K. A., Zeifman A. S., Drennan A. R., Yuan X.-J. Pathogenic role of store-operated and receptor-operated ca(2+) channels in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Journal of Signal Transduction. 2012;2012:16. doi: 10.1155/2012/951497.951497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yu Y., Sweeney M., Zhang S., et al. PDGF stimulates pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by upregulating TRPC6 expression. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2003;284(2):C316–C330. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00125.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yu Y., Fantozzi I., Remillard C. V., et al. Enhanced expression of transient receptor potential channels in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proceedings of the National Acadamy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101(38):13861–13866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405908101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Liu X.-R., Zhang M.-F., Yang N., et al. Enhanced store-operated Ca 2+ entry and TRPC channel expression in pulmonary arteries of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertensive rats. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2012;302(1):C77–C87. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00247.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Diller G.-P., Thum T., Wilkins M. R., Wharton J. Endothelial progenitor cells in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2010;20(1):22–29. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2010.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hill J. M., Zalos G., Halcox J. P. J., et al. Circulating endothelial progenitor cells, vascular function, and cardiovascular risk. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348(7):593–600. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa022287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Condorelli R. A., Calogero A. E., La Vignera S. The importance of the functional network between endothelial microparticles and late endothelial progenitor cells for understanding the physiological aspects of this new vascular repair system. Acta Physiologica. 2018;222(1) doi: 10.1111/apha.12931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhao Y. D., Courtman D. W., Deng Y., Kugathasan L., Zhang Q., Stewart D. J. Rescue of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension using bone marrow-derived endothelial-like progenitor cells: efficacy of combined cell and eNOS gene therapy in established disease. Circulation Research. 2005;96(4):442–450. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000157672.70560.7b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen H., Strappe P., Chen S., Wang L.-X. Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Heart, Lung and Circulation. 2014;23(7):595–601. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2014.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maron B. A., Zamanian R. T., Waxman A. B. Pulmonary Hypertension. New York, NY, USA: Springer International Publishing; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stenmark K. R., Meyrick B., Galie N., Mooi W. J., McMurtry I. F. Animal models of pulmonary arterial hypertension: the hope for etiological discovery and pharmacological cure. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2009;297(6):L1013–L1032. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00217.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bhat L., Hawkinson J., Cantillon M., et al. Evaluation of the effects of RP5063, a novel, multimodal, serotonin receptor modulator, as single-agent therapy and co-administrated with sildenafil, bosentan, and treprostinil in a monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rat model. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2018;827:159–166. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hoetzer G. L., Irmiger H. M., Keith R. S., Westbrook K. M., DeSouza C. A. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase inhibition does not alter endothelial progenitor cell colony forming capacity or migratory activity. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 2005;46(3):387–389. doi: 10.1097/01.fjc.0000175456.53869.ab. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fernandez R. A., Wan J., Song S., et al. Upregulated expression of STIM2, TRPC6, and orai2 contributes to the transition of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells from a contractile to proliferative phenotype. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2015;308(8):C581–C593. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00202.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wan J., Yamamura A., Zimnicka A. M., et al. Chronic hypoxia selectively enhances L- and T-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel activity in pulmonary artery by upregulating Cav1.2 and Cav3.2. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2013;305(2):L154–L164. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00313.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Boucherat O., Chabot S., Paulin R., et al. HDAC6: A Novel Histone Deacetylase Implicated in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1) doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04874-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Remillard C. V., Yuan J. X.-J. TRP channels, CCE, and the pulmonary vascular smooth muscle. Microcirculation. 2006;13(8):671–692. doi: 10.1080/10739680600930313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ong H. L., De Souza L. B., Ambudkar I. S. Role of TRPC channels in store-operated calcium entry. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2016;898:87–109. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-26974-0_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Roos J., DiGregorio P. J., Yeromin A. V., et al. STIM1, an essential and conserved component of store-operated Ca2+ channel function. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2005;169(3):435–445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200502019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lin M.-J., Leung G. P. H., Zhang W.-M., et al. Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation Research. 2004;95(5):496–505. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000138952.16382.ad. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhou C., Townsley M. I., Alexeyev M., Voelkel N. F., Stevens T. Endothelial hyperpermeability in severe pulmonary arterial hypertension: Role of store-operated calcium entry. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2016;311(3):L560–L569. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00057.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang L. Y., Zhang J. H., Yu J., Yang J., Deng M. Y., Kang H. L. Reduction of store-operated Ca(2+) entry correlates with endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in atherosclerotic mice. Stem Cells and Development. 2015;24(13):1582–1590. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang Y.-W., Zhang J.-H., Yu Y., Yu J., Huangame L. Inhibition of store-operated calcium entry protects endothelial progenitor cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis. Biomolecules & Therapeutics. 2016;24(4):371–379. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2015.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lodola F., Laforenza U., Bonetti E., et al. Store-operated Ca2+ entry is remodelled and controls in vitro angiogenesis in endothelial progenitor cells isolated from tumoral patients. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042541.e42541 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang X.-R., Lin M.-J., Sham J. S. K. Physiological functions of transient receptor potential channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 2010;661:109–122. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang J., Xu C., Zheng Q., et al. Orai1, 2, 3 and STIM1 promote store-operated calcium entry in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Cell Death Discovery. 2017;3:p. 17074. doi: 10.1038/cddiscovery.2017.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dragoni S., Laforenza U., Bonetti E., et al. Enhanced Expression of stim, orai, and TRPC transcripts and proteins in endothelial progenitor cells isolated from patients with primary myelofibrosis. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kunichika N., Yu Y., Remillard C. V., Platoshyn O., Zhang S., Yuan J. X. Overexpression of TRPC1 enhances pulmonary vasoconstriction induced by capacitative Ca2+ entry. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2004;287(5):L962–L969. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00452.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Du L., Shen Z., Li Z., et al. TRPC1 Deficiency Impairs the Endothelial Progenitor Cell Function via Inhibition of Calmodulin/eNOS Pathway. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research. 2018;11(4):339–345. doi: 10.1007/s12265-018-9798-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wang P., Liu D., Tepel M., Zhu Z. Transient receptor potential canonical type 3 channels - Their evolving role in hypertension and its related complications. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 2013;61(6):455–460. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31828748a1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Poteser M., Yates AE., Maechler H., Graziani A., Krenn M., Eder P. TRPC3 contributes to PLC-mediated Ca2+ signalling in somatic endothelial progenitor cells. Archiv Für Experimentelle Pathologie Und Pharmakologie. 2017;41 [Google Scholar]
- 42.Moccia F., Lucariello A., Guerra G. TRPC3-mediated Ca2+ signals as a promising strategy to boost therapeutic angiogenesis in failing hearts: The role of autologous endothelial colony forming cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2018;233(5):3901–3917. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Malczyk M., Erb A., Veith C., et al. The role of transient receptor potential channel 6 channels in the pulmonary vasculature. Frontiers in Immunology. 2017;8 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yu Y., Keller S. H., Remillard C. V., et al. A functional single-nucleotide polymorphism in the TRPC6 gene promoter associated with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2009;119(17):2313–2322. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.782458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mohammad T., Knezevic N., Vidisha K. TRPC6 and TRPC1 functionally interact to mediate Ca2+ entry in endothelial cells to induce lung vascular permeability. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics. 1999;116(3):207–15. doi: 10.1046/j.1439-0388.1999.00187.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kinoshita H., Kuwahara K., Kiyonaka S., et al. TRPC3/6 as Potentially Novel Therapeutic Targets for The Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Cardiac Failure. 2011;17(9):p. S153. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2011.06.502. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.