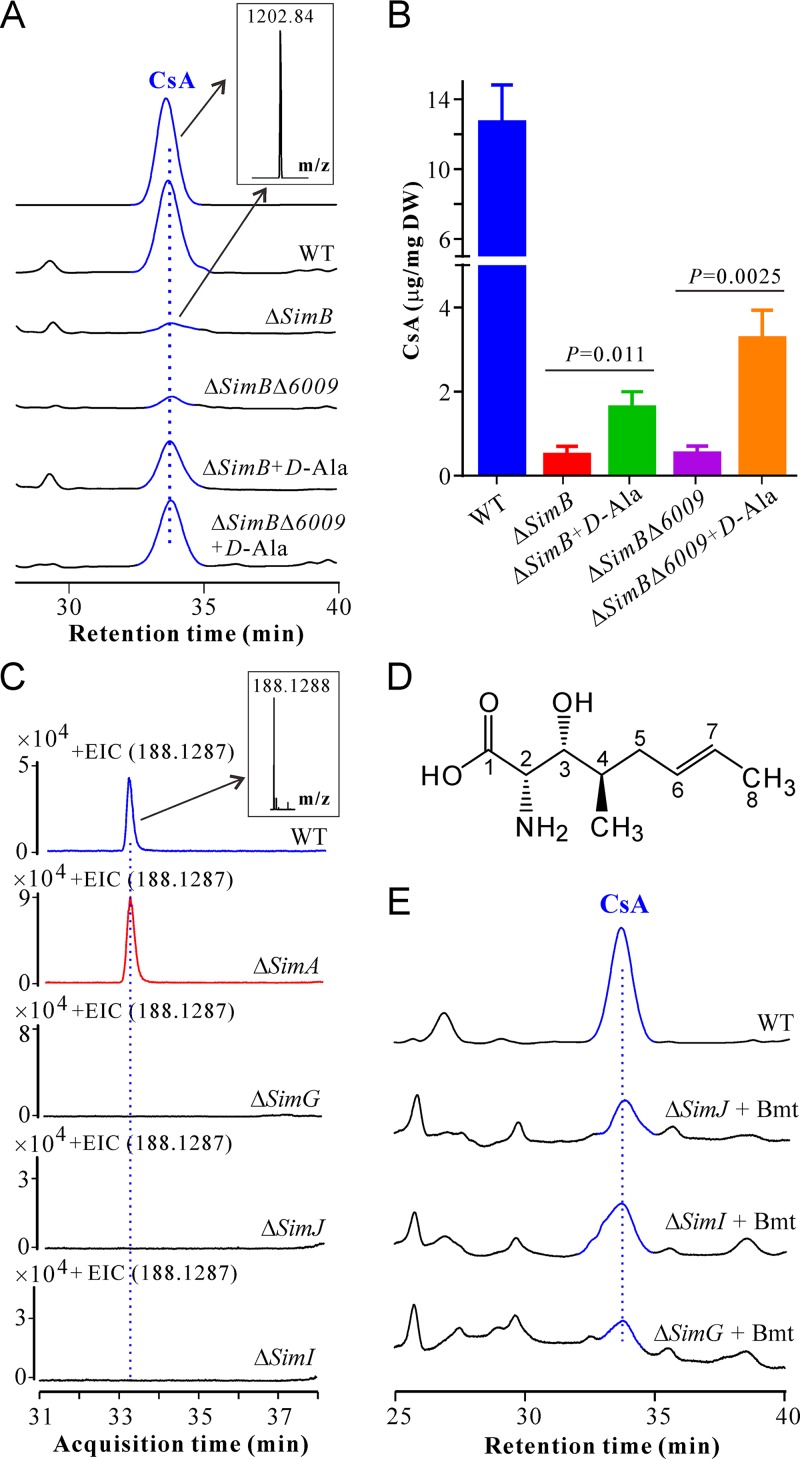
FIG 2.
Verification of the genes involved in d-Ala conversion and Bmt biosynthesis. (A) HPLC analysis of CsA production by WT and different mutants with or without the addition of d-Ala. The inset shows the mass spectra detected for the CsA and ΔsimB samples. m/z, [M+H]+; ΔSimBΔ6009, ΔSimB ΔTINF06009 double mutant. (B) Quantification analysis of CsA production by WT and different mutants. The strains were grown in fructose CSN induction medium with or without the supplementation of d-Ala (at a final concentration of 20 mM) for 10 days. The mycelia were then harvested for CSN extraction. Values are means plus standard errors (SE) (error bars). DW, mycelium dry weight. (C) LC-MS analysis of the extracted ion chromatography (EIC) showing the production or nonproduction of Bmt by WT and mutant strains. m/z, [M+H]+. (D) Chemical structure of Bmt. (E) Supplementation of Bmt (at a final concentration of 85 μM) in the growth medium enabled the null mutants to produce CsA (peaks shown in blue).