Abstract
Multiple neuromodulators act in concert to shape the properties of neural circuits. Different neuromodulators usually activate distinct receptors but can have overlapping targets. Therefore, circuit output depends on neuromodulator interactions at shared targets, a poorly understood process. We explored quantitative rules of co-modulation of two principal targets of neuromodulation: synapses and voltage-gated ionic currents. In the stomatogastric ganglion of the male crab Cancer borealis, the neuropeptides proctolin (Proc) and the crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP) modulate synapses of the pyloric circuit and activate a voltage-gated current (IMI) in multiple neurons. We examined the validity of a simple dose-dependent quantitative rule, that co-modulation by Proc and CCAP is predicted by the linear sum of the individual effects of each modulator up to saturation. We found that this rule is valid for co-modulation of synapses, but not for the activation of IMI, in which co-modulation was sublinear. The predictions for the co-modulation of IMI activation were greatly improved if we assumed that the intracellular pathways activated by two peptide receptors inhibit one another. These findings suggest that the pathways activated by two neuromodulators could have distinct interactions, leading to distinct co-modulation rules for different targets even in the same neuron. Given the evolutionary conservation of neuromodulator receptors and signaling pathways, such distinct rules for co-modulation of different targets are likely to be common across neuronal circuits.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT We examine the quantitative rules of co-modulation at multiple shared targets, the first such characterization to our knowledge. Our results show that dose-dependent co-modulation of distinct targets in the same cells by the same two neuromodulators follows different rules: co-modulation of synaptic currents is linearly additive up to saturation, whereas co-modulation of the voltage-gated ionic current targeted in a single neuron is nonlinear, a mechanism that is likely generalizable. Given that all neural systems are multiply modulated and neuromodulators often act on shared targets, these findings and the methodology could guide studies to examine dynamic actions of neuromodulators at the biophysical and systems level in sensory and motor functions, sleep/wake regulation, and cognition.
Keywords: central pattern generator, neuromodulation, peptide, stomatogastric
Introduction
All nervous systems adapt to changes in the environment and the internal state of the animal. In different contexts, awake or asleep, fed or hungry, light or dark, neuronal circuits produce different output (Xia and Mills, 2004; Inagaki et al., 2014; Wester and McBain, 2014; Burke et al., 2015; Filosa et al., 2016). Context-dependent output is actively shaped by neuromodulators through changes in neuronal and synaptic properties (for review, see Brezina, 2010; Bargmann, 2012; Marder, 2012; Nadim and Bucher, 2014). The combination and distribution of neuromodulators present depends on context and often is the means to convey it (Cohn et al., 2015; Lovett-Barron et al., 2017; White et al., 2017). Consequently, essential behaviors such as breathing, sleeping, learning, and mating, as well as cognitive tasks, rely on combined actions of multiple neuromodulators (Doi and Ramirez, 2008; Woods et al., 2014; He et al., 2015; Yamazoe-Umemoto et al., 2015; Mena et al., 2016; Asahina, 2017; Donlea et al., 2017).
Although much is known about the actions of single neuromodulators, few studies have explored how multiple neuromodulators interact. Most studies of co-modulation have provided qualitative descriptions at the systems level (Brezina et al., 1996; Dickinson et al., 1997; Mesce et al., 2001; Thirumalai and Marder, 2002; Beliez et al., 2014). In general, neuromodulators target intrinsic neuronal excitability and/or synaptic transmission. A neuromodulator can have multiple targets (divergence) and multiple neuromodulators can have overlapping targets (convergence) (for review, see Nadim and Bucher, 2014), resulting in complex co-modulatory effects on neuronal and synaptic function and consequently circuit output. To understand how co-modulation shapes circuit output, it is important to characterize how co-modulation occurs at shared targets. However, only a few studies have explored co-modulation of the direct targets, also mostly qualitatively (McCormick and Pape, 1990; Parker, 2000; Djokaj et al., 2001; Svensson et al., 2001; Park and Spruston, 2012; Garcia et al., 2015).
Here, we focus on convergent co-modulation of synapses and voltage-gated currents by exploring whether the combined actions of neuromodulators on a shared target can be predicted quantitatively from their individual actions and if co-modulation of synaptic and voltage-gated ionic currents in a neuron follows the same rule. For neuromodulators with converging signaling pathways, the most parsimonious prediction would be that their effects at a shared target simply add up linearly to produce a combined effect up to the saturation level. It should be noted, however, that such linear addition does not exclude the possibility that each separate modulator has a nonlinear effect with a distinct dose dependence. In addition, the dynamics and physiological effects of modulating a target can be complex and nonlinear.
In this study, we used the pyloric circuit of the crab stomatogastric ganglion (STG) to determine whether the dose-dependent actions of two peptide neuromodulators on their targets can be predicted by the linear summation of their individual actions up to saturation. Several peptides activate IMI, a voltage-gated ionic current (Golowasch and Marder, 1992; Swensen and Marder, 2000), in STG neurons likely through converging signaling pathways from different receptors (Garcia et al., 2015; Gray et al., 2017). Some also modulate chemical synapses (Thirumalai et al., 2006; Zhao et al., 2011; Garcia et al., 2015). We measured the influence of the two peptide neuromodulators on synaptic currents and on IMI. Because the influence of the peptides on these components can be assayed simultaneously, they provide a good test for understanding the rules of co-modulation of different aspects of neuronal processing. We found that co-modulation of synaptic transmission and the voltage-gated current follows distinct rules. The machinery underlying neuromodulation is evolutionarily well conserved. Most receptors have homologs across invertebrate and vertebrate systems (Mirabeau and Joly, 2013; Lovett-Barron et al., 2017) and many neuromodulators share G-protein-mediated signaling pathways (Doi and Ramirez, 2008). Therefore, such distinct rules for co-modulation of different components are likely to be used in other neuronal circuits and by other neuromodulators.
Materials and Methods
Preparation and electrophysiological recordings.
All experiments were done on wild-caught adult male crabs (Cancer borealis) purchased from local seafood stores. Before experiments, animals were kept in artificial sea water tanks at 13°C. Before dissection, crabs were anesthetized by placing on ice for at least 30 min. The stomatogastric nervous system was dissected out following standard protocols (Blitz et al., 2004; Tohidi and Nadim, 2009), placed in a Petri dish coated with clear silicon elastomer (Sylgard 184; Dow-Corning), and superfused with C. borealis saline containing the following (in mm): 11 KCl, 440 NaCl, 13 CaCl2, 26 MgCl2, 11.2 Trizma base, and 5.1 maleic acid, pH 7.4–7.5. A petroleum jelly well was built around the STG for constant superfusion of chilled (10–12°C) saline during the experiment.
For neuron identification, extracellular motor nerve recordings were obtained with a differential AC amplifier (Model 1700; A-M Systems) using stainless-steel pin wire electrodes placed inside and outside of small petroleum jelly wells built around the nerves. Intracellular recordings and voltage clamp were done with Axoclamp 900A amplifiers (Molecular Devices). The STG was desheathed and the neuron somata were impaled with sharp glass electrodes, pulled with a Flaming-Brown P-97 Puller (Sutter Instruments), and filled with 0.6 m K2SO4 + 20 mm KCl solution (15–30 MΩ electrode resistance). Neurons were identified by their characteristic intracellular waveforms and by matching their activities to the spikes on the corresponding motor nerves. All electrophysiological data were digitized at 5–10 kHz with a Digidata 1440A data acquisition board (Molecular Devices).
Neuromodulatory effects on the strength and dynamics of the synaptic currents.
The neuromodulatory effects on strength and short-term plasticity of the graded component of both the lateral pyloric (LP) to pyloric dilator (PD) and the PD to LP synapses were measured with simultaneous dual two-electrode voltage clamp recordings of the PD and LP neurons.
In voltage-clamp experiments, 100 nm tetrodotoxin citrate (TTX; Biotium; RRID:SCR_013538) saline was bath applied to block action potentials and descending neuromodulatory inputs. The synaptic current was measured as the current elicited in the postsynaptic neuron (held at −50 mV) in response to depolarizing 500 ms voltage steps in the presynaptic neuron (from a holding potential of −60 to 0 mV in 10 mV steps; Fig. 1B,C). The postsynaptic current reported in this study is the mean value of the current during the presynaptic pulse (the postsynaptic current integral divided by the presynaptic voltage step duration of 500 ms). The peak values of the synaptic currents during each voltage step are included in Fig. 2-1.
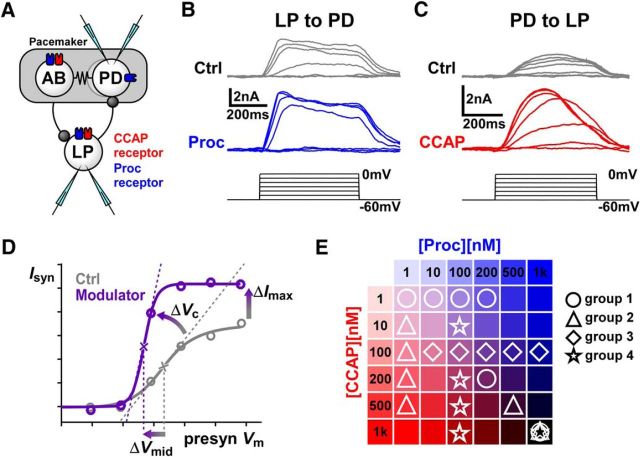
Figure 1.
CCAP and Proc modulate the strength and activation curves of the reciprocal synapses between LP and PD neurons. A, Schematic diagram of the synaptic connectivity between the electrically coupled (resistor symbol) pyloric pacemaker neurons AB and PD and the follower LP neuron. Both synapses (stick-and-ball symbols) are inhibitory. Also shown are the known receptor expression for CCAP and putative receptor expression for Proc in these neurons. The experimental protocol involved simultaneous two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings of the PD and LP neurons. B, Example recordings of postsynaptic currents measured in the PD neuron in response to voltage steps in the presynaptic LP neuron in control saline (Ctrl) and in the presence of 1 μm Proc. Measurements were done in 0.1 μm TTX. C, Example recordings of synaptic currents measured in the LP neuron in response to voltage steps in the presynaptic PD neuron in control saline (Ctrl) and in the presence of 1 μm CCAP. Measurements were done in 0.1 μm TTX. D, To measure the modulatory effects, the mean value of the postsynaptic currents was plotted against the presynaptic voltage and fit with a Boltzmann type sigmoidal function. Changes in Imax, Vmid, and Vc were compared in control and in the presence of the modulator. E, Schematic diagram showing how the 18 different combinations of concentrations of the two modulators were divided into four separate groups of experiments.
To fit the postsynaptic current amplitude as a function of presynaptic voltage (Vpre), we used a sigmoid function of the following form:
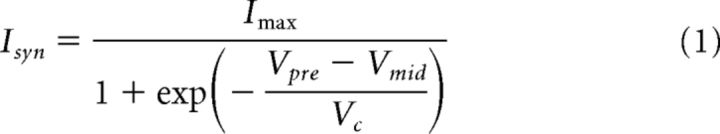 |
where Imax is the maximum current, Vmid is the activation midpoint voltage, and Vc is the activation slope factor at Vmid. In these fits, we assumed that the postsynaptic current was 0 at Vpre = −70 mV.
Proctolin (Proc) (Bachem; RRID:SCR_013558) and CCAP (Bachem) were aliquoted in 1 mm stock solutions and stored at −20°C until use. For each experiment, the aliquots were further diluted to the desired concentrations. The dose-dependent effect of Proc or CCAP on synapses was measured by bath applying each peptide from low to high concentration (1 nm to 1 μm) with a 4 min interval between each concentration. We considered 1 μm to be the saturation concentration of both Proc and CCAP based on previous studies (Zhao et al., 2011). In addition, 1 μm Proc and CCAP were co-applied at the end of each experiment to measure the maximum modulatory effect.
To measure short-term synaptic plasticity, we voltage clamped the presynaptic neuron at a holding potential of −60 mV and applied a set of 5 500-ms identical depolarizing square pulses from −60 to −20 mV at 1 Hz. We measured the mean current amplitude in the postsynaptic neuron (voltage clamped at −50 mV) in response to each pulse. The level of short-term plasticity was quantified as the ratio of the postsynaptic current amplitude elicited by the fifth and first pulses. For the experiments that had two repeated measurements, we averaged the two measurements.
Neuromodulatory effects on IMI.
The modulator-activated inward current IMI was measured in the LP neuron in the same experiments in which we measured the LP to PD synaptic current. Because, in these experiments, the LP neuron membrane potential was stepped from −60 to 0 mV for measuring the LP to PD synapse (using the current measured in the postsynaptic PD neuron), the same voltage steps could be used to measure IMI in the LP neuron (using the voltage-clamp current, ILP, injected in the presynaptic LP neuron). IMI was measured as the difference between ILP measured in the presence of the modulator and ILP measured in control saline (Golowasch and Marder, 1992). To reduce errors due to differences in transient currents, we reported the mean value of the difference current, measured in the second half of each voltage pulse where the currents had reached approximate steady state.
IMI is a mostly noninactivating fast voltage-gated inward current (Golowasch and Marder, 1992; Gray et al., 2017) with an activation curve that is a simple Boltzmann sigmoidal equation Goaillard et al., 2009). The current–voltage (I–V) curve of IMI can therefore be estimated as follows:
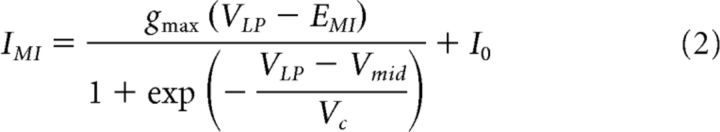 |
where gmax is the maximum conductance of IMI, EMI is the reversal potential, and I0 is the baseline difference current. Vmid is the activation midpoint voltage and Vc is the activation slope factor at Vmid. All measurements of IMI levels with the step protocol were used to estimate the fit parameters in each experiment, allowing only gmax and I0 to change with concentration. The peak currents (in absolute value) obtained from the fit I–V curves were used for analysis.
The protocols for the dose-dependent effects of the modulators and for co-modulation of IMI were the same as those described for the synapses above.
Constructing predictors for single neuromodulators.
For each neuromodulator–synapse pair, we fit a surface to the postsynaptic currents measured at all presynaptic voltages and concentrations in multiple experiments. The equation used to define this surface was a dual sigmoidal function of both the presynaptic voltage (Vpre) and the log peptide concentration (C). This equation was based on Equation 1, so that:
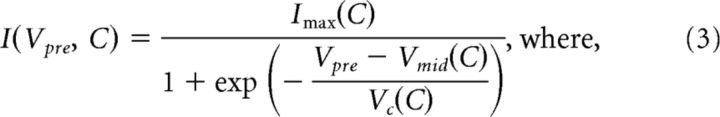 |
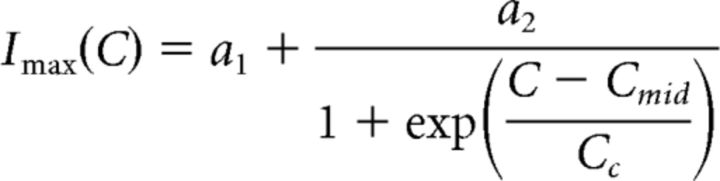 |
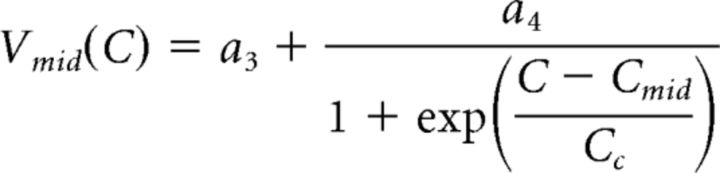 |
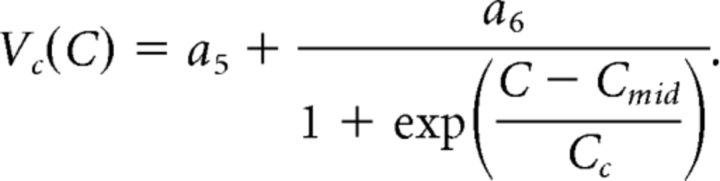 |
In these fits, the unit of peptide concentration is m, and the control value was set at C = −10, thus assuming that 10−10 m concentration had no effect. The enhancement functions for each peptide were defined as the increase produced by the modulator above the control level of the synaptic current at each presynaptic voltage as follows:
The resulting enhancement functions served as predictors for the effect of the neuromodulator on the postsynaptic current at any voltage and concentration.
In the case of IMI, we fit the dose-dependent effects of Proc and CCAP with the sigmoidal curve as follows:
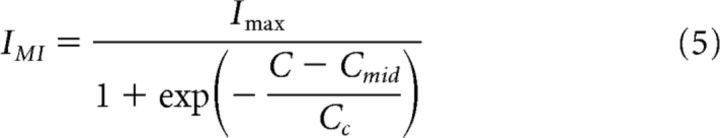 |
where C is the log peptide concentration and Cmid and Cc are, respectively, the half-maximum log concentration and the slope factor. In these fits, the unit of peptide concentration is m and the control value was set at C = −10, assuming that 10−10 m concentration had no effect.
Predicting co-modulation.
We compared the predictions of co-modulation effects with the experimental data from coapplications of Proc and CCAP in 18 different combinations of concentrations for both the LP to PD and the PD to LP synapses and IMI in the LP neuron. These 18 combinations were divided into four separate groups of experiments, with each group only containing four or five combinations (Fig. 1E). In each group of experiments, each peptide was applied in order from lower to higher concentration. Each combination was bath applied for a 4 min interval. At the end of each experiment, Proc and CCAP were co-applied at 1 μm each to record the maximum modulatory effect in that preparation.
The predictions for synapses were calculated by adding up the enhancements produced by each peptide at the respective concentrations (obtained from Eq. 4) and the control value (ICtrl_co−mod) and limiting the sum to the saturation level (Isat_co−mod), which is the synaptic current elicited by both peptides co-applied at 1 μm.
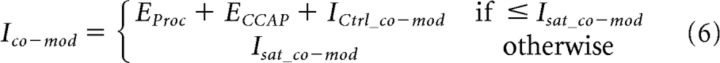 |
For each combination, we measured the co-modulated synaptic currents, as described above, at presynaptic voltages from −60 to 0 mV in 10 mV steps. We then compared the measurement with the prediction for those voltages.
The co-modulation predictions for IMI were calculated by simply adding up the value of IMI activated by each modulator at its respective concentration on the dose–response curve limited to the saturation level.
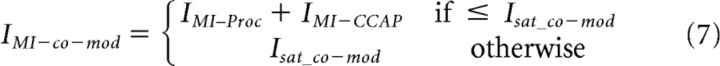 |
The sublinear co-modulation predictions for IMI were calculated by assuming that the presence of each neuromodulator inhibited the activation of IMI by the other modulator in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, in the presence of both modulators, Equation 5 was modified as follows:
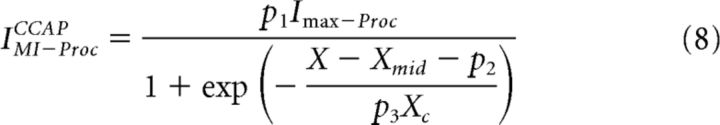 |
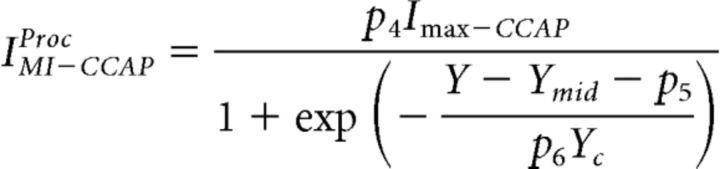 |
where X and Y, respectively, represent the concentrations of Proc and CCAP and Xmid, Xc, Ymid, and Yc are the dose–response parameters (Eq. 5). IMI−ProcCCAP is the dose-dependent level of IMI activated by Proc in the presence of CCAP. The parameters p1, p2, and p3 depend on the presence of CCAP. In our fits, these parameters were restricted so that 0 < p1 ≤ 1 so that the effect of each modulator on the other was inhibitory, and −1.5 < p2 ≤ 1.5 and 0.1 < p3 ≤ 1 so that CCAP could have a modest effect on the dose-dependent activation of IMI by Proc. In the absence of CCAP, p1 = 1, p2 = 0, and p3 = 1 so that IMI−procCCAP simply produced the dose-dependent activation of IMI by Proc alone, as given by Equation 5. IMI−CCAPProc can be described similarly, with the two modulators reversed.
The nonlinear co-modulation rule was provided, as in Equation 7, to be as follows:
 |
Data analysis and statistical analysis.
All data and statistical analysis were done with MATLAB (MathWorks; RRID:SCR_001622) and R (The R Foundation). The details for quantification of electrophysiology data are described above. Statistical tests included Student's t test, one- or two-way repeated-measures (RM)-ANOVA. One-way RM-ANOVA was used to evaluate the dose-dependent effects of individual peptides on synapses to compare changes across treatment of the same groups. Two-way RM-ANOVA was conducted to compare the voltage-dependent effects of single peptides on synapses and the effects of co-modulation on synapses (within the same groups), as well as to compare the co-modulated synaptic current level and the control synaptic current level (among different groups). Paired Student's t test was used to compare the maximum level of IMI activated by co-modulation. Critical significance level was set to α = 0.05. To estimate how well our model predictions fit the experimental results, we used the coefficient of determination R2 measured as follows: R2 = 1 − , where SSR = ∑i=1n (predi − measi)2 is the summed square of the residuals and SST = ∑i=1n(measi − measavg)2 is the total sum of squares. R2 = 1 means that the prediction fits the data perfectly. Note, however, that this R2 is different from the Pearson correlation coefficient where a linear fit to the data is evaluated. In our case, R2 may be < 0, which simply indicates that the mean of the data measavg provides a better prediction than the model. Unless otherwise indicated, all error bars in the figures represent SEM.
Results
We explored the modulatory effects of the two neuropeptides CCAP and Proc on IMI in the LP neuron and on the reciprocal synapses between the LP and the PD neurons. The influence of these peptides on pyloric neurons and synapses can be assayed simultaneously, whereas all other neuromodulatory inputs are removed.
We began by quantifying the individual modulatory effects of CCAP and Proc on both synapses and IMI in the LP neuron across a range of concentrations, ranging from subthreshold to saturation. These dose-dependent quantifications allowed us to build predictors of the modulatory effect of each individual modulator at any concentration.
We then characterized the effect of coapplication of both peptides in two stages. First, we investigated whether co-modulation is history dependent by co-applying the peptides following exposure to either Proc or CCAP because interactions between neuromodulators can depend on the order of application and produce priming or gating (Dickinson et al., 1997; Svensson et al., 2001). Then, in separate experiments, we tested the effect of various combinations of the two peptides applied at different concentrations and compared the results with the predictions of the linear summation rule.
Dose-dependent effect of individual peptides on the synapses
We quantified the individual modulatory effects of CCAP and Proc in separate sets of experiments. In each experiment, we measured the effect of the peptide on both the LP to PD and the PD to LP synapses. Therefore, we will present four different synapse–peptide cases: LP to PD-CCAP, LP to PD-Proc, PD to LP-CCAP, and PD to LP-Proc.
In each synapse–peptide case, we measured the postsynaptic current in control and in increasing concentrations of the peptide with simultaneous two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings of both neurons (Fig. 1A). In the STG, two identical PD neurons and the anterior burster (AB) neuron are strongly electrically coupled and form the pacemaker group. Unless specified otherwise, the PD to LP synapse in this study refers to the combined synaptic current from the pacemaker group (the AB and the two PD neurons) to the LP neuron. As expected for a graded synapse, the amplitude of postsynaptic current increased as the presynaptic step voltage increased (Figs. 1B,C). The I–V relationship of each synapse was fit with the sigmoidal curve given by Equation 1, which is described by three parameters: Imax, Vmid, and Vc. A more positive Vmid indicates a higher threshold for activation and larger Vc means a shallower activation curve (Fig. 1D). For each synapse–peptide pair, we investigated how Imax, Vmid, and Vc were changed by the peptides (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
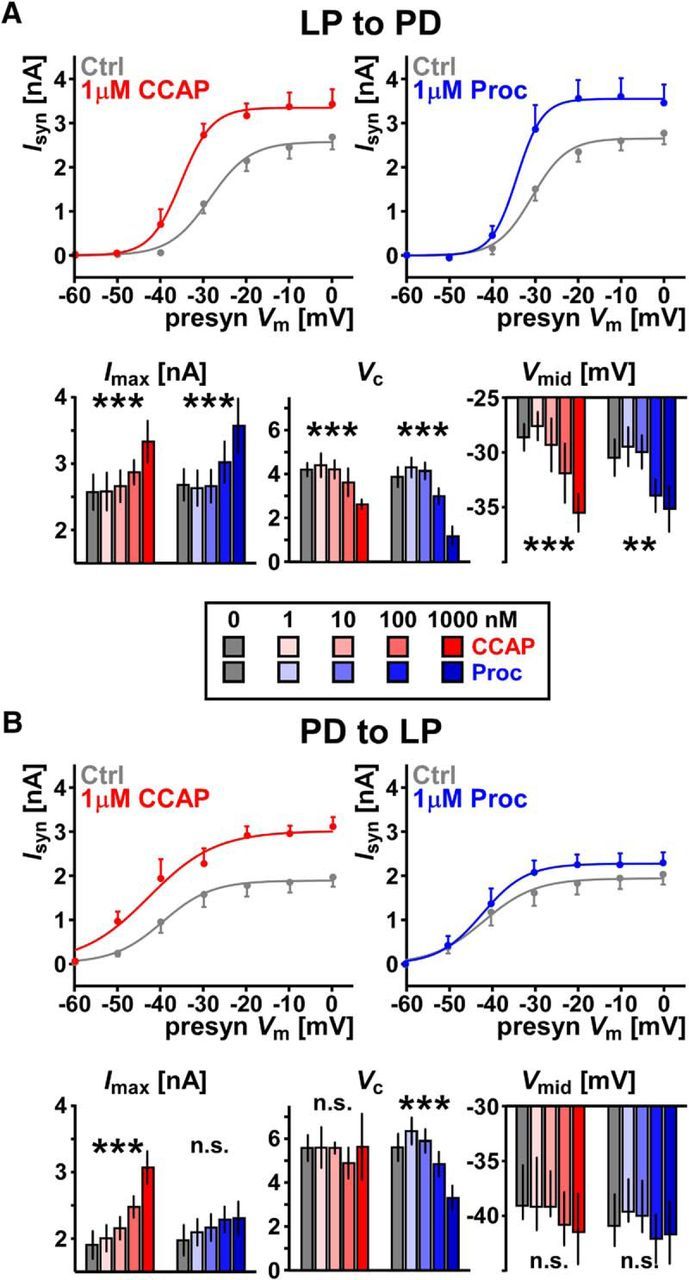
CCAP and Proc modulate the synapses between the LP and PD neurons in a dose-dependent manner. A, Both CCAP and Proc increase the amplitude of the LP to PD postsynaptic current (Isyn). Top panels show mean and SEM of Isyn as well as sigmoidal fits for control and modulators applied at the maximum concentration of 1 μm. As the applied concentration is increased, CCAP increases Imax (F(4,16) = 18.4, p = 7.83 × 10−6), decreases the slope factor Vc (F(4,16) = 7.98, p = 0.00098), and decreases Vmid (F(4,16) = 14.3, p = 3.78 × 10−5). (All tests one-way RM-ANOVA, n = 5). Proc has a similar effect on these three parameters (F(4,20) = 7.32, p = 0.00084 for Imax, F(4,20) = 30.4, p = 3.05 × 10−8 for Vc, and F(4,20) = 5.24, p = 0.0047 for Vmid, one-way RM-ANOVA, n = 6). B, As the applied concentration increases, CCAP, but not Proc, increases the amplitude of the PD to LP synapse. Top panels as in A. CCAP increases Imax (F(4,20) = 22.8, p = 3.31 × 10−7), but not Vmid (F(4,20) = 0.872, p = 0.498) or Vc (F(4,20) = 0.172, p = 0.95), Proc modulates Vc (F(4,20) = 12.4, p = 3.06 × 10−5), but not Imax (F(4,20) = 1.57, p = 0.22) or Vmid (F(4,20) = 2.19, p = 0.107). All tests one-way RM-ANOVA, n = 6. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. All raw data are provided in Figure 2-1.
All data used for the analysis shown in Figure 2, 3 and 4. All individual experiments end with a co-application of Proc and CCAP at 10-6 M. The Excel file contains multiple sheets whose names include the (primary) neuromodulator and the synapse. Data columns 3-9 are the fit parameters according to equation . Data columns 10-end are the raw values, corresponding to the voltage step indicated in the column title. The columns marked as "mean" were measurements of the mean postsynaptic current value during the presynaptic voltage step. The columns marked as "peak" indicate the maximum value of the current during the same step. Only the mean current values were used for the analysis in the Results and Figures 2 to 4. Download Figure 2-1, XLSX file (48.9KB, xlsx)
At the LP to PD synapse, both CCAP and Proc significantly increased Imax, shifted Vmid to more negative potentials, and reduced Vc across concentrations (Fig. 2A). In contrast, at the PD to LP synapse, CCAP only increased Imax, but did not affect Vmid or Vc, whereas Proc only decreased Vc, but did not affect Imax or Vmid (Fig. 2B).
The same peptide differentially modulated different synapses. For example, CCAP changed Imax, Vmid, and Vc at the LP to PD synapse, but only Imax at the PD to LP synapse. In addition, different peptides had different effects on the same synapse. For example, CCAP changed only Imax at the PD to LP synapse, whereas Proc changed Vc. Overall, both CCAP and Proc strengthened both synapses, although the manner of modulation depended on the synapse and the modulator.
The pyloric circuit is rhythmically active, with a frequency between ∼0.5 and 2 Hz (Goaillard et al., 2009). Like many synapses in the STG, the LP to PD and PD to LP synapses exhibit short-term synaptic depression (Tseng and Nadim, 2010; Zhao et al., 2011). In rhythmically active circuits, short-term synaptic plasticity means that the strength of the synapse depends on the period of the rhythm (Manor and Nadim, 2001). This means that depressing synapses are weaker if the rhythm becomes faster, whereas the opposite is true for facilitating synapses. Therefore, neuromodulation of short-term synaptic plasticity can play an important role in shaping circuit output and dynamics. However, at both synapses, we found that neither CCAP nor Proc nor coapplication of both significantly changed the level of short-term synaptic depression with a presynaptic voltage step of 40 mV amplitude (Fig. 3). This finding is consistent with a prior study of the effects of Proc on the PD voltage responses to large LP depolarizations (Zhao et al., 2011).
Figure 3.
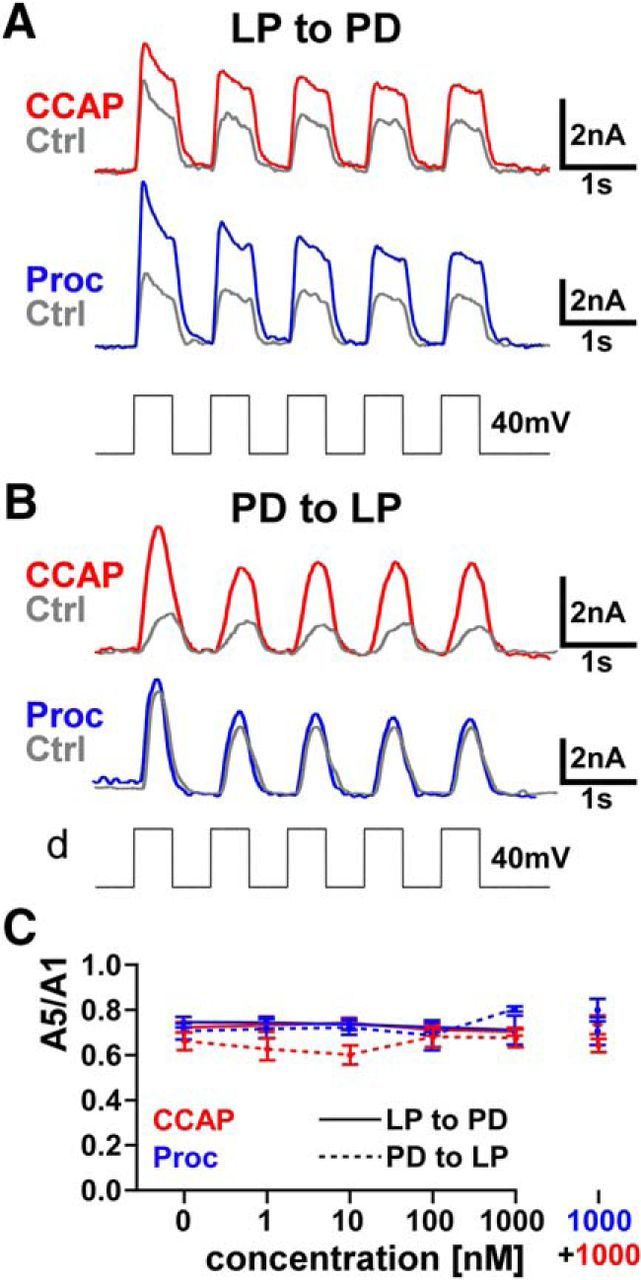
CCAP, Proc, or combinations of both does not modulate short-term synaptic plasticity measured with large presynaptic voltage steps. A, B, Sample experimental traces showing the five postsynaptic currents (with mean amplitude Amp1–Amp5) in response to a set of five presynaptic voltage steps from −60 mV to −20 mV in control and in the presence of either modulator, for the LP to PD (A) and PD to LP (B) synapses. C, Short-term synaptic plasticity was quantified as Amp5/Amp1. This ratio did not change from control to different concentrations of individual neuromodulators or co-modulation. (LP to PD: from control to either CCAP or Proc to co-modulation, F(5,25) = 0.889, p = 0.497 and F(5,25) = 1.19, p = 0.344; PD to LP: from control to either CCAP or Proc to co-modulation, F(5,25) = 1.59, p = 0.199 and F(5,25) = 2.02, p = 0.111. n = 6 for all; all measurements one-way RM-ANOVA).
We used the data shown in Figure 2 to build predictors for each synapse–peptide pair. The predictor is a surface fit to all synaptic current amplitudes measured at different presynaptic voltage steps and modulation concentrations (Fig. 4), which has a sigmoidal relationship with both the presynaptic voltage and the log of the modulator concentration (fit given by Eq. 3). These predictors allowed us to estimate the synaptic current at any voltage and modulator concentration by interpolation. The surface fits also allowed us to visualize and measure the distinct modulation effects of the two peptides on each synapse and of each peptide on the two synapses.
Figure 4.
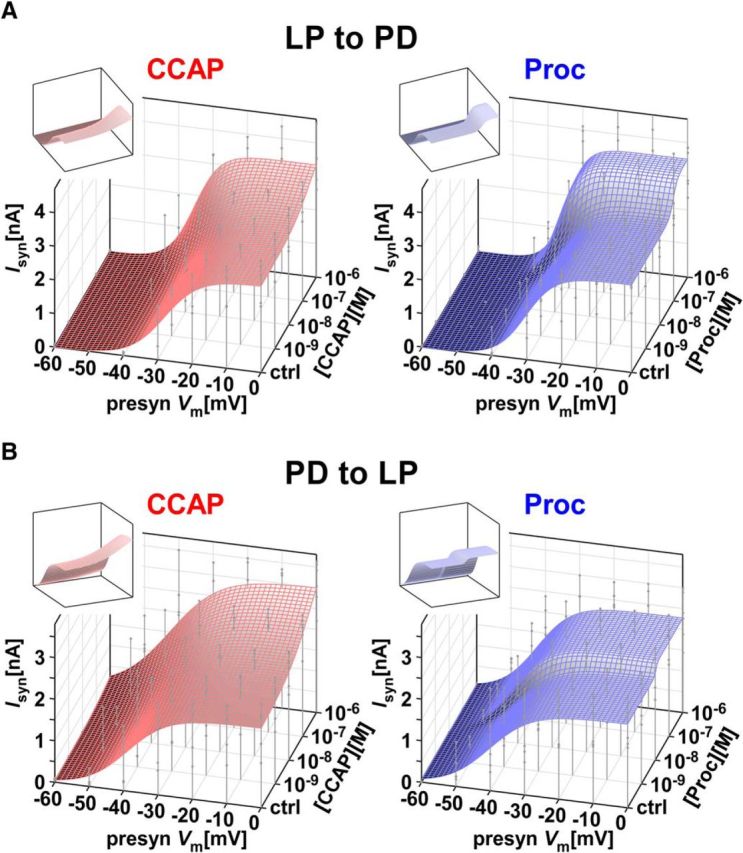
The dose-dependent influence of CCAP and Proc on the activation curves of the two synapses was used to construct predictors of modulation on synapses. A, Double-sigmoidal surface fit (Eq. 3) to the activation data of the LP to PD synapse in different doses of Proc or CCAP can be used to estimate the influence of the respective modulator on the synapse at any presynaptic voltage and any concentration of the modulator. Droplines indicate measurement points of the experimental data, with the filled circles marking the data points. Insets show the same surface from a different viewpoint. B, Same as A, but for the PD to LP synapse. The fit parameters were as follows: A, CCAP: a1 = 3.619, a2 = −1.042, a3 = −38.00, a4 = 9.890, a5 = 3.197, a6 = 1.920, Cmid = −6.556, Cc = 0.5555; A, Proc: a1 = 3.508, a2 = −0.902, a3 = −34.68, a4 = 4.320, a5 = 2.913, a6 = 1.324, Cmid = −7.018, Cc = 0.1359; B, CCAP: a1 = 3.632, a2 = −1.735, a3 = −44.74, a4 = 5.82, a5 = 8.135, a6 = −2.116, Cmid = −6.455, Cc = 0.8039; B, Proc: a1 = 2.273, a2 = −0.2560, a3 = −42.43, a4 = 2.090, a5 = 5.184, a6 = 1.126, Cmid = −7.958, Cc = 0.04605.
Saturation level of the co-modulatory effect on the synapses is not history dependent
Our main hypothesis assumes that the saturation of synaptic co-modulation is not affected by the order of application; that is, one modulator does not gate or prime the effect of the other modulator. Before testing our hypothesis, it was therefore important to verify this assumption. To determine whether the co-modulatory saturation level depended on the prior application of either modulator, we did two separate sets of experiments for each synapse. In each experiment, we saturated the synapse with either Proc or CCAP first and then with both peptides co-applied.
Saturation of neuromodulatory effects can occur when the receptors, the signaling pathways, or the targets themselves reach maximum capacity. Co-modulatory effects at high concentrations depend on the degree to which the different neuromodulators occlude each other's effects. If the separate effects of two neuromodulators saturate because the common target is maximally modulated, then the effect of each modulator should occlude the effect of the other. If the separate effects of two neuromodulators saturate because their respective receptors are saturated, then neither modulator's effect should completely occlude the effect of the other. If the signaling pathways saturate, the occlusion depends on pathway interactions.
We first investigated whether co-modulation produced an additional effect above that of the single neuromodulator at 1 μm (Fig. 5), the presumed saturation concentration of peptide effects in the STG (Zhao et al., 2011). In only one of the four cases did co-modulation increase the effect. At the PD to LP synapse, Proc did not completely occlude the effect of adding CCAP, probably because saturating Proc receptors alone does not fully activate the target. In the other three cases, coapplication did not produce an additional effect (Fig. 5). The fact that complete occlusion was achieved in both synapses by at least one peptide confirms that synapse modulation was maximal when both peptides were applied at 1 μm.
Figure 5.
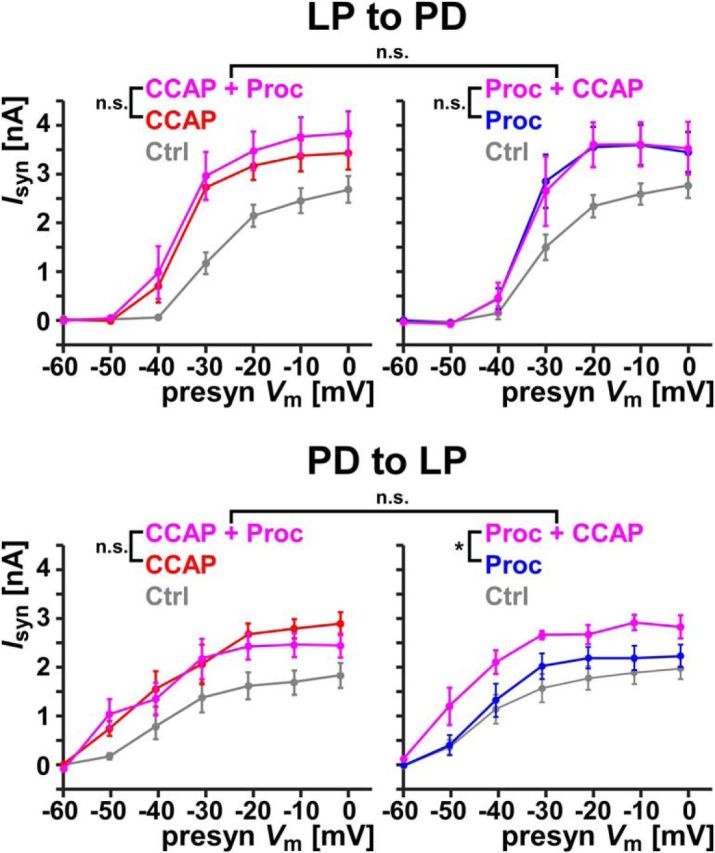
Maximum co-modulation of the synaptic currents by 1 μm CCAP and 1 μm Proc. Each panel shows the effect of co-modulation of either synapse on the synaptic activation curve following modulation by 1 μm of either modulator alone. For the LP to PD synapse (top), co-modulation did not increase the synaptic current significantly compared with either CCAP alone (left, F(1,4) = 3.88, p = 0.120, n = 5) or Proc alone (right, F(1,5) = 0.004, p = 0.949, n = 6). Between the two sets of experiments (left and right), neither control levels (F(1,9) = 0.392, p = 0.547) nor co-modulation levels (F(1,9) = 0.180, p = 0.681) were significantly different. For the PD to LP synapse (bottom), co-modulation did not increase the synaptic current significantly compared with CCAP alone (left, F(1,5) = 0.356, p = 0.576, n = 6), but it did increase the effect of Proc alone (right, F(1,5) = 11.0, p = 0.021, n = 6). Once again, between the two sets of experiments (left and right), neither control levels (F(1,10) = 0.128, p = 0.728) nor co-modulation levels (F(1,10) = 0.572, p = 0.467) were significantly different. All statistical comparisons were two-way RM-ANOVA. *p < 0.05.
At both synapses, co-modulatory effects were not dependent on the order of application. Synaptic activation curves were not statistically different between experiments in which either CCAP or Proc was applied first (Fig. 5). We also verified that the control measurements were not different for each synapse. Therefore, although co-modulation may have additional effects depending on the neuromodulator and the synapse, the saturation level of synaptic co-modulation was not history dependent.
Co-modulatory effects on synapses are linearly additive up to saturation
After establishing that the saturation level of co-modulation is not history dependent, we used Equation 6 to calculate the co-modulation predictions for the synapses. Recall that the individual effects of the two peptides were modeled by the predictors for their dose-dependent effects (Eq. 3 and Fig. 4). The linear summation rule predicts that the co-modulatory effect is the sum of the individual modulatory enhancements due to Proc and CCAP at their respective concentrations (Eq. 4) up to saturation. We tested this prediction on both synapses with 18 different modulator combinations (see Materials and Methods).
We compared our predictions with the experimental results by computing the R2 (see Materials and Methods). We computed these statistics for each combination individually and also computed the overall R2 for all combinations.
For the LP to PD synapse, our prediction matched the experimental results exceedingly well (examples are shown in Fig. 6A; all data are provided in Fig. 6-1). The comparison between predicted and measured values showed high prediction accuracy (Fig. 6B, the identity line indicates a perfect match). For all combinations, we obtained high R2 values with the overall R2 = 0.90, indicating that our predictions fit the data well and had negligible deviation from the data (Fig. 6C). We therefore concluded that co-modulation of LP to PD synapse can be predicted from effects of individual peptides using the linear summation rule.
Figure 6.
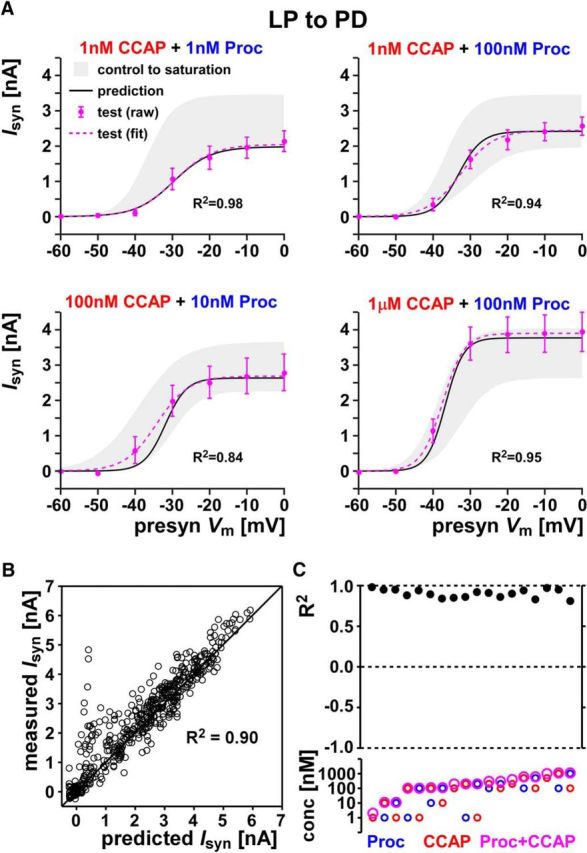
Co-modulatory effect of CCAP and Proc on the LP to PD synapse can be predicted from linear summation up to saturation. A, LP to PD synaptic current activation curve in response to co-applied CCAP and Proc at four different concentration combinations (test, raw and fit) is well predicted by the model (prediction). Also shown is the range of synaptic currents measured in the respective experiments (control to saturation). The R2 values in each case show the goodness of the prediction. B, Prediction values compared with the actual measurements for all data points in the 18 different combinations of co-modulation measurements of the LP to PD synapse. Also shown, for comparison, are the line of perfect prediction (y = x) and overall R2 values. All data points are provided in Figure 6-1. C, R2 values shown for each of the 18 co-modulation combinations of the LP to PD synapse. R2 = 1 indicates perfect predictions, whereas R2 = 0 indicates that the prediction was no better than the mean of the data. The bottom panel shows the concentration of Proc, CCAP, and total concentration (Proc+CCAP) in each case. Data are shown in order of increasing total concentration. Each combination included five or six preparations.
This file contains all data used for the analysis in Figure 6. The Excel file contains two sheets. The sheet named "combpre_LPtoPD", data columns marked with "pre_" indicate predictions from the Linear-Summation-Up-to-Saturation rule at each voltage. The subsequent data columns indicate the measured (test) values in the presence of both modulators. The sheet named "ctrlsat-LPtoPD" contains the control and saturation synaptic currents values for the same experiments as in the other sheet. The control values are measured in the absence of the modulators; the saturation values are with co-application of Proc and CCAP at 10-6 M each. Download Figure 6-1, XLSX file (24.9KB, xlsx)
The predictions for the PD to LP synapse also had high R2 values with the overall R2 = 0.73 (Fig. 7; all data are provided in Fig. 7-1). These values indicate that co-modulation of the PD to LP synapse was predicted well by the linear summation rule, if not quite as accurately as at the LP to PD synapse.
Figure 7.
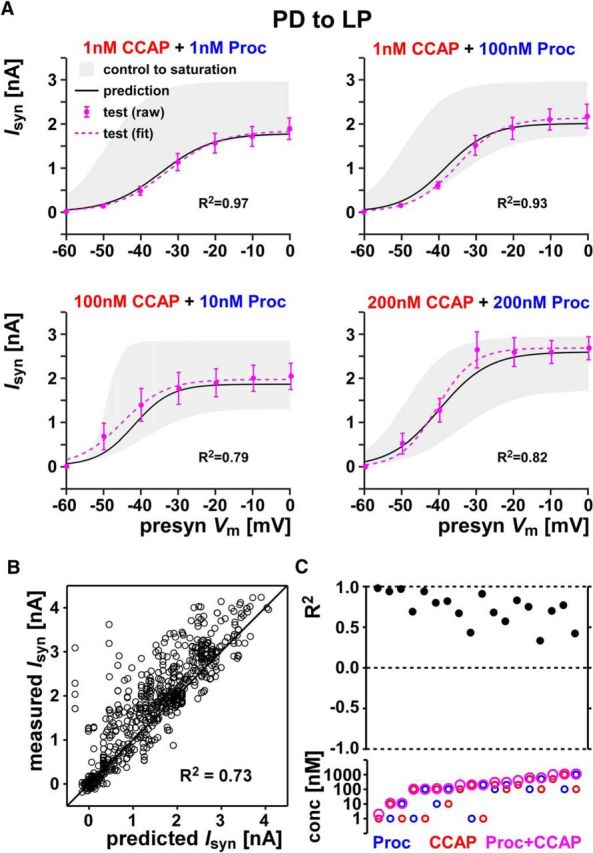
Co-modulatory effect of CCAP and Proc on the PD to LP synapse can be predicted from linear summation up to saturation. A, PD to LP synaptic current activation curve in response to co-applied CCAP and Proc at four different concentration combinations (test, raw and fit) is well predicted by the model (prediction). Also shown is the range of synaptic currents measured in the respective experiments (control to saturation). The R2 values in each case show the goodness of the prediction. B, Prediction values compared with the actual measurements for all data points in the 18 different combinations of co-modulation measurements of the PD to LP synapse. Also shown for comparison are the line of perfect prediction (y = x) and overall R2 values. All data points are provided in Figure 7-1. C, R2 values shown for each of the 18 co-modulation combinations of the PD to LP synapse. R2 = 1 indicates perfect predictions, whereas R2 = 0 indicates that the prediction was no better than the mean of the data. The bottom panel shows the concentration of Proc, CCAP, and total concentration (Proc+CCAP) in each case. Data are shown in order of increasing total concentration. Each combination included five or six preparations.
This file contains all data used for the analysis in Figure 7. The Excel file contains two sheets. The sheet named "combpre_PDtoLP", data columns marked with "pre_" indicate predictions from the Linear-Summation-Up-to-Saturation rule at each voltage. The subsequent data columns indicate the measured (test) values in the presence of both modulators. The sheet named "ctrlsat-PDtoLP" contains the control and saturation synaptic currents values for the same experiments as in the other sheet. The control values are measured in the absence of the modulators; the saturation values are with co-application of Proc and CCAP at 10-6 M each. Download Figure 7-1, XLSX file (24.3KB, xlsx)
Co-modulatory effects on IMI in the LP neuron are not linearly additive
Our data showed that the co-modulatory effects of Proc and CCAP on the synapses were linearly additive up to saturation. This suggests that the intracellular pathways underlying the Proc and CCAP effects converge in the LP and PD neurons without additional interactions. If so, it is reasonable to assume that the activation of IMI by Proc and CCAP would also follow the same rule. The protocols that we used to measure the synaptic current from LP to PD also allowed us to estimate the level of IMI in the LP neuron (see Materials and Methods). Figure 8A shows an example recording of IMI as the current difference between Proc and control. We quantified the dose-dependent activation of IMI in LP in the presence of either Proc or CCAP.
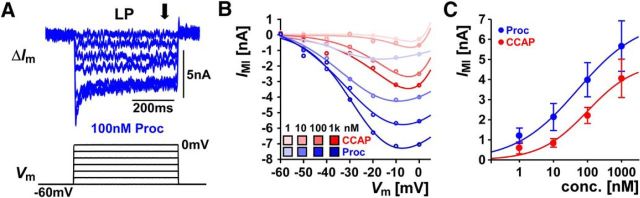
Figure 8.
Both CCAP and Proc activate IMI in the LP neuron. A, Measurement of IMI in the LP neuron. The difference current (ΔIm) was obtained by digital subtraction of the total current measured in control and in the presence of the modulator (here 100 nm Proc) and IMI was calculated as the mean current in the latter half of the voltage step (arrow). B, Example of the IMI I–V curves measured in two experiments in increasing concentrations of CCAP or Proc shown together with the fit of the data points using Equation 2. C, Dose-dependent peak levels of IMI (absolute values) in the presence of Proc, CCAP. Dose-dependent parameters for CCAP: Imax = 4.881, Cmid= −7.000, Cc = 0.6953; for Proc: Imax = 7.000, Cmid= −7.292, Cc = 0.9090.
A dose-dependent analysis showed that both peptides activated IMI starting at nanomolar concentrations and consistently produced larger currents as the concentration increased (Figs. 8B,C). As with the synaptic currents, the maximum level of IMI activated by co-modulation, as measured by applying 1 μm (each) of both modulators at the end of each dose-dependent analysis experiment, did not depend on whether Proc or CCAP was applied first (paired Student's t test, t(5) = 0.396).
To examine the linear summation rule, the dose-dependent curves for the two peptides were used to construct the predictors of the co-modulation effect (Eq. 5). From these individual predictors, we calculated the IMI levels expected to be activated by each peptide at any concentration using linear summation to saturation (Eq. 7 and schematic in Fig. 9A). As for the synaptic currents, we compared the predicted IMI levels to the actual measurements in 18 different co-modulation combinations. We then calculated the R2 for each individual combination and for all combinations together using the peak IMI level derived from the fitted I–V curves (Eq. 2 and Fig. 9B).
Figure 9.
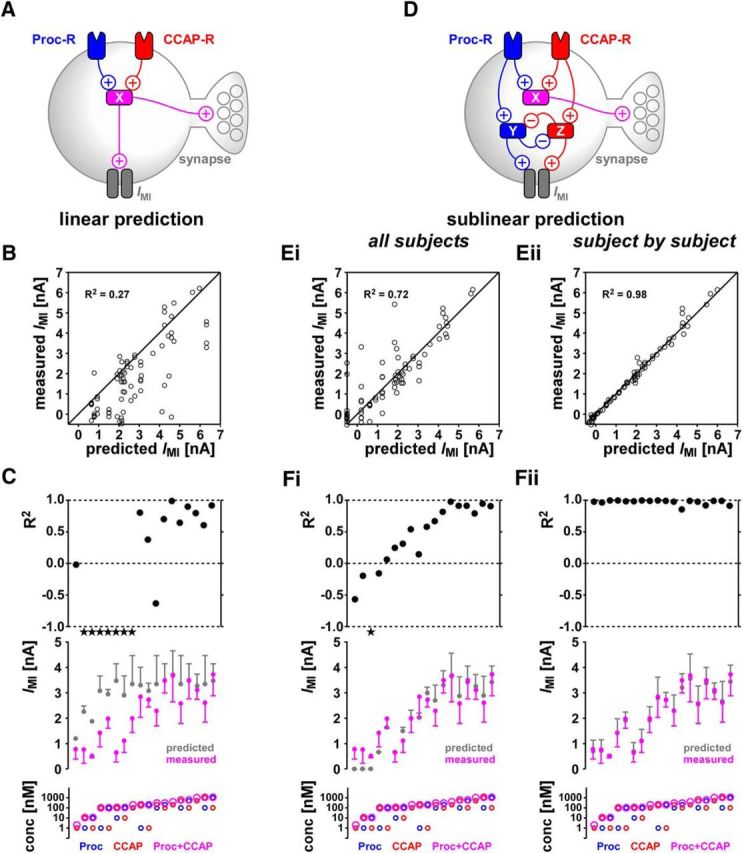
Co-modulatory effects of CCAP and Proc on the levels of IMI in the LP neuron cannot be predicted from linear summation up to saturation. A, Schematic diagram showing the most parsimonious interaction scheme of the pathways activated by the two receptors, leading to a linear summation up to saturation rule. X is the intracellular substrate activated by both receptors. B, Linear-summation-up-to-saturation prediction values compared with the actual measurements of IMI for all data points in the 18 different combinations of co-modulation. Also shown for comparison are the line of perfect prediction (y = x) and overall R2 values. C, Measured and predicted peak IMI values, as well as the R2 values, for each of the 18 co-modulation combinations. R2 = 1 indicates perfect predictions, whereas R2 = 0 indicates that the prediction was no better than the mean of the data. Stars indicate out of range values. The bottom panel shows the concentration of Proc, CCAP, and total concentration (Proc+CCAP) for each case. Data are shown in order of increasing total concentration. Each combination included four or five preparations. D, Schematic diagram, modified from A, showing how the pathways activated by the two receptors may lead leading to a linear summation rule for synapses but inhibit one another when activating IMI. Y and Z are substrates activated by each receptor that activate IMI but inhibit one another. E and F are the same as B and C, but with nonlinear prediction values based on Equation 9. Ei and Fi show prediction results for Equations 8 and 9 with parameters fit to data points in all experiments (p1 = 0.4237, p2 = 0.4424, p3 = 0.1397, p4 = 1.000, p5 = 0.1204, p6 = 0.2645), whereas Eii and Fii show predictions of the same equations with separate parameter fits in individual experiments. All data points are provided in Figure 9-1.
This file contains all prediction and test data used for the analysis in Figure 9. Data columns marked with "comb_" are the measured (test) values of co-modulation, data columns marked with "pred_linear" are predictions from the Linear-Summation-Up-to-Saturation rule, data columns marked with "pred_sublinear_all" are predictions from the sublinear model fit to all data together, data columns marked with "pred_sublinear_indi" are predictions from the sublinear model fit to each preparation individually. The next six columns (p1-p6) provide the fit parameters of equation for the sublinear fits to each preparation. Download Figure 9-1, XLSX file (16.6KB, xlsx)
Surprisingly, and in stark contrast to the synapses, our predictions were far from the measured values of the co-modulated IMI in the LP neuron (Fig. 9B,C; all data are provided in Fig. 9-1. The comparison between predicted and measured IMI values showed an overestimation in most of the data points (Fig. 9B) and, for half of the combinations, R2 values were below 0 (Fig. 9C). The low overall R2 value of 0.27 indicated that our linear summation model was a very poor predictor for the co-modulation of IMI.
Interestingly, and also in contrast to the fairly consistent R2 values across different co-modulation combinations for the synapses, these values varied drastically across different combinations for IMI. The predictions were very poor (R2 < 0) when at least one of the peptides was at a low concentration, but somewhat better (R2 > 0) when the combined concentrations were high, mostly because the predictor estimated the co-modulation to be at saturation (Fig. 9C).
Despite the poor prediction, the linear summation rule provided useful information about the dynamics of IMI co-modulation. The measured IMI levels were almost always lower than the linear predictions (Fig. 9B), indicating that the co-modulatory effect was sublinear. This result suggested a potential inhibitory interaction between the pathways that led from the activation of each peptide receptor to the expression of IMI. Such inhibitory interactions in second messenger pathways have been observed (Fioravante et al., 2006), so we explored a simple inhibitory interaction (shown schematically in Fig. 9D) that would be compatible with the observed results of IMI co-modulation. Our schematic inhibitory interaction leads to a prediction that is formalized by Equation 9. This equation is a modification of our linear summation rule (Eq. 7), with additional parameters that capture how different levels of each modulator would influence the dose–response activation of the other modulator.
Our current experimental data do not provide a direct measurement of the interaction parameters of Equation 9. However, an estimate of the parameters can be obtained by a nonlinear regression fit to the IMI co-modulation data. A fit to all IMI co-modulation data points showed that the new rule produced a much-improved prediction over the linear rule (Fig. 9Ei–Fi) and increased the total R2 values to 0.72. However, the R2 values for some individual combinations of the modulators remained low, or even negative, especially in cases where one modulator was present at a low concentration (Fig. 9Fi). In contrast to the linear rule, the mismatch at low concentrations was mostly because our prediction underestimated the co-modulation of the data, often predicting no activation of IMI when both concentrations were low (Fig. 9Fi, leftmost three data points).
One possible explanation for this poor performance is that the inhibitory interactions of the two modulatory pathways shows variability across preparations. This would imply that a single parameter set for inhibitory interactions cannot capture the variability of the co-modulated IMI levels. We therefore used the data from individual experiments to estimate the parameters of inhibitory interactions within that experiment using the same rule described by Equation 9. Accounting for the experimental variability in this manner provided an almost perfect prediction of the co-modulation effect (Figs. 9Eii–Fii), with an overall R2 value of 0.98. This result indicates that cross-inhibition of the two pathways can, in principle, account for the co-modulation of IMI by these two peptides and can be quantified with a nonlinear summation rule such as the one given by Equation 9.
Discussion
Distinct rules for co-modulation of different subcellular targets
It is common for multiple neuromodulators to target the same ion channel or synapse or have distinct targets within the same neuron (McCormick and Williamson, 1989; Harris-Warrick, 2011; Marder, 2012). Circuit output, therefore, depends on how signaling pathways mediated by distinct neuromodulator receptors converge and interact. Converging neuromodulators could have similar or opposing actions that may result in additive, synergistic, antagonistic, or other nonlinear co-modulatory effects (Nadim and Bucher, 2014). For a given target, it is important to know whether convergent neuromodulators act in a simple additive manner or have more complex nonlinear interactions and if co-modulation of multiple subcellular targets follows the same rule at all shared targets.
Despite recent advances in genetic and imaging tools (Arrigoni and Saper, 2014; Cohn et al., 2015; Shahidi et al., 2015), many systems still lack experimental accessibility or the basic understanding of neuromodulator actions on their cellular and subcellular targets to explore this topic. Peptide neuromodulation of the pyloric circuit of the STG provides a special opportunity to explore the rules of co-modulation of synaptic and intrinsic ionic currents and to understand their consequences at the circuit level (Daur et al., 2016). We observed linearly additive co-modulation of synapses, but sublinearly additive co-modulation of a voltage-gated ionic current in the same neurons. These specific results may be peculiar to the neurons and synapses we studied because co-modulation of other synapses can be nonlinear (Parker, 2000) and co-modulation of voltage-gated currents could be linearly additive. However, the important lesson is that converging co-modulation of synapses and ionic currents by the same neuromodulators, or different subcellular targets in general, can follow distinct rules. Given the complex patterns of divergence and convergence of neuromodulators in many systems, this finding likely has broad functional implications.
Linearly additive co-modulation of pyloric synapses
A single neuromodulator can exert functionally opposing effects on the presynaptic and postsynaptic sides, for example, enhancing transmitter release but reducing postsynaptic responsiveness (Harris-Warrick and Johnson, 2010; Garcia et al., 2015). We therefore did not expect co-modulation of synapses to be simply linearly additive, but, surprisingly, found this to be the case for both synapses. For the LP to PD synapse, CCAP modulation must be presynaptic because PD neurons do not express CCAP receptors (Garcia et al., 2015) (Fig. 1A). However, Proc modulation could have both presynaptic and postsynaptic components. Although Proc receptor expression in these neurons has not been tested in the STG, both neurons show IMI activation in response to Proc application (Swensen and Marder, 2000). For the PD to LP synapse (which represents input from both AB and PD neurons), both modulators could have presynaptic and postsynaptic effects (Swensen and Marder, 2000; Garcia et al., 2015).
Given that we observed linear summation and occlusion, it is likely that modulatory signaling on either presynaptic or postsynaptic side was purely converging without any nonlinear interactions. Linear co-modulation could also occur through spatial segregation, for example, when one neuromodulator acts presynaptically and the other postsynaptically, or by acting on nonoverlapping modulatory microdomains (Lur and Higley, 2015). However, in the case of spatial segregation, no occlusion should occur and the saturation level of co-modulation should be the linear sum of the maximum effects achieved by each neuromodulator.
Sublinear co-modulation of IMI
In contrast to the synapses, we observed nonlinear co-modulation of IMI, which indicated that the signaling pathways targeting IMI were distinct from the pathways targeting the synapses. It was previously suggested that peptides modulate synapses in the STG through their actions on the IMI channel, which might be partially permeable to calcium (Zhao et al., 2011; Gray et al., 2017). However, our results indicate that this is unlikely given that linear co-modulation of the synapses and nonlinear co-modulation of IMI occurred in the same experiments.
The nonlinearity of IMI co-modulation may have two components: sublinear interactions, when at least one modulator is at low concentration, and occlusion, also seen in our previous study (Garcia et al., 2015), when both are at high concentrations (Fig. 9C). We proposed a simple model to explain the sublinear interactions of IMI co-modulation based on cross-inhibition of CCAP- and Proc-activated signaling pathways (Fig. 9D) in which both CCAP and Proc activates intermediate effectors that are reciprocally inhibited. Cross-inhibition between pathways activated by different receptors converging onto the same targets has been reported (Cinar et al., 2008). In both hippocampal and spinal dorsal horn neurons, GABA and glycine receptors asymmetrically inhibit one another through a phosphorylation-dependent mechanism (Li and Xu, 2002; Li et al., 2003). The sensorimotor synapse of the sea slug Aplysia californica, for instance, shows long-term facilitation induced by serotonin and long-term depression induced by the neuropeptide FMRFamide. Both neuromodulators act on G-protein-coupled receptors and their intracellular pathways inhibit one another at the level of the extracellular-regulated kinase cascade (Fioravante et al., 2006).
Another possible mechanism is that the CCAP and Proc receptors can form a heteromer complex and display behaviors distinct from either receptor alone (for review, see Smith and Milligan, 2010). Given the variety of possible mechanisms, a different set of experiments and mathematical modeling will be required to provide an accurate description of the co-modulation rule for IMI.
Distinct co-modulation rules may increase flexibility and functionally uncouple the modulation of different targets
When different neuromodulators converge onto multiple targets, their actions on the shared targets are inextricably linked. However, modulator effects on different targets can be uncoupled by different co-modulation rules. Distinct rules for co-modulation of neuronal excitability and synaptic interactions could functionally uncouple these effects and therefore allow burst phasing and rhythm frequency to be regulated differentially. Furthermore, sublinear co-modulation of IMI may extend the dynamic range for the modulation of neural excitability by producing qualitatively different effects than each individual neuromodulator. Because STG neurons are modulated by many peptides, sublinear co-modulation would ensure that neuronal excitability is not saturated during baseline activity when many peptides may be present at low concentrations. However, when any specific peptide neuromodulator is released at a higher concentration, it can produce a distinct circuit output.
Bridging levels of co-modulation effects
Unraveling the consequences of co-modulation at the circuit level requires examining their interactions at multiple levels. In this study, we took a first step toward identifying the rules of co-modulation of shared targets. However, our study leaves several questions unanswered. First, the signaling pathways resulting in our observed data remain unknown. Second, we bath applied neuromodulators in our study, which was necessary to quantify precise dose-dependent effects, but, as a number of studies in the STG have shown, fails to address the spatiotemporal dynamics of neuromodulation (Nusbaum et al., 2017). Neuromodulators can be released as hormones or as neurotransmitters. In the latter case, spatiotemporal properties of synaptic transmission can be critical in determining circuit output (for review, see Nusbaum et al., 2017). The spatial interactions depend on the architecture of the local circuits, the spatial pattern of neuromodulator release, and the peptidase activity. For neurotransmitter modulators, the temporal dynamics is by necessity determined by the patterns of activity of the modulatory neurons that release these transmitters. The activity patterns of the modulatory neurons, in turn, are subject to feedback from the activity of the target circuits, thereby producing another potential level of complexity. To probe the spatiotemporal dynamics of co-modulation, combining experimental approaches such as stimulating neuromodulatory projection neurons and computational modeling is necessary.
Finally, all of our experiments were done with voltage-clamp steps to characterize the neuromodulatory effects on each target. However, such experiments mask the interactions among circuit components both within neurons and with their synaptic partners. One such example was shown by Zhao et al. (2011) at the LP to PD synapse, where Proc enhances both the burst voltage waveform of the presynaptic LP neuron and the amplitude of the synaptic current. When the LP neuron was voltage clamped with the prerecorded realistic control or Proc voltage waveforms, the resulting synaptic currents were similar in control saline, but different in the presence of Proc. This indicates that the first factor (change in the LP waveform) produces a meaningful effect only in conjunction with the second factor (direct enhancement of synaptic release). Exploring such interactions among cellular or circuit components is important in understanding the functional consequences of co-modulation.
Conclusions
Because neuromodulators do not act independently, understanding their interactions at different concentrations is important for the understanding of circuit dynamics and resulting behaviors. Identifying the mechanisms of co-modulation also provides mechanistic guidance for therapies that target one or more neuromodulatory pathways (Engineer et al., 2011; Peña et al., 2014; Freret et al., 2017). Here, we took a first step toward understanding how neuromodulators interact to shape the circuit output by quantitatively clarifying the co-modulatory rules at the target level. Given that co-modulation is a universal and evolutionarily conserved strategy, our results can provide insight and new hypotheses to test at the system level. We also provide an initial framework to test similar rules in other circuit components, other neuromodulators, and other systems. However, the challenge will remain to translate findings from the level of ionic currents to the effects of co-modulation on actual synaptic function and neuronal excitability and from there to circuit activity. Even in small circuits with identified neurons, such as the pyloric circuit used here, this will require a multipronged approach combining multiple experimental and computational methods.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the National Instituters of Health (Grants MH060605 and NS083319).
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Arrigoni E, Saper CB (2014) What optogenetic stimulation is telling us (and failing to tell us) about fast neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in brain circuits for wake-sleep regulation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 29:165–171. 10.1016/j.conb.2014.07.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asahina K. (2017) Neuromodulation and strategic action choice in drosophila aggression. Annu Rev Neurosci 40:51–75. 10.1146/annurev-neuro-072116-031240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann CI. (2012) Beyond the connectome: how neuromodulators shape neural circuits. Bioessays 34:458–465. 10.1002/bies.201100185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beliez L, Barrière G, Bertrand SS, Cazalets JR (2014) Multiple monoaminergic modulation of posturo-locomotor network activity in the newborn rat spinal cord. Front Neural Circuits 8:99. 10.3389/fncir.2014.00099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitz DM, Beenhakker MP, Nusbaum MP (2004) Different sensory systems share projection neurons but elicit distinct motor patterns. J Neurosci 24:11381–11390. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3219-04.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezina V. (2010) Beyond the wiring diagram: signalling through complex neuromodulator networks. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365:2363–2374. 10.1098/rstb.2010.0105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brezina V, Orekhova I–V, Weiss KR (1996) Functional uncoupling of linked neurotransmitter effects by combinatorial convergence. Science 273:806–810. 10.1126/science.273.5276.806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke PG, Kanbar R, Basting TM, Hodges WM, Viar KE, Stornetta RL, Guyenet PG (2015) State-dependent control of breathing by the retrotrapezoid nucleus. J Physiol 593:2909–2926. 10.1113/JP270053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinar R, Freund TF, Katona I, Mackie K, Szucs M (2008) Reciprocal inhibition of G-protein signaling is induced by CB(1) cannabinoid and GABA(B) receptor interactions in rat hippocampal membranes. Neurochem Int 52:1402–1409. 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.02.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn R, Morantte I, Ruta V (2015) Coordinated and compartmentalized neuromodulation shapes sensory processing in drosophila. Cell 163:1742–1755. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daur N, Nadim F, Bucher D (2016) The complexity of small circuits: the stomatogastric nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 41:1–7. 10.1016/j.conb.2016.07.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson PS, Fairfield WP, Hetling JR, Hauptman J (1997) Neurotransmitter interactions in the stomatogastric system of the spiny lobster: one peptide alters the response of a central pattern generator to a second peptide. J Neurophysiol 77:599–610. 10.1152/jn.1997.77.2.599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djokaj S, Cooper RL, Rathmayer W (2001) Presynaptic effects of octopamine, serotonin, and cocktails of the two modulators on neuromuscular transmission in crustaceans. J Comp Physiol A 187:145–154. 10.1007/s003590100187 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doi A, Ramirez JM (2008) Neuromodulation and the orchestration of the respiratory rhythm. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 164:96–104. 10.1016/j.resp.2008.06.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlea JM, Alam MN, Szymusiak R (2017) Neuronal substrates of sleep homeostasis; lessons from flies, rats and mice. Curr Opin Neurobiol 44:228–235. 10.1016/j.conb.2017.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engineer ND, Riley JR, Seale JD, Vrana WA, Shetake JA, Sudanagunta SP, Borland MS, Kilgard MP (2011) Reversing pathological neural activity using targeted plasticity. Nature 470:101–104. 10.1038/nature09656 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filosa A, Barker AJ, Dal Maschio M, Baier H (2016) Feeding state modulates behavioral choice and processing of prey stimuli in the zebrafish tectum. Neuron 90:596–608. 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.03.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fioravante D, Smolen PD, Byrne JH (2006) The 5-HT- and FMRFa-activated signaling pathways interact at the level of the erk MAPK cascade: potential inhibitory constraints on memory formation. Neurosci Lett 396:235–240. 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.11.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freret T, Lelong-Boulouard V, Lecouflet P, Hamidouche K, Dauphin F, Boulouard M (2017) Co-modulation of an allosteric modulator of nicotinic receptor-cholinesterase inhibitor (galantamine) and a 5-HT4 receptor agonist (RS-67333): effect on scopolamine-induced memory deficit in the mouse. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 234:2365–2374. 10.1007/s00213-017-4664-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia VJ, Daur N, Temporal S, Schulz DJ, Bucher D (2015) Neuropeptide receptor transcript expression levels and magnitude of ionic current responses show cell type-specific differences in a small motor circuit. J Neurosci 35:6786–6800. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0171-15.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goaillard JM, Taylor AL, Schulz DJ, Marder E (2009) Functional consequences of animal-to-animal variation in circuit parameters. Nat Neurosci 12:1424–1430. 10.1038/nn.2404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golowasch J, Marder E (1992) Ionic currents of the lateral pyloric neuron of the stomatogastric ganglion of the crab. J Neurophysiol 67:318–331. 10.1152/jn.1992.67.2.318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M, Daudelin DH, Golowasch J (2017) Activation mechanism of a neuromodulator-gated pacemaker ionic current. J Neurophysiol 118:595–609. 10.1152/jn.00743.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris-Warrick RM. (2011) Neuromodulation and flexibility in central pattern generator networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:685–692. 10.1016/j.conb.2011.05.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris-Warrick RM, Johnson BR (2010) Checks and balances in neuromodulation. Front Behav Neurosci 4:47. 10.3389/fnbeh.2010.00047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He K, Huertas M, Hong SZ, Tie X, Hell JW, Shouval H, Kirkwood A (2015) Distinct eligibility traces for LTP and LTD in cortical synapses. Neuron 88:528–538. 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki HK, Panse KM, Anderson DJ (2014) Independent, reciprocal neuromodulatory control of sweet and bitter taste sensitivity during starvation in drosophila. Neuron 84:806–820. 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.09.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Xu TL (2002) State-dependent cross-inhibition between anionic GABA(A) and glycine ionotropic receptors in rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. Neuroreport 13:223–226. 10.1097/00001756-200202110-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Wu LJ, Legendre P, Xu TL (2003) Asymmetric cross-inhibition between GABAA and glycine receptors in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. J Biol Chem 278:38637–38645. 10.1074/jbc.M303735200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett-Barron M, Andalman AS, Allen WE, Vesuna S, Kauvar I, Burns VM, Deisseroth K (2017) Ancestral circuits for the coordinated modulation of brain state. Cell 171:1411–1423.e17. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lur G, Higley MJ (2015) Glutamate receptor modulation is restricted to synaptic microdomains. Cell Rep 12:326–334. 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.06.029 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor Y, Nadim F (2001) Synaptic depression mediates bistability in neuronal networks with recurrent inhibitory connectivity. J Neurosci 21:9460–9470. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-09460.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder E. (2012) Neuromodulation of neuronal circuits: back to the future. Neuron 76:1–11. 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick DA, Pape HC (1990) Noradrenergic and serotonergic modulation of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current in thalamic relay neurones. J Physiol 431:319–342. 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick DA, Williamson A (1989) Convergence and divergence of neurotransmitter action in human cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:8098–8102. 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8098 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena W, Diegelmann S, Wegener C, Ewer J (2016) Stereotyped responses of drosophila peptidergic neuronal ensemble depend on downstream neuromodulators. Elife 5:e19686. 10.7554/eLife.19686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesce KA, Crisp KM, Gilchrist LS (2001) Mixtures of octopamine and serotonin have nonadditive effects on the CNS of the medicinal leech. J Neurophysiol 85:2039–2046. 10.1152/jn.2001.85.5.2039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabeau O, Joly JS (2013) Molecular evolution of peptidergic signaling systems in bilaterians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:E2028–E2037. 10.1073/pnas.1219956110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadim F, Bucher D (2014) Neuromodulation of neurons and synapses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 29:48–56. 10.1016/j.conb.2014.05.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusbaum MP, Blitz DM, Marder E (2017) Functional consequences of neuropeptide and small-molecule co-transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:389–403. 10.1038/nrn.2017.56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park JY, Spruston N (2012) Synergistic actions of metabotropic acetylcholine and glutamate receptors on the excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 32:6081–6091. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6519-11.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. (2000) Presynaptic and interactive peptidergic modulation of reticulospinal synaptic inputs in the lamprey. J Neurophysiol 83:2497–2507. 10.1152/jn.2000.83.5.2497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña DF, Childs JE, Willett S, Vital A, McIntyre CK, Kroener S (2014) Vagus nerve stimulation enhances extinction of conditioned fear and modulates plasticity in the pathway from the ventromedial prefrontal cortex to the amygdala. Front Behav Neurosci 8:327. 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00327 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi R, Williams EA, Conzelmann M, Asadulina A, Verasztó C, Jasek S, Bezares-Calderón LA, Jékely G (2015) A serial multiplex immunogold labeling method for identifying peptidergic neurons in connectomes. Elife 4:e11147. 10.7554/eLife.11147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith NJ, Milligan G (2010) Allostery at G protein-coupled receptor homo- and heteromers: uncharted pharmacological landscapes. Pharmacol Rev 62:701–725. 10.1124/pr.110.002667 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson E, Grillner S, Parker D (2001) Gating and braking of short- and long-term modulatory effects by interactions between colocalized neuromodulators. J Neurosci 21:5984–5992. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-05984.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swensen AM, Marder E (2000) Multiple peptides converge to activate the same voltage-dependent current in a central pattern-generating circuit. J Neurosci 20:6752–6759. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-18-06752.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirumalai V, Marder E (2002) Colocalized neuropeptides activate a central pattern generator by acting on different circuit targets. J Neurosci 22:1874–1882. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-05-01874.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirumalai V, Prinz AA, Johnson CD, Marder E (2006) Red pigment concentrating hormone strongly enhances the strength of the feedback to the pyloric rhythm oscillator but has little effect on pyloric rhythm period. J Neurophysiol 95:1762–1770. 10.1152/jn.00764.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohidi V, Nadim F (2009) Membrane resonance in bursting pacemaker neurons of an oscillatory network is correlated with network frequency. J Neurosci 29:6427–6435. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0545-09.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng HA, Nadim F (2010) The membrane potential waveform of bursting pacemaker neurons is a predictor of their preferred frequency and the network cycle frequency. J Neurosci 30:10809–10819. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1818-10.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wester JC, McBain CJ (2014) Behavioral state-dependent modulation of distinct interneuron subtypes and consequences for circuit function. Curr Opin Neurobiol 29:118–125. 10.1016/j.conb.2014.07.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White RS, Spencer RM, Nusbaum MP, Blitz DM (2017) State-dependent sensorimotor gating in a rhythmic motor system. J Neurophysiol 118:2806–2818. 10.1152/jn.00420.2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods IG, Schoppik D, Shi VJ, Zimmerman S, Coleman HA, Greenwood J, Soucy ER, Schier AF (2014) Neuropeptidergic signaling partitions arousal behaviors in zebrafish. J Neurosci 34:3142–3160. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3529-13.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia XB, Mills SL (2004) Gap junctional regulatory mechanisms in the AII amacrine cell of the rabbit retina. Vis Neurosci 21:791–805. 10.1017/S0952523804215127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazoe-Umemoto A, Fujita K, Iino Y, Iwasaki Y, Kimura KD (2015) Modulation of different behavioral components by neuropeptide and dopamine signalings in non-associative odor learning of Caenorhabditis elegans. Neurosci Res 99:22–33. 10.1016/j.neures.2015.05.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao S, Sheibanie AF, Oh M, Rabbah P, Nadim F (2011) Peptide neuromodulation of synaptic dynamics in an oscillatory network. J Neurosci 31:13991–14004. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3624-11.2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
All data used for the analysis shown in Figure 2, 3 and 4. All individual experiments end with a co-application of Proc and CCAP at 10-6 M. The Excel file contains multiple sheets whose names include the (primary) neuromodulator and the synapse. Data columns 3-9 are the fit parameters according to equation . Data columns 10-end are the raw values, corresponding to the voltage step indicated in the column title. The columns marked as "mean" were measurements of the mean postsynaptic current value during the presynaptic voltage step. The columns marked as "peak" indicate the maximum value of the current during the same step. Only the mean current values were used for the analysis in the Results and Figures 2 to 4. Download Figure 2-1, XLSX file (48.9KB, xlsx)
This file contains all data used for the analysis in Figure 6. The Excel file contains two sheets. The sheet named "combpre_LPtoPD", data columns marked with "pre_" indicate predictions from the Linear-Summation-Up-to-Saturation rule at each voltage. The subsequent data columns indicate the measured (test) values in the presence of both modulators. The sheet named "ctrlsat-LPtoPD" contains the control and saturation synaptic currents values for the same experiments as in the other sheet. The control values are measured in the absence of the modulators; the saturation values are with co-application of Proc and CCAP at 10-6 M each. Download Figure 6-1, XLSX file (24.9KB, xlsx)
This file contains all data used for the analysis in Figure 7. The Excel file contains two sheets. The sheet named "combpre_PDtoLP", data columns marked with "pre_" indicate predictions from the Linear-Summation-Up-to-Saturation rule at each voltage. The subsequent data columns indicate the measured (test) values in the presence of both modulators. The sheet named "ctrlsat-PDtoLP" contains the control and saturation synaptic currents values for the same experiments as in the other sheet. The control values are measured in the absence of the modulators; the saturation values are with co-application of Proc and CCAP at 10-6 M each. Download Figure 7-1, XLSX file (24.3KB, xlsx)
This file contains all prediction and test data used for the analysis in Figure 9. Data columns marked with "comb_" are the measured (test) values of co-modulation, data columns marked with "pred_linear" are predictions from the Linear-Summation-Up-to-Saturation rule, data columns marked with "pred_sublinear_all" are predictions from the sublinear model fit to all data together, data columns marked with "pred_sublinear_indi" are predictions from the sublinear model fit to each preparation individually. The next six columns (p1-p6) provide the fit parameters of equation for the sublinear fits to each preparation. Download Figure 9-1, XLSX file (16.6KB, xlsx)