In the original article, there was an error in Figure 2C as published. The sequence of the cbsa splice 1 (CBSA-S1) morpholino was incorrectly typed as
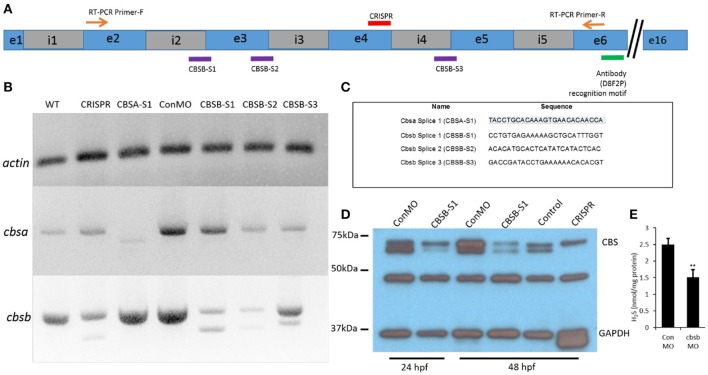
Figure 2.
Loss-of-function efficacy studies. Panel (A) shows a “partial” cartoon representation of the cbsb genomic site with the location of the MO sites (purple rectangles) at appropriate intron (i) and exon (e) junctions, CRISPR-targeted site (red rectangle), site of RT-PCR forward (F) and reverse (R) primers, and the antibody recognition site. Panel (B) shows RT-PCR for three genes (cbsb, cbsa, actin) in total RNA from injected embryos (~24 hpf) (left to right): wild type (WT) control and cbsb CRISPR-injected fish, cbsa splice 1 (CBSA-S1), control morpholino (ConMO), cbsb splice1 (CBSB-S1), cbsb splice 2 (CBSB-S2), cbsb splice 3 (CBSB-S3). Panel (C) shows the sequence of the morpholinos used in this study. Panel (D) shows CBS and GAPDH western blots for ConMO, CBSB-S1 at 24 and 48 hpf along with control and cbsb CRISPR fish at 48 hpf. Panel (E) shows the comparison between CBSB-S1 MO and ConMO-injected embryos for hydrogen sulfide production. n = 3 for both groups (data from three experiments). Twenty embryos in each group in each experiment. **P < 0.01.
TACCTGCACAAAGTGAACACACAACCA
The correct sequence is
TACCTGCACAAAGTGAACACAACCA
The name of the morpholino was changed in the figure from cbsa splice (CBSA-S1) to cbsa splice 1 (CBSA-S1) to match the legend.
The corrected Figure 2 appears below. The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way.
The original article has been updated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.