Abstract
Introduction
Currently, Cardiology Centres are overfilled with patients with degenerative aortic valve stenosis (DAS), usually eldery, with severe concommittant comorbidities, who are referred for further decisions and possible intervention.
Aim
To evaluate changes in the risk profile of patients with severe DAS admitted to the cardiology department a decade ago compared with patients currently being admitted.
Material and methods
We retrospectively evaluated all patients admitted with confirmed severe DAS, hospitalized during 2005–2006 (group I: 140 patients) and in 2016 (group II: 152 patients), admitted for aortic valve intervention. A standard transthoracic echocardiogram, cardiovascular symptom and risk factor distribution, perioperative risk with the logistic EuroSCORE II and STS mortality scores were obtained.
Results
Patients in group II were significantly older (p < 0.001), had more cardiovascular risk factors, and more often presented with atrial fibrillation (27% vs. 11.4%, p = 0.001), renal impairment (34.9% vs. 22.8%; p = 0.024), severe lung disease (17.1% vs. 2.1%, p < 0.001), and extracardiac arteriopathy (40.1% vs. 17.8%, p < 0.001). The aortic valve area (AVA) (p = 0.356), mean-transvalvular pressure gradient (p = 0.215), and left ventricular ejection fraction (p = 0.768) were similar in both groups. However, the prevalence of pulmonary hypertension, severe mitral regurgitation, and low-flow, low-gradient DAS were 3.1-, 8.4- and 1.84-fold more frequent in group II than group I. The percentages of subjects with EuroSCORE II and STS scores ≥ 4% in 2005–2006 were 7.1% and 6.4%, as compared to 27% and 26.3% in 2016 (both p < 0.001). 22% of patients in 2016, as compared to 31% in 2005/2006, were considered ineligible for DAS intervention.
Conclusions
In just a decade, the risk profile of patients admitted with DAS has increased hugely, mainly due to older age, accumulation of comorbidities and more advanced disease at presentation. Although transcatheter aortic valve intervention has expanded the indications for intervention in high-risk patients, the number of patients disqualified from interventional treatment remains high.
Keywords: degenerative aortic valve stenosis, transcatheter aortic valve intervention, aortic valve replacement, risk assessment, EuroSCORE II, STS score
Summary
Currently, Cardiology Centers are overfilled with patients with degenerative aortic valve stenosis, who are referred for further decisions and possible intervention. In this study we evaluated differences in clinical performance, associated comorbidities, echocardiographic findings, and the surgical mortality scores in patients referred to intervention currently and 10 years ago. Also, we compared the proportion of patients reffered to invasive treatment and considered ineligible in years 2005–2006 vs. in 2016.
Introduction
Degenerative aortic valve stenosis (DAS) most commonly affects elderly patients [1, 2] and its prevalence is estimated to be 2–7% in people over the age of 65 [3, 4]. As a result of global population aging, a rapid increase in the incidence of DAS is noted [5, 6].
Aortic valve degeneration is characterized by systematic valve calcification and narrowing, and several risk factors of stenosis progression have been proposed [3–10]. Rapid DAS progression may be associated with the extent of aortic valve and muscle calcifications, the disease activity assessed with positron emission tomography, or CT calcium scoring, or high inflammatory status (CRP, RANTES), also in patients with diabetes, concomitant coronary artery disease, or hemodialysis [7–9]. However, the progression is individually variable and cannot be easily predicted [7–10].
In the beginning, it is typically associated with a peak and mean transvalvular pressure gradient increase, left ventricular hypertrophy, and left atrial enlargement. Along with further DAS deterioration, other cardiac disorders such as left ventricular dysfunction, mitral valve insufficiency, atrial arrhythmias, pulmonary hypertension, and right ventricular dysfunction worsen a patient’s prognosis [10]. Therapeutic decision-making in the elderly with advanced, complicated DAS, accompanied by other cardiac and extracardiac problems, is difficult. At the time of patient referral for invasive intervention, the procedure-related 30-day mortality risk, using the EuroSCORE II and Society of Thoracic Surgeon risk score (STS), is frequently unacceptably high [11–14].
Echocardiography plays the principal role, not only in DAS diagnosis, but more importantly, is crucial in cardiac risk monitoring of congestive heart failure and sudden cardiac death [10, 15, 16]. The complementary role of biomarkers in the process of evaluation of DAS still requires further investigation [17]. If complicated DAS occurs, it is associated with a rapidly increasing risk of heart failure and death in patients managed conservatively, as well as difficult decisions on further management due to perioperative mortality and morbidity risk.
As per current guidelines, intervention for DAS is recommended in patients with symptomatic severe DAS (level of evidence: IB) and in patients with moderate DAS referred for coronary artery bypass or ascending aorta surgery (level of evidence: IIa-C) [11]. Furthermore, AVR is recommended in asymptomatic patients with severe DAS and unexplained left ventricular dysfunction (LVEF < 50%) (level of evidence: IC), as well as an abnormal result of the exercise test (level of evidence: IC).
Aim
The main objective of the present study was to compare the risk profile and comorbidities affecting perioperative risk in patients with symptomatic moderate-to-severe DAS referred for aortic stenosis treatment in 2005–2006, as compared to patients admitted in 2016.
Material and methods
The study group consisted of 292 patients with confirmed symptomatic severe DAS (defined as an aortic valve area < 1.0 cm2 from the continuity equation) referred to our department for aortic valve stenosis intervention.
Group I consisted of 140 consecutive patients (87 men, 53 women), mean age: 64.1 ±8.9 years (range: 40–83), admitted to the hospital between January 2005 and December 2006.
Group II comprised 152 consecutive patients (75 men, 77 women), mean age: 73.1 ±9.6 years (range: 47–91), admitted to the hospital between January 2016 and December 2016.
All subjects were evaluated, including an assessment of clinical symptoms with the New York Heart Association (NYHA) Classification and the Canadian Cardiovascular Society Grading System for exertion-induced angina (CCS), and the distribution of major cardiovascular risk factors (gender, age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus type II, hyperlipidemia).
Transthoracic echocardiography, carotid ultrasonography, and coronary angiography were performed.
Perioperative risk was assessed with the EuroSCORE II and STS scores.
The study protocol was consistent with the requirements of the Helsinki Declaration, and approved by the local Institutional Ethics Committee. All subjects gave informed consent for participation in the study.
Coronary angiography was performed in all patients using COROSCOP (Siemens), equipped with Quantcor QCA V 2.0 quantitative coronary analysis software. Patients with at least one lesion ≥ 50% reduction in lumen diameter within the main branches of the coronary arteries were considered to have significant CAD.
Echocardiographic study
All patients underwent a complete echocardiographic study in compliance with the guidelines of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging [16]. The peak and mean gradient through the aortic valve, the aortic valve area (AVA), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), grading of mitral valve insufficiency, right ventricular dysfunction, and pulmonary hypertension (PH) grading were calculated in groups I and II.
Carotid artery ultrasonography
High-resolution B-Mode, color Doppler, and pulse Doppler ultrasound of both carotid arteries were performed with an ultrasound machine (TOSHIBA APLIO) featuring a linear-array 5–10 MHz transducer. The degree of carotid stenosis was assessed through an increase in the peak systolic and end-diastolic velocities (according to the Bluth criteria) [18]. The carotid artery stenosis was considered significant (> 50% lumen reduction) if peak systolic velocity was > 1.3 m/s, end-diastolic velocity > 0.4 m/s, and lumen reduction exceeded 70% on transverse scans. Experienced sonographers who had no prior knowledge of the subject’s clinical and angiographic characteristics obtained all scans. The importance of carotid artery ultrasonography in DAS has been previously demonstrated [19, 20].
Perioperative risk calculators: EuroSCORE II and STS score
STS score – the Society of Thoracic Surgeons-Predicted Risk of Mortality score (STS-PROM) and the European System for Cardiac Operative Risk Evaluation (EuroSCORE) model (additive and logistic) were used to evaluate the risk in all patients [12, 13].
Two experienced cardiologists working together assessed perioperative risk using calculators which are freely available online: STS score (http://riskcalc.sts.org/stswebriskcalc/#/calculate) and EuroSCORE II (http://www.euroscore.org/calc.html). Variables included in both scores were judged according to guidelines supplied to databases.
Analyzed variables included in the calculation of scores were defined as follows:
Data on disabling ischemic stroke were obtained from a stroke unit and sourced from available medical documentation. Brain imaging was obtained either with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Data on chronic lung disease were collected from available medical documentation and from results of pulmonary function tests.
Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the MDRD formula and for the EuroSCORE II calculator using the Cockcroft-Gault formula. A history of peripheral artery disease including claudication (upper and lower extremities, renal, mesenteric, and abdominal aortic systems) was collected from the patient’s medical history. Data on previous cardiac interventions, procedure urgency, critical perioperative state, and concomitant cardiac surgery were obtained from medical documentation.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as mean ± SD, categorical variables are expressed as frequencies and percentages. Means of analyzed parameters across groups were tested with the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test and frequencies were compared using the χ2 test for independence.
The normal distribution of studied variables was determined using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Differences between mean values of echocardiographic parameters were verified using the Mann-Whitney U test as the distribution of variables was found not to be normal. The U test results were presented as the median and interquartile range.
Statistical analyses were performed using Statistica 12.0 software. Statistical significance was assumed at p < 0.05.
Results
Basic characteristics of patients
Baseline characteristics of study participants are shown in Table I. Subjects in group II, when compared with those in group I, were significantly older. In comparison to group I, group II patients were more often females and showed a significantly increased prevalence of classic cardiovascular risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia (Table I). Group I patients, when compared to group II patients, presented more frequently with symptoms assessed as grade 2 to 4 according to the NYHA classification, but reported fewer symptoms according to the CCS scale (Table I). However, there was no significant difference with respect to prevalence of symptoms in class 4, both according to the NYHA as well as the CCS classification (Table I).
Table I.
Baseline characteristics of study participants
| Parameter | DAS patients 2005/2006 (n = 140) | DAS patients 2016 (n = 152) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic data: | |||
| Age, mean ± SD*# [years] | 64.1 ±8.9 | 73.1 ±9.6 | < 0.001 |
| Median (Q1 : Q3) | 65 (57 : 71) | 74 (67 : 81) | |
| Female, n (%)*# | 53 (37.9) | 77 (50.7) | 0.028 |
| Clinical symptoms, n (%): | |||
| NYHA ≥ II*# | 135 (96.4) | 129 (84.9) | 0.001 |
| NYHA = IV*# | 4 (2.9) | 4 (2.6) | 0.906 |
| CCS ≥ II* | 36 (25.7) | 58 (41.4) | 0.023 |
| CCS = IV*# | 1 (0.7) | 3 (2.0) | 0.355 |
| Risk factors, n (%): | |||
| Hypertension* | 96 (68.6) | 148 (97.3) | < 0.001 |
| Diabetes* | 25 (17.8) | 54 (35.5) | 0.001 |
| On insulin*# | 3 (2.1) | 15 (9.9) | 0.006 |
| Dyslipidemia | 111 (79.3) | 150 (98.6) | < 0.001 |
| CAD*# | 59 (42.1) | 71 (46.7) | 0.433 |
| Previous MI*# | 12 (8.6) | 25 (16.4) | 0.043 |
| Previous PCI* | 6 (9.2) | 39 (25.6) | < 0.01 |
| Laboratory results, mean ± SD: | |||
| LDL cholesterol [mmol/l] | 3.4 ±1.00 | 2.7 ±1.00 | < 0.001 |
| Creatinine [µmol/l] | 87.7 ±21.2 | 88.4 ±23.4 | 0.801 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dl] | 13.7 ±1.6 | 13.1 ±1.6 | 0.435 |
Parameters included in STS score
parameters included in EuroSCORE II.
Echocardiography results
A comparison of echocardiographic characteristics is displayed in Table II. On echocardiography, there were no significant differences between groups with respect to LVEF (57.5 ±12.1%, median 60% vs. 55 ±12.1%, median 60%, p = 0.768), mean aortic valve gradients (48.6 ±19.9 vs. 46.2 ±15.6 mm Hg, p = 0.215), and the AVA (0.87 ±0.3 vs. 0.90 ±0.32 cm2, p = 0.356) (Table II). Peak aortic gradient was higher in group I vs. group II (82.3 ±27.7 vs. 76 ±25.5 mm Hg, p = 0.05).
Table II.
Echocardiographic findings in study participants
| Parameter | DAS patients 2005–2006(n = 140) | DAS patients 2016(n = 152) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left ventricle ejection fraction, mean ± SD (%)*#: | 57.5 ±12.1 | 55 ±12.1 | 0.768 |
| Median (Q1 : Q3) | 60 (51 : 65) | 60 (50 : 65) | |
| LVEF < 50%, n (%) | 26 (18.6) | 28 (18.4) | 0.974 |
| Mean aortic gradient, mean ± SD [mm Hg]: | 48.6 ±19.9 | 46.2 ±15.6 | 0.215 |
| Median (Q1 : Q3) | 48 (35 : 61) | 46 (37 : 54) | |
| Number of patients with MG > 40 mm Hg, n (%) | 97 (69.3) | 95 (62.5) | 0.222 |
| Aortic valve area, mean ± SD [cm2] | 0.87 ±0.3 | 0.9 ±0.32 | 0.356 |
| Low-flow low-gradient DAS, n (%) | 7 (6.4) | 18 (11.8) | 0.037 |
| Pulmonary hypertension, n (%)#: | |||
| Moderate (RVSP: 31–55 mm Hg) | 8 (5.7) | 33 (21.7) | < 0.001 |
| Severe (RVSP > 55 mm Hg) | 4 (2.9) | 8 (5.3) | 0.300 |
| Overall (RVSP ≥ 31 mm Hg) | 12 (8.6) | 42 (27) | < 0.001 |
| Concomitant aortic valve insufficiency, n (%)*: | |||
| Moderate | 12 (8.6) | 20 (13.1) | 0.210 |
| Severe | 6 (4.2) | 1 (0.6) | 0.043 |
| Overall | 18 (12.8) | 21 (13.7) | 0.801 |
| Concomitant severe mitral valve stenosis, n (%)* | 3 (2.1) | 2 (1.3) | 0.586 |
| Concomitant mitral valve regurgitation, n (%)*: | |||
| Moderate | 14 (10) | 16 (10.5) | 0.970 |
| Severe | 1 (0.7) | 9 (5.9) | 0.015 |
| Overall | 15 (10.7) | 25 (16.4) | 0.155 |
| Ascending aorta diameter > 45 mm, n (%)# | 5 (3.5) | 6 (3.9) | 0.866 |
Parameters included in STS score
parameters included in EuroSCORE II.
Low-flow-low-gradient DAS was more frequent in group II vs. group I subjects (11.8% vs. 6.4%, p = 0.037). PH was more frequent in group II vs. group I subjects (27% vs. 8.6%, p < 0.001). Severe mitral regurgitation was more frequent in group II vs. group I subjects (5.9% vs. 0.7%, p = 0.015).
Perioperative risk factor distribution and comorbidities included in STS score and EuroSCORE II
Risk factors and comorbidities influencing perioperative risk scores are shown in Table III.
Table III.
Comorbidities included in STS score and EuroSCORE II
| Parameter | DAS patients 2005–2006(n = 140) | DAS patients 2016(n = 152) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe chronic lung disease, n (%)*# | 3 (2.1) | 26 (17.1) | < 0.001 |
| Renal dysfunction (eGFR < 60), n (%)*# | 32 (22.8) | 53 (34.9) | 0.024 |
| Extracardiac arteriopathy (carotid or PAD), n (%)*# | 25 (17.8) | 61 (40.1) | < 0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%)* | 16 (11.4) | 41 (27) | 0.001 |
| Previous ischemic stroke/TIA, n (%)* | 8 (5.7) | 17 (11.2) | 0.095 |
| Significant coronary artery disease (> 50%), n (%)* | 59 (42.1) | 71 (46.7) | 0.433 |
| Previous MI, n (%)*#: | 12 (8.6) | 25 (16.4) | 0.043 |
| < 21 days before intervention | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | N/A |
| ≤ 90 days before intervention | 0 (0) | 6 (3.95) | 0.049 |
| Previous PCI, n (%)* | 6 (9.2) | 39 (25.6) | < 0.001 |
| Previous cardiac surgery, n (%)*# | 5 (3.7) | 8 (5.3) | 0.484 |
| Intervention urgency, n (%): | |||
| Elective*# | 137 (98) | 141 (92.76) | 0.042 |
| Urgent*# | 1 (0.7) | 9 (5.92) | 0.015 |
| Emergency*# | 2 (1.4) | 2 (1.32) | 0.933 |
| Shock/Critical preoperative status, n (%)*# | 1 (0.7) | 4 (2.63) | 0.207 |
| Active endocarditis, n (%)*# | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | N/A |
| Immunocompromised, n (%)* | 1 (0.7) | 6 (3.95) | 0.071 |
| Poor mobility, n (%)# | 8 (5.7) | 13 (8.6) | 0.348 |
Parameters included in STS score
parameters included in EuroSCORE II.
In group II vs. group I, female subjects were more frequent (50.7% vs. 37.9%, p = 0.028). Extracardiac arteriopathy (40.1% vs. 17.8%, p < 0.001), renal dysfunction (34.9% vs. 22.8%, p = 0.024), atrial fibrillation (27% vs. 11.4%, p = 0.001), and severe chronic lung disease (17.1% vs. 2.1%, p < 0.001) were all more prevalent in group II vs. group I patients. The prevalence of coronary artery disease (at least one major coronary artery with lumen reduction exceeding 50%) was similar in both groups (42.1% vs. 46.7%, p = 0.433), while rates of previous myocardial infarction (16.4% vs. 8.6%, p = 0.043) and PCI (25.6% vs. 9.2%, p < 0.01) were more frequent in group II vs. group I subjects.
Perioperative risk scores
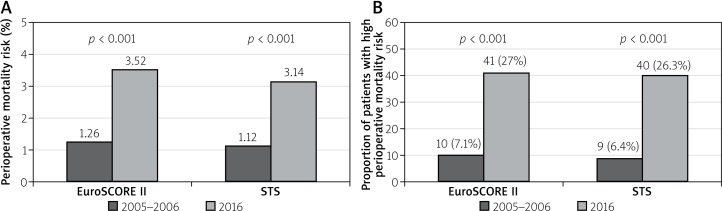
The mean perioperative mortality risk scores in group II were significantly higher than those in group I (EuroSCORE II: 3.52 ±3.97% vs. 1.26 ±2.8% p < 0.001; STS mortality score: 3.14 ±2.7% vs. 1.12 ±2.43; p < 0.001) (Figure 1 A).
Figure 1.
A – Comparison of mean EuroSCORE II and STS scores in group I and group II, B – prevalence of patients with high risk of perioperative mortality STS and EuroSCORE > 4%
The prevalence of subjects with high perioperative mortality risk ≥ 4% was significantly higher in group II than group I. This was with respect to the EuroSCORE II: 41 (27%) vs. 10 (7.1%) (p < 0.001) and STS: 40 (26.3%) vs. 9 (6.4%) (p < 0.001) (Figure 1 B).
Treatment options
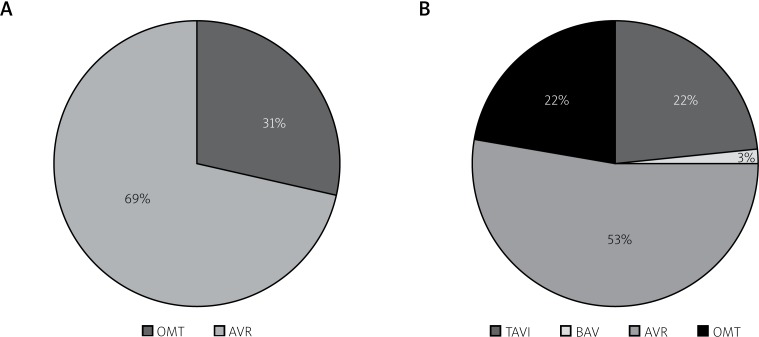
In the year 2005/2006, 69% of patients were referred for AVR, while 31% of subjects were given optimal medical treatment (OMT) without intervention on DAS, due to unacceptably high-operative risk. In the year 2016, although the risk profile of patients increased, 53% of patients were referred for AVR, 22% for TAVI and 3% for balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV). Still, 22% of subjects were considered ineligible for DAS intervention and they were referred for OMT (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
A – Patients referred for aortic valve replacement (AVR) or optimal medical treatment (OMT) in 2005–2006. B – Patients referred for AVR, OMT, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVI) and balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) in 2016
Discussion
The most important finding from our study is that in a period of just one decade, patients with DAS are currently referred for intervention at a more advanced stage of DAS. Whereas echocardiographic parameters of the AVA, mean-transvalvular pressure, and LVEF were similar in both groups, the prevalence of moderate-to-severe PH, severe mitral insufficiency, or AF increased 3.1-, 8-, and 2.5-fold in patients evaluated recently for DAS. Both PH and AF independently increase perioperative risk and, additionally, PH has a negative impact on long-term outcome [21]. Furthermore, low-flow, low-gradient DAS was observed twice as often in 2016 as compared to 2005–2006. Therefore, patients with newly recognized DAS should undergo careful assessment using serial echocardiographic and stress tests. This would aid in optimally timing required interventions.
Thus, echocardiographic findings are valuable, being able to indicate high transvalvular gradient, massive and extensive calcifications, rapid disease progression, as well as atrium enlargement and right ventricular dysfunction [22]. Notably, the risk of intervention significantly increases with DAS progression. Furthermore, in asymptomatic or scarcely symptomatic patients, stress testing should be used to identify high-risk features including reduced exercise tolerance, exercise-induced symptoms, and absolute or relative hypotension [23].
In the present study, symptoms according to NYHA classification in classes 2 and higher were observed in 96.4% of the group I population and in 85% of patients with DAS in 2016. There is substantial controversy over the optimal timing of intervention for these patients, as some advocate early intervention while others favor conservative management until symptom onset [24].
On the one hand, sudden death risk in truly clinically asymptomatic patients with severe DAS was estimated at 1–1.5% per year [25], while intervention risk may exceed 3% [11]. Thus, some experts would advocate a ‘watchful waiting’ attitude. However, we have demonstrated that the policy of ‘watchful waiting’ until symptoms (arrhythmias, pulmonary hypertension or congestive heart failure) appear in higher classes should be reconsidered carefully, as this leads to high perioperative mortality scores in patients. In our study, at the point of invasive DAS management, EuroSCORE II and STS scores of 4% or higher were present in 26–27% of patients, as compared to 6–7% in 2005–2006.
This is in line with other observational studies indicating that the ‘watchful waiting’ attitude leads to advanced patient age and the increasing number of concomitant comorbidities which increase STS and EuroSCORE II risk [12, 13].
Furthermore, Genereux et al. found in a meta-analysis of 4 retrospective studies that patients with severe asymptomatic DAS have a 3.5-fold higher rate of all-cause death when managed with a conservative strategy compared to AVR [22]. Moreover, this meta-analysis favors intervention over optimal medical treatment in terms of cardiovascular risk reduction, e.g. sudden cardiac death [22].
We observed in our present study that currently, as compared to 2005/2006, there are fewer patients with DAS and symptoms of congestive heart failure; however, these patients have higher scores using the EuroSCORE II and STS calculators. This is due to a significant increase in the prevalence of associated cardiovascular risk factors and vital comorbidities such as lung disease, peripheral artery occlusive disease, and disabling stroke in recently admitted patients with DAS. The results from our study are in line with recent epidemiological data which show changes in the profile of patients with valvular disease who attend clinics, wards and emergency units [6, 8, 26–28]. Hypertension, diabetes, peripheral artery disease, renal dysfunction and chronic pulmonary disease have a huge influence on perioperative risk [12, 13, 26].
Another problem arises with symptomatic patients with DAS referred for intervention. Patient mortality increases dramatically with appearance of symptoms [29], exceeding 60% during the 5 years after the time of first hospital admission [27]. Cardiac deaths represent more than half of cases, with heart failure and sudden death as the main causes [30]. In patients over 80 years prognosis is even poorer, and the annual mortality reaches up to 50% [31].
For 15 years, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVI) has been a viable alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement (AVR) for high-surgical-risk subjects [27]. Data from recent trials suggest that performing TAVI in subjects with intermediate periprocedural risk (STS below 4%) may be beneficial and have comparable periprocedural mortality results [32]. However, in patients with DAS and low-to-intermediate periprocedural risk, the primary endpoint of all-cause mortality, stroke, or MI was relatively high at 5 years (39.2% among TAVI-treated patients and 35.8% in AVR-treated patients, p = NS). Notably, the principal concerns regard the high rates of pacemaker implantation (about 40% of patients) and paravalvular leaks (about 21%) in the TAVI-treated patients [33, 34]. Nevertheless, as we face increasing periprocedural mortality risk in patients referred for AVR, the proportion of patients referred for TAVI will naturally increase [35]. Our current study indicates that although there is an increase in the risk profile of patients currently admitted, increased access to invasive treatment options, such as TAVI and AVR, leads to intervention in 78% of patients. Still, 22% of subjects in 2016, as compared to 30% in 2005-2006, were considered ineligible for DAS intervention and were referred for OMT.
Study limitations
The first limitation is that the present study is derived from data of one center, based on a population subset consisting predominantly of symptomatic patients with DAS admitted for intervention. The population of asymptomatic patients with DAS was underrepresented.
Another study limitation is a lack of data concerning intervention outcomes, which could present a real perioperative risk comparison between both groups. Because of this, therapeutic decisions in 2005–2006 cannot be directly extrapolated to currently available guidelines and therapeutic options. Moreover, TAVI was not available in 2005–2006 as a standard procedure. Perioperative risk assessment was performed in 2005–2006 using the old “logistic” EuroSCORE, which is not compatible with the currently used EuroSCORE II. We cannot indicate the proportion of patients in both study periods who were a priori disqualified from even referral for the assessment for potential intervention and a priori deemed “too high risk” by their GP.
Conclusions
Within one decade, the risk profile of patients admitted with DAS has significantly increased, which is mainly due to the accumulation of comorbidities in advanced age and more advanced disease at presentation. Although new treatment methods such as TAVI have expanded the indications for intervention in high-risk patients, the number of patients disqualified from interventional treatment remains high.
A careful diagnostic and qualification process in patients with DAS is crucial for obtaining the best results and reducing the risk. The referral for intervention of DAS should be considered earlier than current recommendations, preferably before echocardiographic features of decompensated DAS and symptoms of heart failure occur.
Acknowledgments
Jakub Baran and Jakub Podolec contributed equally.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Eveborn GW, Schirmer H, Heggelund G, et al. The evolving epidemiology of valvular aortic stenosis. The Tromsø Study. Heart. 2013;99:396–400. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2012-302265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN. Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population based study. Lancet. 2006;368:1005–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vahanian A, Alfieri O, Andreotti F, et al. Guidelines on the management of valvular heart disease (version 2012): The Joint Task Force on the Management of Valvular Heart Disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur Heart J. 2012;33:2451–96. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ramos J, Monteagudo JM, González-Alujas T, et al. Large-scale assessment of aortic stenosis: facing the next cardiac epidemic? Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017 doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jex223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Iung B, Vahanian A. Degenerative calcific aortic stenosis: a natural history. Heart. 2012;98(Suppl 4):iv7–13. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2012-302395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Danielsen R, Aspelund T, Harris TB, et al. The prevalence of aortic stenosis in the elderly in Iceland and predictions for the coming decades: the AGES-Reykjavik study. Int J Cardiol. 2014;176:916–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.08.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tastet L, Simard L, Clavel MA. Severe and asymptomatic aortic stenosis management challenge: knowing that we do not really know. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2017;19:33. doi: 10.1007/s11936-017-0533-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pohle K, Mäffert R, Ropers D, et al. Progression of aortic valve calcification: association with coronary atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk factors. Circulation. 2001;104:1927–32. doi: 10.1161/hc4101.097527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Peeters F, Meex S, Dweck MR, et al. Calcific aortic valve stenosis: hard disease in the heart: a biomolecular approach towards diagnosis and treatment. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:2618–24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Généreux P, Pibarot P, Redfors B, et al. Staging classification of aortic stenosis based on the extent of cardiac damage. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:3351–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Baumgartner H, Falk V, Bax J, et al. Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Kardiol Pol. 2018;76:1–62. doi: 10.5603/KP.2018.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nashef SAM, Roques F, Sharples LD, et al. EuroSCORE II. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;41:734–44. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezs043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.O’Brien SM, Shahian DM, Filardo G, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons 2008 cardiac surgery risk models: part 2 – isolated valve surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:S23–42. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.05.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shahian DM, O’Brien SM, Filardo G, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons 2008 cardiac surgery risk models: part 3 – valve plus coronary artery bypass grafting surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:S43–62. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.05.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Taniguchi T, Morimoto T, Shiomi H, et al. Prognostic impact of left ventricular ejection fraction in patients with severe aortic stenosis. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11:145–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2017.08.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Baumgartner H, Hung J, Bermejo J, et al. Recommendations on the echocardiographic assessment of aortic valve stenosis: a focused update from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2017;30:372–92. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2017.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Podolec J, Baran J, Niewiara Ł, et al. The role of biomarkers as an alternative and completion of the diagnostic and therapeutic pathway in patients with aortic stenosis. J Rare Card Dis. 2016;2:1–1. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bluth EI, Stavros AT, Marich KW, et al. Carotid Duplex sonography: a multicenter recommendation for standardized imaging and Doppler criteria. Radiographics. 1988;8:487–506. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.8.3.3289100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kablak-Ziembicka A, Przewlocki T, Tracz W, et al. Prognostic value of carotid intima-media thickness in detection of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with calcified aortic valve stenosis. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;24:461–7. doi: 10.7863/jum.2005.24.4.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kabłak-Ziembicka A, Przewłocki T, Hlawaty M, et al. Internal carotid artery stenosis in patients with degenerative aortic stenosis. Kardiol Pol. 2008;66:837–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Levy F, Bohbot Y, Sanhadji K, et al. Impact of pulmonary hypertension on long-term outcome in patients with severe aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;19:553–61. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jex166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Genereux P, Stone GW, O’Gara PT, et al. Natural history, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies for patients with asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:2263–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.02.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Das P, Rimington H, Chambers J. Exercise testing to stratify risk in aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:1309–13. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maréchaux S, Hachicha Z, Bellouin A, et al. Usefulness of exercise-stress echocardiography for risk stratification of true asymptomatic patients with aortic valve stenosis. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:1390–7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pellikka PA, Sarano ME, Nishimura RA, et al. Outcome of 622 adults with asymptomatic, hemodynamically significant aortic stenosis during prolonged follow-up. Circulation. 2005;111:3290–5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.495903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Iung B, Baron G, Butchart EG, et al. A prospective survey of patients with valvular heart disease in Europe: the Euro Heart Survey on Valvular Heart Disease. Eur Heart J. 2003;24:1231–43. doi: 10.1016/s0195-668x(03)00201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bonow RO, Greenland P. Population wide trends in aortic stenosis incidence and outcomes. Circulation. 2015;131:969–71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.014846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bobrowska B, Zasada W, Dziewierz A, et al. Comparison of demographics, cardiovascular risk factors profile and prevalence of coexistent atherosclerotic vascular disease in patients with severe aortic stenosis stratified according to dichotomized stenosis severity. Adv Interv Cardiol. 2017;13:331–4. doi: 10.5114/aic.2017.71616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Berry C, Lloyd SM, Wang Y, et al. The changing course of aortic valve disease in Scotland: temporal trends in hospitalizations and mortality and prognostic importance of aortic stenosis. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:1538–47. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Minamino-Muta E, Kato T, Morimoto T, et al. Causes of death in patients with severe aortic stenosis: an observational study. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15316-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ben-Dor I, Pichard AD, Gonzalez MA, et al. Correlates and causes of death in patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis who are not eligible to participate in a clinical trial of transcatheter aortic valve implantation. Circulation. 2010;122:37–42. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.926873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Thyregod HG, Steinbruchel DA, Ihlemann N, et al. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients with severe aortic valve stenosis: 1-year results from the All-Comers NOTION randomized clinical trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:2184–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Witberg G, Lador A, Yahav D, Kornowski R. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in patients at low surgical risk: a meta-analysis of randomized trials and propensity score matched observational studies. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Feb 1; doi: 10.1002/ccd.27518. Epub ahead of print; [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Khan SU, Lone AN, Saleem MA, et al. Transcatheter vs surgical aortic-valve replacement in low- to intermediate-surgical-risk candidates: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Clin Cardiol. 2017;40:974–81. doi: 10.1002/clc.22807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Parma R, Dąbrowski M, Ochała A, et al. The Polish Interventional Cardiology TAVI Survey (PICTS): adoption and practice of transcatheter aortic valve implantation in Poland. Adv Interv Cardiol. 2017;13:10–7. doi: 10.5114/aic.2017.66181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]