Figure 3.
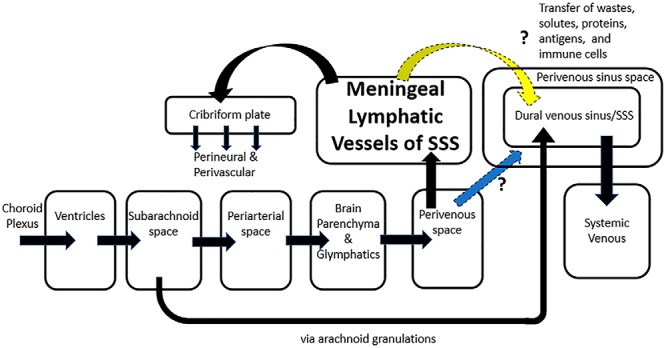
Hypothetical compartmental model incorporating countercurrent flow. Countercurrent flow of the MLV in relation to the venous flow in the SSS provides a new component to the compartmental model (yellow arrow), which hypothesizes the advantage of an additional path that solutes, waste products, pathologic proteins, antigens, and immune cells could be cleared from the CNS more rapidly through exchange from the MLV to the dural venous sinus. An alternative mechanism is that countercurrent, caudal flow of fluid is in the perivenous sinus space of the SSS (blue arrow) akin to the flow of fluid in the perivenous space from glymphatic drainage. Significant advantages potentially exist when perivenous flow has options of flow rostrally in the MLV and/or caudally along the perivenous sinus space in the direction of venous blood flow, as emphasized in this figure by arrows pointing in opposite directions for flow to the cribriform plate versus in the direction of flow of the dural venous sinus/SSS.
