Figure 4.
Effect of TRPC1 Deficiency on the Ability of IFNγ to Induce M1 Macrophages In Vitro
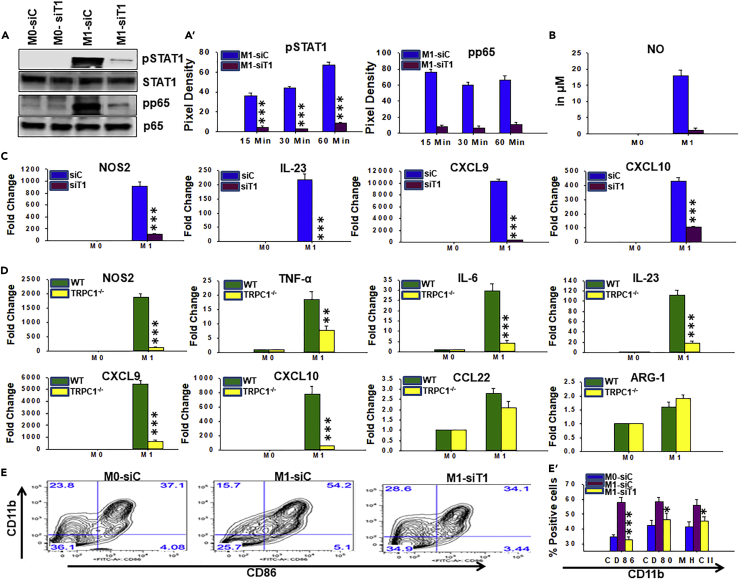
To analyze the effect of TRPC1 deficiency on M1 macrophage functions, BM macrophages from WT and TRPC1−/− mice were generated in vitro. In addition, BM macrophages from C57BL/6 mice were transfected with non-targeting siRNA or TRPC1 siRNA to transiently knock down TRPC1. Cells were cultured in the presence or absence of IFNγ, and the level of M1-associated signature immune mediators and transcriptions factors were measured by western blot, RT-PCR, and colorimetric assay.
(A) BM macrophages transfected with non-targeting siRNA (siC), or TRPC1 siRNA (siT1) were pulsed with medium alone (M0-siC, M0-siT1) or IFNγ (M1-siC, M1-siT1). Immunoblot analysis were performed using anti-pSTAT1, anti-pNFκB p65 (pp65), STAT1, and p65. The average pixel intensity of the pSTAT1 and pp65 protein bands from three independent experiments is shown in A′.
(B) NO was assessed by colorimetric assay in supernatants collected at 24 hr from SiC and siT1 cells treated as described in (A).
(C) The relative mRNA expression of M1 inflammatory mediators, NOS2, IL-23, CXCL9, and CXCL10 in BM macrophages transfected with control siRNA (siC) or TRPC1 siRNA (siT1) and pulsed for 24 hr with IFNγ (M1) versus medium only (M0).
(D) The relative mRNA levels of M1 inflammatory mediators, NOS2, TNF-ᾳ, IL-6, IL-23, CXCL9, and CXCL10, and M2 anti-inflammatory mediators, CCL22 and arginase-1 (ARG-1), were analyzed in BM macrophages from WT and TRPC1−/− mice and pulsed for 24 hr with IFNγ (M1) versus medium only (M0).
(E) BM macrophages transfected with control siRNA or TRPC1 siRNA and pulsed for 24 hr with medium only (M0-siC, M0-siT1) or IFNγ (M1-siC, M1-siT1). The surface expression of costimulatory molecule CD86 was measured by flow cytometry. Plots in (E′) depict the mean ± SEM of M0-siC, M0-siT1, M1-siC, and M1-siT1 cells expressing MHC-II, CD80, or CD86 as measured by flow cytometry (density plots shown in E and Figure S4B).
*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 (Student's t test).
See also Figures S4–S7.