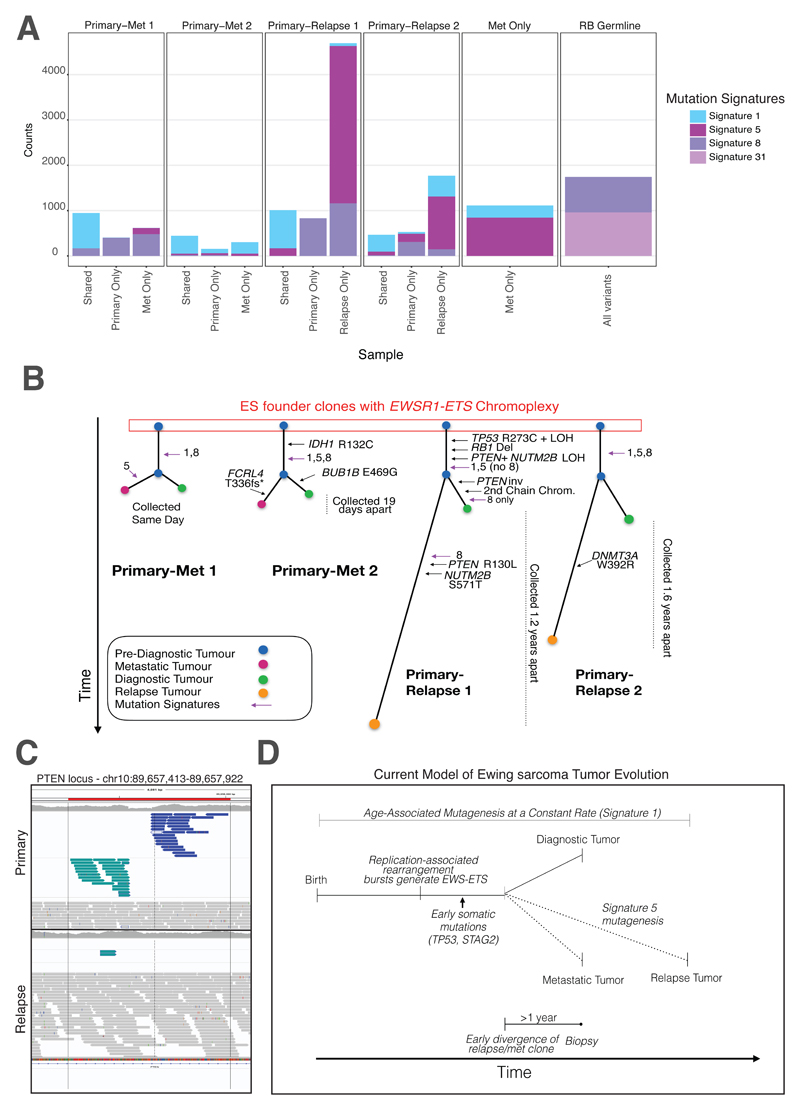
Fig. 5. Mutation Signatures and Relapse and Metastatic ES Tumors.
(A) Prevalence of mutation signatures in relapse and metastatic tumors. Shared and private mutations for four primary-metastatic or relapse pairs are shown (first four columns). Signatures 1 and 5 are common throughout, with signature 5 contributing significantly to the mutations that arise at relapse. Signature 8 was also common throughout the cohort. One metastatic tumor (no paired primary) is also shown to have similar mutation signature patterns as other metastatic/relapse tumors. Lastly, a secondary Ewing sarcoma tumor to a primary retinoblastoma (germline RB1 mutation identified) was also sequenced in this cohort. This patient harbored the rare Signature 31, which likely resulted from the patient’s prior exposure to carboplatin for their primary RB (only patient to receive this treatment in the Toronto cohort). (B) Phylogenetic trees of primary-relapse/metastatic ES. Using the shared and private mutations, we identified the mutational order in ES. Known cancer-driver mutations (IDH1, TP53 etc.) arise early (shared branches). (C) A clonal PTEN inversion. A PTEN inversion was found only in the primary and not in the relapse tissue, suggesting the inversion arose after early divergence of a common clonal ancestor. However, a pathogenic PTEN SNV can be found in the relapse tissue. Together, these point towards parallel, convergent evolution on this gene. (D) Proposed model of Ewing sarcoma tumor evolution. After birth, Signature 1 is operative in all somatic tissues throughout life. ES patients’ cells experience a replication-associated burst of rearrangements that generates the canonical fusion driver. Early somatic cancer gene mutations occur before clonal bifurcation. This occurs 1-2 years before an ES diagnosis, thus the cells that would give rise to the relapse existed years before diagnosis. Signature 5 contributes significantly to the number of mutations seen at relapse.