Abstract
The application of magnification devices in endodontics is mainly meant for visual enhancement and improved ergonomics. This is crucial especially when long hours are spent in a narrow operating space to treat obscure microanatomy. Nevertheless, application of magnification in endodontics has yet to be introduced into the mainstream practice due to various influences in behavioral patterns. By conducting an extensive literature search in the PubMed database, this narrative review paper depicts the present state of magnification devices, their applications within the endodontic practice, factors that influence their usage, the advantages, and shortcomings, as well as the significances of magnification in the field of endodontics. This review paper will encourage clinicians to employ magnification in their practice for improved outcome.
Keywords: Endodontics, lenses, magnification, optics, photonics, visual acuity, visual aids
INTRODUCTION
Endodontics is confined to narrow operating space as it deals with miniscule anatomy. As a result, clinicians who manage intricate cases appear to demand higher visual acuity.
Over the years, many magnification devices have been introduced as bridging tools between the naked eyes and the microscope. In fact, tools, such as an endoscope, magnifying glass, and intraoral camera, have largely been superseded by contemporary devices that seem to be more practical and convenient for application, such as loupes and dental operating microscope (DOM).[1,2,3]
This review describes several common types of magnification devices applied in the discipline of endodontics, the factors that influence their adoption, the advantages, and shortcomings, as well as the importance of using magnification devices for endodontics.
METHODOLOGY
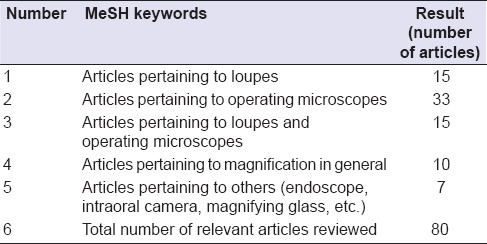
An extensive literature search had been carried out by combing through the PubMed database. The MeSH keywords applied were “endodontics,” “visual aid,” “optics and photonics,” “lenses,” “surveys and questionnaires” and “visual acuity.” As a result, a total of 670 articles were found. The title and the abstract of each article were then screened and only the relevant papers were retrieved in full text. From these texts, additional relevant articles were sought from the list of references. The total number of articles accumulated was 80. Breakdown of relevant articles according to the type of instruments is displayed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Breakdown of relevant articles according to the type of magnification device
LIMITATION OF THE NAKED EYES AND SIGNIFICANCE OF MAGNIFICATION DEVICES (REARRANGED)
Unaided eyes can only see up to the level of canal orifice.[4] Moreover, natural vision would begin to deteriorate at the age of 40.[5] This circumstance has been verified by using miniaturized eye charts placed in teeth.[6] Lack of awareness of this visual handicap is a problem within the dental profession.[7] Nevertheless, age-related visual disability seems to minimize with the use of loupe and could be compensated by using the DOM.[6,8]
PREVALENCE OF MAGNIFICATION DEVICES USAGE
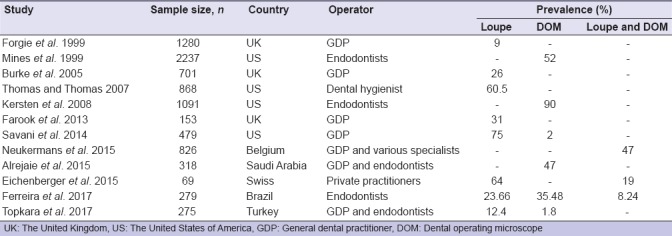
The reported data on the prevalence of use appeared to be limited. Nevertheless, an increasing trend was noted in the United States and the United Kingdom.[9,10,11,12] This reflects the increasing demand for enhanced visual details to achieve clinical excellence in endodontics. Besides, other studies that reported the prevalence of use of magnification devices are shown in Table 2.[7,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]
Table 2.
Articles that reported the prevalence of use of magnification devices
TYPES OF MAGNIFICATION DEVICES
Essentially, loupes are available in several forms as noted in Table 3. In general, flip-up loupe differs from through-the-lens (TTL) loupe in terms of barrel mobility, weight and cost.
Table 3.
Main differences between flip-up loupe and through the lens loupe

Some trendy TTL design may have a small frame rim that does not permit the loupe to sit lower for a steeper declination angle. This may pose some ergonomic challenge requiring additional head tilt. Thus, clinicians must strike a balance between esthetics and ergonomics when selecting the frame design. This is contrary in flip-up loupe as declination angle can be freely adjusted.
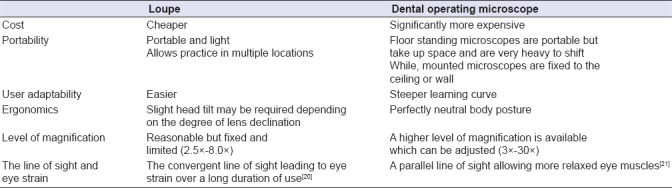
On the other hand, DOM seems to offer better ergonomics and wider range of magnification. Nonetheless, the two major shortcomings of DOM are its high cost and lack of portability.
Table 4 presents a comparison between loupe and DOM. Currently, the gold standard for the practice of endodontics necessitates the application of a microscope.[22]
Table 4.
Main differences between loupe and dental operating microscope
USES OF MAGNIFICATION DEVICES IN ENDODONTICS
Many scenarios have greatly benefited from the use of magnification in endodontics. In fact, this directly influences the decision-making in saving previously thought non-restorable tooth. The enhanced vision and illumination can facilitate the following:
Conservative access opening[26]
Managing sclerosed canals[29]
Confirming canal cleanliness prior to obturation[30]
Outlining and removing pulp stones[31]
Retrieving silver point, separated instrument, and fractured post[34,35,36]
Smaller osteotomy, magnified inspection of resected surface, as well as retropreparation and retrofill in endodontic microsurgery.[37]
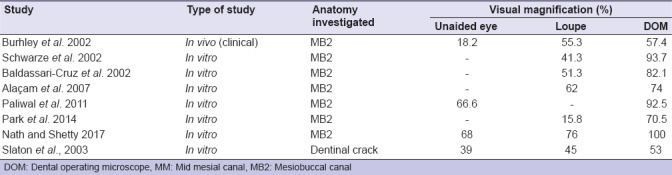
Table 5 showed the prevalence of additional anatomy found with and without using visual magnification. It is apparent that diagnostic power is associated with the level of magnification.[28,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]
Table 5.
Prevalence of additional anatomy found with and without visual magnification
VARIABLES ASSOCIATED WITH THE DIFFERENT LEVELS OF MAGNIFICATION
The two variables directly associated with the levels of magnification are field of view and depth of field (i.e., the range of working distance where an object stays in focus). At higher magnification, the field of view seen is reduced and the depth of field is smaller.[20] A clinician who utilizes higher magnification loupe for endodontics may find it challenging to perform other procedures that require a wider field of view and depth of field.
In contrast, recent microscopes are equipped with continuous range of magnification to accommodate smooth change in the visual field. Some models have motorized control for focusing and magnification to suit the wide range of tasks being performed.
USES OF VARIOUS LEVELS OF MAGNIFICATION IN ENDODONTICS
Adjustments of magnification can be categorized into three levels:[45,46]
Low magnification (3x – 8x)
Appropriate for examination of tooth orientation and positioning of bur or ultrasonic tip. The wide field of view allows comparisons of the adjacent anatomic landmark. This magnification level is used in loupes in which straightforward cases can still be competently performed.
Medium magnification (8x – 16x)
Commonly used in non-surgical and surgical endodontic procedures as it provides an acceptable field of view and depth of field. It is used for performing intricate procedures such as perforation repair, separated instrument retrieval and surgical procedure which requires higher precision and accuracy.
High magnification (16x – 30x)
Employed mostly for close-up examinations and inspections of minute anatomies, e.g., calcified canal orifice and minute cracks. Apart from having a diminutive field of view, immediate loss of focus may ensue following minor movements. The subtle color variance between secondary and tertiary dentin in teeth with calcific metamorphosis can be distinguished at this level.
FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE THE USE OF MAGNIFICATION
Among the factors that encourage clinicians to use magnification devices are exposure to magnification devices via demonstrations and dental conferences, increasing awareness on the benefits of using such technology and health-related issues such as visual deterioration and musculoskeletal pain[7,11,14,47] The usage of this tool is further promoted via social influence by peers and colleagues when encouraging outcomes are reported.
Conversely, several shortcomings have been reported to dissuade its usage e.g. increased treatment time, steep learning curve, issues with infection control and positional difficulties especially when treating the mandibular molars.[9,10,12,14,17,47,48,49,50]
Younger clinicians with good visual acuity and the more skilled, experienced clinicians who rely on tactile sensation and anatomical knowledge are those who still not fully convinced of the benefits of using such device. They are yet to be convinced that overlooked subtle anatomy may conceal untreated areas.[38,51]
The claims of discomfort and restricted visual field could be associated with the shortcomings of working with loupe, which due to its perceptible weight and non-adjustable magnification. Although this is not the case with DOM, the associated high cost and demand for auxiliary support may restrict it as an alternative.
Concerns pertaining to the adverse effect of magnification on visual acuity and visual dependence have already been debunked.[5,6,52] Clinicians who are accustomed to rely on more visual details may find that their normal vision is inadequate without magnification. Besides, the feeling of worsening visual acuity could be due to eye fatigue after long hours of muscle contraction for a converging line of sight upon usage of loupes. Nevertheless, a short rest or an intermittent glance afar is sufficient to address such problem.
ADVANTAGES OF MAGNIFICATION DEVICES
Three primary advantages were identified in relation to the usage of magnification device in endodontics, namely, (1) enhanced visualization, (2) improved working posture, and (3) increased referral.
Enhanced visualization
Ambiguity in clinical diagnosis is minimized with enhanced visual ability.[53] Minute crack, initial caries, and microleakage are clearly observable. Additionally, fine motor skills in endodontics can be improved with higher magnification.[54] The ability to carry out procedures at high precision prevents iatrogenic damage and permits a substantial reduction in treatment time for non-surgical endodontics procedure.[55]
Importantly, intricate cases can be managed with more certainties as the use of microscope ameliorates management of elusive and calcified canals, iatrogenic errors, as well as retreatment cases.[43,56,57]
Endodontic microsurgery performed under magnification offers vast benefits as small surgical site induced minimal trauma and reduced the risk of damaging adjacent structures.[58] Magnification also allows a thorough examination of the resected root end to rule out a fracture, isthmus, and additional canal.[59] Accordingly, the application of micro-instruments creates a deeper and well-centered retro-preparation that addresses a wider area of infected anatomy.[37,60]
LCD monitor or co-observation scope allows the assistant to become more focused and attentive during the procedure. This ascertains efficient workflow when the assistant can operate the suctioning device without obstructing the clinician's view as well as assisting with documentation.
Improved working posture
Good ergonomics allow longer working time without repetitive muscle strain.[61] A survey performed amongst general practitioners revealed that the most frequent reason to retire prematurely was musculoskeletal disorders.[62] Thus, better ergonomics conferred by magnification devices can prevent postural issues that are inherent to dentists in their career.[63]
Increased referral
The use of advanced equipment is reflective of clinicians as being more professional and skillful. As patients trust and confidence are established, more word-of-mouth referrals will ensue. A camera can be adapted to the microscope to enable the clinician to take high-resolution photos to explain the case intricacy or prognosis. This may foster understanding among patients towards the proposed treatment plan.
DRAWBACKS OF MAGNIFICATION DEVICES
Several reported drawbacks are acclimatization period of the new working environment, the high cost of the magnification device and its related accessories, additional steps for infection control, as well as a potential sharp injury at the workplace.
Learning curve
The adjustment period is steeper for devices with higher magnification.[39] Hindrance in the learning curve is especially related to senior dentists who are already suffering from eyesight deterioration. Clinicians who are familiar with loupes may find the transition to using microscope less demanding as the device set up only differs slightly.
The hand-eye coordination must be re-learned as endodontics is performed with indirect vision. This requires some practice as to establish canal or instrument orientation from an inverted image.
Precise and fine movement is essential for mid- to high-level magnification. Minor trembling, which cannot be noticed via naked eyes, could appear very pronounced under magnification.[64] This issue can be controlled by adopting a well-balanced body posture with arms placed closer to the body, in which an operator chair with arm support could be of great assistance.
In reducing dizziness during the initial period of use, clinicians should start and get comfortable with a lower level magnification (×2.5, ×3.0) before increasing the magnification. Additionally, novice users can begin with a shorter duration of use or apply intermittent break if necessary. The trial period with varied designs of magnification devices may aid clinicians to select the equipment they are most comfortable with. When operating with microscopes, clinicians wearing glasses must remember to retract the eyecups. Hinges and fixation stability also play significant roles to decrease movements that may cause dizziness.
Cost
The costs of loupe and microscope are considered impractical, particularly amidst developing nations. The separate lighting system that needs to be attached with the loupe and microsurgical instruments may also incur an added cost. Generally, the microscope is significantly more expensive than the loupe due to various optic designs that provide substantially higher levels of magnification without causing eye strain.[21,65] The heavy optics is, in turn, justifiably supported by hinges and arms that stay static in any position.
Infection control and lens scratching
One obstacle faced when working with magnification is cross-contamination. Operators who use loupe must avoid touching or changing its orientation during treatment. The assistant may help to reposition the loupe or head strap if required. The use of high volume evacuation and suitable working distance are imperative to minimize contamination. Protective cover placed over the loupe prevents lenses from scratching. Surface debris on the lenses can be removed with gentle blowing and blotting. Disinfection of the devices should follow the manufacturer's instructions and professional cleaning and servicing must be sought periodically to maintain its optimum function.
Sharp injuries in endodontics
Sharp injuries can occur due to the careless passing of anesthetic and irrigation needles, and files. Passing skills must be well-coordinated between the clinician and the assistant to avoid injuries. Besides, care is vital when clinicians bring in irrigation or anesthetic needles towards the patient. To avoid sharp injuries when passing the instruments, clinicians should peek down the microscope eyecups or loupes. Operator hand movements during instrument exchange must be limited to only the wrists and fingers to reduce the loss of focus in the visual field.
THE OUTCOME IN ENDODONTICS WHEN USING MAGNIFICATION
In long-term randomized control trials, the comparison made for outcomes of endodontic treatment with and without magnification is challenging, owing to many confounding factors.[66] However, numerous studies seem to support that treatment outcome in endodontics is enhanced with the use of magnification.[67,68,69] Untreated MB2 canal of the maxillary molars that were often overlooked without magnification seemed to decrease the long-term prognosis.[70] Furthermore, when endodontic microsurgery is performed under magnification with modern microsurgical methods, the success rate is 94%, as opposed to 59%, when performed with neither magnification nor cutting-edge instruments.[71]
CONCLUSION
The ability to appreciate the characteristics of magnification devices and the varied levels of magnification will encourage clinicians to use them and eventually increase their proficiency to perform endodontics procedures, hence improving the outcomes.
In the foreseeable future, the use of magnification is likely to become the standard of practice, particularly within the discipline of endodontics. Teleconsultation may also turn into a reality via live streaming when the use of these magnification devices gains wider acceptance by dental practitioners.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Held SA, Kao YH, Wells DW. Endoscope – An endodontic application. J Endod. 1996;22:327–9. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(96)80270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Erten H, Uçtasli MB, Akarslan ZZ, Uzun O, Semiz M. Restorative treatment decision making with unaided visual examination, intraoral camera and operating microscope. Oper Dent. 2006;31:55–9. doi: 10.2341/04-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brüllmann D, Schmidtmann I, Warzecha K, d’Hoedt B. Recognition of root canal orifices at a distance – A preliminary study of teledentistry. J Telemed Telecare. 2011;17:154–7. doi: 10.1258/jtt.2010.100507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Perrin P, Neuhaus KW, Lussi A. The impact of loupes and microscopes on vision in endodontics. Int Endod J. 2014;47:425–9. doi: 10.1111/iej.12165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burton JF, Bridgman GF. Presbyopia and the dentist: The effect of age on clinical vision. Int Dent J. 1990;40:303–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Perrin P, Ramseyer ST, Eichenberger M, Lussi A. Visual acuity of dentists in their respective clinical conditions. Clin Oral Investig. 2014;18:2055–8. doi: 10.1007/s00784-014-1197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Eichenberger M, Perrin P, Ramseyer ST, Lussi A. Visual acuity and experience with magnification devices in Swiss dental practices. Oper Dent. 2015;40:E142–9. doi: 10.2341/14-103-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eichenberger M, Perrin P, Neuhaus KW, Bringolf U, Lussi A. Visual acuity of dentists under simulated clinical conditions. Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17:725–9. doi: 10.1007/s00784-012-0753-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mines P, Loushine RJ, West LA, Liewehr FR, Zadinsky JR. Use of the microscope in endodontics: A report based on a questionnaire. J Endod. 1999;25:755–8. doi: 10.1016/S0099-2399(99)80125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kersten DD, Mines P, Sweet M. Use of the microscope in endodontics: Results of a questionnaire. J Endod. 2008;34:804–7. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Forgie AH, Pine CM, Longbottom C, Pitts NB. The use of magnification in general dental practice in Scotland – A survey report. J Dent. 1999;27:497–502. doi: 10.1016/s0300-5712(99)00030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Farook SA, Stokes RJ, Davis AK, Sneddon K, Collyer J. Use of dental loupes among dental trainers and trainees in the UK. J Investig Clin Dent. 2013;4:120–3. doi: 10.1111/jicd.12002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Burke FJ, Wilson NH, Christensen GJ, Cheung SW, Brunton PA. Contemporary dental practice in the UK: Demographic data and practising arrangements. Br Dent J. 2005;198:39–43. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.4811956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Thomas J, Thomas FD. Dental hygienists’ opinions about loupes in education. Am Dent Hyg Assoc. 2007;81:81–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Savani GM, Sabbah W, Sedgley CM, Whitten B. Current trends in endodontic treatment by general dental practitioners: Report of a United States national survey. J Endod. 2014;40:618–24. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Neukermans M, Vanobbergen J, De Bruyne M, Meire M, De Moor RJ. Endodontic performance by Flemish dentists: Have they evolved? Int Endod J. 2015;48:1112–21. doi: 10.1111/iej.12409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alrejaie M, Ibrahim NM, Malur MH, AlFouzan K. The use of dental operating microscopes by endodontists in the Middle East: A report based on a questionnaire. Saudi Endod J. 2015;5:134. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ferreira AC, Frozoni M, Prado M, Gomes B, Signoretti F, De-Jesus-Soares A. Current trends in technological armamentarium and treatment among Brazilian endodontists. Brazilian J Oral Sci. 2017;16:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Topkara C, Özyürek T, Demiryürek EÖ, Bursalı T, Özler M. Attitudes, materials, and methods preferred in root canal treatment in Turkey: A survey. Priv Pact. 2017;142:51–6. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Shanelec DA. Optical principles of loupes. J Calif Dent Assoc. 1992;20:25–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Apotheker H, Jako GJ. A microscope for use in dentistry. J Microsurg. 1981;3:7–10. doi: 10.1002/micr.1920030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.AAE Special Committee to Develop a Microscope Position Paper. AAE position statement. Use of microscopes and other magnification techniques. J Endod. 2012;38:1153–5. doi: 10.1016/s0099-2399(12)00624-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Forgie AH, Pine CM, Pitts NB. The use of magnification in a preventive approach to caries detection. Quintessence Int. 2002;33:13–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Clark DJ, Sheets CG, Paquette JM. Definitive diagnosis of early enamel and dentin cracks based on microscopic evaluation. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2003;15:391–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.2003.tb00963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mamoun JS, Napoletano D. Cracked tooth diagnosis and treatment: An alternative paradigm. Eur J Dent. 2015;9:293–303. doi: 10.4103/1305-7456.156840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mamoun JS. The maxillary molar endodontic access opening: A microscope-based approach. Eur J Dent. 2016;10:439–46. doi: 10.4103/1305-7456.184153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.de Carvalho MC, Zuolo ML. Orifice locating with a microscope. J Endod. 2000;26:532–4. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200009000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schwarze T, Baethge C, Stecher T, Geurtsen W. Identification of second canals in the mesiobuccal root of maxillary first and second molars using magnifying loupes or an operating microscope. Aust Endod J. 2002;28:57–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-4477.2002.tb00379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Karapinar-Kazandag M, Basrani BR, Friedman S. The operating microscope enhances detection and negotiation of accessory mesial canals in mandibular molars. J Endod. 2010;36:1289–94. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Friedman M, Mora AF, Schmidt R. Microscope-assisted precision dentistry. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1999;20:723–8. 730-1, 735-6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Goga R, Chandler NP, Oginni AO. Pulp stones: A review. Int Endod J. 2008;41:457–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2008.01374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Biswas M, Mazumdar D, Neyogi A. Non surgical perforation repair by mineral trioxide aggregate under dental operating microscope. J Conserv Dent. 2011;14:83–5. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.80729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Daoudi MF. Microscopic management of endodontic procedural errors: Perforation repair. Dent Update. 2001;28:176–80. doi: 10.12968/denu.2001.28.4.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nehme WB. Elimination of intracanal metallic obstructions by abrasion using an operational microscope and ultrasonics. J Endod. 2001;27:365–7. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200105000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Terauchi Y, O’Leary L, Suda H. Removal of separated files from root canals with a new file-removal system: Case reports. J Endod. 2006;32:789–97. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2005.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gencoglu N, Helvacioglu D. Comparison of the different techniques to remove fractured endodontic instruments from root canal systems. Eur J Dent. 2009;3:90–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kim S. Principles of endodontic microsurgery. Dent Clin North Am. 1997;41:481–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Buhrley LJ, Barrows MJ, BeGole EA, Wenckus CS. Effect of magnification on locating the MB2 canal in maxillary molars. J Endod. 2002;28:324–7. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200204000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Baldassari-Cruz LA, Lilly JP, Rivera EM. The influence of dental operating microscope in locating the mesiolingual canal orifice. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93:190–4. doi: 10.1067/moe.2002.118285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Alaçam T, Tinaz AC, Genç O, Kayaoglu G. Second mesiobuccal canal detection in maxillary first molars using microscopy and ultrasonics. Aust Endod J. 2008;34:106–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-4477.2007.00090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Paliwal A, Loomba K, Gaur TK, Jain A, Bains R, Vats A, et al. Dental Operating Microscope (DOM): An adjunct in locating the mesiolingual (mb2) canal orifice in maxillary first molars. Asian J Oral Heal Allied Sci. 2011;1:175. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Park E, Chehroudi B, Coil JM. Identification of possible factors impacting dental students’ ability to locate MB2 canals in maxillary molars. J Dent Educ. 2014;78:789–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nath KS, Shetty K. Comparative evaluation of second mesiobuccal canal detection in maxillary first molars using magnification and illumination. Saudi Endod J. 2017;7:166. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Slaton CC, Loushine RJ, Weller RN, Parker MH, Kimbrough WF, Pashley DH, et al. Identification of resected root-end dentinal cracks: A comparative study of visual magnification. J Endod. 2003;29:519–22. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200308000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Merino EM, Machtou P. Endodontic Microsurgery. London: Quintessence; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim S, Kratchman S, Karabucak B, Kohli M, Setzer F. Microsurgery in Endodontics. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hagge MS. Use of surgical telescopes by senior dental students: A survey. J Prosthodont. 2003;12:271–9. doi: 10.1016/s1059-941x(03)00103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hayes MJ, Taylor JA, Smith DR. Introducing loupes to clinical practice: Dental hygienists experiences and opinions. Int J Dent Hyg. 2016;14:226–30. doi: 10.1111/idh.12128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Alhazzazi TY, Alzebiani NA, Alotaibi SK, Bogari DF, Bakalka GT, Hazzazi LW, et al. Awareness and attitude toward using dental magnification among dental students and residents at King Abdulaziz university, faculty of dentistry. BMC Oral Health. 2016;17:21. doi: 10.1186/s12903-016-0254-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kinomoto Y, Takeshige F, Hayashi M, Ebisu S. Optimal positioning for a dental operating microscope during nonsurgical endodontics. J Endod. 2004;30:860–2. doi: 10.1097/01.don.0000134206.19737.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yoshioka T, Kobayashi C, Suda H. Detection rate of root canal orifices with a microscope. J Endod. 2002;28:452–3. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200206000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Christensen GJ. Magnification in dentistry: Useful tool or another gimmick? J Am Dent Assoc. 2003;134:1647–50. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mamoun JS. A rationale for the use of high-powered magnification or microscopes in general dentistry. Gen Dent. 2009;57:18–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bowers DJ, Glickman GN, Solomon ES, He J. Magnification's effect on endodontic fine motor skills. J Endod. 2010;36:1135–8. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wong AW, Zhu X, Zhang S, Li SK, Zhang C, Chu CH, et al. Treatment time for non-surgical endodontic therapy with or without a magnifying loupe. BMC Oral Health. 2015;15:40. doi: 10.1186/s12903-015-0025-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Schirrmeister JF, Hermanns P, Meyer KM, Goetz F, Hellwig E. Detectability of residual epiphany and gutta-percha after root canal retreatment using a dental operating microscope and radiographs – An ex vivo study. Int Endod J. 2006;39:558–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.de Mello Junior JE, Cunha RS, Bueno CE, Zuolo ML. Retreatment efficacy of gutta-percha removal using a clinical microscope and ultrasonic instruments: Part I – An ex vivo study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108:e59–62. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kim S, Kratchman S. Modern endodontic surgery concepts and practice: A review. J Endod. 2006;32:601–23. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2005.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Arens DE. Introduction to magnification in endodontics. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2003;15:426–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8240.2003.tb00970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wuchenich G, Meadows D, Torabinejad M. A comparison between two root end preparation techniques in human cadavers. J Endod. 1994;20:279–82. doi: 10.1016/s0099-2399(06)80816-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Maillet JP, Millar AM, Burke JM, Maillet MA, Maillet WA, Neish NR, et al. Effect of magnification loupes on dental hygiene student posture. J Dent Educ. 2008;72:33–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Brown J, Burke FJ, Macdonald EB, Gilmour H, Hill KB, Morris AJ, et al. Dental practitioners and ill health retirement: Causes, outcomes and re-employment. Br Dent J. 2010;209:E7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2010.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lindegård A, Nordander C, Jacobsson H, Arvidsson I. Opting to wear prismatic spectacles was associated with reduced neck pain in dental personnel: A longitudinal cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:347. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1145-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rubinstein R. The anatomy of the surgical operating microscope and operating positions. Dent Clin North Am. 1997;41:391–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sitbon Y, Attathom T, St. Georges AJ. Minimal intervention dentistry II: Part 1. Contribution of the operating microscope to dentistry. Br Dent J. 2014;216:125–30. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2014.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Del Fabbro M, Taschieri S, Lodi G, Banfi G, Weinstein RL. Magnification devices for endodontic therapy. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. 2015;12:CD005969. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005969.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Taschieri S, Del Fabbro M, Testori T, Francetti L, Weinstein R. Endodontic surgery using 2 different magnification devices: Preliminary results of a randomized controlled study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64:235–42. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2005.10.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Monea M, Hantoiu T, Stoica A, Sita D, Sitaru A. The impact of operating microscope on the outcome of endodontic treatment performed by postgraduate students. Eur Sci J. 2015;11:305–11. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Khalighinejad N, Aminoshariae A, Kulild JC, Williams KA, Wang J, Mickel A, et al. The effect of the dental operating microscope on the outcome of nonsurgical root canal treatment: A retrospective case-control study. J Endod. 2017;43:728–32. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wolcott J, Ishley D, Kennedy W, Johnson S, Minnich S, Meyers J, et al. A 5 yr clinical investigation of second mesiobuccal canals in endodontically treated and retreated maxillary molars. J Endod. 2005;31:262–4. doi: 10.1097/01.don.0000140581.38492.8b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Setzer FC, Shah SB, Kohli MR, Karabucak B, Kim S. Outcome of endodontic surgery: A meta-analysis of the literature – Part 1: Comparison of traditional root-end surgery and endodontic microsurgery. J Endod. 2010;36:1757–65. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2010.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


