Abstract
Oxidative stress induced by hypoxia/ischemia resulted in the excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the relative inadequate antioxidants. As the initial barrier to environmental pollutants and allergic stimuli, airway epithelial cell is vulnerable to oxidative stress. In recent years, the antioxidant effect of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has attracted much attention. Therefore, in this study, we explored the impact of H2S on CoCl2-induced cell injury in 16HBE14o- cells. The effect of CoCl2 on the cell viability was detected by Cell Counting Kit (CCK-8) and the level of ROS in 16HBE14o- cells in response to varying doses (100–1000 μmol/L) of CoCl2 (a common chemical mimic of hypoxia) was measured by using fluorescent probe DCFH-DA. It was shown that, in 16HBE14o- cells, CoCl2 acutely increased the ROS content in a dose-dependent manner, and the increased ROS was inhibited by the NaHS (as a donor of H2S). Moreover, the calcium ion fluorescence probe Fura-2/AM and fluorescence dye Rh123 were used to investigate the intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) and mitochondria membrane potential (MMP) in 16HBE14o- cells, respectively. In addition, we examined apoptosis of 16HBE14o- cells with Hoechst 33342. The results showed that the CoCl2 effectively elevated the Ca2+ influx, declined the MMP, and aggravated apoptosis, which were abrogated by NaHS. These results demonstrate that H2S could attenuate CoCl2-induced hypoxia injury via reducing ROS to perform an agonistic role for the Ca2+ influx and MMP dissipation.
1. Introduction
Hypoxia or ischemia causes an imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the antioxidant defense system leading to oxidative stress, which is closely linked to the pathogenesis of acute and chronic airway disorders [1]. Exposure to oxidants may cause a free radical-initiated lipid peroxidation and induce rapid changes in membrane lipid composition in the serum, heart, lung, liver, and kidney of hypoxic rats [2–4]. Increased amount of ROS has been directly linked to oxidation of proteins, DNA, and lipids, which may induce inflammation and direct cellular injury through regulation of multiple proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators in the various tissues especially in the airway and lung. Growing evidence suggests that accumulative ROS [5–8] and proinflammatory mediators may increase the airway microvascular permeability and mucus secretion and lead to the development of airway hypersensitivity and the remodeling of extracellular matrix and blood vessels [9]. Intracellular excessive ROS induced by hypoxia leads to intracellular Ca2+ accumulation [10] and a decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) via promoting the open of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore [11, 12] and results in cellular injury, reduced cell survival, and induced cell apoptosis.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a flammable, malodorous gas with the smell of rotten eggs and initially classified as an environmental hazard. However, H2S has been identified as the third endogenous signaling gasotransmitter (after NO and CO) produced by a series of enzymes in mammals and has efficiently anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory properties [13]. Accumulating evidence shows that H2S presents a protective effect against oxidative stress on various tissues such as kidney [14], central nervous system [15–17], cardiomyocytes [18, 19], lung [20, 21], and so on. Moreover, H2S increases the level of glutathione (GSH) by enhancing the activity of γ-glutamyl-cysteine synthetase [22] and scavenges superoxide free radical, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and reduces the accumulation of lipid peroxidations [23].
The airway epithelial cell is the initial cell type encountered by inhaled environmental factors and medications for the treatment of airway diseases. The deciduous ciliated cells in asthma patients suggest that the patients' airway epithelial barrier is often compromised [24, 25]. As the first physical barrier, the airway epithelia preventing invasion of inhaled environmental agents are easily stressed, damaged, and even denuded. An inability to recover intercellular contacts and deficient repair response after injury may be responsible for the activated and damaged phenotype of the asthma bronchial epithelium. Nevertheless, the effects of H2S in the airway against oxidative stress remain unclear. Our study focused on the effects of H2S by using the sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) as a donor on cell injury induced by Cobalt Chloride (CoCl2), a commonly used chemical reagent in establishing hypoxia models in vitro, in human bronchial epithelial cell line (16HBE14o-).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells Culture
The immortalized human bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE14o- was purchased from the cell bank in central laboratory of Central South University. Cells were maintained in a mixture medium of DMEM:F12 (1:1) (Hyclone, USA) with 3.15 mg/L glucose and supplemented with 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomycin, and 10% fetal bovine serum (Hyclone, USA) and incubated at 37°C in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. 16HBE14o- cells during a logarithmic growth phase were treated with NaHS (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC, ROS scavenger, Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, China) for 30 min or 60 min prior to exposure to CoCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, USA), respectively.
2.2. Detection of Cell Viability by CCK-8 Assay
The effect of CoCl2 on the cell viability was measured by the Cell Counting Kit (CCK-8) [26] and cells were cultured in the same condition as above. Cells were treated with or without CoCl2 in the presence or absence of NaHS. Briefly, cells were counted, adjusted, and seeded in a 96-well plate. Cells were seeded in five copies for each treatment group. The cells in control group were treated with an equal volume (100 μl) of DMEM. 10 μl CCK-8 solution was added to each well according to the manufacturer's protocol and then the cell culture plate was incubated for 1–4 h. The optical density at 450 nm was detected with a microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). Each determination was performed at least three times.
2.3. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Content
Intracellular ROS levels were measured in reference to previous reports [15]. After the incubation with 5 μmol/L DCFH-DA for 50 min at 37°C in dark, cells in a logarithmic growth phase (2 × 105 cells per well in a confocal dish) were washed with EBSS (in mg/ L: 6800 NaCl, 400 KCl, 264 CaCl2·2H2O, 200 MgCl2·7H2O, 2200 NaHCO3, 140 NaH2PO4·H2O, and 1000 glucose, pH 7.2) for three times. Next, the fluorescence intensity of DCF was monitored by laser scanning confocal microscope (SP5, Leica) system and analyzed with LAS AF 2.5.1.6757 software (Germany).
2.4. Measurements of [Ca2+]i
[Ca2+]i measurement in 16HBE14o- cells was performed according to previous descriptions [15]. Briefly, 16HBE14o- cells were incubated with Fura-2/AM (1 μM, Invitrogen, USA) at 37°C for 40 min in dark after cells inoculated in a confocal dish were treated. Then, the cells were washed with EBSS (containing 1000 mg/L glucose) for three times and examined by fluorescence inversion microscope (IX71, Olympus). Calcium ion concentration was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy imaging system (CellR-MT20, Germany) and manifested in the ratio of F340/380.
2.5. Measurements of MMP
MMP in 16HBE14o- cells was detected in reference to previous report [18]. In brief, Rhodamine 123 (Rh123, Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, China) is a fluorescent dye that can be absorbed by living cellular mitochondria. The absorption values alter with the change of MMP and the fluorescence intensity of the cells. Therefore, MMP can be measured through detecting the changes of Rh123 fluorescence intensity. After the treatment, 16HBE14o- cells were incubated with 5 μg/ml Rh123 at 37°C for 45 min. Then, the cells were washed with EBSS (containing 1000 mg/L glucose) for three times. Three randomly selected fields were taken with a laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica, Germany). The monochromators on the excitation side were set at 488 nm and on the emission side at 525 nm. The fluorescence intensity was analyzed with LAS AF 2.5.1.6757 software (Germany). Three independent experiments were repeated.
2.6. Measurements of Cell Injury
Quantification of cell injury refers to the prior literature [19]. Cells were incubated with 10 μg/ml Hoechst 33342 (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, China) for 5 min after the treatment and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room temperature followed by washing with PBS twice. Uniformly stained nuclei were scored as healthy and viable cells. Condensed or fragmented nuclei were scored as damaged cells. 16HBE14o- cells were imaged with fluorescence microscope (Ti-u, Nikon). The assay was repeated for three times.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0. The data were presented as mean ± SD and analyzed using one-way ANOVA for multiple comparisons or t-test between two groups. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. H2S Promoted Cell Viability of 16HBE14o- Cells Inhibited by CoCl2
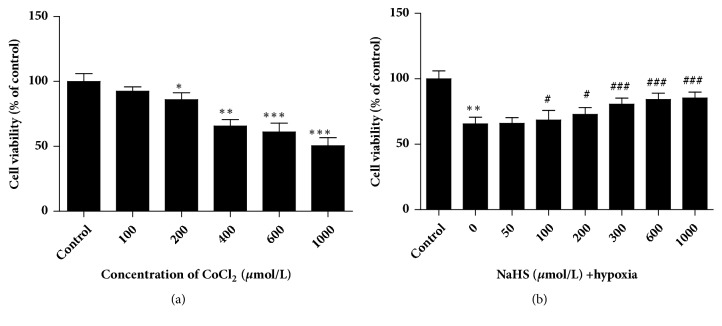
The results in Figure 1(a) showed that CoCl2-precondition had the significant dose-dependent inhibitory effect on cell viability in 16HBE14o- cells. Administration of NaHS displayed the protective effect of H2S on CoCl2-induced 16HBE14o- cell injury (Figure 1(b)). Referring to our results and related studies, we selected CoCl2 at the concentration of 400 μM [27, 28] and NaHS at the concentration of 300 μM [29, 30] to treat 16HBE14o-cells in the subsequent experiments.
Figure 1.
The effects of CoCl2 and H2S on the viability of 16HBE14o- cells were determined by CCK-8. (a) The viability of 16HBE14o- cells preconditioned with a series of CoCl2 concentration (0, 100, 200, 400, 600, or 1000 μmol/L). (b) The viability of 16HBE14o- cells treated with 400 μmol/L CoCl2 and NaHS in varying doses (0, 100, 200, 400, 600, or 1000 μmol/L) (mean± SD, n=4, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control group, #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 versus hypoxia group).
3.2. H2S Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced ROS in 16HBE14o- Cells
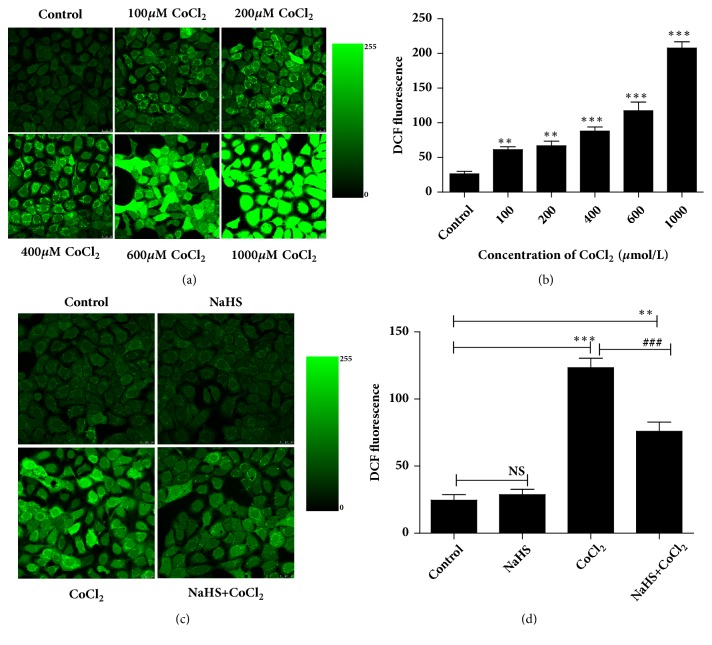
DCF immunofluorescence intensity was analyzed to verify the potential role of H2S in hypoxia-induced intracellular ROS content. The DCF fluorescence intensity increased to 2.32-, 2.53-, 3.34-, 4.45-, and 7.88-fold of control group to correspond with the CoCl2 concentration of 100, 200, 400, 600, and 1000 μM (p < 0.01, p <0.001, Figures 2(a) and 2(b)). This demonstrated that the level of ROS was significantly elevated with a dose-dependent manner in cultured 16HBE14o- cells by pretreatment of CoCl2.
Figure 2.
Hydrogen sulfide decreased the level of ROS induced by hypoxia in 16HBE14o- cells. Generation of ROS was determined by laser scanning confocal microscope analysis after staining the cells with DCFH-DA. (a, b) 16HBE14o- cells were pretreated with CoCl2 in varying doses (0, 100, 200, 400, 600, or 1000 μmol/L). (c, d) 16HBE14o- cells were pretreated with CoCl2 (400 μmol/L) and NaHS (300 μmol/L) separately or together. Results are mean values ± SD of independent experiments performed in triplicate (NS, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control group, ###p < 0.001 versus hypoxia group, n=3).
Next, we treated 16HBE14o- cells individually or simultaneously with 300 μM of NaHS and 400 μM of CoCl2 and detected the content of ROS in epithelial cells. Figures 2(c) and 2(d) showed that H2S had no significant effect alone but could effectively decrease the generation of ROS by 47.9% (p <0.001) in hypoxia group; however, the DCF intensity was still higher than that in the control group. These data suggested that H2S inhibits hypoxia-induced ROS.
3.3. The Role of ROS on [Ca2+]i Induced by Hypoxia
In order to explore the effect of hypoxia on [Ca2+]i in 16HBE14o- cells, calcium ion fluorescence probe Fura-2/AM and fluorescent microscopy imaging system (CellR-MT20) were used to detect [Ca2+]i. 16HBE14o- cells were treated with 1 mM NAC (a specific ROS scavenger) and 400 μM CoCl2 individually or simultaneously. The F340/380 ratio was used to indicate the concentration of cytosolic calcium.
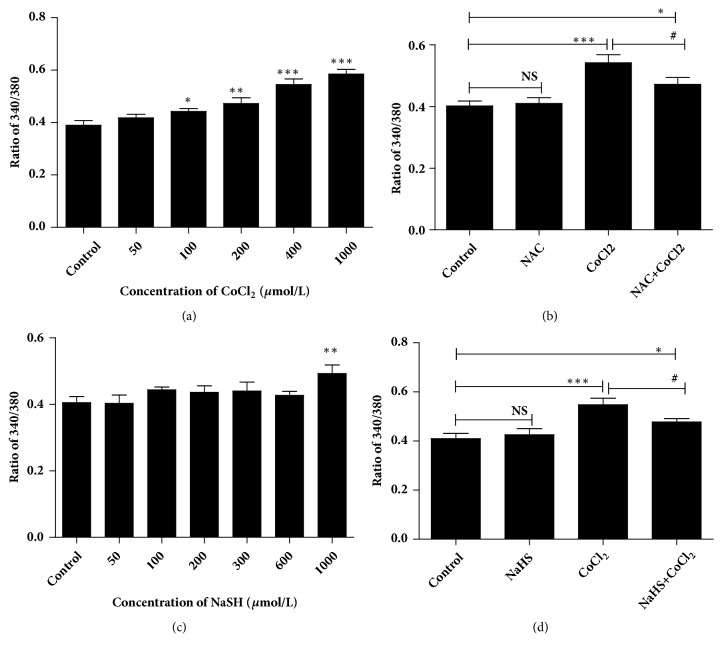
Hypoxia promoted F340/380 ratio value in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3(a)). The [Ca2+]i was decreased from 0.54 ± 0.058 (hypoxia group) to 0.47 ± 0.049 by treatment of NAC (Figure 3(b)). Compared with the control group, F340/380 ratio value in the NAC group has no significant difference. These data indicated that hypoxia increased the [Ca2+]i mediated by its intracellular ROS.
Figure 3.
Hydrogen sulfide inhibited ROS-induced intracellular [Ca2+]i in 16HBE14o- cells. Logarithmic growth cells were incubated with calcium ion fluorescence probe Fura-2/AM and the F340/380 ratio value was detected by laser scanning confocal microscope. (a) The effect of CoCl2 on intracellular [Ca2+]i in different doses (0, 50, 100, 200, 400, or 1000 μmol/L). (b) NAC (1 mM, scavenger of ROS) inhibited the increase in F340/380 ratio induced by hypoxia (CoCl2, 400 μmol/L). (c) Effects of hydrogen sulfide on [Ca2+]i in different doses (0, 50, 100, 200, 300, 600, or 1000 μmol/L). (d) Effects of hydrogen sulfide (NaHS, 300 μmol/L) on [Ca2+]i induced by hypoxia (CoCl2, 400 μmol/L). The results were from 3 independent experiments (NS, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01,∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control group, #p < 0.05 versus hypoxia group, n=3).
3.4. H2S Attenuates [Ca2+]i Induced by Hypoxia in 16HBE14o- Cells
To determine the effect of H2S on [Ca2+]i during hypoxia, we firstly treated the 16HBE14o- cells with NaHS in different concentrations. As shown in Figure 3(c), a trifling elevation in [Ca2+]i was detected in 16HBE14o- cells except for at the concentration of 1000 μM. Similar to NAC, H2S could effectively suppress CoCl2-induced increase in F340/380 ratio value (from 0.55± 0.059 to 0.48± 0.031), and the [Ca2+]i was still higher than that in the control group (Figure 3(d)). However, treatment with NaHS (300 μM) alone had no significant effect on [Ca2+]i. The above-mentioned results (Figure 3) demonstrate that H2S attenuates [Ca2+]i induced by hypoxia via reducing ROS.
3.5. H2S Promoted MMP of 16HBE14o- Cells Inhibited by Hypoxia
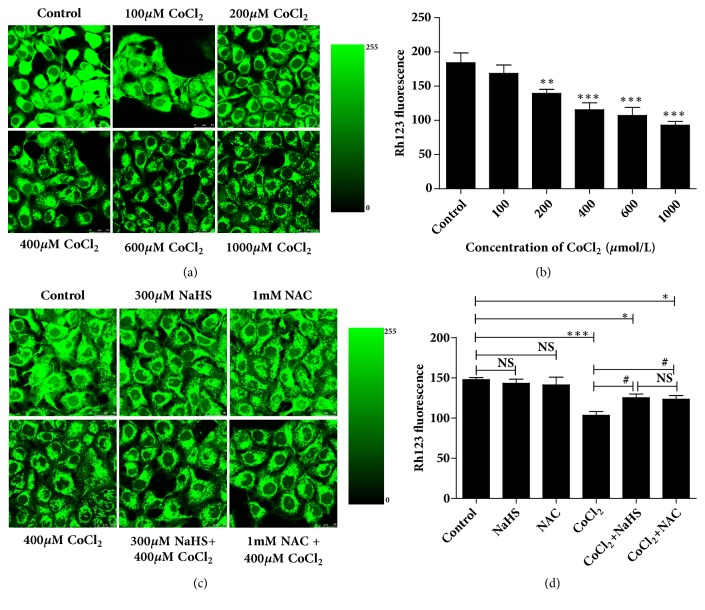
We used the fluorescent microscopy software and fluorescence dye Rh123 to investigate the MMP in 16HBE14o- cells during hypoxia. We found that cells with hypoxia decreased the fluorescence intensity of Rh123 in a concentration-dependent manner (Figures 4(a) and 4(b)). The fluorescence intensity decreased by 8.49%, 24.28%, 37.30%, 41.85%, and 49.48% versus control group corresponding with the CoCl2 concentration of 100, 200, 400, 600, and 1000 μM (Figures 4(a) and 4(b)).
Figure 4.
Effects of hydrogen sulfide on MMP induced by hypoxia in 16HBE14o- cells. MMP in 16HBE14o- cells was detected by incubating the cells with Rh123 and analyzed with the fluorescent microscopy software. (a, b) Cells were pretreated with CoCl2 in different concentration (0, 100, 200, 400, 600, or 1000 μmol/L). (c, d) 16HBE14o- cells were pretreated with NaHS (300 μmol/L), NAC (1mM), and CoCl2 (400 μmol/L) separately or together. Experiments were repeated for three times (NS, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control group, #p < 0.05 versus hypoxia group, n=3).
Data of Figures 4(c) and 4(d) mean that NaHS (300 μM) and NAC (1 mM) markedly inhibited the decrease of MMP in 16HBE14o- cells during hypoxia (CoCl2, 400 μM), while the MMP was still higher than that in the control. In addition, there were no effects with the pretreatment of NAC or NaHS alone. These results indicate that the MMP in 16HBE14o- cells decreases during hypoxia, which was arrogated by H2S through reducing the ROS content.
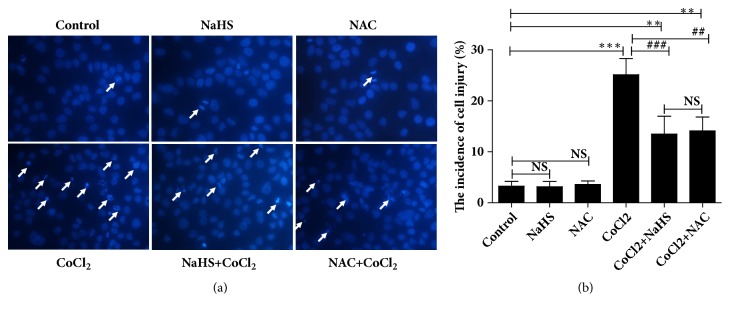
3.6. Effects of H2S on Cell Apoptosis Induced by Hypoxia
To confirm the role of H2S in hypoxia-induced apoptosis, 16HBE14o- cells were incubated with Hoechst 33342 and treated with NAC (1 mM) or NaHS (300 μM) with/without hypoxia (CoCl2, 400 μM). As shown in Figure 5, cells in control had normal phenotype and showed diffused staining of the chromatin. Hypoxia significantly elevated the ratio of damaged cells, but NAC and NaHS could effectively inhibit hypoxia-induced cell injury. After exposure to hypoxia, more cells presented typical morphological changes of cell injury such as chromatin condensation, cell shrinkage, chromatin margination, or apoptotic bodies. However, the cells of NAC or NaHS group had no more serious apoptosis than that in the control group. This suggested that H2S alleviate the hypoxia-induced apoptosis by reducing the level of ROS in the cultured 16HBE14o- cells.
Figure 5.
The effects of hydrogen sulfide on hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Exponential growth cells were stained with Hoechst 33342. The nuclei in control, NAC (1 mM), and NaHS (300 μM) groups have the normal phenotype demonstrating bright colors and homogeneity. The apoptotic nuclei emitted bright fluorescence and condensed. The number of apoptotic nuclei was significantly increased by CoCl2 (400 μM) treatment. NAC and NaHS significantly decreased the apoptosis of 16HBE14o- cells (NS, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control group, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus hypoxia group, n=3).
4. Discussion
In the present study, we explored the contribution of H2S in cell injury induced by hypoxia in 16HBE14o- cells. It was demonstrated that in 16HBE14o- cells pretreatment with NaHS during hypoxia (i) the level of ROS decreased, (ii) the [Ca2+]i was reduced and MMP was elevated, and (iii) the cell apoptosis was relieved. Our results suggested that the H2S plays a protective role in CoCl2-induced cell injury in 16HBE14o- cells by reducing the ROS content to regulate the level of [Ca2+]i and MMP.
Oxidative stress induced by hypoxia/ischemia resulted from the imbalance between ROS and the antioxidant defense system. Accumulating evidence has suggested that ROS induced by hypoxia/ischemia stroke is closely associated with the exacerbation of atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease [31], and the pathogenesis of airway disorders such as adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), cystic fibrosis, idiopathic fibrosis, COPD, and asthma [1, 32–34]. Airway cells and tissues were exposed to oxidative stress such as environmental pollutants, infections, inflammatory reactions, or decreased levels of antioxidants and the excessive ROS could cause a variety of deletion effects in the airway [12]. In order to mimic hypoxia, we treated the 16HBE14o- cells with CoCl2 for a short period of time which is a common chemical mimic of hypoxia in vitro [28, 35]. We found that CoCl2 had the significant dose-dependent inhibitory effect and H2S had the protective effect on cell viability in 16HBE14o- cells. Our data showed that hypoxia significantly elevated the level of ROS, leading to intracellular Ca2+ accumulation and MMP decrease in cultured 16HBE14o- cells, and aggravating apoptosis of 16HBE14o- cells.
Accumulating evidence showed that oxidative stress could lead to the MMP disruption and apoptosis [10, 11, 15, 16, 36] and these were attenuated by H2S. Robert F and Isabel CP reported that H2S could induce the airway smooth muscle relaxation and inhibited the Ca2+ release in smooth muscle cells [37, 38]. The endogenous production of H2S was decreased in the lung tissue of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (HPH) followed by oxidative stress [20]. Furthermore, injury and apoptosis of epithelial cells and their defective repair are closely related to the pathogenetic process and development of COPD and asthma [39, 40]. It has been demonstrated that H2S can react with ROS and work as a scavenger of oxygen-derived free radicals [23, 41, 42]. Our data show that H2S exerted inhibitory effects similar to the ROS scavenger NAC on hypoxia-induced ROS elevation and ROS-mediated cytosolic calcium influx and the disruption of MMP. Our studies also found that H2S remarkably attenuated apoptosis in cultured 16HBE14o- cells induced by hypoxia. These data indicate that cytosolic calcium influx and the disruption of MMP mediated by ROS are involved in hypoxia-induced bronchial epithelial cells apoptosis. H2S played the protective role in the process of oxidative stress which may be associated with NF-κB pathway, BDNF pathway, and ROS-activated ERK1/2 pathway [43–45]. However, 2–4 mM of NaHS in vitro caused shrinkage and death of the cells [46]. Therefore, the concentration of H2S is also crucial. Therefore, the corresponding signaling pathway and the concentration of H2S need further study.
In conclusion, our findings confirmed that H2S attenuated hypoxia-induced cell injury in 16HBE14o- cells. Moreover, H2S antagonized hypoxia-induced accumulation of [Ca2+]i and dissipation of MMP to relieve cell apoptosis by increasing the scavenging of ROS. These data reveal that the clearance of ROS is responsible for the protective effect of H2S against hypoxia-mediated cell injury.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSFC (National Natural Science Foundation of China) [31771277, 81670002, 31671188], the Hunan Natural Science Foundation [2017JJ2402], Open Foundation of Hunan College Innovation Program [16K097], the Fundamental Research Funds for the Postgraduate of Central South University [2013zzts070], and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Food and Drug Vocational College [2016YZ009].
Contributor Information
Xiao-Ai Liu, Email: liuxa@gdyzy.edu.cn.
Xiao-Qun Qin, Email: qinxiaoqun@csu.edu.cn.
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Park S. J., Lee Y. C. Antioxidants as novel agents for asthma. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 2006;6(2):235–240. doi: 10.2174/138955706775475948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hsu S. W., Chang T. C., Wu Y. K., Lin K. T., Shi L. S., Lee S. Y. Rhodiola crenulataextract counteracts the effect of hypobaric hypoxia in rat heartviaredirection of the nitric oxide and arginase 1 pathway. Bmc Complementary & Alternative Medicine. 2017;17:p. 29. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1524-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tian Y.-M., Guan Y., Li N., et al. Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through enhancing HIF1 signaling in rats. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2016;118:90–97. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2016.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lüneburg N., Siques P., Brito J., et al. Long-term chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia in rats causes an imbalance in the asymmetric dimethylarginine/nitric oxide pathway and ros activity: a possible synergistic mechanism for altitude pulmonary hypertension? Pulmonary Medicine. 2016;2016:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2016/6578578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Huang W.-C., Fang L.-W., Liou C.-J. Phloretin attenuates allergic airway inflammation and oxidative stress in asthmatic mice. Frontiers in Immunology. 2017;8:p. 134. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tsai T.-L., Chang S.-Y., Ho C.-Y., Yu R. K. Role of ATP in the ROS-mediated laryngeal airway hyperreactivity induced by laryngeal acid-pepsin insult in anesthetized rats. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2009;106(5):1584–1592. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91517.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taylor-Clark T. E., Undem B. J. Sensing pulmonary oxidative stress by lung vagal afferents. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology. 2011;178(3):406–413. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ruan T., Lin Y. J., Hsu T. H., et al. Sensitization by pulmonary reactive oxygen species of rat vagal lung C-fibers: The roles of the TRPV1, TRPA1, and P2X receptors. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(4):p. e91763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.de Boer W. I., Yao H., Rahman I. Future therapeutic treatment of COPD: struggle between oxidants and cytokines. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2007;2:205–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.He F., Wu Q., Xu B., et al. Suppression of Stim1 reduced intracellular calcium concentration and attenuated hypoxia/reoxygenation induced apoptosis in H9C2 cells. Bioscience Reports. 2017;37(6) doi: 10.1042/BSR20171249.BSR20171249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shu B., Yang W. W., Yang H. T. Expression pattern of E2F6 in physical and chemical hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008;60(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Teixeira J., Basit F., Swarts H. G., et al. Extracellular acidification induces ROS- and mPTP-mediated death in HEK293 cells. Redox Biology. 2018;15:394–404. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Calvert J. W., Coetzee W. A., Lefer D. J. Novel insights into hydrogen sulfide-mediated cytoprotection. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2010;12(10):1203–1217. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xia M., Chen L., Muh R. W., Li P. L., Li N. Production and actions of hydrogen sulfide, a novel gaseous bioactive substance, in the kidneys. Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics. 2009;329:1056–1062. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.149963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Luo Y., Yang X., Zhao S., et al. Hydrogen sulfide prevents OGD/R-induced apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dysfunction and suppressing an ROS-mediated caspase-3 pathway in cortical neurons. Neurochemistry International. 2013;63(8):826–831. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hu L.-F., Lu M., Wu Z.-Y., Wong P. T.-H., Bian J.-S. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits rotenone-induced apoptosis via preservation of mitochondrial function. Molecular Pharmacology. 2009;75(1):27–34. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.047985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Luo Y., Liu X., Zheng Q., et al. Hydrogen sulfide prevents hypoxia-induced apoptosis via inhibition of an H2O2-activated calcium signaling pathway in mouse hippocampal neurons. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2012;425(2):473–477. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhu Y. Z., Zhong J. W., Ho P., et al. Hydrogen sulfide and its possible roles in myocardial ischemia in experimental rats. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2007;102(1):261–268. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00096.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sun W.-H., Liu F., Chen Y., Zhu Y.-C. Hydrogen sulfide decreases the levels of ROS by inhibiting mitochondrial complex IV and increasing SOD activities in cardiomyocytes under ischemia/reperfusion. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2012;421(2):164–169. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.03.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wei H.-L., Zhang C.-Y., Jin H.-F., Tang C.-S., Du J.-B. Hydrogen sulfide regulates lung tissue-oxidized glutathione and total antioxidant capacity in hypoxic pulmonary hypertensive rats. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2008;29(6):670–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Madden J. A., Ahlf S. B., Dantuma M. W., Olson K. R., Roerig D. L. Precursors and inhibitors of hydrogen sulfide synthesis affect acute hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in the intact lung. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2012;112(3):411–418. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01049.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kimura H. Hydrogen sulfide: its production and functions. Experimental Physiology. 2011;96(9):833–835. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2011.057455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Geng B., Chang L., Pan C., et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulation of myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2004;318(3):756–763. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.04.094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chanez P. Severe asthma is an epithelial disease. European Respiratory Journal. 2005;25(6):945–946. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00038605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Takizawa H. Bronchial epithelial cells in allergic reactions. Current Drug Targets - Inflammation and Allergy. 2005;4(3):305–311. doi: 10.2174/1568010054022123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li L., Liu M., Kang L., et al. HHEX: A crosstalker between HCMV infection and proliferation of VSMCs. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 2016;6, article no. 169 doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang C., Yang Z., Zhang M., et al. Hydrogen sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation in hacat cells through inhibition of ROS/NF-κB/COX-2 pathway. PLoS ONE. 2011;6 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021971.e21971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yang Y., Hui L. I., Sun Z. P., et al. Effects of iPSC-MSCs on mitochondria of PC12 cells injured by CoCl_2. Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology. 2015 [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu X., Pan L., Zhuo Y., Gong Q., Rose P., Zhu Y. Z. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is involved in the pro-angiogenic effect of hydrogen sulfide under hypoxic stress. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 2010;33(9):1550–1554. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shen Y., Guo W., Wang Z., Zhang Y., Zhong L., Zhu Y. Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide in hypoxic human umbilical vein endothelial cells: a possible mitochondria-dependent pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013;14(7):13093–13108. doi: 10.3390/ijms140713093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Siti H. N., Kamisah Y., Kamsiah J. The role of oxidative stress, antioxidants and vascular inflammation in cardiovascular disease (a review) Vascular Pharmacology. 2015;71:40–56. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2015.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hyunyun K., Yun J., Sang-Mo K. Therapeutic strategies for oxidative stress-related cardiovascular diseases: Removal of excess reactive oxygen species in adult stem cells. Oxidative Medicine & Cellular Longevity. 2017;2016(2483163) doi: 10.1155/2016/2483163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.McNicholas W. T. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and obstructive sleep apnea: overlaps in pathophysiology, systemic inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2009;180(8):692–700. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200903-0347pp. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sugiura H., Ichinose M. Oxidative and nitrative stress in bronchial asthma. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2008;10(4):785–797. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brusevold I. J., Husvik C., Schreurs O., Schenck K., Bryne M., Søland T. M. Induction of invasion in an organotypic oral cancer model by CoCl2, a hypoxia mimetic. European Journal of Oral Sciences. 2010;118(2):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2010.00720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tian Y., Du Y.-Y., Shang H., et al. Calenduloside E analogues protecting H9c2 cardiomyocytes against H2O2-induced apoptosis: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2017;8:p. 862. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fitzgerald R., DeSantiago B., Lee D. Y., et al. H2S relaxes isolated human airway smooth muscle cells via the sarcolemmal KATP channel. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2014;446(1):393–398. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Castro-Piedras I., Perez-Zoghbi J. F. Hydrogen sulphide inhibits Ca2+ release through InsP3 receptors and relaxes airway smooth muscle. The Journal of Physiology. 2013;591(23):5999–6015. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.257790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bucchieri F., Marino Gammazza A., Pitruzzella A., et al. Cigarette smoke causes caspase-independent apoptosis of bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatic donors. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(e0120510) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kazuyoshi. Epithelial cell apoptosis and lung remodeling. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2007;4(6):419–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tyagi N., Moshal K. S., Sen U., et al. H2S protects against methionine-induced oxidative stress in brain endothelial cells. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2009;11(1):25–33. doi: 10.1089/ars.2008.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li L., Li M., Li Y., et al. Exogenous H2S contributes to recovery of ischemic post-conditioning-induced cardioprotection by decrease of ROS level via down-regulation of NF-κB and JAK2-STAT3 pathways in the aging cardiomyocytes. Cell & Bioscience. 2016;6:p. 26. doi: 10.1186/s13578-016-0090-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zheng J., Zhao T., Yuan Y., Hu N., Tang X. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) attenuates uranium-induced acute nephrotoxicity through oxidative stress and inflammatory response via Nrf2-NF-κB pathways. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 2015;242(1):353–362. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gao S., Li W., Zou W., et al. H2S protects PC12 cells against toxicity of corticosterone by modulation of BDNF-TrkB pathway. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica. 2015;47(11):915–924. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmv098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dong X. B., Yang C. T., Zheng D. D., et al. Inhibition of ROS-activated ERK1/2 pathway contributes to the protection of H 2 S against chemical hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2 cells. Molecular & Cellular Biochemistry. 2012;362:149–157. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fujii Y., Funakoshi T., Unuma K., Noritake K., Aki T., Uemura K. Hydrogen sulfide donor NaHS induces death of alveolar epithelial L2 cells that is associated with cellular shrinkage, transgelin expression and myosin phosphorylation. Journal of Toxicological Sciences. 2016;41(5):645–654. doi: 10.2131/jts.41.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.