Abstract
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences that protect against chromosomal shortening. They are replenished by telomerase, an enzyme that may be activated by estrogen. Women have longer telomeres than men; this difference might be due to estrogen exposure. We hypothesized that reproductive histories reflecting greater estrogen exposure will be associated with longer blood cell telomeres. Among women in the Sister Study (n= 1,048), we examined telomere length in relation to self-reported data on reproductive history. The difference between age at menarche and last menstrual period was used to approximate the reproductive period. Relative telomere length (rTL) was measured using qPCR. After adjustment, rTL decreased with longer reproductive period (β= -0.019, 95% CI: -0.04, -0.00, p= 0.03). Premenopausal women had shorter rTL than postmenopausal women (β= -0.051, 95% CI: -0.12, 0.01, p= 0.13). Longer breastfeeding duration was associated with longer rTL (β= 0.027, 95% CI: 0.01, 0.05, p=0.01); increasing parity was associated with shorter rTL (β = -0.016, 95% CI: -0.03, 0.00, p=0.07). Duration of exogenous hormone use was not associated with rTL. Reproductive histories reflecting greater endogenous estrogen exposure were associated with shorter rTL. Our findings suggest that longer telomeres in women are unlikely to be explained by greater estrogen exposure.
Keywords: telomeres, reproductive history, estrogen, qPCR
Introduction
Telomeres are noncoding, hexanucleotide repetitive sequences that are located at the end of chromosomes. They serve as a buffer against end-to-end fusions, DNA damage checkpoint activation, and chromosomal shortening [1]. With each cell division, telomere length decreases due to incomplete end replication. Telomere shortening may be further influenced by endogenous factors including oxidative stress [2,3] and lifestyle factors such as multivitamin use, work schedule and physical activity [4–6]. Telomere length may additionally be used as a marker of disease risk [7–11] and may serve as a biomarker of the aging process [12].
Telomerase is the enzyme responsible for replenishing telomere length. It is generally active in cell-types with high replication rates, including germ, stem and immune cells [13,14]. Telomerase may be activated by estrogen; gene sequence analysis of the promoter region of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) identified two estrogen response elements [15–17]. Estrogen-receptor alpha concentrations in hormone-sensitive tissues have been shown to mediate the relationship between estrogen and expression of TERT [18–20]. Moreover, estrogen deficiency in aromatase knockout female mice has been associated with decreased TERT expression resulting in shorter telomeres [21].
In human studies, women generally have longer telomeres than men [22,23]. Some studies suggest this sex difference may widen across the life course implying that women and men may have different rates of telomere erosion [24–27]. Life course estrogen exposure may explain these observations but there is little consensus across studies. Findings regarding long-term exogenous hormone use and blood cell telomere length are mixed [28–31]. Current endogenous estrogen production, estimated using menopausal status and circulating hormone concentrations, generally suggest inverse associations [32,33]. Notably, studies focused on endogenous estrogen generally have not accounted for potential exogenous sources.
Here, we examine the relationship between estrogen and telomere length using a life course approach that estimates exposure history to both endogenous and exogenous estrogen. Estrogen exposure in women can be approximated using characteristics of their reproductive histories. For example, reproductive period, calculated as the difference between age at menarche and last menstrual period, as well as other reproductive factors, may reflect endogenous estrogen production [34–36]. Birth control and hormone use duration can be used to estimate exogenous estrogen exposures. We hypothesize that among women, reproductive histories reflecting greater estrogen exposure over the life course will be associated with longer blood cell telomeres.
RESULTS
Age was inversely associated with relative telomere length (rTL) quartile (P-trend< 0.01) (Table 1). After adjustment for participant age, older paternal age at birth was associated with increasing telomere length quartiles (P-trend= 0.05). Longer age-adjusted breastfeeding duration was associated with increasing relative telomere length quartiles (P-trend= 0.03).
Table 1. Age-standardized characteristics of Sister Study participants by quartile of telomere length (n= 1,048).
| Relative telomere length quartile | ||||||
| 1 (shorter) | 2 | 3 | 4 (longer) | P | ||
| Age (yr.) | 58.1 ± 8.9 | 54.6 ± 8.8 | 54.0 ± 8.7 | 52.8 ± 9.2 | < 0.01 | |
| White (%) | 94.1 | 90.8 | 87.1 | 96.4 | 0.45 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.8 ± 6.5 | 26.8 ± 5.2 | 27.6 ± 5.9 | 27.2 ± 5.6 | 0.90 | |
| Maternal age (yr.) | 28.7 ± 5.9 | 28.5 ± 5.7 | 28.5 ± 6.1 | 29.3 ± 5.9 | 0.30 | |
| Paternal age (yr.) | 32.0 ± 6.8 | 31.4 ± 6.6 | 32.2 ± 7.0 | 32.8 ± 7.0 | 0.05 | |
| Physical activity (METs/wk.) | 48.2 ± 30.3 | 50.0 ± 30.9 | 54.4 ± 32.2 | 51.5 ± 29.5 | 0.15 | |
| Alcohol intake (drinks/wk.) | 3.1 ± 4.8 | 2.9 ± 4.3 | 3.0 ± 4.5 | 2.9 ± 4.4 | 0.90 | |
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Never (%) | 53.3 | 54.0 | 55.3 | 56.6 | 0.51 | |
| Former (%) | 38.1 | 38.1 | 38.2 | 35.6 | 0.61 | |
| Current (%) | 8.6 | 7.9 | 6.5 | 7.8 | 0.75 | |
| Pack years | 7.0 ± 12.7 | 6.3 ± 11.2 | 6.8 ± 12.5 | 7.2 ± 16.6 | 0.78 | |
| Reproductive period (yr.) | 34.2 ± 6.9 | 33.2 ± 7.8 | 33.2 ± 7.3 | 33.3 ± 7.2 | 0.15 | |
| Premenopausal (%) | 40.9 | 35.7 | 37.2 | 37.7 | 0.43 | |
| Hormone use (ever, %)1 | 68.4 | 68.5 | 67.7 | 67.4 | 0.78 | |
| Birth control pill (ever, %) | 78.6 | 88.0 | 86.7 | 81.8 | 0.17 | |
| Menarche age (yr.) | 12.5 ± 1.5 | 12.6 ± 1.4 | 12.6 ± 1.4 | 12.7 ± 1.4 | 0.26 | |
| Parity (total births) | 2.0 ± 1.5 | 2.0 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 1.3 | 1.9 ± 1.4 | 0.21 | |
| Breastfeeding duration (yr.) | 0.6 ± 1.1 | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 0.7 ± 1.1 | 0.9 ± 1.7 | 0.03 | |
| Breast cancer (%) | 37.4 | 38.7 | 34.5 | 38.5 | 0.97 | |
All values, except age, are age-standardized means ± standard deviations.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; METs, metabolic equivalent tasks.
1 Restricted to postmenopausal women (n= 654)
In individual linear regression models, after adjusting for age, race, and paternal age, we found an inverse association with reproductive period (for each 5-year increase in duration of reproductive period, βper 5-year= -0.015, 95% confidence interval (CI)= -0.03, 0.00, P= 0.05) and a positive association with breastfeeding duration (βper year= 0.017, 95% CI: -0.00, 0.03, P= 0.06) (Table 2). Premenopausal women generally had shorter telomeres than postmenopausal women (β= -0.052, 95% CI: -0.12, 0.01, P= 0.11). After restriction to postmenopausal women, we similarly observed an inverse, though not statistically significant, association with age at menopause, such that women who transitioned to postmenopausal status later had shorter telomeres (data not shown).
Table 2. Adjusted associations between reproductive histories and relative telomere length, separate models (n= 1,048).
| β (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Reproductive period (per 5 yrs.) | -0.015 (-0.03, 0.00) | 0.05 |
| Parity (per birth) | -0.007 (-0.02, 0.01) | 0.40 |
| Menopause status (pre- vs post) | -0.052 (-0.12, 0.01) | 0.11 |
| Breastfeeding (per yr.) | 0.017 (-0.00, 0.03) | 0.06 |
| BC pill use (per 10 yrs.) | 0.009 (-0.02, 0.04) | 0.62 |
| Hormone use (per 10 yrs.)1 | 0.003 (-0.03, 0.04) | 0.86 |
Models adjusted for age at blood draw (yrs.), race/ethnicity (White, Black, Hispanic, Other), and paternal age (yrs.)
Abbreviation: birth control, BC.
1Analysis restricted to postmenopausal women (n= 654)
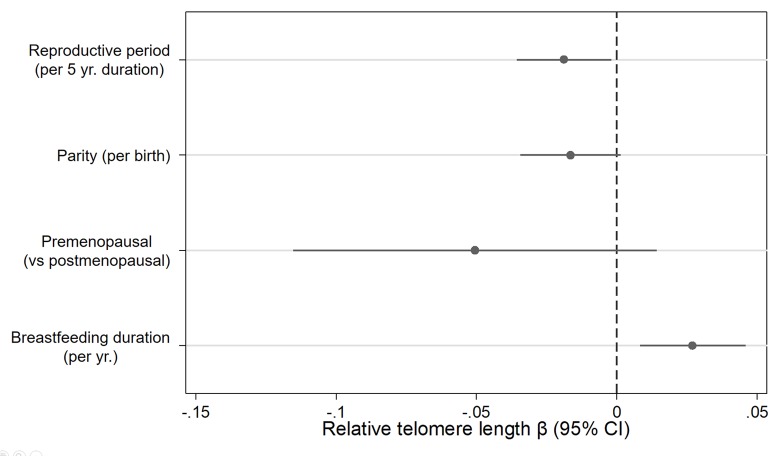
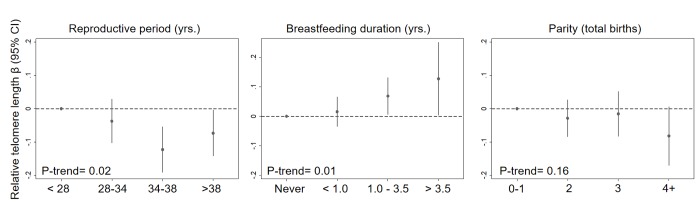
In a single model with mutual adjustment for reproductive factors, we found inverse associations between telomere length and reproductive period (βper 5 years = -0.019, 95% CI: -0.04, -0.00, P= 0.03), parity (βper birth= -0.016, 95% CI: -0.03, 0.00, P= 0.07) and premenopausal status (β= -0.051, 95% CI: -0.12, 0.01, P= 0.13) (Figure 1). We also observed a positive association between telomere length and breastfeeding duration (βper year = 0.027, 95% CI= 0.01, 0.05, P= 0.01). The association with parity was strongest for women with four or more births relative to women with 0 or 1 births (β = -0.08, 95% CI= -0.17, 0.01, P= 0.07) (Figure 2). Finally, women who breastfed the longest (> 3.5 years) had longer telomeres than women who never breastfed (β = 0.13, 95% CI= 0.00, 0.25, P= 0.04). When we excluded women who had developed breast cancer before September 2016, associations remained consistent (Supplementary Table 1). Restriction to White women also did not appreciably change our results (Supplementary Table 2).
Figure 1.
Relationship between relative telomere length and reproductive histories associated with endogenous estrogen exposure. Estimates derived from a model that included reproductive period (yrs.), parity (births), menopause status (pre- vs post), breast feeding duration (yrs.), age at blood draw (yrs.), race/ethnicity (White, Black, Hispanic, Other), paternal age (yrs.), and duration of hormone use (yrs.) and birth control pill use (yrs.).
Figure 2.
Relationship between relative telomere length and reproductive histories associated with endogenous estrogen exposure in a mutually adjusted model by categories. The model additionally adjusted for age at blood draw (yrs.), race/ethnicity (White, Black, Hispanic, Other), paternal age (yrs.), menopausal status (pre- vs post), and duration of hormone use (yrs.) and birth control pill use (yrs.).
Findings using a replication sample are reported in Supplementary Table 3. Associations of rTL with reproductive period and breastfeeding were not replicated. Although the direction of the association was similar for our findings for parity, point estimates for all associations were weaker compared to estimates from the discovery population.
DISCUSSION
Based on the observed sex differences in blood cell telomere length over the life course and known estrogen binding sites on telomerase, we hypothesized that reproductive histories representing greater life course estrogen exposure would be associated with longer blood cell telomeres. We found instead that longer reproductive periods (representing longer lifetime estrogen exposure) and premenopausal status (i.e. current estrogen exposure) were associated with shorter telomeres. Longer breastfeeding duration, a marker of reduced estrogen exposure [37], was associated with longer telomeres. We found exogenous hormone use did not influence blood cell telomeres. Our observed associations were contrary to our hypothesis and suggest life course estrogen exposure does not explain longer telomere length in women.
Our findings are, however, consistent with observations from other large cohort populations suggesting greater exposure to current endogenous estrogen may be associated with shorter telomere lengths. In the Nurse’s Health Study, De Vivo et al. (2009) found that higher circulating concentrations of estradiol and estrone were associated with shorter telomeres [32]. Dalgård et al. (2015) examined the rate of leukocyte telomere attrition among pre-, peri-, and postmenopausal women and found that, after accounting for age effects, the rate of attrition was fastest among premenopausal women (~20 base pairs/year vs ~15 base pairs/year) [33]. We also found additional support that exogenous hormone use may not be associated with blood cell telomere length [33,38]. To our knowledge, we are the first to report an association between telomere length and maternal breastfeeding history. Taken together, our findings suggest endogenous, but not exogenous, sources of estrogen may increase blood cell telomere erosion.
This inverse relationship may be explained by estrogenic stimulation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) [39,40]. HSCs give rise to blood cell subtypes including leukocytes and erythrocytes [41]. Interestingly, both erythrocyte turnover and HSC division may be regulated by estrogen [42]. Longer exposures to estrogen may therefore result in replacement of reduced erythrocyte populations by increasing HSC replication rates. As HSC telomeres shorten with each round of replication, subsequently differentiated blood cells may have shortened telomeres. This potential mechanism is supported by the finding that leukocyte and HSC telomere lengths are highly correlated [43]. This process has not been explicitly examined but supports the finding that longer estrogen exposure may result in replicative shortening of telomeres.
Although qPCR methods are optimized for measuring telomeres in large study populations, there are considerable limitations worth noting. Most importantly, assay reliability across study populations is generally limited due to technical variation [44]. qPCR also provides a relative estimate of telomere length which may be dependent on a reference population. Reference populations have not been standardized, making comparisons across studies difficult. qPCR additionally only provides an average telomere length measurement across all chromosomes resulting in non-specific measurements which may limit the ability to detect associations [45]. Finally, blood-based telomere length measurements are often derived from mixed cell populations which may introduce measurement error [46]. In our analysis, the replication population was oversampled for women who had high perceived stress, were current smokers, and non-White race. Additional model adjustment for these factors generally did not influence effect estimates or improve replication.
Sex differences in telomere length have been observed at birth suggesting telomere length may be established in utero [47,48]. It is therefore possible that reproductive history may only have modest effects on telomere length. Paternal age is a well-established, strong predictor of offspring telomere length at birth [48–51]. We adjusted for paternal age in our statistical models, thereby accounting for some inter-individual variation in telomere length. This allowed us to assess life course reproductive factor and telomere length associations more accurately. As reproductive factors are often related to each other, we used a single, mutually adjusted model to account for relationships between the reproductive factors which potentially results in more valid association estimates.
In summary, we observed inverse associations between blood cell telomere length and reproductive history characteristics representing both current and longer life course endogenous estrogen exposure. Although this finding suggests estrogen is not the driver of known sex differences in telomere length, it is consistent with prior reports and may suggest estrogenic stimulation of HSCs may outweigh upregulation of telomerase.
METHODS
Study population
The Sister Study is a prospective cohort study of 50,884 women designed to investigate environmental and lifestyle risk factors for breast cancer [52]. To be eligible for enrollment women had to be between 35 and 74 years old, have no history of breast cancer themselves, but have a sister who had been diagnosed with breast cancer. The breast cancer probands were not enrolled in the Sister Study. A case-cohort subsample of the study participants (n= 1,077) was previously selected to examine associations between whole blood cell telomere length and breast cancer risk and is described in detail elsewhere [53]. All women were cancer-free at the time of blood collection. Of the women who subsequently developed breast cancer, their blood samples were collected more than a year prior (mean= 460 days) to diagnosis and telomere length was not related to breast cancer risk [53]. Thus, the entire sample was included in this analysis. Participants gave written informed consent and the study protocol was approved by the NIEHS and Copernicus Group Institutional Review Boards.
Reproductive history assessment
Information on reproductive life events was collected at study enrollment via a computer assisted telephone interview, including age at onset of menarche and last menstrual period. Information was also collected on reproductive behaviors associated with endogenous estrogen production including breastfeeding duration and parity, and exogenous estrogen exposure including duration of birth control pill and hormone use.
Replication sample
We used an earlier, independent sample of Sister Study participants for replication of our findings. This study sample, drawn from early cohort participants (n= 647), was selected to examine associations between measures of stress and telomere length and was oversampled for women with high or very high perceived stress, current smokers, and non-Whites [54]. Forty-one women were tested in both the study population and the replication sample. To keep the replication sample independent from the main study sample, these women were excluded from the replication sample. Women missing exposure and covariate information were also excluded resulting in a final replication sample size of 597 participants.
Telomere length measurements
Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood samples collected at enrollment. rTL was measured using established qPCR methods as previously described [53]. Briefly, telomere length was measured as the relative ratio (T/S ratio) of telomere repeat copy number (T) to single gene copy number (S) using a monochrome, multiplex qPCR protocol. This method amplifies telomere and single genes in a single reaction tube; T/S ratios derived from this method correlate with terminal restriction fragment lengths measured by Southern blot [55]. A five-point standard curve was included in quadruplicate on each assay plate. Standard curve efficiencies for both T and S primers were above 90% and regression coefficients were at least 0.99 in all PCR runs. The average coefficient of variation was 11% and intra-class correlation coefficient of a single T/S ratio was 0.85. In the replication sample, the T/S ratio was assessed using an earlier qPCR protocol which employed separate reaction tubes to amplify telomere and single genes [56].
Statistical analysis
Among a sample of women who were cancer free at blood draw, we conducted a cross-sectional study of estimated history of estrogen exposure and telomere length. We explored normality of estimated relative telomere length across the sample population using histograms and kernel density plots. Reproductive period was calculated as the difference between age at menarche and last menstrual period. We used linear and binary regression models to examine age-adjusted distributions of participant characteristics by relative telomere length quartiles. Trend across telomere quartiles was tested by treating telomere length quartile as an ordinal variable.
To examine associations between reproductive history characteristics and rTL we estimated beta values and 95% CIs using linear regression models adjusted for covariates. Telomere length was treated as a continuous variable. Reproductive period, parity, breastfeeding duration, and duration of birth control and hormone use were modelled continuously; menopausal status was treated as dichotomous. Although all the women in the study were cancer-free at time of enrollment, we also conducted a sensitivity analysis restricting the analysis to those who did not develop breast cancer through September 2016 (n= 664), the end of follow-up for the case-cohort analysis.
In all models, potential adjustment covariates included age at blood draw (yrs.), body mass index (kg/m2), race/ethnicity (White, Black, Hispanic, Other), smoking status (current, former, never), alcohol intake (drinks/wk.), maternal and paternal age at birth (yrs.), physical activity (metabolic equivalent tasks (METs)/wk.), and case-cohort subgroup (case/random cohort). Covariates were included in the model if they were significant predictors of blood cell telomere length. We included age at blood draw and race/ethnicity as a priori covariates. Paternal age at birth was selected as it was associated with telomere length in the study sample and is known predictor of relative telomere length [51]. In analyses exploring relationships with duration of hormone use, we restricted to postmenopausal women (n= 654). We examined associations between reproductive factors (reproductive period, parity, menopause status, breastfeeding duration, and birth control and hormone use) and telomere length both in individual models and in a single, mutually adjusted model. To reproduce findings from the discovery sample, we repeated all analyses in the replication subsample of participants. As the replication population was oversampled for women with high or very high perceived stress, current smokers, and non-Whites, we conducted additional analyses adjusting for the oversampled characteristics. We conducted all analyses among women with complete covariate information (n= 1,048) using Stata version 14.2 (College Station, TX).
Data availability
Data access is restricted but can be made available upon reasonable request.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the participants of the Sister Study. We would also like to thank Drs. Kaitlyn Gam and Emily Werder for providing the internal review.
Abbreviations:
- BMI
Body mass index
- METs
Metabolic equivalent tasks
- HSC
Hematopoietic stem cells
- qPCR
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- rTL
Relative telomere length
- TERT
Telomerase reverse transcriptase
Footnotes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS: JKK and JAT developed the research question and study design. DPS and JAT collected the data. JKK conducted the data analysis and interpreted the results. JKK drafted the manuscript. JAT, CGP, and DPS offered critical revisions.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chong L, van Steensel B, Broccoli D, Erdjument-Bromage H, Hanish J, Tempst P, de Lange T. A human telomeric protein. Science. 1995; 270:1663–67. 10.1126/science.270.5242.1663 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fouquerel E, Lormand J, Bose A, Lee HT, Kim GS, Li J, Sobol RW, Freudenthal BD, Myong S, Opresko PL. Oxidative guanine base damage regulates human telomerase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016; 23:1092–100. 10.1038/nsmb.3319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kawanishi S, Oikawa S. Mechanism of telomere shortening by oxidative stress. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004; 1019:278–84. 10.1196/annals.1297.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Xu Q, Parks CG, DeRoo LA, Cawthon RM, Sandler DP, Chen H. Multivitamin use and telomere length in women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009; 89:1857–63. 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Parks CG, DeRoo LA, Miller DB, McCanlies EC, Cawthon RM, Sandler DP. Employment and work schedule are related to telomere length in women. Occup Environ Med. 2011; 68:582–89. 10.1136/oem.2010.063214 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tucker LA. Physical activity and telomere length in U.S. men and women: an NHANES investigation. Prev Med. 2017; 100:145–51. 10.1016/j.ypmed.2017.04.027 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sun Y, Zhang L, Zhao L, Wu X, Gu J. Association of leukocyte telomere length in peripheral blood leukocytes with endometrial cancer risk in Caucasian Americans. Carcinogenesis. 2015; 36:1327–32. 10.1093/carcin/bgv133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Julin B, Shui I, Heaphy CM, Joshu CE, Meeker AK, Giovannucci E, De Vivo I, Platz EA. Circulating leukocyte telomere length and risk of overall and aggressive prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015; 112:769–76. 10.1038/bjc.2014.640 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Haycock PC, Heydon EE, Kaptoge S, Butterworth AS, Thompson A, Willeit P. Leucocyte telomere length and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014; 349:g4227. 10.1136/bmj.g4227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hou L, Joyce BT, Gao T, Liu L, Zheng Y, Penedo FJ, Liu S, Zhang W, Bergan R, Dai Q, Vokonas P, Hoxha M, Schwartz J, Baccarelli A. Blood Telomere Length Attrition and Cancer Development in the Normative Aging Study Cohort. EBioMedicine. 2015; 2:591–96. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.04.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhao J, Zhu Y, Lin J, Matsuguchi T, Blackburn E, Zhang Y, Cole SA, Best LG, Lee ET, Howard BV. Short leukocyte telomere length predicts risk of diabetes in american indians: the strong heart family study. Diabetes. 2014; 63:354–62. 10.2337/db13-0744 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Blackburn EH, Epel ES, Lin J. Human telomere biology: A contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science. 2015; 350:1193–98. 10.1126/science.aab3389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL, Shay JW. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994; 266:2011–15. 10.1126/science.7605428 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Counter CM, Gupta J, Harley CB, Leber B, Bacchetti S. Telomerase activity in normal leukocytes and in hematologic malignancies. Blood. 1995; 85:2315–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bourdeau V, Deschênes J, Métivier R, Nagai Y, Nguyen D, Bretschneider N, Gannon F, White JH, Mader S. Genome-wide identification of high-affinity estrogen response elements in human and mouse. Mol Endocrinol. 2004; 18:1411–27. 10.1210/me.2003-0441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cong YS, Wen J, Bacchetti S. The human telomerase catalytic subunit hTERT: organization of the gene and characterization of the promoter. Hum Mol Genet. 1999; 8:137–42. 10.1093/hmg/8.1.137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kyo S, Takakura M, Kanaya T, Zhuo W, Fujimoto K, Nishio Y, Orimo A, Inoue M. Estrogen activates telomerase. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:5917–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Misiti S, Nanni S, Fontemaggi G, Cong YS, Wen J, Hirte HW, Piaggio G, Sacchi A, Pontecorvi A, Bacchetti S, Farsetti A. Induction of hTERT expression and telomerase activity by estrogens in human ovary epithelium cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 20:3764–71. 10.1128/MCB.20.11.3764-3771.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cha Y, Kwon SJ, Seol W, Park KS. Estrogen receptor-alpha mediates the effects of estradiol on telomerase activity in human mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cells. 2008; 26:454–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Grasselli A, Nanni S, Colussi C, Aiello A, Benvenuti V, Ragone G, Moretti F, Sacchi A, Bacchetti S, Gaetano C, Capogrossi MC, Pontecorvi A, Farsetti A. Estrogen receptor-alpha and endothelial nitric oxide synthase nuclear complex regulates transcription of human telomerase. Circ Res. 2008; 103:34–42. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.169037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bayne S, Jones ME, Li H, Pinto AR, Simpson ER, Liu JP. Estrogen deficiency leads to telomerase inhibition, telomere shortening and reduced cell proliferation in the adrenal gland of mice. Cell Res. 2008; 18:1141–50. 10.1038/cr.2008.291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gardner M, Bann D, Wiley L, Cooper R, Hardy R, Nitsch D, Martin-Ruiz C, Shiels P, Sayer AA, Barbieri M, Bekaert S, Bischoff C, Brooks-Wilson A, et al. , and Halcyon study team. Gender and telomere length: systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp Gerontol. 2014; 51:15–27. 10.1016/j.exger.2013.12.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Benetos A, Okuda K, Lajemi M, Kimura M, Thomas F, Skurnick J, Labat C, Bean K, Aviv A. Telomere length as an indicator of biological aging: the gender effect and relation with pulse pressure and pulse wave velocity. Hypertension. 2001; 37:381–85. 10.1161/01.HYP.37.2.381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Möller P, Mayer S, Mattfeldt T, Müller K, Wiegand P, Brüderlein S. Sex-related differences in length and erosion dynamics of human telomeres favor females. Aging (Albany NY). 2009; 1:733–39. 10.18632/aging.100068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Barrett EL, Richardson DS. Sex differences in telomeres and lifespan. Aging Cell. 2011; 10:913–21. 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00741.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Iwama H, Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH, Hayashi S, Yahata N, Ando K, Toyama K, Hoshika A, Takasaki M, Mori M, Shay JW. Telomeric length and telomerase activity vary with age in peripheral blood cells obtained from normal individuals. Hum Genet. 1998; 102:397–402. 10.1007/s004390050711 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mayer S, Brüderlein S, Perner S, Waibel I, Holdenried A, Ciloglu N, Hasel C, Mattfeldt T, Nielsen KV, Möller P. Sex-specific telomere length profiles and age-dependent erosion dynamics of individual chromosome arms in humans. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2006; 112:194–201. 10.1159/000089870 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee DC, Im JA, Kim JH, Lee HR, Shim JY. Effect of long-term hormone therapy on telomere length in postmenopausal women. Yonsei Med J. 2005; 46:471–79. 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.4.471 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shen J, Terry MB, Liao Y, Gurvich I, Wang Q, Senie RT, Santella RM. Genetic variation in telomere maintenance genes, telomere length and breast cancer risk. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e44308. 10.1371/journal.pone.0044308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cassidy A, De Vivo I, Liu Y, Han J, Prescott J, Hunter DJ, Rimm EB. Associations between diet, lifestyle factors, and telomere length in women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010; 91:1273–80. 10.3945/ajcn.2009.28947 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jacobs EG, Kroenke C, Lin J, Epel ES, Kenna HA, Blackburn EH, Rasgon NL. Accelerated cell aging in female APOE-ε4 carriers: implications for hormone therapy use. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e54713. 10.1371/journal.pone.0054713 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.De Vivo I, Prescott J, Wong JY, Kraft P, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ. A prospective study of relative telomere length and postmenopausal breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009; 18:1152–56. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dalgård C, Benetos A, Verhulst S, Labat C, Kark JD, Christensen K, Kimura M, Kyvik KO, Aviv A. Leukocyte telomere length dynamics in women and men: menopause vs age effects. Int J Epidemiol. 2015; 44:1688–95. 10.1093/ije/dyv165 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Madigan MP, Troisi R, Potischman N, Dorgan JF, Brinton LA, Hoover RN. Serum hormone levels in relation to reproductive and lifestyle factors in postmenopausal women (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 1998; 9:199–207. 10.1023/A:1008838412423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gruber CJ, Tschugguel W, Schneeberger C, Huber JC. Production and actions of estrogens. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:340–52. 10.1056/NEJMra000471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chubak J, Tworoger SS, Yasui Y, Ulrich CM, Stanczyk FZ, McTiernan A. Associations between reproductive and menstrual factors and postmenopausal sex hormone concentrations. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004; 13:1296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Newcomb PA, Trentham-Dietz A. Breast feeding practices in relation to endometrial cancer risk, USA. Cancer Causes Control. 2000; 11:663–67. 10.1023/A:1008978624266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li Y, Deng B, Ouyang N, Yuan P, Zheng L, Wang W. Telomere length is short in PCOS and oral contraceptive does not affect the telomerase activity in granulosa cells of patients with PCOS. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017; 34:849–59. 10.1007/s10815-017-0929-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sidorov I, Kimura M, Yashin A, Aviv A. Leukocyte telomere dynamics and human hematopoietic stem cell kinetics during somatic growth. Exp Hematol. 2009; 37:514–24. 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Werner B, Beier F, Hummel S, Balabanov S, Lassay L, Orlikowsky T, Dingli D, Brümmendorf TH, Traulsen A. Reconstructing the in vivo dynamics of hematopoietic stem cells from telomere length distributions. eLife. 2015; 4:4. 10.7554/eLife.08687 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Seita J, Weissman IL. Hematopoietic stem cell: self-renewal versus differentiation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010; 2:640–53. 10.1002/wsbm.86 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nakada D, Oguro H, Levi BP, Ryan N, Kitano A, Saitoh Y, Takeichi M, Wendt GR, Morrison SJ. Oestrogen increases haematopoietic stem-cell self-renewal in females and during pregnancy. Nature. 2014; 505:555–58. 10.1038/nature12932 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kimura M, Gazitt Y, Cao X, Zhao X, Lansdorp PM, Aviv A. Synchrony of telomere length among hematopoietic cells. Exp Hematol. 2010; 38:854–59. 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.06.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Martin-Ruiz CM, Baird D, Roger L, Boukamp P, Krunic D, Cawthon R, Dokter MM, van der Harst P, Bekaert S, de Meyer T, Roos G, Svenson U, Codd V, et al. Reproducibility of telomere length assessment: an international collaborative study. Int J Epidemiol. 2015; 44:1673–83. 10.1093/ije/dyu191 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Montpetit AJ, Alhareeri AA, Montpetit M, Starkweather AR, Elmore LW, Filler K, Mohanraj L, Burton CW, Menzies VS, Lyon DE, Jackson-Cook CK. Telomere length: a review of methods for measurement. Nurs Res. 2014; 63:289–99. 10.1097/NNR.0000000000000037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim S, Sandler DP, Carswell G, Weinberg CR, Taylor JA. Reliability and short-term intra-individual variability of telomere length measurement using monochrome multiplexing quantitative PCR. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e25774. 10.1371/journal.pone.0025774 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Benetos A, Dalgård C, Labat C, Kark JD, Verhulst S, Christensen K, Kimura M, Horvath K, Kyvik KO, Aviv A. Sex difference in leukocyte telomere length is ablated in opposite-sex co-twins. Int J Epidemiol. 2014; 43:1799–805. 10.1093/ije/dyu146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Factor-Litvak P, Susser E, Kezios K, McKeague I, Kark JD, Hoffman M, Kimura M, Wapner R, Aviv A. Leukocyte Telomere Length in Newborns: Implications for the Role of Telomeres in Human Disease. Pediatrics. 2016; 137:e20153927. 10.1542/peds.2015-3927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Aviv A, Susser E. Leukocyte telomere length and the father’s age enigma: implications for population health and for life course. Int J Epidemiol. 2013; 42:457–62. 10.1093/ije/dys236 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hjelmborg JB, Dalgård C, Mangino M, Spector TD, Halekoh U, Möller S, Kimura M, Horvath K, Kark JD, Christensen K, Kyvik KO, Aviv A. Paternal age and telomere length in twins: the germ stem cell selection paradigm. Aging Cell. 2015; 14:701–03. 10.1111/acel.12334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kimura M, Cherkas LF, Kato BS, Demissie S, Hjelmborg JB, Brimacombe M, Cupples A, Hunkin JL, Gardner JP, Lu X, Cao X, Sastrasinh M, Province MA, et al. Offspring’s leukocyte telomere length, paternal age, and telomere elongation in sperm. PLoS Genet. 2008; 4:e37. 10.1371/journal.pgen.0040037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sandler DP, Hodgson ME, Deming-Halverson SL, Juras PS, D’Aloisio AA, Suarez LM, Kleeberger CA, Shore DL, DeRoo LA, Taylor JA, Weinberg CR, and Sister Study Research Team. The Sister Study Cohort: Baseline Methods and Participant Characteristics. Environ Health Perspect. 2017; 125:127003. 10.1289/EHP1923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kim S, Sandler DP, Carswell G, De Roo LA, Parks CG, Cawthon R, Weinberg CR, Taylor JA. Telomere length in peripheral blood and breast cancer risk in a prospective case-cohort analysis: results from the Sister Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2011; 22:1061–66. 10.1007/s10552-011-9778-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Parks CG, Miller DB, McCanlies EC, Cawthon RM, Andrew ME, DeRoo LA, Sandler DP. Telomere length, current perceived stress, and urinary stress hormones in women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009; 18:551–60. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cawthon RM. Telomere length measurement by a novel monochrome multiplex quantitative PCR method. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009; 37:e21. 10.1093/nar/gkn1027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Cawthon RM. Telomere measurement by quantitative PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002; 30:e47. 10.1093/nar/30.10.e47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data access is restricted but can be made available upon reasonable request.