Abstract
Background
The ability to accurately diagnose and objectively localize pain generators in chronic pain sufferers remains a major clinical challenge since assessment relies on subjective patient complaints and relatively non-specific diagnostic tools. Developments in clinical molecular imaging, including advances in imaging technology and radiotracer design, have afforded the opportunity to identify tissues involved in pain generation based on their pro-nociceptive condition. The sigma-1 receptor (S1R) is a pro-nociceptive receptor upregulated in painful, inflamed tissues, and it can be imaged using the highly specific radioligand 18F-FTC-146 with PET.
Case presentation
A 50-year-old woman with a 7-year history of refractory, left-knee pain of unknown origin was referred to our pain management team. Over the past several years, she had undergone multiple treatments, including a lateral retinacular release, radiofrequency ablation of a peripheral nerve, and physical therapy. While certain treatments provided partial relief, her pain would inevitably return to its original state. Using simultaneous positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MRI) with the novel radiotracer 18F-FTC-146, imaging showed increased focal uptake of 18F-FTC-146 in the intercondylar notch, corresponding to an irregular but equivocal lesion identified in the simultaneously acquired MRI. These imaging results prompted surgical removal of the lesion, which upon resection was identified as an inflamed, intraarticular synovial lipoma. Removal of the lesion relieved the patient’s pain, and to date the pain has not recurred.
Conclusion
We present a case of chronic, debilitating knee pain that resolved with surgery following identification of the pathology with a novel clinical molecular imaging approach that detects chronic pain generators at the molecular and cellular level. This approach has the potential to identify and localize pain-associated pathology in a variety of chronic pain syndromes.
Keywords: PET/MRI, sigma-1 receptor, chronic pain, knee pain, molecular imaging, intraarticular synovial lipoma, 18F-FTC-146
Background
Accurate and objective identification of peripheral pain generators remains a significant clinical challenge in the management of individuals suffering from pain. The sigma-1 receptor (S1R), an inter-organelle signal modulator located predominantly in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, is widely distributed in the central nervous system and in peripheral organs and is associated with various neurological diseases, including neuropathic pain.1,2 Increased expression of S1Rs is thought to modulate chronic pain by contributing to hypersensitivity and sensitization of the central nervous system.1 The PET radioligand, 18F-FTC-146 (6-(3-[18F]fluoropropyl)–3-(2-(azepan-1-yl)ethyl) benzo[d]thiazol-2(3 hours)-one), is a highly specific S1R antagonist that has been shown in preclinical experiments to bind specifically to the S1R and can therefore serve as a tool for visualizing these receptors in vivo.3,4 Use of this tracer in conjunction with PET/MRI has identified sites of nerve injury in a rat neuropathic pain model, since increased S1R is present at the site of nerve injury.2 In addition, local administration of the non-radioactive form of 18F-FTC-146 blocks S1Rs in neuromas of rats, resulting in pain relief.2 For this reason and from similar results shown by others, S1R antagonists represent a promising therapy for chronic pain.
The biodistribution of clinical-grade 18F-FTC-146 is being evaluated in both healthy volunteers and patients with chronic pain (chronic sciatica and complex regional pain syndrome) as part of our first-in-human clinical trial of this novel radioligand (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02753101).5 In healthy, asymptomatic volunteers, normal physiologic uptake of this radiotracer is observed in S1R-rich brain regions and specific peripheral organs, such as the pancreas and the spleen. In this report, we describe one of the patients from this clinical trial: a woman whose pain of 7 years resolved following the surgical removal of an intraarticular lipoma that showed high uptake of the S1R-specific radiotracer 18F-FTC-146 on simultaneous PET/MRI.
Case presentation
A 50-year-old woman presented to our nerve clinic with left-knee pain, which had begun 7 years previously with no apparent inciting event. She described the pain as sharp, at times stabbing, and radiating down the lateral aspect of her leg to her foot. She was unable to flex the knee beyond 60° without increased pain. She also described extreme difficulty in ambulating, standing up from a seated position, walking on grass, and going down stairs.
Shortly after the initial onset of the pain, the patient had undergone common peroneal nerve decompression. This had provided initial relief of her symptoms, but the pain returned. Injections with lidocaine and cortisone provided only slight relief, and injection with triamcinolone into the knee caused an increase in pain. She referred herself to a spine center for the pain in December 2009 (she had visited this clinic previously for a lumbar and cervical spinal fusion) as the pain had been worsening over the course of the year. A lumbar-spine MRI and straight-leg raise test were negative. The spine surgeon did not feel the pain was spine-related and referred the patient to orthopedic surgery.
The orthopedist reached a diagnosis of patellofemoral syndrome, and recommended a patellar brace, foot orthotics, physical therapy, and an exercise program. This did not prove effective, and the patient sought a second orthopedics opinion. Knee arthroscopic surgery with lateral patellar release (anterior interval release, major synovectomy, denervation of the inferior pole of the patella and modified lateral release) was performed. This provided temporary relief; at follow-up 4 weeks after surgery she had minimal discomfort and her range of motion had improved (3–125°). The pain, however, returned to its original state, while MRI of the left knee remained negative. Non-contrast enhanced MRI was performed because there was no indication of tumor. Medications, including pregabalin, tramadol, gabapentin, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, were largely ineffective.
She was referred to the Pain Management Center at Stanford University Medical Center and ultimately assessed by a multidisciplinary team, consisting of peripheral nerve surgeons, anesthesiologist-pain physicians, and radiologists. They suspected scarring around the nerve resulting from her left common peroneal neurolysis, and complex regional pain syndrome was suggested as a possible diagnosis. The patient’s pain decreased following ultrasound-guided left popliteal scar neuroma radiofrequency ablation at 60°C and a popliteal block but returned to its pre-procedure state after 3 months.
The patient enrolled in our clinical imaging trial, which uses simultaneous 18F-FTC-146 PET/MRI in patients with chronic pain and controls. The study protocol was approved by the Stanford University Institutional Review Board, and all participants provided written informed consent that included permission to publish details and images. The scan revealed focal increased uptake of the radiotracer in the inter-condylar region of the left knee (Figure 1A, B). MRI showed an irregular, mass-like but equivocal lesion of intermediate signal intensity in the same area on fat-suppressed proton density and T2-weighted images, appearing to represent a complex ganglion cyst or localized pigmented villonodular synovitis. Interestingly, there was no increased 18F-FTC-146 uptake at the scarring around the common peroneal nerve, where radiofrequency ablation had been performed. While this lesion had been present in MRIs obtained in previous years (Figure 1C, D), it had not been noticed or commented upon.
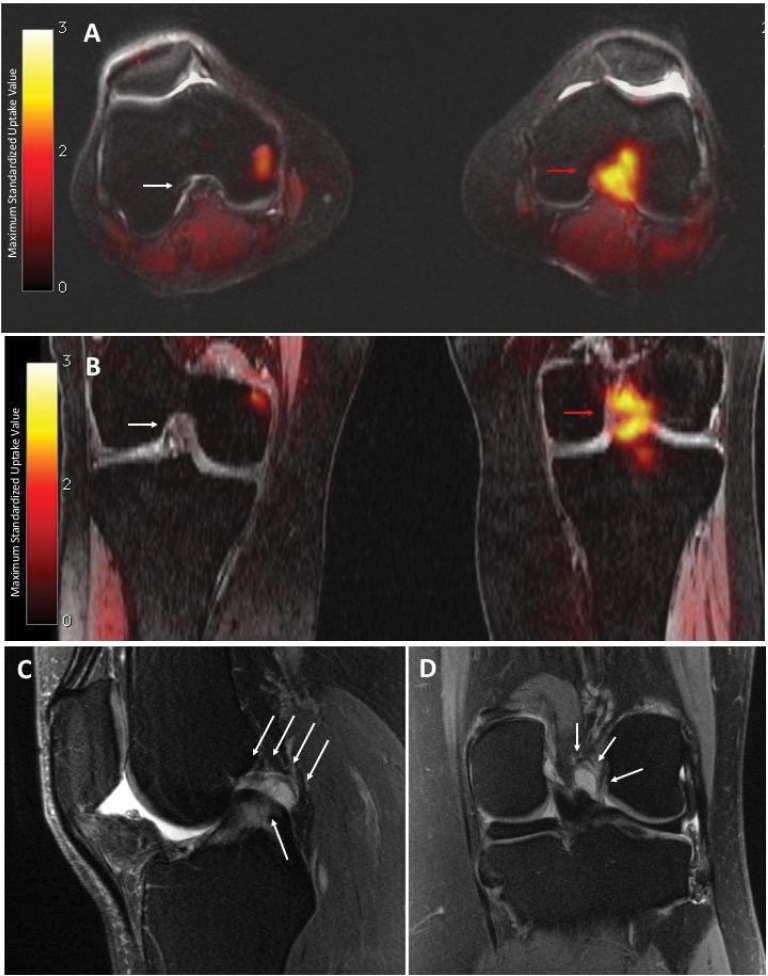
Figure 1.
PET/MRI and MRI of the left knee
Notes: Axial (A) and coronal (B) PET/MRI show high uptake of 18F-FTC-146 in the intercondylar notch (red arrows: maximum standardized uptake value = 2.04). By comparison, the intercondylar notch of the right knee is normal (white arrow: maximum standardized uptake value = 0.17). MRI shows small joint effusion, with no synovitis, and an amorphous, mass-like in the intercondylar notch, initially presumed to be a ganglion cyst or localized pigmented villonodular synovitis/fibrous lesion. Sagittal (C) and coronal (D) MRI (T2-weighted with fat saturation) of the left knee, acquired approximately 3 years before PET/MRI study, show abnormal high-signal amorphous, mass-like but equivocal lesion in the intercondylar notch (white arrows). This had been overlooked or regarded as clinically insignificant.
The patient underwent arthroscopic removal of the intraarticular mass. During surgery, an area of inflammation was seen just posterior to the posterior cruciate ligament, matching the MRI. Biopsy showed mature adipose tissue with synovial lining, revealing the mass to be an intraarticular synovial lipoma (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
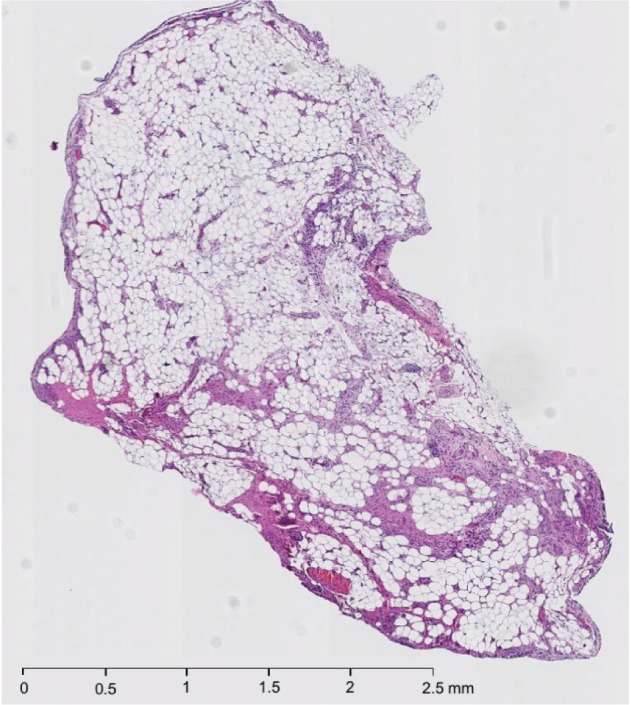
Hematoxylin and eosinstain section of the left-knee mass
Notes: The mass (pale tan tissue measuring 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.1 cm) was biopsied anteriorly from between the anterior cruciate ligament and the posterior cruciate ligament. This was one of three masses removed during knee arthroscopy, synovial biopsy, and synovectomy. The section shows mature adipose cells with overlying synovial lining. The infiltration and presence of inflammatory cells in this specimen is consistent with an inflamed synovial lipoma.
In the weeks following surgery, her pain was well controlled and she was no longer taking narcotic pain medications. She went to physical therapy to improve strength and range of motion. At 1-year follow up, she had discontinued all medications and was completely free of pain. Upon physical examination, the site of surgery had healed well and she achieved full extension and flexion to 130°. MRI was performed and showed no evidence of a residual or recurrent mass.
Conclusion
We present a case of a woman whose chronic knee pain was resolved by removal of an intraarticular synovial lipoma, which had shown increased uptake of the novel, S1R-specific radioligand 18F-FTC-146 on simultaneous PET/MRI. The patient had previously undergone a variety of unsuccessful orthopedic surgeries and denervating interventions. Intraarticular synovial lipoma is rare in the knee; most cases involve the fat pad areas, rather than the intercondylar notch. Symptoms of intraarticular synovial lipoma are vague and depend on the size of the mass. If present, pain is thought to be caused by impingement or entrapment of the mass.6 The pain in this case was most likely secondary to the lipoma being a vascularized, space-occupying lesion caught between cruciate ligaments. Symptoms mimicking peroneal neuropathy, as in the present case, have not been reported in the literature. The lack of radiotracer uptake in the scar suggested that the common peroneal nerve, which had been suspected as the cause of pain, was most likely not the pain generator.
The high uptake of the tracer may be rationalized by the known presence of the free nerve endings in the synovium, and the presence of S1R on nerves and inflammatory cells.7 As S1Rs are associated with inflammatory processes that facilitate modulation of calcium ion channels,8,9 we hypothesize there may have been mechanical irritation of this mass with subsequent inflammation and increased expression of S1Rs in the synovial lipoma of the patient’s knee. This likely became a debilitating inflammatory pain generator that was ultimately detected by PET via increased uptake of the S1R-targeting radiotracer. While validity of this hypothesis is limited by the lack of immunohistological evidence showing S1R in the mass, the removal of the mass resulted in complete pain relief.
This case illustrates the promising application of 18F-FTC-146 PET/MRI as an improvement over MRI alone as an imaging modality for detecting pain generators. The ability to characterize painful or inflammatory pathology according to increased S1R density may prove to be an important clinical imaging method to objectively identify pain generators. The ongoing clinical investigation will be helpful in validating this process.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jun Park (radiochemist) for synthesizing the radiotracer, Dawn Holley and Harsh Gandhi (PET/MRI technologists) for acquiring the images, and the PET/MRI Metabolic Service Center for its support. This study is funded in part by GE Healthcare and the Ben and Catherine Ivy Foundation.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Zamanillo D, Romero L, Merlos M, Vela JM. Sigma 1 receptor: a new therapeutic target for pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;716(1-3):78–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shen B, Behera D, James ML, et al. Visualizing nerve injury in a neuropathic pain model with [18F]FTC-146 PET/MRI. Theranostics. 2017;7(11):2794–2805. doi: 10.7150/thno.19378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.James ML, Shen B, Nielsen CH, et al. Evaluation of σ-1 receptor radioligand 18F-FTC-146 in rats and squirrel monkeys using PET. J Nucl Med. 2014;55(1):147–153. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.113.120261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shen B, James ML, Andrews L, et al. Further validation to support clinical translation of [(18)F]FTC-146 for imaging sigma-1 receptors. EJNMMI Res. 2015;5(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13550-015-0122-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hjørnevik T, Cipriano PW, Shen B, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of 18F-FTC-146 in humans. J Nucl Med. 2017;58(12):2004–2009. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.117.192641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hill JA, Martin WR, Milgram JW. Unusual arthroscopic knee lesions: case report of an intra-articular lipoma. J Natl Med Assoc. 1993;85(9):697–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hirasawa Y, Okajima S, Ohta M, Tokioka T. Nerve distribution to the human knee joint: anatomical and immunohistochemical study. Int Orthop. 2000;24(1):1–4. doi: 10.1007/s002640050001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Monnet FP. Sigma-1 receptor as regulator of neuronal intracellular Ca2+: clinical and therapeutic relevance. Biol Cell. 2005;97(12):873–883. doi: 10.1042/BC20040149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tejada MA, Montilla-García A, Sánchez-Fernández C, et al. Sigma-1 receptor inhibition reverses acute inflammatory hyperalgesia in mice: role of peripheral sigma-1 receptors. Psychopharmacology. 2014;231(19):3855–3869. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]