Abstract
It is estimated that between 8000 and 15 000 Trypanosoma cruzi infected babies are born every year to infected mothers in Chagas disease endemic countries. Currently, poor access to and performance of the current diagnostic algorithm, based on microscopy at birth and serology at 8–12 months after delivery, is one of the barriers to congenital Chagas disease (CCD) control. Detection of parasite DNA using molecular diagnostic tools could be an alternative or complement to current diagnostic methods, but its implementation in endemic regions remains limited. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of CCD cases would have a positive clinical and epidemiological impact. In this paper, we analysed the burden of CCD in Latin America, and the potential use of molecular tests to improve access to early diagnosis and treatment of T. cruzi infected newborns.
Keywords: chagas disease, molecular tools, PCR, LAMP, Trypanosoma cruzi
Summary box.
Congenital Chagas disease (CCD) remains a public health problem in endemic countries.
The current diagnostic algorithm based on sequential use of microscopy and serology misses a significant number of CCD cases.
Robust, standardised and easier to implement molecular diagnostic methods for CCD are now available.
Algorithms to diagnose CCD cases using molecular tools in endemic regions should be developed and implemented.
Accurate and up-to-date data are needed on the number of infants screened and the number cases of CCD diagnosed.
Introduction
In 1998, Russomando et al concluded that ‘the PCR has a clear advantage over conventional techniques for the early detection of congenital transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi infection’.1 Twenty years later, in endemic countries, the use of molecular tools to diagnose infants infected with T. cruzi, the parasite that causes Chagas disease by congenital transmission from infected mothers, is still limited. The arguments put forward to justify the limited use of molecular tools to diagnose congenital Chagas disease (CCD) in these countries are diverse, including: limited evidence that molecular tests perform better than standard procedures (eg, parasitology at birth and/or serology 8–12 months after birth), lack of standardisation, complexity and cost.
Diagnosing CCD should be a priority in endemic countries, as this has proven clinical and epidemiological benefits. In endemic countries such as Bolivia and Chile, controlling CCD is considered a cost-effective strategy2 3 as, in contrast to the disease in adults, the cure rate in infants less than 1 year old is almost 100% and tolerance to treatment is quite good.4 The cure rate decreases in older paediatric patients undergoing chronic infection.5 Treated and cured children would not develop cardiac and/or gastrointestinal forms of Chagas disease.6 Furthermore, if there is no reinfection later in life, treated girls will be significantly less likely to transmit the infection to their infants when they get older.7 Thus, the best diagnostic strategies for congenital Chagas should therefore be implemented to ensure that cases are identified and treated promptly.
The 63rd World Health Assembly held in Geneva on 21 May 2010 urged governments to ‘establish systems of early detection, in particular for the detection of new infections, congenital infections in newborns ‘.8 In endemic countries, the current strategy to diagnose and treat CCD is based on a series of steps which leave much to be desired. First, T. cruzi-infected mothers should be identified by serological analysis. Children born to an infected mother should then be tested either by microscopy shortly after birth and/or serology 8–12 months after birth. Children who are positive by microscopy (parasites observed in capillary or umbilical cord blood) and/or serology are considered to be CCD cases and are treated.9 Serological tests cannot be used to diagnose T. cruzi infection in babies soon after they are born as maternal antibodies could cause false positive results. While algorithms for diagnosis of CCD vary from country to country, they adhere to the general multistep process, which has well-reported limitations, in particular the low sensitivity of microscopy and the loss to follow-up at 8–12 months.10 11 A number of studies have corroborated the results of Russomando et al and have shown that molecular tools performed 1 month after birth, in place of microscopy, outperform the current diagnostic algorithm.10–16 However, despite their availability, molecular tests are rarely used to diagnose CCD. To our knowledge, Chile is the only endemic country that routinely uses PCR as part of a national strategy,17 while Argentina is scaling up its use. In the rest of Latin America, PCR is sometimes mentioned in the guidelines as a potential diagnostic tool but is not included in diagnostic algorithms.18 19 In contrast, PCR is part of the diagnostic algorithm for CCD in non-endemic high-income countries, such as Spain20 and Switzerland.21
In this paper, we demonstrate that CCD remains a public health problem in Latin America by estimating the burden of disease, the number of children born to T. cruzi infected mothers who should be screened so they can be treated if required and the number of CCD cases missed by the current diagnostic strategy. We have also analysed the limitations and arguments that preclude implementation of molecular tests to diagnose CCD in those countries and suggest ways to overcome them.
Burden of CCD and number of newborns that should be tested for the disease
The WHO estimates that in 2010, there were 8668 new cases of CCD in Latin American countries.22 These CCD cases represented 22% (8668/38 593) of all new cases of Chagas disease that year.22 The weight that congenital transmission has in the burden of Chagas disease will continue to increase in significance, as other modes of transmission (eg, vector and blood-transfusion) are being controlled. Transmission of Chagas disease through blood transfusion was interrupted in most Latin American countries (20 out of 21) by 201523 and vectorial transmission has been interrupted in a number of endemic countries and regions.8 Congenital infection of T. cruzi is now the first cause of new cases of Chagas disease in Argentina.24 The number of CCD cases is used to estimate the burden of congenital transmission; however, there is another key parameter that should be considered when planning and assessing CCD control programmes: the number of babies that should be tested. The number of children born to infected mothers is significantly larger than the number of CCD cases as the transmission rate of T. cruzi from mother to child is around 5% (95% CI 4% to 6%) in endemic countries.25 As it happens with the chronic form of Chagas disease, epidemiological data on CCD are scarce. There are no estimates on the number of children born to T. cruzi-infected mothers in endemic countries who should have been tested at birth.
In this paper, we have adapted the model developed by WHO to estimate the burden of Chagas disease in Latin America in 201022 26 to estimate the number of babies born to T. cruzi-infected mothers in the region in 2010. First, we derived demographic data from the WHO report,22 which was based on 2010 national censuses, whenever these data were available. For those countries without data in the WHO report, population projections were obtained from the United Nations and the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean. Population tables on women of childbearing age (15–44 years of age) were obtained from the U.S. Census Bureau International Data Base, while annual numbers of births by country were extracted from PAHO/WHO Basic Indicators 2010. We used the T. cruzi infection prevalence ranges reported per country22 27 28 to calculate the total population infected and the number of infected women of childbearing age. Finally, we derived birth rates per country—adjusting the rates by a factor of 1.5 due to higher birth rates in rural areas22—of infected women of childbearing age, in order to develop a range estimate of the number of babies born to infected mothers.
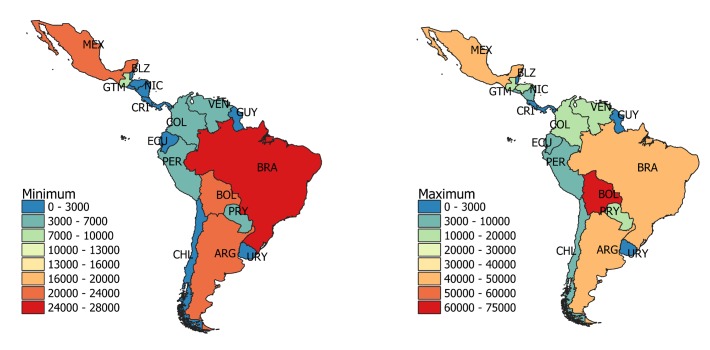
The number of babies that would need to be tested per year varies from 157 972 to 214 074, depending on the estimate of the prevalence of T. cruzi infection (table 1). Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia and Mexico are the countries where most tests should be conducted (figure 1). Taking 5% as the average T. cruzi transmission rate from infected mothers to newborns,25 the annual prevalence of CCD cases in Latin America in 2010 ranged from 7899 to 10 704. These numbers are similar to those estimated by WHO in previous reports: 15 000 in 2006 and 8700 in 2010.22 28 Our estimates can be used as a reference but some limitations in the calculations should be considered: for example, the performance of serological tests and the congenital transmission rate vary among countries.26 Accurate and up-to-date data are needed in endemic countries.
Table 1.
Estimated number of infants born to T. cruzi-infected mothers and number of congenital Chagas disease cases in 2010 in endemic countries
| Countries | Population* | Range of T. cruzi infection prevalence† | Range of population infected | Range of women of childbearing age infected | Range of children born from T. cruzi infected women | Range of congenital cases‡ |
| Argentina | 41 343 000 | 2.20%–4.13% | 909 546–1 707 466 | 200 158–375 751 | 22 894–42 894 | 1142–2145 |
| Belize | 315 000 | 0.30%–0.74% | 945–2331 | 222–547 | 34–83 | 2–4 |
| Bolivia | 9 947 000 | 6.10%–18.00% | 606 767–1 790 460 | 144 198–425 504 | 23 609–70 551 | 1195–3528 |
| Brazil | 190 755 799 | 0.60%–1.02% | 1 144 535–1 945 709 | 284 883–484 301 | 26 622–45 257 | 1331–2263 |
| Chile | 17 095 000 | 0.70%–1.00% | 119 665–170 950 | 27 088–38 697 | 2654–3792 | 133–190 |
| Colombia | 45 805 000 | 0.50%–0.96% | 229 025–439 728 | 52 828–101 430 | 6864–13 179 | 343–659 |
| Costa Rica | 4 516 000 | 0.17%–0.53% | 7677–23 935 | 1887–5882 | 194–606 | 10–30 |
| Ecuador | 14 483 499 | 0.40%–1.74% | 57 934–252 013 | 14 134–61 485 | 1664–7238 | 83–362 |
| El Salvador | 6 952 000 | 1.30%–3.70% | 90 376–257 224 | 19 472–55 420 | 2436–6932 | 122–347 |
| Guatemala | 13 550 000 | 1.20%–1.98% | 162 600–268 290 | 38 058–62 796 | 8275–13 653 | 414–683 |
| French Guyana, Gayana Surinam | 1 501 962 | 0.80%–1.29% | 12 016–19 375 | 2386–3848 | 67–108 | 3–5 |
| Honduras | 7 989 000 | 0.92%–4.20% | 73 499–335 538 | 17 191–78 481 | 2799–12 776 | 140–639 |
| Mexico | 112 468 855 | 0.78%–1.50% | 877 257–1 687 033 | 2 17 759–4 18 768 | 23 323–44 852 | 1166–2243 |
| Nicaragua | 5 604 000 | 0.52%–4.60% | 29 141–257 784 | 7552–66 804 | 1096–9695 | 55–485 |
| Panama | 3 557 687 | 0.01%–0.52% | 356–18 500 | 79–4089 | 10–545 | 1–27 |
| Paraguay | 8 668 000 | 2.13%–5.50% | 184 628–476 740 | 32 938–85 050 | 4927–12 722 | 246–636 |
| Peru | 28 948 000 | 0.44%–0.69% | 127 371–199 741 | 31 282–49 056 | 3966–6219 | 198–311 |
| Uruguay | 3 301 000 | 0.24%–0.80% | 7922–26 408 | 1684–5612 | 179–595 | 9–30 |
| Venezuela | 27 223 000 | 0.71%–1.16% | 193 283–315 787 | 48 532–79 292 | 6393–10 445 | 320–522 |
| Latin America | 544 023 802 | 1.07%–1.45% | 5 821 055–7 888 345 | 1 404 704–1 903 571 | 157 972–214 074 | 7899–10 704 |
Figure 1.
Estimated number of infants born to T. cruzi-infected mothers who should have been tested for congenital Chagas disease in 2010 in Latin American countries. The minimum and maximum number of babies that would need to be tested per country are presented. The estimates are presented in detail in table 1.
Sensitivity of the congenital Chagas disease diagnostic algorithm
There are no accurate records on the number of infants born to infected mothers that are actually tested in endemic countries. Such data would be useful in estimating the coverage achieved by CCD control programmes and the likely number of cases missed. Sensitivity, defined as the number of Chagas disease cases correctly identified by the diagnostic algorithm, depends on (1) the characteristics of the tests used (eg, sensitivity of microscopy and serology) and (2) the capacity of the health system to screen mothers and newborns when required, including the follow-up of babies 8–12 months after birth.
We used the number of pregnant women screened, their seroprevalence, the number of babies tested and the number of CCD cases identified in Bolivia in 2009, as reported by Alonso-Vega et al,29 to estimate the number of CCD cases missed by the national control programme (NCP) that year. The calculations summarised in table 2 indicate that 174 patients with CCD would have been missed, as the programme is unable to test all the babies born to T. cruzi-infected mothers. This estimate assumes that all pregnant women at risk in Bolivia were screened (319 014 pregnancies estimated in Bolivia in 2009), using a test with a sensitivity of 100%, and the diagnostic algorithm for babies (microscopy and serology) was also 100% sensitive. Had the sensitivity of the algorithm been reduced to 80% (ie, loss to follow-up of babies tested by microscopy but not by serology at 8–12 months), then the total number of CCD cases in Bolivia in 2009 would have been 629 and only 52% (n=329) would have been identified by the NCP.
Table 2.
Number of pregnant women screened, babies tested and CCD cases identified by Bolivia’s national control programme in 2009, and the estimated number of CCD cases missed due to inadequate coverage
| Variable | Estimates | Source |
| Pregnant women | ||
| # of pregnant women screened | 112 160 | Tables 5–829 |
| # of pregnant women who are also seropositive | 24 748 | Tables 5–829 |
| Seroprevalence in pregnant women | 22% | Calculated: 24 748/112 160 |
| Babies born to infected mothers | ||
| # of babies tested | 16 185 | Tables 5–829 |
| # of babies not tested (assuming one baby per pregnancy) | 8563 | Calculated: 24 748–16 185 |
| % babies tested following the diagnostic algorithm | 65% | Calculated: 16 185/24 748 |
| Congenital Chagas disease (CCD) cases | ||
| # CCD cases identified | 329 | Tables 5–829 |
| Rate of congenital transmission | 2% | Calculated: 329/16 185 |
| # of CCD cases missed because babies were not tested | 174 | Calculated: 2%x8563 |
CCD, congenital Chagas disease.
This case study illustrates the limitations of the current diagnostic tools and the health system in identifying all CCD cases in Bolivia, which may be similar to the situation in other Latin American countries.
Implementation of molecular tools to test for congenital Chagas disease
Development of point-of-care (PoC) tests to diagnose CCD remains a priority30 31 and some biomarkers have shown promising results.32 33 Until these PoC tests are developed, molecular tools for detection of parasite DNA remain the best alternatives to complement current methods. A number of reasons for the limited implementation of molecular tools in the diagnosis of CCD in endemic countries have been identified. We review the most relevant here.
Lack of clinical evidence
PCR has been shown to have a higher sensitivity for parasite detection than other conventional methods such as microscopy, hemoculture or xenodiagnosis.1 10 16 34 It is also superior to conventional methods in the diagnosis and follow-up of infected newborns. Up to 100% sensitivity has been reported in the detection of T. cruzi in neonates within the first 3 months of age, which qualifies PCR for early-stage diagnosis of CCD.24 35–37 However, PCR may not be ideal in cases of CCD without persistent parasitaemia, and as a result, sampling at different time points from birth may be needed.38 A cohort study in an endemic setting in Bolivia that included PCR in the algorithm for detecting vertical transmission of Chagas disease demonstrated its superiority over serology and microscopy.14
Lack of standardisation
There are a number of factors affecting the diagnostic performance of PCR that could be a hindrance to standardisation across settings where the use of home-brewed PCR methods is the rule. From the source, volume and timing of clinical sampling to more technical issues such as the use of anticoagulants and/or stabilising agents, the method used to purify DNA, the target DNA sequence, primers and probes design, the chemistry used in the reaction and the platform in which the test is performed.39 There is evidence that blood sampling at 1 month after birth improves accuracy of molecular diagnosis.26 40 And there have been successful examples of validating and harmonising home-brewed or commercial PCR and real-time quantitative PCR methods.41 42 Both efforts will hopefully contribute to implement a strategy for a timely and effective diagnosis of CCD.
Complexity
Real-time PCR kits for detection of T. cruzi are commercially available such as RealCycler CHAG (Progenie, Spain) or TCRUZIDNA.CE (Diagnostics Bioprobes Srl, Italy) but their implementation in low-resource settings is limited due to their cost and the need for cold chain for transport and storage. Thus, the lack of robust, field amenable and ready-to-use PCR formats has limited its use to reference laboratories. A method that could overcome these hurdles is loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of DNA. This test is performed at constant temperature (60°C–65°C), enabling amplification with high efficiency, in a short time. A thermocycler is not required but a simpler device that allows for isothermal incubation such as a thermal block. Results are easily visualised using simple detection methods.43 An advantage of LAMP is that it uses multiple primers targeting different regions of the target DNA, which makes it highly sensitive and specific. Recently, the analytical sensitivity and specificity of a LAMP kit developed by Eiken Chemical Co. (Japan, Loopamp Trypanosoma cruzi Detection Kit) on clinical samples from CCD cases were shown to be similar to those of PCR in Argentina.44 The simplicity of its format, with reagents dried down in reaction tubes that can be stored at room temperature, enables its use for the diagnosis of CCD in resource-limited settings.44 Other groups have developed similar LAMP kits to detect T. cruzi DNA.45 Another platform that meets the criteria for implementation of molecular diagnosis at such sites is recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA), which also enables sensitive, specific and rapid amplification of DNA under isothermal conditions. The RPA reaction runs optimally at 37°C–42°C which may present an advantage in terms of energy costs saving. This test can also be produced in dry format and has shown great potential in the diagnosis of infections by protozoan parasites.46 A prototype RPA test coupled with lateral flow assay for product detection has been used to identify T. cruzi infection in dogs, showing similar performance to qPCR.47
Cost and implementation
While molecular tests may be more expensive than serology or microscopy, their superior diagnostic performance would enable the detection and treatment of a higher number of cases. The high efficacy of treatment of CCD may provide an opportunity to demonstrate that molecular tests are cost-effective, as shown in Chile.3 Testing for different pathogens using the same platform would reduce costs related to implementation of molecular diagnostics in resource-limited settings. For example, the Loopamp platform by Eiken Chemical Co. has been used to develop LAMP tests for the diagnosis of Chagas disease, leishmaniasis, malaria and tuberculosis, the latter endorsed by WHO.48–50 As these diseases are coendemic in various geographic regions, health systems have the possibility of using this platform to test for multiple pathogens.
The barriers to implementing these technologies in resource-limited settings may have less to do with their complexity and more with the fact that they require the engagement and commitment of different stakeholders to align the necessary resources.51
Conclusion
It is 20 years since Russomando et al made their statement about the superiority of PCR over conventional techniques and yet molecular tools to diagnose CCD in endemic countries have still not been broadly implemented. These tools may not be perfect38 but undoubtedly have a role to play in CCD control programmes, particularly if we take advantage of recently developed technologies. Improved access to prompt and accurate diagnosis for babies at risk of T. cruzi infection should be integrated with other interventions: vector control to avoid reinfection, treatment of women of childbearing age to prevent congenital transmission,7 interruption of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and syphilis52 and screening of congenital disorders in newborns using dried blood spots.53 Delaying the implementation of more efficient diagnostic algorithms sentences a significant number of children to the risk of developing Chagas disease and transmitting T. cruzi parasites to the next generation.
Recommendations
Estimate the number of infants born to T. cruzi-infected mothers, and the number of newborns tested in endemic countries per year. These indicators should be used to monitor coverage of CCD control programmes.54
Develop target product profiles to define the technical requirements of point-of-care diagnostic tools (molecular and others) for CCD30 55 and support the development and implementation of novel tools to diagnose CCD.
Establish sample banks of CCD cases and controls to allow a rapid and standardised evaluation of new tools (molecular or others) to diagnose congenital transmission of T. cruzi. These sample banks should be representative of the different endemic areas and should include different sample types (eg, blood and urine).
Develop and evaluate algorithms to diagnose CCD using molecular tools based on the evidence and experience of control programmes that are currently employing these tools.
Acknowledgments
FIND is grateful to its donors, public and private, who have helped bring innovative new diagnostics for diseases of poverty. A full list of FIND’s donors can be found at: https://www.finddx.org/donors/. The Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi) is grateful to its donors, public and private, who have provided funding to DNDi since its inception in 2003. A full list of DNDi’s donors can be found at http://www.dndi.org/donors/donors/.
Footnotes
Handling editor: Dr Alberto L Garcia-Basteiro
Contributors: AP, IC and MR-J analysed the data. AP drafted the first version of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: AP, IC, MR-J, ZK and JMN are employees of the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). FIND contributed to the development of the Loopamp Trypanosoma cruzi Detection Kit. However, FIND does not have any financial interest in the product. The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data statement: No additional data are available.
References
- 1. Russomando G, de Tomassone MM, de Guillen I, et al. . Treatment of congenital chagas’ disease diagnosed and followed up by the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1998;59:487–91. 10.4269/ajtmh.1998.59.487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Billot C, Torrico F, Carlier Y. [Cost effectiveness study of a control program of congenital Chagas disease in Bolivia]. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2005;38(Suppl 2):108–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Castillo M, Sergio R, Saldivia L, 2013. Costo-efectividad del screening y tratamiento de mujeres embarazadas y recién nacidos por transmisión de Chagas congénito. Available from: http://www.orasconhu.org/case/sites/default/files/files/CHAGAS-CONGENITO-2013.pdf [accessed 4 May 2018].
- 4. Carlier Y, Sosa-Estani S, Luquetti AO, et al. . Congenital chagas disease: an update. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2015;110:363–8. 10.1590/0074-02760140405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ribeiro I, Sevcsik AM, Alves F, et al. . New, improved treatments for Chagas disease: from the R&D pipeline to the patients. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2009;3:e484 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000484 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Fabbro De Suasnábar D, Arias E, Streiger M, et al. . Evolutive behavior towards cardiomyopathy of treated (nifurtimox or benznidazole) and untreated chronic chagasic patients. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 2000;42:99–109. 10.1590/S0036-46652000000200007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Fabbro DL, Danesi E, Olivera V, et al. . Trypanocide treatment of women infected with Trypanosoma cruzi and its effect on preventing congenital Chagas. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014;8:e3312 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.World Health Organization, 2010. World Health Assembly 63.20 Chagas Disiase: control and elimination. Available from: http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/mediacentre/WHA_63.20_Eng.pdf?ua=1[accessed 4 May 2018].
- 9. Carlier Y, Torrico F, Sosa-Estani S, et al. . Congenital Chagas disease: recommendations for diagnosis, treatment and control of newborns, siblings and pregnant women. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2011;5:e1250 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001250 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Bua J, Volta BJ, Perrone AE, et al. . How to improve the early diagnosis of Trypanosoma cruzi infection: relationship between validated conventional diagnosis and quantitative DNA amplification in congenitally infected children. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2476 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002476 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Bern C, Verastegui M, Gilman RH, et al. . Congenital trypanosoma cruzi transmission in santa cruz, bolivia. Clin Infect Dis 2009;49:1667–74. 10.1086/648070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Virreira M, Torrico F, Truyens C, et al. . Comparison of polymerase chain reaction methods for reliable and easy detection of congenital Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;68:574–82. 10.4269/ajtmh.2003.68.574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Montes-Rincón LM, Galaviz-Silva L, González-Bravo FE, et al. . Trypanosoma cruzi seroprevalence in pregnant women and screening by PCR and microhaematocrit in newborns from Guanajuato, Mexico. Acta Trop 2016;164:100–6. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.08.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Messenger LA, Gilman RH, Verastegui M, et al. . Toward improving early diagnosis of congenital Chagas disease in an endemic setting. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:268–75. 10.1093/cid/cix277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Diez CN, Manattini S, Zanuttini JC, et al. . The value of molecular studies for the diagnosis of congenital chagas disease in northeastern Argentina. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2008;78:624–7. 10.4269/ajtmh.2008.78.624 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Mora MC, Sanchez Negrette O, Marco D, et al. . Early diagnosis of congenital Trypanosoma cruzi infection using PCR, hemoculture, and capillary concentration, as compared with delayed serology. J Parasitol 2005;91:1468–73. 10.1645/GE-549R.1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. CG C, Collao EH, Pezzi FF, 2014. Norma general técnica control y prevención nacional de la enfermedad de Chagas. Available from: http://web.minsal.cl/sites/default/files/NORMATECNICA_CHAGAS_FINAL.pdf [accessed 26 Jan 2017].
- 18. Ministerio de Salud y Deportes , 2011. Manual de normas para el diagnóstico y tratamiento de Chagas congénito. Available from: https://www.minsalud.gob.bo/images/Documentacion/dgss/Epidemiologia/NORMATIVOSPNCH/ManualChagasCongénito219.pdf [accessed 26 Jan 2017].
- 19. República Bolivariana de Venezuela Ministerio del Poder Popular para la Salud. , 2014. Guía de diagnostico, atención y manejo clínico de la enfermedad de Chagas en Venezuela. Available from: http://svmi.web.ve/wh/documentos/Guia_Chagas_2015.pdf [accessed 26 Jan 2017].
- 20.Conselleria de sanitat - Comunitat Valenciana., 2012. la enfermedad de Chagas importada - protocolo de actuación en la Comunidad Valenciana. Available from: http://publicaciones.san.gva.es/publicaciones/documentos/V-5243-2008.pdf [accessed 26 Jan 2017].
- 21. Jackson Y, Myers C, Diana A, et al. . Congenital transmission of chagas disease in latin american immigrants in Switzerland. Emerg Infect Dis 2009;15:601–3. 10.3201/1504.080438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. World Health Organization Chagas disease in Latin America: an epidemiological update based on 2010 estimates. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2015;90:33–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. WHO , 2015. Report of the WHO Strategic and Technial Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases. Geneva. Available from: http://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/NTD_STAG_report_2015.pdf?ua=1 [accessed 17 Jun 2016].
- 24. Cura CI, Ramírez JC, Rodríguez M, et al. . Comparative study and analytical verification of PCR methods for the diagnosis of congenital Chagas disease. J Mol Diagnostics 2017;19:673–81. 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.05.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Howard EJ, Xiong X, Carlier Y, et al. . Frequency of the congenital transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2014;121:22–33. 10.1111/1471-0528.12396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Carlier Y, Truyens C. Maternal–fetal transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi : American Trypanosomiasis Chagas Disease. Elsevier, 2017:517–59. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Requena-Méndez A, Aldasoro E, de Lazzari E, et al. . Prevalence of Chagas disease in Latin-American migrants living in Europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2015;9:e0003540 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.PAHO, 2006. Estimación cuantitativa de la enfermedad de Chagas en las Americas. Available from: http://ops-uruguay.bvsalud.org/pdf/chagas19.pdf [accessed 6 May 2018].
- 29. Alonso-Vega C, Billot C, Torrico F. Achievements and challenges upon the implementation of a program for national control of congenital Chagas in Bolivia: results 2004-2009. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2304 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002304 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Picado A, Angheben A, Marchiol A, et al. . Development of diagnostics for Chagas disease: where should we put our limited resources? PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017;11:e0005148 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.World Health Organization. Research priorities for Chagas disease, human African trypanosomiasis and leishmaniasis. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 2012;(975):v–xii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Ramírez JC, Parrado R, Sulleiro E, et al. . First external quality assurance program for bloodstream Real-Time PCR monitoring of treatment response in clinical trials of Chagas disease. PLoS One 2017;12:1–15. 10.1371/journal.pone.0188550 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Mallimaci MC, Sosa-Estani S, Russomando G, et al. . Early diagnosis of congenital Trypanosoma cruzi infection, using shed acute phase antigen, in Ushuaia, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;82:55–9. 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Britto C, Silveira C, Cardoso MA, et al. . Parasite persistence in treated chagasic patients revealed by xenodiagnosis and polymerase chain reaction. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2001;96:823–6. 10.1590/S0074-02762001000600014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Schijman AG. Molecular diagnosis of Trypanosoma cruzi . Acta Trop 2018;184:59–66. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.02.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Schijman AG, Altcheh J, Burgos JM, et al. . Aetiological treatment of congenital Chagas’ disease diagnosed and monitored by the polymerase chain reaction. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003;52:441–9. 10.1093/jac/dkg338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Velázquez EB, Rivero R, De Rissio AM, et al. . Predictive role of polymerase chain reaction in the early diagnosis of congenital Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Acta Trop 2014;137:195–200. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2014.05.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Volta BJ, Perrone AE, Rivero R, et al. . Some limitations for early diagnosis of congenital chagas infection by PCR. Pediatrics 2018;141(Suppl 5):S451–S455. 10.1542/peds.2016-3719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Alonso-Padilla J, Gallego M, Schijman AG, et al. . Molecular diagnostics for chagas disease: up to date and novel methodologies. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2017;17:699–710. 10.1080/14737159.2017.1338566 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Buekens P, Cafferata ML, Alger J, et al. . Congenital Transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi in Argentina, Honduras, and Mexico: An Observational Prospective Study. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2018;98:478–85. 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0516 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Schijman AG, Bisio M, Orellana L, et al. . International study to evaluate PCR methods for detection of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA in blood samples from Chagas disease patients. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2011;5:e931 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000931 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Abras A, Ballart C, Llovet T, et al. . Introducing automation to the molecular diagnosis of Trypanosoma cruzi infection: A comparative study of sample treatments, DNA extraction methods and real-time PCR assays. PLoS One 2018;13:e0195738 10.1371/journal.pone.0195738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Notomi T, Mori Y, Tomita N, et al. . Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): principle, features, and future prospects. J Microbiol 2015;53:1–5. 10.1007/s12275-015-4656-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Besuschio SA, Llano Murcia M, Benatar AF, et al. . Analytical sensitivity and specificity of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) kit prototype for detection of Trypanosoma cruzi DNA in human blood samples. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017;11:e0005779 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005779 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Rivero R, Bisio M, Velázquez EB, et al. . Rapid detection of Trypanosoma cruzi by colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A potential novel tool for the detection of congenital Chagas infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2017;89:26–8. 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2017.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Castellanos-Gonzalez A, White AC, Melby P, et al. . Molecular diagnosis of protozoan parasites by recombinase polymerase amplification. Acta Trop 2018;182:4–11. 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.02.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Jimenez-Coello M, Shelite T, Castellanos-Gonzalez A, et al. . Efficacy of recombinase polymerase amplification to diagnose Trypanosoma cruzi infection in dogs with cardiac alterations from an endemic area of Mexico. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2018;18:417–23. 10.1089/vbz.2017.2258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Mukhtar M, Ali SS, Boshara SA, et al. . Sensitive and less invasive confirmatory diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in Sudan using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018;12:e0006264 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. World Health Organization The use of loop-mediated isothermal amplifi cation (TB-LAMP) for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Perera RS, Ding XC, Tully F, et al. . Development and clinical performance of high throughput loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of malaria. PLoS One 2017;12:e0171126 10.1371/journal.pone.0171126 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Peeling RW, Boeras DI, Nkengasong J. Re-imagining the future of diagnosis of Neglected Tropical Diseases. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2017;15:271–4. 10.1016/j.csbj.2017.02.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Plus PE, 2017. Framework for elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, Syphilis, Hepatitis B, and Chagas. PAHO. Available from: http://iris.paho.org/xmlui/handle/123456789/34306 [accessed 7 May 2018].
- 53. Therrell BL, Padilla CD, Loeber JG, et al. . Current status of newborn screening worldwide: 2015. Semin Perinatol 2015;39:171–87. 10.1053/j.semperi.2015.03.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Tarleton RL, Gürtler RE, Urbina JA, et al. . Chagas disease and the london declaration on neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014;8:e3219 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Porrás AI, Yadon ZE, Altcheh J, et al. . Target product profile (TPP) for chagas disease point-of-care diagnosis and assessment of response to treatment. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2015;9:e0003697 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003697 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]