Abstract
Introduction Would adolescent girls in Germany choose a different method of contraception to the combined oral contraceptive if provided with the appropriate information? Is there a need for long-acting contraception among our adolescent girls? How satisfied are female patients with the information they receive at their respective gynaecology practices, and how much do the girls know about different methods of contraception?
Materials and Methods In the study “Thinking About Needs in COntraception” (TANCO), not only female patients, but also their respective gynaecologists were surveyed online about current methods of contraception, their satisfaction with these methods, and also their level of knowledge concerning the individual methods of contraception, the situation related to advice about different contraceptive options and their general satisfaction with gynaecological care. This article presents the data from the subset of adolescent girls aged 14 to 19 years (n = 2699) out of the total of 18 521 women surveyed.
Results The girls surveyed were familiar with at least the name of more than five different methods of contraception (average 5.3). The doctors assumed that the respondents would know only 4.2 different methods. When asked explicitly about how the individual methods of contraception work, clear deficits became evident. This applies not only to the entire population of respondents, but also the users of the respective contraceptive method. In addition, a strong interest in long-acting contraception emerged from the survey, particularly among young women.
Discussion The data from the TANCO study reveal a clear discrepancy between the existing contraception almost exclusively in the form of the contraceptive pill and the contraceptive options considered by adolescent girls if they are thoroughly informed. The need for education into alternatives to the pill is high, as is the willingness to use such alternatives after receiving information – much higher than the figures suggested by the gynaecologists.
Key words: adolescents, contraception, long-acting contraception, knowledge, adolescents
Zusammenfassung
Einleitung Würden sich Adoleszentinnen in Deutschland nach entsprechender Aufklärung für eine andere Form der Verhütung als die Einnahme eines oralen kombinierten Kontrazeptivums entscheiden? Besteht ein Bedürfnis nach Langzeitverhütung bei unseren Adoleszentinnen? Wie zufrieden sind die Patientinnen mit der Informationsvermittlung in den betreuenden Frauenarztpraxen und wie viel eigenes Wissen haben die Mädchen über verschiedene Methoden der Verhütung?
Material und Methoden In der Studie „Thinking About Needs in COntraception“ (TANCO) wurden neben Patientinnen auch deren betreuende Frauenärzte/innen in einer Online-Umfrage nach aktueller Form der Verhütung, Zufriedenheit hiermit, aber auch über den Wissensstand zu einzelnen Verhütungsmethoden, der Beratungssituation in Bezug auf verschiedene kontrazeptive Optionen und ihre allgemeine Zufriedenheit mit der frauenärztlichen Betreuung befragt. Von den 18 521 befragten Frauen werden für diesen Artikel die Daten der Adoleszentinnen zwischen 14 und 19 Jahren (n = 2699) dargestellt.
Ergebnisse Zumindest dem Namen nach kannten die Befragten mehr als 5 verschiedene Verhütungsmethoden (im Durchschnitt 5,3). Ärzte gingen davon aus, dass die Befragten nur 4,2 unterschiedliche Methoden kennen. Wird nun explizites Wissen über die Wirkweise einzelner Verhütungsmethoden abgefragt, fallen hier deutliche Defizite auf. Dies betrifft nicht nur das gesamte Kollektiv der Befragten, sondern auch die Verwenderinnen der jeweiligen Verhütung. Weiterhin hat sich in der Befragung ein starkes Interesse gerade junger Frauen an einer Langzeitverhütung gezeigt.
Diskussion Die Daten der TANCO-Studie zeigen eine deutliche Diskrepanz zwischen der tatsächlich bestehenden fast ausschließlichen Verhütung mittels Pille und den von Adoleszentinnen in Betracht gezogenen Optionen zur Verhütung, wenn denn ausführliche Aufklärung stattfindet. Der Bedarf nach Aufklärung über Alternativen zur Pille ist hoch und auch die Bereitschaft, diese Alternativen nach erfolgter Aufklärung anzuwenden, liegt deutlich über den von den Frauenärzten angenommenen Prozentsätzen.
Schlüsselwörter: Adoleszentinnen, Verhütung, Langzeitverhütung, Wissen, Jugendliche
Introduction
Numerous methods of reliable contraception are available to women in Germany with a desire for contraception. The rate of women who would like a reliable method of contraception but do not have such access is relatively low; Germany ranks third to last worldwide with respect to this issue 1 . This also applies to the situation of contraceptive use among adolescents in Germany. The data from the survey conducted by the Federal Centre for Health Education (Bundeszentrale für gesundheitliche Aufklärung [BZgA]) into youth sexuality in 2015 reveal that 96% of adolescents claimed to have used contraception when last having sexual intercourse 2 . One reason for this positive trend must certainly be, among other things, the fact that the costs for prescription-only contraceptives in Germany are covered by medical insurance until an individual turns 20 years of age, meaning that any potential financial difficulties cannot be the cause for failing to use contraception. Another positive factor is that underage girls may also be prescribed contraception without having to involve or obtain consent from their parents, provided the prescribing gynaecologist assumes that consent would be forthcoming. On searching for information on how much adolescent girls know about individual methods of contraception, no data can be found. The available data are limited to the age as of which adolescents use contraception, and which methods are used. For instance, according to the BZgA data from 2015, where multiple responses were possible, 48% of adolescents used a condom, 70% the pill, and 9% another method when they had last had sexual intercourse. The alternatives to the pill, namely the vaginal ring, the implant, and the three-month injection, accounted for 4% and the coil (without differentiating between hormonal and copper) 2% 2 . Most adolescent girls use a combined oral contraceptive, sometimes along with a condom, as their chosen method of contraception. The reliability and handling of this contraceptive method, in particular, are rated positively by the adolescent girls. Conversely, only one in ten of the adolescent respondents reported problems with taking the pill. First and foremost are compliance problems, which directly affect the contraceptive reliability of the pill. Two-thirds of the girls thus reported that they have once forgotten to take the pill; more than one-third described forgetting to take the pack with them for an overnight stay, meaning they could not take the pill; almost one-third of the girls expressed uncertainty concerning efficacy in the event of vomiting or diarrhoea. Adverse effects, such as interim bleeding (30%), weight gain (24%), headaches (16%) and decreased sexual desire (15%) were also described by the girls as problems associated with taking the pill 2 . Based on this information, i.e. problems with routine intake and adverse effects, the question arises as to why so few adolescent girls opt for alternative reliable methods to the pill. In a large prospective cohort study conducted in the USA (10 000 women aged 14 – 45 years), namely the Contraceptive CHOICE Project, women received standardised information on every common, reliable method of contraception. Consequently, 67% of the participating women, irrespective of their age, opted for long-acting contraception (after analysing the data from the first 2500 women enrolled). It should be added here that the costs for the chosen contraceptive method were reimbursed 3 . The data from the Contraceptive CHOICE Project give rise to the question whether the decision in favour of a combined oral contraceptive tends to be taken primarily due to limited knowledge of alternative methods of contraception, also in Germany. Would adolescent girls in Germany choose a different method of contraception to the combined oral contraceptive if provided with the appropriate information? Is there a need for long-acting contraception among our adolescent girls? How satisfied are female patients with the information they receive at their respective gynaecology practices, and how much do the girls know about different methods of contraception? Do they even want more information about any of the available contraceptives? And how do the gynaecologists themselves assess their patientsʼ situation? The “Thinking About Needs in COntraception” (TANCO) study was the first to address these questions concerning the situation of contraceptive use in Germany. A total of 18 521 female patients were surveyed 4 . Of these, 15% (n = 2699) were adolescents aged between 14 and 19 years. Below, the results are presented and discussed based on the subset of adolescents.
Materials and Methods
The “Thinking About Needs in COntraception” (TANCO) study was conducted between May and November 2015 by means of an anonymous online survey.
Selection of participating gynaecologists
Both female patients and their respective gynaecologists were recruited. The study was conducted by an independent market research company supervised scientifically by private lecturer Dr. med. P. G. Oppelt. Gynaecologists registered with the health insurance companies were selected according to practice location (German federal state), type of practice (single or joint) and gender of the physician. A total of 3000 practices were approached and 1089 gynaecologists recruited. Based on the current gender distribution in the outpatient sector, the ratio of female to male gynaecologists was 75 to 25%.
Selection of female participants
The participating women were recruited by the gynaecologists themselves. They were provided with online access where they were also provided with detailed information on the subject of contraception. The patients were between 14 and 50 years old. A total of 18 521 female patients were surveyed, 15% (n = 2699) of whom were between 14 and 19 years old.
Content and analysis of the questionnaires
After agreeing to take part in the survey, the participants were given access to detailed informational materials about contraception. The basic data collected from the patients comprised their age, current occupation, household income, relationship status and any existing desire to have a child.
Both the gynaecologists and the participating women were given a questionnaire containing 32 to 37 questions (depending on the filter, not all questions necessarily had to be answered). The patients were asked about their current method of contraception and how satisfied they were with it, as well as about their general knowledge concerning individual methods of contraception, the situation related to the advice received on different contraceptive options, and overall satisfaction with their gynaecological care.
According to the questions aimed at the patients, the gynaecologists were asked how they themselves judge their advice and the satisfaction of their patients with the contraceptives they use. They were also asked how they would assess their patientsʼ knowledge related to the relevant contraceptive methods.
Results
Selected results from the subgroup of adolescents (14 – 19 years) in the TANCO study are presented below. The results for the gynaecologists always relate to the entire population, as they were not surveyed separately by age group.
What contraceptive methods are used by adolescent girls in Germany?
Out of the total of 2699 adolescents surveyed, 97.5% responded that at that time they were using contraception.
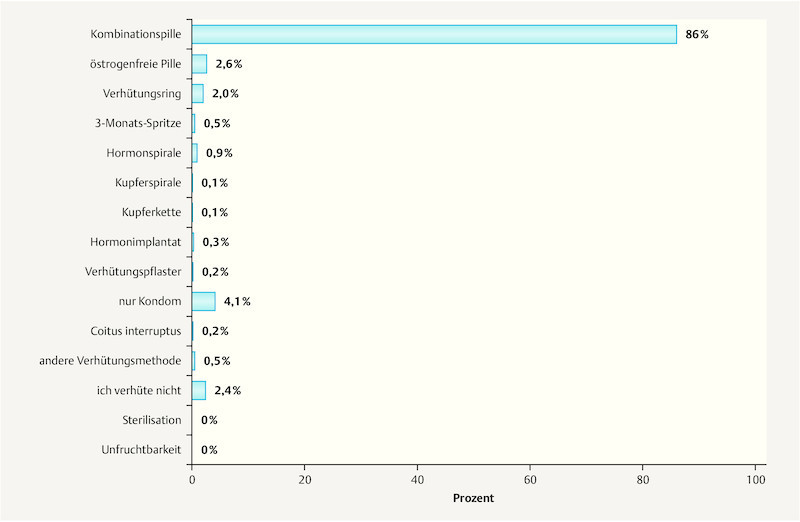
Combined oral contraceptives were being used by 86% of the adolescents, with condoms the second most common method at 4.1%, as the sole method of contraception. The vaginal ring was being used by 2% of the respondents. Long-acting, coitus-independent intrauterine devices (hormone coil, copper coil and copper chain) accounted for 1.1% in total. Other forms of long-acting hormonal contraception (three-month injection and hormone implant) totalled 0.8%. Almost as many respondents, namely 0.7%, were using unreliable methods of contraception (coitus interruptus, LH test, temperature method and morning-after pill). A total of 2.5% of the adolescents were using no contraception at all ( Fig. 1 ).
Fig. 1.
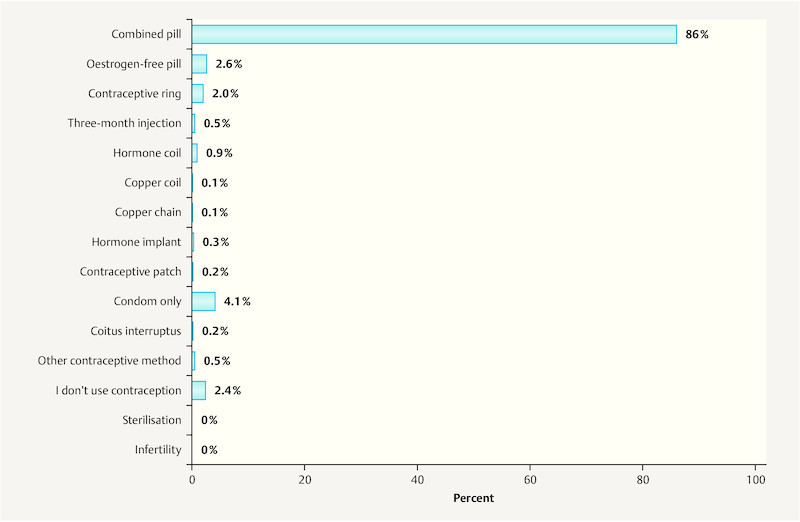
Distribution of contraceptive method currently in use (n = 2699 respondents).
The active substances most frequently found in combined pills were dienogest and levonorgestrel – in each case combined with ethinylestradiol (dienogest + ethinylestradiol 35%; levonorgestrel + ethinylestradiol 30%).
Persistence and previously used contraceptive method
Amongst those using a combined pill, 71% reported that it was the first contraceptive method they had used, while 29% had already used an alternative method of contraception, whereby the condom accounted for 88%. Of the adolescents responding that they were not currently using contraception, 36% had already used a contraceptive. Among those using an unreliable method of contraception (such as coitus interruptus, LH test or temperature method), 40% had already used another type of contraceptive. Of those using a hormonal or copper coil, almost all had previously used another form of contraception.
Compliance
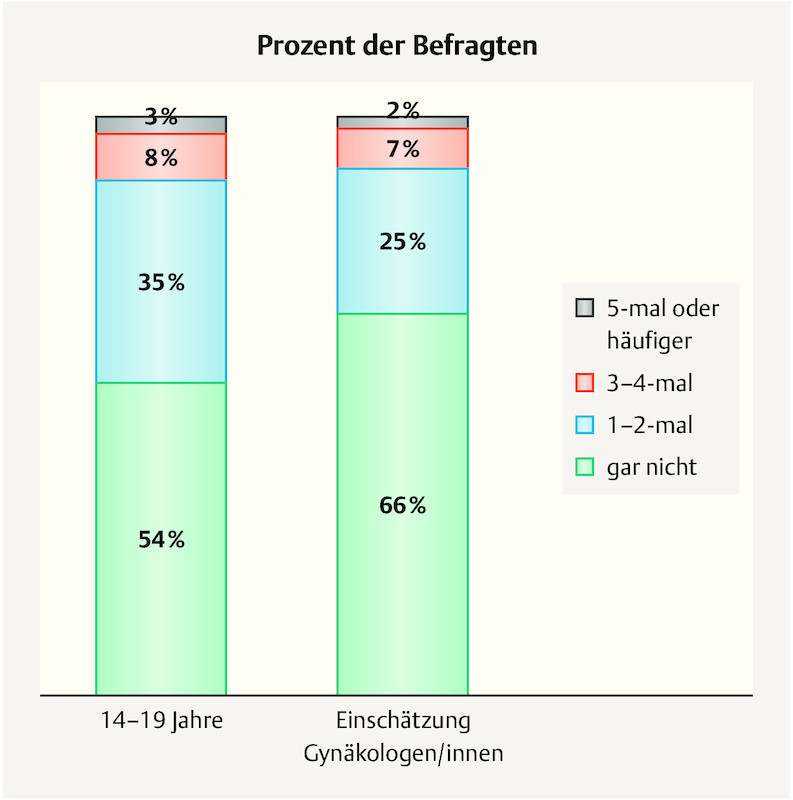
The proportion of patients finding the daily ingestion of the pill inconvenient was estimated by the gynaecologists at 28%. However, only 11% of pill users (combined pill) and 16% of those using the oestrogen-free pill actually reported that this was the case. This is not in tune with the high level of non-compliance among the adolescents: almost half had forgotten to take the pill once or twice in the previous three months alone (46% of combined pill users), and 11% of all pill users had even forgotten to take it more than three times during the previous three months ( Fig. 2 ). Comparing the dosage errors according to age (in a total of 18 521 women), they were roughly the same in all age groups, suggesting that compliance does not improve even with the growing routine of taking the pill. The treating gynaecologists estimated the compliance of their patients as much higher, on the other hand, at 66%.
Fig. 2.
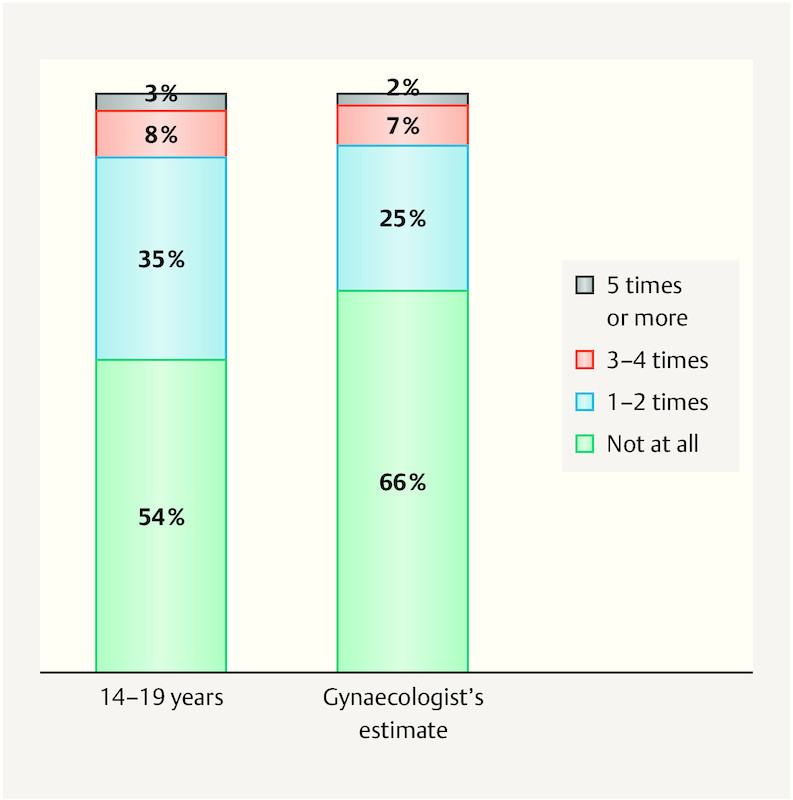
Frequency and percentage of pill users forgetting to take the pill in the previous three months, and an estimation by the gynaecologists on the frequency of forgetting.
Familiarity with contraceptive methods
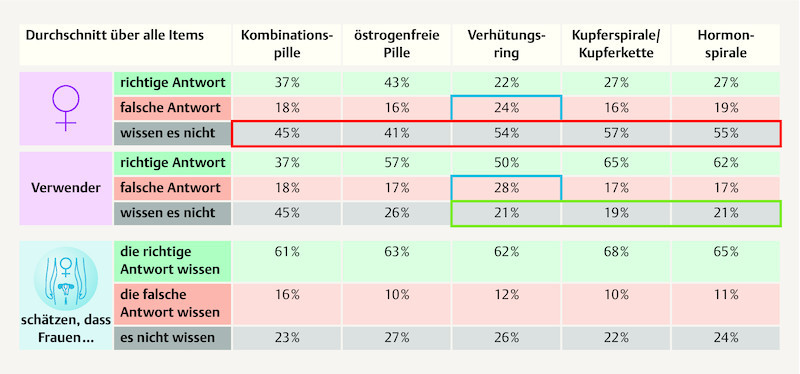
Almost two thirds of the girls (65%) believed they were (very) well-informed on the subject of contraception. At 59%, the gynaecologists estimated the level of information as somewhat lower (good or very good). The respondents recognised at least the name of more than five different methods of contraception (on average 5.3). The doctors assumed that the respondents would know an average of only 4.2 different methods. Looking at the distribution based on the present contraceptive method, users of the pill were able to name fewer potential methods of contraception (5.2) than users of the oestrogen-free pill, who on average named 5.4, and users of the vaginal ring who in fact could name 6.5 different methods of contraception.
Knowledge of the mechanism of action of different methods of contraception
The detailed knowledge of the participants concerning the individual methods of contraception was examined with a set of 12 questions (identical for each method).
Significant deficits become evident with respect to explicit knowledge about the mechanism of action of individual contraceptive methods (in particular the pill, oestrogen-free pill, vaginal ring, copper-based intrauterine devices, or levonorgestrel-based intrauterine devices). This applies not only to the entire group of patients, but also to the users of the respective contraceptive methods.
Combined pill
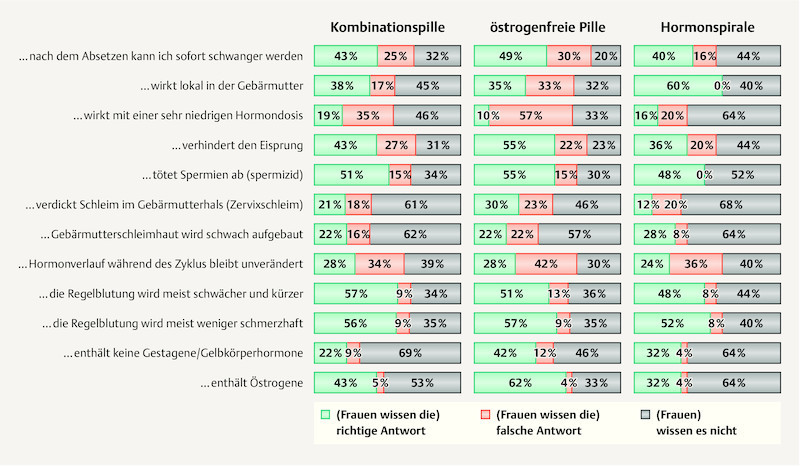
Only 43% of the respondents knew that the combined pill prevents ovulation. The doctors believed that 83% of the women would be aware of this. The fact that the hormone combination can have a positive effect on menstruation was also clear to only half of the women (44% incorrect or no answer). The physicians believed, on the other hand, that more than 90% of the women would know that menstrual periods are usually shorter, weaker and less painful when taking the pill. The women were particularly uncertain with respect to the content of progestogens (77% incorrect or no answer), the hormone dose (incorrect answer or no answer 81%) and the effects on cervical mucus, the endometrium and hormonal pattern during the cycle (79, 78, 73% incorrect or no answer) – in other words, even for the most commonly used method of contraception most of those surveyed (including even the users themselves) did not know how contraception with the pill works. Yet it is precisely this knowledge which is pivotal to understanding what to do, for example, in the event of a dosage error.
Vaginal ring
Compared with the knowledge of the women concerning oral contraceptives, the level of knowledge about the contraceptive ring is even lower. A major finding here, for instance, is that only 16% of the adolescents were aware that the contraceptive ring has no local effect. Only 21% of the respondents knew that the vaginal ring prevents ovulation. The doctors believed that 70% of the women would be aware of this. Only 20% knew that the ring can have a positive effect on menstruation. The doctors believed, on the other hand, that 84% of the respondents would know this. The only question answered correctly by more than half of the women was when pregnancy can occur after discontinuation (61% correct). The doctors also assumed in the case of the contraceptive ring that the level of knowledge among the women would be more comprehensive ( Fig. 3 ).
Fig. 3.
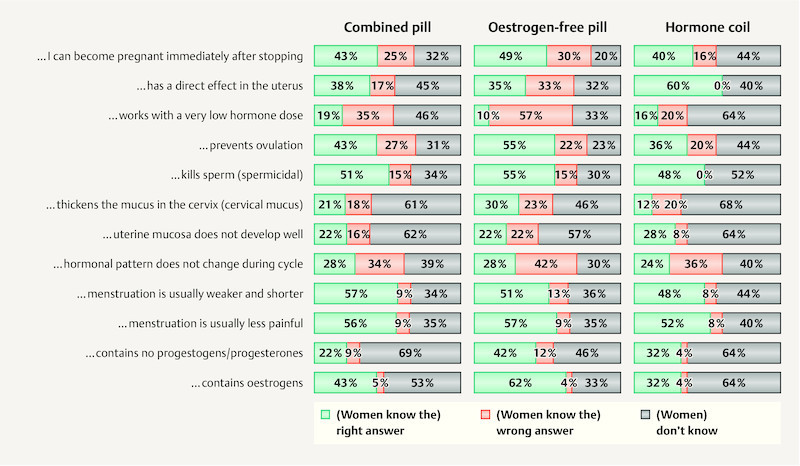
Knowledge of the mechanism of action of the combined pill in adolescents according to the method currently used (combined pill n = 2321, oestrogen-free pill n = 69 and hormone coil n = 25).
Copper coil/copper chain
More than two-thirds of the adolescents were unaware that hypermenorrhoea and dysmenorrhoea could be induced (71% incorrect or no answer in each case). The doctors believed, on the other hand, that more than two-thirds of the women would know that the copper coil and chain influence menstruation (79 and 78%, respectively, expected correct answers). The only questions concerning the copper coil and copper chain that were answered correctly by more than half of the women were whether you could become pregnant immediately after removal of the copper coil (52% correct) and that these methods have a local effect in the uterus (64% correct). However, 48% did not know whether the copper methods prevent ovulation and 21% assumed, even, that ovulation is prevented.
Hormone coil
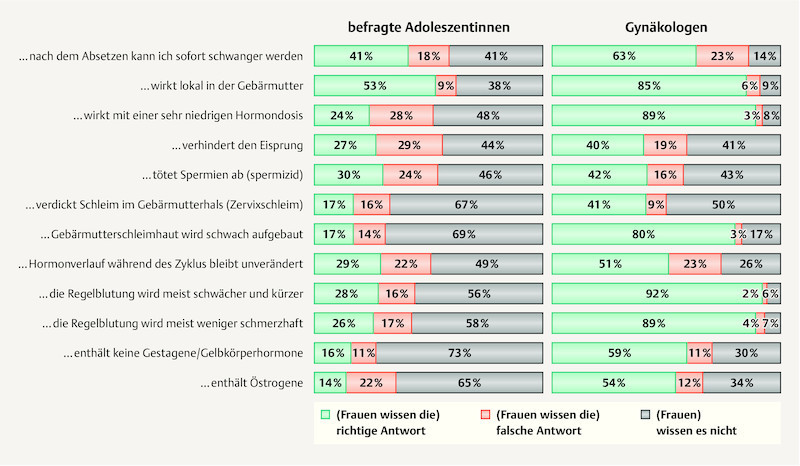
There was also a lot of ignorance concerning this method. As for the hormone content, 84 and 87% could not give the correct answer to the question on the progestogen and oestrogen content, respectively, of the hormone coil. Even users of the hormone coil were unable to correctly answer 80% of these questions. Of all those surveyed, 53% were at least aware that the hormone coil exerts a local effect in the uterus; among users this figure was 92%. The questions about conceiving after discontinuing use produced a similar picture (41% correct answers out of all the women, 96% from users of the hormone coil). The questions about the influence of the hormone coil on menstruation were answered incorrectly by 72% of all respondents, but only 4% of hormone coil users ( Fig. 4 ).
Fig. 4.
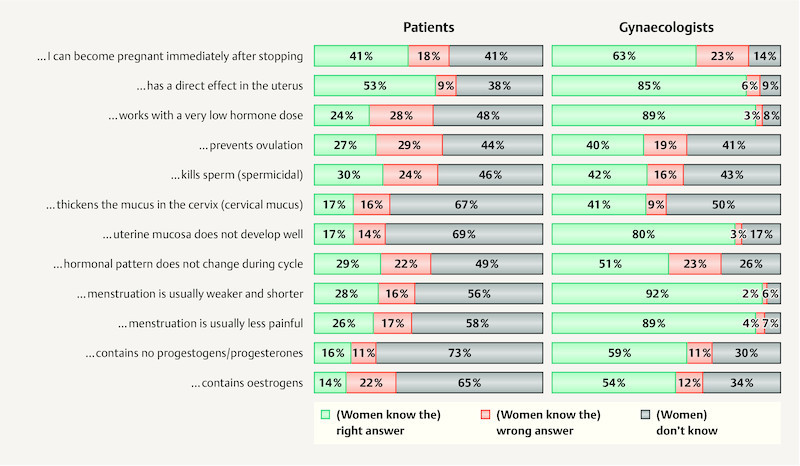
Knowledge of the mechanism of action of the hormone coil among adolescents (n = 2699) and estimation by gynaecologists (n = 1089) concerning knowledge of the hormone coil overall among the respondents.
Overall picture of knowledge concerning the mechanisms of action in adolescents
It is clear from the analysis that detailed knowledge concerning the individual methods, which is so important with respect to the mechanism of action and reliability of contraception, is in some cases very limited. On the whole, the number of questions that could be answered correctly by more than half of the women was much lower than the number of questions answered incorrectly or not answered at all. Knowledge concerning the contraceptive ring was particularly sparse: on average the participants answered correctly in only 22% and incorrectly in 24% of cases, and could not give an answer at all to 54% of the questions. This could be explained by the fact that the name of the contraceptive method suggests a local effect; though the method is indeed applied locally it has a similar systemic effect as combined oral products once absorbed through the vaginal mucosa. The highest level of knowledge was ascertained in relation to the oestrogen-free pill: an average of 43% of the answers were correct, 16% incorrect, and 41% of the questions could not be answered.
An average of 37% of the questions were answered correctly by users of a combined pill. With 65 and 50% correct answers, respectively, users of intrauterine contraceptive methods (copper coil/chain n = 4; hormone coil n = 25) proved to be most familiar with their method of contraception. The fact that gynaecologists consistently overestimate their patientsʼ knowledge and thus presume an awareness of many facts and circumstances appears to be of particular significance. However, in some cases such knowledge does still need to be imparted, especially as far as the reliability of contraception is concerned ( Fig. 5 ). Women on the combined pill, for instance, may be unsure whether an additional contraceptive method should be used, or whether the morning-after pill may even be necessary depending on the week in which a dosage error has occurred.
Fig. 5.
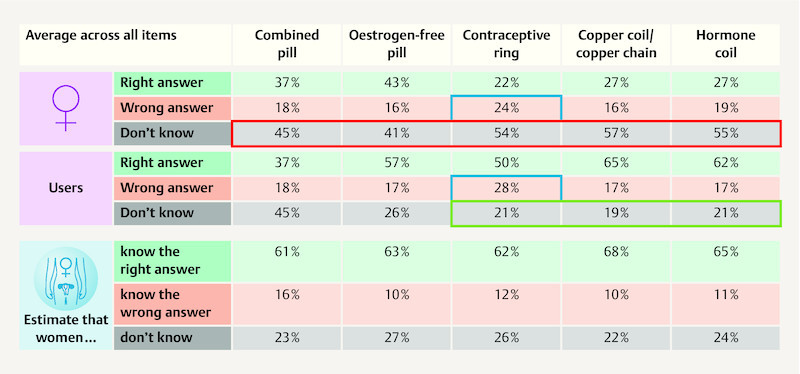
Overall picture of the knowledge of adolescents (n = 2699) and assessment by gynaecologists (n = 1089).
Potential for long-acting hormonal contraception in the group of 14 – 19-year-olds
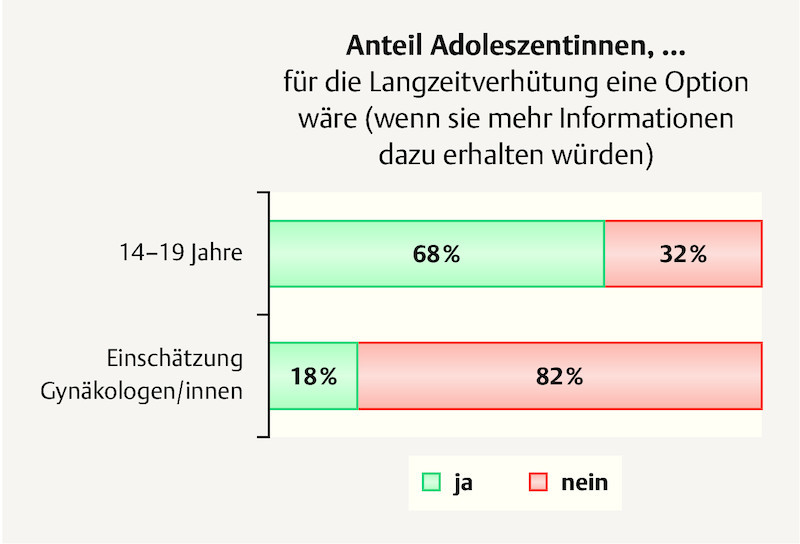
Among all respondents, 57% reported that they would like more information on long-acting contraception. The doctors assumed an interest of 25%.
After the participants had received a short description of long-acting contraceptive methods, 68% claimed that long-acting hormonal contraceptive would be an option. There is still a considerable gap between the desire of the patients and the perception of the gynaecologists, as the latter estimated that only 18% would be prepared to consider long-acting contraception.
The fact that long-acting contraception would resonate with such magnitude among young women, in particular, was perhaps not to be expected. The interest shown by adolescents and young women aged 20 – 24 years in long-acting contraception was significantly higher in fact than the average across all women ( Fig. 6 ). The huge interest in long-acting contraception on the part of young women and their desire for a reliable contraceptive method is contrasted strongly by the number of young women actually using long-acting contraception.
Fig. 6.
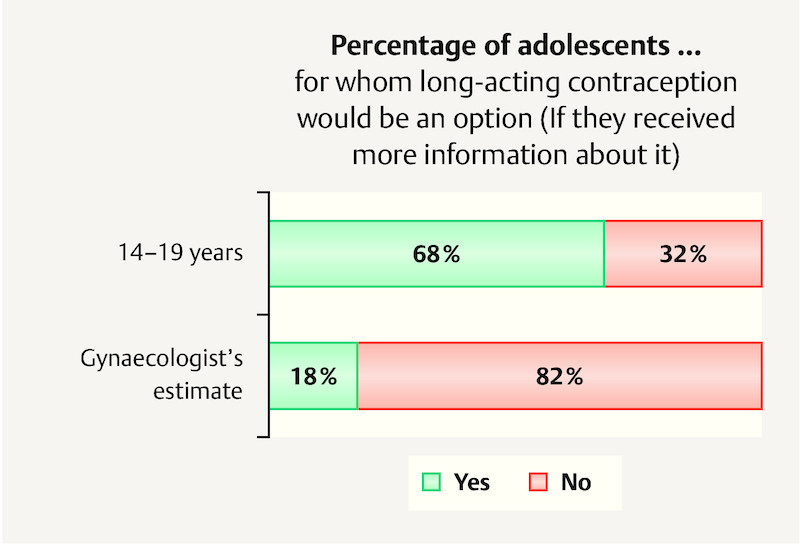
Potential for long-acting contraception by age (from Oppelt PG, Baier F, Fahlbusch C, Heusinger K, Hildebrandt T, Breuel C, Dittrich R. What do patients want to know about contraception and which method would they prefer? Arch Gynecol Obstet 2017; 295: 1483 – 1491).
Need for information on contraceptive methods
Considering the level of knowledge among the respondents, which was indeed low, the question arises as to whether there is a need among adolescent girls to be well-informed about common methods of contraception. A clear majority of the girls (70%) would like more information on alternative contraceptives to the pill. Again, there is a divergence here from the estimates made by the gynaecologists. Only 30% of the latter assumed that such information is desired.
A total of 51% of all participants agreed with the following statement: “Would you like to be informed occasionally/comprehensively by your gynaecologist about different methods of contraception?” Only 21% of the gynaecologists, however, expected the respondents to agree with this question.
Discussion
Only 2.4% of the adolescents who completed the questionnaire as part of the TANCO study and thus were under gynaecological supervision were using no form of contraception at the time. The vast majority of the adolescents were using a combined oral product (86%) ( Fig. 1 ). Alternative methods, such as the contraceptive ring and other long-acting contraceptives, were clearly underrepresented. The fact that the combined pill is generally the first step towards “reliable contraception” is evident not only from the large number of current users, but also from the fact that the majority of current users of a combined pill mostly have never previously used contraception or have used a condom. The majority of adolescents currently using a different method to the combined pill, moreover, previously used an oral contraceptive.
The question arises why reliable alternatives to the pill play such a minor role in the contraceptive practices of adolescents. Is there no need for alternatives? Are the existing alternatives not of interest to adolescents? Or do they perhaps have no idea about the possible alternatives to the pill?
The analysis of the data on awareness of the mechanism of action of various contraceptives clearly demonstrates that knowledge is indeed generally lacking among patients. This applies not only to the patientsʼ knowledge of how contraceptive methods work in general but also to the mechanism of action of the contraception they are actually using ( Fig. 3 and 4 ). Even with respect to the most commonly used method of contraception, i.e. the combined pill, most of those surveyed and even users themselves are not aware of how the contraceptive actually works. It is striking that users of intrauterine contraceptive methods (copper coil and levonorgestrel-based IUD) are far better informed than users of the pill – not only about the mechanism of action of their own contraceptive but also about other methods. This indicates that adolescents opting for an alternative form of contraception to the pill make a much more informed decision. Perhaps they are informed more thoroughly about all contraceptive methods by gynaecologists only if they specifically ask or if there are risk factors related to taking the pill, given that adolescents mostly present at the medical practice with no prior, specific expectations concerning the nature of their contraception, no risk factors, and a general desire for contraception, i.e. to take the pill. The surveyed gynaecologists assumed, at least, that only 25% of women would want more information on long-acting contraception and that it would be considered as an option in only 18%. However, 57% of adolescents in fact would like more information on long-acting contraception while 68% would indeed consider using long-acting contraception if they were to receive more information about it ( Fig. 6 ). These findings also confer with the data from the Contraceptive CHOICE project of 2010, in which 7637 women aged between 14 and 45 years were asked to select a contraceptive method, irrespective of cost, after attending a detailed, structured consultation 3 , 5 . A high level of willingness to use a long-acting contraceptive was also noted here in the subset of adolescents after they had been appropriately informed. A total of 69% of patients aged 14 – 17 years and 61% of those aged 18 – 20 years decided in favour of this form of contraception 5 , 6 , 7 . One reason why gynaecologists are wary about inserting intrauterine devices is the fear of a painful procedure. In 2014, a study into intrauterine devices involving 304 adolescents aged 12 – 17 years revealed that more than half of the patients found the insertion to be painless or only slightly painful. Only 10.9% reported that the procedure was very painful. This study also revealed a high level of satisfaction with the chosen method of contraception; 83.9% of the subjects were satisfied or very satisfied with the levonorgestrel-based intrauterine device 8 .
Looking at the degree of satisfaction in users of the pill, only 11% reported that they found taking the pill very inconvenient or inconvenient. This conflicts with the poor level of compliance in terms of regular intake, as 46% of adolescents stated that they had forgotten to take their pill at least once/twice in the previous three months ( Fig. 2 ). The compliance figures are also consistent with earlier surveys into this subject 9 , 10 , 11 .
Considering the insights gained into adolescentsʼ knowledge of contraceptives, compliance, and satisfaction with taking the pill, it must be assumed that due to the lack of awareness of alternative methods of contraception adolescents believe that taking the pill every day is an indispensable aspect of using a contraceptive that is regarded as reliable; hence, they do not question the necessity of daily intake.
The TANCO study also demonstrated that the doctors regard the compliance of the women under their care as better. This appears to explain why doctors underestimate the potential of information on alternative contraceptive methods ( Fig. 2 ).
Summary
Given its high level of reliability, simple handling and recognised additional benefit, the combined pill is certainly a legitimate first-line choice for contraception in most adolescents.
The findings of the TANCO study, however, reveal that the reliability of the pill is reduced on account of limited compliance. On the other hand, the data from the TANCO study reveal a clear discrepancy between the existing contraception, which was almost exclusively the pill, and the contraceptive options taken into consideration by the adolescent girls if comprehensively informed. The need for education into alternatives to the pill is high, as is the willingness to use such alternatives after receiving information – much higher than the figures suggested by the gynaecologists. With the insights into what female patients would like subsequent to the survey conducted as part of the TANCO study and awareness of limited compliance in taking the pill, we must at least question whether there is any justification for using combined oral contraceptives almost exclusively in adolescents or whether other contraceptive methods should be considered in a larger number of adolescents than was previously the case. It seems that a rethink is certainly necessary among gynaecologists concerning the need to comprehensively inform adolescents about the various methods of contraception, including long-acting contraceptives, as at present the practice does not reflect what patients want. Only if a patient is regularly informed comprehensively about all common, reliable methods of contraception can she decide whether an alternative contraceptive to her current method would be feasible. In the consultation itself it is helpful to support the information being provided with visual material 12 and offer the patient informational material so that she can again go over what has been discussed 12 .
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest/Interessenkonflikt Author Patricia G. Oppelt: lectures and expert opinions for Jenapharm; Gedeon Richter; MSD. The other authors have no conflict of interest. Autor Patricia G. Oppelt: Vorträge und Gutachten für Jenapharm; Gedeon Richter; MSD. Für sonstige Autoren besteht kein Interessenkonflikt.
References/Literatur
- 1.Alkema L, Kantorova V, Menozzi C. National, regional, and global rates and trends in contraceptive prevalence and unmet need for family planning between 1990 and 2015: a systemic and comprahensive analysis. Lancet. 2013;381:1642–1652. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bode H, Heßling A. Köln: Bundeszentrale für gesundheitliche Aufklärung; 2015. Jugendsexualität 2015. Die Perspektive der 14- bis 25-Jährigen. Ergebnisse einer aktuellen Repräsentativen Wiederholungsbefragung. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Secura G M, Allsworth J E, Madden T. The Contraceptive CHOICE Project: reducing barriers to long-acting reversible contraception. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;203:1150–1.15E9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.04.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Oppelt P G, Baier F, Fahlbusch C. What do patients want to know about contraception and which method would they prefer? Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2017;295:1483–1491. doi: 10.1007/s00404-017-4373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Madden T, Mullersman J L, Omvig K J. Structured contraceptive counseling provided by the Contraceptive CHOICE Project. Contraception. 2013;88:243–249. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2012.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mestad R, Secura G, Allsworth J E. Acceptance of long-acting reversible contraceptive methods by adolescent participants in the Contraceptive CHOICE Project. Contraception. 2011;84:493–498. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2011.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McNicholas C, Madden T, Secura G. The contraceptive CHOICE project round up: what we did and what we learned. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2014;57:635–643. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gemzell-Danielsson K, Dermout S, Lukkari-Lax E. A phase III single-arm study of a new 13.5 mg levonorgestrel intrauterine contraceptive system in postmenarcheal adolescents: an evaluation of efficacy, bleeding, user satisfaction, and placement. Fertil Steril. 2014;102:e141–e142. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rosenberg M J, Waugh M S, Meehan T E. Use and misuse of oral contraceptives: risk indicators for poor pill taking and discontinuation. Contraception. 1995;51:283–288. doi: 10.1016/0010-7824(95)00074-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brynhildsen J. Combined hormonal contraceptives: prescribing patterns, compliance, and benefits versus risks. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2014;5:201–213. doi: 10.1177/2042098614548857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aubeny E, Buhler M, Colau J C. Oral contraception: patterns of non-compliance. The Coraliance study. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2002;7:155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schweickhardt A, Fritzsche K. Deutscher Ärzteverlag; 2007. Kursbuch ärztliche Kommunikation: Grundlagen und Fallbeispiele aus Klinik und Praxis; mit 15 Tabellen. [Google Scholar]