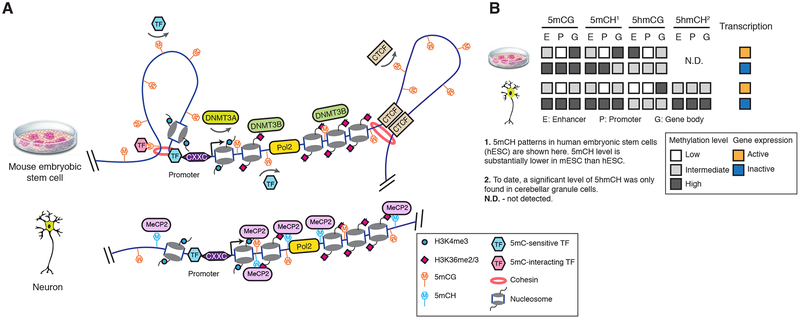
Figure 2.
The function and regulation of DNA methylation in diverse genomic contexts. (A) Gene promoter CpG islands are protected from 5mC by a CXXC domain containing proteins. De novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A activity is inhibited by H3K4me3. At distal regulatory elements, 5mC can either prohibit the binding of 5mC-sensitive TFs, or interact with TFs with preference for methylated binding sequence. DNA methylation at CTCF binding sites regulates chromatin conformation by modulating CTCF binding. In mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs, top), DNMT3B is recruited to transcribed regions by H3K36me and establishes gene body methylation. In post-mitotic neurons (bottom), 5mCH is bound by MeCP2. (B) Transcription outputs are correlated with 5mC and 5hmC levels of enhancers, promoters and gene bodies.