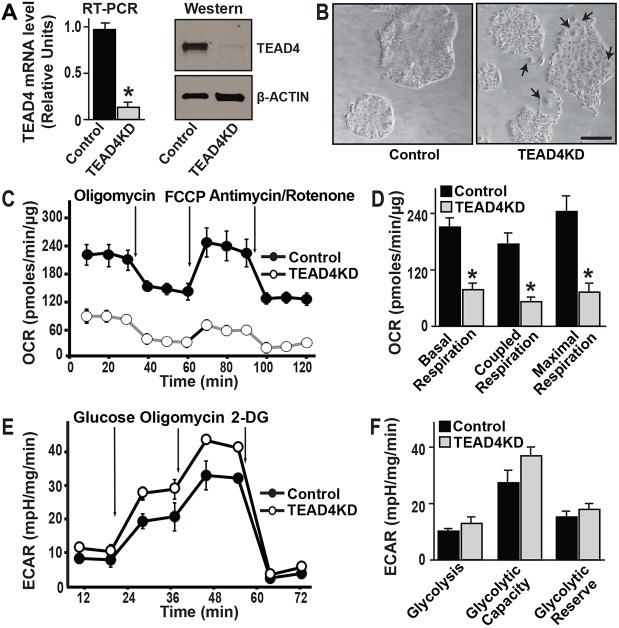
Fig. 2.
TEAD4 is important for oxidative respiration in mouse TSC. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR and western blot analyses showing depletion of TEAD4 mRNA and protein expression in TSCs upon shRNA-mediated RNAi (TEAD4KD). (B) Micrographs of control and TEAD4-depleted TSC colonies (passage 2 after RNAi) in TSC culture conditions. The TEAD4KD TSCs are characterized with more visible cellular boundaries in cell colonies and the presence of higher numbers of differentiated trophoblast giant cells (TGCs, arrows), indicating propensity toward differentiation. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C) A mitochondrial stress test was performed to measure oxygen consumption rates (OCRs) in control and TEAD4KD TSCs. (D) Quantitative analyses of OCR in control versus TEAD4KD TSCs. Plots show strong reduction in oxidative respiration in TEAD4KD TSCs. (E) Control and TEAD4KD TSCs were subjected to a glycolysis stress test by adding glucose, oligomycin and 2-deoxy glucose (2-DG) at different time intervals and changes in the extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) were measured. The graphs show representative ECAR profiles. (F) Plots show only modest changes in glycolysis rate and maximal glycolytic capacity in TSCs upon TEAD4 depletion. *P<0.001. Data are mean±s.e.m.