Abstract
Background/aim
Retraction of the upper incisors/canines requires maximum anchorage. The aim of the present study was to analyze the efficacy of mini implants in comparison to conventional devices in patients with need for en masse retraction of the front teeth in the upper jaw.
Material and methods
An electronic search of PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE and hand searching were performed. Relevant articles were assessed, and data were extracted for statistical analysis. A random effects model, weighted mean differences (WMD), and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were computed for horizontal and vertical anchorage loss at the first molars in the analyzed patient treatments.
Results
A total of seven RCTs employing direct anchorage through implants in the alveolar ridge were finally considered for qualitative and quantitative analysis, and further five publications were considered for the qualitative analysis only (three studies: indirect anchorage through implant in the mid-palate, two studies: direct/indirect anchorage in the alveolar ridge). In the control groups, anchorage was achieved through transpalatal arches, headgear, Nance buttons, intrusion arches, and differential moments.
WMD [95% CI, p] in anchorage loss between test and control groups amounted to − 2.79 mm [− 3.56 to − 2.03 mm, p < 0.001] in the horizontal and − 1.76 mm [− 2.56 to − 0.97, p < 0.001] favoring skeletal anchorage over control measures. The qualitative analysis revealed that minor anchorage loss can be associated with indirect anchorage, whereas anchorage gain was commonly associated with direct anchorage. Implant failures were comparable for both anchorage modalities (direct 9.9%, indirect 8.6%).
Conclusion
Within its limitations, the meta-analysis revealed that maximum anchorage en masse retraction can be achieved by orthodontic mini implants and direct anchorage; however, the ideal implant location (palate versus alveolar ridge) and the beneficial effect of direct over indirect anchorage needs to be further evaluated.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s40729-018-0144-4) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Bone screws, Orthodontic anchorage procedures, TAD, En masse retraction, Mini implants, Micro implants, Systematic review, Meta-analysis
Review
Background
Extraction of the permanent teeth for retraction of the protruded front teeth is a routine approach in orthodontics. Various techniques such as headgear, Nance button, and transpalatal arches (TPA) have been proposed to achieve sufficient anchorage [5, 8, 9, 12, 28, 31, 45]. Nevertheless, anchorage control turned out to be highly demanding as the conventional approaches were commonly associated with anchorage loss, i.e., mesial migration of the posterior dental anchorage units.
In order to improve anchorage control, differential moments have been described and monitored in clinical studies [25, 26]. The outcomes were promising, but nevertheless, anchorage loss and unexpected space opening most probably due to activation failures have also been reported. Some authors suggested that consecutive canine and front retraction may be more effective than en masse retraction of the front segment to preserve anchorage. Despite this, the effectiveness of this approach is still discussed, and controversial outcomes have been reported [18, 60].
In the past two decades, temporary orthodontic anchorage devices (TADs) including orthodontic mini implants and mini-plates have been introduced to improve anchorage control [39, 56, 57]. Orthodontic implants can be loaded directly after insertion and are usually removed after treatment completion [17, 36]. Therefore, orthodontic mini implants most often have a smooth surface to ease removal [32], whereas mini-plates are more invasive and require surgical intervention and flap preparation [6]. For this reason, orthodontic mini implants are frequently used, and two concepts are predominant: One is to stabilize a dental anchorage unit by connecting it to the implant (indirect anchorage), and the other is to directly load the orthodontic mini implant with the reactive forces (direct anchorage) [42].
Accordingly, there is a need to identify if orthodontic mini implants are more effective to control anchorage compared to conventional devices, and to assess if the direct or indirect anchorage concept is more beneficial. The aim of this systematic review was therefore to address the following question: “In patients with a need for en masse retraction of the upper front teeth, what is the efficacy of orthodontic mini implants for anchorage quality compared with conventional devices?”
Methods
This systematic review was structured and conducted according to the preferred reporting items of the PRISMA statement [34].
Focused question
The focused question serving for literature search was structured according to the PICO (Patients, Intervention, Control, Outcome) format: “In patients with a need for en masse retraction of the upper front teeth, what is the efficacy of orthodontic mini implants for anchorage control compared with conventional devices?” According to the PICO convention, this question has been formulated as follows:
Patients: for which subgroups of patients with a need for en masse retraction of the upper incisors/canines
Intervention: do orthodontic mini implants have a benefit over conventional devices?
Control: compared to forgoing orthodontic mini implants (compared to conventional treatment)
Outcome: with regard to treatment efficacy (anchorage control), treatment duration, potential harms (inflammation, implant loss)
Search strategy
The PubMed database of the US National Library of Medicine, EMBASE, and the Web of Knowledge of Thomson Reuters were used as electronic databases to perform a systematic search for relevant articles published in the dental literature between 1992 and Dec 31, 2017. Furthermore, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) was searched manually.
A commercially available software program (Endnote X7, Thomson, London, UK) was used for electronic title management. Screening was performed independently by two authors (K.B. and M.W.). Disagreement regarding inclusion during the first and second stage of study selection was resolved by discussion.
The combination of key words (i.e., Medical Subject Headings MeSH) and free text terms included:
-
Search terms PubMed/MEDLINE (including MeSH terms)
- (“en-masse retraction” OR “incisor retraction” OR “front retraction” OR “orthodontic gap closure” OR or “orthodontic space closure” OR “extraction therapy” [mh])AND (“mini implants” OR “micro screws” OR “micro implants” OR “skeletal anchorage” OR “palatal implant” OR “skeletal” OR “skeletal anchorage” OR “implant” OR “bone screw” OR “temporary anchorage device” OR “TAD” OR “Bone screws”[mh] OR “intraosseous screw” OR “dental implants”[mh])
- AND (“anchorage loss” OR “anchorage quality” OR “quality of life” OR “benefit” or “harm” OR “efficacy” OR “side effects” OR “effect” OR “orthodontic anchorage procedures”[mh] OR “treatment outcome”[mh])
-
Search terms EMBASE (including EMTREE terms)
- (“en-masse retraction” OR “incisor retraction” OR “front retraction” OR “orthodontic gap closure” OR “orthodontic space closure” OR “extraction therapy” [EMTREE]) AND (“mini implants” OR “micro screws” OR “micro implants” OR “skeletal anchorage” OR “palatal implant” OR “skeletal” OR “skeletal anchorage” OR “implant”[EMTREE] OR “bone screw”[EMTREE] OR “tooth implant”[EMTREE] “temporary anchorage device” OR “TAD” OR “Bone screws” OR “intraosseous screw” OR “dental implants”) AND (“anchorage loss” OR “anchorage quality” or “quality of life” OR “benefit” OR “harm” OR “efficacy” OR “side effects” OR “effect” OR “orthodontic anchorage”[EMTREE] OR “treatment outcome”)
Hand search
The electronic search was complemented by a hand search of the following journals: American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Oorthopedics, The Angle Orthodontist, European Journal of Orthodontics, Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics, Orthodontics and Craniofacial Research, and Seminars in Orthodontics.
Finally, the references of all selected full-text articles and related reviews were scanned. If required, the corresponding authors were contacted and requested to provide missing data or information.
Study selection
During the first stage of study selection, the titles and abstracts were screened and evaluated according to the following inclusion criteria:
English language
Prospective controlled clinical trials (CCT) (for qualitative synthesis) or randomized controlled clinical trials (RCT) (for qualitative and quantitative synthesis, parallel group designs) in humans comparing mini implant based on conventional anchored treatments
Patients: general population (all ethnicities, community dwelling)
Measurement of anchorage loss of the first upper molars during retraction
At the second stage of selection, all full-text articles identified during the first stage were acquired. During this procedure, the pre-selected publications were evaluated according to the following exclusion criteria:
Patients younger than 12 years
No bilateral extraction of one upper premolar per site
Inclusion of less than five patients
Lack of clinical data on anchorage loss
Measurement of anchorage loss not by superimposition of lateral cephalograms or superimposition of study casts
Previous orthodontic treatment
Treatment in control group not specified
Inclusion of diseased patients, e.g., patients with systemic diseases, periodontal disease, and syndromes
Other treatment than en masse retraction and mini implants
Other sources of skeletal anchorage than orthodontic mini implants or micro implants
Data extraction and method of analysis
At least two review authors examined the titles and abstracts of the identified studies and reports independently. Reports which were clearly not relevant were excluded, whereas full-text documents were retrieved for all potentially relevant studies and eligibility was assessed according for the criteria defined in advance. Disagreements were resolved by open discussion occasionally arbitrated by an independent assessor (D.D.). A data extraction template was generated including the items’ study design, population, type of implants, number of implants, location of the implants, time points of observation, treatment duration, control intervention, measurement method, and primary and secondary outcomes as well as risk of bias (Additional file 1). Data extraction was performed independently by at least two review authors.
For qualitative and quantitative data analysis, the horizontal and vertical anchorage loss values associated with direct and indirect anchorage against a control measure were defined as primary outcomes. For qualitative data analysis, transversal anchorage loss, treatment duration, and implant failures with direct and indirect anchorage were defined as secondary outcomes.
Quality assessment of selected studies
A quality assessment of all selected full-text articles was performed according to the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias (low, high, unclear) including the following domains: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other sources of bias.
Quality assessment was performed in two different phases. In the first phase, quality assessment was conducted independently by at least two authors (A.P., C.B., K.B.) based on the published full-text articles. In the second phase, disagreements were resolved by discussion. A risk of bias table was completed for each included study.
Dealing with missing data and zero values
When data were not available in the printed report, we calculated the missing information whenever possible (e.g., by subtracting pre- and post en masse retraction values). In cases where a zero variance (0.00 mm) was presented in the summary tables, these values were changed to 0.01 mm to enable meta-analysis. The corresponding authors of the published studies were contacted when needed.
Data synthesis
Heterogeneity among the clinical trials, meta-analysis (i.e., weighted mean differences and 95% confidence intervals, random effects model to account for potential methodological differences between studies), forest plots, and publication bias (Egger’s regression to quantify the bias captured by funnel plots) were assessed using a software program (Review Manager (RevMan) version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012).
Results
Description of studies
Study selection
The search for the review was undertaken at December 31, 2017. A total of 2046 potentially relevant titles and abstracts were found during the electronic and manual search (676 after duplicate removal) of which 99 titles were considered relevant for abstract screening. During the first stage of study selection, 58 publications were excluded based on the abstract. For the second phase, the complete full-text articles of the remaining 41 publications were thoroughly evaluated. A total of 29 papers had to be excluded at this stage because they did not comply with the inclusion or exclusion criteria of the present systematic review (Table 1).
Table 1.
List of excluded studies (with reason)
| Reference | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Barros et al. (2017) [3] | Anchorage loss at first molar not specified |
| Borsos et al. (2012) [7] | No en masse retraction (two step canine and front retraction) |
| Dai et al. (2009) [10] | Chinese language |
| Durrani et al. (2017) [13] | Anchorage loss a first molar not specified |
| El-Beialy et al. (2009) [14] | Anchorage loss a first molar not specified |
| Garfinkle et al. (2008) [16] | Anchorage loss at first molar not specified |
| Heo et al. (2007) [18] | No mini implants used for anchorage |
| Herman et al. (2006) [19] | Anchorage loss a first molar not specified |
| Janson et al. (2013) [22] | Anchorage loss a first molar not specified |
| Jee et al. (2014) [23] | Use of mini implants and mini-plates |
| Kuroda et al. (2009) [27] | T0 ceph before leveling (anchorage loss not specified during en masse retraction only) |
| Liu et al. (2011) [29] | Anchorage loss at first molar not specified |
| Ma et al. (2015) [30] | Full-text unavailable (requested but no response from authors) |
| Miyazawa et al. (2010) [33] | Anchorage loss at first molar not specified |
| Monga et al. (2016) [35] | Retrospective study |
| Park et al. (2004) [38] | Case report |
| Park et al. (2007) [40] | Case report |
| Park et al. (2008) [41] | Retrospective study |
| Santiago et al. (2009) [43] | No en masse retraction, anchorage loss at first molar not specified |
| Shi et al. (2008) [44] | Extraction of premolars or molars |
| Thiruvenkatachari et al. (2006) [46] | Canine retraction only |
| Turkoz et al. (2011) [47] | No premolars extracted |
| Upadhyay et al. (2012) [51] | No premolar extraction |
| Gollner et al. (2009) [17] | No premolar extraction |
| Wehrbein et al. (1996a) [55] | Case report |
| Wehrbein et al. (1996b) [56] | Case report |
| Xu et al. (2008) [59] | Language not meeting inclusion criteria |
| Xun et al. (2004) [61] | Language not meeting inclusion criteria |
| Yao et al. (2008) [62] | Retrospective study, mini-plates, and mini implants used |
Finally, a total of 12 publications (reporting on 12 studies) were considered for the qualitative and a total of 9 publications for the quantitative assessment (Fig. 1). However, only two RCTs were found comparing indirect anchorage with conventional anchorage devices, whereas 7 studies compared direct anchorage with the control intervention. At this stage, it was decided to perform the quantitative analysis only for the direct anchorage groups. The two studies comparing indirect anchorage with a control intervention were included in the qualitative analysis only. Summary details of the included studies are given in Table 2.
Fig. 1.
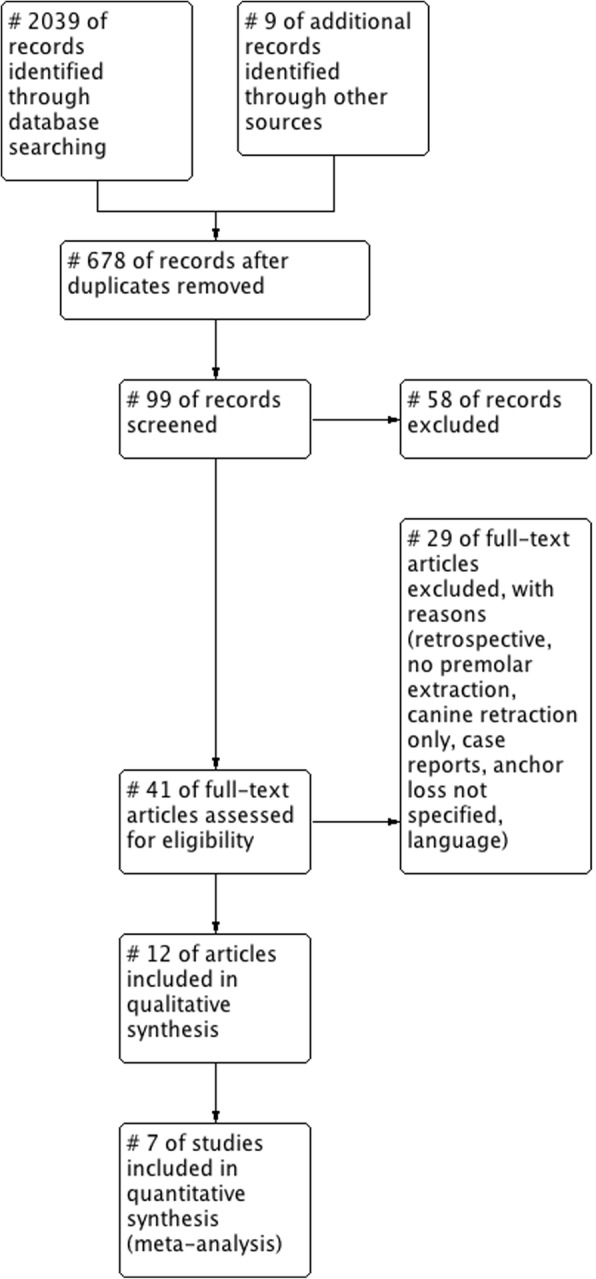
PRISMA study flow diagram
Table 2.
Characteristics of the included studies (TPA transpalatal arch, RCT randomized controlled clinical trial, CCT controlled clinical trial)
| Reference | Number of patients | Type of study (RCT/CCT/other) | Control intervention | Type of implant (length, material) | Number of implants | Location of implant | Mode of anchorage (direct/indirect) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Sibaie and Hajeer [1] | 56 (28 implant, 28 non implant) | RCT | TPA | Self-drilling titanium mini implants (1.6 mm diameter and 7 mm length; Tuttlingen, Germany) | 2 | Between the maxillary second premolar and first molar | Direct |
| Basha et al. [4] | 14 (7 implant, 7 non implant) | RCT | TPA | Surgical steel mini implants (1.3 mm diameter, 8 mm length; SK Surgical, Pune, India.) | 2 | Placed between the roots of second premolar and first molar in the maxilla | Direct |
| Benson et al. [5] | 51 (23 implant; 24 non implant) | RCT | Headgear | Ortho implant, (6 mm length, Straumann, Waldenburg, Switzerland) | 1 | Midpalatal | Indirect |
| Chopra et al. [9] | 50 (25 implant; 25 non implant) | RCT | Nance button; lingual arch | Self-drilling titanium ortho implants | 4 | Buccal alveolar bone between the second premolars and first molars in all the four quadrants | Indirect |
| Davoody et al. [11] | 46 (23 implant, 23 non-implant group) | RCT | Intrusion arch and mushroom loops | 1.8–2 mm in width, 8–9 mm in length | 4 | Placed between maxillary second premolars and first molars in all four quadrants | Direct |
| Liu et al. [28] | 34 | RCT | TPA | Self-tapping titanium mini-screw implants (8 mm length, 1.2 mm diameter, Cibei, Ningbo, China) | 2 | Between the roots of the first molar and the second premolar | Direct |
| Upadhyay et al. [49] | 30 (15 implant, 15 non-implant) | RCT | Treatment in control group not specified: Nance holding arch, extraoral traction, banding of the second molars, and differential moments | Custom made at our institute by modifying conventional surgical screws, measuring 1.3 mm in diameter and 8 mm in length | 2 | Placed between the maxillary second premolar and first molar, preferably between the attached and movable mucosae | Direct |
| Upadhyay et al. [48] | 23 | Other (cohort study) | No control group | Titanium mini implants (1.3 mm in diameter and 8 mm in length) | 2 | Placed between the roots of the first molar and the second premolar in both upper quadrants | Direct |
| Upadhyay et al. [50] | 40 (20 implant, 20 non implant) | RCT | Conventional methods such as headgears, transpalatal arches, banding of second molars, application of differential moments | Titanium mini implants (1.3 mm diameter, 8 mm length) | 4 | Between the roots of the first molar and second premolar in all four quadrants | Direct |
| Victor et al. [52] | 20 (10 implant, 10 non-implant) | RCT | NiTi closed coil spring | Absoanchor—SH 1312-08; (1.3 mm diameter, 8 mm length) | 4 | Placed between the roots of second premolar and first molar in the upper arch, the screw insertion was angulated at 40° and 8 mm gingival to the archwire | Direct |
| Wehrbein et al. [54] | 9 | Other (cohort study) | No control group | Orthosystem (diameter 3.3 mm, lengths are 4 and 6 mm) | 1 | Midpalatal | Indirect |
| Wilmes et al. [57] | 20 (10 in implant group of which 5 patients had additional transversal reinforcement and 5 did not, 10 in non-implant group) | CCT | TPA | 2.0 × 10 mm, Dual Top™, Jeil Medical Corporation, Seoul, South Korea, or 2.0 × 11 mm, BENEFIT, Mondeal Medical Systems, Mühlheim a.d. Donau, Germany | 1 | Placed in the anterior palate | Indirect |
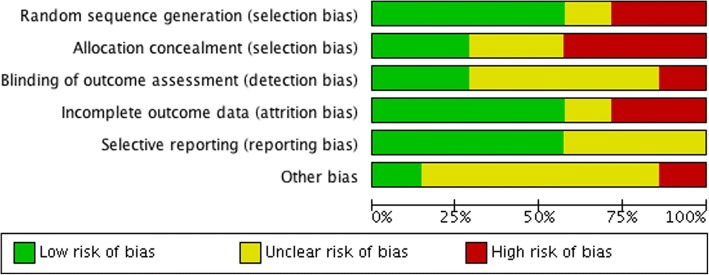
Risk of bias in the included studies
The review author’s judgment about each risk of bias item for each included RCT is presented in Table 3 and Fig. 2. From the studies included in the meta-analysis, two studies were assessed at low risk of bias [11, 49], three studies at moderate risk [1, 28, 50], and two at high risk of bias [4, 52]. Risk of bias was not judged for the studies included in the qualitative synthesis that either had no control group, employed indirect anchorage (see above, the “Study selection” section), had more than one test group, or lacked a non-implant control group [5, 9, 48, 54, 57].
Table 3.
Risk of bias judgment according to the Cochrane Collaboration
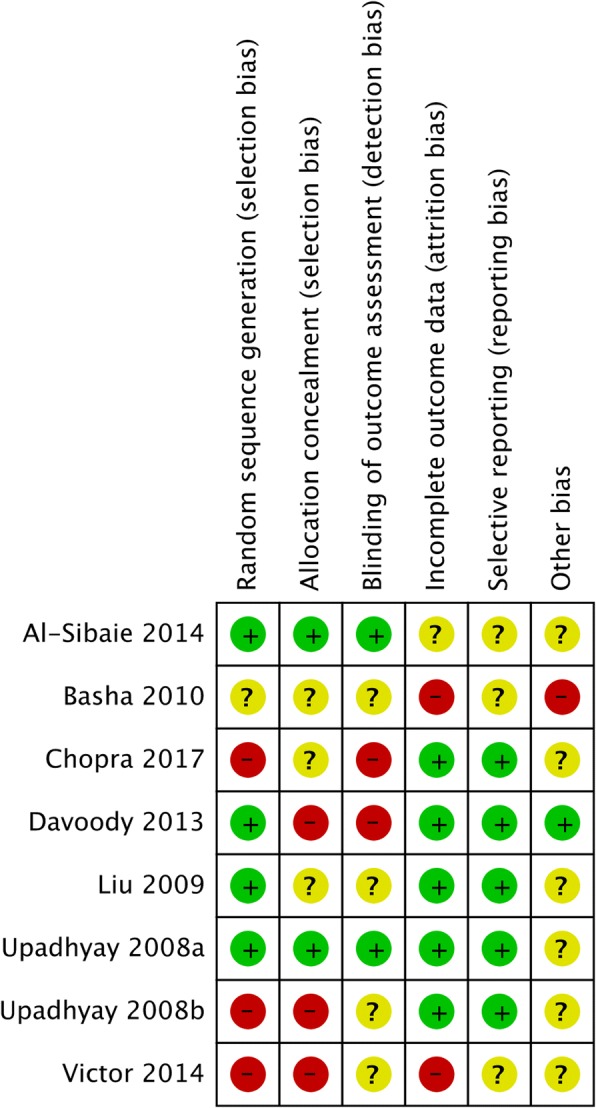
Fig. 2.
Graphic visualization of the risk of bias judgements
Characteristics of the patients
The study samples consisted of patients exhibiting an Angle Class II,1 malocclusion [1, 5], patients with an Angle Class I requiring front retraction with maximum anchorage [4], patients exhibiting dental bi-maxillary protrusion with Angle Class I [9], patients with a need for extraction of four premolars (one in each quadrant) and maximum anchorage for front retraction [28], patients in need of extraction of the first upper premolars and front retraction [52], Angle Class I [49], patients with Angle Class II,1 with dental protrusion [50], or either Angle Class I or Class II with dental protrusion [11].
The study samples considered for the qualitative synthesis consisted of females exhibiting Angle Class II,1 malocclusion with upper dental protrusion and an overjet of at least 7 mm [48], patients with a dental Class II, a need for extraction of the first upper premolars and front retraction [54], or Class III patients with a need for pre-surgical decompensation through premolar extraction and front retraction [57].
Interventions
The majority of studies employed mini implants in direct anchorage mode placed bilaterally in the alveolar ridge. After leveling, alignment, and placement of a passive stainless-steel arch (varying from 0.019″ × 0.025″ to 0.016″ × 0.0022″), the implants were placed between the tooth roots. Retraction was achieved through sliding mechanics using either power chains or nickel titanium coil springs of usually 100–200 g. Implant lengths varied from 7 to 9 mm, and the diameter varied from 1.2 to 2.0 mm (Table 2). All implants were loaded within 3 days [1, 11, 28, 48–50, 52].
In the majority of the indirect anchorage groups, a single mini implant was placed in the anterior palate and connected to the first molars through an individually fabricated transpalatal arch [5, 54, 57]. Whereas three studies used the Straumann® Ortho (Basel, Switzerland) system and employed loading after 3 months of healing [5, 54], one study used either a 2 × 10 mm Dual Top™ (Jeil Medical Corporation, Seoul, South Korea) or a 2.0 × 11 mm BENEFIT® (Mondeal Medical Systems, Mühlheim, Germany) implant and employed immediate loading. One study employed indirect anchorage through a mini implant located in the alveolar ridge [9] (Table 2).
In the control groups, the majority of studies employed transpalatal arches. Interventions such as headgear, Nance button, intrusion arches, and differential moments were also employed (Table 2).
Effects of intervention
Anchorage loss
Anchorage loss was a common finding for all control interventions. In the test groups, anchorage loss was also associated with indirect anchorage using mid-palatal implants. Mesial tooth migration was always lower in indirect anchorage mode compared to conventional anchorage groups (if evaluated) [5, 54, 57].
In detail, anchorage loss associated with indirect anchorage and a mid-palatal implant amounted to 1.5 ± 2.6 mm versus 3 ± 3.4 mm [5], 0.7 ± 0.4 (right molar) and 1.1 ± 0.3 mm (left molar) [54], 1.73 ± 0.39 mm (horseshoe), and 0.36 ± 0.11 mm (posterior reinforcement) versus 4.21 ± 1.17 mm [57]. An anchorage loss of 0.2 ± 0.35 mm versus 2.0 mm ± 0.65 mm was also observed in one study employing indirect anchorage using two implants in the alveolar ridge [9].
In contrast, no anchorage loss [4] or anchorage gain/reverse anchorage loss (distal movement) was observed in the groups employing direct anchorage through implants located interdentally in the alveolar ridge [1, 11, 28, 48–50, 52].
Vertical anchorage loss with molar extrusion was another common observation for the control interventions [1, 11, 28, 49, 50, 52]. In the majority of the studies, molar intrusion was commonly associated with direct skeletal anchorage [11, 28, 48–50, 52], but one study observed a minor extrusion tendency of 0.02 ± 0.93 mm associated with direct anchorage [1]. Vertical anchorage loss associated with indirect anchorage has not been evaluated.
Transversal anchorage loss with a mean expansion of 1.73 ± 0.39 mm following retraction was observed in one study employing indirect anchorage through a mid-palatal mini implant coupled with a horseshoe arch [57]. This tendency of transversal expansion could be reduced to 0.36 ± 0.11 mm by integration of a posterior reinforcement element. In contrast, a significant decrease in inter-molar width was observed in two studies employing direct anchorage through mini implants in the alveolar ridge [48, 50]. The inter-molar width reduction amounted to − 1.83 ± 1.29 mm [50] and may be counterbalanced by a transpalatal arch or by applying buccal crown torque on the molars [48]. The remaining studies, which analyzed lateral cephalograms only, did not report on anchorage loss in the transversal dimension. None of the studies compared transversal changes following skeletal anchorage with conventional control measures.
Retraction velocity and treatment duration
In the test groups, the monthly rate of posterior movement from the incisors amounted to 0.35 mm with a mean retraction duration of 12.9 months [1], 0.85 mm with a mean retraction duration of 6.0 months [4], 0.11 mm with a mean retraction duration of 21.76 months [9], 0.28 mm with a mean retraction duration of 26 months [28], 0.85 mm with a mean retraction duration of 8.61 months [49], and 0.44 mm with a mean retraction duration of 9.4 months [48].
Implant failures
The overall success rates of the orthodontic mini implants varied among the studies. A success rate of 95.7% with a loss of 2 from 46 implants was reported by Upadhyay et al. [48], and the implants could be replaced immediately. Two patients developed a peri-implant inflammation which was resolved through improved oral hygiene. A loss of 5 of 72 implants was reported by Upadhyay et al. [49], and in 2 patients, treatment was discontinued due to inflammation, which was resolved through improved oral hygiene. Davoody et al. [11] observed a success rate of 84% (5 of 30 implants), and Basha et al. [4] reported a success rate of 71.4%. In their study, 4 of 14 implants became loose during treatment but could be replaced subsequently. In further 4 patients, treatment was discontinued due to inflammation, which was resolved through improvement of oral hygiene. A success rate of 96% with a loss of 2 from 50 implants in the upper alveolar ridge due to peri-implant inflammation was observed by Chopra et al. [9], who employed indirect anchorage in the alveolar ridge. Similar values were reported by Benson et al. [5], who employed indirect anchorage through a mini implant in the mid-palate. In their study, in 6 of 24 patients, the implant failed to reach primary stability. In 4 patients, the implant had to be replaced during treatment, and in 2 patients, treatment was compromised due to implant failure. All implant failures occurred among the first implants placed by the surgeon, and no implant loss was observed for implants with sufficient primary stability.
A success rate of 100% with no signs of implant mobility, inflammation, or loss were observed in two studies [54, 57] in which indirect anchorage through mid-palatal implants was employed.
Summarizing these findings, implant loss was observed at 8 of 93 implants (8.6%) in the indirect anchorage group. In the direct anchorage groups, implant loss was reported for 16 of 162 implants (9.9%).
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis was performed on RCTs reporting on anchorage loss at the first molar.
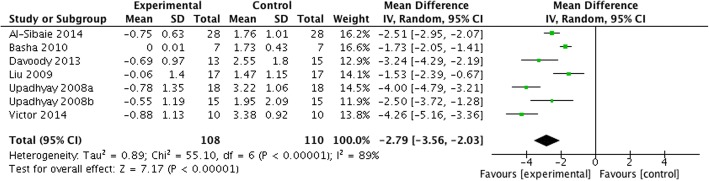
Based on seven studies [1, 4, 11, 28, 49, 50, 52], the weighted mean differences (WMD) [95% CI, p] in horizontal anchorage loss between test and control groups amounted up to − 2.79 mm [− 3.56 to − 2.03 mm, p < 0.0001] favoring skeletal anchorage over conventional anchorage devices (Fig. 3). The heterogeneity among the analyzed studies was high (τ2 = 0.89, I2 = 89%).
Fig. 3.
Forest plot for anchorage loss in the horizontal dimension
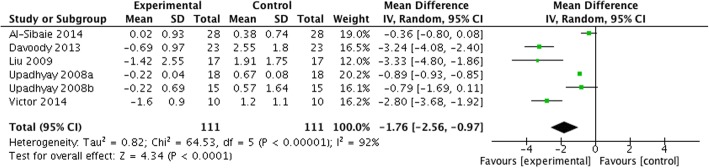
Based on six studies [1, 11, 28, 48–50, 52], the WMD [95% CI, p] in vertical anchorage loss between test and control groups amounted to − 1.76 [−.56 to − 0.97 mm, p < 0.0001] favoring skeletal anchorage over control measures. The heterogeneity among the studies was high (τ2 = 0.82, I2 = 92%) (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Forest plot for anchorage loss in the vertical dimension
Funnel plots of the intervention effect estimates (presented as mean differences) plotted against standard errors are presented in Figs. 5 and 6. Their symmetricity suggests the absence of publication bias.
Fig. 5.
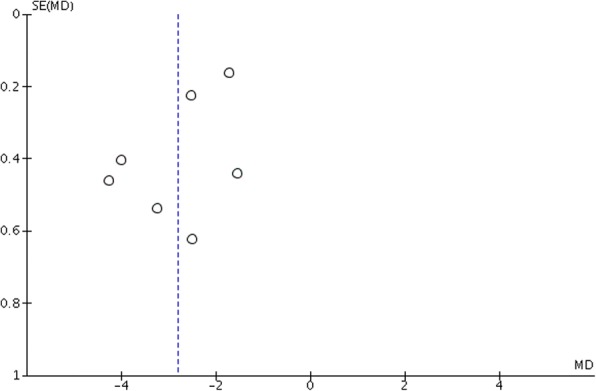
Funnel plot for anchorage loss in the horizontal dimension (MD mean difference, SE standard error)
Fig. 6.
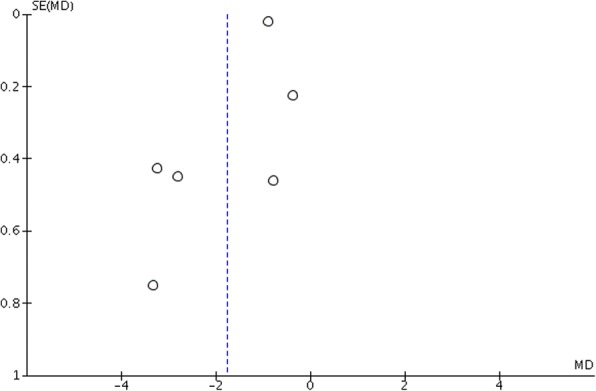
Funnel plot for anchorage loss in the vertical dimension (MD mean difference, SE standard error)
Discussion
The present systematic review was conducted to address the following focused question: “In patients with a need for en masse retraction of the upper front teeth, what is the efficacy of orthodontic mini implants for anchorage control compared with conventional anchorage devices?”
The literature search revealed that efficacy of anchorage control of orthodontic mini implants in comparison to conventional devices was evaluated in nine randomized clinical trials (RCTs) [1, 4, 5, 9, 11, 28, 48–50, 52]. Seven of these studies employed direct anchorage in the alveolar ridge, whereas one study employed indirect anchorage together with a buccal implant [9], and one study used a mid-palatal implant and indirect anchorage [5]. Each of these studies reported on anchorage loss in the horizontal dimension, whereas vertical and transversal anchorage loss was only addressed in six and one of these studies, respectively. One cohort study also evaluated vertical anchorage loss associated with mini implants [48], whereas transversal changes have also been addressed in one controlled clinical trial and in one cohort study [54, 57].
Data syntheses of respective RCTs revealed a gain of anchorage for direct anchorage in the horizontal and vertical dimension, whereas indirect anchorage was associated with minor amounts of anchorage loss. Conventional treatments were commonly associated with a mesial migration and extrusion of the first upper molars.
Even though all studies favored orthodontic mini implants over conventional devices, distal migration and slight molar intrusion were only observed in groups employing direct anchorage through mini implants in the alveolar ridge. It has been suggested that the distal and intrusive forces result from the direction of the retraction forces causing some binding (or increase in friction) of the archwire to the brackets or tubes. Friction may have prevented sliding thus causing the force to be transmitted through the archwire to the dentition [11, 48, 50]. Whether this effect will be more pronounced if a coil spring is left in place for a couple of months after completion of front retraction as suggested by Upadhyay et al. [48] has not been analyzed so far. Notably, the observed effects varied from absolute anchorage with no tooth migration [4] to varying amounts of distal migration up to − 0.88 mm ± 1.13 mm. Hence, the underlying biomechanical causes need to be further analyzed.
Indirect anchorage through implants in the alveolar ridge was associated with mesial molar migration in all studies included in the present review [5, 9, 54, 57]. Nonetheless, anchorage loss with indirect anchorage was significantly lower compared to the conventional devices [5, 9, 57]. It has been suggested that the anchorage loss at indirectly anchored mid-palatal implants may be caused by a slight bending of the transpalatal bars which pass from the implant to the anchor teeth [54]. Additionally, implant migration, which describes a displacement of an implant while maintaining stability, may have contributed to the findings [5].
Transversal changes have not been compared to conventional devices, and controversial transversal effects have been reported in orthodontic mini implant groups [48, 54, 57]. Whereas an expansion tendency was observed in conjunction with palatal implants and indirect anchorage [57], inter-molar width reduction and palatal tipping of the molar crowns were observed in a study employing direct anchorage and implants in the alveolar ridge [48]. Hence, posterior reinforcement and application of differential moments have been suggested to avoid these side effects in the respective studies.
Implant loosening or complete failures have been reported in some studies, whereas others observed a 100% success rate. Discontinuation of treatment owing to inflammation was reported for implants placed in the alveolar ridge only. However, in several cases, resolution was successfully achieved through improved oral hygiene [4, 48, 49]. Whereas adverse effects including root damage, or loss of tooth sensibility have been reported in literature [15, 21], none of these complications were reported in the included studies. Also, no failures due to root contact have been reported in the included studies, even though root proximity is considered to be a major risk factor for implant loosening [53].
The implant failure rates of 9.9% and 8.6% were comparable between direct and indirect anchorage groups and also lower compared to the failure rate of 13.5% reported by two systematic reviews [2, 37]. Interestingly, two of three studies reporting on implant failures in the alveolar palate observed a 100% success rate that relates to the achievement of the respective treatment goal [54, 57]. In the other study evaluating mid-palatal implants, implant failure was observed only among the first series of implants placed by an unexperienced surgeon, and no implant losses were noted for implants that had reached primary stability [5]. This finding is in line with other studies reporting on high success rates for orthodontic implants in the alveolar palate [20, 24, 36, 58].
Conclusions
The present systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that orthodontic mini implants are associated with a significantly lower anchorage loss at the first upper molars compared to conventional anchorage devices for en-masse retraction in the maxilla. However, the ideal implant location (anterior palate versus alveolar ridge) and the most beneficial concept (direct or indirect anchorage) need to be further evaluated. The heterogeneity was high among the included studies, control groups were not always homogenous, and two included studies were judged of high risk of bias. Further high-quality prospective, randomized clinical trials are needed to investigate the anchorage efficacy of orthodontic mini implants in comparison to conventional techniques.
Additional file
Data extraction template. (CSV 2 kb)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the work of S. Moscarino, E. Burceck, and J. Bartz who assisted in the abstract screening and hand searching.
Funding
The study was self-funded by the authors.
Availability of data and materials
The data extracted for the meta-analysis are available in the Additional file 1.
Authors’ contributions
KB formulated the PICO question, created the data extraction template, and performed the database and hand searching, title and abstract screening, evaluation of full-text articles for eligibility, data extraction, risk of bias judgment, calculation of the meta-analysis, and manuscript writing. AP and CB assisted in the abstract screening and performed the data extraction and risk of bias judgment. BW was involved in the formulation of the PICO question, and he critically revised the article. MW was involved in the creation of the data extraction template and performed database searching, hand searching, abstract screening, and evaluation of full-text articles for eligibility. DD was involved in the formulation of the PICO question and resolution of disagreements, and he also critically revised the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
Kathrin Becker, Annika Pliska, Caroline Busch, Benedict Wilmes, Michael Wolf, and Dieter Drescher declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Al-Sibaie S, Hajeer MY. Assessment of changes following en-masse retraction with mini-implants anchorage compared to two-step retraction with conventional anchorage in patients with class II division 1 malocclusion: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Orthod. 2014;36(3):275–283. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjt046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alharbi Fahad, Almuzian Mohammed, Bearn David. Miniscrews failure rate in orthodontics: systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Orthodontics. 2018;40(5):519–530. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjx093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barros SE, Janson G, Chiqueto K, Baldo VO, Baldo TO. Root resorption of maxillary incisors retracted with and without skeletal anchorage. A J Orthod Dent Orthop. 2017;151(2):397–406. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.06.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Basha AG, Shantaraj R, Mogegowda SB. Comparative study between conventional en-masse retraction (sliding mechanics) and en-masse retraction using orthodontic micro implant. Implant Dent. 2010;19(2):128–136. doi: 10.1097/ID.0b013e3181cc4aa5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Benson PE, Tinsley D, O'Dwyer JJ, Majumdar A, Doyle P, Sandler PJ. Midpalatal implants vs headgear for orthodontic anchorage--a randomized clinical trial: cephalometric results. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2007;132(5):606–615. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bilodeau JE. Retreatment of a transfer patient with bialveolar protrusion with mini bone-plate anchorage. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2014;146(4):506–513. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2013.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Borsos G, Voko Z, Gredes T, Kunert-Keil C, Vegh A. Tooth movement using palatal implant supported anchorage compared to conventional dental anchorage. Ann Anat. 2012;194(6):556–60. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2012.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Choi YJ, Chung CJ, Choy K, Kim KH. Absolute anchorage with universal t-loop mechanics for severe deepbite and maxillary anterior protrusion and its 10-year stability. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(4):583–594. doi: 10.2319/052809-304.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chopra SS, Mukherjee M, Mitra R, Kochar GD, Kadu A. Comparative evaluation of anchorage reinforcement between orthodontic implants and conventional anchorage in orthodontic management of bimaxillary dentoalveolar protrusion. Med J Armed Forces India. 2017;73(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2016.01.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dai JY, Zhang MM, Sun M, Ni H. Treating high angle bimaxillary protrusion with three kinds of extraction method: a clinical study. West China J Stomat. 2009;27(3):268–71 275. [PubMed]
- 11.Davoody AR, Posada L, Utreja A, Janakiraman N, Neace WP, Uribe F, Nanda R. A prospective comparative study between differential moments and miniscrews in anchorage control. Eur J Orthod. 2013;35(5):568–576. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de Almeida MR, Herrero F, Fattal A, Davoody AR, Nanda R, Uribe F. A comparative anchorage control study between conventional and self-ligating bracket systems using differential moments. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(6):937–942. doi: 10.2319/022813-170.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Durrani OK, Shaheed S, Khan A, Bashir U. Comparison of in-vivo failure of single-thread and dualthread temporary anchorage devices over 18 months: A split-mouth randomized controlled trial. Am J Orthod Dento Orthoped. 2017;152(4):451–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2017.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.El-Beialy AR, Abou-El-Ezz AM, Attia KH, El-Bialy AM, Mostafa YA. Loss of anchorage of miniscrews: A 3-dimensional assessment. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2009;136(5):700–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.10.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fah R, Schatzle M. Complications and adverse patient reactions associated with the surgical insertion and removal of palatal implants: a retrospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(6):653–658. doi: 10.1111/clr.12152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garfinkle JS, Cunningham LL, Jr, Beeman CS, Kluemper GT, Hicks EP, Kim MO. Evaluation of orthodontic mini-implant anchorage in premolar extraction therapy in adolescents. Am J Orthod Dento Orthoped. 2008;133(5):642–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.04.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gollner P, Jung BA, Kunkel M, Liechti T, Wehrbein H. Immediate vs. conventional loading of palatal implants in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20(8):833–837. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Heo W, Nahm DS, Baek SH. En masse retraction and two-step retraction of maxillary anterior teeth in adult Class I women: a comparison of anchorage loss. Angle Orthod. 2007;77(6):973–978. doi: 10.2319/111706-464.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Herman RJ, Currier GF, Miyake A. Mini-implant anchorage for maxillary canine retraction: A pilot study. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2006;130(2):228–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.02.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Holm M, Jost-Brinkmann PG, Mah J, Bumann A. Bone thickness of the anterior palate for orthodontic miniscrews. Angle Orthod. 2016;86(5):826–831. doi: 10.2319/091515-622.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hourfar J, Bister D, Lisson JA, Ludwig B. Incidence of pulp sensibility loss of anterior teeth after paramedian insertion of orthodontic mini-implants in the anterior maxilla. Head Face Med. 2017;13(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13005-016-0134-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Janson G, Gigliotti MP, Estelita S, Chiqueto K. Influence of miniscrew dental root proximity on its degree of late stability. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42(4):527–34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jee JH, Ahn HW, Seo KW, et al. En-masse retraction with a preformed nickel-titanium and stainless steel archwire assembly and temporary skeletal anchorage devices without posterior bonding. Korean J Orthod. 2014;44(5):236–45. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2014.44.5.236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kawa D, Kunkel M, Heuser L, Jung BA. What is the best position for palatal implants? A CBCT study on bone volume in the growing maxilla. Clin Oral Investig. 2017;21(2):541–549. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1913-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kuhlberg AJ, Burstone CJ. T-loop position and anchorage control. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1997;112(1):12–18. doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(97)70268-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kuhlberg AJ, Priebe DN. Space closure and anchorage control. Semin Orthod. 2001;7(1):42–49. doi: 10.1053/sodo.2001.21073. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kuroda S, Yamada K, Deguchi T, Kyung HM, Takano-Yamamoto T. Class II malocclusion treated with miniscrew anchorage: comparison with traditional orthodontic mechanics outcomes. Am J Orthod Dento Orthoped. 2009;135(3):302–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Liu YH, Ding WH, Liu J, Li Q. Comparison of the differences in cephalometric parameters after active orthodontic treatment applying mini-screw implants or transpalatal arches in adult patients with bialveolar dental protrusion. J Oral Rehabil. 2009;36(9):687–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2842.2009.01976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu H, Lv T, Wang NN, Zhao F, Wang KT, Liu DX. Drift characteristics of miniscrews and molars for anchorage under orthodontic force: 3-dimensional computed tomography registration evaluation. Am J Orthod Dento Orthoped. 2011;139(1):e83–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2010.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ma YP, Guo YM, Chai Y, Zhang H, Wang P. Comparison of miniscrews and headgear facebow in treatment of skeletal class II adults of hyperdivergent. J Dalian Med Univ. 2015;37(2):169–72. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Martins RP, Buschang PH, Gandini LG., Jr Group a t-loop for differential moment mechanics: an implant study. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2009;135(2):182–189. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.02.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Melsen B, Dalstra M. Skeletal anchorage in the past, today and tomorrow. Orthod Fr. 2017;88(1):35–44. doi: 10.1051/orthodfr/2016052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Miyazawa K, Kawaguchi M, Tabuchi M, Goto S. Accurate pre-surgical determination for self-drilling miniscrew implant placement using surgical guides and cone-beam computed tomography. Eur J Orthod. 2010;32(6):735–40. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjq012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Monga N, Kharbanda OP, Samrit V. Quantitative and qualitative assessment of anchorage loss during en-masse retraction with indirectly loaded miniscrews in patients with bimaxillary protrusion. Am J Orthod Dento Orthoped. 2016;150(2):274–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nienkemper M, Wilmes B, Pauls A, Drescher D. Impact of mini-implant length on stability at the initial healing period: a controlled clinical study. Head Face Med. 2013;9:30. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-9-30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Papageorgiou SN, Zogakis IP, Papadopoulos MA. Failure rates and associated risk factors of orthodontic miniscrew implants: a meta-analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2012;142(5):577–595.e577. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2012.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Park HS, Kwon TG, Sung JH. Nonextraction treatment with microscrew implants. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(4):539–49. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(2004)074<0539:NTWMI>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Park HS, Kwon OW, Sung JH. Microscrew implant anchorage sliding mechanics. World J Orthod. 2005;6(3):265–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Park YC, Choi YJ, Choi NC, Lee JS. Esthetic segmental retraction of maxillary anterior teeth with a palatal appliance and orthodontic mini-implants. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2007;131(4):537–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2005.05.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Park HS, Yoon DY, Park CS, Jeoung SH. Treatment effects and anchorage potential of sliding mechanics with titanium screws compared with the Tweed-Merrifield technique. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;133(4):593–600. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.02.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ren Y. Mini-implants for direct or indirect orthodontic anchorage. Evid Based Dent. 2009;10(4):113. doi: 10.1038/sj.ebd.6400687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Santiago RC, de Paula FO, Fraga MR, Assis N, Vitral RWF. Correlation between miniscrew stability and bone mineral density in orthodontic patients. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2009;136(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shi YT, Ping Y, Shan LH, Song JS, Qiu ZX. Stability of mini-implant during orthodontic treatment as anchorage. J Clin Rehab Tis Eng Res. 2008;12(26):5109–12. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Smith RJ, Burstone CJ. Mechanics of tooth movement. Am J Orthod. 1984;85(4):294–307. doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(84)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Thiruvenkatachari B, Pavithranand A, Rajasigamani K, Kyung HM. Comparison and measurement of the amount of anchorage loss of the molars with and without the use of implant anchorage during canine retraction. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2006;129(4):551–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2005.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Turkoz C, Iscan HN. Evaluation of extraction and non-extraction treatment effects by two different superimposition methods. Eur J Orthod. 2011;33(6):691–9. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjq143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Upadhyay M, Yadav S, Nagaraj K, Nanda R. Dentoskeletal and soft tissue effects of mini-implants in Class II division 1 patients. Angle Orthod. 2009;79(2):240–247. doi: 10.2319/013008-52.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Upadhyay M, Yadav S, Nagaraj K, Patil S. Treatment effects of mini-implants for en-masse retraction of anterior teeth in bialveolar dental protrusion patients: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;134(1):18–29.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Upadhyay M, Yadav S, Patil S. Mini-implant anchorage for en-masse retraction of maxillary anterior teeth: a clinical cephalometric study. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2008;134(6):803–810. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Upadhyay M, Yadav S, Nagaraj K, Uribe F, Nanda R. Mini-implants vs fixed functional appliances for treatment of young adult Class II female patients: a prospective clinical trial. Angle Orthod. 2012;82(2):294–303. doi: 10.2319/042811-302.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Victor D, Prabhakar R, Karthikeyan MK, Saravanan R, Vanathi P, Raj Vikram N, Adarsh Reddy P, Sudeepthi M. Effectiveness of mini implants in three-dimensional control during retraction - a clinical study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(2):227–232. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/7801.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Watanabe H, Deguchi T, Hasegawa M, Ito M, Kim S, Takano-Yamamoto T. Orthodontic miniscrew failure rate and root proximity, insertion angle, bone contact length, and bone density. Orthod Craniofacial Res. 2013;16(1):44–55. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wehrbein H, Feifel H, Diedrich P. Palatal implant anchorage reinforcement of posterior teeth: a prospective study. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1999;116(6):678–686. doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(99)70204-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wehrbein H., Merz B. R., Diedrich P., Glatzmaier J. The use of palatal implants for orthodontic anchorage. Design and clinical application of the orthosystem. Clinical Oral Implants Research. 1996;7(4):410–416. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1996.070416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wehrbein H, Glatzmaier J, Mundwiller U, Diedrich P. The orthosystem--a new implant system for orthodontic anchorage in the palate. J Orofac Orthop. 1996;57(3):142–153. doi: 10.1007/BF02191878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wilmes B, Olthoff G, Drescher D. Comparison of skeletal and conventional anchorage methods in conjunction with pre-operative decompensation of a skeletal class III malocclusion. J Orofac Orthop. 2009;70(4):297–305. doi: 10.1007/s00056-009-9909-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Winsauer H, Vlachojannis C, Bumann A, Vlachojannis J, Chrubasik S. Paramedian vertical palatal bone height for mini-implant insertion: a systematic review. Eur J Orthod. 2014;36(5):541–549. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Xu YL, et al. Cephalometric analysis of implant anchorage-assisted retraction of anterior teeth. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2008;17(1):20–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Xu TM, Zhang X, Oh HS, Boyd RL, Korn EL, Baumrind S. Randomized clinical trial comparing control of maxillary anchorage with 2 retraction techniques. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2010;138(5):544.e541–544.e549. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2009.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Xun CL, Zeng XL, Wang X. Clinical application of miniscrew implant for maximum anchorage cases. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004;39(6):505–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yao CC, Lai EH, Chang JZ, Chen I, Chen YJ. Comparison of treatment outcomes between skeletal anchorage and extraoral anchorage in adults with maxillary dentoalveolar protrusion. Am J Orthod Dento Orthoped. 2008;134(5):615–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data extraction template. (CSV 2 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The data extracted for the meta-analysis are available in the Additional file 1.