Abstract
PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites spheres were synthesized using a simple and efficient one-step hydrothermal process. The morphology and structure of PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites spheres were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques. The PANI/TiO2 nanocomposite sphere-based sensor exhibits good selectivity, sensitivity (5.4 to 100 ppm), repeatability, long-term stability and low detection limit (0.5 ppm) to ammonia at room temperature (20 ± 5°C). It also shows a good linearity relationship in the range of 0.5–5 and 5–100 ppm. The excellent NH3 sensing performance is mainly due to the formation of the p-n heterostructure in the nanocomposites.
Keywords: gas sensing, polyaniline, TiO2, NH3, nanocomposites
Introduction
Polyaniline (PANI), as an intrinsically conductive polymer, is the widely used material in anti-corrosion, anti-static electricity, stealth and so on. Since its low density, excellent processability, excellent flexibility, and good electrical conductivity, (Bhadra et al., 2009; Baker et al., 2017) polyaniline is also attracting more attention in the field of gas sensing. However, pure PANI sensors often show lower sensitivity or higher detection limit than semiconductor metal oxide sensors (Sutar et al., 2007; Kebiche et al., 2012). The addition of semiconducting metal oxides not only improves gas-sensing properties, but also avoids high operating temperatures. In recent years, SnO2, ZnO, TiO2, and In2O3 have been chosen as the addition of polyaniline to prepare ammonia sensors, which can used at room temperature (Guo et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2015; Dai et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2018). Most of the materials reported so far have been prepared by electrospinning, interfacial synthesis, or mechanical mixing (Talwar et al., 2014; Li et al., 2015; Nie et al., 2016). Pawar et al. synthesized PANI and TiO2 by chemical oxidative polymerization and sol-gel method, respectively. Then, they mixed PANI and TiO2 by mechanical mixing method to prepare PANI-TiO2 nanocomposites. The response of the sensor to 100 ppm NH3 is 50% (Pawar et al., 2011a). Liu et al. prepared the PANI-TiO2-Au ternary nanocomposite thin film by in-situ self-assembly method. The response of the sensor is 2.23 toward 50 ppm NH3, and the detection limit is 1 ppm (Liu et al., 2017). Their synthetic methods basically need more than one-step reactions. And the recovery time, sensitivity and other properties of the sensors need to be further improved.
In this work, the PANI/TiO2 nanocomposite was synthesized by one step hydrothermal method. The PANI/TiO2 nanocomposite exhibits good selectivity, sensitivity (5.4 to 100 ppm), repeatability, long-term stability, and low detection limit (0.5 ppm) to ammonia at room temperature. Meanwhile, the sensor exhibits a good liner relationship in the range of 0.5–5 and 5-100 ppm.
Experimental
All reagents were of analytical grade, offered by Aladdin Reagent Company, and used without further purification.
Preparation of PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites and pure PANI
1.147 g of ammonium persulfate (APS) was added to 10 mL of HCl (1 mol·L−1) to obtain solution A. In 10 mL of anhydrous ethanol, tetrabutyl titanate (TBT), and 0.47 mL of aniline were added to obtain solution B. Solution C is the mixture of 10 mL absolute ethanol and 0.47 mL aniline. The mixture solution of A and B were poured into a 50 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and kept at 100°C for 2 h. The mixtures of solution A and C were treated as the same. The PANI/TiO2 nanocomposite and pure PANI was obtained after washing several times by deionized water and ethanol. With other conditions remaining constant, the amount of TBT added in solution B is 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, or 0.2 mol·L−1, respectively, to make products PT1, PT2, PT3, PT4. The synthetic routes of the samples are shown in Scheme S1.
Characterization of PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites
The phase structure of the products were analyzed by X-ray powder diffractometer (XRD, Rigaku, D/MAX-3B) with Cu Kα1 radiation (λ = 1.54059 Å). Raman spectra of products were tested by a LabRAM HR800 laser confocal microscopic Raman spectrometer. The morphology and structure of products were investigated by scanning electron microscope (SEM, FEI/Philips, XL-30) and transmission electron microscope (TEM, Jeol, Jem-2100). Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was executed by a Perkin-Elmer instruments corporation thermogravimetric analyzer. The specific surface area and pore size distribution were detected by nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurement at 77 K using the TriStar II 3020 system.
Fabrication and gas sensing measurement of the PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites sensors
The products were made into a paste with ethanol and coated on the surface of Al2O3 tube whose length was 4 mm and internal diameter was 0.8 mm. The Al2O3 tube brought with two gold electrodes which spaced 1 mm and the distance between two gold electrodes was 1 mm. Two platinum wires were connected with each gold electrode. After a Ni/Cr wire passed through the Al2O3 tube, it was welded to the base together with the platinum wires.
The responses of sensors were recorded by JF02E type gas sensor measurement system (Kunming Guiyan Jinfeng Technology Co. Ltd., China). The static testing method was used to measure the property of sensors. After a certain amount of NH3 was injected into a vacuum 10 L glass bottle, the pressure was returned to the atmospheric pressure. The gas sensor was placed in the glass bottle for testing. The sensor's response to NH3 was defined as S = Rg/Ra. Rg and Ra were the resistance values of the sensor in NH3 and air, respectively. The response time is 100s, the recovery time is defined as the time that the resistance changed 90%. The sensor response to humidity measured by the saturated solution of LiCl (11.3 RH%), CH3COOK (23.4 RH%), MgCl2 (32.8 RH%), K2CO3(43 RH%), Mg(NO3)2 (54.3 RH%), CuCl2 (67 RH%), NaCl (75.3 RH%), KCl (85 RH%), and KNO3 (93.5 RH%; Yang et al., 2017).
Results and discussion
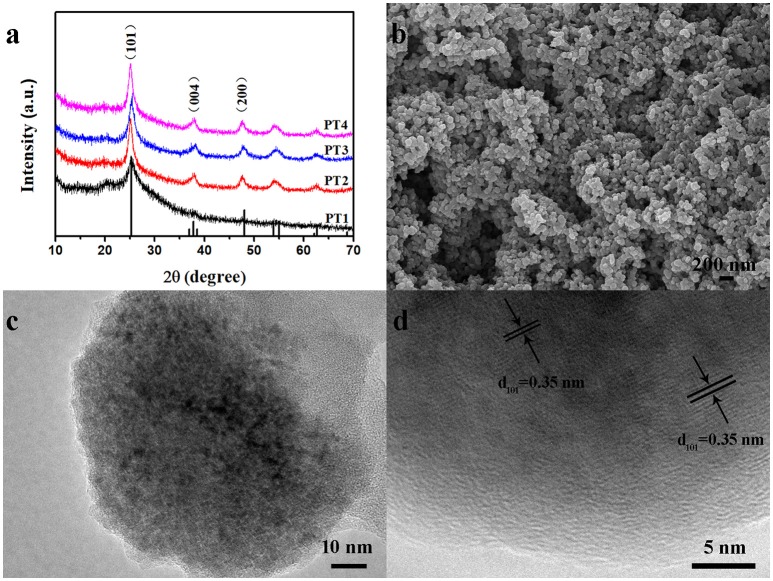
The XRD peaks of the nanocomposites samples PT1, PT2, PT3, and PT4, shown in Figure 1a at 25°, is consistent with the XRD diffraction peak of pure PANI. As is shown in Figure S1, the diffraction peak of the pure PANI appears at about 25°. Other peaks at 25.3°, 37.8°, and 48.0° are corresponding to (101), (004), and (200) crystal planes of anatase crystal structure TiO2 (JCPDS Card NO.21-1272). This reminds that TiO2 is present in the nanocomposites. Further, the Raman spectrum of the nanocomposites was analyzed, as shown in Figure S2. The peaks at 164, 406, 635 cm−1 are the characteristic peaks of TiO2, and 1,595 cm−1 is attributed to the C-C stretching vibration of benzenoid ring in PANI, which further proves the presence of TiO2 in the nanocomposites (Chen and Mao, 2007). Through the thermogravimetric analysis (Figure S3) to determine the TiO2 content of PT1, PT2, PT3 and PT4 is 3.04, 19.48, 21.09, and 38.75%, respectively. The response of the PT1, PT2, PT3, PT4 nanocomposites and pure PANI to 20–100 ppm NH3 at room temperature is shown in Figure S4. As can be seen from the figure, the PT3 nanocomposites sensor has better response to NH3 than the other four sensors. Figure S5 exhibits the pore structure and specific surface area of the PT1, PT2, PT3, and PT4 nanocomposites, which were detected by N2 adsorption-desorption measurement and Barrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) pore size distribution analysis. The BET specific surface area of the PT1, PT2, PT3, and PT4 nanocomposites are 26.76, 46.13, 47.73, and 55.80 m2·g−1, respectively. The result shows that the specific surface area increase as the TiO2 content rises. The gas-sensing performance of the sensor is generally related to the micro-structure of sensing material, specific surface area and so on. Compared with other four sensors, the morphology of the PT3 nanocomposites is uniform (Figure S6), many TiO2 nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed on the surface of the PANI nanospheres, which makes the nanocomposites have many p-n heterostructure and a large specific surface area. These will increase the contact area of PT3 nanocomposites, make the NH3 molecules diffuse easily and provide more active sites for the efficient adsorption of NH3, which is more conducive to the reaction of the nanocomposite with NH3. Therefore, a more detailed characterization of the PT3 nanocomposites was performed.
Figure 1.
XRD patterns of the PT1, PT2, PT3 and PT4 nanocomposites (a); SEM (b), TEM (c), and HRTEM (d) images of the PT3 nanocomposites.
The morphology and structure of the PT3 nanocomposites were tested by SEM and TEM. In Figure 1b, it is found that the PT3 nanocomposites were composed by the stacking of nanoparticles whose diameter is about 80 nm. Figure 1c indicates the same result that the PT3 nanocomposites is composed of nanoparticles, stacked on top of each other. In addition, the HRTEM image of the PT3 nanocomposites (Figure 1d) shows characteristic lattice fringes of TiO2 with a pitch of 0.35 nm, corresponding to the (101) crystal plane of TiO2. This is consistent with the XRD result that there is TiO2.
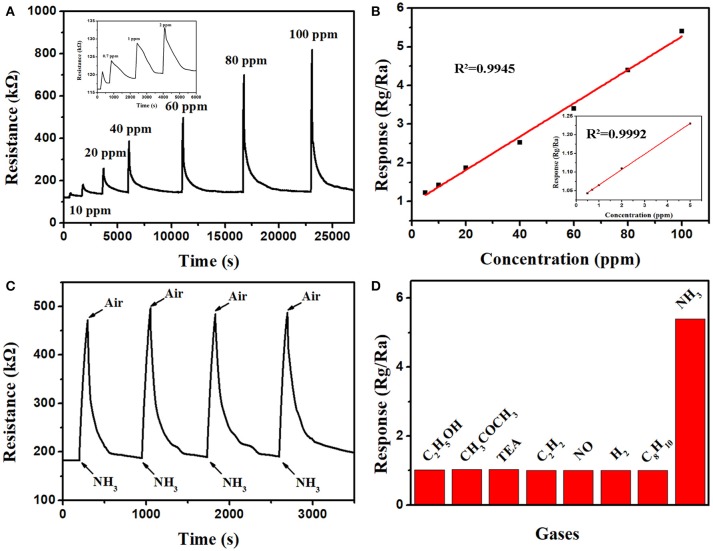
The gas sensing properties of the PT3 nanocomposites sensor was further studied. The response-recovery curves for 0.5–100 ppm NH3 at room temperature are shown in Figure 2A. To 100 ppm NH3, the sensitivity of PT3 nanocomposite sensor is 5.4, the response time is 100 s, and the recovery time is 232 s. Moreover, the sensitivity of the PT3 nanocomposite sensor presents a clear linear relationship with the NH3 concentration between 0.5 and 5 ppm (R2 = 0.9992) and 5 and 100 ppm (R2 = 0.9945) (Figure 2B). The PT3 nanocomposite sensor performed four consecutive tests on 50 ppm of NH3 at room temperature (Figure 2C). The corresponding sensitivities are 2.59, 2.6, 2.56, and 2.56, respectively. And the relative deviation is 1.75%. This shows that the PT3 nanocomposite sensor has a satisfactory reproducibility. The interference of other seven gases to the sensor was further researched (Figure 2D). The responds at room temperature to 100 ppm ethanol (C2H5OH), acetone (CH3COCH3), triethylamine (TEA), ethyne (C2H2), NO, H2, styrene (C8H8), and NH3 are 1.020, 1.034, 1.027, 1.006, 1.008, 1.007, 1.010, and 5.423, respectively. The result proves that the PT3 nanocomposite sensor is more sensitive to NH3 at room temperature. The influence of humidity was studied in the humidity range of 11.3–93.5% at room temperature (Figure S7a). The maximum response of the sensor is 1.4. It means that the effect of humidity to the sensor is much small. In order to deeply investigate the long-term stability, the sensor responds to 50 ppm NH3 every 5 days at room temperature. During the 2 months monitoring time (Figure S7b), the response of the sensor was reduced by < 2% after 60 days. Our investigation leads us to conclude that the sensor has a good long-term stability.
Figure 2.
The response-recovery curves (A) and the linear relationship (B) of the PT3 nancomposites sensor to different concentrations of NH3; the reproducibility of the PT3 nancomposites sensor to 50 ppm NH3 (C); the selectivity of the PT3 nanocomposites sensor to 100 ppm of eight gases (D).
Compared the gas sensing property between the PANI-TiO2 nanocomposites sensor with the reported sensor in Table 1. The results show that the PT3 nanocomposites sensor exhibits excellent sensitivity and good response to NH3 gas at room temperature. The detection limit of PANI-TiO2 nanocomposites sensor is lower and sensitivity is better than the other reported sensors. The improvement of the NH3 sensing property of PT3 sensor is might attributed to the following reasons. First, One-step synthesis is more conducive to the dispersion of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the surface of PANI. Secondly, the p-n heterostructure formed between TiO2 and PANI can provide a synergistic effect, which can effectively improve the ability to adsorb NH3. Therefore, the PT3 nanocomposites has potential application value in detecting NH3 at room temperature.
Table 1.
Summary of recent publications of PANI-TiO2 nanocomposities based NH3 sensors.
| Sensing materials | Detection limit | Response/NH3 concentration | Response time (s) | Recovery time (s) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANI/TiO2 | 45 ppb | 38.3/10.5 ppm | 600 | – | Li et al., 2015 |
| PANI-TiO2-Au | 1 ppm | 2.23/50 ppm | 122 | – | Liu et al., 2017 |
| PANI/TiO2 | 23 ppm | < 6/94 ppm | 2 s | 25 s | Tai et al., 2008 |
| PA6/TiO2/PANI | – | 2.6/250 ppm | 150 s | 450 s | Pang et al., 2014 |
| cellulose/TiO2/PANI | 10 ppm | 3.57/100 ppm | < 150 s | 800 s | Pang et al., 2016 |
| PANI/TiO2 | 25 ppb | >0.8/200 ppb | 80 s | – | Li et al., 2011 |
| PANI/TiO2 | – | 48%/100 ppm | 40 s | 70 s | Pawar et al., 2012 |
| CSA Doped PANi- TiO2 | 20 ppm | 0.75/100 ppm | 49 s | 413 s | Pawar et al., 2011b |
| PANi-TiO2 | 20 ppm | 50%/100 ppm | 40 s | 70 s | Pawar et al., 2011a |
| TiO2-SiO2/PANI | 10 ppm | 23/100 ppm | < 500 s | – | Pang et al., 2018 |
| TiO2-PANI/PA6 | – | 18.3/250 ppm | 250 s | – | Wang et al., 2012 |
| PANi-TiO2 | – | 3.9/60 ppm | 35 s | 140 s | Bairi et al., 2015 |
| PANI/TiO2 | 0.5 ppm | 5.4/100 ppm | 100 s | 232 s | This work |
The possible sensing mechanism of the PT3 nanocomposites sensor for detecting NH3 is as shown in Figure S8. TiO2 is an n-type semiconductor with a 3.2 eV forbidden band width. And PANI is a p-type semiconductor with a 2.8 eV forbidden band width. At the contact interface, the TiO2 and PANI interact to form a p-n heterostructure. The p-n heterostructure will make a positively charged depletion layer. So, the activation energy and enthalpy of physisorption for NH3 will reduce as a result to cause the enhancement of gas sensitivity (Costello et al., 1996; Tai et al., 2010). In addition, the LUMO level of PANI and the conduction band of TiO2 are well helps charge transfer. It can also effectively improve the gas sensing performance (Li et al., 2006; Tai et al., 2008). When the sensor is exposed to NH3, H+ on -NH- site of PANI combines with NH3, cause the electron hole concentration in the PANI to be low. The resistance of the sensor will increase. When the sensor is exposed to air after NH3, PANI gets H+ from , the electron hole concentration of PANI recovers. The resistance decreases to the initial value (Figure S8b).
Conclusion
In summary, the PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites, which is consisted of uniform nanoparticles, are synthesized by one-step hydrothermal synthesis. At room temperature, the sensor based on PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites has a good linear relationship (0.9945 to 5–100 ppm), high response to NH3 (5.4 to 100 ppm), and the detection limit is 0.5 ppm. The response and recovery time to 100 ppm NH3 is 100 and 232 s, respectively. With small humidity effects, the sensor exhibits excellent selectivity, good reproducibility and long-term stability to NH3. Moreover, the excellent gas sensing property of PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites can be rewarded to p-n heterostructure. The more charge transfer on the surfaces where PANI is in contact with TiO2, the beter gas-sensing performance of PANI/TiO2. These results illustrate that the PANI/TiO2 nanocomposites sensor has great potential application for detecting NH3 at room temperature.
Author contributions
CZ performed the experiments, analyzed the data with the help from YX and XC. XD wrote the manuscript with input from all authors. YX conceived the study. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work is financial supported by International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2016YFE0115100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (21771060, 21547012, and 21305033), the Project of Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. B2015007), and the Project of Nitro Graduate Innovation Research of Heilongjiang University (YJSCX2018-062HLJU). We thank the Key Laboratory of Functional Inorganic Material Chemistry, Ministry of Education, Heilongjiang University for supporting this study.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2018.00493/full#supplementary-material
References
- Bairi V. G., Bourdo S. E., Sacre N., Nair D., Berry B. C., Biris A. S., et al. (2015). Ammonia gas sensing behavior of tanninsulfonic acid doped polyaniline-TiO2 composite. Sensors 15, 26415–26429. 10.3390/s151026415 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C., Huang X., Nelsonc W., Kaner R. B. (2017). Polyaniline nanofibers: broadening applications for conducting polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev 6, 1510–1525. 10.1039/C6CS00555A [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhadra S., Khastgir D., Singha N., Lee H. (2009). Progress in preparation, processing and applications of polyaniline. Prog. Polym. Sci. 34, 783–810. 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.04.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Chen H. I., Hsu C. S., Huang C. C., Wu J. S., Chou P. C., et al. (2015). Characteristics of ZnO nanorods-based ammonia gas sensors with a cross-linked configuration. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 221, 491–498. 10.1016/j.snb.2015.06.122 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Mao S. (2007). Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem. Rev. 107, 2891–2959. 10.1021/cr0500535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello L., Evans P., Ewen R. J., Honeybourne C., Ratcliffe N. M. (1996). Novel composite organic-inorganic semiconductor sensors for the quantitative detection of target organic vapours. J. Mater. Chem. 6, 289–294. 10.1039/JM9960600289 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dai L., Liu Y., Meng W., Yang G., Zhou H., He Z., et al. (2016). Ammonia sensing characteristics of La10Si5MgO26-based sensors using In2O3 sensing electrode with different morphologies and CuO reference electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 228, 716–724. 10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.106 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W., Duan X., Shen Y., Qi K. Z., Wei C. Y., Zheng W. J. (2013). Ionothermal synthesis of mesoporous SnO2 nanomaterials and their gas sensitivity depending on the reducing ability of toxic gases. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 11221–11225. 10.1039/c3cp51663f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebiche H., Debarnota D., Merzoukib A., Poncin-Epaillard F., Haddaoui N. (2012). Relationship between ammonia sensing properties of polyaniline nanostructures and their deposition and synthesis methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 737, 64–71. 10.1016/j.aca.2012.06.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Zhu L., Wu Y., Harima Y., Zhang A., Tang H. (2006). Hybrid composites of conductive polyaniline and nanocrystalline titanium oxide prepared via self-assembling and graft polymerization. Polymer 47, 7361–7367. 10.1016/j.polymer.2006.08.059 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Ban H. T., Zhao H. J., Yang M. J. (2015). Facile preparation of a composite of TiO2 nanosheets and polyaniline and its gas sensing properties. RSC Adv. 5, 106945–106952. 10.1039/C5RA20879C [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Gong J., He G., Deng Y. (2011). Fabrication of polyaniline/titanium dioxide composite nanofibers for gas sensing application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 129, 477–482. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.04.045 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Tai H. L., Zhang P., Ye Z. B., Su Y. J., Jiang Y. D. (2017). Enhanced ammonia-sensing properties of PANI-TiO2-Au ternary self-assembly nanocomposite thin film at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 246, 85–95. 10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.046 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nie Q., Pang Z., Lu H., Cai Y. B., Wei Q. F. (2016). Ammonia gas sensors based on In2O3/PANI hetero-nanofibers operating at room temperature. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 7, 1312–1321. 10.3762/bjnano.7.122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang Z., Fu J., Luo L., Huang F., Wei Q. (2014). Fabrication of PA6/TiO2/PANI composite nanofibers by electrospinning-electrospraying for ammonia sensor. Colloids Surf. A 461, 113–118. 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.07.038 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pang Z., Yang Z., Chen Y., Zhang J., Wang Q., Huang F., et al. (2016). A room temperature ammonia gas sensor based on cellulose/TiO2/PANI composite nanofibers, Colloids Surf. A 494, 248–255. 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.01.024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pang Z., Yu J., Li D., Nie Q., Zhang J., Wei Q. (2018). Free-standing TiO2-SiO2/PANI composite nanofibers for ammonia sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 3576–3583. 10.1007/s10854-017-8287-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pawar S. G., Chougule M. A., Patil S. L., Raut B. T., Godse P. R., Sen S., et al. (2011a). Room temperature ammonia gas sensor based on polyaniline-TiO2 nanocomposite. IEEE Sens. J. 11, 3417–3423. 10.1109/JSEN.2011.2160392 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pawar S. G., Chougule M. A., Sen S., Patil V. B. (2012). Development of nanostructured polyaniline-titanium dioxide gas sensors for ammonia recognition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 125, 1418–1424. 10.1002/app.35468 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pawar S. G., Patil S. L., Chougule M. A., Raut B. T., Godase P. R., Mulik R. N., et al. (2011b). New method for fabrication of CSA doped PANi-TiO2 thin-film ammonia sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 11, 2980–2985. 10.1109/JSEN.2011.2152391 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sutar D. S., Padma N., Aswal D. K., Deshpande S. K., Gupta S. K., Yakhmi J. V. (2007). Preparation of nanofibrous polyaniline films and their application as ammonia gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 128, 286–292. 10.1016/j.snb.2007.06.015 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tai H., Jiang Y., Xie G., Yu J. (2010). Preparation, characterization and comparative NH3-sensing characteristic studies of PANI/inorganic oxides nanocomposite thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26, 605–613. 10.1016/S1005-0302(10)60093-X [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tai H. L., Jiang Y., Xie G., Yu J., Chen X., Ying Z. (2008). Influence of polymerization temperature on NH3 response of PANI/TiO2 thin film gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 129, 319–326. 10.1016/j.snb.2007.08.013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Talwar V., Singh O., Singh R. (2014). ZnO assisted polyaniline nanofibers and its application as ammonia gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 191, 276–282. 10.1016/j.snb.2013.09.106 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Dong X., Pang Z., Du Y., Xia X., Wei Q., et al. (2012). Ammonia sensing behaviors of TiO2-PANI/PA6 composite nanofibers, Sensors 12, 17046–17057. 10.3390/s121217046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Zhang X., Cheng X., Xu Y., Gao S., Zhao H., et al. (2017). Hierarchical NiO Cube/Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide composite with enhanced H2S sensing properties at low temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 26293–26303. 10.1021/acsami.7b04969 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Zeng W., Ye H., Li Y. (2018). Enhanced carbon monoxide sensing properties of TiO2 with exposed (001) facet: a combined first-principle and experimental study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 442, 507–516. 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.036 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.