Abstract
Background
Shigella spp. are Gram-negative intracellular pathogenic bacteria belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae and can cause bacterial dysentery, a severe diarrheal disease. The pathophysiological impact of the Gram-negative bacteria is highly related to the composition and structural variability of lipopolysaccharides, the major lipoid components of the outer membrane. Out of the 114 genes involved in the lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis pathway, 47 genes are specific to Shigella spp. Changes in the specific genes can lead to loss of the O polysaccharide side chain, resulting in rough (R) type bacteria with increased sensitivity to temperature, or hydrophobic antibiotics. The formation of various different lipopolysaccharides or lipooligosaccharides has been observed previously in a mutant line showing altered biological properties, but the genetic background has not been investigated in detail.
Results
The parental strain of the mutant line, Shigella sonnei 4303, was subjected to whole genome sequencing to gain a better insight into the structure and biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharides. The sequencing revealed a 4,546,505 bp long genome including chromosomal and plasmid DNA, and the lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes were also identified. A comparison of the genome was performed with the phylogenetically closely related, wild type, well characterized, highly virulent strain, S. sonnei 53G.
Conclusion
Analysis of the lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic genes helped us to get more insight into the pathogenicity and virulence of the bacteria. The genome revealed high similarities with S. sonnei 53G, which can be used as a standard in characterizing the S. sonnei 4303’s R-type isogenic derivatives.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13099-018-0274-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Shigellosis, Shigella sonnei 4303, Genome, Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis
Background
Lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) are of importance in bacterial physiology, and also in host-bacteria crosstalk [1]. The pathogenicity of Gram-negative bacteria is influenced by the molecular variability (structures and lengths) of LPSs, e.g., serum sensitivity and biofilm forming ability of Gram-negative bacteria are correlated with the lengths of O sidechains. Previous studies have described that R-type bacteria with truncated LPS molecules (so-called lipooligosaccharides—LOSs) are more sensitive to hydrophobic antibiotics [2].
Recent studies suggested that Shigella sonnei have become more dominant in developed countries [3]. The history of S. sonnei 4303 dates back more than 60 years, when the phenomenon of phase variation in S. sonnei was examined [4]. This non-pathogenic strain was formed by plasmid loss from a pathogenic S. sonnei phase I. strain, due to the instable nature of the virulence plasmid [5]. Later, intensive studies were carried out on the strain and its R-type isogenic derivatives, and the chemical structures and structural variabilities of their lipopolysaccharides and lipooligosaccharides (LOSs) have been described. Several interesting R mutants were characterized, including an absolute R-type strain (S. sonnei 4350) and a strain having truncated LPSs with a d-glycero-d-mannoheptose component incorporated in the structure (S. sonnei 4351) [6–12]. The lack of appropriate genome-scale information of the investigated strains, including structurally different LPSs, however, hinders our ability to answer fundamental biosynthetic questions. In order to gain more insight into the mechanism of the LPS/LOS biosynthesis S. sonnei 4303 was subjected to whole genome sequencing.
Methods
The genomic library was made by enzymatic shearing with the Ion Xpress Plus fragment library kit, followed by size selection on a 2% agarose E-Gel SizeSelect Gel (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA USA). The template was prepared with 100 pM of the library on an Ion One Touch 2 system (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Samples were loaded on an Ion 316v2 Chip and sequenced on an Ion Torrent PGM sequencer, with the Ion PGM Sequencing 200 Kit v2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) in compliance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. De novo assembly was performed using the SPAdes v3.1 Genome Assembler software [13]. For whole-genome alignment, scaffolds in the draft assemblies were reordered to the S. sonnei 53G as reference sequence in Mauve software with default parameters [14]. Sequence annotation was performed using Prokka v. 1.9 [15]. MeDuSa (Multi-Draft based Scaffolder) web server was used for genome scaffolding [16]. The genome sequence of S. sonnei 4303 has been deposited in the GenBank under the accession number PRJNA361576.
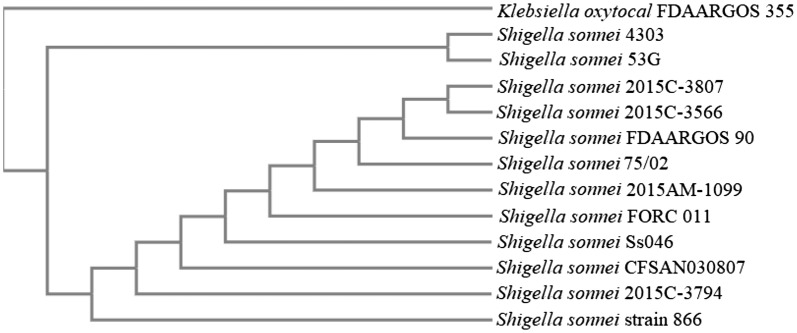
Phylogenetic analysis was performed with the closest relatives selected by 16S rRNA sequences through NCBI (BLASTn). Phylogenetic analysis was performed by Clustal Omega with default settings [17]. Multiple sequence alignment was completed with adk, fumC, gyrB, mdh, purA housekeeping genes and rRNA genes. The resulted phylogenetic tree represents 12 S. sonnei strains including S. sonnei 4303 and an outgroupped strain, Klebsiella oxytocal FDAARGOS 355.
Nomenclature of the LPS genes were used according to KEGG database [18].
Detailed methodological strategy is described in Additional file 1.
Quality assurance
Morphological and biochemical characterization identified the strain as S. sonnei. The genomic DNA used for sequencing was isolated from a single colony of the bacteria. The 16S rDNA gene was extracted from the genome using RNAmmer 1.2 server [19]. The identity of the strain was confirmed through BLAST annotation against NCBI microbial 16S database.
Results and discussion
In total 4,262,518 high quality reads were generated and used to create the genome of S. sonnei 4303, which yielded a 100-fold coverage. The genome is 4.5 Mbps in size, and contains 4554 predicted genes, 10 rRNA genes, 60 tRNA genes as well as a CRISPR region. In our comparative studies, the genome of a well characterized, highly pathogenic and phylogenetically highly related strain, S. sonnei 53G was used as standard (Fig. 1). S. sonnei 53G was isolated in Japan [20] and was used in different serological studies [21].
Fig. 1.
Distance matrix tree showing the phylogenetic relationships of 12 S. sonnei strains including S. sonnei 4303 and Klebsella oxytocal FDAARGOS 355. Phylogenetic analysis was performed by Clustal Omega with 16S rRNA and 5 housekeeping genes (adk, fumC, gyrB, mdh, purA)
Since the primary aim of this study was to create a solid and strain specific information about the genetic background with regards to LPS modifications, the genes involved in the LPS biosynthetic pathway have been further analyzed in silico. According to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways database, 114 genes participate in these complex biological processes. Screening for the presence/absence of these genes in the S. sonnei 4303 and in the S. sonnei 53G strains revealed 47 genes specific to S. sonnei. Comparative DNA analysis on this common subset of S. sonnei genes revealed six sequence polymorphisms (summarized in Table 1).
Table 1.
Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes according to Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes in Shigella sonnei 4303
| Gene name/synonym(s) | Similarity to Shigella sonnei 53G (%) |
|---|---|
| Lipid A | |
| lpxB | 100 |
| lpxA | 100 |
| lpxD | 100 |
| lpxL/htrB | 100 |
| lpxM/msbB | 100 |
| pagP | 99a |
| eptA | 100 |
| lpxC | 100 |
| lpxH | 100 |
| arnT | 100 |
| lpxK | 100 |
| lpxT/yeiU | 99b |
| lpxP/ddg | 99a |
| Core region | |
| waaA/kdtA | 100 |
| rfaC/waaC | 100 |
| rfaF/waaF | 100 |
| waaQ | 100 |
| rfaG/waaG | 100 |
| rfaI | 100 |
| waaR | 100 |
| waaV | 99c |
| waaW | 100 |
| rfaP/waaP | 100 |
| rfaY/waaY | 100 |
| eptB | 100 |
| eptC | 100 |
| waaH | 100 |
| O antigen | |
| rfaL | 100 |
| wecA | 100 |
| wzzB | 100 |
| Unusual sugar | |
| kdsD | 100 |
| kdsA | 99d |
| kdsC | 100 |
| kdsB | 100 |
| gmhA | 100 |
| gmhC/hldE | 100 |
| gmhB | 100 |
| gmhD/rfaD/hldD | 100 |
| arnA | 99d |
| arnB | 100 |
| arnC | 100 |
| arnD | 100 |
| arnE | 100 |
| arnF | 100 |
| wecB | 100 |
| wbpA/wecC | 100 |
aSingle-nucleotide polymorphism coding nonsense mutation
bTwo gaps and new stop codon
cThe gene has 100% similarity to Shigella sonnei Ss046’s waaV gene
dSingle nucleotide polymorphism coding missense mutation
Our former study on the LPS structure of S. sonnei 4303 indicated that the lipid A molecules contain only 1 phosphate group at position 1 [6]. Modification of lipid A with an additional phosphate group at position 1, forming a 1-diphosphate species, is mediated by the undecaprenyl phosphotransferase, LpxT. The mutation of lpxT/yeiU encoding gene may explain the monophosphorylated position 1 in S. sonnei 4303.
Taken together, the whole-genome sequencing strategy revealed the mutation of the lpxT, and the presence of new variants of the pagP, lpxP, kdsA and arnA genes. The sequenced genome can be used as a reference for characterizing R-type isogenic derivatives of S. sonnei 4303, to reveal the genetic background of mutants with the truncated lypopolysaccharides [6], e.g., having a d-glycero-d-mannoheptose in the core part [7, 8].
Additional file
Additional file 1. Complete methodological strategy to the “Genome sequence of Shigella sonnei 4303”. Experimental design, Sampling protocol and storage, Nucleic acid isolation, Library preparation and sequencing, Read quality assessment, Comparative genomics.
Authors’ contributions
FK and BK contributed to the conception of study. CF contributed to the design of the study and led the project with FK. BK was involved in the creation of lipopolysaccharide rough R-type mutant line and description of LPS biosynthesis. LD-N, PU and ZT worked on genome sequencing. ZB assembled and annotated the genome, LD-N and PU analyzed the data. LD-N drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analyzed are available in the GeneBank repository, with Accession Number PRJNA361576, Assembly GCA_002073875.2.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
Sponsorship: This work was supported by the National Research, Development and Innovation Office K-125275. The work was partially supported by the EFOP-3.6.3-VEKOP-16-2017-00009, GINOP-2.3.2-15-2016-00021, and PTE-AOK-KA-2017-19 Grants.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- LOS
lipooligosaccharide
- LPS
lipopolysaccharide
Contributor Information
Laura Deutsch-Nagy, Email: laura.nagy@aok.pte.hu.
Ferenc Kilár, Email: ferenc.kilar@aok.pte.hu.
References
- 1.Gnauck A, Lentle RG, Kruger MC. The characteristics and function of bacterial lipopolysaccharides and their endotoxic potential in humans. Int Rev Immunol. 2016;35(3):189–218. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2015.1087518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kim HS, Lee MA, Chun SJ, Park SJ, Lee KH. Role of NtrC in biofilm formation via controlling expression of the gene encoding an ADP-glycero-manno-heptose-6-epimerase in the pathogenic bacterium, Vibrio vulnificus. Mol Microbiol. 2007;63(2):559–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thompson CN, Duy PT, Baker S. The rising dominance of Shigella sonnei. An intercontinental shift in the etiology of bacillary dysentery. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9:e0003708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rauss K, Kétyi I, Vertényi A, Vörös S. Studies on the nature of phase variation of Shigella sonnei. Acta microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1954;8:53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schuch R, Maurelli AT. Virulence plasmid instability in Shigella flexneri 2a is induced by virulence gene expression. Infect Immun. 1997;65(9):3686–3692. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.9.3686-3692.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kocsis B, Kontrohr T, László V, Milch H. Isolation and characterization of different Shigella sonnei rough mutants. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1980;27:217. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kontrohr T, Kocsis B. Isolation of adenosine 5′-diphosphate-d-glycero-d-mannoheptose. An intermediate in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis of Shigella sonnei. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:7715–7718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kocsis B, Kontrohr T. Isolation of adenosine 5′-diphosphate-d-glycero-d-mannoheptose, the assumed substrate of heptose transferase(s), from Salmonella Minnesota R595 and Shigella sonnei Re mutants. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:11858–11860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bui A, Kilár A, Dörnyei A, Poór V, Kovács K, Kocsis B, Kilár F. Carbohydrate composition of endotoxins from R-type isogenic mutants of Shigella sonnei studied by capillary electrophoresis and GC-MS. Croat Chem Acta. 2011;84:393–398. doi: 10.5562/cca1795. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kilár A, Dörnyei A, Bui A, Szabo Z, Kocsis B, Kilár F. Structural variability of endotoxins from R-type isogenic mutants of Shigella sonnei. J Mass Spectrom. 2011;46:61–70. doi: 10.1002/jms.1863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Makszin L, Kilár A, Felső P, Péterfi Z, Kocsis B, Kilár F. Quantitative microfluidic analysis of S- and R-type endotoxin components with chip capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2012;33:3351–3360. doi: 10.1002/elps.201200167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kilár A, Dörnyei A, Kocsis B. Structural characterization of bacterial lipopolysaccharides with mass spectrometry and on- and off-line separation techniques. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2013;32:90–117. doi: 10.1002/mas.21352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nurk S, Bankevich A, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Korobeynikov A, Lapidus A, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin A, Sirotkin A, Sirotkin Y, et al. Assembling single-cell genomes and mini-metagenomes from chimeric MDA products. J Comput Biol. 2013;20(10):714–737. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2013.0084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT. ProgressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(6):e11147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Seemann T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(14):2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Emanuele B, Beatrice D, Marco G, Sara B, Marie-France S, Pietro L, Pierluigi C, Renato F, Marco F. MeDuSa: a multi-draft based scaffolder. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(15):2443–2451. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McWilliam H, Li W, Uludag M, Squizzato S, Park YM, Buso N, Peter AC, Lopez R. Analysis Tool Web Services from the EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acid Res. 2013;41(1):597–600. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Pathway Database. Japan. 2018. https://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/get_htext?ko01005.keg. Accessed 1 Sept 2018.
- 19.Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(9):3100–3108. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kopecko DJ, Washington O, Formal SB. Genetic and physical evidence for plasmid control of Shigella sonnei form I cell surface antigen. Infect Immun. 1980;29(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.207-214.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Formal SB, Baron LS, Kopecko DJ, Washington O, Powell C, Life CA. Construction of a potential bivalent vaccine strain: introduction of Shigella sonnei form I antigen genes into the galE Salmonella typhi Ty21a typhoid vaccine strain. Infect Immun. 1981;34(3):746–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.746-750.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Complete methodological strategy to the “Genome sequence of Shigella sonnei 4303”. Experimental design, Sampling protocol and storage, Nucleic acid isolation, Library preparation and sequencing, Read quality assessment, Comparative genomics.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed are available in the GeneBank repository, with Accession Number PRJNA361576, Assembly GCA_002073875.2.