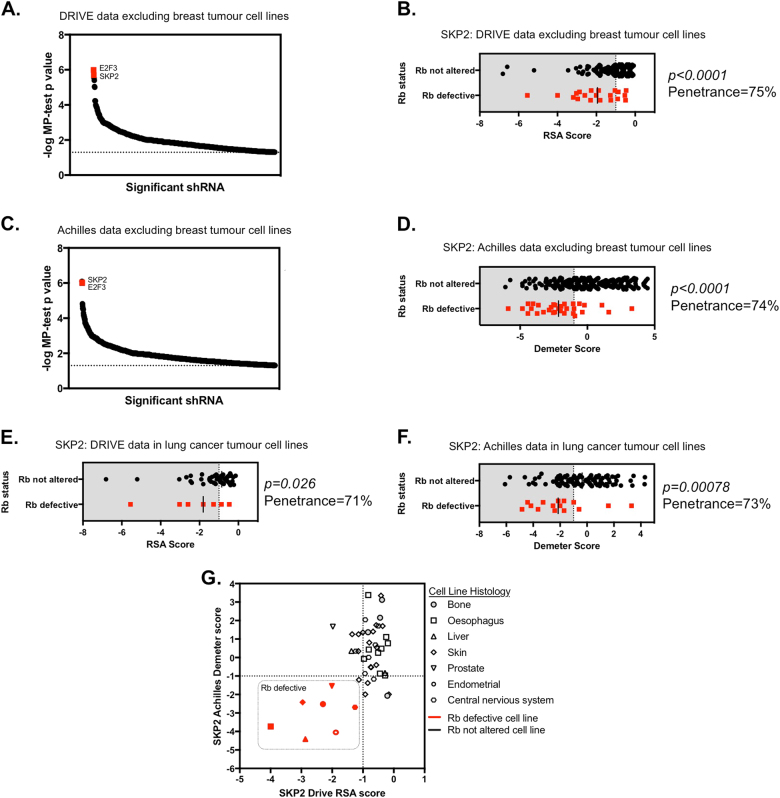
Fig. 7.
SKP2 identified as a highly penetrant Rb synthetic lethal effect in other histologies in two independently derived data sets. a Scatter plot of 775 p < 0.05 significant Rb synthetic lethal effects identified from the MP test analysis of 373 non-breast cancer TCLs in the Drive study (step one in Fig. 1a). All 775 p < 0.05 effects are ranked ordered by MP test p value. SKP2 and E2F3 are highlighted. b Scatter plot illustrating RSA scores in 373 non-breast TCLs with Rb annotation for SKP2 sensitivity from the Drive data analysis. c Scatter plot of 1467 p < 0.05 significant Rb synthetic lethal effects identified from the MP test analysis of 467 non-breast TCLs in the Achilles study (step one in Fig. 1a). All 1467 p < 0.05 effects are ranked ordered by MP test p value. SKP2 and E2F3 are highlighted. d Scatter plots illustrating Demeter scores in 1467 non-breast TCLs with Rb annotation for SKP2 sensitivity from the Achilles data analysis. e, f Scatter plots illustrating RSA and Demeter scores in 63 and 115 lung TCLs with Rb annotation for SKP2 sensitivity from the Drive and Achilles studies, respectively. g Scatter plot of intersect of cell line between the two data sets showing SKP2 sensitivity in Drive RSA scores (x axis) and Achilles Demeter scores (y axis) for selected histologies with only a single Rb-defective line. This graph illustrates a trend between Rb defects and sensitivity to SKP2 shRNA across seven different histotypes