Abstract
To understand the evolutionary dynamics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-encoding genes in Escherichia coli, we undertook a comparative genomic analysis of 116 whole plasmid sequences of human or animal origin isolated over a period spanning before and after the use of third-generation cephalosporins (3GCs) using a gene-sharing network approach. The plasmids included 82 conjugative, 22 mobilizable and 9 non-transferable plasmids and 3 P-like bacteriophages. ESBL-encoding genes were found on 64 conjugative, 6 mobilizable, 2 non-transferable plasmids and 2 P1-like bacteriophages, indicating that these last three types of mobile elements also play a role, albeit modest, in the diffusion of the ESBLs. The network analysis showed that the plasmids clustered according to their genome backbone type, but not by origin or period of isolation or by antibiotic-resistance type, including type of ESBL-encoding gene. There was no association between the type of plasmid and the phylogenetic history of the parental strains. Finer scale analysis of the more abundant clusters IncF and IncI1 showed that ESBL-encoding plasmids and plasmids isolated before the use of 3GCs had the same diversity and phylogenetic history, and that acquisition of ESBL-encoding genes had occurred during multiple independent events. Moreover, the blaCTX-M-15 gene, unlike other CTX-M genes, was inserted at a hot spot in a blaTEM-1-Tn2 transposon. These findings showed that ESBL-encoding genes have arrived on wide range of pre-existing plasmids and that the successful spread of blaCTX-M-15 seems to be favoured by the presence of well-adapted IncF plasmids that carry a Tn2-blaTEM-1 transposon.
Keywords: Escherichia coli, plasmid, extended-spectrum β-lactamase, CTX-M-15, gene-sharing network
Data Summary
One hundred and sixteen complete sequences of plasmids have been deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive (www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/) under the accession numbers: LT985213 to LT985387 (project PRJEB24625), FO818745, FQ482074, LO017736, LO017737 and LO017738. For individual plasmid accession numbers, please refer to Tables S1 and S2 (available with the online version of this article).
Impact Statement.
Since the 2000s, an explosive spread of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), enzymes that hydrolyse and cause resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins, has been observed, impacting both human and animal health. Among ESBLs, CTX-M and especially CTX-M-15 type enzymes have taken over from the SHV and TEM type ESBLs, and Escherichia coli is now the major host. The large majority of these ESBLs are plasmid encoded. The data from our comparative whole plasmid sequence analysis give a picture of the evolutionary dynamics of acquisition of plasmid-borne ESBL-encoding genes in E. coli. The results indicate that ESBL-encoding genes have arrived multiple times on a wide range of pre-existing plasmids and that a highly dynamic pattern of mobility concerning different nested physical units represented by the ESBL-encoding gene, the multi-resistance region and the plasmid, multiplies the potential of ESBL spread. The results also highlight the importance of the well-adapted IncF plasmid associated with the Tn2-blaTEM-1 transposon in the successful spread of the CTX-M-15 ESBL in E. coli.
Introduction
The emergence and spread of resistance to third-generation cephalosporins (3GCs), mediated mainly by extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) [1], is an increasing health problem. An important component of this emergence is mediated by the spread of plasmid-borne ESBL-encoding genes [2]. The CTX-M family of ESBLs currently predominates worldwide and has taken over from the SHV and TEM type ESBLs that were predominant in the 1990s [3]. Among these, CTX-M-15 belonging to the CTX-M-1 group appears to be the most widespread, followed by CTX-M-14, another common variant of the CTX-M enzymes [4, 5]. In recent years, the prevalence of Escherichia coli that produce ESBLs has dramatically increased. Consequently, E. coli is now recognized as the major source of ESBLs [5, 6]. ESBL-producing E. coli are commonly isolated from community or hospital infections and from human faecal carriage, and are also increasingly detected in food-producing, companion and wildlife animals, as well as in the environment. As a consequence, these resistant E. coli can impact on both animal and human health [1, 5]. In addition to the selective pressure exerted by the use of 3GCs, other factors may contribute to the emergence and success of E. coli producing ESBLs and in particular those producing CTX-M-15 ESBLs: the mobile elements involved in the capture/mobilization of the ESBL-encoding gene, the genetic background of ESBL-carrying plasmids [7] and the host strain carrying the plasmid. For instance, E. coli clones of phylogenetic group B2 and sequence type (ST) 131; of phylogenetic group D, and ST315, ST393 and ST405; and of phylogroup F and ST648 have largely contributed to the dissemination of ESBL worldwide [8–11].
The objective of this work was to better understand the evolutionary dynamics of the acquisition of plasmid-borne ESBL-encoding genes in E. coli. Therefore, we first sequenced ESBL-encoding plasmids of diverse types in terms of incompatibility group, type of ESBL (CTX-M, SHV and TEM) and ecosystem (human or animal) originating from 73 ESBL E. coli strains. These strains were selected from well-characterized human and animal E. coli collections [12–18]. Second, we sequenced non-ESBL plasmids originating from 18 human and animal E. coli strains isolated before the introduction of the 3GCs in clinical therapy (ECOR collection and personal collections) [19, 20]. Third, we sequenced the plasmid content of an E. coli strain of the Murray collection isolated during the pre-antibiotic era [21, 22]. Using complete and circularized plasmid sequences, we performed comparative genomic analyses to determine the structure of the plasmid communities, as well as the phylogenetic relationships of the closely related plasmids. We also investigated the relationships between the plasmids and their main features, such as their origin, antibiotic gene content and size and the phylogenetic history of the host strain.
Methods
Bacterial strains and plasmids
To carry out our comparative plasmid analysis, we selected ESBL-encoding plasmids, and plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs originating from human and animal collections of E. coli strains. ESBL-encoding plasmids, previously obtained after transfer by conjugation in E. coli K-12 J53rifr or, in absence of conjugation, by electroporation in E. coli K-12 DH10B from human and animal E. coli collections [12–18, 23], were selected according to diversity in terms of their incompatibility group determined by PCR based replicon typing (PBRT) [24] and of the type of ESBL-encoding gene they carried (Table S1). From the human ESBL-producing E. coli collections [12, 17, 18, 23], 63 plasmids were selected. Among them, 50 were typable by PBRT [IncF (n=18), IncA/C (n=12), IncI1 (n=8), IncN (n=5), IncL/M (n=4), IncK (n=2), IncY (n=1)] and 13 were non-typable. A total of 35 plasmids encoded a CTX-M-type ESBL [CTX-M-15 (n=13), CTX-M-14 (n=10), CTX-M-9 (n=2), CTX-M-3 (n=2), CTX-M-2 (n=2), CTX-M-1(n=6)], 12 a SHV-type ESBL [SHV-12 (n=7), SHV-2 (n=3), SHV-5(n=1), SHV-3(n=1)] and 16 a TEM-type ESBL [TEM-52 (n=5), TEM-24 (n=4), TEM-21 (n=2), TEM-3 (n=5)]. From the animal ESBL-producing E. coli collection [13–15], 10 plasmids, all typable by PBRT, were selected [IncF (n=1), IncI1 (n=7), IncHI1 (n=1) and IncHI2 (n=1)]. Nine plasmids encoded a CTX-M-type ESBL [CTX-M-1 (n=5), CTX-M-2 (n=3), CTX-M-15 (n=1)] and one plasmid encoded a TEM-52 ESBL.
Plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs came from: (i) 15 strains of the ECOR collection [19], which represent the diversity of the E. coli population, 6 were of human origin and 9 of animal origin; (ii) 3 strains of human origin isolated between 1958 and 1969 [20] (INRA, UR1282, personal collection); (iii) 1 strain of human origin from the Murray collection isolated before the use of antibiotics [21, 22] (Table S2). These strains, with the exception of two ECOR strains and the strain from the Murray collection, were resistant to at least one antibiotic. Resistant plasmids were transferred by conjugation in E. coli K-12 J53rifr or, in the absence of conjugation, by electroporation in E. coli K-12 DH10B using one of the following antibiotics as selective agents, according to the resistance phenotype of the strain: ampicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline, sulfonamides. Eight of the resistant plasmids were typable by PBRT [IncF (n=4), IncI1 type (n=1), IncB/O type (n=2), IncX (n=1)] and eight were non-typable. PBRT of the antibiotic-sensitive ECOR strains showed that one had non-typable plasmids and the other a plasmid of IncF type. The Murray collection strain had a plasmid of IncF type.
Parental strain chromosome phylotyping
The parental strains were assigned to one of the seven E. coli phylogenetic groups, A, B1, B2, C, D, E, F, or to Escherichia clade I using the quadruplex PCR-based method developed by Clermont et al. [25]. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was performed using the Institut Pasteur MLST (MLST IP) scheme based on the partial sequences of eight genes (dinB, icdA, pabB, polB, putP, trpA, trpB, uidA) as described previously [26] (http://bigsdb.web.pasteur.fr/). Phylogenetic analysis was performed with the concatenated sequences of the eight genes, using the maximum-likelihood method implemented in the PhyML program [27] with Escherichia fergusonii as the outgroup.
Plasmid DNA sequencing and annotation
Plasmid DNA was purified from the E. coli K-12 recipient strains and from the three antibiotic-sensitive strains with the Macherey-Nagel nucleobond BAC100 kit and sequenced according to two strategies: transposition for small-sized plasmids (<30 kb) (template generation system II; Finnzymes) and high-density pyrosequencing on a 454 GSFlx instrument with titanium chemistry (Roche) for large-sized plasmids (>30 kb). The reads generated, of a mean length of 350 bp (40× coverage), were assembled de novo by the Newbler assembler [28] into contigs and produced circularized sequences. Combinational PCRs and Sanger sequencing were used to fill in gaps.
An automatic annotation was undertaken using the MicroScope platform (www.genoscope.cns.fr/agc/microscope) [29]. Genomic object annotations were subsequently validated by a manual expert annotation. All the data generated during the annotation processes were integrated into the Prokaryotic Genomic DataBase (PkGDB) browsable via the MicroScope platform GUI. Annotation of insertion sequences was performed using the IS Finder resource (https://isfinder.biotoul.fr/) [30].
Classification of the plasmids
The plasmids were classified according to their mobility characteristics as described elsewhere [31]. Conjugative plasmids having a set of genes encoding a mating pair formation (MPF) and a relaxase were called MPF plasmids. Plasmids having a relaxase gene but no MPF genes were called MOB (mobilizable) plasmids. Plasmids having no MPF genes and no relaxase gene were called RelN (relaxase negative) plasmids (non-transferable plasmids). MPF plasmids were classified further according to their incompatibility (Inc) group [24], and the MOB and RelN plasmids according to the type of their replication system: MOBRNA and RelNRNA for plasmids with a RNAII/RNAI replication system similar to that of the colE1 plasmid [32, 33], and MOBrep and RelNrep for plasmids with a replication protein system. Plasmid MLST (pMLST) was performed on complete sequences of IncF, IncI1 and IncN by submitting the amplicon sequence to the Plasmid MLST website (http://pubmlst.org/plasmid/) [34].
Statistical analysis
To describe associations between variables, a factorial analysis of correspondence (FAC) was conducted. FAC uses a covariance matrix based on χ2 distances. R software [35] (http://CRAN.R-project.org) was used for FAC with a two-way table. The table had 116 rows, corresponding to the 116 plasmids studied and 14 columns corresponding to the 14 variables: plasmid type (MPF, MOB, RelN and phage), type of ESBL-encoding gene (CTX-M, SHV, TEM), plasmids with non-ESBL resistance genes, plasmids with no resistance genes, size of the plasmids (0–30 kb, 30–100 kb, 100–>200 kb) and period of isolation (before or after the use of 3GCs). For each column, each plasmid was coded as a binary code: present=1, absent=0.
Comparative genomic analyses of the sequenced plasmids
To reconstruct the evolutionary history of the plasmids by identifying those having the most similar gene content, comparative genomic analyses were performed. For each plasmid, the annotated gene sequences and the whole genome (scaffold) sequence were downloaded from the PkGDB database (Prokaryotic Genomic DataBase) [29]. The whole genomes were concatenated to create a blast database [36, 37]. Each gene present in the annotated genomes was then blast analysed on the whole genome database with a strict e-value (0.0001). We thus obtained a matrix of the number of genes shared between each pair of plasmids. We used the Jaccard distance (JD) to transform the matrix of shared genes between any two plasmids into a matrix of distance between the plasmids. The JD between any two plasmids is defined as the percentage of non-shared genes between the two plasmids, being 0 when two plasmids have the exact same gene content and 1 when two plasmids do not share any genes. The distance between any two plasmids can assume any value between 0 and 1, depending on the number of genes they share and the total number of genes present in the two plasmids. As many of the plasmids have few or no genes in common, a standard gene clustering is not suited for our plasmid database. We thus developed a phylogenetic approach inspired from network theory [38] to cluster the plasmids. Using the package Igraph [39] from the R software [35], we explored how the plasmids are attached at different thresholds in the JD from its minimum distance (JD=0) to its maximum distance (JD=1). In particular, we focused on the behaviour of two quantities: the size of the biggest cluster of connected plasmids [40] and the number of clusters, which were computed using in-house R scripts. The network was drawn using the function plot.igraph. Each node of the network stands for a plasmid and a link between two nodes is drawn. The clusters were isolated and a subset of plasmids having the same set of shared genes were manually isolated in each cluster [41]. For each subset of plasmids, the set of shared genes were retrieved and concatenated using Perl scripts. The concatenated sets of genes were then aligned using the program Mauve [42] and a tree was built using the program PhyML [27] under the evolution model GTR (general time reversible).
Results
Sequencing of the plasmid collection
Sequencing of the plasmid content of the 89 recipient strains, which exhibited at least one plasmid-borne antibiotic-resistance gene, showed that 14 of them contained two to four different types of plasmids. Of these 14 recipient strains, 11 were transconjugants (21.5 %) and contained 26 plasmids (mean=2.36), and 3 were electroporants (7.8 %) and contained 6 plasmids (mean=2). Direct plasmidome sequencing of the three sensitive strains showed that the strains contained two to four different types of plasmids (mean=3) (Table S2). Therefore, a total of 116 plasmids was further studied, including 74 ESBL-resistance plasmids, 17 non-ESBL-resistance plasmids and 25 plasmids without any resistance genes. Among these, 87 and 29 originated from strains isolated before and after the use of 3GCs, respectively, and 91 and 25 originated from human and animal strains, respectively.
Classification of the plasmids
First, we classified the plasmids as described in Methods. A total of 82 of the 116 plasmids were MPF plasmids, which included 26 IncF, 17 Inc I1, 13 IncA/C, 5 IncN, 4 IncL/M, 2 IncK, 2 IncB/O, 2 IncHI, 3 IncX1, 2 IncX4, 1 IncX2, 1 IncN2, 1 IncY, 1 IncX-like, 1 IncN-like, 1 IncNA (NA, non-attributed); 22 plasmids were MOB plasmids that included 17 MOBRNA plasmids and 5 MOBrep plasmids; and 9 plasmids were RelN plasmids that included 8 RelNRNA plasmids and 1 RelNrep plasmid of IncR type (Table 1). In addition, three temperate bacteriophages that replicate like plasmids were evidenced. Two displayed a high level of identity to the P1-like bacteriophage genomes [43, 44] and one to the P2-like bacteriophage genomes [45] (Table 1).
Table 1. Distribution of the plasmids studied according the type of mobilization and replication/control system, the presence of resistance genes and the type of ESBL-encoding gene carried.
| Plasmid type | No. of plasmids | No. of plasmids encoding at least one ESBL | No. of non-ESBL-encoding plasmids with resistance genes | No. of plasmids without resistance genes | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTX-M | TEM | SHV | ||||||||||||||||||
| -1 | -2 | -3 | -9 | -14 | -15 | Total | -3 | -21 | -24 | -52 | Total | -2 | -3 | -5 | -12 | Total | ||||
| MPF plasmids* | ||||||||||||||||||||
| IncF | 26 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 15 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5† | 1† | ||||||||
| IncI1 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2† | 2‡ | |||||||||
| IncA/C | 13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| IncL/M | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| IncN | 5 | 4 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||
| IncX group | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2† | 1† | |||||||||||||
| IncX1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1† | ||||||||||||||||
| IncX2 | 1 | 1† | ||||||||||||||||||
| IncX4 | 2 | 1 | 1† | |||||||||||||||||
| IncHI | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| IncK | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| IncB/O | 2 | 1† | 1† | |||||||||||||||||
| IncY | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| IncN2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| IncX-like | 1 | 1‡ | ||||||||||||||||||
| IncN-like | 1 | 1† | ||||||||||||||||||
| IncNA | 1 | 1† | ||||||||||||||||||
| MOB plasmids§ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| MOBrep | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1† | 3‡ | |||||||||||||||
| MOBrepB1 | 4 | 1 | 3‡ | |||||||||||||||||
| MOBrepB2 | 1 | 1† | ||||||||||||||||||
| MOBRNA | 17 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 1‡, 1† | 6‡, 4† | |||||||||||||
| RelN plasmids|| | ||||||||||||||||||||
| IncR | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| RelNRNA | 8 | 1 | 1 | 4† | 3† | |||||||||||||||
| Phage | ||||||||||||||||||||
| P1-Like | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| P2-like | 1 | 1† | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 11 | 14 | 44 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 17 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 13 | 18 | 24 | |
*MPF conjugative plasmids [31].
†Isolated before the use of 3GCs.
‡Isolated after the use of 3GCs.
§MOBrep, plasmids with a replication protein system; MOBRNA, plasmids with a RNAII/RNAI replication/control system.
||RelNRNA, plasmids with a RNAII/RNAI replication/control system.
The sequencing results showed that the PBRT non-typable ESBL-encoding plasmid selected for the study [24] had a replicon type that was not included in the panel used at the time of the typing or not yet available or that the plasmids had mismatches in the primer sequences used for typing.
Besides the IncF plasmids, which frequently display several replicons (FII with or without FIA/FIB/FIC) [46], some of the plasmids carried supplementary replicons (Tables S1 and S2). The two replication protein genes, repA and repC, of an IncQ-1 plasmid [47] were found inserted between two IS26 elements on two IncFII-FIB plasmids, one IncHI1 plasmid and one P1-like bacteriophage. A complete core genome of an IncR plasmid [48] and a partial core genome of an IncN2 plasmid [49] were found on two IncA/C plasmids. A FIB replicon was found inserted between two IS629 elements on a MOBRNA plasmid. As noted by Osborn et al. [50], the existence of mosaic replicons causes additional complications for the classification of bacterial plasmids and for attempts to assess the evolutionary relationships between plasmids and their replicons [50].
Relationships between the plasmids and their main characteristics
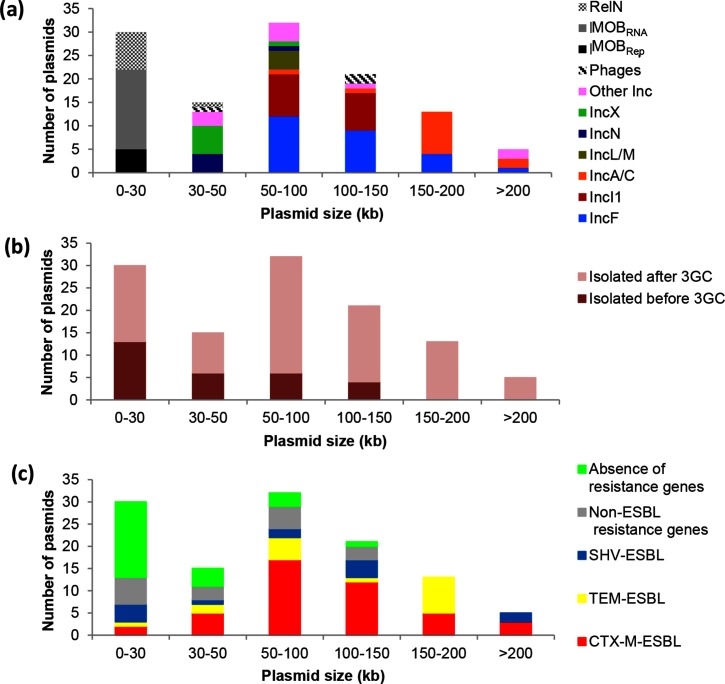
We next studied various characteristics of the plasmids, i.e. their size and the presence or absence of antibiotic-resistance genes, as well as the period of isolation of the strain (after or before the use of 3GCs). First, as observed elsewhere [31], all the MOB and the RelNRNA plasmids had a small size lower than 25 kb with a mean of 9.4 kb (2.9–23.5 kb), and all the MPF plasmids, the bacteriophage and the RelN-IncR plasmid had a size higher than 30 kb with a mean size of 104 kb (34–239 kb). Most of the smallest MPF plasmids (30–55 kb) were the IncN and IncX plasmids, and most of the biggest plasmids (>150 kb) were the IncA/C plasmids (Fig. 1a). Secondly, of the 87 plasmids isolated after the use of the 3GCs, we identified 67 MPF plasmids (20 IncF, 15 IncI1, 13 IncA/C, 4 IncL/M, 5 IncN, 2 IncK, 2 IncX1, 1 IncX4, 2 IncHI, 1 IncY, 1 IncN2 and 1 IncN-like plasmid), 4 MOBrep plasmids, 12 MOBRNA plasmids, 1 RelN-IncR plasmid, 1 RelNRNA plasmid and 2 P1-like bacteriophages. CTX-M-type genes were carried by 40 MPF plasmids, 1 MOBrep plasmid, the RelNRNA plasmid and 1 P1-like bacteriophage. ESBL-TEM-type genes were carried by 16 MPF plasmids, the RelN-IncR plasmid and 1 MOBRNA plasmid. Lastly, ESBL-SHV-type genes were carried by eight MPF plasmids, four MOBRNA plasmids and one P1-like bacteriophage (Fig. 1b, c, Tables 1 and S1). The 29 plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs included 15 MPF plasmids (six IncF, two IncI1, two IncB/O, one IncX1, one IncX2, one IncX4, one IncX-like and one IncNA), 1 MOBrep plasmid, 5 MOBRNA plasmids, 7 RelNRNA plasmids and 1 P2-like bacteriophage. Resistance genes were found on 11 MPF plasmids, on 1 MOBRNA plasmid, on the MOBrep and on 4 RelNRNA plasmids (Fig. 1b, c, Tables 1 and S2).
Fig. 1.
Distribution of the characteristics of the plasmids according to their size (kb). (a) Type of plasmids: MPF plasmids [31] indicated by their incompatibility group (Inc), MOB plasmids indicated by their replication system (MOBrep for replication protein system and MOBRNA for a RNAI/RNAII replication/control system) and RelN plasmids (non-transferable). (b) Isolation period of the plasmids: before or after the use of 3GCs. (c) Resistance type: plasmids with at least one ESBL-encoding gene, plasmids with non-ESBL resistance genes and plasmids with no resistance genes.
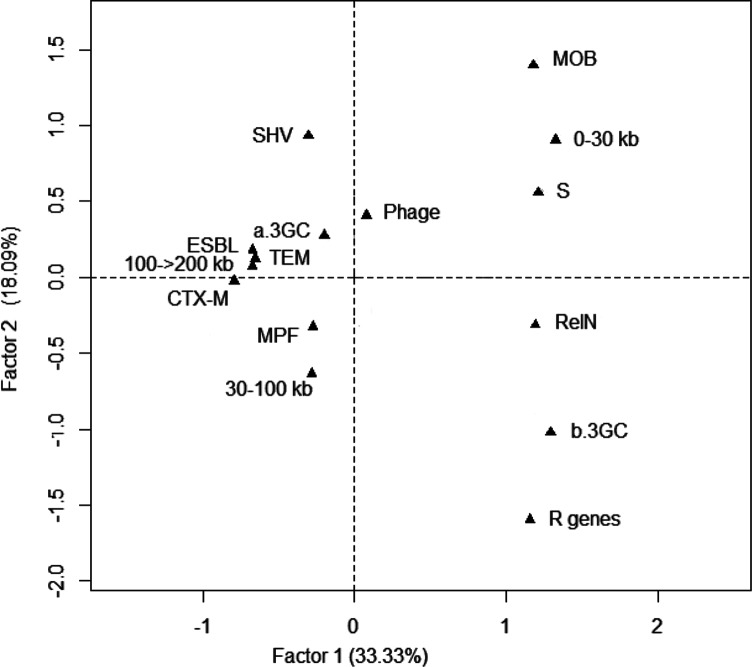
To assess the global relationships between the plasmid type (MPF, MOB, RelN or phage), size, period of isolation, type of resistance and type of ESBL-encoding gene carried by the plasmids, a FAC was conducted with the 116 plasmids as individuals and the 16 characteristics as qualitative variables. Projections of the variables on the plane F1/F2, which accounted for 52.4 % of the total variance, showed that the variables plasmid isolated before (b.3GC) or after (a.3GC) the 3GCs were clearly distinguished by the first factor and that there was an association with the variables type of plasmid, type of resistance and size. The variable b.3GC was projected on the positive value of F1 with the variables MOB, RelN, size of 0–30 kb, plasmid with no resistance gene or plasmid with non-ESBL resistance genes, whereas the a.3GC variable was projected on the negative value of F1 with the variables MPF, sizes of more than 30 kb and presence of an ESBL-encoding gene. On the positive value of F1, the FAC showed a clear association between the variables MOB plasmid and plasmid with no resistance gene both projected on the positive value of F2, and an association between the variables RelN plasmid and plasmid with non-ESBL resistance gene both projected on the negative value of F2 (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Graphical representation of the results of the FAC carried out with whole data from the 116 E. coli plasmids. Projections of the variables on the F1/F2 plane: type of plasmids (MPF, MOB, RelN and phage), size of the plasmids (0–30, 30–100, 100–>200 kb), resistance type [plasmids with at least one ESBL-encoding gene (ESBL), plasmids with non-ESBL resistance genes (R genes), plasmids with no resistance genes (S, sensitive)], type of ESBL-encoding gene (TEM, SHV, CTX-M) and period of isolation [before the use of the 3GCs (b.3GC) or after the use of the 3GCs (a.3GC)]. The percentage of the total variance represented by each factor is indicated.
Plasmid cluster determination
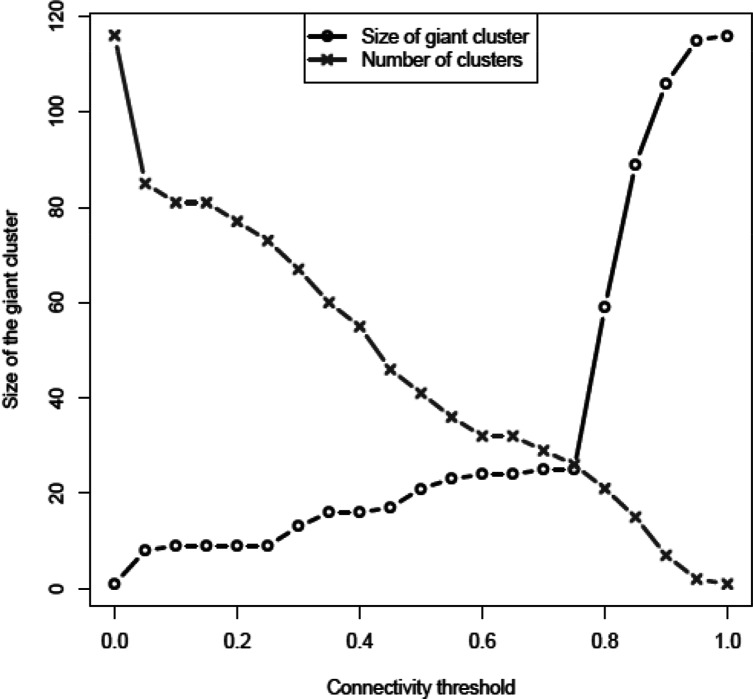
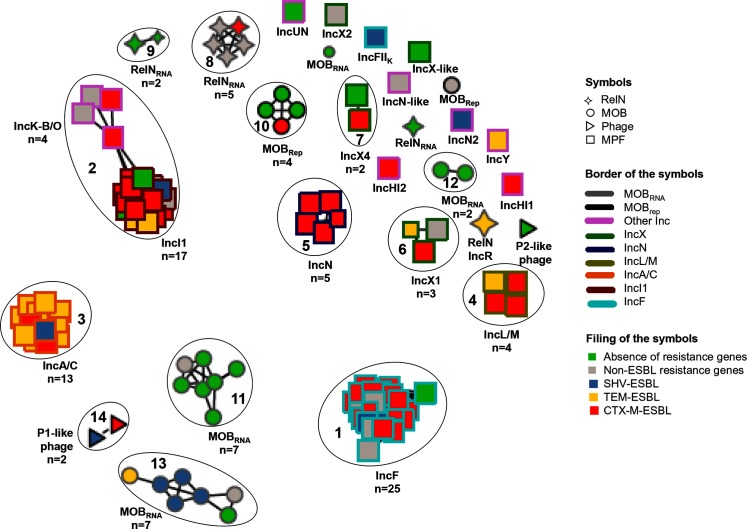
Plasmid clusters were obtained as described in Methods using a phylogenetic approach inspired from network theory [38]. After computing the JD between any pair of plasmids in terms of the plasmids’ gene content, we looked for an optimal data driven distance threshold allowing definition of clusters composed of related plasmids. To this end, we focused on two quantities: the size of the biggest cluster of connected plasmids (called giant component) [40] and the number of clusters as a function of the connectivity threshold. The size of the biggest cluster (Fig. 3) has clearly two regimes: one for low connectivity thresholds (up to 0.75) where the size is almost stable, and one for high thresholds, where the size of the biggest cluster grows quickly until all the plasmids are linked in a single connected component. The sudden transition between these two regimes is related to a well-studied phenomenon in network theory called percolation [38, 40]. In the present analysis, the percolation transition can be explained as the point where the plasmids’ phylogenetic structure is shrouded by horizontal gene transfer (HGT). Below this percolation threshold, we assumed that plasmids were clustered by descendants and that the noise due to HGT was minimal. Thus, the plasmid network was drawn with links between two nodes (plasmids) when their distance was at most 0.75. Using this approach, the graph obtained showed that 102 plasmids were divided into 14 clusters of at least two plasmids (the clusters are surrounded in black and numbered in Fig. 4). A further 14 plasmids were not linked to any other plasmid (singleton plasmids).
Fig. 3.
Dimension of the giant cluster as a function of the threshold in minimum number of genes by two plasmids. The line with crosses represents the number of clusters of connected plasmids at different distances between the plasmids, while the line with circles represents the size of the biggest cluster of plasmids (giant component) at different distances between the plasmids. Note the intersection of the lines at the connectivity threshold (0.75).
Fig. 4.
Graph of the plasmid network at a JD of 0.75 (percentage of non-shared genes between two plasmids). Symbols indicate the type of plasmid or phage: MPF, MOB and RelN. Colour codes of the borders of the symbols indicate the type of incompatibility group (Inc) for the MPF plasmids and the type of replication system for the MOB plasmids. MOBRNA is for plasmids with an RNAII/RNAI replication system and MOBrep for plasmids with a replication protein system. The fill colour of the symbols indicates the plasmid's type of resistance: red, blue and yellow are for plasmids carrying at least one ESBL-encoding gene. Clusters of at least two plasmids are surrounded in black and numbered.
Cluster analysis
We first correlated the clusters obtained with the classification made previously on mobility type and of replication/control type systems. Among the 14 clusters, 7 contained MPF plasmids (clusters 1 to 7), 2 contained RelNRNA plasmids (clusters 8 and 9), 1 contained MOBrep plasmids (cluster 10), 3 contained MOBRNA plasmids (cluster 11 to 13) and 1 contained phages (cluster 14) (Fig. 4). We then explored further the plasmid content of the various clusters.
MPF clusters
In each of the seven MPF clusters, plasmids were of the same incompatibility group or complex. Cluster 1 contained 25 of the 26 IncF plasmids. Only an IncFIIk plasmid (RCS36) encoding a SHV-3 ESBL (Table S1) was found as a singleton, clearly showing that this plasmid type, described in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains [46], differed from the other IncFII plasmids. Cluster 2 contained the 17 IncI1 plasmids, the 2 IncK plasmids and the 2 IncB/O plasmids, which is consistent since all these plasmids belong to the I-complex [51]. Cluster 3 contained the 13 IncA/C plasmids, and cluster 4 the 4 IncL/M plasmids. Cluster 5 contained the five IncN plasmids excluding the IncN2 plasmid and the IncN-like plasmid found as singletons, showing that these latter plasmids have a low degree of sequence similarity with the IncN plasmids. Of the seven IncX plasmids, cluster 6 contained the three IncX1 plasmids and cluster 7 the two IncX4 plasmids, excluding the IncX2 and IncX-like plasmids found as singletons (Tables S1 and S2). The IncX-type plasmids, which are known to be diverse [52, 53], are clearly clustered according to their IncX-subgroup, stressing the low degree of sequence similarity between the IncX sub-types.
RelNRNA clusters
Of the eight RelNRNA plasmids, five were found in cluster 8, two in cluster 9 and one was a singleton, corresponding to three different families of plasmids. Indeed, in each cluster the plasmid backbones were closely related, while between the clusters the plasmid backbones had no sequence similarity.
MOBrep cluster
Of the five MOBrep plasmids, four were found in cluster 10 and one was a singleton. Plasmids of cluster 10 were closely related and had no sequence similarity with the singleton plasmid, showing two different plasmid families that we named MOBrepB1 for the plasmids of cluster 10 and MOBrepB2 for the singleton (Tables S1 and S2).
MOBRNA clusters
The 17 MOBRNA plasmids were distributed in three clusters (clusters 11, 12 and 13) and only 1 plasmid was a singleton. To better characterize these three MOBRNA plasmid clusters, we looked at their type of mobilization system and typed them in silico by the plasmid relaxase gene typing (PRaseT) developed by Compain et al. [54]. Cluster 11 contained seven MOBRNA plasmids. Six of them had a backbone similar to the colE1 backbone [32] that includes a mobilization system, mbeABCDE [55], of relaxase gene type (RGT) P5-1 as colE1. The last plasmid did not share these characteristics and, therefore, belonged to a different family of plasmids (see below). An HGT containing a colicin E1 carried by this last plasmid and three plasmids of the cluster blurred the phylogenetic signal. Cluster 12 contained two plasmids that had a mobilization system that diverged from the one of colE1 and were not typed by PRaseT. Thus, they were considered as belonging to a different plasmid family. Cluster 13 contained seven plasmids that according to their mobilization system belonged to three different families. In this cluster, the effect of HGT hindered the phylogenetic signal. Indeed, a large resistance module carrying the blaSHV-12 gene acquired by four plasmids belonging to each of the three families linked the plasmids together and thereby plasmids of their respective families (data not shown). In this cluster, three plasmids had a mobilization system mobABCD of RGT P5-2 as pTPqnrS-1a, two plasmids had a mobilization system mobBC of RGT C11 as ColEST258 and the last two plasmids had a unique small relaxase gene, mob, of RGT P5-3 as pHUSEC41-4. These last two plasmids had the same backbone as the plasmid linked by HGT to the colE1-type plasmids of cluster 11 and the MOBRNA singleton plasmid.
Phage cluster
The two P1-like bacteriophages were found in cluster 14, while the P2-like bacteriophage was found as a singleton showing that these two types of phage had no sequence similarity.
Singletons
In addition to the singleton plasmids previously cited, four other MPF plasmids were found as singletons: the two IncHI plasmids, one of subgroup IncHI1 and the other of subgroup IncHI2, stressing the low degree of sequence similarity between the two IncHI subgroup [56], the only plasmid of IncY group, and a plasmid that showed no sequence similarity with any of known MPF plasmid. The last singleton was a RelNrep plasmid of IncR group [48] (Table 1).
Relationship between the types of plasmids and the phylogeny of the parental strains
We explored the clonal diversity, using the MLST IP [26], of the available parental strains of the plasmids studied (72/73 of the ESBL-producing strains and 17/19 of the strains isolated before the use of the 3GCs) in relation to the type of plasmid. Parental strains were distributed into 6 of the 7 lineages belonging to E. coli sensu stricto [25] (phylogroups A, B1, B2, D, C and F for the ESBL-producing strains and phylogroups A, B1, D, C, E and F for the strains isolated before the use of 3GCs) and showed a high diversity (Fig. 5). In each of the phylogroups, the diversity of the plasmids in terms of genome backbone and clusters and the diversity of the type of resistances was high underlying that, in each cluster of plasmids, the plasmids originated from E. coli strains of various backgrounds.
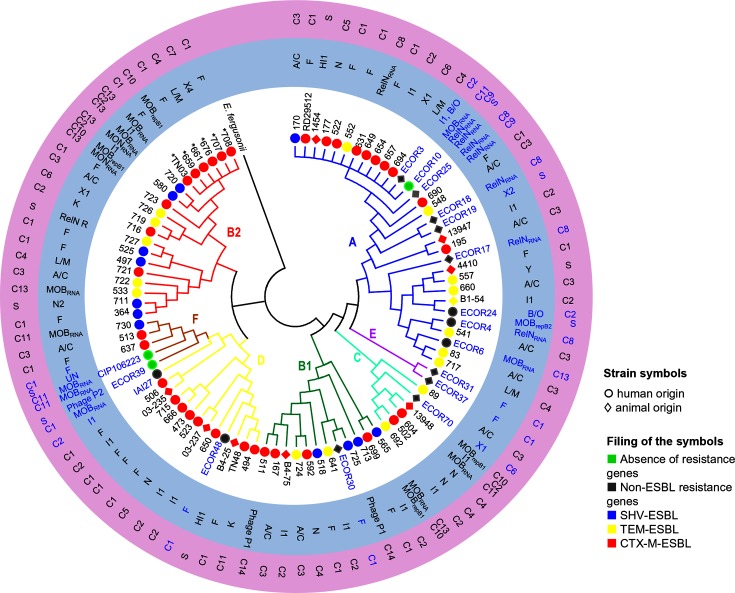
Fig. 5.
Phylogeny of the E. coli host strains. Phylogenetic tree reconstructed from the alignment of the concatenated sequences of eight genes of the MLST IP scheme using PhyML under the GTR model, with E. fergusonii as the outgroup. The phylogroups are indicated with the colours blue (A), green (B1), red (B2), turquoise (C), yellow (D), purple (E) and brown (F). First circle (no background): strain ID in blue for the strains isolated before the use of 3GCs and in black for the strains isolated after the use of 3GCs. * indicates strains of ST43 (ST131 Achtman MLST scheme); symbols indicate strain origin, fill colour of the symbols indicates the type of resistance (red, blue and yellow are for strains carrying at least one ESBL-encoding gene). Second circle (blue background): corresponding plasmids studied for each strain, MPF plasmids are indicated by their Inc group, and MOB plasmids and RelN plasmids by the type of replication system. Third circle (purple background): cluster number (C1 to C13) to which the plasmids belong, as defined in Fig. 4, and S (singleton) for plasmids not linked to a cluster.
Phylogeny of the IncF plasmids of cluster 1 and IncI1 plasmids of cluster 2
To explore more thoroughly the results presented above on a global scale, we analysed at a finer scale the evolutionary history of the plasmids for the two clusters containing the most plasmids, i.e. the MPF clusters 1 and 2 (Fig. 6). Complete data of the other clusters will be presented elsewhere. We reconstructed the phylogenetic trees using for each cluster of plasmids a pool of shared genes as described in Methods. As in each group of plasmids none of the plasmids shared a common resistance gene, the resistance genes did not influence the evolutionary history of the plasmids.
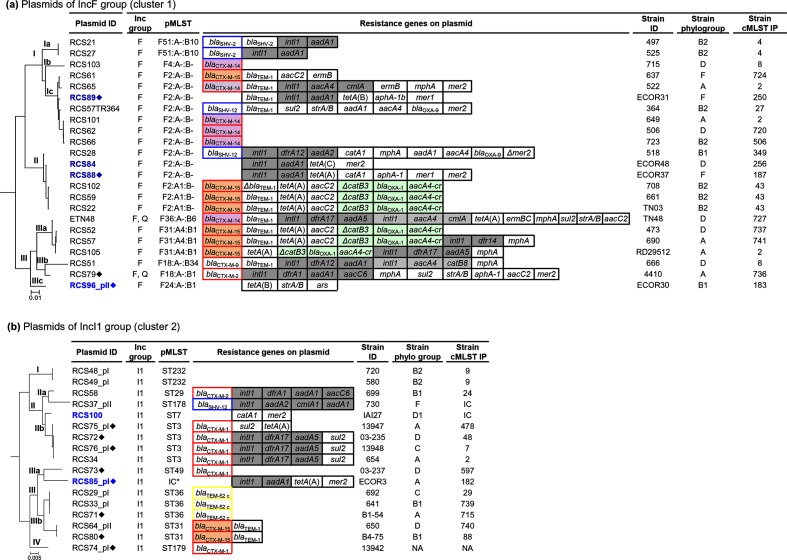
Fig. 6.
Phylogenetic trees of (a) 23 IncFII plasmids and (b) 17 IncI1 plasmids reconstructed as described in Methods. pMSLT, resistance genes on the plasmids, parental strain phylogroup and Institut Pasteur scheme chromosomal MLST (cMLST IP) are indicated to the right of the tree. Plasmid IDs are in blue for the strains isolated before the use of 3GCs and in black for the strains isolated after the use of 3GCs. ♦, plasmids isolated from animal strains. ESBL-encoding genes are framed in red for CTX-M-type genes, yellow for TEM-type genes and in blue for SHV-type genes. blaCTX-M-14 genes are shaded in violet and blaCTX-M-15 genes in orange. Integrons and their gene cassettes are shaded in grey. The IS26 transposition cat-blaOXA-1-aacA4-cr cassette array is shaded in turquoise. NA, Non-available; IC, incomplete ST. Bar, the approximate distance of substitution of nucleotides per site.
IncF plasmids of cluster 1
The core genomes of IncFII plasmids have a mosaic structure [57] and have been shown to have an extensive diversity [58]. As the more genes we use the more reliable is the tree, we built a tree with 25 genes (the replication gene repA1 and 24 genes of the tra operon) shared by 23 of the 25 plasmids of the cluster. The two excluded plasmids were RCS93_pI, originating from a strain of the Murray collection [21, 22], in which all but three of the tra operon genes were missing, and RCS70 that belonged to group C of the IncF/MOBF12 plasmids [59], while all the other IncFII plasmids of the cluster belonged to group A.
The phylogenetic tree obtained showed that the 23 IncF plasmids were distributed in three main branches, I to III, divided in sub-branches (Fig. 6a). Distribution of the plasmids in the branches was correlated with the plasmid STs (pSTs) attributed to the plasmids by pMLST [34]. However, pMLST lacked the sensitivity to discriminate the plasmids as pST F2 was attributed to 13 out of 23 plasmids that were distributed in two very divergent branches of the phylogenetic tree (7 in branch I and 6 in branch II). The four plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs, all from ECOR strains (three from animals and one from humans), were found distributed in the three branches of the phylogenetic tree along with ESBL-encoding plasmids, showing that ESBL-encoding plasmids have the same diversity and phylogenetic history as plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs (Fig. 6a).
We looked at the type of ESBL found on plasmids of the different branches and sub-branches. The seven blaCTX-M-15 plasmids were distributed in the three branches of the tree, the six blaCTX-M-14 plasmids were distributed in two branches (branches I and III), and the two blaSHV-12 plasmids were distributed in two branches of the tree (branches I and II). Only the two blaSHV-2 plasmids closely clustered in sub-branch Ia. Furthermore, closely related plasmids carried different ESBL-encoding genes, such as plasmids of sub-branch Ic that carried either a blaCTX-M-15, a blaCTX-M-14 or a blaSHV-12 gene, plasmids of branch II that carried either a blaCTX-M-15 or a blaSHV-12 gene, and plasmids of sub-branch IIIa that carried either a blaCTX-M-15 or a blaCTX-M-14 gene.
With the exception of four blaCTX-M-14 genes, all the other ESBL-encoding genes were found associated with various resistance modules on multi-resistance regions (MRRs) (Fig. 6a). However, five of the blaCTX-M-15 genes were on similar MRRs containing the same three resistance modules [a tetA(A) module, an aacC2 module and an IS26-mediated cassette array (IS26-aacA4-cr-blaOXA-1-catB3Δ- IS26)] [60–62]. These particular blaCTX-M-15 MRRs were carried by three closely related plasmids of branch II (RCS22, RCS59 and RCS102) and two plasmids (RCS52 and RCS57) of branch IIIa showing movement of the association resistance module-blaCTX-M-15 gene between distantly related plasmids.
As observed in Figs 5 and 6(a), the background of the parental strains inferred by the phylogenetic group and the MLST IP was very diverse: the 23 strains were represented by five of the seven phylogroups that included 18 STs. Similar plasmids isolated from E. coli strains of the same phylogenetic background were demonstrated twice: in branch Ia, the two blaSHV-2 plasmids of pST F51 : A-B10 originating from B2-ST4 strains; and in branch II, the three blaCTX-M-15 plasmids of pST F2 : A1 : B- originating from B2-ST43-H30 strains (ST131, Achtman MLST scheme). All the parental strains of these two groups of plasmids were isolated at various times in different hospital locations validating the clonal dissemination of these two types of ESBL-encoding strain. Conversely, we observed the dissemination of single plasmids. Indeed, in sub-branch Ic, three closely related blaCTX-M-14 plasmids (RCS101, RCS62 and RCS68) (Fig. 6a), were found in strains of three different phylogenetic backgrounds (phylogroup A, D and B2, respectively). Thus, we did not evidence any predominant association between branches/sub-branches of the tree and ESBL type.
IncI1 plasmids of cluster 2
In contrast to the IncF plasmids, the major part of the backbones of the IncI1 plasmids are highly conserved [63]. Thus, we were able to build a tree with 52 shared genes that included all the 17 IncI1 plasmids and excluded the IncB/O and IncK plasmids. The phylogenetic tree obtained showed that the plasmids were distributed in four main branches, I to IV (Fig. 6b). pMLST assigned the plasmids to 10 different pSTs. The correlation between the pSTs and the distribution of the plasmids in the branches of the tree was consistent as all the plasmids assigned to the same pST were found in the same branch. However, as previously observed [63], clusters of plasmids of different pSTs were found in a same sub-branch stressing a close evolutionary relationship between the different pST lineages. This was the case for plasmids of pST7 and pST3 clustered in sub-branch IIb and plasmids of pST31 and pST36 clustered in sub-branch IIIb. The two plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs were found clustered in two branches of the phylogenetic tree, branches II and III, along with the ESBL-encoding plasmids showing as for the IncF plasmids that the IncI1 ESBL-encoding plasmids have the same diversity and phylogenetic history as the plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs.
Various ESBL-encoding genes were found on the plasmids distributed in the two main branches of the tree (blaSHV-12, blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-2 gene in branch II, and blaTEM-52, blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-15 gene in branch III) and blaCTX-M-1 gene, the most represented ESBL-encoding gene among the IncI1 plasmids of this study, was found on distantly related plasmids distributed in three branches, II, II and IV. However, IncI1 plasmids that closely clustered together in sub-branches were of the same pST type and carried the same ESBL-encoding gene. Then, in sub-branch IIIb, all the plasmids of pST36 carried a blaTEM-52 gene and all the plasmids of pST31 carried a blaCTX-M-15 gene inserted in a Tn2-blaTEM-1 transposon, and in branch IIb all the plasmids of pST3 carried a blaCTX-M-1 gene with the same accessory resistance module (Fig. 6b). This was in agreement with previous works showing circulation of a number of prevalent IncI1 plasmids among bacterial species of animal and human reservoirs [63–66].
The background of the parental strains was diverse in term of phylogenetic group and MLST IP, which validated the clonal dissemination of the plasmids of the three pST-ESBL combination groups cited above. Only the two plasmids of pST232 (RCS48_pI and RCS49_pI) in branch I originated from strains of the same phylogenetic background (B2-ST9). These plasmids, which co-transferred by conjugation MOBRNA plasmids harbouring blaSHV-I2, were isolated at different times in different hospital locations, suggesting in this case the dissemination of a clonal SHV-12-producing strain.
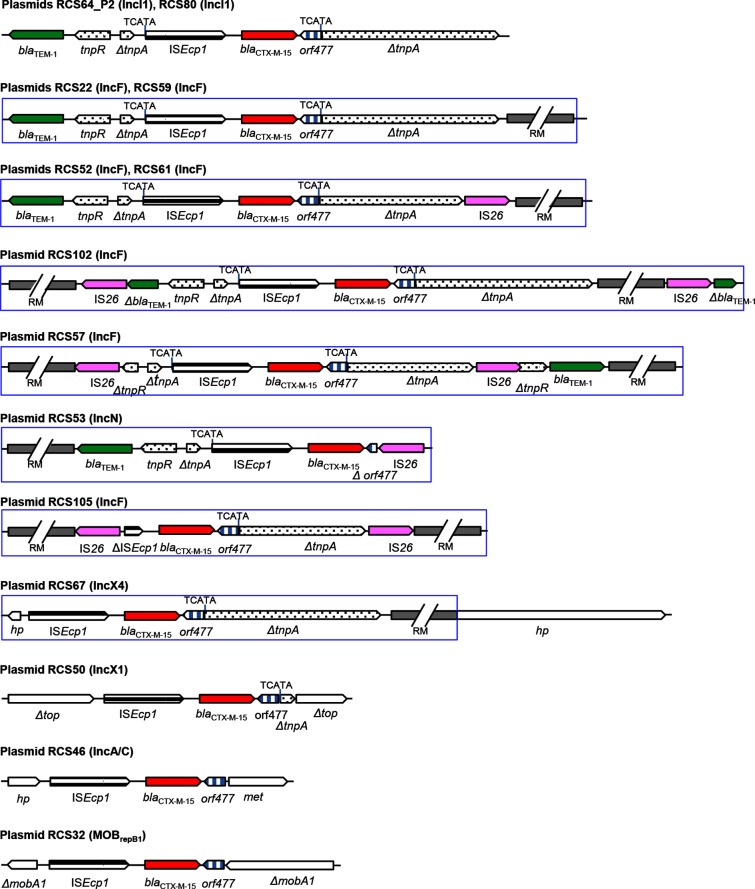
blaCTXM-15 insertion site environment
We explored in detail the insertion site environment of the 14 plasmids of our collection carrying blaCTX-M-15 and performed additional epidemiological analysis. We found that on 12 of the 14 plasmids (7 IncF, 2 IncI1, 1 IncN, 1 IncX1 and 1 IncX4 plasmids), the blaCTX-M-15 transposition (ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15-orf477) had happened first at the target duplicate site (TCATA) of a Tn2 transposon (blaTEM-1-tnpR-ΔtnpA-Tn2-ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15-orf477-ΔtnpA) (Fig. 7). On nine plasmids, the insertion of the blaCTX-M-15 gene in the Tn2 was found on MRRs and six times the transposition unit was truncated at various positions (IRtnp and IRTEM end of Tn2, orf477, and ISEcp1) by IS26 elements (Fig. 7) putatively mediating their rearrangement on the MRRs [60]. On two plasmids, RCS50 (IncX1) and RCS67 (IncX4), the blaCTX-M-15 transposition unit was inserted at a different site but a scar of a previous transposition at the Tn2 specific target duplicate site was evident (Fig. 7). Other ESBLs of the CTX-M-1 group, such as CTX-M-1 and CTX-M-3, have the same transposition units as CTX-M-15 with the difference that beyond the right-hand inverted repeat (IRR) of ISEcp1 is generally found, in addition to the 48 bp sequence present for the blaCTX-M-15, a 32 bp sequence for blaCTX-M-1 and a 79 bp sequence for blaCTX-M-3 [67]. In our study, none of the 11 blaCTX-M-1 genes and none of the 3 blaCTX-M-3 genes was inserted in a Tn2 transposon (data not shown). We, thus, assessed the prevalence of the insertion of the transposition unit in Tn2 of bla genes of the CTX-M-1 group carried by non-redundant strains of published and personal collections [16, 23, 68] using primers designed to overlap the insertion site upstream the ISEcp1 and upstream the orf477 gene (Table S3). We tested 22 strains carrying a blaCTX-M-1 and 2 strains carrying a blaCTX-M-3 that were all negative. Of the 45 strains carrying a blaCTX-M-15, 39 (86.6 %) strains were positive (10 were positive for both PCR and 29 were positive for the PCR overlapping the insertion site upstream of the orf477 gene).
Fig. 7.
Schematic representation of the genetic environment of blaCTX-M-15 genes found in 14 plasmids of the study. The transposition unit ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15-orf477 was inserted in 12 plasmids at a specific target duplicate site (TCATA) in tnpA of a blaTEM-1-Tn2 transposon. tnpA, transposase of Tn2 transposon; tnpR, resolvase of Tn2 transposon; top, topoisomerase gene; hp, gene encoding a hypothetical protein of unknown function; met, gene encoding a methylase; mobA1, mobilization (relaxase) gene. RM, resistance module associated with blaCTX-M-15 containing different resistance genes or identical genes with different organizations on MRRs. MRRs are framed in blue.
Discussion
To have a full picture of the spread of ESBL-encoding genes in E. coli, we undertook a comprehensive comparative analysis of the sequences of a large number of diverse plasmids from human and animal strains isolated over a large period of time spanning before and after the use of 3GCs. For all the plasmids, we obtained high-quality circular sequences whose annotation was manually checked.
The relationship between the type of plasmid and the type of antibiotic resistance showed that although ESBL-encoding genes are mainly found on MPF plasmids, the MOB and RelN plasmids as well as the P1-like bacteriophages also play a role, albeit modest, in the diffusion of the ESBLs, and that the small RelN plasmids play a role in the diffusion of non-ESBL resistance genes compared to the MOB plasmids.
Classification and reconstruction of the evolutionary relationship of plasmids is challenging. The great variability in their gene content, mostly due to HGT events, often blurs any phylogenetic signal. Thus, we used a gene-sharing network method that allows circumventing the noisy HGT effect on the phylogenetic history reconstruction. With the exception of the small MOBRNA plasmids of clusters 11 and 13, where large HGT hindered the phylogenetic signal of the different MOBRNA families, all the other plasmids clustered according to the type of their genome backbone, e.g. Inc group for MPF and the various plasmid families as described earlier for the MOB and RelNRNA plasmids. Thus, the plasmids having the same type of genome backbone were linked in the same cluster independently of their type of antibiotic resistance (no resistance gene, non-ESBL resistance genes or type of ESBL-encoding genes) and consequently independently of their origin (human or animal) or their period of isolation (before or after the use of the 3GCs). For each cluster of plasmids, we checked for the diversity of the parental strains as a link between specific clones and/or phylogroups and plasmids, including ESBL-producing plasmids [1, 9, 11, 23]. Globally, we did not retrieve any association between the type of plasmids and the phylogeny of the parental strains.
The analysis at a finer scale of the evolutionary history of the plasmids for the two major clusters, the IncF and IncI1 clusters, confirmed that the ESBL-encoding plasmids have the same phylogenetic history as plasmids isolated before the use of the 3GCs, suggesting that ESBL arrived at random on pre-existing plasmids and not on particular selected plasmids. It showed that the acquisition of the various ESBL-encoding genes has happened independently through multiple events on related or unrelated plasmids and that movement of the association resistance module-blaCTX-M-15 gene had happened on the IncF plasmids. We observed also that in contrary to the IncF plasmids, the occurrence of clonal diffusion of ESBL IncI1 plasmids is important [63–66].
Among CTX-M enzymes, CTX-M-15 belonging to the CTX-M-1 group appears to be the most widespread, particularly in E. coli [5], and surveys in several different countries have indicated that blaCTX-M-15 is often carried on IncF plasmids [3, 11, 12, 60, 62, 69–71]. blaCTX-M-15 is found as part of a transposition unit that has been described many times, inserted into a specific target duplicate site (TCATA) in the tnpA of a blaTEM-1-Tn2 transposon [60, 72, 73]. Only once, on plasmid pSH4469, has a different target duplicate site been found on a Tn2 transposon [72]. In our study, the majority (12/14) of the blaCTX-M-15 was inserted into this specific target unlike the blaCTX-M-1 and blaCTX-M-3 genes, although they belong to the same CTX-M-1 group. However, to our knowledge, the insertion in the tnpA of Tn2 had been described for blaCTX-M-3 at a different target duplicate site as on pEK204 [72, 74, 75], but has never been described for blaCTX-M-1. Our additional epidemiological analysis on strains of our collections carrying bla genes of the CTX-M-1 group showed that the majority of the blaCTX-M-15 genes were found inserted into the specific target, in agreement with previous observations that blaCTX-M-15 but not blaCTX-M-1 genes easily transpose on plasmids carrying blaTEM-1-Tn2 at the specific duplicated site TCATA. In E. coli, ampicillin resistance is mainly conferred by the blaTEM-1 gene that is located on a Tn2 transposon [12, 76, 77]. Ampicillin resistance in E. coli rises from 27 % in the community to 55 % in hospital infections, and has increased during the last two decades [76, 78–81]. Therefore, the wide spread of the CTX-M-15 enzymes, but not the CTX-M-1 nor the CTX-M-3 enzymes, among E. coli strains seemed to be linked to a hot spot of insertion on the blaTEM-1-Tn2 transposon, a transposon largely found on IncF plasmids, one of the most prevalent plasmids in E. coli strains [12, 57, 82].
The main conclusions of our work are that ESBL-encoding genes arrived multiple times on a wide range of pre-existing plasmids and that a highly dynamic pattern of mobility was observed concerning different nested physical units represented by the ESBL-encoding gene, the MRR and finally the plasmid. The combination of these different levels multiplies the potential of ESBL-encoding gene spread. Furthermore, the successful spread of the CTX-M-15 ESBL-encoding gene in E. coli seemed to be favoured by its arrival in a Tn2- blaTEM-1 transposon borne on well-adapted IncF plasmids.
Data bibliography
Genoscope CEA. European Nucleotide Archive, PRJEB24625 (2018).
Genoscope CEA. European Nucleotide Archive, LO017736 (2016).
Genoscope CEA European Nucleotide Archive, LO017737 (2016).
Genoscope CEA. European Nucleotide Archive, LO017738 (2016).
Genoscope CEA. European Nucleotide Archive, FO818745 (2015).
Genoscope CEA. European Nucleotide Archive, FQ482074 (2010).
Supplementary Data
Funding information
This work was supported by a grant from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (grant ANR-10-GENM-0012) to C. B. This work was also partially supported by a grant from the ‘Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale’ to E. D. (Equipe FRM 2016, grant number DEQ20161136698).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Abbreviations: 3GC, third-generation cephalosporin; ESBL, extended-spectrum β-lactamase; FAC, factorial analysis of correspondence; GTR, general time reversible; HGT, horizontal gene transfer; JD, Jaccard distance; MLST, multilocus sequence typing; MLST IP, Institut Pasteur MLST; MOB, mobilizable; MPF, mating pair formation; MRR, multi-resistance region; PBRT, PCR-based replicon typing; pMLST, plasmid MLST; PRaseT, plasmid relaxase gene typing; pST, plasmid sequence type; RelN, relaxase negative; RGT, relaxase gene type; ST, sequence type.
All supporting data, code and protocols have been provided within the article or through supplementary data files. Three supplementary tables are available with the online version of this article.
References
- 1.Coque TM, Baquero F, Canton R. Increasing prevalence of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2008;13:19044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carattoli A. Plasmids and the spread of resistance. Int J Med Microbiol. 2013;303:298–304. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cantón R, Coque TM. The CTX-M β-lactamase pandemic. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006;9:466–475. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pitout JD, Laupland KB. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: an emerging public-health concern. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:159–166. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(08)70041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Woerther PL, Burdet C, Chachaty E, Andremont A. Trends in human fecal carriage of extended-spectrum β-lactamases in the community: toward the globalization of CTX-M. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26:744–758. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00023-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Livermore DM, Canton R, Gniadkowski M, Nordmann P, Rossolini GM, et al. CTX-M: changing the face of ESBLs in Europe. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;59:165–174. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Woodford N, Turton JF, Livermore DM. Multiresistant Gram-negative bacteria: the role of high-risk clones in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011;35:736–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nicolas-Chanoine MH, Blanco J, Leflon-Guibout V, Demarty R, Alonso MP, et al. Intercontinental emergence of Escherichia coli clone O25:H4-ST131 producing CTX-M-15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;61:273–281. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Blanco J, Mora A, Mamani R, López C, Blanco M, et al. National survey of Escherichia coli causing extraintestinal infections reveals the spread of drug-resistant clonal groups O25b:H4-B2-ST131, O15:H1-D-ST393 and CGA-D-ST69 with high virulence gene content in Spain. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:2011–2021. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mathers AJ, Peirano G, Pitout JD. The role of epidemic resistance plasmids and international high-risk clones in the spread of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015;28:565–591. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00116-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Coque TM, Novais A, Carattoli A, Poirel L, Pitout J, et al. Dissemination of clonally related Escherichia coli strains expressing extended-spectrum β-lactamase CTX-M-15. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:195–200. doi: 10.3201/eid1402.070350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Marcadé G, Deschamps C, Boyd A, Gautier V, Picard B, et al. Replicon typing of plasmids in Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum β-lactamases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;63:67–71. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Smet A, Martel A, Persoons D, Dewulf J, Heyndrickx M, et al. Comparative analysis of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-carrying plasmids from different members of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from poultry, pigs and humans: evidence for a shared β-lactam resistance gene pool? J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009;63:1286–1288. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Meunier D, Jouy E, Lazizzera C, Kobisch M, Madec JY. CTX-M-1- and CTX-M-15-type β-lactamases in clinical Escherichia coli isolates recovered from food-producing animals in France. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2006;28:402–407. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2006.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smet A, Boyen F, Flahou B, Doublet B, Praud K, et al. Emergence of CTX-M-2-producing Escherichia coli in diseased horses: evidence of genetic exchanges of blaCTX-M-2 linked to ISCR1. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67:1289–1291. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Birgy A, Mariani-Kurkdjian P, Bidet P, Doit C, Genel N, et al. Characterization of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli strains involved in maternal-fetal colonization: prevalence of E. coli ST131. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:1727–1732. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03255-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Deschamps C, Clermont O, Hipeaux MC, Arlet G, Denamur E, et al. Multiple acquisitions of CTX-M plasmids in the rare D2 genotype of Escherichia coli provide evidence for convergent evolution. Microbiology. 2009;155:1656–1668. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.023234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lavollay M, Mamlouk K, Frank T, Akpabie A, Burghoffer B, et al. Clonal dissemination of a CTX-M-15 β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli strain in the Paris area, Tunis, and Bangui. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:2433–2438. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00150-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ochman H, Selander RK. Standard reference strains of Escherichia coli from natural populations. J Bacteriol. 1984;157:690–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.690-693.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Picard B, Garcia JS, Gouriou S, Duriez P, Brahimi N, et al. The link between phylogeny and virulence in Escherichia coli extraintestinal infection. Infect Immun. 1999;67:546–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.2.546-553.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hughes VM, Datta N. Conjugative plasmids in bacteria of the 'pre-antibiotic' era. Nature. 1983;302:725–726. doi: 10.1038/302725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baker KS, Burnett E, McGregor H, Deheer-Graham A, Boinett C, et al. The Murray collection of pre-antibiotic era Enterobacteriacae: a unique research resource. Genome Med. 2015;7:97. doi: 10.1186/s13073-015-0222-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Branger C, Zamfir O, Geoffroy S, Laurans G, Arlet G, et al. Genetic background of Escherichia coli and extended-spectrum β-lactamase type. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:54–61. doi: 10.3201/eid1101.040257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Carattoli A, Bertini A, Villa L, Falbo V, Hopkins KL, et al. Identification of plasmids by PCR-based replicon typing. J Microbiol Methods. 2005;63:219–228. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2005.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Clermont O, Christenson JK, Denamur E, Gordon DM. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013;5:58–65. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jaureguy F, Landraud L, Passet V, Diancourt L, Frapy E, et al. Phylogenetic and genomic diversity of human bacteremic Escherichia coli strains. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:560. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Guindon S, Gascuel O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol. 2003;52:696–704. doi: 10.1080/10635150390235520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kumar S, Blaxter ML. Comparing de novo assemblers for 454 transcriptome data. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:571. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Médigue C, Calteau A, Cruveiller S, Gachet M, Gautreau G, et al. MicroScope-an integrated resource for community expertise of gene functions and comparative analysis of microbial genomic and metabolic data. Brief Bioinform. 2017 doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Siguier P, Perochon J, Lestrade L, Mahillon J, Chandler M. ISfinder: the reference centre for bacterial insertion sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D32–D36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Smillie C, Garcillán-Barcia MP, Francia MV, Rocha EP, de La Cruz F. Mobility of plasmids. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010;74:434–452. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00020-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chan PT, Ohmori H, Tomizawa J, Lebowitz J. Nucleotide sequence and gene organization of ColE1 DNA. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:8925–8935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Haneda T, Okada N, Miki T, Danbara H. Sequence analysis and characterization of sulfonamide resistance plasmid pRF-1 from Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis. Plasmid. 2004;52:218–224. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2004.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Carattoli A, Zankari E, García-Fernández A, Voldby Larsen M, Lund O, et al. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:3895–3903. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02412-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.R Core Team . R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, et al. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Brilli M, Mengoni A, Fondi M, Bazzicalupo M, Liò P, et al. Analysis of plasmid genes by phylogenetic profiling and visualization of homology relationships using Blast2Network. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:551. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Newman MEJ. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev Soc Ind Appl Math. 2003;45:167–256. doi: 10.1137/S003614450342480. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Csárdi G, Nepusz T. The igraph Software Package for Complex Network Research. InterJournal. 2006 [Google Scholar]
- 40.Callaway DS, Newman ME, Strogatz SH, Watts DJ. Network robustness and fragility: percolation on random graphs. Phys Rev Lett. 2000;85:5468–5471. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.5468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Barabási AL, Oltvai ZN. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:101–113. doi: 10.1038/nrg1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT. progressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Billard-Pomares T, Fouteau S, Jacquet ME, Roche D, Barbe V, et al. Characterization of a P1-like bacteriophage carrying an SHV-2 extended-spectrum β-lactamase from an Escherichia coli strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:6550–6557. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03183-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Łobocka MB, Rose DJ, Plunkett G, Rusin M, Samojedny A, et al. Genome of bacteriophage P1. J Bacteriol. 2004;186:7032–7068. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7032-7068.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nilsson AS, Haggård-Ljungquist E. Evolution of P2-like phages and their impact on bacterial evolution. Res Microbiol. 2007;158:311–317. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2007.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Villa L, García-Fernández A, Fortini D, Carattoli A. Replicon sequence typing of IncF plasmids carrying virulence and resistance determinants. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65:2518–2529. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Loftie-Eaton W, Rawlings DE. Diversity, biology and evolution of IncQ-family plasmids. Plasmid. 2012;67:15–34. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2011.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Compain F, Frangeul L, Drieux L, Verdet C, Brisse S, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of two multidrug-resistant IncR plasmids from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:4207–4210. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02773-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Partridge SR, Paulsen IT, Iredell JR. pJIE137 carrying blaCTX-M-62 is closely related to p271A carrying blaNDM-1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56:2166–2168. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05796-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Osborn AM, da Silva Tatley FM, Steyn LM, Pickup RW, Saunders JR. Mosaic plasmids and mosaic replicons: evolutionary lessons from the analysis of genetic diversity in IncFII-related replicons. Microbiology. 2000;146:2267–2275. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-9-2267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Praszkier J, Wei T, Siemering K, Pittard J. Comparative analysis of the replication regions of IncB, IncK, and IncZ plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1991;173:2393–2397. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2393-2397.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stokes MO, Abuoun M, Umur S, Wu G, Partridge SR, et al. Complete sequence of pSAM7, an IncX4 plasmid carrying a novel blaCTX-M-14b transposition unit isolated from Escherichia coli and Enterobacter cloacae from cattle. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:4590–4594. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01157-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Johnson TJ, Bielak EM, Fortini D, Hansen LH, Hasman H, et al. Expansion of the IncX plasmid family for improved identification and typing of novel plasmids in drug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Plasmid. 2012;68:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2012.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Compain F, Poisson A, Le Hello S, Branger C, Weill FX, et al. Targeting relaxase genes for classification of the predominant plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae. Int J Med Microbiol. 2014;304:236–242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Varsaki A, Moncalián G, Garcillán-Barcia MP, Drainas C, de La Cruz F. Analysis of ColE1 MbeC unveils an extended ribbon-helix-helix family of nicking accessory proteins. J Bacteriol. 2009;191:1446–1455. doi: 10.1128/JB.01342-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Whiteley M, Taylor DE. Identification of DNA homologies among H incompatibility group plasmids by restriction enzyme digestion and Southern transfer hybridization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983;24:194–200. doi: 10.1128/AAC.24.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Boyd EF, Hill CW, Rich SM, Hartl DL. Mosaic structure of plasmids from natural populations of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1996;143:1091–1100. doi: 10.1093/genetics/143.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ho WS, Yap KP, Yeo CC, Rajasekaram G, Thong KL. The complete sequence and comparative analysis of a multidrug-resistance and virulence multireplicon IncFII plasmid pEC302/04 from an extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli EC302/04 indicate extensive diversity of IncFII plasmids. Front Microbiol. 2015;6:1547. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Fernandez-Lopez R, de Toro M, Moncalian G, Garcillan-Barcia MP, de La Cruz F. Comparative genomics of the conjugation region of F-like plasmids: five shades of F. Front Mol Biosci. 2016;3:71. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Partridge SR, Zong Z, Iredell JR. Recombination in IS26 and Tn2 in the evolution of multiresistance regions carrying blaCTX-M-15 on conjugative IncF plasmids from Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:4971–4978. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00025-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Johnson TJ, Danzeisen JL, Youmans B, Case K, Llop K, et al. Separate F-type plasmids have shaped the evolution of the H30 subclone of Escherichia coli sequence type 131. mSphere. 2016;1:e00121-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00121-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Irrgang A, Falgenhauer L, Fischer J, Ghosh H, Guiral E, et al. CTX-M-15-producing E. coli isolates from food products in Germany are mainly associated with an IncF-type plasmid and belong to two predominant clonal E. coli lineages. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:2318. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Smith H, Bossers A, Harders F, Wu G, Woodford N, et al. Characterization of epidemic IncI1-Iγ plasmids harboring ambler class A and C genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica from animals and humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:5357–5365. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05006-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Haenni M, Saras E, Métayer V, Doublet B, Cloeckaert A, et al. Spread of the blaTEM-52 gene is mainly ensured by IncI1/ST36 plasmids in Escherichia coli isolated from cattle in France. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67:2774–2776. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Madec JY, Haenni M, Métayer V, Saras E, Nicolas-Chanoine MH. High prevalence of the animal-associated bla CTX-M-1 IncI1/ST3 plasmid in human Escherichia coli isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:5860–5861. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00819-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Leverstein-van Hall MA, Dierikx CM, Cohen Stuart J, Voets GM, van den Munckhof MP, et al. Dutch patients, retail chicken meat and poultry share the same ESBL genes, plasmids and strains. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:873–880. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Eckert C, Gautier V, Arlet G. DNA sequence analysis of the genetic environment of various blaCTX-M genes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;57:14–23. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Courpon-Claudinon A, Lefort A, Panhard X, Clermont O, Dornic Q, et al. Bacteraemia caused by third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli in France: prevalence, molecular epidemiology and clinical features. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:557–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Li JJ, Spychala CN, Hu F, Sheng JF, Doi Y. Complete nucleotide sequences of blaCTX-M-harboring IncF plasmids from community-associated Escherichia coli strains in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:3002–3007. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04772-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hu F, O'Hara JA, Rivera JI, Doi Y. Molecular features of community-associated extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli strains in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:6953–6957. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03321-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lahlaoui H, de Luca F, Maradel S, Ben-Haj-Khalifa A, Ben Hamouda H, et al. Occurrence of conjugative IncF-type plasmids harboring the blaCTX-M-15 gene in Enterobacteriaceae isolates from newborns in Tunisia. Pediatr Res. 2015;77:107–110. doi: 10.1038/pr.2014.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kim JS, Kim J, Jeon SE, Kim SJ, Kim NO, et al. Complete nucleotide sequence of the IncI1 plasmid pSH4469 encoding CTX-M-15 extended-spectrum β-lactamase in a clinical isolate of Shigella sonnei from an outbreak in the Republic of Korea. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2014;44:533–537. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Stoesser N, Sheppard AE, Pankhurst L, De Maio N, Moore CE, et al. Evolutionary history of the global emergence of the Escherichia coli epidemic clone ST131. Mbio. 2016;7:e02162-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02162-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Woodford N, Carattoli A, Karisik E, Underwood A, Ellington MJ, et al. Complete nucleotide sequences of plasmids pEK204, pEK499, and pEK516, encoding CTX-M enzymes in three major Escherichia coli lineages from the United Kingdom, all belonging to the international O25:H4-ST131 clone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:4472–4482. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00688-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Dhanji H, Doumith M, Rooney PJ, O'Leary MC, Loughrey AC, et al. Molecular epidemiology of fluoroquinolone-resistant ST131 Escherichia coli producing CTX-M extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in nursing homes in Belfast, UK. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011;66:297–303. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bailey JK, Pinyon JL, Anantham S, Hall RM. Commensal Escherichia coli of healthy humans: a reservoir for antibiotic-resistance determinants. J Med Microbiol. 2010;59:1331–1339. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.022475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Briñas L, Zarazaga M, Sáenz Y, Ruiz-Larrea F, Torres C. Beta-lactamases in ampicillin-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from foods, humans, and healthy animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:3156–3163. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.10.3156-3163.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Massot M, Daubié AS, Clermont O, Jauréguy F, Couffignal C, et al. Phylogenetic, virulence and antibiotic resistance characteristics of commensal strain populations of Escherichia coli from community subjects in the Paris area in 2010 and evolution over 30 years. Microbiology. 2016;162:642–650. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lefort A, Panhard X, Clermont O, Woerther PL, Branger C, et al. Host factors and portal of entry outweigh bacterial determinants to predict the severity of Escherichia coli bacteremia. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49:777–783. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01902-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Kronvall G. Antimicrobial resistance 1979-2009 at Karolinska hospital, Sweden: normalized resistance interpretation during a 30-year follow-up on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli resistance development. APMIS. 2010;118:621–639. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2010.02660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Tadesse DA, Zhao S, Tong E, Ayers S, Singh A, et al. Antimicrobial drug resistance in Escherichia coli from humans and food animals, United States, 1950–2002. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012;18:741–749. doi: 10.3201/eid1805.111153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.de Toro M, Garcilláon-Barcia MP, de La Cruz F. Plasmid diversity and adaptation analyzed by massive sequencing of Escherichia coli plasmids. Microbiol Spectr. 2014;2:PLAS-0031-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0031-2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.