Therapy for bacteremia caused by Staphylococcus aureus is often ineffective, even when treatment conditions are optimal according to experimental protocols. Adapted subclones, such as those bearing mutations that attenuate agr-mediated virulence activation, are associated with persistent infection and patient mortality.
KEYWORDS: Staphylococcus aureus, gene regulation, genome analysis
ABSTRACT
Therapy for bacteremia caused by Staphylococcus aureus is often ineffective, even when treatment conditions are optimal according to experimental protocols. Adapted subclones, such as those bearing mutations that attenuate agr-mediated virulence activation, are associated with persistent infection and patient mortality. To identify additional alterations in agr-defective mutants, we sequenced and assembled the complete genomes of clone pairs from colonizing and infected sites of several patients in whom S. aureus demonstrated a within-host loss of agr function. We report that events associated with agr inactivation result in agr-defective blood and nares strain pairs that are enriched in mutations compared to pairs from wild-type controls. The random distribution of mutations between colonizing and infecting strains from the same patient, and between strains from different patients, suggests that much of the genetic complexity of agr-defective strains results from prolonged infection or therapy-induced stress. However, in one of the agr-defective infecting strains, multiple genetic changes resulted in increased virulence in a murine model of bloodstream infection, bypassing the mutation of agr and raising the possibility that some changes were selected. Expression profiling correlated the elevated virulence of this agr-defective mutant to restored expression of the agr-regulated ESAT6-like type VII secretion system, a known virulence factor. Thus, additional mutations outside the agr locus can contribute to diversification and adaptation during infection by S. aureus agr mutants associated with poor patient outcomes.
INTRODUCTION
In contrast to organisms that acquire genes for pathogenesis, Staphylococcus aureus appears to have adapted to infection and the hospital environment through virulence-attenuating mutations that partially or completely inactivate the quorum-sensing virulence regulator agr (1–8). In vitro, the Agr quorum-sensing system coordinates a switch from an establishment mode, in which genes for adhesins and protective surface proteins are expressed, to an invasive mode, in which genes for factors that promote host cell and tissue destruction are activated (reviewed in reference 9). agr-deficient mutants are attenuated for virulence in animal models of acute infection, and agents that block agr function and quorum sensing exhibit anti-infective properties in animals (10). However, agr-defective clinical isolates that are “locked” in a low-cell-density (noninvasive) regulatory state arise during infection, particularly in patients with endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and bacteremia (5, 11–13). In this situation, the agr-defective mutants are often associated with persistent infection, the emergence of host and synthetic antimicrobial resistance, and poor outcomes, opposite what is expected from animal infection studies and from the in vitro cytotoxic properties of these strains (11, 13–18). Thus, the emergence of naturally occurring agr-defective mutants during infection provides an opportunity to study how the pathogen shifts to a more persistent state. Moreover, understanding how S. aureus adapts to the challenges of invasive infection is central to managing serious, complicated disease.
In the present work, we mapped all genetic changes outside the agr locus that accompany agr mutation in the human host. We examined naturally occurring agr-defective mutants from a previously characterized collection of 158 pairs of predominantly methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) clones from nasal carriage and from infecting sites of the same patient (12, 19). Strain pairs from individual patients were genotypically isogenic based on pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) banding patterns and spa types (12, 19). Although agr-defective mutants were infrequent in the original study population (5% [19]), among the 158 bacteremic patients, 15 exhibited agr-defective S. aureus in blood samples. Of these patients, 5 were nasally colonized with a genotypically isogenic agr-positive (agr+) strain, indicating that a within-host loss of agr function had occurred. Moreover, these pairs provided a unique set of strains for comparisons that would allow the identification of mutational changes located outside the agr regulon. Complete genome sequencing was used to compare the 5 pairs of clones from nasal and infecting sites that demonstrated a within-host loss in agr function and uniformly agr+ clone pairs from patients without a loss.
RESULTS
Whole-genome sequencing confirms the relatedness of colonizing and infecting isolates within patients.
Individual clones from all 5 pairs of isolates with a loss of agr function in the infecting isolate were examined by whole-genome sequencing (Table 1) (these samples were called cases). Because genetic heterogeneity may not be limited to agr-defective strains, we sequenced pairs of clonal isolates from 7 additional subjects as controls. These control isolates did not demonstrate a within-host loss of agr function, but they were represented by a bacteremia sample and a colonization sample. To avoid potentially confounding effects of mutations associated with the adaptation of hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains to the health care environment, which in some cases may have occurred decades ago (1, 3), we examined both MSSA and MRSA (see Table S1 in the supplemental material), since unlike MRSA, MSSA clones usually do not disseminate in hospitals (20, 21). Thus, whole-genome sequencing was expected to provide a broad characterization of the range and potential diversity of mutations associated with human bacteremia. Case and control groups were balanced for MSSA/MRSA, each containing two patients with MRSA isolate pairs as determined by the presence of mecA. In an additional 3 instances (2 cases and 1 control), available isolates from the presumed focus of infection (e.g., pneumonia or skin and soft tissue infection) were included in the analysis to assess their roles as reservoirs for variants.
TABLE 1.
Summary of variants in infecting strains compared to the colonizing strain in each patient
| Patient | Strain type | agr statusa | No. of SNVs |
No. of insertions/deletions of ≤5 nt |
No. of structural variants of >5 nt |
Total no. of variantsd (no. of variants in core genome/no. of variants in accessory genome) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonsynonymous (I/C/U)e | Stop gain (I/C)e | Stop loss (I/C)e | Synonymous (I/C/U)e | Intergenic (I/C/U)e | Otherb | Intergenic (I/C)e | Frameshift (I/C)e | Structural variant (I/C)e | Repeat expansion (I/C)e | Variable regionc | Inversion | Plasmid loss | ||||
| Cases | ||||||||||||||||
| 53 | Blood | − | 46/48/7 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 21/49/37 | 21/20/52 | 7 | 13/13 | 5/6 | 3/3 | 3/4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 362 (137/225) |
| 60 | Blood | − | 0/1/0 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/1 | 1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (4/1) |
| 73 | Blood | − | 5/6/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 4/3/37 | 4/1/0 | 0 | 1/2 | 1/0 | 2/0 | 1/1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 68 (22/46) |
| 117 | Blood | − | 0/0/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1/0 | 2/0/0 | 0 | 1/0 | 0/0 | 0/2 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 (4/4) |
| 117 | Focus | + | 1/0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1/0 | 1/0/0 | 0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (3/2) |
| 135 | Blood | − | 1/3/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1/1 | 0/3/1 | 0 | 3/4 | 0/1 | 3/3 | 0/1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 28 (6/22) |
| 135 | Focus | − | 1/3/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1/1 | 0/3/1 | 0 | 6/0 | 1/1 | 4/3 | 0/1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28 (5/23) |
| Controls | ||||||||||||||||
| 35 | Blood | + | 0/2/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 (0/4) |
| 36 | Blood | + | 0/2/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 1 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 (3/3) |
| 45 | Blood | + | 1/0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (1/0) |
| 63 | Blood | + | 2/2/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (4/0) |
| 108 | Blood | + | 0/0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 2/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (2/1) |
| 152 | Blood | + | 0/0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 (2/1) |
| 152 | Focus | + | 0/0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/1/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 (1/4) |
| 158 | Blood | + | 1/1/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0/0/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 (2/1) |
+, wild type; −, agr defective.
Uncategorized SNV in the gene in one strain but not in the gene in the other.
Variable region with a different sequence at the same position.
Variant counts in the total, core, and accessory genomes.
Ancestry of mutations was determined by PAML analysis. I, infecting strain (blood or infection focus); C, colonizing strain (nares); U, undetermined ancestry (i.e., associated with variably present repeat and/or mobile elements).
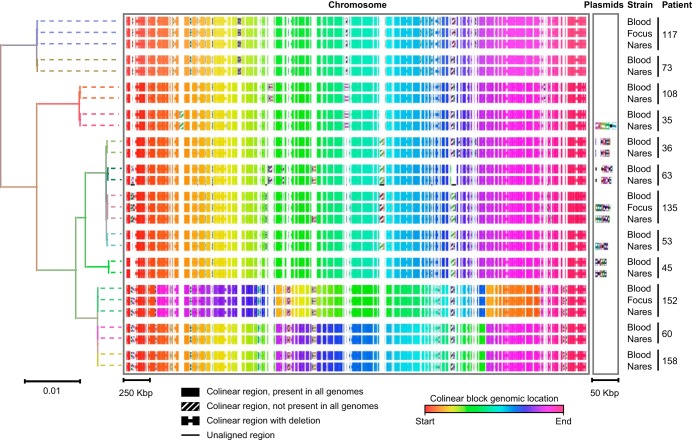
Closed genomes were obtained by using Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) RS-II long-read sequencing for all 27 isolates (5 pairs of case strains, 7 pairs of control strains, and 3 foci), including 9 distinct plasmids from 6 patients. Additional Illumina sequencing was performed to address insertion/deletion (indel) errors associated with homopolymer regions in the PacBio data, resulting in a correction of 4 to 159 variants per genome. A description of strains, genome size, sequence quality, and the presence of plasmids can be found in Table S1. Phylogenetic analysis and multisequence alignment of the genomic data confirmed that blood, infection focus, and nares strains from each patient were more closely related to each other than to strains from other patients (Fig. 1) or to 39 reference strains having completely sequenced genomes (obtained from the NCBI) (Fig. S1).
FIG 1.
Genomic comparison of study strains with block alignments. Shown is a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on core genome SNVs of all patient clones (left), with a graphical representation of the complete genome alignment (right). Branches in the phylogenetic tree are colored according to the patient from whom each strain originated. Bars indicating the number of substitutions per site in the phylogenetic tree or the alignment block length are shown at the bottom. Dotted lines are included in the tree as guides and do not reflect genetic distance. Core colinear blocks present in all isolate genomes are shown as solid rectangles in the multiple alignment and are colored according to the block location in each genome to highlight inversions (key at the bottom). Noncore regions present in only a subset of genomes are each represented with a unique striped fill pattern.
We identified mutations in cases and controls by comparing the complete genome of each infecting strain (i.e., blood or infection focus) to that of the colonizing strain (i.e., nares) from the same patient. In aggregate, our analysis identified 420 single nucleotide variants (SNVs), 66 indels of <5 nucleotides (nt), 44 larger structural variants (SVs) (>5 nt), and 3 plasmid losses across all strain pairs, which we further categorized by type and predicted impact on coding sequences (Table 1). Variants were unevenly distributed across genome pairs (Fig. S2), related to whether they were located within core genomic regions present in all sequenced strains and complete NCBI genomes (Fig. S1) or within accessory genomic regions found in only a subset of strains. The number of variants per megabase was 6.3-fold higher in the accessory genome, suggesting a higher rate of evolution than in the core genome. Notably, variants associated with tandem repeat (TR) regions in the accessory genome, which would not be readily detected without long-read sequencing (22), contributed substantially to the number of SNV differences between colonizing and infecting strains of patient 53 (101 SNVs in 5 TR regions) and patient 73 (34 SNVs in one TR region) with a loss of agr function. Presumably, the SNVs in these regions do not represent independent events but rather resulted from repeat expansions and contractions.
The largest numbers of core (n = 137) and accessory (n = 225) variants between the blood and nares strains were observed with patient 53 (this patient acquired agr-defective, catheter-associated bacteremia in an adult intensive care unit). The number of variants is large, considering that the reported mutation rate is 2.7 to 3.3 mutations per Mb per year for the S. aureus core genome (23, 24). Nevertheless, at least 2 observations support the idea that the two strains arose from a common ancestor in the same individual host. First, the agr-defective infecting and agr+ colonizing isolates shared the same pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and spa types (Table S1), which were found in only 1.3% (n = 5) of isolates from the two patient populations (158 cases plus 229 uninfected controls) in the parent study (12, 19). Mixed infection with such a rare subtype is unlikely. Second, genomic sequencing analysis for patient 53 indicated that the agr-defective infecting isolate was much more closely related to the agr+ colonizing isolate than to all 5 genotypically related strains from the parent study (Fig. S1), arguing against superinfection by a locally circulating clone. Thus, the clonality of isolates from patient 53 was confirmed, consistent with genotyping results from the original studies (12, 19) and other work indicating that carriage is the most common origin of S. aureus infection (8, 19, 25–27).
Loss of agr function is associated with genomic divergence of colonizing and infecting strains.
The number of sequence differences between strain pair genomes from cases with a loss of agr function (range, 5 to 362) was significantly higher than for controls (range, 1 to 6) by a nonparametric Wilcoxon test (P = 3.25 × 10−3), even after excluding focus strains (P = 4.67 × 10−3) and patient 53 (P = 1.01 × 10−2) from the analysis. The increased number of variants accompanying the loss of agr in the infecting strains was apparent in both the core and accessory genomes and across all variant types. Thus, within-host loss of agr function was associated with increased genetic divergence between the colonizing and infecting subclones. We did not find significant differences in mutation frequencies between MRSA and MSSA isolates among cases or controls. The variant pattern of the three focal isolates closely matched that of the blood isolates in most cases (Table 1), consistent with their role as the clinically presumed focus of infection.
To address the directionality of mutation, we reconstructed the ancestral sequence for the set of subclones from each patient using the PAML package (28). Nucleotide sequence variations between strains from blood, foci, or nares were compared to the ancestral sequence to infer the mutation ancestry. By performing phylogenetic analyses with closely related reference strains (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material), we inferred ancestry for 268 of the 420 single nucleotide variants (Table 1 and Fig. S2). The remaining 144 SNVs were located mostly in accessory genome regions; recombination events associated with TRs and mobile genetic elements in these regions preclude reliable reconstruction of their ancestry (24). Likewise, structural variants and indels that are subject to similar constraints were omitted from the PAML analysis; they are discussed below. Analysis of the number of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site (dS) (silent) relative to the number of nonsynonymous substitutions per nonsynonymous site (dN) (amino acid altering) indicated that variants were overall under negative selection (ratios of 0.58 and 0.32 for blood and nares isolates, respectively). However, dN/dS ratios can be difficult to interpret for sequence data of a population in which variants have not yet fixed (29). When considering only mutations specific to the infecting strains, agr-defective strains from cases showed an increased mutational burden relative to agr+ infecting strains from controls (P = 0.023). Moreover, the cases with a loss of agr functionality showed comparable numbers of mutations in colonizing and infecting strains (Table 1). This suggests that the parental wild-type (WT) strains and agr-defective variants evolved concurrently, resulting in substantial genetic divergence between the colonizing and infecting isolates within a given patient.
Variations in agr-defective strains impact genes vital to cell processes and virulence.
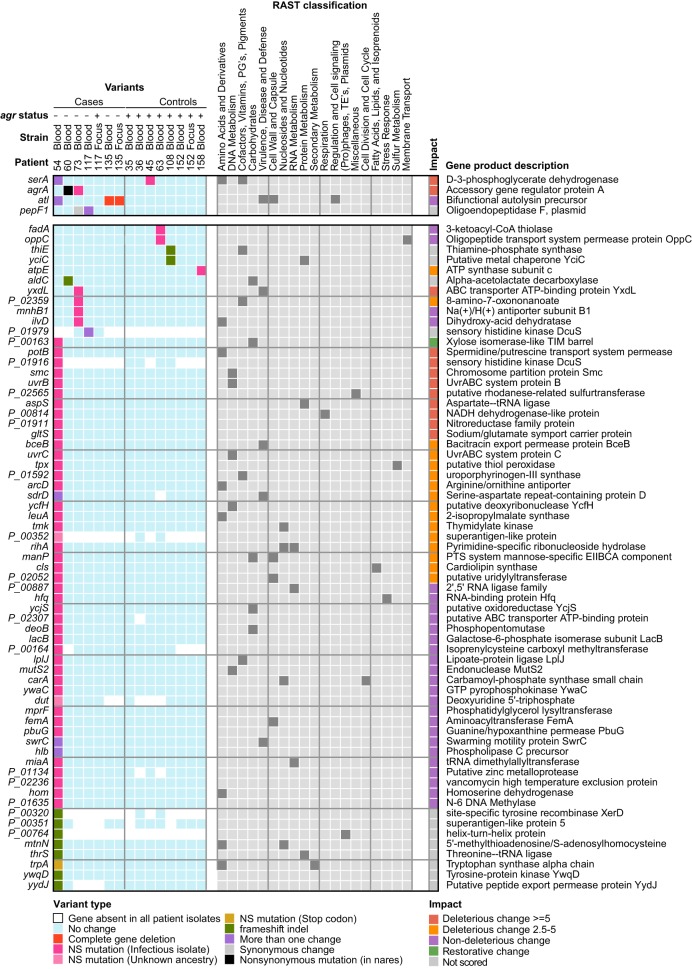
Nonsynonymous SNVs (NS-SNVs) and frameshift indels specific to agr-defective blood strains occurred within genes whose products are involved in metabolism, cell wall synthesis, and the DNA repair/damage response, along with several stress response, regulatory, and drug/metal resistance genes (Fig. 2; see also Table S2 in the supplemental material). All predicted amino acid changes were unique to individual strains, suggesting that polymorphisms did not reflect “hot spots” for mutation within particular genes. However, although most genes were mutated in only one of the strains, three (serA, atl, and pepF1) were independently mutated in different patients (Fig. 2), in addition to the recurrent agrA mutations identified previously (12). For example, two unique NS-SNVs in serA, which encodes an enzyme involved in serine biosynthesis, were identified in agr-defective blood strains of patients 45 and 53. One gene, malL, encoding an oligo-1,6-glucosidase, was recurrently mutated in the agr+ nares strains of two patients (patients 73 and 158). Parallelism of mutated genes in different strains suggests within-host adaptation.
FIG 2.
Map of SNVs and indels found in infecting strains. Shown is a mutation matrix of genes (rows) affected by variants of <5 nt that are unique to infecting strains (columns) or for which an ancestral state could not be determined. Genes mutated in multiple patients are grouped at the top, and the color key for different mutation types is shown at the bottom. RAST subsystem classifications associated with each gene are shown in the center (gray). PROVEAN scores (90) were calculated for each nonsynonymous mutation to assess the impact of a variant on the biological function of the encoded protein and are displayed in the rightmost column, with the key shown below. In cases where multiple variants were found in a gene, the PROVEAN score with the highest absolute value for each gene is shown. PG's prosthetic groups; TE's, transposable elements; PTS, phosphotransferase system.
The agr-defective blood strain of patient 53 had a multitude of genetic changes, including genes having multiple mutations and mutations embedded in the same pathways. For example, swrC was altered by an NS-SNV and by an insertion. Likewise, the cflB gene was altered by an insertion, an NS-SNV, and a synonymous mutation. Multiple mutations would be expected if genes are not transcribed and their sequences are not subjected to selection. However, some genes harbored primary and secondary mutations that are predicted to be deleterious, which may signal genetic instability that can enhance adaptation under certain conditions, such as when selection favors a phenotype requiring a combination of two or more mutations that are individually neutral or deleterious (30).
The highly mutated blood strain from patient 53 harbored an NS-SNV in uvrABC, which is a potential mutator gene that is induced by DNA damage as part of the SOS regulon (31, 32). In order to assess whether the uvrABC mutation could have contributed to the extensive genetic differences between the blood and nares strains, we assessed the frequency of mutation to rifampin resistance in patient 53. In contrast to the comparison of control isogenic WT and mutS-inactivated hypermutator strains, the agr-defective strain and its parent strain showed similar mutation frequencies in vitro, ∼1 mutation per 107 cells (Fig. S3), indicating that the genetic diversification between the blood and nares strains from patient 53 was unrelated to a uvrABC mutation.
Structural variants in agr-defective strains.
Our high-quality complete genome assemblies enabled the identification of structural variants and plasmid losses that distinguished blood from nares strains (Table 2; see also Table S3 in the supplemental material). Structural variants consisted of deletions of prophage and insertion sequences, tandem repeat contractions and expansions, and indel events of >5 bp. The ancestral state for indels and SVs could not be determined by using sequence alignments; however, SVs were more common (28 versus 8) among patients with a loss of agr function (Table 2). Moreover, phage-associated gene loss was more frequently observed in agr-defective infecting strains. For example, nares and blood strains of patient 135 differed by a 43,757-bp prophage similar to Staphylococcus phage SA13, which contains a variety of genes, including atl and dnaC (DNA helicase). An NS-SNV in atl and a deletion of dnaC were identified in the agr-defective variant from this patient, suggesting parallel evolution. Additionally, prophage φSa3 was excised in the agr-defective blood strain of patient 53. φSa3 excision occurs frequently in S. aureus, particularly during infection and antimicrobial treatment (33–35). φSa3 inserts into the beta-toxin gene, inactivating the gene in the majority of S. aureus clonal groups (36, 37). Excision of φSa3 restores beta-toxin production but at the same time results in the loss of φSa3-borne virulence factors, such as sak and scn. As such, φSa3 mobilization is thought to alter virulence properties of the strains.
TABLE 2.
Structural variants and plasmid losses in infecting compared to colonizing strains in each patient
| Patient | Strain type | agr statusa | Type of event | Fragment length (bp) | No. of genes | Event description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | ||||||
| 53 | Blood | − | Insertion | 4,156 | 7 | Insertion of 4 paralogs of essI and 4 genes encoding hypothetical proteins in the ess locus |
| Repeat expansion | 120 | 1 | Expansion in gene sdrD | |||
| Repeat contraction | 90 | 1 | Contraction in gene sdrE | |||
| Deletion | 21 | 0 | Deletion in intergenic region | |||
| Repeat contraction | 69 | 0 | 350 bp upstream of setC | |||
| Repeat expansion | 57 | 0 | Intergenic region | |||
| Repeat contraction | 56 | 0 | Intergenic region | |||
| Deletion | 1,674 | 0 | Deletion of 4 genes encoding hypothetical proteins and a partial deletion of 1 gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Repeat expansion | 59 | 0 | Intergenic region | |||
| Deletion | 43,046 | 66 | Deletion of a φSa3 prophage containing scn, sak, lytN, dnaC, xerC, and 61 genes encoding hypothetical proteins; excision restores hlb | |||
| Repeat contraction | 100 | 0 | Intergenic region | |||
| Repeat expansion | 6 | 1 | Expansion in swrC | |||
| Insertion | 1,152 | 0 | Intergenic region | |||
| Repeat expansion | 128 | 1 | Expansion in clfB | |||
| Plasmid loss | 23,160 | 24 | Loss of plasmid containing racA, entD, entA, entG, acuI, ohrR, bin3, cadC, and 16 genes encoding hypothetical proteins | |||
| 60 | Blood | − | None | |||
| 73 | Blood | − | Repeat expansion | 90 | 1 | Expansion in gene bbp |
| Repeat contraction | 23 | 1 | Expansion in a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Insertion | 1,074 | 1 | Insertion of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Insertion | 60 | 0 | Insertion in the intergenic region | |||
| 117 | Focus | + | None | |||
| 117 | Blood | − | Deletion | 27 | 1 | In gene pepF |
| Deletion | 30 | 1 | In a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| 135 | Focus | − | Insertion | 462 | 1 | Insertion alters a gene encoding a hypothetical protein |
| Deletion | 462 | 1 | Deletion of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Deletion | 43,757 | 69 | Prophage deletion; contains atl, dnaC, hin, lytN, pezA, and ssb | |||
| Insertion | 20 | 0 | Insertion of 20 bp in the intergenic region | |||
| Deletion | 125 | 1 | Deletion alters a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Repeat contraction | 22 | 1 | In a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Insertion | 1,332 | 2 | Insertion in dpiB; contains a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Insertion | 1,332 | 24 | Insertion of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein into plasmid pPS00077.1A.1 | |||
| 135 | Blood | − | Insertion | 462 | 1 | Insertion alters a gene encoding a hypothetical protein |
| Deletion | 462 | 1 | Deletion of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Deletion | 43,757 | 69 | Prophage deletion; contains atl, dnaC, hin, lytN, pezA, and ssb | |||
| Insertion | 20 | 0 | Insertion of 20 bp in the intergenic region | |||
| Deletion | 125 | 1 | Deletion alters a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Repeat contraction | 22 | 1 | In a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Insertion | 1,332 | 2 | Insertion in dpiB contains a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Plasmid loss | 26,241 | 23 | Loss of a plasmid containing nhaX, dauA, hin, bin, tnsB, blaI, blaR1, blaZ, repB, qacC, norG, and 10 genes encoding hypothetical proteins | |||
| Controls | ||||||
| 35 | Blood | + | Repeat expansion | 56 | 0 | 238 bp upstream of the hslO gene |
| Plasmid loss | 39,353 | 41 | Loss of a plasmid containing etb, hin, yxlF, ccr, lagD, ltnA2, cadC, and 35 genes encoding hypothetical proteins | |||
| 36 | Blood | + | Repeat expansion | 1,548 | 3 | Alters a gene encoding a hypothetical protein |
| 45 | Blood | + | None | |||
| 63 | Blood | + | None | |||
| 108 | Blood | None | ||||
| 152 | Focus | + | Insertion | 1,332 | 2 | Deletion of gene encoding hypothetical protein alters another gene encoding a hypothetical protein |
| Deletion | 1,332 | 1 | Insertion alters a gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| Variable region | 578/1,330 | Deletion of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein; the inserted sequence alters another gene encoding a hypothetical protein | ||||
| Deletion | 581 | Partial deletion of the mpr gene | ||||
| 152 | Blood | + | Insertion | 1,332 | 1 | Contains a gene encoding a hypothetical protein |
| Deletion | 1,332 | 2 | Deletion of a gene encoding a hypothetical protein; alters another gene encoding a hypothetical protein | |||
| 158 | Blood | + | Inversion | 6,939 | 1 | Contains aphA, aadK, ycgJ, and 6 genes encoding hypothetical proteins |
+, functional; −, nonfunctional.
In 2 control patients and 1 case patient, a plasmid present in colonizing strains was absent from infecting strains. Thus, plasmids followed the pattern of prophage-associated gene loss during infection. The 3 deleted plasmids contained a variety of genes involved in the stress response, virulence, and resistance to antimicrobials and metals (Table 2).
Naturally occurring non-agr-associated mutations ameliorate agr-defective phenotypes.
To obtain a more detailed assessment of how mutation remodels agr-defective mutants, we screened for phenotypes in isolates from patient 53 after controlling for the status of the agr regulon. We focused our analyses on this strain set, reasoning that some of the complex mutations seen in the blood strain could compensate for the requirement for agr for producing well-known phenotypes in vitro and in vivo. We engineered an agr knockout of the wild-type nares strain (Δagr) and complemented the naturally occurring agr mutant blood strain (Δagr::agr-I+) (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). Wild-type agr genes were transduced in single copies to the naturally occurring agr-defective variant by using the staphylococcal pathogenicity island 1 (SaPI1) attC locus as the insertion site, as described previously (38).
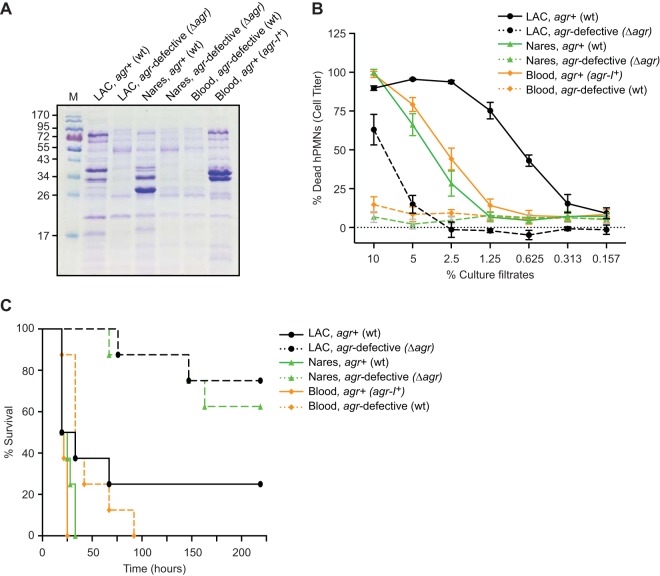
We next characterized the naturally occurring and engineered agr+ and agr-defective variants of the infecting strain from patient 53 and its colonizing counterpart for in vitro virulence properties. The agr locus is required for the production of many of the S. aureus secreted virulence factors, as exemplified by S. aureus strain LAC (Fig. 3A) (39). Similarly to the control isogenic strain LAC, the nares and blood agr-defective mutants from patient 53 demonstrated nearly identical reduced-exoprotein profiles (Fig. 3A). The protein banding pattern from the complemented agr+ blood infection mutant was subtly different from that of the wild-type agr+ nares strain, indicating that agr functionality did not entirely account for differences in relative exoprotein abundances. Cytotoxicity assays of cell extracts indicated that the nares and blood agr+ strains were characterized by high cytotoxicity. In contrast, the naturally occurring agr-defective mutant and the agr knockout strain showed similarly weak killing of neutrophils (Fig. 3B), consistent with the downregulation of many exoprotein genes by the inactivation of agr (39–41). Collectively, these data indicate that non-agr-associated mutations in the agr-defective strain had minor effects on the exoprotein expression pattern and cytotoxicity beyond those associated with agr inactivation.
FIG 3.
Phenotypic characterization of clinical and genetically manipulated strains from patient 53. (A) Exoprotein profiles of strains grown in TSB for 5 h. Extracts were prepared from culture supernatants and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Coomassie blue staining. M, protein ladder. (B) Intoxication of primary human neutrophils (hPMNs) with culture filtrates from the indicated S. aureus strains and controls (USA300 LAC wild type and agr mutant) as a percentage (vol/vol). Results represent the standard errors of the means (SEM) of data from 5 donors and 2 independent colonies. (C) Survival among mice infected with the indicated strains via intravenous inoculation (1 × 108 CFU). Mouse survival results are for 15 mice per group. P values for differences in survival were determined by Bonferroni-corrected log rank (Mantel-Cox) tests (P = 1.03 × 10−1 for agr-defective LAC versus agr+ LAC, P = 1.20 × 10−3 for the agr-defective nares strain versus the agr+ nares strain, P = 1.92 × 10−2 for the agr-defective blood strain versus the agr+ blood strain, P = 1 for the agr-defective nares strain versus agr-defective LAC, P = 1.80 × 10−3 for the agr-defective blood strain versus agr-defective LAC, and P = 2.40 × 10−3 for the agr-defective blood strain versus the agr-defective nares strain).
To determine whether the complex genetic alterations in the agr-defective blood strain could modulate virulence in vivo, we infected mice systemically with the strain set from patient 53 and monitored survival during this bacteremic infection. In contrast to its attenuated cytotoxicity phenotype in vitro, the naturally occurring agr-defective blood strain caused significantly greater murine mortality than the agr-defective nares knockout strain (P = 2.4 × 10−3) and the LAC control (P = 1.8 × 10−3) (Fig. 3C). The integration of agr into the chromosomal SaPI1 insertion site (attC) led to a further increase in virulence, suggesting that additional mutations in the agr-defective blood strain were responsible for restoring murine mortality near the level observed for the agr+ parental strain (Fig. 3C). Altogether, these data suggest that genetic changes that accompany agr-inactivating mutations in this strain enhanced virulence through pathways other than those involved in cytotoxicity.
Gene expression profiling reveals a compensatory mutation that restores ess activity.
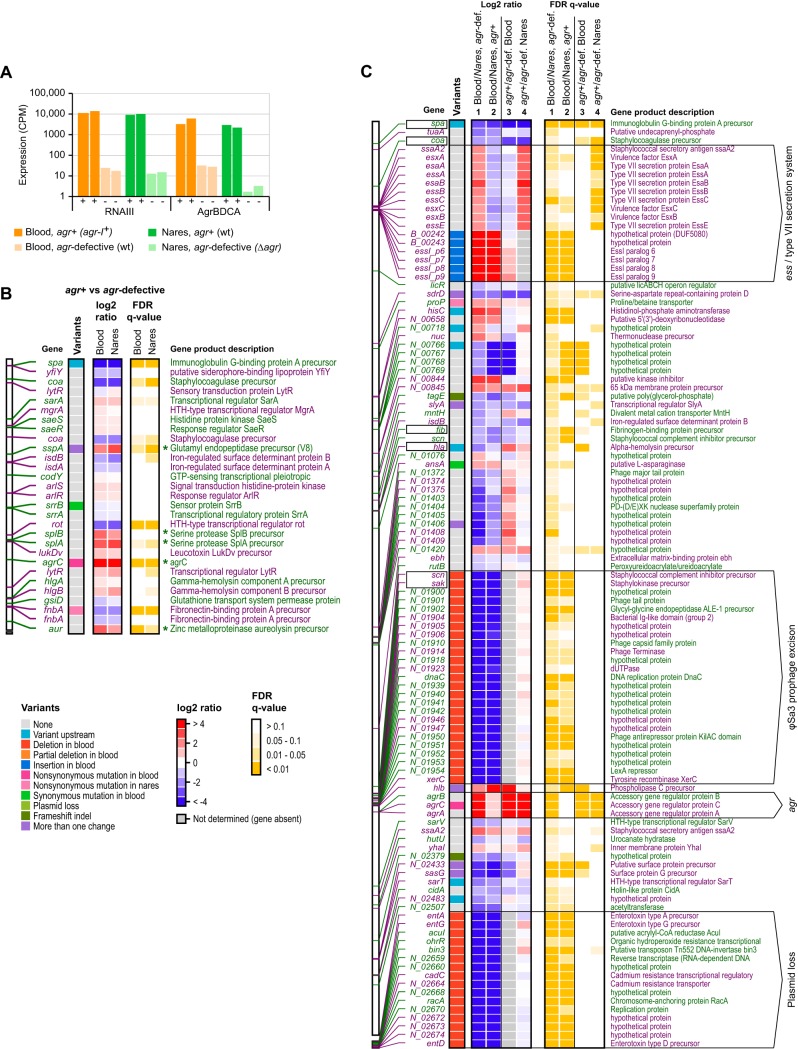
We next sought to identify signaling pathways that are activated or repressed as a result of the additional mutations found in the agr-defective blood strain of patient 53 that could explain its greatly increased virulence in the murine infection model. To this end, we compared transcriptome sequencing (RNA-Seq) expression profiles of the strain set from patient 53 under late-exponential-phase growth conditions. As expected, we observed robust expression of agr (Fig. 4A) and induction and repression of known agr-regulated genes (42) (for example, protein A, fibronectin binding protein [downregulated], V8 serine protease, and splA-splB [upregulated]) in agr+ compared to agr-defective strains (Fig. 4B), thereby indicating agr quorum-sensing activity. Some residual expression of agrBDCA occurred in the naturally occurring agr-defective blood strain compared to the engineered agr-defective nares strain (Fig. 4A), likely representing the basal activity of the agr P2 promoter, activity seen when the agr autoinducing circuit is inactivated owing to a genotypic defect rather than to mobile element replacement (43). Nonetheless, the expression of the RNAIII agr effector was reduced by 4 orders of magnitude in both the blood and nares agr-defective strains, indicating that agr was inactivated.
FIG 4.
Identification of patient 53 strain-specific changes in gene expression. (A) Bar plot showing expression levels in counts per million (CPM) of RNAIII and agrBDCA during late-exponential-phase growth in natural and laboratory-derived agr+ or agr-defective strains of isolates from patient 53. Experiments were performed in duplicate, and levels are plotted for each replicate individually. (B) Overview of expression changes between natural and laboratory-derived agr+ and agr-defective strains of blood and nares origins for 29 toxins, proteases, surface proteins, transporters, and regulatory genes implicated in S. aureus virulence and pathogenesis (42). The left column shows variants found in or near each gene. Center columns indicate the average changes in expression under the experimental conditions labeled at the top. Rightmost columns indicate false discovery rate (FDR)-corrected P values for the expression changes shown in the center columns. Identifications and descriptions are shown on the sides, and color keys are shown at the bottom. The position of each gene in the nares strain reference genome is indicated on the far left, and alternating colors of position markers and descriptions are used to denote directly adjacent genes on the same strand (i.e., putative operons). Known agr-regulated genes are highlighted by asterisks. Results are derived from the same experiment as the one for panel A. (C) Summary of expression changes for 103 genes with significant differences in expression between agr-defective blood (wild-type [wt]) and nares (Δagr) isolates from patient 53. The figure layout is the same as for panel B, and strain comparisons are indicated at the top. Selected genomic regions are annotated on the far right, and virulence genes are boxed on the left. Column numbers and names are shown at the top. HTH, helix-turn-helix; agr-def., agr-defective.
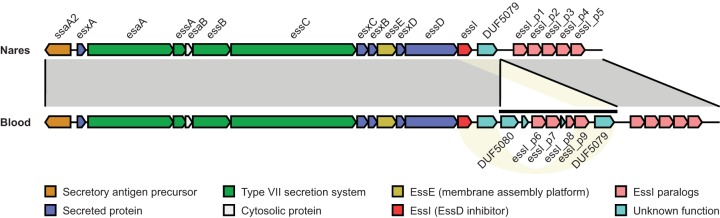
Overall, the late-log-phase profiles from the agr-defective blood and nares strains had similar expression profiles despite their substantial genetic differences (Fig. 4C). In total, 109 genes showed significant (false discovery rate [FDR] q value of ≤0.05) expression changes in the naturally occurring agr-defective blood strain compared with the engineered agr-defective nares strain (33 upregulated and 77 downregulated). Many of the downregulated genes (41/77; 53%) showed a complete loss of expression in the agr-defective blood strain due to the loss of prophage φSa3 and a plasmid. For example, the expression of sak and scn was abolished, and the expression of beta-toxin was increased in the agr-defective blood strain, consistent with φSa3 excision (Fig. 4C, column 1). Likewise, we did not observe expression of plasmid-borne virulence factors, such as ent, in the agr-defective blood strain. Several other virulence factors (spa, coa, fib, and hla) were downregulated in both the naturally occurring agr-defective and engineered agr+ blood strains compared to their nares counterparts (Fig. 4C, columns 1 and 2). As a notable exception, a gene cluster encoding the agr-regulated S. aureus ESAT6-like secretion system (ESS) and ESS-associated virulence factors was significantly upregulated in the agr-defective blood strain compared to the engineered agr-defective nares strain (Fig. 4C, column 1). Indeed, ssaA2, esaAB, essABCE, and esxABC transcripts were restored to levels similar to those seen in the agr+ colonizing and engineered blood strains (Fig. 4C, columns 2 and 3). The changes in ess gene expression were associated with a 4-kb insertion at the locus containing 4 hypothetical proteins and 4 genes encoding paralogs of the EssI inhibitor (Table 2 and Fig. 5). Taken together, the expression changes observed in late log phase, when agr is active, suggest partial compensation for the absence of conventional agr-mediated gene regulation.
FIG 5.
Rearrangement of the ess locus in patient 53 blood and nares strains. Matching ess regions in the nares (top) and blood (bottom) strains of patient 35 are indicated by shaded areas (gray) and connecting lines. The 4-kb inserted element and candidate regions for homologous recombination are highlighted by a horizontal line and yellow shading, respectively. Gene colors correspond to the type of encoded proteins, according to the key at the bottom.
DISCUSSION
The various stages of invasive infection reflect an array of environmental challenges to S. aureus. Experimental (44–47) and observational (8, 48–51) work suggests that mutation of global regulators constitutes a “one-step” mechanism of adaptation that drives adaptive leaps made by microbes. The present comprehensive identification of variations using complete genome assemblies revealed that the number of mutations in S. aureus clone pairs having a loss of agr function is increased compared to uniformly wild-type controls. Although an outlier strain (patient 53) that increased the mean diversity of agr mutants existed in the study sample, the increase remains significant even when the outlier is removed from the analysis. S. aureus evolved in vivo through the accumulation of point mutations and structural events, such as phage mobilization and plasmid loss.
The increased frequency of non-agr-associated mutations that we observed in agr-defective strain pairs can be explained by at least two hypotheses. First, systemic synthetic and host antimicrobial exposures in patients could enhance the mutational burden in both colonizing and infecting sites, thereby affecting divergence between the wild-type agr+ strain and the agr-defective mutant. Indeed, extensive within-host genetic variation has been described for S. aureus and other pathogens associated with global regulator mutation not only during infection (49, 51–53) but also in the transition between colonization and infection (8, 49, 54, 55). Given that agr-defective mutants are associated with long-term invasive infections (15, 18, 56), a second, but not mutually exclusive, hypothesis is that the correlation between agr function and the extent of mutations reflects differences in the durations of colonization or infection between cases and controls that we were unable to address in our study. Consistent with this idea, S. aureus isolates obtained from patients with invasive infection demonstrate greater genomic diversity than those obtained from patients with asymptomatic carriage- and those associated with superficial infection (57). In these scenarios, agr mutation serves as a proxy for exposure to the necessary milieu and the time required for both the colonizing and infecting bacteria to evolve, potentially resulting in substantial genetic divergence of the two populations.
The frequency and specificity with which compensatory mutations develop in a given patient as a consequence of being infected with an agr-defective strain require evaluation of additional strains, virulence, and a detailed examination of clinical histories (e.g., duration of disease and antimicrobials used for treatment). Nevertheless, the number of isolates studied here is sufficient to reveal that additional mutations can create complex changes that may provide a substrate to optimize the within-host specificity of agr-defective mutants. Comparative analysis of knockouts and complemented clones from the outlier patient 53 revealed that the agr-regulated ESS pathway was highly expressed in the agr-defective blood isolate, a finding that was associated with the presence of a 4.1-kb sequence element in genes encoding the ess locus inhibitor, EssI. The ESS pathway has been linked to pathogenesis in mouse models of abscess formation (58–60), and it modulates host immune responses, including cytokine production (61). Thus, enhanced expression of ess can potentially explain why we observed enhanced virulence of the agr-defective strain in vivo but not in cytotoxicity assays. Within-host conditions vary, and as a result, the relative benefits of an ess mutant phenotype may not apply to individuals other than patient 53. Additionally, other factors, such as φSa3 excision that restored beta-toxin production, may have contributed to the virulent phenotype of the naturally occurring mutant, as beta-toxin is associated with virulence in animal models of infection (35).
Future work will extend our observations on genetic changes in different hosts with agr-defective S. aureus infection to investigate diversity within individual hosts. Currently, little is known about intrahost variation in S. aureus genomes during infection, and such uncertainty may be greater in the setting of a high mutational burden. Thus, although the single colony analyzed in this study likely represented the dominant strain in the specimen, further subclonal heterogeneity may have been overlooked.
In conclusion, we find that a loss of agr function is associated with increased genomic complexity in colonizing and infecting strains across multiple patients as well as mutations that can potentially compensate for the loss of agr function during infection. Such changes may favor the expansion or persistence of S. aureus populations within patients. Nevertheless, by analogy to cancer biology (62, 63), they may also create new vulnerabilities that can be exploited for prognosis and treatment. Recognition of within-host genetic variability associated with global regulator inactivation also has important ramifications for our ability to understand intrapatient and interpatient heterogeneity. Thus, our findings have significance for establishing thresholds to differentiate the relatedness of S. aureus isolates for epidemiological purposes in hospitals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and culture conditions.
S. aureus isolates were obtained from a previous multicenter study of bacteremic patients. In the original study, nares cultures were obtained at the time when patients were diagnosed with S. aureus bacteremia (19). The majority of these isolates (92% of blood and 97% of nares isolates) were methicillin-susceptible S. aureus. Isolates were further characterized and screened for agr functionality in subsequent work (12). Inactivating mutations in agr were identified in most of the ∼10% of blood isolates that were found to be agr defective (12).
Culturing and DNA and RNA extraction.
For genomic DNA (gDNA) extraction, isolates were grown from single colonies in tryptic soy broth (TSB) liquid cultures overnight at 37°C with shaking at 225 rpm. Cells underwent high-molecular-weight (HMW) DNA extraction using enzymatic lysis with lysozyme, lysostaphin, and proteinase K and Qiagen Genomic-Tip columns, as described previously (64).
For RNA extraction, cultures grown overnight were diluted, grown to late log phase (optical density [OD] of ∼0.80), and stabilized in RNAlater. Total RNA was isolated and purified by using the Qiagen RNeasy minikit. Lysozyme and lysostaphin were used for cell wall degradation, followed by two cycles of 2 min of bead beating with 1 ml of 0.1-mm silica beads in a mini-bead beater (BioSpec), and RNA was eluted in nuclease-free water. Isolated RNA was treated with 1 μl of Baseline Zero DNase (Epicentre) at 37°C for 30 min, and rRNA depletion was performed by using an Epicenter Ribo-Zero magnetic gold kit (Illumina), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
DNA library preparation and sequencing.
Quality control, DNA quantification, and gDNA library preparation and sequencing were performed as described previously (64). Briefly, DNA was gently sheared by using Covaris G-tube spin columns into ∼20,000-bp fragments and end repaired before ligating SMRTbell adapters (Pacific Biosciences). The resulting library was treated with an exonuclease cocktail to remove unligated DNA fragments, followed by two additional (AMPure XP) purification steps and Sage Science Blue Pippin size selection to deplete SMRTbells of <7,000 bp. Libraries were then sequenced by P5 enzyme chemistry on the Pacific Biosciences RS-II platform.
For Illumina sequencing, genomic DNA was sheared to an average fragment size of 200 bp by using a Bioruptor Pico sonicator (Diagenode). Amplicon sequence libraries were prepared by using the end repair, A-tailing, and adapter ligation NEBNext DNA library prep modules for Illumina from New England BioLabs, according to the manufacturer's protocol. Following final purification with AMPure XP beads and secondary PCR (8 cycles) to introduce barcoded primers, multiplexed libraries were sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform in a single-end 100-nt-run format.
Whole-genome assembly.
PacBio sequencing data were assembled by using the HGAP3 version 2.2.0 assembly pipeline (65), and a custom postassembly pipeline (66) was used to finalize each genome. Briefly, genomes were circularized and reoriented to the origin of replication (ori) by using Circlator (67). In cases where chromosomes or plasmids did not assemble into complete circularized contigs, manual curation was performed by using Contiguity (68). Next, Illumina reads were mapped to the curated PacBio assemblies, and consensus calling was performed by using the mpileup function of SAMtools to correct SNVs and small indels in homopolymer regions. To recover small plasmids that might have been lost during size selection of PacBio reads, the Illumina reads were also assembled de novo by using SPAdes version 3.7.1 (69). Contigs with <10× coverage and contigs mapping in full to the PacBio assembly were removed. The remaining contigs were circularized by using Circlator or Contiguity and aligned to the nonredundant nucleotide collection by using BLAST+ to identify plasmid sequences. Genes were annotated by using PROKKA (70) and visualized by using ChromoZoom (71) and the Integrated Genome Browser (IGB) (72). InterProScan (73) was used to annotate protein domains and gene ontology (GO) categories for annotated genes.
Phylogenetic analysis.
A set of 80 publically available finished S. aureus genomes listed in the Genomes Online Database (74) were downloaded from RefSeq (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/) and used to select a subset of closely related reference genomes. Briefly, a pairwise comparison of all RefSeq reference strains against all sequenced strains was performed by using MUMmer (version 3.1) (75). MUMi scores (76) were used to calculate the genetic distance between sequenced strains and the RefSeq strains. All RefSeq strains within a short genetic distance from at least one patient isolate (MUMi score of <0.05) were included in the phylogenetic analysis. Parsnp (77) was used to align the subset of RefSeq strains and the sequenced strains, filtering for recombinant regions.
For visualization of the whole-genome alignments, all 23 sequenced strains were aligned by using Mugsy (version 1r2.2) (78). Mugsy alignments were processed with Gblocks (version 0.91b) with default settings and a minimum block size set to 1,000 (79), and a tree was then created by using RAxML (version 8.2.4) (80), using the general time-reversible model. The untrimmed Mugsy alignment was visualized by using ChromatiBlocks (https://github.com/mjsull/chromatiblock).
Variant calling and ancestral reconstruction.
The ancestral sequence for each set of patient isolates was inferred by using the PAML package (28) (version 1.3.1). Briefly, the phylogenetic tree of all patient strains and 39 complete reference genomes was used to identify a clade of closely related strains for each patient isolate set, within a genetic distance of 0.001 (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). We then generated a multiple alignment of the genomes in each clade (78) and used BaseML (from the PAML package) to infer the sequence of the most recent common ancestor for each strain set using a general time-reversible model. As there were no genomes within a genetic distance of 0.001 from the two isolates from patient 45, isolates from patients 135 and 53 (which were closest) were used to infer an ancestral sequence. A custom script (https://github.com/mjsull/GWviz/tree/mssa-paper) was used to determine all SVs from a Nucmer (version 3.1) (75) alignment. The dN/dS ratios for blood and nares strains were calculated by using yn00, which is part of the PAML software package, using default settings. We also cross-referenced variants with the ancestral sequence to determine whether the variant arose in the nares, infection focus, or blood. A graphic of all variants between these genomes was also generated (Fig. S2). Finally, recombinant DNA was detected within the closely related clades by using Gubbins (version 2.2.0), using default settings (81).
RAST subsystem assignment.
To determine whether mutations arose in specific classes of genes or pathways, genes were clustered and assigned a subsystem. Genes were matched between patients by their PROKKA-annotated common gene names. If PROKKA did not assign a common name to a predicted gene, genes were grouped if they aligned reciprocally along >90% of their length with an identity of >90% by using BLASTP (82). Subsystems were assigned to each gene annotated with PROKKA by using the RAST annotation server. A list of genes, variants found in each strain, the subsystem assigned to each gene, and the groupings of hypothetical proteins can be found in Table S3 in the supplemental material.
Directional RNA-Seq.
After RNA extraction, barcoded stranded RNA-Seq libraries were prepared by using the TruSeq stranded total RNA sample preparation kit (Illumina). RNA quality and quantity were assessed by using the Agilent Bioanalyzer and the Qubit RNA broad-range assay kit (Thermo Fisher), respectively. Finally, libraries were pooled and sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq platform in a 100-bp single-end read run format with 6 samples per lane.
Differential gene expression analysis.
Raw reads were first trimmed by removing Illumina adapter sequences from 3′ ends using cutadapt (83), with a minimum match of 32 bp and allowing for a 15% error rate. Trimmed reads were mapped to the reference genome by using Bowtie2 (84), and htseq-count (85) was used to produce strand-specific transcript count summaries. Read counts were then combined into a numeric matrix and used as the input for differential gene expression analysis with the limma R package (86) in Bioconductor. Normalization factors were computed on the data matrix by using the weighted trimmed mean of M values (TMM) method, followed by voom (87) mean-variance transformation in preparation for limma linear modeling. Data were fitted to a design matrix containing all sample groups, and pairwise comparisons between the groups of interest were performed. eBayes-adjusted P values were corrected for multiple testing by using the Benjamini-Hochberg (BH) method and used to select genes with significant expression differences (q < 0.05).
Spontaneous Rifr mutant recovery assay.
Cells were grown in TSB medium for 16 or 48 h at 37°C with constant shaking. Undiluted and serially diluted samples were spotted onto rifampin (5× MIC = 40 ng/ml)-containing tryptic soy agar (TSA) plates and drug-free agar for mutants and total numbers of cells, respectively, as described previously (88). After spot plating, plates were incubated at 37°C, and colonies were counted after 24 h. S. aureus RN6734 mutS::pG+host9 (Erm) was generated by transducing the disrupted allele from RN4220 (88). Phage 80α was used to transduce the marker-disrupted allele; transductants were selected on TSA plates containing the appropriate antimicrobial.
Exoproteomic profiling.
Cultures grown in TSB overnight were diluted 100-fold in 5 ml fresh TSB in 15-ml conical tubes and grown for 5 h at 37°C with constant shaking. The cultures were normalized to the lowest OD at 600 nm (OD600) and centrifuged, and the culture filtrates were collected by filtration. Cells were pelleted by centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and 1.3 ml of the supernatant was precipitated with 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) overnight at 4°C. Proteins were pelleted by centrifugation at 15,000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C, and the pellet was washed with 100% ethanol. The protein pellet was dried and resuspended in 30 μl of TCA-SDS buffer, and 16 μl of the sample was resolved on a 15% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, followed by Coomassie staining.
Cytotoxicity assays.
Cytotoxicity assays were performed as described previously (89). Briefly, cultures grown overnight in TSB were diluted 100-fold in 5 ml fresh TSB in 15-ml conical tubes and grown for 5 h at 37°C with constant shaking. The cultures were normalized to the lowest OD600 and centrifuged, and the culture filtrates were collected by filtration. The supernatants were then mixed with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (hPMNs) from 6 healthy individuals. Approximately 2 × 105 hPMNs were added to a final volume of 100 μl/well of RPMI (Gibco) supplemented with 10 mM HEPES. Cells were intoxicated for 1 h at 37°C in 5% CO2. Ten microliters of CellTiter 96 Aqueous One solution (Promega) was added, the mixture was incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 2 h, and the absorbance was measured at 595 nm by using a PerkinElmer EnVision 2103 multilabel reader. Cell survival indicates neutrophil viability in the presence of 0.1% Triton (positive control) and media (negative control).
Mouse infections.
Five-week-old female ND4 Swiss Webster mice (Harlan Laboratories) were anesthetized intraperitoneally with 250 to 300 μl of Avertin (2,2,2-tribromoethanol dissolved in tert-amyl alcohol and diluted to a final concentration of 2.5% [vol/vol] in sterile saline). S. aureus cultures grown for 3 h were washed, resuspended in 1× phosphate-buffered saline, and normalized for the corresponding CFU counts (∼3.5 × 107 to 5 × 107 CFU). One hundred microliters of the inoculum was administered retro-orbitally, and mice were monitored every 4 to 6 h for signs of morbidity (hunched posture, lack of movement, paralysis, and an inability to acquire food or water), at which time the animals were euthanized and survival curves were plotted over time (in hours).
Accession number(s).
Genome assemblies and RNA-Seq data have been deposited under NCBI BioProject accession no. PRJNA393749.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Karl Drlica for critical comments on the manuscript. This research was supported in part through the computational resources and staff expertise provided by the Department of Scientific Computing at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. RN4220 MutS::pG+host9 (Erm) was a generous gift from Ian Chopra and Alexander O'Neill, University of Leeds (United Kingdom).
This research was supported in part by an NIAID-supported NRSA institutional research training grant for global health research (T32 AI07647); the CTSA/NCATS KL2 Program (KL2TR001435; Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai); the New York State Department of Health Empire Clinical Research Investigator Program (awarded to Judith A. Aberg; Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai) (D.R.A.); and NIH grants F30 AI122673 (T.R.P.), T32 AI007180 (W.E.S.), R01 AI103268 and NIAID HHSN272201400019C (B.S. and V.J.T.), R01 AI093613 (A.R.R.), and R01 AI119145 (H.V.B. and A.B.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00331-18.
REFERENCES
- 1.Baines SL, Holt KE, Schultz MB, Seemann T, Howden BO, Jensen SO, van Hal SJ, Coombs GW, Firth N, Powell DR, Stinear TP, Howden BP. 2015. Convergent adaptation in the dominant global hospital clone ST239 of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. mBio 6:e00080-. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00080-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cheung GY, Kretschmer D, Duong AC, Yeh AJ, Ho TV, Chen Y, Joo HS, Kreiswirth BN, Peschel A, Otto M. 2014. Production of an attenuated phenol-soluble modulin variant unique to the MRSA clonal complex 30 increases severity of bloodstream infection. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004298. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.DeLeo FR, Kennedy AD, Chen L, Bubeck Wardenburg J, Kobayashi SD, Mathema B, Braughton KR, Whitney AR, Villaruz AE, Martens CA, Porcella SF, McGavin MJ, Otto M, Musser JM, Kreiswirth BN. 2011. Molecular differentiation of historic phage-type 80/81 and contemporary epidemic Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:18091–18096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111084108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Laabei M, Uhlemann AC, Lowy FD, Austin ED, Yokoyama M, Ouadi K, Feil E, Thorpe HA, Williams B, Perkins M, Peacock SJ, Clarke SR, Dordel J, Holden M, Votintseva AA, Bowden R, Crook DW, Young BC, Wilson DJ, Recker M, Massey RC. 2015. Evolutionary trade-offs underlie the multi-faceted virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Biol 13:e1002229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Painter KL, Krishna A, Wigneshweraraj S, Edwards AM. 2014. What role does the quorum-sensing accessory gene regulator system play during Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia? Trends Microbiol 22:676–685. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Shopsin B, Drlica-Wagner A, Mathema B, Adhikari RP, Kreiswirth BN, Novick RP. 2008. Prevalence of agr dysfunction among colonizing Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Infect Dis 198:1171–1174. doi: 10.1086/592051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shopsin B, Eaton C, Wasserman GA, Mathema B, Adhikari RP, Agolory S, Altman DR, Holzman RS, Kreiswirth BN, Novick RP. 2010. Mutations in agr do not persist in natural populations of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis 202:1593–1599. doi: 10.1086/656915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Young BC, Wu CH, Gordon NC, Cole K, Price JR, Liu E, Sheppard AE, Perera S, Charlesworth J, Golubchik T, Iqbal Z, Bowden R, Massey RC, Paul J, Crook DW, Peto TE, Walker AS, Llewelyn MJ, Wyllie DH, Wilson DJ. 2017. Severe infections emerge from commensal bacteria by adaptive evolution. Elife 6:e30637. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Novick RP. 2003. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol Microbiol 48:1429–1449. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wright JS III, Jin R, Novick RP. 2005. Transient interference with staphylococcal quorum sensing blocks abscess formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:1691–1696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407661102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mwangi MM, Wu SW, Zhou Y, Sieradzki K, de Lencastre H, Richardson P, Bruce D, Rubin E, Myers E, Siggia ED, Tomasz A. 2007. Tracking the in vivo evolution of multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by whole-genome sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:9451–9456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609839104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Smyth DS, Kafer JM, Wasserman GA, Velickovic L, Mathema B, Holzman RS, Knipe TA, Becker K, von Eiff C, Peters G, Chen L, Kreiswirth BN, Novick RP, Shopsin B. 2012. Nasal carriage as a source of agr-defective Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. J Infect Dis 206:1168–1177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Suligoy CM, Lattar SM, Noto Llana M, Gonzalez CD, Alvarez LP, Robinson DA, Gomez MI, Buzzola FR, Sordelli DO. 2018. Mutation of Agr is associated with the adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to the host during chronic osteomyelitis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:18. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chong YP, Park SJ, Kim HS, Kim ES, Kim MN, Park KH, Kim SH, Lee SO, Choi SH, Jeong JY, Woo JH, Kim YS. 2013. Persistent Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: a prospective analysis of risk factors, outcomes, and microbiologic and genotypic characteristics of isolates. Medicine (Baltimore) 92:98–108. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e318289ff1e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fowler VG Jr, Sakoulas G, McIntyre LM, Meka VG, Arbeit RD, Cabell CH, Stryjewski ME, Eliopoulos GM, Reller LB, Corey GR, Jones T, Lucindo N, Yeaman MR, Bayer AS. 2004. Persistent bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection is associated with agr dysfunction and low-level in vitro resistance to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein. J Infect Dis 190:1140–1149. doi: 10.1086/423145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kim T, Kim ES, Park SY, Sung H, Kim MN, Kim SH, Lee SO, Choi SH, Jeong JY, Woo JH, Chong YP, Kim YS. 2017. Phenotypic changes of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus during vancomycin therapy for persistent bacteraemia and related clinical outcome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 36:1473–1481. doi: 10.1007/s10096-017-2956-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Park SY, Chong YP, Park HJ, Park KH, Moon SM, Jeong JY, Kim MN, Kim SH, Lee SO, Choi SH, Woo JH, Kim YS. 2013. agr dysfunction and persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia in patients with removed eradicable foci. Infection 41:111–119. doi: 10.1007/s15010-012-0348-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schweizer ML, Furuno JP, Sakoulas G, Johnson JK, Harris AD, Shardell MD, McGregor JC, Thom KA, Perencevich EN. 2011. Increased mortality with accessory gene regulator (agr) dysfunction in Staphylococcus aureus among bacteremic patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:1082–1087. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00918-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.von Eiff C, Becker K, Machka K, Stammer H, Peters G. 2001. Nasal carriage as a source of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Study group. N Engl J Med 344:11–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200101043440102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Goering RV, Shawar RM, Scangarella NE, O'Hara FP, Amrine-Madsen H, West JM, Dalessandro M, Becker JA, Walsh SL, Miller LA, van Horn SF, Thomas ES, Twynholm ME. 2008. Molecular epidemiology of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from global clinical trials. J Clin Microbiol 46:2842–2847. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00521-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grundmann H, Aanensen DM, van den Wijngaard CC, Spratt BG, Harmsen D, Friedrich AW, European Staphylococcal Reference Laboratory Working Group. 2010. Geographic distribution of Staphylococcus aureus causing invasive infections in Europe: a molecular-epidemiological analysis. PLoS Med 7:e1000215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Copin R, Shopsin B, Torres VJ. 2017. After the deluge: mining Staphylococcus aureus genomic data for clinical associations and host-pathogen interactions. Curr Opin Microbiol 41:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.11.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Harris SR, Feil EJ, Holden MT, Quail MA, Nickerson EK, Chantratita N, Gardete S, Tavares A, Day N, Lindsay JA, Edgeworth JD, de Lencastre H, Parkhill J, Peacock SJ, Bentley SD. 2010. Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread. Science 327:469–474. doi: 10.1126/science.1182395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Young BC, Golubchik T, Batty EM, Fung R, Larner-Svensson H, Votintseva AA, Miller RR, Godwin H, Knox K, Everitt RG, Iqbal Z, Rimmer AJ, Cule M, Ip CL, Didelot X, Harding RM, Donnelly P, Peto TE, Crook DW, Bowden R, Wilson DJ. 2012. Evolutionary dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus during progression from carriage to disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:4550–4555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113219109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Luzar MA, Coles GA, Faller B, Slingeneyer A, Dah GD, Briat C, Wone C, Knefati Y, Kessler M, Peluso F. 1990. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage and infection in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. N Engl J Med 322:505–509. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002223220804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nguyen MH, Kauffman CA, Goodman RP, Squier C, Arbeit RD, Singh N, Wagener MM, Yu VL. 1999. Nasal carriage of and infection with Staphylococcus aureus in HIV-infected patients. Ann Intern Med 130:221–225. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-3-199902020-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yu VL, Goetz A, Wagener M, Smith PB, Rihs JD, Hanchett J, Zuravleff JJ. 1986. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage and infection in patients on hemodialysis. Efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis. N Engl J Med 315:91–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198607103150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yang Z. 2007. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24:1586–1591. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kryazhimskiy S, Plotkin JB. 2008. The population genetics of dN/dS. PLoS Genet 4:e1000304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Drake JW, Bebenek A, Kissling GE, Peddada S. 2005. Clusters of mutations from transient hypermutability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12849–12854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503009102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pruteanu M, Baker TA. 2009. Controlled degradation by ClpXP protease tunes the levels of the excision repair protein UvrA to the extent of DNA damage. Mol Microbiol 71:912–924. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Painter KL, Strange E, Parkhill J, Bamford KB, Armstrong-James D, Edwards AM. 2015. Staphylococcus aureus adapts to oxidative stress by producing H2O2-resistant small-colony variants via the SOS response. Infect Immun 83:1830–1844. doi: 10.1128/IAI.03016-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Goerke C, Matias y Papenberg S, Dasbach S, Dietz K, Ziebach R, Kahl BC, Wolz C. 2004. Increased frequency of genomic alterations in Staphylococcus aureus during chronic infection is in part due to phage mobilization. J Infect Dis 189:724–734. doi: 10.1086/381502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Goerke C, Wirtz C, Fluckiger U, Wolz C. 2006. Extensive phage dynamics in Staphylococcus aureus contributes to adaptation to the human host during infection. Mol Microbiol 61:1673–1685. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Salgado-Pabon W, Herrera A, Vu BG, Stach CS, Merriman JA, Spaulding AR, Schlievert PM. 2014. Staphylococcus aureus beta-toxin production is common in strains with the beta-toxin gene inactivated by bacteriophage. J Infect Dis 210:784–792. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Coleman DC, Arbuthnott JP, Pomeroy HM, Birkbeck TH. 1986. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus of the beta-lysin determinant from Staphylococcus aureus: evidence that bacteriophage conversion of beta-lysin activity is caused by insertional inactivation of the beta-lysin determinant. Microb Pathog 1:549–564. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Winkler KC, de Waart J, Grootsen C. 1965. Lysogenic conversion of staphylococci to loss of beta-toxin. J Gen Microbiol 39:321–333. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-3-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Geisinger E, Chen J, Novick RP. 2012. Allele-dependent differences in quorum-sensing dynamics result in variant expression of virulence genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 194:2854–2864. doi: 10.1128/JB.06685-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chapman JR, Balasubramanian D, Tam K, Askenazi M, Copin R, Shopsin B, Torres VJ, Ueberheide BM. 2017. Using quantitative spectrometry to understand the influence of genetics and nutritional perturbations on the virulence potential of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Cell Proteomics 16:S15–S28. doi: 10.1074/mcp.O116.065581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dunman PM, Murphy E, Haney S, Palacios D, Tucker-Kellogg G, Wu S, Brown EL, Zagursky RJ, Shlaes D, Projan SJ. 2001. Transcription profiling-based identification of Staphylococcus aureus genes regulated by the agr and/or sarA loci. J Bacteriol 183:7341–7353. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.24.7341-7353.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Queck SY, Jameson-Lee M, Villaruz AE, Bach TH, Khan BA, Sturdevant DE, Ricklefs SM, Li M, Otto M. 2008. RNAIII-independent target gene control by the agr quorum-sensing system: insight into the evolution of virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Cell 32:150–158. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Date SV, Modrusan Z, Lawrence M, Morisaki JH, Toy K, Shah IM, Kim J, Park S, Xu M, Basuino L, Chan L, Zeitschel D, Chambers HF, Tan MW, Brown EJ, Diep BA, Hazenbos WL. 2014. Global gene expression of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 during human and mouse infection. J Infect Dis 209:1542–1550. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Traber KE, Lee E, Benson S, Corrigan R, Cantera M, Shopsin B, Novick RP. 2008. agr function in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Microbiology 154:2265–2274. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/011874-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Quan S, Ray JC, Kwota Z, Duong T, Balazsi G, Cooper TF, Monds RD. 2012. Adaptive evolution of the lactose utilization network in experimentally evolved populations of Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet 8:e1002444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Saxer G, Krepps MD, Merkley ED, Ansong C, Deatherage Kaiser BL, Valovska MT, Ristic N, Yeh PT, Prakash VP, Leiser OP, Nakhleh L, Gibbons HS, Kreuzer HW, Shamoo Y. 2014. Mutations in global regulators lead to metabolic selection during adaptation to complex environments. PLoS Genet 10:e1004872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Spencer CC, Bertrand M, Travisano M, Doebeli M. 2007. Adaptive diversification in genes that regulate resource use in Escherichia coli. PLoS Genet 3:e15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kumar K, Chen J, Drlica K, Shopsin B. 2017. Tuning of the lethal response to multiple stressors with a single-site mutation during clinical infection by Staphylococcus aureus. mBio 8:e01476-. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01476-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Carter MQ, Parker CT, Louie JW, Huynh S, Fagerquist CK, Mandrell RE. 2012. RcsB contributes to the distinct stress fitness among Escherichia coli O157:H7 curli variants of the 1993 hamburger-associated outbreak strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7706–7719. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02157-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Das S, Lindemann C, Young BC, Muller J, Osterreich B, Ternette N, Winkler AC, Paprotka K, Reinhardt R, Forstner KU, Allen E, Flaxman A, Yamaguchi Y, Rollier CS, van Diemen P, Blattner S, Remmele CW, Selle M, Dittrich M, Muller T, Vogel J, Ohlsen K, Crook DW, Massey R, Wilson DJ, Rudel T, Wyllie DH, Fraunholz MJ. 2016. Natural mutations in a Staphylococcus aureus virulence regulator attenuate cytotoxicity but permit bacteremia and abscess formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E3101–E3110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1520255113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kisiela DI, Radey M, Paul S, Porter S, Polukhina K, Tchesnokova V, Shevchenko S, Chan D, Aziz M, Johnson TJ, Price LB, Johnson JR, Sokurenko EV. 2017. Inactivation of transcriptional regulators during within-household evolution of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 199:e00036-. doi: 10.1128/JB.00036-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Smith EE, Buckley DG, Wu Z, Saenphimmachak C, Hoffman LR, D'Argenio DA, Miller SI, Ramsey BW, Speert DP, Moskowitz SM, Burns JL, Kaul R, Olson MV. 2006. Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:8487–8492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602138103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lieberman TD, Flett KB, Yelin I, Martin TR, McAdam AJ, Priebe GP, Kishony R. 2014. Genetic variation of a bacterial pathogen within individuals with cystic fibrosis provides a record of selective pressures. Nat Genet 46:82–87. doi: 10.1038/ng.2848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Yang L, Jelsbak L, Marvig RL, Damkiaer S, Workman CT, Rau MH, Hansen SK, Folkesson A, Johansen HK, Ciofu O, Hoiby N, Sommer MO, Molin S. 2011. Evolutionary dynamics of bacteria in a human host environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:7481–7486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018249108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Azarian T, Daum RS, Petty LA, Steinbeck JL, Yin Z, Nolan D, Boyle-Vavra S, Hanage WP, Salemi M, David MZ. 2016. Intrahost evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 among individuals with reoccurring skin and soft-tissue infections. J Infect Dis 214:895–905. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wen H, Wang K, Liu Y, Tay M, Lauro FM, Huang H, Wu H, Liang H, Ding Y, Givskov M, Chen Y, Yang L. 2014. Population dynamics of an Acinetobacter baumannii clonal complex during colonization of patients. J Clin Microbiol 52:3200–3208. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00921-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fowler VG Jr, Nelson CL, McIntyre LM, Kreiswirth BN, Monk A, Archer GL, Federspiel J, Naidich S, Remortel B, Rude T, Brown P, Reller LB, Corey GR, Gill SR. 2007. Potential associations between hematogenous complications and bacterial genotype in Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Infect Dis 196:738–747. doi: 10.1086/520088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Long SW, Beres SB, Olsen RJ, Musser JM. 2014. Absence of patient-to-patient intrahospital transmission of Staphylococcus aureus as determined by whole-genome sequencing. mBio 5:e01692-. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01692-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Anderson M, Chen YH, Butler EK, Missiakas DM. 2011. EsaD, a secretion factor for the Ess pathway in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 193:1583–1589. doi: 10.1128/JB.01096-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Burts ML, DeDent AC, Missiakas DM. 2008. EsaC substrate for the ESAT-6 secretion pathway and its role in persistent infections of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 69:736–746. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Burts ML, Williams WA, DeBord K, Missiakas DM. 2005. EsxA and EsxB are secreted by an ESAT-6-like system that is required for the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:1169–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405620102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Anderson M, Ohr RJ, Aly KA, Nocadello S, Kim HK, Schneewind CE, Schneewind O, Missiakas D. 2017. EssE promotes Staphylococcus aureus ESS-dependent protein secretion to modify host immune responses during infection. J Bacteriol 199:e00527-. doi: 10.1128/JB.00527-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, Lee W, Yuan J, Wong P, Ho TS, Miller ML, Rekhtman N, Moreira AL, Ibrahim F, Bruggeman C, Gasmi B, Zappasodi R, Maeda Y, Sander C, Garon EB, Merghoub T, Wolchok JD, Schumacher TN, Chan TA. 2015. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 348:124–128. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Johnson BE, Mazor T, Hong C, Barnes M, Aihara K, McLean CY, Fouse SD, Yamamoto S, Ueda H, Tatsuno K, Asthana S, Jalbert LE, Nelson SJ, Bollen AW, Gustafson WC, Charron E, Weiss WA, Smirnov IV, Song JS, Olshen AB, Cha S, Zhao Y, Moore RA, Mungall AJ, Jones SJM, Hirst M, Marra MA, Saito N, Aburatani H, Mukasa A, Berger MS, Chang SM, Taylor BS, Costello JF. 2014. Mutational analysis reveals the origin and therapy-driven evolution of recurrent glioma. Science 343:189–193. doi: 10.1126/science.1239947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Altman DR, Sebra R, Hand J, Attie O, Deikus G, Carpini KW, Patel G, Rana M, Arvelakis A, Grewal P, Dutta J, Rose H, Shopsin B, Daefler S, Schadt E, Kasarskis A, van Bakel H, Bashir A, Huprikar S. 2014. Transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus via deceased donor liver transplantation confirmed by whole genome sequencing. Am J Transplant 14:2640–2644. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Chin CS, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, Clum A, Copeland A, Huddleston J, Eichler EE, Turner SW, Korlach J. 2013. Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat Methods 10:563–569. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Chacko K, Sullivan M, Beckford C, Altman D, Ciferri B, Pak T, Sebra R, Kasarskis A, Hamula C, van Bakel H. 2018. Genetic basis of emerging vancomycin, linezolid, and daptomycin heteroresistance in a case of persistent Enterococcus faecium bacteremia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62:e02007-. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02007-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hunt M, Silva ND, Otto TD, Parkhill J, Keane JA, Harris SR. 2015. Circlator: automated circularization of genome assemblies using long sequencing reads. Genome Biol 16:294. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0849-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sullivan MJ, Ben Zakour NL, Forde BM, Stanton-Cook M, Beatson SA. 2015. Contiguity: contig adjacency graph construction and visualisation. PeerJ PrePrints 3:e1273. doi: 10.7287/peerj.preprints.1037v1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA. 2012. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Seemann T. 2014. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30:2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pak TR, Roth FP. 2013. ChromoZoom: a flexible, fluid, Web-based genome browser. Bioinformatics 29:384–386. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Nicol JW, Helt GA, Blanchard SG Jr, Raja A, Loraine AE. 2009. The Integrated Genome Browser: free software for distribution and exploration of genome-scale datasets. Bioinformatics 25:2730–2731. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Pesseat S, Quinn AF, Sangrador-Vegas A, Scheremetjew M, Yong SY, Lopez R, Hunter S. 2014. InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30:1236–1240. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Mukherjee S, Stamatis D, Bertsch J, Ovchinnikova G, Verezemska O, Isbandi M, Thomas AD, Ali R, Sharma K, Kyrpides NC, Reddy TB. 2017. Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) v.6: data updates and feature enhancements. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D446–D456. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Delcher AL, Salzberg SL, Phillippy AM. 2003. Using MUMmer to identify similar regions in large sequence sets. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics Chapter 10:Unit 10.3. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1003s00. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chun J, Rainey FA. 2014. Integrating genomics into the taxonomy and systematics of the Bacteria and Archaea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:316–324. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.054171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Treangen TJ, Ondov BD, Koren S, Phillippy AM. 2014. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol 15:524. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0524-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Angiuoli SV, Salzberg SL. 2011. Mugsy: fast multiple alignment of closely related whole genomes. Bioinformatics 27:334–342. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Castresana J. 2000. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stamatakis A. 2014. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Croucher NJ, Page AJ, Connor TR, Delaney AJ, Keane JA, Bentley SD, Parkhill J, Harris SR. 2015. Rapid phylogenetic analysis of large samples of recombinant bacterial whole genome sequences using Gubbins. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e15. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Martin M. 2011. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 17:10–12. doi: 10.14806/ej.17.1.200. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. 2012. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W. 2015. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31:166–169. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, Smyth GK. 2015. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 43:e47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Law CW, Chen Y, Shi W, Smyth GK. 2014. voom: precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts. Genome Biol 15:R29. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-2-r29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.O'Neill AJ, Chopra I. 2002. Insertional inactivation of mutS in Staphylococcus aureus reveals potential for elevated mutation frequencies, although the prevalence of mutators in clinical isolates is low. J Antimicrob Chemother 50:161–169. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkf118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Balasubramanian D, Ohneck EA, Chapman J, Weiss A, Kim MK, Reyes-Robles T, Zhong J, Shaw LN, Lun DS, Ueberheide B, Shopsin B, Torres VJ. 2016. Staphylococcus aureus coordinates leukocidin expression and pathogenesis by sensing metabolic fluxes via RpiRc. mBio 7:e00818-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00818-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Choi Y, Chan AP. 2015. PROVEAN Web server: a tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics 31:2745–2747. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.